Effect of Lead Toxicity on Liver of Male Albino Mice Ultrastructural Study
|
|
|
- Christopher Nicholson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Effect of Lead Toxicity on Liver of Male Albino Mice Ultrastructural Study Shatha Mahmoud Hasan College of Medicine Al-Nahrin University Dep.of biology. دراسة دقيقة حول تا ثير سمية نترات الرصاص على آبد الفي ران البيض شذى محمود حسن قسم علوم الحياة آلية طب النهرين الخلاصة: تهدف هذه الدراسة بالكشف عن التغيرات الت ي يمك ن ان تح دثها س مية الرص اص ف ي خلاي ا الفي ران الب يض. ت م تع ريض مجم وعتين م ن الفي ران الب يض آ ل مجموع ه تح وي ٦ حيوان ات إل ى ترآيز ٢٥% من نترات الرصاص في مياه الشرب لمدة ٤ اشهر بينما مجموعة التحكم احت وت عل ى ماء مقطر فقط. لقد أوض حت خلاي ا الكب د للحيوان ات المعامل ة بالرص اص وبالمقارن ة م ع مجموع ة ال تحكم تغي رات ش ديدة ف ي التراآي ب الدقيق ة الت ي تش مل المايتوآن دريا والش بكة الاندوبلازمي ة واللايسوسوم. أظهرت النتاي ج ان التعرض لتراآيز منخفضة م ن الرص اص ع ن طري ق مي اه الش رب ق ادرة على احدث تغيرات شديدة في التراآيب الدقيقة لعينات خلايا هذه الا نسجة. Abstract Lead is a multi targeted toxicant causing effects in different organs of the body. The present ultrastructural study was undertaken on the hepatic tissue of male albino mice.two groups of male albino mice, 6 animals each were used. The treated group was exposed to 0.25% lead nitrate in drinking water for 4 months,and control group, in comparison with respective control mice. Chronic exposure to subtoxic doses of lead produced ultrastructural alterations in hepatocytes involving mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes and nuclei. The present study shows chronic exposure to low subtoxic doses of lead, it can induce adverse subcellular alterations in the hepatic tissues. Introduction Lead is being an ubiquitous environmental contaminant due to its significant role in modern industry.however, both occupational and environmental exposures remain a serious problem in many developing and industrializing countries [1]. It has many undesired effects, including neurological behavioura[2,3], immunological [4, 5, 6, 7], renal [8, 9, 10], hepatic [9], and haematological dysfunctions [11, 12]. Lead toxicity is closely related to its accumulation in certain tissues such as hepatic tissue and however, interfere with hepatic functions and limited ultrastructural changes(8, 9). Investigations have been done on the tissues of experimental animals exposed to lead ( 8,10). Studies the alterations at the ultra structural level in the hepatic tissues due to chronic lead exposure are rather limited and need more information about this effect. With this objective, the present ultra structural study was undertaken on hepatic tissue of male albino mice exposed to lead nitrate in the drinking water. Key words: hepatocyte-lead nitrate-toxicity 214
2 Materials and Methods In this study were used 12 male albino mice of the same age Animals were randomly divided into two groups of 6 mice. Each animals were caged at room temperature, lead nitrate was administered in drinking water at the rate of 0.25% for the treated group while the control group was given distilled water. The animals from each group were killed by dislocation of the neck. Electron microscopy: Small pieces of liver from each experimental mice of both groups were transferrd immediately to buffered gluteraldehyde fixative for 3hr, washed in 2 changes of phosphate buffer (PH7.2) at 4cº. Tissue specimens were post fixed in 1%. osmium tetroxide in phosphate buffer for 2hr at 4cº, then washed in phosphate buffer. Tissue specimens were then dehydrated in ascending grades of ethanol alcohol, cleared 2 changes of propylene Oxide,infiltrated gradually in resin and embedded Epon 812 at 60 cº for 2 days. Ultra thin sections (0.5micron) were cut using class knife and stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate. Tissue sections were then examined and photographed by transmission electron microscope Philips (CM10). Results Examination under electron microscope of the hepatic tissues of control mice,show the normal ultrastructural pattern scattered mitochondria and rough endoplasmic reticulum ( Fig. 1). The ultrastructural changes induced by lead chronic exposure in the hepatocytes of the treated mice were as follows: The mitochondrial ultra structural abnormalities were evident at 4 months of lead nitrate treatment. There was a general reduction in the number of mitochondria in hepatocytes in comparison with those of the control mice, and the mitochondria became swollen and it matrix was of variable density. In the swollen mitochondria, cristae were marginated and short if compared to the well-preserved parallel ones of the control mice. In many of the affected mitochondria, there was a loss of cristae structures and low density or destructed rough endplasmic reticulum (RER),due to fragmentation structures representing the damaged mitochondria were noticed(fig2&3). 215
