Biology TOPIC : CELL : THE UNIT OF LIFE. Marks : 120 mks Time : ½ hr
|
|
|
- Jared Pope
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TOPIC : CELL : THE UNIT OF LIFE Date : Marks : 120 mks Time : ½ hr 1. Match column-i with column-ii and select the correct option from the codes given below. A. Leeuwenhoek i) First saw and described a living cell B. Robert Brown ii) Presence of cell wall is unique to plant cells C. Schleiden iii) Discovered the nucleus D. Schwann iv) All plants are composed of different kind of cells (a) (b) (c) (d) A-(i) B-(iii), C-(iv), D-(ii) A-(i), B-(iii), C-(ii), D-(iv) A-(iii), B-(i), C-(iv), D-(ii) A-(i), (B)-(iv), C-(ii), D-(iii) 2. Arrange the following steps in a correct sequence as per Gram s staining technique : Treatment with 0.5% iodine solution (1), washing with water (2), treatment with absolute alcohol/acetone (3), staining with weak alkaline solution of crystal violet (4). (a) (b) (c) (d) Correct sequence of layers of bacterial cell envelope from outward to inward is (a) Cell wall Glycocalyx Cell membrane (b) Cell membrane Glycocalyx Cell wall (c) Glycocalyx Cell wall Cell membrane (d) Glycocalyx Cell membrane Cell wall 4. If you remove the fimbriae from the bacterial cell, which of the following would you expect to happen? (a) The bacteria could no longer swim (b) The bacteria would not adhere to the host tissue (c) Transportation of molecules across the membrane would stop (d) The shape of bacteria would change. 5. Polyribosomes are aggregation of (a) ribosomes and rrna (b) peroxisomes (c) several ribosomes held together by a strong of mrna (d) rrna 6. Match with and select the correct option from the codes given below. A. Dictyosomes i) Storage B. Mitochondria ii) Photosynthesis C. Vacuoles iii) Transport D. Grana iv) Secretion v) Respiration Page 1 of 6
2 A B C D (a) (iv) (v) (i) (ii) (b) (i) (ii) (iv) (iii) (c) (iv) (i) (ii) (iii) (d) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) 7. A phosphlipid molecule is amphipathic and produces two layers coming in contact with H2O. The head of phospholipid emolecule is (a) at an angle of 40 (b) at the outer surface (c) on the inner side (d) embedded in protein molecules. 8. Match the cell organelles given in with cellular proceses in and select the correct option from the codes given below. A. Lysosomes i) Protein synthesis B. Ribosomes ii) Hydrolytic activity C. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum iii) Steroid synthesis D. Centriole iv) Formation of spindle A B C D (a) (ii) (i) (iii) (iv) (b) (i) (iii) (iv) (ii) (c) (i) (iv) (iii) (ii) (d) (iv) (iii) (i) (ii) 9. Match the with and select the correct option from the codes given below. A. RER i) Intracellular and extracellular B. SER ii) Lipid synthesis C. Golgi complex iii) Protein synthesis and secretion D. Lysosomes iv) Move materials out of the cells (a) A-(iii) B-(ii) C-(iv) D-(i) (b) A-(ii) B-(iii) C-(iv) D-(i) (c) A-(i) B-(iii) C-(ii) D-(iv) (d) A-(iv) B-(ii) C-(iii) D-(i) 10. Read the given statements and select the correct option. Statement 1 :Chloroplast and mitochondria are semiautonomous bodies. Statement 2 : Chloroplast and mitochondria have their own DNA and protein synthesizing machinery. (a) Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1. (b) Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1. (c) Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect. (d) Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect. 11. Bright colour of petals, is due to the presence of (a) chloroplast (b) anthocyanin (c) chromoplast (d) leucoplast 12. The function of glyoxysome is (a) protein metabolism (b) carbohydrate reticulum (c) fat metabolism (d) protein synthesis. Page 2 of 6
3 13. Identify A and B in the given figure and select the correct option. A B (a) Grana thylakoid Stroma thylakoid (b) Stroma thylakoid Grana thylakoid (c) Granum Stroma (d) Stroma Granum 14. The chromosome in which centromere lies slightly away from the middle of the chromosome resulting into one shorter arm and one longer arm, is called as (a) metacentric (b) submetacentric (c) acrocentric (d) telocentric 15. Read the given statements. (i) Centromere is present in the middle of the chromosome and forms two equal arms. (ii) Chromosome has a terminal centromere. (iii) Centromere lies close to the end of the chromosome forming one extremely short and one very long arm. (iv) Centromere lies slightly away from the middle of the chromosome resulting into one shorter arm and one longer arm. Select the correct option as per the codes given below. Metacentric Submetacentric Acrocentric Telocentric (a) (i) (iv) (iii) (ii) (b) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (c) (iv) (i) (iii) (ii) (d) (iv) (ii) (iii) (i) 16. Select the incorrect statement regarding the plasma membrane. (a) Ratio of proteins and lipids varies considerably in different cell types. (b) 52% proteins and 40% lipids constitute the membrane of human RBC. (c) Arrangement of proteins (P) and Lipids (L) is L-P-P-L. (d) Head of lipid is hydrophilic. 