Hydroxychloroquine Use Associated With Improvement in Lipid Profiles in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
|
|
|
- Melanie Cain
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 63, No. 4, April 2011, pp DOI /acr , American College of Rheumatology SPECIAL THEME ARTICLE: VASCULAR COMORBIDITY IN THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES Hydroxychloroquine Use Associated With Improvement in Lipid Profiles in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients STEPHANIE J. MORRIS, 1 MARY CHESTER M. WASKO, 2 JANA L. ANTOHE, 1 JENNIFER A. SARTORIUS, 1 H. LESTER KIRCHNER, 1 SORINA DANCEA, 1 AND ANDRONIKI BILI 1 Objective. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Disease-modifying therapies that improve risk factors for CVD, such as dyslipidemia, are desired. This study used an electronic health record to determine if hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) use was associated with an improvement in lipid levels in an inception RA cohort. Methods. All adult individuals with the initial diagnosis of RA between January 1, 2001, and March 31, 2008, were identified (n 1,539). Only patients with at least one lipid level post RA diagnosis were included (n 706). Information on demographics, medical history, body mass index (BMI), laboratory measures, and medications were collected at office visits. Potential risk and protective factors for dyslipidemia were controlled for in linear mixed-effects regression models for low-density lipoprotein (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL/HDL, and total cholesterol/hdl. Results. Patients were 69% women and 98% white, with a median age of 65 years and a median BMI of 29.8 kg/m 2.In the adjusted regression models, HCQ use was associated with the following average differences in lipids: LDL decrease of 7.55 mg/dl (P < 0.001), HDL increase of 1.02 mg/dl (P 0.20), total cholesterol decrease of 7.70 mg/dl (P 0.002), triglycerides decrease of mg/dl (P 0.06), LDL/HDL decrease of (P 0.008), and total cholesterol/hdl decrease of (P 0.006), which were stable over time. Conclusion. Use of HCQ in this RA cohort was independently associated with a significant decrease in LDL, total cholesterol, LDL/HDL, and total cholesterol/hdl. Considering these results, its safety profile, and low cost, HCQ remains a valuable initial or adjunct therapy in this patient population at high risk for CVD. INTRODUCTION Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (1). Atherogenic dyslipidemia is recognized as an important risk factor for CVD. Data from the general population suggest that optimizing lipid levels in this group would help to minimize this risk (2). Patients with active RA have 1 Stephanie J. Morris, DO, Jana L. Antohe, MD, Jennifer A. Sartorius, MS, H. Lester Kirchner, PhD, Sorina Dancea, MD, Androniki Bili, MD, MPH: Geisinger Health System, Danville, Pennsylvania; 2 Mary Chester M. Wasko, MD, MSc: (current address: West Penn Allegheny Health, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania) University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Dr. Wasko has received consultant fees (less than $10,000 each) from Centocor and UCB. Address correspondence to Androniki Bili, MD, MPH, Geisinger Health System, 100 North Academy Avenue, MC 13-41, Danville, PA abili1@geisinger.edu. Submitted for publication June 29, 2010; accepted in revised form October 26, abnormal lipid profiles that are related to disease activity (3). A drug that both treats rheumatic joint disease and improves lipid levels would therefore be advantageous in managing patients with RA. Previous studies have shown that hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), an antimalarial medication used in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, has modest favorable effects on the lipid profiles of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and RA. However, these studies were small and had short observation times. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the relationship between HCQ use and lipid profiles in an RA inception cohort of 706 patients using electronic health records containing physician diagnoses, laboratory values, and medications, hypothesizing that HCQ will have a favorable effect on lipid levels. MATERIALS AND METHODS Data for this study were extracted by the Geisinger Health System Information Technology Department from the elec- 530
2 Improving Lipid Levels in RA Patients Using HCQ 531 tronic health records (EPIC). Validation of the data was performed by the Information Technology Department. In addition, one of the investigators (AB) performed chart reviews on 18 known RA patients, documenting 100% concordance between the data received from the Information Technology Department and chart documentation in all 10 variables per patient, including RA diagnosis, laboratory values, and medication use patterns. The Rheumatology Department at Geisinger Health System entered the electronic health records system completely by January 1, All adult (age 18 years) individuals with an initial diagnosis of RA within the Geisinger Health System between January 1, 2001, and March 31, 2008, were identified (n 1,539). The first date was considered the index date. RA was defined as a patient with a diagnosis with an International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision code of at 2 outpatient encounters with a Geisinger Health System rheumatologist. The diagnosis of RA was validated against the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria (4) by one of the authors (SD) who manually reviewed 100 random charts. Of these 100, 97 patients with the study definition of RA met the ACR criteria for a diagnosis of RA. Of the 3 patients who did not meet the criteria, one had the diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis, one had mixed connective tissue disease, and the third had juvenile idiopathic arthritis. This high concordance rate of 97% between ACR criteria and the study definition of RA was deemed sufficient to proceed with study analyses. Only patients with at least one lipid level post RA diagnosis were included (n 706). Many of the 706 RA patients had repeated post-ra lipid measurements, resulting in 2,851 lipid-level results. The time in days from each patient s RA diagnosis date to each lipid result date was calculated (RA duration). Outcomes. The primary outcomes are levels of total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and triglycerides (cobas Roche/Hitachi Diagnostics) in HCQ users versus nonusers. In addition, two rates were included as outcomes, LDL/HDL and total cholesterol/hdl (the atherogenic index), that have recently been reported to be important predictors of increased cardiovascular events (5). Variables. Demographics included age at RA diagnosis, sex, and race. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared for each patient. The maximum BMI over the observation period was used. Comorbidities. Hypertension was defined as 2 or more outpatient visits within 2 years with a diagnosis of hypertension or at least 2 consecutive measurements of elevated systolic blood pressure ( 140 mm Hg) or elevated diastolic blood pressure ( 90 mm Hg). Diabetes mellitus was defined as having 1 or more outpatient visits with a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, a nonfasting blood glucose result of 200 mg/dl, a glycosylated hemoglobin result of 7%, or a hypoglycemic medication order ( -glucosidase inhibitors, amino acid derivatives, biguanides, insulinsensitizing agents, meglitinide analogs, sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, exenatide, pramlintide, sitagliptin, antidiabetic combination medications, or insulin). Medications. A typical dosage of 400 mg/day of HCQ (6.5 mg/kg) was identified as a time-varying primary predictor. Twenty-one patients who would be most likely to receive a lower dose of HCQ due to their weight were identified in the cohort with a BMI of 20 kg/m 2. One of the investigators (SJM) manually reviewed electronic records. Of the 21 patients, 15 were receiving 400 mg/day, 2 were receiving 300 mg/day, and 4 were receiving 200 mg/ day of HCQ. Additional medications captured as time varying included nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), glucocorticoids, methotrexate, and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab), hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors, and other lipid-lowering medications (antihyperlipidemic combinations, bile sequestrants, fibric acid derivatives, intestinal cholesterol absorption inhibitors, nicotinic acid derivatives, and miscellaneous antihyperlipidemics). Exposure to medications included medication order start and stop dates to capture therapeutic segments during the observation period. Continuous HCQ use was defined as a discontinuation gap of 3 months. Laboratory measures. Rheumatoid factor (by latex agglutination method, positive at 14 IU/ml; Roche Diagnostics), anti cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies (by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, positive at 20 units; Inova Diagnostics), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR; by Westergren method), and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels (cobas Roche/Hitachi Diagnostics) were measured. Only results that were performed at a Geisinger Health System facility were utilized in this study. Statistical analysis. Each patient s postindex HCQ status was evaluated for each lipid measurement result date. Potential risk and protective factors for dyslipidemia were controlled for in a linear mixed-effects regression model for each lipid outcome. The time in years from each patient s RA diagnosis date to each lipid result date was calculated and included in all models. Nonlinear time trends and interactions between HCQ and time were checked for all models. In the model, HCQ and all other medications were treated as time-varying covariates as yes/no indicators evaluated at each lipid result date. A secondary analysis also was performed, in which HCQ was treated as cumulative duration of exposure. In this model, the continuous duration of HCQ up to the lipid result date was calculated. Results are expressed as the average fixedeffects estimates over time for HCQ. To better understand the effect of statins, statin use was categorized as high potency, medium potency, and low potency (6) for the 359 patients that were ever receiving statins (using the closest statin order prior to the first lipid result). In order to investigate the possible impact of statin exposure, an additional, identical sensitivity analysis was performed only on patients that were not receiving statins. RESULTS Among the 706 incident RA patients, 98% had an LDL result, 96% had an HDL result, 97.5% had a total choles-