3 Fig1.Electron micrograph of h epatocytes of control mice Demonstrating the normal ultra structural pattern. Microchondri (m) have distinct cristae.note the RER(r).X14000 Fig2. Electron micrograph of hepatocytes from treated mice recived 0.25% lead nitrate for 4 months.the mitochondria (m) are swollen, often vacuolated with distruptedcristae X Fig3. Electron micrograph of hepatocytes from treated mice recevid 0.25% lesd nitrate for 4 months.the hepatocyte shows distruction of cristae of mitochondria(m) and almost complete destruction of RER.X8000. and in (fig.4) show increase in the number of lysosome within the hepatocytes of lead treated mice at 4 monthes,some of the lysosome containing hepatocytes had autophagic vacuoles and showed indistinct outlines due to partial cell destruction.and affected 216
4 hepatocytes frequently contained large number of droplets. These droplets varied in size and more observed at the peripherey of cells (Fig.5). Occasionally, some hepatocytes appeared as shrunken condensed cells which had irregular outlines (fig. 6). Fig4. Electron micrograph of hepatocytes from treated mice received0.25%lead nitrate for 4 months.numerous of lysosomal structures(ls)of variable size are seen.x Fig5. Electron micrograph of hepatocytes from treated mice received0.25%lead nitrate for 4 months. Note the cytoplasmic lipid (Ld) X
5 Fig6. Electron micrograph of hepatocytes fromtreated mice received 0.25%lead nitrate for 4 months demonestratating clumped of adjacent to heterochromatin irregular nuclear membrane (arrow) (X25000). Discussion These ultrastruractural alterations due to lead intoxication wich involved mitochondria, RER, and lysosomes. has been shown to have strong affinity for mitochondria and is usually associated with changes in the parenchymal cells (12,13) The results of the present investigation indicate clearly that the mitochondria are highly susceptible to lead toxicity and mitochondrial swelling was a frequent ultrastructural finding.this swelling is thought to be related to change in osmolarity that leads to an influx of salts and water through the inner mitochondrial membrane which becomes distended. Consequently, the outer membrane eventually ruptures due to osmotic swelling as a result of water and ion accumulation (11).this alteration may be related to expansion of mitochondrial matrix as evidenced by the decreased metrical electron density. The high degree of swelling of mitochondria might indicate impaired electron transport as a consequence to interaction of lead with the mitochondrial membranes Regular spacing and orientation of the mitochondrial cristae were lost with no changes in the lysosomal membrane system in the cardiac papillary muscle of rats given lead at the rate of 1000ug/1 in drinking water for 59 weeks (14).Similar mitochondrial swelling had been observed in other tissues of lead exposed animals such as the heart, cerebellum and kidney (15). The disorientation and fragmentation of the mitochondrial cristae might indicate a special lead affinity for mitochondrial membranes which play a key role in the functional integrity of this organelle (8,16). Cells with noticeable mitochondrial changes, as observed here, are unable to perform efficient functions specially the oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production (17, 18) The demonstrated increase in the number of lysosomal-related structures in affected hepatocytes might be an indication of an increase in the autophagic activity, as a removal mechanism of defective organelles in the affected cells.. The increase in the lysosomes number might also reflect an increase of the synthesis of hydrolytic and detoxifying enzymes (19).In this respect, Some previous studies showed that lead poisoning increases the number of lysosomes in the renal tubular cells (10). The destruction and decreased number of tubular arrays of the RER and mitochondrial- RER associates can be considered as an 218
