Innate Immunity in the Intestine
|
|
|
- Wilfrid Lambert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Master s course in biomedical sciences Innate Immunity in the Intestine Dr. Kathy McCoy February 26 th,
2 Host-Microbial Homeostasis: Innate Immunity Pharynx & upper respiratory tract ~ Barriers - Sensing the microbiota acid in stomach (Helicobacter pylori) Distal small intestine (ileum) CFU/ml Large intestine (colon) 1012 CFU/ml ~ Antimicrobial peptides - Sampling the microbiota - Intestinal mononuclear cells - Innate lymphoid cells Skin CFU/ml ~1011 2
3 Barriers: Physical, chemical, immune Lumen Mucus Commensal bacteria Enterocyte SFB CX 3 CR1 + DCs Macrophage IgA Goblet cell AMPs M cell CD103 + CD11b + DCs Tregs B cell CD103 + CD11b - DCs Enterodocrine cell Lamina Propria Stem cell Paneth cells Th17 Peyer s Patch Plasma cells FIGURE 1 Intestinal mucosal surface at the steady state. The intestinal epithelial barrier is a highly organized mucosal surface that prevents the entry of microbes into the lamina propria. The epithelium is constituted of a single layer of intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) covered by a stratified mucus layer. epithelial stem cells that proliferate and give rise to daughter cells. These cells include enterocytes, mucus-producing goblet cells, hormone-producing enteroendocrine cells, AMP-producing Paneth cells at the base of the crypts and finally, M cells that sample antigens from the intestinal lumen in order to 3
4 Epithelial cell tight junctions b Microvilli -Regulators of paracellular transport Claudin Occludin ZO1 MLCK F-actin Myosin -catenin 1 Tight junction - Proinflammatory cytokines (IFNγ, TNFα) can increase intestinal permeability E-cadherin Adherens junction -catenin Keratin Desmoglein Desmocollin Desmoplakin Desmosome 4
5 Mucus thickness differs along the intestine Stomach Small intestine Large intestine 10 3 /g Bacterial load /g 800 Mucus thickness (µm) Bacteria Bacterial products MAMPs Metabolites Isolated lymphoid follicles (ILF) Ileum Colon Outer layer Antrum 200 Corpus Duodenum Jejunum 100 Inner layer ILF ILF ILF Peyer s patch Immune system 5
6 Inner mucus layer is sterile - mucins seceted by goblet cells oligomerise to form a sticky gel - there are two layers of mucus - muc2-/- mice spontaneously develop colitis Vaishnava et al 2011 Science 334:255 6
7 Paneth cells secrete antimicrobial proteins b Human BD1, BD2, Lysozym Host-derived AMP BD3 and BD4 SLPI (AMP)Staphylococcus Cathelicidin Antimicrobial a proteins such as REG3γ Mucus layer RNase7 Psoriasin Lactoferrin epidermidis αmsh Catesta Calprot - small intestinal enterocyte express REG3γ & REG3β - large intestinal enterocytes express β-defensins and cathelicidins Enterocyte Goblet cell Mucin Antimicrobial proteins such as α-defensins, ANG4 and REG3γ -many AMP target cell or cell membrane functions Cathelicidin through enzymatic (eg lysozyme) and non-enzymatic disruption (defensins) Mast cell Sebocytes Paneth cell Human BD1, BD2 and BD3 Histone H4 Psoriasin Cathelicidin Cathe Dermc Huma and BD Eccrin gland E Nature Reviews Immunology 504 JULY 2012 VOLUME 12 Figure 1 Epithelial barriers of the intestine and skin. a The intestinal epithelium 7
8 Antimicrobial proteins families Table 1 Major antimicrobial protein families in skin and intestine Family α-defensins (cryptdins in mice) Representative proteins DEFA5, DEFA6 (in humans); cryptdins 1 16 (in mice) Mechanism of action Membrane disruption β-defensins BD1, BD2, BD3 Membrane disruption; lipid II binding (BD3) Calprotectin (S100A8 S100A9) Cathelicidins C-type lectins Tissue sites of expression Small intestine Large intestine, skin, respiratory tract Cellular sites of expression Paneth cells, neutrophils, macrophages Enterocytes, keratinocytes, respiratory tract epithelial cells Target organisms Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa Refs 8 86,133 NA Metal chelation Abscesses Neutrophils Staphylococcus aureus 39 LL37 (in humans); CRAMP (in mice) HIP/PAP (in