17. All plastids have essentially the same structure because (a) they have to perform the same function. (b) they are localised in the aerial parts of plants (c) one type of plastids can differentiate into another type of plastids depending upon the cell requirements. (d) all plastids have to store starch, lipids and proteins. 18. In chloroplasts, chlorophyll is present in the (a) outer membrane (b) inner membrane (c) thylakoids (d) stroma. 19. These are the densely stained reticular structures present near the nucleus, consisting of many flat, disc shaped cisternae of m diameter. These are (a) chloroplasts (b) endoplasmic reticulum (c) mitochondriar (d) Golgi apparatus. 20. The cell organelle involved in the glycosylation of proteins is (a) ribosome (b) peroxisome (c) mitochondrion (d) endoplasmic reticulum 3 P a g e
4 21. Cells which are secretory in function have abundant (a) lysosomes (b) endoplasmic reticulum (c) dictyosomes (d) osteosomes 22. Ribosomes of the cytoplasm, chloroplast and mitochondrion are respectively (a) 805, 805 and 705 (b) 805, 705 and 705 (c) 705 in all (d) 805 in all. 23. The molecules in the membrane that limit its permeability are the (a) carbohydrates (b) phospholipids (c) proteins (d) water 24. Which of the following represents the features of lysosomes? (a) A lower ph than the cytoplasm (b) Reduced hydrolase activity (c) Double membrane envelope (d) All of these 25. Integral cell membrane proteins (a) are partially embedded in lipid layers (b) are completely embedded in lipid layers (c) show lateral but not vertical movements within bilayer of lipid (d) All of these 26. According to the modern concept, cell membrane is (a) solid (b) quasifluid (c) fluid (d) solidified sheath 27. A cell, which is very active in the synthesis and secretion of proteins, would be expected to have (a) equal amount of RER and SER (b) more SER than RER (c) more RER than SER (d) more Golgi bodies and no ER. 28. Choose the incorrect statement regarding cell membrane. (a) Generally smaller molecules pass easily and readily than large molecules. (b) Water soluble substance pass through it less readily than lipid soluble substance. (c) Membranes are selectively permeable. (d) None of these 29. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is well developed in the cells which synthesize. (a) steroids (b) proteins (c) carbohydrates (d) all of these 30. Mechanical support, enzyme circulation/protein synthesis and detoxification of drugs are function of (a) dictyosomes (b) chloroplast (c) ribosomes (d) ER. Page 4 of 6
5 Solutions 1. (a) 2. (a) The grouping of bacteria is based upon reaction of bacteria to Gram s stain (Christian Gram,1884). Bacteria are first stained with weakly alkaline solution of crystal violet and then treated with 0.5% iodine solution. This is followed by washing with water and then with alcohol or acetone. Bacteria which retain blue or purple colour are known as Gram (+) bacteria (e.g., Bacillus subtills). Bacteria which do not retain any stain and become colourless are called do not retain any stain and become colourless are called Gram (-) bacteria (e.g., Escherichia coli). Washing of the stain in Gram (-ve) bacteria is due to high lipid content of their cell wall which gets dissolved in organic solvents like acetone. 3. (c) Glycocalyx is the outermost of the cell envelope. Cell wall lies between membrane and glycocalyx. 4. (b) Fimbriae are hair like structures present in large number in bacteria. They help in attaching bacteria to solid surfaces or host tissues. 5. (c) Ribosomes may occur singly as monosomes or in rosettes and helical groups called polyribosomes. The different ribosomes are connected with a 10 20A thick stand of mrna. They are formed during periods of active protein synthesis when a number of copies of the same polypeptide are required. 