6 indication of impaired protein synthesis in the affected hepatocytes. The demonstrated shrunken dark hepatocytes may represent a form of degenerated hepatocytes. The appearance of these cells may indicate an evidence of single cell necrosis(apoptosis) or shrinkage necrosis as a consequence of lead toxicity. Shrinkage necrosis is considered as an expression of programmed cell death in response to pathological changes(20) The accumulation of fat droplets in the cytoplasm of the affected hepatocytes may suggest lead interference with lipid removal from these cells through impairment of ATPdependent fatty acids(21). References: 1. Ycebilgic,G.,R Bilgin, L.Tamer,S.Tukel,effectof lead on Na-K ATPase and Ca2+ ATPase activities and lipid peroxidation in blood of worker IntJ.Toxicol 2003, 22, DE Marco,M.,R.Halpern,H.M.T.Barros,Early behavioral effects of lead perintal exposure in rat pups, Toxicology, 2005, 211, Morira,E.GI.Vssiliefe,Developmental lead exposure: behavioral alterations in the short and long term, Neurotox. Teratol., 2001, 23, BUNN, T.L., P.J. PARSONS, E. KAO, R.R. DIETERT, Exposure to lead during critical windows of embryonic development: differential immunotoxic outcome based on stage of exposure and gender, Toxicol. Sci., 2001, 64, BUNN, T.L., P.J. PARSONS, E. KAO, R.R. DIETERT, Gender-based profiles of developmental immunotoxicity to lead in the rat: assessment in juveniles and adults, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health, 2001, Part A 64, Ercal,N.,R.Neal,P.Treeratphan,P.M.Lutz,T.C.Hammond,P,A.Denner,D.R.Spitz,role for oxidative stress in suppressing serum immunoglobulin levels in leadexposed exposure and gender, Fisher 344 rats, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 2000, 39, Bjorklund, H., B. Lind, M. Piscator, B. Hoffer, L. Olson, Lead, zinc and copper levels in intraocular brain tissue grafts, brain and blood of lead exposed rats Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 1981, 60, Fowler, B.A, Ultrastructural and biochemical localization of organelle damage from nephrotoxic agents. Environ. Health. Perspectives, 91: Flora, S.; Kumar, D. and Sachan, S Combined exposure to lead and ethanol on tissue concentration of essential metals and some biochemical indices in rat. Biological Trace ElementResearch. 28: Vicente-Ortega, V., Martinez-Garcia, AF., Cremadescompos, A, Rodr-iguez- Vicente, J., Calderon- Rubiales, F. and Martinez Diaz, F Ultrastructural investigation of lead-induced intranuclear inclusion bodies in mice. Ultrastruct. PathwI., 20: King, D.W., CM. Fenoglio, and Leckowich, J.H General pathologij. Principles and dynamics. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia. 12. Aldridge, W.N Effect of metals on cells, subcellular elements and macromolecules. Maniloff,.R. Coleman and M.W. Miller(Eds.), pp , Thomas and Springfield, IIIinio. 13. Racker, E Membranes of mitochondria and chloroplasts. Van Nostrand- Reinhold press, New York. 219
7 14. Morgan, R V.; Moore, F. M. and Pearce, L. K Clinical and laboratory findings in small companion animals with lead poisoning: 347 cases ( ). JAVMA. 199 (1): Bull, RJ Lead and energy metabolism. In: Lead toxicitlj. Singhal, RL. and Thomas, J.A. (Eds.), Urban & Schwarzenberg, Munich. 16. Shlan.M.G., M.S. Mostafa, M.M. Hassouna, S.E. Hassab EL-Nabi, A. Elrafaie Amelioration of lead toxicity on rat liver with vitamin C and silymarin supplements,taxicology,2005,2006, Brierly, GP In: Biochemical effects of environmental pollutants. S.D. Lee (Ed.), P.397. Ann Arbor Science. Michigan. 18. Kendall, RJ. and Scanlon, P.F Histology and ultrastructural of kidney tissue from ringed turtle doves that ingested lead. J. Environ. Pathol Toxicol. Oncol., 6: Spit, b.j., A.A Wibowo, V.J. Feron, and RL. kidneys of rabbits treated with lead acetate. Arch Toxicol., 49: Wyllie, A.H., Kerr, J.F.R. and Currie, AR Cell death: The significance of apoptosis. Int. Rev. Cytol., 68: Piasek, M.; Kostial K. and Bunarevic, A The effect of lead exposure on pathohis-tological changes in the liver and kidney in relation to age in rats. Arh. Hig. Rada. Toksikol. 40 (1):
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS
 Onderstepoort]. vet. Res. 40 (2), 53-58 (1973) ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS G. LECATSAS, B. J. ERASMUS and H. J. ELS, Veterinary Research Institute, Onderstepoort ABSTRACT
Onderstepoort]. vet. Res. 40 (2), 53-58 (1973) ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS G. LECATSAS, B. J. ERASMUS and H. J. ELS, Veterinary Research Institute, Onderstepoort ABSTRACT
PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury.
 Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis
 J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich)
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE
 TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE PAUL F. PARAKKAL. From the Department of Dermatology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02118 INTRODUCTION
TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE PAUL F. PARAKKAL. From the Department of Dermatology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02118 INTRODUCTION
Initially, the patients did not receive extra vitamin E except for a very
 EFFECT OF VITAMIN E ON MEMBRANES OF THE INTESTINAL CELL BY I. MOLENAAR, F. A. HOMMES, W. G. BRAAMS, AND H. A. POLMAN CENTER FOR MEDICAL ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AND DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS, UNIVERSITY OF GRONINGEN,
EFFECT OF VITAMIN E ON MEMBRANES OF THE INTESTINAL CELL BY I. MOLENAAR, F. A. HOMMES, W. G. BRAAMS, AND H. A. POLMAN CENTER FOR MEDICAL ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AND DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS, UNIVERSITY OF GRONINGEN,
FIXATION BY MEANS OF GLUTARALDEHYDE-HYDROGEN PEROXIDE REACTION PRODUCTS
 FIXATION BY MEANS OF GLUTARALDEHYDE-HYDROGEN PEROXIDE REACTION PRODUCTS CAMILLO PERACCHIA and BRANT S. MITTLER. From the Department of Anatomy, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina 27706,
FIXATION BY MEANS OF GLUTARALDEHYDE-HYDROGEN PEROXIDE REACTION PRODUCTS CAMILLO PERACCHIA and BRANT S. MITTLER. From the Department of Anatomy, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina 27706,
R,;habdomyosarcoma, the most common
 Fine-structural classification of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma Arnold J. Kroll Six cases of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma were studied with the electron microscope. Tumor cells (rhabdomyoblasts) could be classified
Fine-structural classification of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma Arnold J. Kroll Six cases of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma were studied with the electron microscope. Tumor cells (rhabdomyoblasts) could be classified
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
THE CELL Cells: Part 1
 THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
Marah karablieh. Osama khader. Muhammad khatatbeh. 0 P a g e
 15 Marah karablieh Osama khader 0 P a g e Muhammad khatatbeh Cardiac Muscle Physiology Introduction The heart has two ventricles and two atriums. The heart wall is composed primarily of spirally arranged
15 Marah karablieh Osama khader 0 P a g e Muhammad khatatbeh Cardiac Muscle Physiology Introduction The heart has two ventricles and two atriums. The heart wall is composed primarily of spirally arranged
Cigarette smoking habits among paramedical students in Baghdad- Iraq
 Cigarette smoking habits among paramedical students in Baghdad- Iraq Faraj Hato Juni* الخلاصة ھدفت الدراسة وصفلوتحلی ل ظ اھرة الت دخین ب ین ط لاب المعاھ د الطبی ة وم واقفھم تج اه ھ ذه الظاھرة. دراس ة تخدمت
Cigarette smoking habits among paramedical students in Baghdad- Iraq Faraj Hato Juni* الخلاصة ھدفت الدراسة وصفلوتحلی ل ظ اھرة الت دخین ب ین ط لاب المعاھ د الطبی ة وم واقفھم تج اه ھ ذه الظاھرة. دراس ة تخدمت
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY
 Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
QUESTIONSHEET 1. The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D A (a) Identify A,, C, and D. A:... :... C:... D:... [4] (b) Outline the role of each
QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D A (a) Identify A,, C, and D. A:... :... C:... D:... [4] (b) Outline the role of each
Cell Structure and and Function Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
Intercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida
 JouRNAL OF BAcTEROLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 1139-1143 Vol. 123, No. 3 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ntercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida K. R. JOSH, J. B. GAVN,*
JouRNAL OF BAcTEROLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 1139-1143 Vol. 123, No. 3 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ntercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida K. R. JOSH, J. B. GAVN,*
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
SACE Stage 2 Biology Notes - Cells
 SACE Biology Year 2016 Mark 20.00 Pages 26 Published Jan 4, 2017 SACE Stage 2 Biology Notes - Cells By Elizabeth (99.75 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Elizabeth. Elizabeth achieved
SACE Biology Year 2016 Mark 20.00 Pages 26 Published Jan 4, 2017 SACE Stage 2 Biology Notes - Cells By Elizabeth (99.75 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Elizabeth. Elizabeth achieved
Peroxisomes. Endomembrane System. Vacuoles 9/25/15
 Contains enzymes in a membranous sac that produce H 2 O 2 Help survive environmental toxins including alcohol Help the cell use oxygen to break down fatty acids Peroxisomes Endo System Components of the
Contains enzymes in a membranous sac that produce H 2 O 2 Help survive environmental toxins including alcohol Help the cell use oxygen to break down fatty acids Peroxisomes Endo System Components of the
HEPATITIS B AND C By Dr. Najib ul Haq
 HEPATITIS B AND C By Dr. Najib ul Haq Hepatitis A and E Geographic Distribution of Chronic HBV Infection HBsAg Prevalence 8% - High 2-7% - Intermediate
HEPATITIS B AND C By Dr. Najib ul Haq Hepatitis A and E Geographic Distribution of Chronic HBV Infection HBsAg Prevalence 8% - High 2-7% - Intermediate
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS*
 Onderstepoort J. vet. Res. (1968), 35 (1), 139-150 Printed in the Repub. of S. Afr. by The Government Printer, Pretoria ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS* G. LECATSAS, Veterinary
Onderstepoort J. vet. Res. (1968), 35 (1), 139-150 Printed in the Repub. of S. Afr. by The Government Printer, Pretoria ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS* G. LECATSAS, Veterinary
(From The Rockefeller Institute) Materials and Methods. Observations with the Electron Microscope
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE
 ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE by D. L. Lee ABSTRACT Infective stage larvae of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis are immobilized within
ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE by D. L. Lee ABSTRACT Infective stage larvae of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis are immobilized within
the structure of their ducts has been
 Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
4. Lysosomes, Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, Mitochondria, and Inclusions
 4. Lysosomes, Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, Mitochondria, and Inclusions Undergraduate Graduate Histology Lecture Series Larry Johnson, Professor Veterinary Integrative Biosciences Texas A&M University