humans); REG3γ (in mice) Membrane disruption Peptidoglycan recognition; killing mechanism unknown Large intestine, skin, lung, urinary tract Small intestine Neutrophils, mast cells, epithelial cells Epithelial cells (Paneth cells, enterocytes) Galectins GAL4, GAL8 Unknown Intestine Broad expression, including by epithelial cells Lipocalin Lipocalin 2 Sequestration of iron-laden siderophores Lysozyme NA Enzymatic attack on bacterial cell wall peptidoglycan Peptidoglycan recognition proteins PGLYRP1 4 in mammals Activation of bacterial two-component systems; PGLYRP2 is an amidase that targets peptidoglycan Phospholipase A2 NA Hydrolysis of bacterial membrane phospholipids Broad expression, including intestine and lung Intestine, eye, and more; secretions, including tears, saliva Liver, intestine, skin, mammary gland Intestine; secretions, including tears, inflammatory fluids Macrophages, epithelial cells Intestinal Paneth cells Epithelial cells Paneth cells, macrophages Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, viruses, fungi 36 Gram-positive bacteria 11,12, 23 Bacteria bearing blood group antigens 134 Escherichia coli 135, 136 Gram-positive bacteria; some activity against Gram-negative bacteria Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria Gram-positive bacteria 139 Psoriasin (S100A7) NA Unknown Skin Keratinocytes Escherichia coli 12 RNases ANG4, RNase7 Unknown Skin, intestine Epithelial cells Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria 26,38 Nature Reviews Immunology 504 JULY 2012 VOLUME 12 8
9 Innate immune receptors: pattern recognition -Toll-like receptors: bacterial and viral molecules -Mannose receptor: microbial surface carbohydrates -NOD receptors bacterial peptidoglycans 9
10 PRR signalling in intestinal epithelial cells A B Pathogens Commensal bacteria Commensal bacteria NOD1/2 TLR Defensins Alpi RegIIIγ Insufficient epithelial signallin Reduction of mucosal antibacte Loss of epithelial barrier integrit Impaired epithelial repair capac? RLR TLR ROS IL-17C SIGIRR A20 PPARγ IKK1/2 NEMO RelA IL15 IL-7 IEL? proil1β proil-18 Inflammasome ACUTE SITUATION Altered cell composition and tissue homeostasis Reduced nutrient and water absorption Clinical disease CX 3 CR1 + Proliferation Differentiation Cell survival CCL20 CCL28 April TSLP TGFβ IL1β IL-18 CHRONIC SITUATION Perpetuating inflammation Altered microbiota composition Progressive tissue destruction EMBO Chronic reports disorder VOL 13 NO (e.g. Inflammatory bowel disease) 10
11 quantified by Q-PCR determination of 16S rrna / gene copy number in the terminal ileum. N = 5 mice per position between Myd88 and wild-type mice did not exhibit reduced mucus p genotype. Data are from three groups of littermates. *, P < 0.05; error bars, mean TSEM; ns, not significant. (fig. S2, A and B). The increase in mucosa- or secretion (fig. S3, A and B). T associated bacteria was unlikely to result from a gest that MyD88-dependent inna Epithelial cell MyD88 is required for excluding bacteria from inner mucus layer Fig. 1. MyD88 promotes p of the microbiota and th surface. (A) Visualization of ization relative to the small surface by FISH. Sections we probe that recognizes the 1 all bacteria (green) and co 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylind sualize nuclei (blue). Scale b indicate thewith distance Fig. 2. Epithelial cell MyD88 is necessary and sufficient to limit bacterial association the from smallt DIEC Tg 11
12 Antimicrobial peptides: Constitutive & regulated Subset of α-defensins expressed independently of the microbiota Bacteria Subset of regulated α-defensins REG3γ Cathelicidin β-defensins Kerat MDP MAMP MYD88 Epithelium TCF4 NOD2 NF-κB TLR MYD88 CYP27B1 Keratino hyperpro Paneth cell Enterocyte IL-22R 1,25-OH vitamin D3 25-OH vitamin D3 Lamina propria IL-22 Endosome T H 17 mat Innate lymphoid cell TLR9 Dendritic cell Type I IFN Nature Reviews Immunology 504 JULY 2012 VOLUME 12 12
13 Innate cells: Sampling the microbiota 8 JUNE 2012 VOL 336 SCIENCE 13