6. (a) 7. (b) The lipid molecules are amphipathic, i.e., they possess both polar hydrophilic (water loving) and nonpolar hydrophobic (water repelling) ends. The hydrophilic region is in the form of a head occurring at outer surface while the hydrophobic part contains two tails of fatty acids. Hydrophobic tails usually occur towards the centre of the membrane. It results in the formation of a lipid bilayer. Most common lipid in the bilayer is phospholipid. 8. (a) 9. (a) 10. (a) 11. (b) Anthocyanins are one of the groups of flavonoid pigments. They occur in the cell vacuoles of various plant organs and are responsible for many of the blue, red and purple colours in plants (particularly in flowers). 12. (a) Glyaxysomes are microbodies which contain enzymes for - oxidation of fatty acids and glyoxylate pathway. They are considered to be special peroxisomes. They occur abundantly in germinating endosperm cells of oil seeds. 13. (b) 14. (b) In submetacentric type of chromosome, the centromere lies at some distance away from the midpoint, dividing the chromosome into two unequal arms. 15. (a) 16. (c) Acccording to Robertson s concept of until membrane, the cell membrane is trilaminar. It has a thickness of about 75A with a central lipid layer of 35A thick and two peripheral protein layers of 20A each. 17. (c) Plastids are double membranous, semi-autonomous organelles which store and synthesise various types of organic compounds. They develop from colourless precursors proplastids. Proplastids have the ability to divide and differentiate into various types of plastids. 18. (c) The thylakoid membrane contains photosynthetic pigments, namely, chlorophyila,chlorophyilb, carotenoids (carotene, xanthophyils) and plastoquinone. 19. (d) Camillo Golgi discovered the Golgi apparatus as reticular structure. Typically it is um in diameter but its shape and size depend upon the physiological state of the cell. 20. (d) In many cells proteins released from the endoplasmic reticulum are combined with carbohydrate to produce complexes like glycoproteins. This occurs in both Golgi complex and rough endoplasmic reticulum as they contain enzymes called glycosytransferases. 21. (c) Dictyosome is a cup-shaped structure of flattened membranous vesicles found in plant cell. They modify proteins from the ER, and may also polymerise sugars to polysaccharides. They then package these materials for delivery to destinations within the cell, for secretion, or for storage. 22. (b) 23. (b) The lipid bilayer comprising mostly of phospholipid limits the permeability of the membrane. 24. (a) Lysosomes store the hydrolyzing enzymes of the cell. About 40 enzymes have been recorded to occur in them. All the enzymes do not occur in the same lysosome but there are different sets of enzymes in different types of lysosomes. The important enzymes are acid phosophatases, sulphatases, proteases, peptidases, nucleases, lipases and glycosidases. They are also called acid hydrolases because these digestive enzymes usually function in acidic medium or ph of 4.5, this ph is lower than that of cytoplasm. Acidic conditions are maintained inside the lysosomes by pumping of H+ or protons into them. 25. (d) 26. (b) Fluid mosaic, model is the most recent and widely accepted model of a biomembrane which was proposed by Singer and Nicolson in Fluid mosaic model describes cell membrane as quasifluid, i.e., protein icebergs in a sea of lipids. According to 5 P a g e
6 this model, there is a bilayer of lipid molecules (phospholipid) with globular protein molecules (2 types integral and peripheral) and sterols which are arranged in different manner in different regions of the plasma membrane. 27. (c) The RER offers extensive surface on which protein synthesis can be conveniently carried on by ribosomes. The proteins formed on ribosomes pass into the ER lumen where they are modified. Then the modified proteins move into the transitional area, where the ER buds off membranous sacs, the transport vesicles, carrying the proteins to the Golgi apparatus. Here, they are further processed and packaged into secretary vesicles for export by exocytosis at the plasma membrane. 28. (d) 29. (a) The SER provides surface for the synthesis of lipids, including phospholipids, cholesterol, steroid homones (sex hormones, adrenal corticoid hormones), ascorbic acid and visual pigments. 30. (d) ER functions as cytoskeleton or skeletal framework by providing mechanical support to colloidal cytoplasmic matrix. It conducts information from cell to cell. RER helps in protein synthesis SER takes part in detoxification of toxic chemicals in liver. Page 6 of 6
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure.