4. Lysosomes, Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, Mitochondria, and Inclusions Undergraduate Graduate Histology Lecture Series Larry Johnson, Professor Veterinary Integrative Biosciences Texas A&M University
Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside the nucleus but within the cell membrane, includes the organelles, cytosol, and
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
AN ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE STARCH-CONTAINING PLASTIDS IN THE FERN TODEA BARBARA
 J. Cell Sci. 4, 211-221 (1969) 211 Printed in Great Britain AN ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE STARCH-CONTAINING PLASTIDS IN THE FERN TODEA BARBARA H. M. SMITH* AND D. S. SMITHf Department of Biology,
J. Cell Sci. 4, 211-221 (1969) 211 Printed in Great Britain AN ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE STARCH-CONTAINING PLASTIDS IN THE FERN TODEA BARBARA H. M. SMITH* AND D. S. SMITHf Department of Biology,
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cellular Injury. Intracellular degeneration. By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall /20/2018 1
 Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells. Special Reference to the Well-Developed Agranular Endoplasmic Reticulum
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
Chapter 2 Cell. Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology
 Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(9): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(9):4307-4318 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Histopathological and ultrastructural changes
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2012, 4(9):4307-4318 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Histopathological and ultrastructural changes
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Heyam Awad
 number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF MELANIN-PHAGOCYTOSIS BY CUTANEOUS VESSELS IN CELLULAR BLUE NEVUS*
 THE JOURNAL 05' INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkinl Co. Vol. 62, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF MELANIN-PHAGOCYTOSIS BY CUTANEOUS VESSELS IN CELLULAR
THE JOURNAL 05' INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkinl Co. Vol. 62, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF MELANIN-PHAGOCYTOSIS BY CUTANEOUS VESSELS IN CELLULAR
4/12/17. Cells. Cell Structure. Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on. Range of Cell Sizes BIOL 100
 Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Objectives. By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles
 Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment
 Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Cell Structure. Present in animal cell. Present in plant cell. Organelle. Function. strength, resist pressure created when water enters
 Cell Structure Though eukaryotic cells contain many organelles, it is important to know which are in plant cells, which are in animal cells and what their functions are. Organelle Present in plant cell
Cell Structure Though eukaryotic cells contain many organelles, it is important to know which are in plant cells, which are in animal cells and what their functions are. Organelle Present in plant cell
Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey*
 Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey* DAVID S. MAXWELL, PH.D. Principal Contributor and Leader of Discussion HE inclusion of animal material m a y be justified as a means
Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey* DAVID S. MAXWELL, PH.D. Principal Contributor and Leader of Discussion HE inclusion of animal material m a y be justified as a means
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
8. Ultrastructural examination of the liver of the rainbow trout
 Józef Szarek, Izabella Babińska, Beata Szynaka, Anna Andrzejewska, Emilia Strzyżewska, Joanna Wojtacka, Krzysztof Wąsowicz, Anna Wiśniewska, Magdalena Szweda, Krystyna Dublan 8. Ultrastructural examination
Józef Szarek, Izabella Babińska, Beata Szynaka, Anna Andrzejewska, Emilia Strzyżewska, Joanna Wojtacka, Krzysztof Wąsowicz, Anna Wiśniewska, Magdalena Szweda, Krystyna Dublan 8. Ultrastructural examination
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 1: an introduction
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 1: an introduction CNS course This is a 7 hour course and the topics covered are important for your clinical years and your work as
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 1: an introduction CNS course This is a 7 hour course and the topics covered are important for your clinical years and your work as
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
The Cytoplasm Li Shulei Department of Histology & Embryology
 The Cytoplasm Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Cell components Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Organelles Cytoplasmic deposits Cytoskeleton Cytosol ( Matrix ) Nucleus Plasma membrane
The Cytoplasm Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Cell components Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Organelles Cytoplasmic deposits Cytoskeleton Cytosol ( Matrix ) Nucleus Plasma membrane
*Need a summary just not covered yet!
 *Need a summary just not covered yet! Organelle Pupil Organelle Pupil Nucleus KO N Microtubules + centrioles LF Endoplasmic reticulum ED Plant cell wall OC Ribosomes KL Chloroplasts RK Golgi apparatus
*Need a summary just not covered yet! Organelle Pupil Organelle Pupil Nucleus KO N Microtubules + centrioles LF Endoplasmic reticulum ED Plant cell wall OC Ribosomes KL Chloroplasts RK Golgi apparatus
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head
 CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Hydrophobic regions of protein Hydrophilic regions of protein
CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Hydrophobic regions of protein Hydrophilic regions of protein
Mechanisms of Cell Injury
 Causes of Cell Injury 1- oxygen deprivation (anoxia) 2- physical agents 3- chemical agents 4- infections agents 5- immunologic reactions 6- genetic defects 7- nutritional imbalances Mechanisms of Cell
Causes of Cell Injury 1- oxygen deprivation (anoxia) 2- physical agents 3- chemical agents 4- infections agents 5- immunologic reactions 6- genetic defects 7- nutritional imbalances Mechanisms of Cell
CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH
 CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH INTRODUCTION Cell Injury is a result of the sequence of events that occur if the limits of the adaptive capability of cells are exceeded or there is no adaptive response is possible,
CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH INTRODUCTION Cell Injury is a result of the sequence of events that occur if the limits of the adaptive capability of cells are exceeded or there is no adaptive response is possible,
A Compact and a Dispersed Form of the Golgi Apparatus
 A Compact and a Dispersed Form of the Golgi Apparatus of Fish Liver 1 D. James Morre and Carole A. Lembi Department of Botany and Plant Pathology Purdue University, Lafayette, Indiana 47907, and H. H.