3 532 Morris et al Table 1. Characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis patients by HCQ use* Overall (n 706) Never (n 450) Ever (n 256) P Women 486 (69) 298 (66) 188 (73) White 689 (98) 441 (98) 248 (97) Hypertension 485 (69) 314 (70) 171 (67) Diabetes mellitus 262 (37) 168 (37) 94 (37) Positive rheumatoid factor (n 489 [69%]) 385 (79) 226 (79) 159 (78) Positive anti-ccp antibodies (n 233 [33%]) 98 (42) 54 (44) 44 (40) Medication use (ever) TNF inhibitors 213 (30) 145 (32) 68 (27) NSAIDs 537 (76) 341 (76) 196 (77) Steroids 624 (88) 397 (88) 227 (89) Methotrexate 418 (59) 286 (64) 132 (52) Statins 359 (51) 238 (53) 121 (47) Statin potency Low potency 28 (12) 15 (10) 13 (17) Medium potency 110 (49) 80 (54) 30 (39) High potency 88 (39) 53 (36) 35 (45) Other lipid-lowering agents 100 (14) 64 (14) 36 (14) Age, median (IQR) years 65.0 (57 75) 66.0 (59 76) 61.5 (54 72) BMI (n 676 [96%]), median (IQR) kg/m (26 34) 29.7 (26 34) 30.1 (26 36) Total cholesterol, median (IQR) mg/dl 194 ( ) 194 ( ) LDL, median (IQR) mg/dl 111 (88 132) 108 ( ) HDL, median (IQR) mg/dl 51 (42 61) 52 (44 64) Triglycerides, median (IQR) mg/dl 144 ( ) 132 ( ) LDL/HDL, median (IQR) 2.13 ( ) 2.13 ( ) Total cholesterol/hdl, median (IQR) 3.81 ( ) 3.67 ( ) CRP level (n 234 [33%]), median (IQR) of maximum mg/liter 7.7 ( ) 7.2 ( ) 8.0 ( ) ESR (n 513 [73%]), median (IQR) of maximum mm/hour 31.0 (16 56) 33.0 (18 58) 29.0 (14 54) * Values are the number (percentage) unless otherwise indicated. HCQ hydroxychloroquine; anti-ccp anti cyclic citrullinated peptide; TNF tumor necrosis factor ; NSAIDs nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs; IQR interquartile range; BMI body mass index; LDL low-density lipoprotein; HDL high-density lipoprotein; CRP C-reactive protein; ESR erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Obtained either from chi-square tests (frequencies), Wilcoxon s test (medians), or the Kruskal-Wallis test (means). A total of 226 patients had a statin order prior to the first lipid result and were included in the statin potency (6) analysis. Age calculated at the time of rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis. Lipid levels prior to inclusion in the cohort (the closest measurement prior to inclusion; n 313 in the HCQ never user group and n 185 in the HCQ ever user groups). terol result, and 95% had a triglycerides result; 95% had all 4 lipid panel results at least once. Approximately 30% had only 1 lipid panel result during observation, approximately 17% had 2, approximately 12% had 3, and 11% had 4; the remaining had 5 or more lipid panel results during the study timeframe, resulting in a total of 2,851 lipid results. The median time between results was 183 days (interquartile range [IQR] days). The general characteristics of the patients are listed in Table 1. A total of 256 patients (36%) were ever receiving HCQ. The median exposure time to HCQ was 1.98 years (IQR years). Patients were predominantly women (69%) and 98% were white, with a median age of 65 years and a median BMI of 29.8 kg/m 2. Rheumatoid factor (69% known) and anti cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies (33% known) were positive in 79% and 42%, respectively. The HCQ ever users were more likely to be women and younger, and less likely to have ever been treated with methotrexate compared with the HCQ never users. Statin use was similar in the two groups, including the categorization by statin potency, with the exception of the medium-potency statin category that was more prevalent in the HCQ never users. Lipid levels prior to inclusion in the study cohort were available in 185 HCQ ever users and 313 HCQ never users, and there were no differences in the median total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglycerides levels or between the median LDL/HDL and total cholesterol/hdl ratios between the two groups. In the regression models, after adjusting for demographic features, BMI, ESR, CRP level, rheumatoid factor, anti cyclic citrullinated peptide, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and use of glucocorticoids, NSAIDs, anti tumor necrosis factor therapy, methotrexate, and lipidlowering medications, HCQ was associated with the following average differences in lipids: LDL decrease of 7.55 mg/dl (P 0.001), HDL increase of 1.02 mg/dl (P 0.20), total cholesterol decrease of 7.70 mg/dl (P 0.002), triglycerides decrease of mg/dl (P 0.06), LDL/HDL decrease (P 0.008), and total cholesterol/hdl decrease of (P 0.006) (Figures 1 and 2). These effects were found to be stable over time, as demonstrated by a lack of a significant interaction between HCQ use and time since diagnosis. Cumulative exposure to HCQ models resulted in the same directional and significant findings. The sensitivity analysis in the 347 patients that were not receiving statins after RA diagnosis found very similar
4 Improving Lipid Levels in RA Patients Using HCQ 533 Figure 1. Association of hydroxychloroquine effect with lowdensity lipoprotein (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), total cholesterol, and triglycerides. results. HCQ use was associated with the following average differences in lipids: LDL decrease of mg/dl (P 0.001), HDL decrease of 1.89 mg/dl (P 0.161), total cholesterol decrease of mg/dl (P 0.001), triglycerides decrease of mg/dl (P 0.048), LDL/HDL decrease (P 0.041), and total cholesterol/hdl decrease of (P 0.222). These results suggest that HCQ use is independently associated with lower LDL, total cholesterol, LDL/HDL, and total cholesterol/hdl in patients with RA. Patients taking HCQ also had an increase in HDL and a decrease in triglycerides, although these findings were not statistically significant. The observations from this study are consistent with the previously reported association of antimalarial agents with a favorable lipid profile in smaller studies, although this study did not find a significant association of HCQ use with increased HDL. In a study of 155 patients with RA or SLE, an association was found between HCQ treatment and low serum levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL (7). In another study of 66 patients with RA, an increase in HDL in patients taking HCQ was reported compared to an increase in total cholesterol and triglycerides and a decrease in HDL in patients taking gold (8). These results were confirmed in a study of 100 RA patients that compared the effects of gold and HCQ on lipids. Patients treated with gold had a decrease in HDL and an increase in triglycerides. Patients in the HCQ group had an increase in HDL and no significant changes in total cholesterol and triglycerides. There were no significant differences in efficacy for disease response between the two groups (9). In a longitudinal cohort of 264 patients with SLE, HCQ therapy was associated with lower serum cholesterol (10). Patients with active RA have altered lipid metabolism characterized by hypocholesterolemia with a global reduction of total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, very LDL, and triglycerides (11,12). RA patients have been shown to have low levels of HDL and higher lipoprotein(a) (13) and increased total cholesterol/hdl, which is associated with an increased risk of CVD (14). It has been reported that higher inflammatory marker levels correlate inversely with total cholesterol and HDL levels, and with related levels of apolipoproteins B and A-I. Reduced HDL and elevated lipoprotein(a) correlate with elevated CRP levels in patients with RA (15). There is some evidence that controlling disease activity may improve lipid profiles (15,16). HCQ has a relatively weak antiinflammatory effect; therefore, it is unlikely that the beneficial effect on lipids is conferred solely by controlling systemic inflammation. The mechanism by which this effect is mediated is uncertain. It has been reported that chloroquine, a medication structurally similar to HCQ, is an inhibitor of cholesterol biosynthesis in rat hepatocytes (17). In cultured human fibroblasts and mouse adrenal cells, chloroquine has multiple effects on cholesterol metabolism. Chloroquine also inhibits lysosomal hydrolysis of cholesteryl esters through an increase in the ph within lysosomes and inactivates acid proteases. Additionally, it stimulates the capacity of LDL receptor and the activity of HMG-CoA reductase, and slows the degradation of HMG-CoA reductase (17). A significant concern regarding the present study is confounding by indication. Since the allocation of a patient to treatment with HCQ was not randomized, it is DISCUSSION Figure 2. Association of hydroxychloroquine effect with lowdensity lipoprotein (LDL)/high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and total cholesterol (Chol)/HDL.