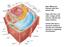 Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. Animal cells have a lysosome (related to vacuole) and centrioles (function
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. Animal cells have a lysosome (related to vacuole) and centrioles (function
Cell wall components:
 Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. The Cell Wall The primary cell wall is capable of rapid expansion during
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. The Cell Wall The primary cell wall is capable of rapid expansion during
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-08 CELL: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS
 CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-08 CELL: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS Study of form, structure, and composition of cell is called cytology. Cell is the structural and functional unit of
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-08 CELL: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS Study of form, structure, and composition of cell is called cytology. Cell is the structural and functional unit of
Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside the nucleus but within the cell membrane, includes the organelles, cytosol, and
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Structure and Function. Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages and 68-69
 Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Unit 2:The Cell. Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology
 Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts, *Mitochondria. *Learn these from text/connect1. Fertilization of a human cell
 Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
Key Concepts: - Cells are the Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory, Surface to Volume - 2 Cell Types Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic - Cell Membrane Membrane Structure - Cell Organelles Endomembrane system, *Chloroplasts,
First to View Cells. copyright cmassengale
 CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Plant Cells. Chapter 3
 Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Chapters 2 and 3. Pages and Pages Prayer Attendance Homework
 Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Cell Structure. Present in animal cell. Present in plant cell. Organelle. Function. strength, resist pressure created when water enters
 Cell Structure Though eukaryotic cells contain many organelles, it is important to know which are in plant cells, which are in animal cells and what their functions are. Organelle Present in plant cell
Cell Structure Though eukaryotic cells contain many organelles, it is important to know which are in plant cells, which are in animal cells and what their functions are. Organelle Present in plant cell
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
CELLS CELL THEORY. There are two types of cells: 9/26/2016 CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES. Which is more complicated? REMEMBER YOU ARE EUKARYOTIC!
 CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
Cell Category? Prokaryote
 CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE
 CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE Separates cell from its environment Controls substances that enter and leave the cell Selectively permeable allows certain substances to pass COMPOSITION Composed of 2 layers of
CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE Separates cell from its environment Controls substances that enter and leave the cell Selectively permeable allows certain substances to pass COMPOSITION Composed of 2 layers of
A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Cell Structure and and Function Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS. All living things are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all of the processes of life.
 CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
Plasma Membrane. comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure. Cells. Why are cells so small? 9/15/2016. Schleiden and Schwann proposed Cell Theory in
 Cell Structure Cells Cells are sacs of fluid that are reinforced by proteins and surrounded by membranes. Inside the fluid float organelles. Organelles: structures inside the cell that are used for metabolic
Cell Structure Cells Cells are sacs of fluid that are reinforced by proteins and surrounded by membranes. Inside the fluid float organelles. Organelles: structures inside the cell that are used for metabolic
Draw and Complete the Chart.