A Compact and a Dispersed Form of the Golgi Apparatus of Fish Liver 1 D. James Morre and Carole A. Lembi Department of Botany and Plant Pathology Purdue University, Lafayette, Indiana 47907, and H. H.
High resolution structural evidence suggests the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum forms microdomains with Acidic Stores (lyososomes) in the heart.
 High resolution structural evidence suggests the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum forms microdomains with Acidic Stores (lyososomes) in the heart. Daniel Aston, Rebecca A. Capel, Kerrie L. Ford, Helen C. Christian,
High resolution structural evidence suggests the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum forms microdomains with Acidic Stores (lyososomes) in the heart. Daniel Aston, Rebecca A. Capel, Kerrie L. Ford, Helen C. Christian,
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Inner Life of Cell. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Unit A: Cells. Ch. 4 A Tour of the Cell
 Unit A: Cells Ch. 4 A Tour of the Cell Standards By the end of this unit you should be able to: Recognize and explain the function of each organelle Look at micrographs/diagrams/pictures and correctly
Unit A: Cells Ch. 4 A Tour of the Cell Standards By the end of this unit you should be able to: Recognize and explain the function of each organelle Look at micrographs/diagrams/pictures and correctly
LIGHT AND TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPICAL OBSERVATIONS ON RAT SCIATIC NERVE INDUCED BY ELECTROCUTION
 LIGHT AND TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPICAL OBSERVATIONS ON RAT SCIATIC NERVE INDUCED BY ELECTROCUTION DOAA SAFWAT * ; ADEL SHEHATA ISMAIL ** ; MAHMUD ABD EL-NASER ** ; OMAR H. BAYUOMI *** and SALAH
LIGHT AND TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPICAL OBSERVATIONS ON RAT SCIATIC NERVE INDUCED BY ELECTROCUTION DOAA SAFWAT * ; ADEL SHEHATA ISMAIL ** ; MAHMUD ABD EL-NASER ** ; OMAR H. BAYUOMI *** and SALAH
Electron Microscope Studies of HeLa Cells Infected with Herpes Virus
 244 STOKER, M. G. P., SMITH, K. M. & Ross, R. W. (1958). J. gen. Microbiol. 19,244-249 Electron Microscope Studies of HeLa Cells Infected with Herpes Virus BY M: G. P. STOKER, K. M. SMITH AND R. W. ROSS
244 STOKER, M. G. P., SMITH, K. M. & Ross, R. W. (1958). J. gen. Microbiol. 19,244-249 Electron Microscope Studies of HeLa Cells Infected with Herpes Virus BY M: G. P. STOKER, K. M. SMITH AND R. W. ROSS
CELLS.
 CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s)
 Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
2. scanning electron microscope vs. transmission electron microscope. nucleus, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, ribosomes
 Honors Biology Unit 2 Chapter 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL 1. light microscope 2. scanning electron microscope vs. transmission electron microscope 3. surface area to volume ratio 4. prokaryotic cell vs. animal
Honors Biology Unit 2 Chapter 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL 1. light microscope 2. scanning electron microscope vs. transmission electron microscope 3. surface area to volume ratio 4. prokaryotic cell vs. animal
Basophilic. Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue
 Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
ن و ل ه. Structure and Function of Cells 17/04/2013. Hakim Sabzevari University, Dr M.R.Vaezi K. ر ل: ل وا ز ت ا. اازۀ ه ز و ا ا
 Structure and Function of Cells اازۀ ه ز و ا ا ن و ل ه ه ە '&دات از ل $ #" ا! ر ل ن : ل وا ز ت ا هە ه ز از ل $#"! % ا له & ()' از له از +* &د % ا-د % له از واه ا 0 /.$!"#$. %!(2 او 1 د%ن ر ل: ل وا ز ت
Structure and Function of Cells اازۀ ه ز و ا ا ن و ل ه ه ە '&دات از ل $ #" ا! ر ل ن : ل وا ز ت ا هە ه ز از ل $#"! % ا له & ()' از له از +* &د % ا-د % له از واه ا 0 /.$!"#$. %!(2 او 1 د%ن ر ل: ل وا ز ت
Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 4 Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function Eucaryotic and Procaryotic cells differ in the use of their cell membranes.! EC have membrane delimited nuclei! Play a role in the structure of many other
Chapter 4 Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function Eucaryotic and Procaryotic cells differ in the use of their cell membranes.! EC have membrane delimited nuclei! Play a role in the structure of many other
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
The Study of Cells The diversity of the cells of the body The following figure shows the proportion of cell size of the variety of cells in the body
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport
 Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell
 Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell Cell basic unit of life o Small o Self-sufficient o Self-replicating Cell Theory organisms are composed of cells and all cells come from the division of other cells Cells
Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell Cell basic unit of life o Small o Self-sufficient o Self-replicating Cell Theory organisms are composed of cells and all cells come from the division of other cells Cells
psittaci by Silver-Methenamine Staining and
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, July 1972, p. 267-271 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 111, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Location of Polysaccharide on Chlamydia psittaci by Silver-Methenamine