5 534 Morris et al possible that patients with less severe or better controlled disease were treated with HCQ, thus confounding the results. While it is impossible to eliminate confounding by indication in observational studies, there were several safeguards to limit its influence in the results of the present study. Although the patients in the HCQ ever users group were younger and less likely to have ever been treated with methotrexate, they were not more likely to have positive rheumatoid factor or have been treated with steroids or tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (surrogate markers of disease severity). Furthermore, the two groups had similar median levels of ESR and CRP (surrogate markers of disease activity). Median lipid levels prior to inclusion in the study cohort and statin use were similar in the two groups, including categorization by statin potency, with the exception of the medium-potency statin category that was more prevalent in the HCQ never users, which, if any, would bias the results toward favorable lipid profiles in the HCQ never users group. At the analysis level, a linear mixed-effects regression model controlled for characteristics that were different between the groups and could potentially be associated with lipid profiles. The present study reports on an incident RA cohort using electronic health records with physician diagnoses, laboratory values, and medications. Adjustment was performed for major confounders that affect lipid profiles; however, other risk factors for dyslipidemia, such as family history, central adiposity, and physical activity, were not available in this cohort. Additional limitations include that the disease activity was not measured directly, although surrogate measures as CRP levels and ESR are reported. The data were extracted from documentation for routine medical care and not systematically collected for research purposes, resulting in missing laboratory values in a number of patients. More than 50% of patients were excluded due to the fact that lipid profiles were not available. This likely resulted from patients having primary care physicians outside of the Geisinger Health System. Finally, the study cohort is ethnically homogeneous, limiting the generalizability of our findings. The findings of this study support the potential benefit of HCQ in improving the atherogenic lipid profiles in patients with RA. This is particularly important in this patient population that has a higher risk for CVD. Although HCQ has only modest disease-modifying effects in the treatment of RA, its apparent effects on lipid profiles, and elsewhere reported inhibition of platelet aggregation and reduction in diabetes mellitus risk, along with its excellent safety profile and low cost, make it a beneficial first-line or adjunct therapy for RA patients, particularly those with traditional CVD risk factors. AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS All authors were involved in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content, and all authors approved the final version to be published. Dr. Bili had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Study conception and design. Morris, Wasko, Kirchner, Dancea, Bili. Acquisition of data. Morris, Antohe, Kirchner, Dancea, Bili. Analysis and interpretation of data. Morris, Wasko, Sartorius, Kirchner, Bili. REFERENCES 1. Wolfe F, Mitchell DM, Sibley JT, Fries JF, Bloch DA, Williams CA, et al. The mortality of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1994;37: Kahn R, Robertson RM, Smith R, Eddy D. The impact of prevention on reducing the burden of cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2008;118: Lazarevic MB, Vitic J, Mladenovic V, Myones BL, Skosey JL, Swedler WI. Dyslipoproteinemia in the course of active rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 1992;22: Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1988;31: Shai I, Rimm EB, Hankinson SE, Curhan G, Manson JE, Rifai N, et al. Multivariate assessment of lipid parameters as predictors of coronary heart disease among postmenopausal women: potential implications for clinical guidelines. Circulation 2004;110: Meyer JW, Schultz JS, O Donnell JC, Patel PA, Sasane RM. Patterns and effectiveness of lipid-lowering therapies in a managed care environment. Value Health 2005;8: Wallace DJ, Metzger AL, Stecher VJ, Turnbull BA, Kern PA. Cholesterol-lowering effect of hydroxychloroquine in patients with rheumatic disease: reversal of deleterious effects of steroids on lipids. Am J Med 1990;89: Blyth TH, McDonald AG, Capell HA, Hunter JA. A comparison of hydroxychloroquine and myocrisin in rheumatoid arthritis [abstract]. Br J Rheumatol 1994;33 Suppl: Munro R, Morrison E, McDonald AG, Hunter JA, Madhok R, Capell HA. Effect of disease modifying agents on the lipid profiles of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 1997;56: Petri M, Lakatta C, Magder L, Goldman D. Effect of prednisone and hydroxychloroquine on coronary artery disease risk factors in systemic lupus erythematosus: a longitudinal data analysis. Am J Med 1994;96: Svenson KL, Lithell H, Hallgren R, Selinus I, Vessby B. Serum lipoprotein in active rheumatoid arthritis and other chronic inflammatory arthritides. I. Relativity to inflammatory activity. Arch Intern Med 1987;147: Park YB, Lee SK, Lee WK, Suh CH, Lee CW, Lee CH, et al. Lipid profiles in untreated patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 1999;26: Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, Wallberg-Jonsson S, Dahlen G. Lipoprotein (a), lipids, and lipoproteins in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 1991;50: Stampfer MJ, Sacks FM, Salvini S, Willett WC, Hennekens CH. A prospective study of cholesterol, apolipoproteins, and the risk of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 1991;325: Cho JY, Park JS, Baik KU, Lee JG, Kim HP, Yoo ES, et al. Differential effect of phosphodiesterase IV inhibitor RP73401 on various inflammatory and immune responses relevant to rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacol Res 2004;49: Park YB, Choi HK, Kim MY, Lee WK, Song J, Kim DK, et al. Effects of antirheumatic therapy on serum lipid levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study. Am J Med 2002;113: Beynen AC, van der Molen AJ, Geelen MJ. Inhibition of hepatic cholesterol biosynthesis by chloroquine. Lipids 1981; 16:472 4.
The Framingham Coronary Heart Disease Risk Score
 Plasma Concentration of C-Reactive Protein and the Calculated Framingham Coronary Heart Disease Risk Score Michelle A. Albert, MD, MPH; Robert J. Glynn, PhD; Paul M Ridker, MD, MPH Background Although
Plasma Concentration of C-Reactive Protein and the Calculated Framingham Coronary Heart Disease Risk Score Michelle A. Albert, MD, MPH; Robert J. Glynn, PhD; Paul M Ridker, MD, MPH Background Although
Clinical Policy: Etanercept (Enbrel) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.250 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid
 Clinical Policy: (Enbrel) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.250 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid Coding Implications Revision Log Description (Enbrel ) is tumor necrosis
Clinical Policy: (Enbrel) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.250 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid Coding Implications Revision Log Description (Enbrel ) is tumor necrosis
SCIENTIFIC STUDY REPORT
 PAGE 1 18-NOV-2016 SCIENTIFIC STUDY REPORT Study Title: Real-Life Effectiveness and Care Patterns of Diabetes Management The RECAP-DM Study 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction: Despite the well-established
PAGE 1 18-NOV-2016 SCIENTIFIC STUDY REPORT Study Title: Real-Life Effectiveness and Care Patterns of Diabetes Management The RECAP-DM Study 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction: Despite the well-established
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the most common systemic
 Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality in Women Diagnosed With Rheumatoid Daniel H. Solomon, MD, MPH; Elizabeth W. Karlson, MD; Eric B. Rimm, ScD; Carolyn C. Cannuscio, ScD; Lisa A. Mandl, MD, MPH; JoAnn
Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality in Women Diagnosed With Rheumatoid Daniel H. Solomon, MD, MPH; Elizabeth W. Karlson, MD; Eric B. Rimm, ScD; Carolyn C. Cannuscio, ScD; Lisa A. Mandl, MD, MPH; JoAnn
Table S1. Read and ICD 10 diagnosis codes for polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL TEXT Text S1. Multiple imputation TABLES Table S1. Read and ICD 10 diagnosis codes for polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis Table S2. List of drugs included as immunosuppressant
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL TEXT Text S1. Multiple imputation TABLES Table S1. Read and ICD 10 diagnosis codes for polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis Table S2. List of drugs included as immunosuppressant
Mandana Nikpour 1,2, Murray B Urowitz 1*, Dominique Ibanez 1, Paula J Harvey 3 and Dafna D Gladman 1. Abstract
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Importance of cumulative exposure to elevated cholesterol and blood pressure in development of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Importance of cumulative exposure to elevated cholesterol and blood pressure in development of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective
Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD INTRODUCTION
 2 Hyperlipidemia Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION RISK CATEGORIES AND TARGET LDL-CHOLESTEROL TREATMENT OF LDL-CHOLESTEROL SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS OLDER AND YOUNGER ADULTS ADDITIONAL
2 Hyperlipidemia Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION RISK CATEGORIES AND TARGET LDL-CHOLESTEROL TREATMENT OF LDL-CHOLESTEROL SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS OLDER AND YOUNGER ADULTS ADDITIONAL
Abstract. Introduction. Daniel Li 1, Alex Meara 2, Brian LaMoreaux 2, Guy Brock 3, Wael Jarjour 2
 Research Article http://www.alliedacademies.org/archives-of-general-internal-medicine/ ISSN : 2591-7951 Assessment of cardiovascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Daniel Li 1, Alex Meara 2,
Research Article http://www.alliedacademies.org/archives-of-general-internal-medicine/ ISSN : 2591-7951 Assessment of cardiovascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Daniel Li 1, Alex Meara 2,
Hydroxychloroquine and Risk of Diabetes in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
 PRELIMINARY COMMUNICATION Hydroxychloroquine and Risk of Diabetes in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Mary Chester M. Wasko, MD, MSc Helen B. Hubert, MPH, PhD Vijaya Bharathi Lingala, PhD Jennifer R.