 Draw and Complete the Chart. In this True/False Activity; you and your partner will discuss the question, record your response (both), and share your answer with the class. Be prepared to justify your
Draw and Complete the Chart. In this True/False Activity; you and your partner will discuss the question, record your response (both), and share your answer with the class. Be prepared to justify your
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
NUCLEOLUS CELL MEMBRANE MITOCHONDRIA CELL WALL CHLOROPLAST NUCLEAR MEMBRANE VACOULE NUCLEUS ORGANELLE CARD ORGANELLE CARD ORGANELLE CARD
 CELL MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CELL WALL MITOCHONDRIA NUCLEAR MEMBRANE CHLOROPLAST NUCLEUS VACOULE CENTRAL VACOULE LEUCOPLAST CHROMOPLAST LYSOSOME CYTOPLASM CYTOSKELETON CENTRIOLE RIBOSOME CHROMATIN ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
CELL MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CELL WALL MITOCHONDRIA NUCLEAR MEMBRANE CHLOROPLAST NUCLEUS VACOULE CENTRAL VACOULE LEUCOPLAST CHROMOPLAST LYSOSOME CYTOPLASM CYTOSKELETON CENTRIOLE RIBOSOME CHROMATIN ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
*Need a summary just not covered yet!
 *Need a summary just not covered yet! Organelle Pupil Organelle Pupil Nucleus KO N Microtubules + centrioles LF Endoplasmic reticulum ED Plant cell wall OC Ribosomes KL Chloroplasts RK Golgi apparatus
*Need a summary just not covered yet! Organelle Pupil Organelle Pupil Nucleus KO N Microtubules + centrioles LF Endoplasmic reticulum ED Plant cell wall OC Ribosomes KL Chloroplasts RK Golgi apparatus
Cell Biology. a review! Cell Theory & Cell Structures
 Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
LECTURE 3 CELL STRUCTURE
 LECTURE 3 CELL STRUCTURE HISTORY The cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 examining very thin slices of cork and saw a multitude of tiny pores that remarked looked like the walled compartments
LECTURE 3 CELL STRUCTURE HISTORY The cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 examining very thin slices of cork and saw a multitude of tiny pores that remarked looked like the walled compartments
Household pin w/ bactera. Cell Structure and Function
 Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Review Atoms have energy levels Electrons hang out in regions surrounding atomic nucleus First shell may hold two electrons (1 orbital) Second shell
Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Review Atoms have energy levels Electrons hang out in regions surrounding atomic nucleus First shell may hold two electrons (1 orbital) Second shell
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
Chapter 1 Plasma membranes
 1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
THE CELL Cells: Part 1
 THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Image Guide. Do NOT Write on this page. It is an Image guide for test questions.
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Starch grains - excess sugars
 (a) Membrane system - site of light reactions (photosynthesis) - chlorpophyll pigments - enzymes - electron carriers - flattened, fluid-filled sacs (called thylakoids which are stacked to form grana) -
(a) Membrane system - site of light reactions (photosynthesis) - chlorpophyll pigments - enzymes - electron carriers - flattened, fluid-filled sacs (called thylakoids which are stacked to form grana) -
11/1/2014. accumulate in brain.
 EU 4.A: Interactions within biological systems lead to complex properties. EU 4.B: Competition and cooperation are important aspects of biological systems. EU 4.C: Naturally occurring diversity among and
EU 4.A: Interactions within biological systems lead to complex properties. EU 4.B: Competition and cooperation are important aspects of biological systems. EU 4.C: Naturally occurring diversity among and
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Cytology. Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges
 Chapter 7: A Tour of the Cell Cytology Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges Prokaryotic cells Nucleoid No organelles with membranes Ribosomes
Chapter 7: A Tour of the Cell Cytology Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges Prokaryotic cells Nucleoid No organelles with membranes Ribosomes
1) All organisms are made up of one or more cells and the products of those cells.