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, July 1972, p. 267-271 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 111, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Location of Polysaccharide on Chlamydia psittaci by Silver-Methenamine
Electrolytes & [H + ] Disturbances in Peptic Ulcer Patients
![Electrolytes & [H + ] Disturbances in Peptic Ulcer Patients Electrolytes & [H + ] Disturbances in Peptic Ulcer Patients](/thumbs/74/70449737.jpg) Electrolytes & [H + ] Disturbances in Peptic Ulcer Patients, M.B.CH.B. C.A.M.B. Iraq / Al-Hilla / Babylon University / College of Medicine / Department Of Medicine Abstract In the body even a very small
Electrolytes & [H + ] Disturbances in Peptic Ulcer Patients, M.B.CH.B. C.A.M.B. Iraq / Al-Hilla / Babylon University / College of Medicine / Department Of Medicine Abstract In the body even a very small
General Biology. The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell. All organisms are made of cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 3. A Tour of the Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell All organisms are made of cells The cell is the simplest collection of
General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 3. A Tour of the Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell All organisms are made of cells The cell is the simplest collection of
The effect of ginger (Zingibar officinale) aqueous extract on some biochemical parameters and kidney function in male mice
 The effect of ginger (Zingibar officinale) aqueous extract on some biochemical parameters and kidney function in male mice Mustafa Abd Almajeed Hussein M.Sc. Lecturer, Department of Physiology, College
The effect of ginger (Zingibar officinale) aqueous extract on some biochemical parameters and kidney function in male mice Mustafa Abd Almajeed Hussein M.Sc. Lecturer, Department of Physiology, College
THE FORM OF HAEMOGLOBIN IN THE ERYTHROCYTES OF THE COD, GADUS CALLARIAS
 J. Cell Set. 8, 407-412 (1971) 407 Printed in Great Britain THE FORM OF HAEMOGLOBIN IN THE ERYTHROCYTES OF THE COD, GADUS CALLARIAS N.W.THOMAS Department of Anatomy, Marischal College, Aberdeen, Scotland
J. Cell Set. 8, 407-412 (1971) 407 Printed in Great Britain THE FORM OF HAEMOGLOBIN IN THE ERYTHROCYTES OF THE COD, GADUS CALLARIAS N.W.THOMAS Department of Anatomy, Marischal College, Aberdeen, Scotland
Cell Theory All living matter is composed of one or more The cell is the structural and functional unit of life All cells come from pre-existing cell
 Cell Theory All living matter is composed of one or more The cell is the structural and functional unit of life All cells come from pre-existing cell Prokeryotic Bacteria or archaea Cell wall, small circular
Cell Theory All living matter is composed of one or more The cell is the structural and functional unit of life All cells come from pre-existing cell Prokeryotic Bacteria or archaea Cell wall, small circular
The Effect of Using Citrus Wood Charcoal in Broiler Rations on the Performance of Broilers. Baha Eddin Abu Bakr
 An - Najah Univ. J. Res. (N. Sc.) Vol. 22, 2008 The Effect of Using Citrus Wood Charcoal in Broiler Rations on the Performance of Broilers اثر استخدام فحم الحمضيات في العلف على أداء صيصان اللحم Baha Eddin
An - Najah Univ. J. Res. (N. Sc.) Vol. 22, 2008 The Effect of Using Citrus Wood Charcoal in Broiler Rations on the Performance of Broilers اثر استخدام فحم الحمضيات في العلف على أداء صيصان اللحم Baha Eddin
FINE STRUCTURE STUDY OF POLLEN DEVELOPMENT IN HAEMANTHUS KATHERINAE BAKER
 J. Cell Sci. 8, 289-301 (1971) 289 Printed in Great Britain FINE STRUCTURE STUDY OF POLLEN DEVELOPMENT IN HAEMANTHUS KATHERINAE BAKER I. FORMATION OF VEGETATIVE AND GENERATIVE CELLS JEAN M. SANGER AND
J. Cell Sci. 8, 289-301 (1971) 289 Printed in Great Britain FINE STRUCTURE STUDY OF POLLEN DEVELOPMENT IN HAEMANTHUS KATHERINAE BAKER I. FORMATION OF VEGETATIVE AND GENERATIVE CELLS JEAN M. SANGER AND
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
1. (a) (i) Ability to distinguish points (close together); 1 (ii) Electrons have a shorter wavelength; 1
 1. (a) (i) Ability to distinguish points (close together); 1 Electrons have a shorter wavelength; 1 (b) (i) Golgi / nucleus / mitochondrion / endoplasmic reticulum / chromosome / larger ribosomes; R Membrane
1. (a) (i) Ability to distinguish points (close together); 1 Electrons have a shorter wavelength; 1 (b) (i) Golgi / nucleus / mitochondrion / endoplasmic reticulum / chromosome / larger ribosomes; R Membrane
Cytology II Study of Cells
 Cytology II Study of Cells Biology 20 Cellular Basis of Life 1. Basic unit of Life 2. Composed of one or more cells 3. Arises from pre-existing cells Asexual (Mitosis)/Sexual (Meiosis) 4. Surrounded by
Cytology II Study of Cells Biology 20 Cellular Basis of Life 1. Basic unit of Life 2. Composed of one or more cells 3. Arises from pre-existing cells Asexual (Mitosis)/Sexual (Meiosis) 4. Surrounded by
Cellular compartments
 Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Chapters 2 and 3. Pages and Pages Prayer Attendance Homework
 Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
The Cell. The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes.