PRELIMINARY COMMUNICATION Hydroxychloroquine and Risk of Diabetes in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Mary Chester M. Wasko, MD, MSc Helen B. Hubert, MPH, PhD Vijaya Bharathi Lingala, PhD Jennifer R.
B. Patient has not reached the percentage reduction goal with statin therapy
 Managing Cardiovascular Risk: The Importance of Lowering LDL Cholesterol and Reaching Treatment Goals for LDL Cholesterol The Role of the Pharmacist Learning Objectives 1. Review the role of lipid levels
Managing Cardiovascular Risk: The Importance of Lowering LDL Cholesterol and Reaching Treatment Goals for LDL Cholesterol The Role of the Pharmacist Learning Objectives 1. Review the role of lipid levels
Normal Fasting Plasma Glucose and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis
 CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Normal Fasting Plasma Glucose and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis Gregory A. Nichols, PhD, Teresa A. Hillier, MD, MS, Jonathan B. Brown, PhD, MPP Center for Health Research, Kaiser
CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Normal Fasting Plasma Glucose and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosis Gregory A. Nichols, PhD, Teresa A. Hillier, MD, MS, Jonathan B. Brown, PhD, MPP Center for Health Research, Kaiser
J. van Aken* H. van Dongen* S. le Cessie F.C. Breedveld T.W.J. Huizinga. * both authors contributed equally
 CHAPTER Comparison of long term outcome of patients with rheumatoid arthritis presenting with undifferentiated arthritis or with rheumatoid arthritis: an observational cohort study J. van Aken* H. van
CHAPTER Comparison of long term outcome of patients with rheumatoid arthritis presenting with undifferentiated arthritis or with rheumatoid arthritis: an observational cohort study J. van Aken* H. van
Marshall Tulloch-Reid, MD, MPhil, DSc, FACE Epidemiology Research Unit Tropical Medicine Research Institute The University of the West Indies, Mona,
 Marshall Tulloch-Reid, MD, MPhil, DSc, FACE Epidemiology Research Unit Tropical Medicine Research Institute The University of the West Indies, Mona, Jamaica At the end of this presentation the participant
Marshall Tulloch-Reid, MD, MPhil, DSc, FACE Epidemiology Research Unit Tropical Medicine Research Institute The University of the West Indies, Mona, Jamaica At the end of this presentation the participant
JUPITER NEJM Poll. Panel Discussion: Literature that Should Have an Impact on our Practice: The JUPITER Study
 Panel Discussion: Literature that Should Have an Impact on our Practice: The Study Kaiser COAST 11 th Annual Conference Maui, August 2009 Robert Blumberg, MD, FACC Ralph Brindis, MD, MPH, FACC Primary
Panel Discussion: Literature that Should Have an Impact on our Practice: The Study Kaiser COAST 11 th Annual Conference Maui, August 2009 Robert Blumberg, MD, FACC Ralph Brindis, MD, MPH, FACC Primary
LEPTIN AS A NOVEL PREDICTOR OF DEPRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH THE METABOLIC SYNDROME
 LEPTIN AS A NOVEL PREDICTOR OF DEPRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH THE METABOLIC SYNDROME Diana A. Chirinos, Ronald Goldberg, Elias Querales-Mago, Miriam Gutt, Judith R. McCalla, Marc Gellman and Neil Schneiderman
LEPTIN AS A NOVEL PREDICTOR OF DEPRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH THE METABOLIC SYNDROME Diana A. Chirinos, Ronald Goldberg, Elias Querales-Mago, Miriam Gutt, Judith R. McCalla, Marc Gellman and Neil Schneiderman
Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL
 Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL Sung-Joon Lee, PhD Division of Food Science Institute of Biomedical Science and Safety Korea University Composition of Lipoproteins:
Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL Sung-Joon Lee, PhD Division of Food Science Institute of Biomedical Science and Safety Korea University Composition of Lipoproteins:
A: Epidemiology update. Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups
 A: Epidemiology update Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups Women (n = 27,939; mean age 54.7 years) who were free of symptomatic cardiovascular (CV) disease at baseline were
A: Epidemiology update Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups Women (n = 27,939; mean age 54.7 years) who were free of symptomatic cardiovascular (CV) disease at baseline were
Statin therapy in patients with Mild to Moderate Coronary Stenosis by 64-slice Multidetector Coronary Computed Tomography
 Statin therapy in patients with Mild to Moderate Coronary Stenosis by 64-slice Multidetector Coronary Computed Tomography Hyo Eun Park 1, Eun-Ju Chun 2, Sang-Il Choi 2, Soyeon Ahn 2, Hyung-Kwan Kim 3,
Statin therapy in patients with Mild to Moderate Coronary Stenosis by 64-slice Multidetector Coronary Computed Tomography Hyo Eun Park 1, Eun-Ju Chun 2, Sang-Il Choi 2, Soyeon Ahn 2, Hyung-Kwan Kim 3,
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. C-Reactive Protein Concentration and Incident Hypertension in Young Adults
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION C-Reactive Protein Concentration and Incident Hypertension in Young Adults The CARDIA Study Susan G. Lakoski, MD, MS; David M. Herrington, MD, MHS; David M. Siscovick, MD, MPH; Stephen
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION C-Reactive Protein Concentration and Incident Hypertension in Young Adults The CARDIA Study Susan G. Lakoski, MD, MS; David M. Herrington, MD, MHS; David M. Siscovick, MD, MPH; Stephen
Bariatric Surgery versus Intensive Medical Therapy for Diabetes 3-Year Outcomes
 The new england journal of medicine original article Bariatric Surgery versus Intensive Medical for Diabetes 3-Year Outcomes Philip R. Schauer, M.D., Deepak L. Bhatt, M.D., M.P.H., John P. Kirwan, Ph.D.,
The new england journal of medicine original article Bariatric Surgery versus Intensive Medical for Diabetes 3-Year Outcomes Philip R. Schauer, M.D., Deepak L. Bhatt, M.D., M.P.H., John P. Kirwan, Ph.D.,
Supplemental Figures and Legends
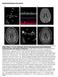 Supplemental Figures and Legends Online Figure 1. 18 year old female with SLE and acute homonymous hemianopsia, confusional state, and cognitive dysfunction. A. This TEE four chamber view demonstrates
Supplemental Figures and Legends Online Figure 1. 18 year old female with SLE and acute homonymous hemianopsia, confusional state, and cognitive dysfunction. A. This TEE four chamber view demonstrates
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
 BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
TREAT-TO-TARGET IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 TREAT-TO-TARGET IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS To receive up to 10 CME credits for this activity, complete the evaluation, attestation and post-test answer sheet (minimum passing grade of 70%) and return all
TREAT-TO-TARGET IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS To receive up to 10 CME credits for this activity, complete the evaluation, attestation and post-test answer sheet (minimum passing grade of 70%) and return all
Comparison of long-term clinical outcome with etanercept and adalimumab treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with respect to immunogenicity
 7 Comparison of long-term clinical outcome with etanercept and adalimumab treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with respect to immunogenicity Charlotte Krieckaert* Anna Jamnitski* Mike Nurmohamed Piet Kostense
7 Comparison of long-term clinical outcome with etanercept and adalimumab treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with respect to immunogenicity Charlotte Krieckaert* Anna Jamnitski* Mike Nurmohamed Piet Kostense
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Pedersen SB, Langsted A, Nordestgaard BG. Nonfasting mild-to-moderate hypertriglyceridemia and risk of acute pancreatitis. JAMA Intern Med. Published online November 7, 2016.