 CELL ORGANELLES - NOTES CELL THEORY Cells are the basic unit of life. The Cell Theory states that: 1) All organisms are made up of one or more cells and the products of those cells. 2) All cells carry
CELL ORGANELLES - NOTES CELL THEORY Cells are the basic unit of life. The Cell Theory states that: 1) All organisms are made up of one or more cells and the products of those cells. 2) All cells carry
Don t Freak Out. Test on cell organelle on Friday!
 Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
4 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS. Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
What Are Cell Membranes?
 What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
History of the Cell. History of the Cell 10/24/2013. Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function. Robert Hooke (1665) Robert Hooke (1665)
 Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
The Cell. The building blocks of life
 The Cell The building blocks of life Learning Goals I can describe the cell theory. I can differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. I can describe the similarities and differences between
The Cell The building blocks of life Learning Goals I can describe the cell theory. I can differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. I can describe the similarities and differences between
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
Chapter 7: Inside the Cell
 Chapter 7: Inside the Cell 7.1 Bacterial and Archael Cell Structures and Their Functions - Eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound compartment called a nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. - Morphology
Chapter 7: Inside the Cell 7.1 Bacterial and Archael Cell Structures and Their Functions - Eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound compartment called a nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. - Morphology
Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function.
 Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
PLANT CELL. Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines 2
 PLANT CELL Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1,2 1 Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines 2 Department of Biological Sciences, School of Science and Technology, Centro
PLANT CELL Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1,2 1 Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines 2 Department of Biological Sciences, School of Science and Technology, Centro
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment
 Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Cellular Boundaries. Cell Organelles. The Nucleus and Cell Control. Cell Membrane. Cell Wall. Nucleus 10/11/2012. Cell Membrane Cell Wall
 Cell Organelles Cellular Boundaries Protects cell Support and shape Controls what comes in and out of the cell Selectively permeable the process in which a membrane allows some molecules to pass through
Cell Organelles Cellular Boundaries Protects cell Support and shape Controls what comes in and out of the cell Selectively permeable the process in which a membrane allows some molecules to pass through
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Organisms are Made of Cells Principles of the Cell Theory Cell Diversity Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cell Membrane Membrane Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Internal Cell Structure
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Organisms are Made of Cells Principles of the Cell Theory Cell Diversity Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cell Membrane Membrane Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Internal Cell Structure
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Chapter 3: Cytology. Cytology is the study of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. We are made up of trillions of cells.
 PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
A TOUR OF THE CELL 10/1/2012
 A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
Ch. 4 Cells: The Working Units of Life
 Ch. 4 Cells: The Working Units of Life Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Types of cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized functions
Ch. 4 Cells: The Working Units of Life Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Types of cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized functions
Cells! Cells! Cells! Cells: The Working Units of Life
 Cells! Cells! Cells! Cells: The Working Units of Life Cell Theory Cell theory was the first unifying theory of biology. Schleiden and Schwann developed the first two statements of the cell theory. All
Cells! Cells! Cells! Cells: The Working Units of Life Cell Theory Cell theory was the first unifying theory of biology. Schleiden and Schwann developed the first two statements of the cell theory. All
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
SACE Stage 2 Biology Notes - Cells
 SACE Biology Year 2016 Mark 20.00 Pages 26 Published Jan 4, 2017 SACE Stage 2 Biology Notes - Cells By Elizabeth (99.75 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Elizabeth. Elizabeth achieved
SACE Biology Year 2016 Mark 20.00 Pages 26 Published Jan 4, 2017 SACE Stage 2 Biology Notes - Cells By Elizabeth (99.75 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, Elizabeth. Elizabeth achieved
Lesson Overview. 7.2 Cell Structure
 7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism
 Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
Cell Structure Animal/Human
 Cell Structure Animal/Human cell is basic unit of all life; structural and functional if its alive, must contain at least a single cell the function of an organism is the summation of functions of its
Cell Structure Animal/Human cell is basic unit of all life; structural and functional if its alive, must contain at least a single cell the function of an organism is the summation of functions of its
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. The structure of cells is more or less the same in the simplest to the most
 The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. The structure of cells is more or less the same in the simplest to the most complicated plants and animals. Hand out pictures ANIMAL
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. The structure of cells is more or less the same in the simplest to the most complicated plants and animals. Hand out pictures ANIMAL
Cell Structure and Organelles SBI4U 2016/10/14
 Cell Structure and Organelles SBI4U 2016/10/14 Inside the cell These are generalizations, not rules! Everything inside the cell membrane besides the nucleus is called the cytoplasm; The liquid is known
Cell Structure and Organelles SBI4U 2016/10/14 Inside the cell These are generalizations, not rules! Everything inside the cell membrane besides the nucleus is called the cytoplasm; The liquid is known
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes
 Review: Characteristics of Living Things Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes 1. Made of 2. Require 3. (species) 4. Maintain 5. 6. to environment 7. 8. materials with surroundings (water,
Review: Characteristics of Living Things Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes 1. Made of 2. Require 3. (species) 4. Maintain 5. 6. to environment 7. 8. materials with surroundings (water,
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Plant organelle used for storage. Some store starches and lipids and pigments. Named according to the color or pigment that they contain.