14 Intestinal mononuclear phagocytes: macrophages and dendritic cells Immunol Res DOI /s
15 - Critical role in the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis - Act without antigen-specific receptors Innate lymphoid cells Precursor% Id2&dep& RORγt&dep& GATA;3&dep& T;bet&dep& LTi 4 % RORγt + &ILC& LTi 0 % IL017 + %% ILC% IL022 + %ILC% %(NKp46+% ILC)% ILC1% Thymic%NK% NK&cells&& & & cnk% %cells% ILC2,&nuocytes&& & ILC2% IL017% IL022% IFNγ% IL04,5,%13% Lymph organs formation Tissue repair after injury Colitogenic cells Extracellular bacteria Protection against microbial pathogens Extracellular parasites Wojno%Cell%host%&%microbe%2012% Spits%et%a.%Annu%Rev%Immunol%2010% 15
16 Innate immunity controls intestinal homeostasis CX3CR1 + MP TSLP Granulocytes IL 22 IL 17 IFN CD103 + DC ILC γδ TGF RA IL 18 IL 23 Macrophage siga IL 12 IL 1 IL 6 IL 10 T reg B cell TNF a T eff IL 10 TGF NK b Th1 Th17 16
17 Balanced innate immune activation maintains intestinal homeostasis Intestinal inflammation Level of innate immune activation Hyporesponsive Homeostasis Hyperresponsive IEC integrity + proliferation Anti-microbial peptide production Mucus, AMP, siga and IEC barrier PRR compartmentalization Myeloid MAMP detection Pro inflammatory cytokines + chemokines Luminal sampling Tolerogenic DCs Tolerogenic pathways Pathogen/parasite clearance PRR activation of IEC Innate regulatory cytokines Leucocyte accumulation + activation IEC proliferation 17
Intestinal Microbiota in Health and Disease
 Intestinal Microbiota in Health and Disease February 27, 2015 Master s Course in Gastroenterology Prof. Kathy McCoy 1 Overview Overview of Gut Microbiota Microbiota in Health Microbiota in Disease 2 Gut
Intestinal Microbiota in Health and Disease February 27, 2015 Master s Course in Gastroenterology Prof. Kathy McCoy 1 Overview Overview of Gut Microbiota Microbiota in Health Microbiota in Disease 2 Gut
Overview of the immune system
 Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of the Immune System
 Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of the Immune System Patricia Denning, M.D. Associate Professor in Pediatrics Division of Neonatology Emory University School of Medicine What is NEC? What is NEC? Necrotizing
Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of the Immune System Patricia Denning, M.D. Associate Professor in Pediatrics Division of Neonatology Emory University School of Medicine What is NEC? What is NEC? Necrotizing
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Cutaneous Immunology: Innate Immune Responses. Skin Biology Lecture Series
 Cutaneous Immunology: Innate Immune Responses Skin Biology Lecture Series The Immune Response: Innate and Adaptive Components Source: Wolff, Goldsmith, Katz, Gilchrest, Paller, Leffell. Fitzpatrick s Dermatology
Cutaneous Immunology: Innate Immune Responses Skin Biology Lecture Series The Immune Response: Innate and Adaptive Components Source: Wolff, Goldsmith, Katz, Gilchrest, Paller, Leffell. Fitzpatrick s Dermatology
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE
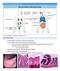 LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
Innate Immunity. Natural or native immunity
 Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Components of the innate immune system
 Components of the innate immune system Before our discussion about innate immunity Differences between innate and adaptive systems: Innate immune system = natural = native -Germline: prepared before exposure
Components of the innate immune system Before our discussion about innate immunity Differences between innate and adaptive systems: Innate immune system = natural = native -Germline: prepared before exposure
Immunology Lecture- 1
 Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Innate Immunity. Natural or native immunity
 Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription (-) TLR2 PGN MDP. MyD88 IRAK ECSIT TRAF6 NIK. Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IKK.