Supplementary Online Content Pedersen SB, Langsted A, Nordestgaard BG. Nonfasting mild-to-moderate hypertriglyceridemia and risk of acute pancreatitis. JAMA Intern Med. Published online November 7, 2016.
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC Update on the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Sabrina Fallavollita MDCM McGill University Canadian Society of Internal Medicine
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC Update on the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Sabrina Fallavollita MDCM McGill University Canadian Society of Internal Medicine
Clinical Policy: Certolizumab (Cimzia) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.247 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid
 Clinical Policy: (Cimzia) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.247 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid Coding Implications Revision Log Description (Cimzia ) is a tumor necrosis
Clinical Policy: (Cimzia) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.247 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid Coding Implications Revision Log Description (Cimzia ) is a tumor necrosis
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors
 Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
Clinical Trial Synopsis TL-OPI-518, NCT#
 Clinical Trial Synopsis, NCT# 00225264 Title of Study: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Comparator-Controlled Study in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Comparing the Effects of Pioglitazone HCl vs Glimepiride
Clinical Trial Synopsis, NCT# 00225264 Title of Study: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Comparator-Controlled Study in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Comparing the Effects of Pioglitazone HCl vs Glimepiride
Hydroxychloroquine Use Is Associated With Decreased Incident Cardiovascular Events in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Hydroxychloroquine Use Is Associated With Decreased Incident Cardiovascular Events in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Tarun S. Sharma, MD;* Mary Chester M. Wasko, MD, MSc;* Xiaoqin Tang,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Hydroxychloroquine Use Is Associated With Decreased Incident Cardiovascular Events in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Tarun S. Sharma, MD;* Mary Chester M. Wasko, MD, MSc;* Xiaoqin Tang,
Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease. Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010
 Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010 Relationships Between Diabetes and Ischemic Heart Disease Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Different Categories
Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010 Relationships Between Diabetes and Ischemic Heart Disease Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Different Categories
THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ Disclosures: On National Advisory Boards of: (1) Pfizer Pharmaceuticals (2) MSD (3) Roche Pharmaceuticals (4) Abbott International: AfME Rheumatology
THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ Disclosures: On National Advisory Boards of: (1) Pfizer Pharmaceuticals (2) MSD (3) Roche Pharmaceuticals (4) Abbott International: AfME Rheumatology
James R. O Dell, M.D. University of Nebraska Medical Center
 Not everyone in the world needs a biologic: Lessons from TEAR and RACAT James R. O Dell, M.D. University of Nebraska Medical Center Disclosure Declaration James O Dell, MD Advisory Board for Crescendo,
Not everyone in the world needs a biologic: Lessons from TEAR and RACAT James R. O Dell, M.D. University of Nebraska Medical Center Disclosure Declaration James O Dell, MD Advisory Board for Crescendo,
Heart Online First, published on March 29, 2005 as /hrt SCIENTIFIC LETTER
 Heart Online First, published on March 29, 2005 as 10.1136/hrt.2004.056523 Manuscript ID: HEARTJNL/2004/056523 March 18, 2005 SCIENTIFIC LETTER Effects of HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibition on Endothelial Function
Heart Online First, published on March 29, 2005 as 10.1136/hrt.2004.056523 Manuscript ID: HEARTJNL/2004/056523 March 18, 2005 SCIENTIFIC LETTER Effects of HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibition on Endothelial Function
Table S1. Characteristics associated with frequency of nut consumption (full entire sample; Nn=4,416).
 Table S1. Characteristics associated with frequency of nut (full entire sample; Nn=4,416). Daily nut Nn= 212 Weekly nut Nn= 487 Monthly nut Nn= 1,276 Infrequent or never nut Nn= 2,441 Sex; n (%) men 52
Table S1. Characteristics associated with frequency of nut (full entire sample; Nn=4,416). Daily nut Nn= 212 Weekly nut Nn= 487 Monthly nut Nn= 1,276 Infrequent or never nut Nn= 2,441 Sex; n (%) men 52
Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both
 Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both Lluís Masana Vascular Medicine and Metabolism Unit. Sant Joan University Hospital. IISPV. CIBERDEM Rovira i Virgili
Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both Lluís Masana Vascular Medicine and Metabolism Unit. Sant Joan University Hospital. IISPV. CIBERDEM Rovira i Virgili
The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema
 The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema Dept Cardiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden,
The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema Dept Cardiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden,
ANTIHYPERLIPIDEMIA. Darmawan,dr.,M.Kes,Sp.PD
 ANTIHYPERLIPIDEMIA Darmawan,dr.,M.Kes,Sp.PD Plasma lipids consist mostly of lipoproteins Spherical complexes of lipids and specific proteins (apolipoproteins). The clinically important lipoproteins, listed
ANTIHYPERLIPIDEMIA Darmawan,dr.,M.Kes,Sp.PD Plasma lipids consist mostly of lipoproteins Spherical complexes of lipids and specific proteins (apolipoproteins). The clinically important lipoproteins, listed
Achieving Cholesterol Management Goals: Identifying Clinician-Centered Challenges to Optimal Patient Care
 Achieving Cholesterol Management Goals: Identifying Clinician-Centered Challenges to Optimal Patient Care Purpose Explore the adherence rates to cholesterol treatment targets among patients who seek care
Achieving Cholesterol Management Goals: Identifying Clinician-Centered Challenges to Optimal Patient Care Purpose Explore the adherence rates to cholesterol treatment targets among patients who seek care
A. Jamnitski J.H. Levels I.A.M. van den Oever M.T. Nurmohamed. J Rheumatol Jun;40(6):
 Chapter 2.2 High-density lipoprotein profiling changes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors: a cohort study A. Jamnitski J.H. Levels I.A.M. van den Oever
Chapter 2.2 High-density lipoprotein profiling changes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors: a cohort study A. Jamnitski J.H. Levels I.A.M. van den Oever
ADHD and Adverse Health Outcomes in Adults
 Thomas J. Spencer, MD This work was supported in part by a research grant from Shire (Dr. Spencer) and by the Pediatric Psychopharmacology Council Fund. Disclosures Dr. Spencer receives research support
Thomas J. Spencer, MD This work was supported in part by a research grant from Shire (Dr. Spencer) and by the Pediatric Psychopharmacology Council Fund. Disclosures Dr. Spencer receives research support
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Solomon SD, Uno H, Lewis EF, et al. Erythropoietic response
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Solomon SD, Uno H, Lewis EF, et al. Erythropoietic response
Why Do We Treat Obesity? Epidemiology
 Why Do We Treat Obesity? Epidemiology Epidemiology of Obesity U.S. Epidemic 2 More than Two Thirds of US Adults Are Overweight or Obese 87.5 NHANES Data US Adults Age 2 Years (Crude Estimate) Population
Why Do We Treat Obesity? Epidemiology Epidemiology of Obesity U.S. Epidemic 2 More than Two Thirds of US Adults Are Overweight or Obese 87.5 NHANES Data US Adults Age 2 Years (Crude Estimate) Population
The Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Pharmacologic and Nonpharmacologic Myocardial Infarction Predictors in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 58, No. 9, September 2008, pp 2612 2621 DOI 10.1002/art.23811 2008, American College of Rheumatology The Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Pharmacologic and Nonpharmacologic
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 58, No. 9, September 2008, pp 2612 2621 DOI 10.1002/art.23811 2008, American College of Rheumatology The Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Pharmacologic and Nonpharmacologic
Established Risk Factors for Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
 Getting Patients to Make Small Lifestyle Changes That Result in SIGNIFICANT Improvements in Health - Prevention of Diabetes and Obesity for Better Health Maureen E. Mays, MD, MS, FACC Director ~ Portland
Getting Patients to Make Small Lifestyle Changes That Result in SIGNIFICANT Improvements in Health - Prevention of Diabetes and Obesity for Better Health Maureen E. Mays, MD, MS, FACC Director ~ Portland
LONGITUDINAL TREATMENT PATTERNS AND ASSOCIATED OUTCOMES IN PATIENTS WITH NEWLY DIAGNOSED SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS. Hong Kan 7/12/2016
 LONGITUDINAL TREATMENT PATTERNS AND ASSOCIATED OUTCOMES IN PATIENTS WITH NEWLY DIAGNOSED SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Hong Kan 7/12/2016 1 Acknowledgements Research conceptualization and design, programming
LONGITUDINAL TREATMENT PATTERNS AND ASSOCIATED OUTCOMES IN PATIENTS WITH NEWLY DIAGNOSED SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Hong Kan 7/12/2016 1 Acknowledgements Research conceptualization and design, programming
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Schauer PR, Kashyap SR, Wolski K, et al. Bariatric surgery
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Schauer PR, Kashyap SR, Wolski K, et al. Bariatric surgery
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Materials and Methods. Study design
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Materials and Methods Study design The ELSA-Brasil design and concepts have been detailed elsewhere 1. The ELSA-Brasil is a cohort study of active or retired 15,105 civil servants,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Materials and Methods Study design The ELSA-Brasil design and concepts have been detailed elsewhere 1. The ELSA-Brasil is a cohort study of active or retired 15,105 civil servants,
300 Biomed Environ Sci, 2018; 31(4):
 300 Biomed Environ Sci, 2018; 31(4): 300-305 Letter to the Editor Combined Influence of Insulin Resistance and Inflammatory Biomarkers on Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-based Prospective Cohort Study of
300 Biomed Environ Sci, 2018; 31(4): 300-305 Letter to the Editor Combined Influence of Insulin Resistance and Inflammatory Biomarkers on Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-based Prospective Cohort Study of
Epidemiology and Prevention
 Epidemiology and Prevention Associations of Pregnancy Complications With Calculated Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Middle Age The Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and
Epidemiology and Prevention Associations of Pregnancy Complications With Calculated Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Middle Age The Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and
Know Your Number Aggregate Report Single Analysis Compared to National Averages
 Know Your Number Aggregate Report Single Analysis Compared to National s Client: Study Population: 2242 Population: 3,000 Date Range: 04/20/07-08/08/07 Version of Report: V6.2 Page 2 Study Population Demographics
Know Your Number Aggregate Report Single Analysis Compared to National s Client: Study Population: 2242 Population: 3,000 Date Range: 04/20/07-08/08/07 Version of Report: V6.2 Page 2 Study Population Demographics
Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 Mod Rheumatol (2007) 17:28 32 Japan College of Rheumatology 2007 DOI 10.1007/s10165-006-0532-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hisashi Yamanaka Yoshiya Tanaka Naoya Sekiguchi Eisuke Inoue Kazuyoshi Saito Hideto Kameda
Mod Rheumatol (2007) 17:28 32 Japan College of Rheumatology 2007 DOI 10.1007/s10165-006-0532-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hisashi Yamanaka Yoshiya Tanaka Naoya Sekiguchi Eisuke Inoue Kazuyoshi Saito Hideto Kameda
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin and
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin and
Annual Rheumatology & Therapeutics Review for Organizations & Societies
 Annual Rheumatology & Therapeutics Review for Organizations & Societies Comparative Effectiveness Studies of Biologics Learning Objectives Understand the motivation for comparative effectiveness research
Annual Rheumatology & Therapeutics Review for Organizations & Societies Comparative Effectiveness Studies of Biologics Learning Objectives Understand the motivation for comparative effectiveness research
Non-commercial use only
 Reumatismo, 2016; 68 (2): 90-96 Real-world experiences of folic acid supplementation (5 versus 30 mg/week) with methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a comparison study K.T. Koh 1, C.L. Teh 2,
Reumatismo, 2016; 68 (2): 90-96 Real-world experiences of folic acid supplementation (5 versus 30 mg/week) with methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a comparison study K.T. Koh 1, C.L. Teh 2,
Best Lipid Treatments
 Best Lipid Treatments Pam R. Taub MD, FACC Director of Step Family Cardiac Rehabilitation and Wellness Center Associate Professor of Medicine UC San Diego Health System Overview of Talk Review of pathogenesis
Best Lipid Treatments Pam R. Taub MD, FACC Director of Step Family Cardiac Rehabilitation and Wellness Center Associate Professor of Medicine UC San Diego Health System Overview of Talk Review of pathogenesis
Misperceptions still exist that cardiovascular disease is not a real problem for women.
 Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in the Cynthia A., MD University of California, San Diego ARHP 9/19/08 Disclosures Research support Wyeth, Lilly, Organon, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer Consultant fees
Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in the Cynthia A., MD University of California, San Diego ARHP 9/19/08 Disclosures Research support Wyeth, Lilly, Organon, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer Consultant fees
Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Metabolic Syndrome, and the Natural History of Type 2 Diabetes
 Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Metabolic Syndrome, and the Natural History of Type 2 Diabetes Genetics, environment, and lifestyle (obesity, inactivity, poor diet) Impaired fasting glucose Decreased β-cell
Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Metabolic Syndrome, and the Natural History of Type 2 Diabetes Genetics, environment, and lifestyle (obesity, inactivity, poor diet) Impaired fasting glucose Decreased β-cell
Joslin Diabetes Center Advances in Diabetes and Thyroid Disease 2013 Consensus and Controversy in Diabetic Dyslipidemia
 Consensus and Controversy in Diabetes and Dyslipidemia Om P. Ganda MD Director, Lipid Clinic Joslin diabetes Center Boston, MA, USA CVD Outcomes in DM vs non- DM 102 Prospective studies; 698, 782 people,
Consensus and Controversy in Diabetes and Dyslipidemia Om P. Ganda MD Director, Lipid Clinic Joslin diabetes Center Boston, MA, USA CVD Outcomes in DM vs non- DM 102 Prospective studies; 698, 782 people,
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR Safety and Efficacy of Tocilizumab as Monotherapy and in Combination with Methotrexate
 New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2009 Safety and Efficacy of Tocilizumab as Monotherapy and in Combination with Methotrexate Report on EULAR 2009 presentations Tocilizumab inhibits
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2009 Safety and Efficacy of Tocilizumab as Monotherapy and in Combination with Methotrexate Report on EULAR 2009 presentations Tocilizumab inhibits
Lipids Board Review. Ira Goldberg, MD New York University School of Medicine. Which of the following is the best initial therapy choice?