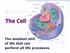 The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
Histological and Ultrastructural studies of Caecal tonsil in Chicken (Gallus domesticus)
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 6 (2015) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Histological and Ultrastructural studies of Caecal tonsil in Chicken (Gallus domesticus) T.A.Kannan 1*,
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 6 (2015) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Histological and Ultrastructural studies of Caecal tonsil in Chicken (Gallus domesticus) T.A.Kannan 1*,
Cell structure and function flash cards
 Process Cell structure and function flash cards involved in aerobic respiration releasing ATP / energy has a double membrane folded into cristae (to make large SA) mostly occurs in mitochondria; needing
Process Cell structure and function flash cards involved in aerobic respiration releasing ATP / energy has a double membrane folded into cristae (to make large SA) mostly occurs in mitochondria; needing
AP Biology. Tour of the Cell 1
 Tour of the Cell 1 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Why organelles? Specialized structures specialized functions cilia
Tour of the Cell 1 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Why organelles? Specialized structures specialized functions cilia
General Concepts of Exposure Assessment of Chemical Contaminants in Food & Water
 General Concepts of Exposure Assessment of Chemical Contaminants in Food & Water Office of Research and Development National Center for Environmental Assessment What You Can Expect to Learn from this Course
General Concepts of Exposure Assessment of Chemical Contaminants in Food & Water Office of Research and Development National Center for Environmental Assessment What You Can Expect to Learn from this Course
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1
 ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
Chapter 3. Cell Structure
 Chapter 3 Cell Structure Looking at Cells l The invention of microscopes allowed scientists to view cells for the first time l Scientists use the metric system to measure the size of cells l Metric Units
Chapter 3 Cell Structure Looking at Cells l The invention of microscopes allowed scientists to view cells for the first time l Scientists use the metric system to measure the size of cells l Metric Units
Cell Structure Text Ref Pg 4-7, 63-81
 Cell Structure Text Ref Pg 4-7, 63-81 The Cellular Basis of Life Before people had a scientific explanation for where life came from, they believed in the theory of spontaneous generation, where organisms
Cell Structure Text Ref Pg 4-7, 63-81 The Cellular Basis of Life Before people had a scientific explanation for where life came from, they believed in the theory of spontaneous generation, where organisms
basic unit structure and function
 Chapter 3 Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells vary in their shape, size, and arrangements, but all cells have similar components with a particular
Chapter 3 Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells vary in their shape, size, and arrangements, but all cells have similar components with a particular
HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS
 12 Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 1 12-21 2002 Research Report HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS YM Shivarajashankara, a AR Shivashankara, a P Gopalakrishna Bhat, b S Muddanna
12 Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 1 12-21 2002 Research Report HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS YM Shivarajashankara, a AR Shivashankara, a P Gopalakrishna Bhat, b S Muddanna
Eukaryotic cell. Premedical IV Biology
 Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
Structure and Function of Cells
 Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
shehab Moh Tarek ... ManarHajeer
 3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
OCR (A) Biology GCSE. Topic 1: Cell Level Systems
 OCR (A) Biology GCSE Topic 1: Cell Level Systems Notes (Content in bold is for higher tier only) Cell structures Microscopes (1.1a and c) Light (optical) microscopes The specimen is placed onto a slide,
OCR (A) Biology GCSE Topic 1: Cell Level Systems Notes (Content in bold is for higher tier only) Cell structures Microscopes (1.1a and c) Light (optical) microscopes The specimen is placed onto a slide,
