BABS1202 APPLIED BIOMOLECULAR SCIENCES
|
|
|
- Gwen Reeves
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BABS1202 APPLIED BIOMOLECULAR SCIENCES CELL STRUCTURE BINARY FISSION VS. MITOSIS Bacteria and archaea have no nucleus and no centromeres Binary fission cannot be divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase METABOLISM Metabolism: set of chemical reactions that happen in living organisms to maintain life Metabolic processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, respond to their environments Catabolism: breaks down organic matter (captures energy) into smaller molecules Anabolism: uses energy to construct components of cells Biological energy comes from solar energy in the form of chemical energy in bonds and ATP, or more stably in chemical bonds between carbon atoms (carbohydrates) Autotrophs: an organism that produces its own food using energy from light or other inorganic chemical reactions e.g. plants through photosynthesis Heterotrophs: animals that obtain their energy from food, requires organic substrates to get its chemical energy for growth and development ENVIRONMENTAL CHANGES Positive response: causes the organism to move towards the stimulus Negative response: causes the organism to move away from the stimulus CHEMICALS OF LIFE Carbohydrates/Saccharides: most abundant, simple organic compounds, storage/transport of energy and structural components, monosaccharides can be linked together to form polysaccharides or oligosaccharides Proteins: polymers formed from linking various amino acids joined by peptide bonds, many different levels of organisation, amino acids differ by side chain (R group), 20 essential amino acids
2 Lipids: any fat soluble (lipophilic) molecules, energy storage, structural components of cell membranes, examples include fats, oils, waxes, cholesterol, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K), monoglcerides, diglycerides, phospholipids Nucleic acids: polymers formed from linking of various nucleotides, used in storage/transfer of genetic information, examples include DNA and RNA, three components in a nucleotide (pentose sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base) CELLS Cells: always enclosed by a membrane, always contains cytoplasm and genetic material, mechanism for protein manufacture (ribosomes) All cells have genes, and replicate their DNA and produce proteins by transcribing DNA to RNA and translating RNA to proteins Viruses: not a cell as it is DNA/RNA surrounded by protein, dependant on host cell s functions for proteins synthesis, in the extracellular state the virus is known as a virion (metabolically inert), entering the cell allows the intracellular state to be initiated and virus replication occurs
3 Major components of eukaryotic cells Cytoplasm Cytosol Nucleolus/Nucleole Nuclear Envelope Chromosome Chromatin Nucleoplasm Nucleus Nuclear Envelope Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough ER Smooth ER Transport Vesicles Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes Cell Membrane Phospholipid Bilayer and Plasma Membrane Mitochondria Chloroplast Eukaryote Cytoskeleton Region between the membrane and the nucleus, contains organelles of the cell Gelatin-like aqueous fluid filling the cytoplasm, solution containing salts, minerals and organic compounds Within the nucleus, non-membrane bound, composed of protein and nucleic acids, site of ribosomal RNA transcription Double lipid membrane system, encloses nucleus, selectively permeable pores to allow RNA and ribosomes out of the nucleus and nuclear proteins in One DNA molecule and associated proteins Complex of DNA and proteins that make up eukaryotic chromosome, when cell is not dividing it exists as a mass of long, thin fibres Fluid interior portion of nucleus DNA directs RNA synthesis Outer nuclear membrane is constant with rough ER, ribosomes attached to the surface, RNA exists nucleus through a nuclear pore Non membrane-bound, converts genetic information carried by messenger RNA into proteins, ribosomes coordinate protein synthesis by placing the mrna, trna and associated protein factors in correct positions, ribosomal components of ribosomes catalyse some of the chemical reactions during translation, structurally consists of small and large subunit, biochemically consists of ribosomal RNA (rrna) and some 50 structural proteins, catalyse the assembly of individual amino acids into polypeptide chains, uses mrna as a template to join together the correct sequence of amino acids Continuous with outer membrane of the nuclear envelope, mesh of interconnected membranes Rough appearance due to numerous ribosomes attached along ER, connects nuclear envelope through the mrna to ribosomes, involved in protein synthesis and transport Lacks rough surface, manufactures lipids (fatty acids, phospholipids, sterols), involved in cholesterol metabolism and membrane synthesis, packaged in transport vesicles and sent to Golgi Small membrane bound sac, proteins and lipids packaged in transport vesicles to Golgi Consists of 3 20 flattened stacks of membrane-bound sacs (cisternae), complex network of tubules and vesicles located at edge of cisternae; modifies, sorts and packages proteins and other materials from ER then stored or secreted; receives and binds to first layer (cis) then are modified as they pass through the layers (molecular tags allows sorting and packaging, indicates destination) then leaves through the trans face Small