 Lipids Board Review Ira Goldberg, MD New York University School of Medicine 1. A 22 year old male college student is referred for severe hypertriglyceridemia ( 1500 mg/dl [ 17.0 mmol/l]). He has a history
Lipids Board Review Ira Goldberg, MD New York University School of Medicine 1. A 22 year old male college student is referred for severe hypertriglyceridemia ( 1500 mg/dl [ 17.0 mmol/l]). He has a history
On May 2001, the Third Adult
 THE RISK OF DIABETES: CAN WE IMPACT CHD THROUGH THE ATP III CHOLESTEROL GUIDELINES? * Based on a presentation given by Steven M. Haffner, MD, MPH ABSTRACT Diabetes has been recognized among diabetologists
THE RISK OF DIABETES: CAN WE IMPACT CHD THROUGH THE ATP III CHOLESTEROL GUIDELINES? * Based on a presentation given by Steven M. Haffner, MD, MPH ABSTRACT Diabetes has been recognized among diabetologists
Diabetic Dyslipidemia
 Diabetic Dyslipidemia Dr R V S N Sarma, M.D., (Internal Medicine), M.Sc., (Canada), Consultant Physician Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a significant cause of illness, disability, and death among individuals
Diabetic Dyslipidemia Dr R V S N Sarma, M.D., (Internal Medicine), M.Sc., (Canada), Consultant Physician Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a significant cause of illness, disability, and death among individuals
SITA 100 mg (n = 378)
 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of Sulfonylurea Background Therapy at Baseline and During the Treatment Period. Sulfonylurea at baseline, n (%) SITA 100 mg (n = 378) CANA 300 mg (n = 377) Total (N = 755)
Supplementary Table 1. Summary of Sulfonylurea Background Therapy at Baseline and During the Treatment Period. Sulfonylurea at baseline, n (%) SITA 100 mg (n = 378) CANA 300 mg (n = 377) Total (N = 755)
Effectiveness of a Multidisciplinary Patient Assistance Program in Diabetes Care
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Senior Honors Projects Honors Program at the University of Rhode Island 2009 Effectiveness of a Multidisciplinary Patient Assistance Program in Diabetes Care
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Senior Honors Projects Honors Program at the University of Rhode Island 2009 Effectiveness of a Multidisciplinary Patient Assistance Program in Diabetes Care
CLINICAL. Determinants of Compliance With Statin Therapy and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Goal Attainment in a Managed Care Population
 Determinants of Compliance With Statin Therapy and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Goal Attainment in a Managed Care Population Jennifer S. Schultz, PhD; John C. O Donnell, PhD; Ken L. McDonough, MD;
Determinants of Compliance With Statin Therapy and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Goal Attainment in a Managed Care Population Jennifer S. Schultz, PhD; John C. O Donnell, PhD; Ken L. McDonough, MD;
Committee Approval Date: May 9, 2014 Next Review Date: May 2015
 Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru248 Topic: Benlysta, belimumab Date of Origin: May 13, 2011 Committee Approval Date: May 9, 2014 Next Review Date: May 2015 Effective Date: June 1, 2014 IMPORTANT
Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru248 Topic: Benlysta, belimumab Date of Origin: May 13, 2011 Committee Approval Date: May 9, 2014 Next Review Date: May 2015 Effective Date: June 1, 2014 IMPORTANT
Hyperlipidemia. Prepared by : Muhannad Mohammed Supervisor professor : Dr. Ahmed Yahya Dallalbashi
 Hyperlipidemia Prepared by : Muhannad Mohammed Supervisor professor : Dr. Ahmed Yahya Dallalbashi Outline The story of lipids Definition of hyperlipidemia Classification of hyperlipidemia Causes of hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia Prepared by : Muhannad Mohammed Supervisor professor : Dr. Ahmed Yahya Dallalbashi Outline The story of lipids Definition of hyperlipidemia Classification of hyperlipidemia Causes of hyperlipidemia
Non-fasting lipids and risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes mellitus
 Diabetologia (2011) 54:73 77 DOI 10.1007/s00125-010-1945-z SHORT COMMUNICATION Non-fasting lipids and risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes mellitus S. van Dieren & U. Nöthlings & Y.
Diabetologia (2011) 54:73 77 DOI 10.1007/s00125-010-1945-z SHORT COMMUNICATION Non-fasting lipids and risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes mellitus S. van Dieren & U. Nöthlings & Y.
Patient #1. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour
 Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
A comparison of statistical methods for adjusting the treatment effects in genetic association studies of quantitative traits
 34 1 Journal of the Korean Society of Health Information and Health Statistics Volume 34, Number 1, 2009, pp. 53 62 53 한경화 1), 임길섭 2), 박성하 3), 장양수 4), 송기준 2) 1), 2), 3), 4) A comparison of statistical
34 1 Journal of the Korean Society of Health Information and Health Statistics Volume 34, Number 1, 2009, pp. 53 62 53 한경화 1), 임길섭 2), 박성하 3), 장양수 4), 송기준 2) 1), 2), 3), 4) A comparison of statistical
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Association between Raised Blood Pressure and Dysglycemia in Hong Kong Chinese
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online June 12, 2008 Raised Blood Pressure and Dysglycemia Association between Raised Blood Pressure and Dysglycemia in Hong Kong Chinese Bernard My Cheung,
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online June 12, 2008 Raised Blood Pressure and Dysglycemia Association between Raised Blood Pressure and Dysglycemia in Hong Kong Chinese Bernard My Cheung,
Medical evidence suggests that
 COMBINATION THERAPY TO ACHIEVE LIPID GOALS David G. Robertson, MD* ABSTRACT Coronary heart disease (CHD) remains the leading cause of death in the United States despite recent advances in treatment and
COMBINATION THERAPY TO ACHIEVE LIPID GOALS David G. Robertson, MD* ABSTRACT Coronary heart disease (CHD) remains the leading cause of death in the United States despite recent advances in treatment and
See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
 Clinical Policy: (Actemra) Reference Number: HIM.PA.SP32 Effective Date: 05/17 Last Review Date: Line of Business: Health Insurance Marketplace Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at
Clinical Policy: (Actemra) Reference Number: HIM.PA.SP32 Effective Date: 05/17 Last Review Date: Line of Business: Health Insurance Marketplace Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at
Figure S1. Comparison of fasting plasma lipoprotein levels between males (n=108) and females (n=130). Box plots represent the quartiles distribution
 Figure S1. Comparison of fasting plasma lipoprotein levels between males (n=108) and females (n=130). Box plots represent the quartiles distribution of A: total cholesterol (TC); B: low-density lipoprotein
Figure S1. Comparison of fasting plasma lipoprotein levels between males (n=108) and females (n=130). Box plots represent the quartiles distribution of A: total cholesterol (TC); B: low-density lipoprotein
Supplemental Table 1. Key Inclusion Criteria Inclusion Criterion OPTIMA PREMIER 18 years old with RA (per 1987 revised American College of General
 Supplemental Table 1. Key Inclusion Criteria Inclusion Criterion OPTIMA PREMIER 18 years old with RA (per 1987 revised American College of General Rheumatology classification criteria) 34 ; erythrocyte
Supplemental Table 1. Key Inclusion Criteria Inclusion Criterion OPTIMA PREMIER 18 years old with RA (per 1987 revised American College of General Rheumatology classification criteria) 34 ; erythrocyte
journal of medicine The new england Rosuvastatin to Prevent Vascular Events in Men and Women with Elevated C-Reactive Protein Abstract
 The new england journal of medicine established in 1812 november 20, 2008 vol. 359 no. 21 to Prevent Vascular Events in Men and Women with Elevated C-Reactive Protein Paul M Ridker, M.D., Eleanor Danielson,
The new england journal of medicine established in 1812 november 20, 2008 vol. 359 no. 21 to Prevent Vascular Events in Men and Women with Elevated C-Reactive Protein Paul M Ridker, M.D., Eleanor Danielson,
Supplementary Note Details of the patient populations studied Strengths and weakness of the study
 Supplementary Note Details of the patient populations studied TVD and NCA patients. Patients were recruited to the TVD (triple vessel disease) group who had significant coronary artery disease (defined
Supplementary Note Details of the patient populations studied TVD and NCA patients. Patients were recruited to the TVD (triple vessel disease) group who had significant coronary artery disease (defined
Acarbose Decreases the Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk of Diabetic Patients and. Attenuates the Incidence and Severity of Collagen-induced Arthritis in Mice
 Acarbose Decreases the Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk of Diabetic Patients and Attenuates the Incidence and Severity of Collagen-induced Arthritis in Mice Authors: Chi-Chen Lin, Der-Yuan Chen, Ya-Hsuan Chao,
Acarbose Decreases the Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk of Diabetic Patients and Attenuates the Incidence and Severity of Collagen-induced Arthritis in Mice Authors: Chi-Chen Lin, Der-Yuan Chen, Ya-Hsuan Chao,
Optimizing risk assessment of total cardiovascular risk What are the tools? Lars Rydén Professor Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden
 Optimizing risk assessment of total cardiovascular risk What are the tools? Lars Rydén Professor Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Cardiovascular Disease Prevention (CVD) Three Strategies for CVD
Optimizing risk assessment of total cardiovascular risk What are the tools? Lars Rydén Professor Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Cardiovascular Disease Prevention (CVD) Three Strategies for CVD
MOLINA HEALTHCARE OF CALIFORNIA
 MOLINA HEALTHCARE OF CALIFORNIA HIGH BLOOD CHOLESTEROL IN ADULTS GUIDELINE Molina Healthcare of California has adopted the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel
MOLINA HEALTHCARE OF CALIFORNIA HIGH BLOOD CHOLESTEROL IN ADULTS GUIDELINE Molina Healthcare of California has adopted the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel
The Hospital for Sick Children Technology Assessment at SickKids (TASK)
 The Hospital for Sick Children Technology Assessment at SickKids (TASK) THE USE OF BIOLOGIC RESPONSE MODIFIERS IN POLYARTICULAR-COURSE JUVENILE IDIOPATHIC ARTHRITIS Report No. 2010-01 Date: January 11,
The Hospital for Sick Children Technology Assessment at SickKids (TASK) THE USE OF BIOLOGIC RESPONSE MODIFIERS IN POLYARTICULAR-COURSE JUVENILE IDIOPATHIC ARTHRITIS Report No. 2010-01 Date: January 11,
Safety and effectiveness of biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis
 1. Title: Safety and effectiveness of biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis 2. Background: The population of older individuals with rheumatoid arthritis
1. Title: Safety and effectiveness of biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis 2. Background: The population of older individuals with rheumatoid arthritis
Adrenocorticotropic hormone gel in patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis: a case series
 International Journal of Clinical Rheumatology For reprint orders, please contact: reprints@futuremedicine.com Adrenocorticotropic hormone gel in patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis: a case series
International Journal of Clinical Rheumatology For reprint orders, please contact: reprints@futuremedicine.com Adrenocorticotropic hormone gel in patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis: a case series
Hae Sun Suh, B.Pharm., Ph.D. Jason N. Doctor, Ph.D.