 Animal Cell: Plant Cell: Plastid: Plant organelle used for storage. Some store starches and lipids and pigments. Named according to the color or pigment that they contain. Chloroplasts:contain light absorbing
Animal Cell: Plant Cell: Plastid: Plant organelle used for storage. Some store starches and lipids and pigments. Named according to the color or pigment that they contain. Chloroplasts:contain light absorbing
Cell morphology. Cell organelles structure and function. Chapter 1: UNIT 1. Dr. Charushila Rukadikar
 UNIT 1 Cell morphology Cell organelles structure and function Chapter 1: Dr. Charushila Rukadikar Assistant Professor Department Of Physiology ZMCH, Dahod Physiology The science that is concerned with
UNIT 1 Cell morphology Cell organelles structure and function Chapter 1: Dr. Charushila Rukadikar Assistant Professor Department Of Physiology ZMCH, Dahod Physiology The science that is concerned with
Cell and Cell Membrane Structure and Function
 Lesson 3 Cell and Cell Membrane Structure and Function Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 The Cell Theory Three principles comprise the cell theory 1) Every living organism is made up of one or
Lesson 3 Cell and Cell Membrane Structure and Function Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 The Cell Theory Three principles comprise the cell theory 1) Every living organism is made up of one or
Structure and Function of Cells
 Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
(a) TEM of a plasma. Fimbriae. Nucleoid. Ribosomes. Plasma membrane. Cell wall Capsule. Bacterial chromosome
 0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
Cell Theory. Cells are the basic unit of life.
 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20
 Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
CELLS.
 CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam
 Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
Structure Characteristics Function. Double layer of phospholipid molecules studded with proteins
 CELL BOOKLETS: Instructions for creating the pages Take 4 pieces of white computer type paper. Cut them so that you have 4 slips from each page that measure 8-1/2 x 2-3/4 inches. You will have 8 slips
CELL BOOKLETS: Instructions for creating the pages Take 4 pieces of white computer type paper. Cut them so that you have 4 slips from each page that measure 8-1/2 x 2-3/4 inches. You will have 8 slips
Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell
 Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell Cell basic unit of life o Small o Self-sufficient o Self-replicating Cell Theory organisms are composed of cells and all cells come from the division of other cells Cells
Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell Cell basic unit of life o Small o Self-sufficient o Self-replicating Cell Theory organisms are composed of cells and all cells come from the division of other cells Cells
4/12/17. Cells. Cell Structure. Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on. Range of Cell Sizes BIOL 100
 Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Biology Structures in Cells. 1.3 Structures in Cells
 Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
A Tour of the cell. 2- Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions
 A Tour of the cell 1- To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry 2- Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions 3- The eukaryotic cell s
A Tour of the cell 1- To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry 2- Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions 3- The eukaryotic cell s