organelles that contain enzymes, enzymes break down lipids, carbohydrates and proteins, removes junk and clutter Plasma membrane separates inside from outside, controls traffic of materials into and out of the cell One polar hydrophilic head towards aqueous solutions, two non-polar hydrophobic tails orientated away from water; proteins, sidedness proteins, carbohydrates and lipids distributed asymmetrically between two sides of membrane, composed of macromolecules (proteins, glycoproteins, glycolipids, cholesterol, phospholipids) Membrane-enclosed organelle, 1 10 micrometers, generates most of cell s ATP, involved in signalling, cell cycle, growth and death Membrane bound organelles found in plant cells, algae and bacteria, can photosynthesise, absorb light to produce sugar Network of fibrous proteins distributed throughout cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, linked to organelles and plasma membrane
4 BACTERIAL CELL Average human body consists cells, at least number of microorganisms Importance of bacteria: agriculture, food, environment, health Bounded by a chemically complex cell wall (capsule or slime layer) Must be in an aqueous environment to replicate PLASMA MEMBRANE All living organisms have plasma membrane as its major point of contact with the environment (semipermeable membrane) Encloses the cytoplasm of cells Integral membrane proteins allow channel and movement of substances Membranes contain proteins, lipids and carbohydrates One polar hydrophilic head oriented towards aqueous solutions, both inside and outside cell Two non-polar hydrophobic tails are oriented away from the water
5 Functions Permeability Barrier Prevents leakage, gateway for transport of molecules in and out of the cell Energy Conservation Generation of proton motive force (chemiosmosis) Cellular respiration Protein Anchor Site of many proteins involved in genetic transport and chemotaxis Fimbriae attaching to the cell CELL WALL Supply structural integrity and shape Resists damage due to osmotic pressure protects against lysis (pressure inside is greater than outside) Provides some degree of resistance to diffusion of molecules Single bag-like, seamless molecule Composed of polysaccharide chains cross linked with short chains of amino acids: peptide and glycan Gram negative bacteria: atmospheres
6 Most bacterial cell walls contain peptidoglycan Divided into 2 major groups: gram positive (purple) or gram negative (pink/red) Gram Staining Bacteria morphology * bacillus is known as rod
7 Peptidoglycan: alternating NAM and NAG molecules form a carbohydrate backbone (glycan), rows of NAG and NAM are linked by polypeptides (peptide), always attached to the NAG portion Polypeptide cross-bridges vary but they always have a peptide side-chain, consisting of amino acids attached to NAGs Peptidoglycan (murein): mesh-like layer outside the plasma membrane, polymer of sugars (alternating NAG and NAM residues) and amino acids, peptide chain of three to five amino acids attached to NAM or can be cross-linked to alternate peptide chain of another strand PEPTIDOGLYCAN ASSEMBLY 1. In the cytoplasm, amino acids attach to N-acetyl muramic acid (NAM) 2. N-acetyl glucosamine (NAG) is added to NAM to form a peptidoglycan precursor 3. The peptidoglycan precursor is transported across membrane to cell wall acceptor 4. Peptidoglycan precursors bind to cell wall acceptors and undergo cross-linking by means of transpeptidase and D-alanyl carboxy peptidase (penicillin binding proteins, PCB s) 5. A polymer of NAM & NAG cross-linked by four amino acids is formed Beta-lactam (penicillins and cephiasporins) antibiotics contain a beta lactam ring, binding to crosslinking enzymes transpeptidase and D-alanyl carboxy peptidase, preventing cross-linking and peptidoglycan synthesis
8 CAPSULE Most bacteria contain some sort of polysaccharide layer that lies outside the cell envelope Glycocalyx: type of capsule found in bacteria, thin layer of tangled polysaccharide fibres Capsule can protect cells from phagocytic cells such as macrophages (virulence factor) Capsules protect against desiccation and hydrophobic toxins ENVELOPE Protects against toxic chemicals and physical trauma Cell wall is mechanically strong, turgor pressure, inside of the cell maintained at a higher pressure than the outside Slime capsule protects from noxious chemicals and from predators Membranes act as selective barriers Envelope must also sense the environment envelope of a cell is its interface with the outside world Gram positive has a larger cell wall and capsule whilst gram negative has an outer membrane NUCLEOID Densely packed, irregularly shaped, single circle of DNA, several million base pairs Some bacteria have linear chromosomes Chromosome can be 1000 times longer than the bacterial cell due to DNA condensed through histone-like protein and supercoiling Centrally located in the cell During division, two copies might migrate to opposite poles FLAGELLA Flagella (singular: flagellum) are long, thin, whip-like appendages Allows bacterial movement (motility) Can be several times longer than the cell, averaging 10 micrometers Movement driven by propeller-like rotation at 60 cell lengths/second Types of flagella Monotrichous Single flagellum Lophotrichous A tuft of flagella found at one of the cell pole Amphitrichous Single flagellum found at each of two opposite poles Peritrichous Multiple flagella found at several locations about the cell