 Podium Presentation, May 18, 2009 Comparison of Cardiovascular Event Rates in Subjects with Type II Diabetes Mellitus who Augmented from Statin Monotherapy to Statin Plus Fibrate Combination Therapy with
Podium Presentation, May 18, 2009 Comparison of Cardiovascular Event Rates in Subjects with Type II Diabetes Mellitus who Augmented from Statin Monotherapy to Statin Plus Fibrate Combination Therapy with
To help you with terms and abbreviations used in this document that may be unfamiliar to you, a glossary is provided on the last pages.
 ARTHRITIS CONSUMER EXPERTS 910B RICHARDS STREET VANCOUVER BC V6B 3C1 CANADA T: 604.974-1366 F: 604.974-1377 WWW.ARTHRITISCONSUMEREXPERTS.ORG Arthritis Consumer Experts In Health Care and Research Decision-making
ARTHRITIS CONSUMER EXPERTS 910B RICHARDS STREET VANCOUVER BC V6B 3C1 CANADA T: 604.974-1366 F: 604.974-1377 WWW.ARTHRITISCONSUMEREXPERTS.ORG Arthritis Consumer Experts In Health Care and Research Decision-making
THE EFFECT OF SECONDHAND SMOKE EXPOSURE ON HIGH MOLECULAR WEIGHT ADIPONECTIN LEVELS IN ADULT WOMEN: A PRELIMINARY REPORT
 THE EFFECT OF SECONDHAND SMOKE EXPOSURE ON HIGH MOLECULAR WEIGHT ADIPONECTIN LEVELS IN ADULT WOMEN: A PRELIMINARY REPORT Siti Hajar MH 1, Harmy MY 1, Norhayati MN 1, Aida HGR 2, Hamid JJM 3 Department
THE EFFECT OF SECONDHAND SMOKE EXPOSURE ON HIGH MOLECULAR WEIGHT ADIPONECTIN LEVELS IN ADULT WOMEN: A PRELIMINARY REPORT Siti Hajar MH 1, Harmy MY 1, Norhayati MN 1, Aida HGR 2, Hamid JJM 3 Department
Learning Objectives. Patient Case
 Joseph Saseen, Pharm.D., FASHP, FCCP, BCPS Professor and Vice Chair, Department of Clinical Pharmacy University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus Learning Objectives Identify the 4 patient populations
Joseph Saseen, Pharm.D., FASHP, FCCP, BCPS Professor and Vice Chair, Department of Clinical Pharmacy University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus Learning Objectives Identify the 4 patient populations
Abatacept (Orencia) for active rheumatoid arthritis. August 2009
 Abatacept (Orencia) for active rheumatoid arthritis August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to
Abatacept (Orencia) for active rheumatoid arthritis August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to
Lipoprotein (a): Is it important for Friedewald formula?
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ALBANIAN MEDICAL JOURNAL Lipoprotein (a): Is it important for Friedewald formula? Murat Can 1, Berrak Guven 1 1 Bulent Ecevit University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Biochemistry
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ALBANIAN MEDICAL JOURNAL Lipoprotein (a): Is it important for Friedewald formula? Murat Can 1, Berrak Guven 1 1 Bulent Ecevit University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Biochemistry
Supplementary table 1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of participants by paraoxonase-1 (PON-1) gene polymorphisms
 Supplementary table 1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of participants by paraoxonase-1 (PON-1) gene polymorphisms QQ QR/RR n = 36 n = 80 Men (%) 20 (55) 54 (67) 0.216 Age (years) 57 ± 10 56 ±
Supplementary table 1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of participants by paraoxonase-1 (PON-1) gene polymorphisms QQ QR/RR n = 36 n = 80 Men (%) 20 (55) 54 (67) 0.216 Age (years) 57 ± 10 56 ±
Patient characteristics associated with response to NSAID monotherapy in children with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis
 Sura et al. Pediatric Rheumatology (2018) 16:2 DOI 10.1186/s12969-017-0219-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Patient characteristics associated with response to NSAID monotherapy in children with systemic
Sura et al. Pediatric Rheumatology (2018) 16:2 DOI 10.1186/s12969-017-0219-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Patient characteristics associated with response to NSAID monotherapy in children with systemic
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 48, No. 2, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /06/$32.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 48, No. 2, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.043
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 48, No. 2, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.043
Clinical Policy: Etanercept (Enbrel) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.250 Effective Date: 08/16 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid
 Clinical Policy: (Enbrel) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.250 Effective Date: 08/16 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this
Clinical Policy: (Enbrel) Reference Number: CP.PHAR.250 Effective Date: 08/16 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this
PIEDMONT ACCESS TO HEALTH SERVICES, INC. Guidelines for Screening and Management of Dyslipidemia
 PIEDMONT ACCESS TO HEALTH SERVICES, INC. Policy Number: 01-09-021 SUBJECT: Guidelines for Screening and Management of Dyslipidemia EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/2008 REVIEWED/REVISED: 04/12/10, 03/17/2011, 4/10/2012,
PIEDMONT ACCESS TO HEALTH SERVICES, INC. Policy Number: 01-09-021 SUBJECT: Guidelines for Screening and Management of Dyslipidemia EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/2008 REVIEWED/REVISED: 04/12/10, 03/17/2011, 4/10/2012,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Leibowitz M, Karpati T, Cohen-Stavi CJ, et al. Association between achieved low-density lipoprotein levels and major adverse cardiac events in patients with stable ischemic
Supplementary Online Content Leibowitz M, Karpati T, Cohen-Stavi CJ, et al. Association between achieved low-density lipoprotein levels and major adverse cardiac events in patients with stable ischemic
Page 1. Disclosures. Background. No disclosures
 Population-Based Lipid Screening in the Era of a Childhood Obesity Epidemic: The Importance of Non-HDL Cholesterol Assessment Brian W. McCrindle, Cedric Manlhiot, Don Gibson, Nita Chahal, Helen Wong, Karen
Population-Based Lipid Screening in the Era of a Childhood Obesity Epidemic: The Importance of Non-HDL Cholesterol Assessment Brian W. McCrindle, Cedric Manlhiot, Don Gibson, Nita Chahal, Helen Wong, Karen
Comparison between ESR and C-Reactive Protein(CRP) as a Marker of Disease activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Original Article Comparison between ESR and C-Reactive Protein(CRP) as a Marker of Disease activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Ali M.E. Yousef 1, Fatemah A. Elshabacy 2, Sherry K. Abdelrahman
Original Article Comparison between ESR and C-Reactive Protein(CRP) as a Marker of Disease activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Ali M.E. Yousef 1, Fatemah A. Elshabacy 2, Sherry K. Abdelrahman
HIGH LDL CHOLESTEROL IS NOT AN INDEPENDENT RISK FACTOR FOR HEART ATTACKS AND STROKES
 HIGH LDL CHOLESTEROL IS NOT AN INDEPENDENT RISK FACTOR FOR HEART ATTACKS AND STROKES A study published in the British Medical Journal shows that not only is high LDL cholesterol not a risk factor for all-caused
HIGH LDL CHOLESTEROL IS NOT AN INDEPENDENT RISK FACTOR FOR HEART ATTACKS AND STROKES A study published in the British Medical Journal shows that not only is high LDL cholesterol not a risk factor for all-caused