9 PMF provides energy to drive flagella Requires ~1000 H+ translocated per rotation Rotation can be clockwise or counterclockwise; reversible Bacteria can move in response to stimuli (taxis) Runs: movements of cell in single direction for some time due to counterclockwise flagella rotation; increase with favourable stimuli (positive chemotaxis, positive phototaxis) Tumbles: abrupt, random, changes in direction due to clockwise flagellar rotation; increase with unfavourable stimuli (negative chemotaxis, negative phototaxis) PILI Thin, hollow protein tubes originating from the cytoplasmic membrane Attachment to surfaces and motility (i.e. twitching) DNA transfer (conjugation) and delivery of proteins or toxins in host cells F: long conjugation pill or sex pilus enables conjugation
10 Conjugation: transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another by cell-to-cell contact Typically, in Gram-negative bacteria it is the transfer of DNA (plasmid) from a donor bacterium with a sex pilus to a recipient bacterium to enable genetic recombination FIMBRIAE Short attachment pili, structurally related to pili Shorter and straighter than flagella and more numerous Attachment to surfaces (virulence factor) Resistance to phagocytosis End of shaft is adhesive tip structure having a shape corresponding to that of specific glycoprotein or glycolipid receptors on a host cell ENDOSPORES Produced by some bacteria (members of Bacillus and Clostridium) Comprises of bacterium s DNA, ribosomes and dipicolinic acid Dipicolinic acid forms a complex with calcium ions and binds water molecules, causing dehydration which creates heat resistance of macromolecules
Ch 4. Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
 Ch 4 Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Objectives Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Identify the three basic shapes of bacteria. Describe
Ch 4 Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Objectives Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Identify the three basic shapes of bacteria. Describe
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
 Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms 1 Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms 1 Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
 Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Cell Structure. Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell. Cytoplasmic Membrane 4/6/2011. Chapter 3. Cytoplasmic membrane
 Cell Structure Chapter 3 Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell Cytoplasmic membrane Delicate thin fluid structure Surrounds cytoplasm of cell Defines boundary Defines boundary Serves as a selectively permeable
Cell Structure Chapter 3 Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell Cytoplasmic membrane Delicate thin fluid structure Surrounds cytoplasm of cell Defines boundary Defines boundary Serves as a selectively permeable
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
Don t Freak Out. Test on cell organelle on Friday!
 Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Structure of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells
 Structure of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Review of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Nucleus vs nucleoid DNA : circular vs linear, presence of histones Membranous organelles Cell wall-peptidoglycan Cell
Structure of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Review of Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells Nucleus vs nucleoid DNA : circular vs linear, presence of histones Membranous organelles Cell wall-peptidoglycan Cell
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
First to View Cells. copyright cmassengale
 CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
Bacterial Structures. Capsule or Glycocalyx TYPES OF FLAGELLA FLAGELLA. Average size: µm 2-8 µm Basic shapes:
 PROKARYOTIC One circular chromosome, not in a membrane No histones No organelles Peptidoglycan cell walls Binary fission EUKARYOTIC Paired chromosomes, in nuclear membrane Histones Organelles Polysaccharide
PROKARYOTIC One circular chromosome, not in a membrane No histones No organelles Peptidoglycan cell walls Binary fission EUKARYOTIC Paired chromosomes, in nuclear membrane Histones Organelles Polysaccharide
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20
 Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Chapter 4. Prokaryotic Cells. Prokaryotic cells. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells. Comparing Prokaryotic and. Eukaryotic cells.
 Chapter 4 Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells No nucleus No organelles Cell walls composed of peptidoglycan Reproduce asexually via binary fission
Chapter 4 Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells No nucleus No organelles Cell walls composed of peptidoglycan Reproduce asexually via binary fission
it selectively allows some molecules to pass into the organism
 Multiple Choice Quiz Procaryotic Cell Structure and Function Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function Choose the best answer 1. The significance of the plasma membrane is that it selectively allows some
Multiple Choice Quiz Procaryotic Cell Structure and Function Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function Choose the best answer 1. The significance of the plasma membrane is that it selectively allows some
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function.
 Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Biology Structures in Cells. 1.3 Structures in Cells
 Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Cell Structure and Function Topics External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification An Infectious Exam Patient with Tuberculosis
Cell Structure and Function Cell Structure and Function Topics External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification An Infectious Exam Patient with Tuberculosis
Plasma Membrane. comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
The further from the nucleus, the higher the electron s energy Valence shell electrons participate in biological reactions
 Chemistry of Life Revision: The further from the nucleus, the higher the electron s energy Valence shell electrons participate in biological reactions Atoms exchange electrons with other elements to form
Chemistry of Life Revision: The further from the nucleus, the higher the electron s energy Valence shell electrons participate in biological reactions Atoms exchange electrons with other elements to form
Introduction. Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters).
 Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
Cell Structure and Function. Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages and 68-69
 Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Household pin w/ bactera. Cell Structure and Function
 Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Review Atoms have energy levels Electrons hang out in regions surrounding atomic nucleus First shell may hold two electrons (1 orbital) Second shell
Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Review Atoms have energy levels Electrons hang out in regions surrounding atomic nucleus First shell may hold two electrons (1 orbital) Second shell
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Microbiology: A Systems Approach
 Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan & Talaro Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles: the Bacteria and the Archaea Chapter 4 Fig. 4.1 3 3 parts flagella filament long, thin, helical structure composed
Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan & Talaro Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles: the Bacteria and the Archaea Chapter 4 Fig. 4.1 3 3 parts flagella filament long, thin, helical structure composed
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
4/12/17. Cells. Cell Structure. Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on. Range of Cell Sizes BIOL 100
 Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles
 Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles Topics: External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms Prokaryotes include two small groups
Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles Topics: External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms Prokaryotes include two small groups
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Chapters 2 and 3. Pages and Pages Prayer Attendance Homework
 Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
4 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS. Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
A Tour of the Cell. reference: Chapter 6. Reference: Chapter 2
 A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
Bio10 Cell Structure SRJC
 3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside the nucleus but within the cell membrane, includes the organelles, cytosol, and
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Chapter 3: Cytology. Cytology is the study of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. We are made up of trillions of cells.
 PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
BIOSC 041. v Today s lecture. v Today s lab. v Note- Monday is a holiday good time to do some reading!
 BIOSC 041 v Today s lecture Review questions Chapter 6, Cells More review questions v Today s lab Quick review of lab safety The Scientific Method start thinking about which environments you might want
BIOSC 041 v Today s lecture Review questions Chapter 6, Cells More review questions v Today s lab Quick review of lab safety The Scientific Method start thinking about which environments you might want
Classification of Infectious Agents. Dr W. D. Colby
 Classification of Infectious Agents Dr W. D. Colby Nonliving Infectious Agents PRIONS: abnormally configured self-replicating protein templates VIRUSES: nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) genes packaged in protein
Classification of Infectious Agents Dr W. D. Colby Nonliving Infectious Agents PRIONS: abnormally configured self-replicating protein templates VIRUSES: nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) genes packaged in protein
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Lesson Overview. 7.2 Cell Structure
 7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
Microbiology. Morphology & Ultra-Structure of Microorganism. Prof. Dr. Batool Hassan Al-Ghurabi
 Microbiology Morphology & Ultra-Structure of Microorganism Prof. Dr. Batool Hassan Al-Ghurabi Microbiology: the study of organisms too small to be seen without magnification. Micro - too small to be seen
Microbiology Morphology & Ultra-Structure of Microorganism Prof. Dr. Batool Hassan Al-Ghurabi Microbiology: the study of organisms too small to be seen without magnification. Micro - too small to be seen
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #7
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Cell and Cell Membrane Structure and Function
 Lesson 3 Cell and Cell Membrane Structure and Function Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 The Cell Theory Three principles comprise the cell theory 1) Every living organism is made up of one or
Lesson 3 Cell and Cell Membrane Structure and Function Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 The Cell Theory Three principles comprise the cell theory 1) Every living organism is made up of one or
Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell.
 Section 3: Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Section 3: Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Image Guide. Do NOT Write on this page. It is an Image guide for test questions.
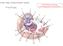 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
Chapter 3: Cellular Structure
 Chapter 3: Cellular Structure 1. Prokaryotic Cell Structure 2. Eukaryotic Cell Structure 1. Prokaryotic Cell Structure A. Cell Shape B. External Structures C. Internal (Cytoplasmic) Structures A. Cell
Chapter 3: Cellular Structure 1. Prokaryotic Cell Structure 2. Eukaryotic Cell Structure 1. Prokaryotic Cell Structure A. Cell Shape B. External Structures C. Internal (Cytoplasmic) Structures A. Cell
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
(a) TEM of a plasma. Fimbriae. Nucleoid. Ribosomes. Plasma membrane. Cell wall Capsule. Bacterial chromosome
 0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12
 Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
Plant Cells. Chapter 3
 Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s)
 Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is
 AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is continuous v Small cell size is becoming more necessary as
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is continuous v Small cell size is becoming more necessary as
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1
 Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Fig. LPS in Gram negative bacteria
 Structure of bacterial cell Dentistry college - first class Medical biology- Lec.3 Lecturer D. Hanan S A- Cell wall ***Chemical composition of the cell wall Bacteria are divided into two separated groups
Structure of bacterial cell Dentistry college - first class Medical biology- Lec.3 Lecturer D. Hanan S A- Cell wall ***Chemical composition of the cell wall Bacteria are divided into two separated groups
Cell Structure and Function
 Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Same bacteria on pinhead Fig. 4-1c, p.50 Review: Ionic Bonds Na has 11p and 10e making it (+) Cl has 18e and 17 p making it (-) The attraction
Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Same bacteria on pinhead Fig. 4-1c, p.50 Review: Ionic Bonds Na has 11p and 10e making it (+) Cl has 18e and 17 p making it (-) The attraction
CELLS.
 CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3)
 Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3) Topics Characteristics (comparison) External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification 1 Relative size of bacterial cell
Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3) Topics Characteristics (comparison) External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification 1 Relative size of bacterial cell
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting
 Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles Defined. Class Copy CELL STUDY NOTES Class Copy
 Cell Theory States: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Organelles Defined Golgi
Cell Theory States: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Organelles Defined Golgi
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells
 What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
Cytoskeleton. Provide shape and support for the cell. Other functions of the cytoskeleton. Nucleolus. Nucleus
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
O.k., Now Starts the Good Stuff (Part I) Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function
 O.k., Now Starts the Good Stuff (Part I) Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function Prokaryotic Characteristics DNA not enclosed in membrane. No histone proteins associated with DNA. Lack membrane-bound organelles
O.k., Now Starts the Good Stuff (Part I) Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function Prokaryotic Characteristics DNA not enclosed in membrane. No histone proteins associated with DNA. Lack membrane-bound organelles
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Cell Biology. a review! Cell Theory & Cell Structures
 Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
A TOUR OF THE CELL 10/1/2012
 A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Chapter 7: Inside the Cell
 Chapter 7: Inside the Cell 7.1 Bacterial and Archael Cell Structures and Their Functions - Eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound compartment called a nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. - Morphology
Chapter 7: Inside the Cell 7.1 Bacterial and Archael Cell Structures and Their Functions - Eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound compartment called a nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. - Morphology
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
NUCLEOLUS CELL MEMBRANE MITOCHONDRIA CELL WALL CHLOROPLAST NUCLEAR MEMBRANE VACOULE NUCLEUS ORGANELLE CARD ORGANELLE CARD ORGANELLE CARD
 CELL MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CELL WALL MITOCHONDRIA NUCLEAR MEMBRANE CHLOROPLAST NUCLEUS VACOULE CENTRAL VACOULE LEUCOPLAST CHROMOPLAST LYSOSOME CYTOPLASM CYTOSKELETON CENTRIOLE RIBOSOME CHROMATIN ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
CELL MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CELL WALL MITOCHONDRIA NUCLEAR MEMBRANE CHLOROPLAST NUCLEUS VACOULE CENTRAL VACOULE LEUCOPLAST CHROMOPLAST LYSOSOME CYTOPLASM CYTOSKELETON CENTRIOLE RIBOSOME CHROMATIN ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
Objectives. To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles.
 Cell Organelles 3.2 Objectives To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles. Basic Cellular Structures Cell membrane (cytoplasmic
Cell Organelles 3.2 Objectives To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles. Basic Cellular Structures Cell membrane (cytoplasmic
Delve AP Biology Lecture 4: 10/9/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang
 Today s Agenda: I. Review of organelles II. More important organelles III. Plasma membrane structure IV. Diffusion and transport Delve AP Biology Lecture 4: 10/9/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang I. Review
Today s Agenda: I. Review of organelles II. More important organelles III. Plasma membrane structure IV. Diffusion and transport Delve AP Biology Lecture 4: 10/9/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang I. Review
Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units
 Cell Theory Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life Organismal activity depends on individual and collective
Cell Theory Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life Organismal activity depends on individual and collective