 D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription CARD CARD NOD2 LRR RICK/Rip2 NIK MDP TRAF6 PGN TLR2 MyD88 IRAK ECSIT (-) IKK Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IκB NF-κB atanabe et al, 2004 NF-κB IL-12p40
D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription CARD CARD NOD2 LRR RICK/Rip2 NIK MDP TRAF6 PGN TLR2 MyD88 IRAK ECSIT (-) IKK Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IκB NF-κB atanabe et al, 2004 NF-κB IL-12p40
Gut Microbiota and IBD. Vahedi. H M.D Associate Professor of Medicine DDRI
 Gut Microbiota and IBD Vahedi. H M.D Associate Professor of Medicine DDRI 1393.3.1 2 GUT MICROBIOTA 100 Trillion Microbes - 10 times more than cells in our body Collective weight of about 1kg in human
Gut Microbiota and IBD Vahedi. H M.D Associate Professor of Medicine DDRI 1393.3.1 2 GUT MICROBIOTA 100 Trillion Microbes - 10 times more than cells in our body Collective weight of about 1kg in human
Innate Immunity. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter 3. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
17 th International Conference of the Inflammation Research Association: Wednesday AM (Day 4) September 9-13, 2012
 17 th International Conference of the Inflammation Research Association: Wednesday AM (Day 4) September 9-13, 2012 The Sagamore Resort, Bolton Landing, NY, USA The following report includes highlights
17 th International Conference of the Inflammation Research Association: Wednesday AM (Day 4) September 9-13, 2012 The Sagamore Resort, Bolton Landing, NY, USA The following report includes highlights
Innate immunity. Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco. FOCiS
 1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
Fc receptors, phagocytosis role 128
 Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
Studies on probiotics effects on innate immune functions in the gastrointestinal tract of broiler chicks (SUMMARY)
 Doctoral Thesis Studies on probiotics effects on innate immune functions in the gastrointestinal tract of broiler chicks (SUMMARY) ELSAYED SEDDEK IBRAHEM MOHAMMED Department of Bioresource Science Graduate
Doctoral Thesis Studies on probiotics effects on innate immune functions in the gastrointestinal tract of broiler chicks (SUMMARY) ELSAYED SEDDEK IBRAHEM MOHAMMED Department of Bioresource Science Graduate
Genetics. Environment. You Are Only 10% Human. Pathogenesis of IBD. Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function IBD
 Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
7/6/2009. The study of the immune system and of diseases that occur as a result of inappropriate or inadequate actions of the immune system.
 Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Lines of defense. Innate Immunity. Immunity. First line of defense: Skin and mucous membranes 11/20/2016. Chapter 16 BIO 220
 Lines of defense Innate Immunity Chapter 16 BIO 220 Immunity The ability to ward off disease caused by microbes or their products and to protect against environmental agents such as pollen, chemicals,
Lines of defense Innate Immunity Chapter 16 BIO 220 Immunity The ability to ward off disease caused by microbes or their products and to protect against environmental agents such as pollen, chemicals,
SCFA in gut health. Kristin Verbeke. On behalf of the Prebiotic Task Force of ILSI Europe
 SCFA in gut health Kristin Verbeke Translational Research in Gastrointestinal Disorders KU Leuven On behalf of the Prebiotic Task Force of ILSI Europe Acetic acid Major anions in the large intestine Propionic
SCFA in gut health Kristin Verbeke Translational Research in Gastrointestinal Disorders KU Leuven On behalf of the Prebiotic Task Force of ILSI Europe Acetic acid Major anions in the large intestine Propionic
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy
 Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology. Robin Lorenz
 Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
Microbial control of the mucosal barrier function
 Microbial control of the mucosal barrier function Implications for local and systemic immune homeostasis Ida H. Hiemstra Microbial control of the mucosal barrier function ISBN: 978-94-6182-321-2 Author:
Microbial control of the mucosal barrier function Implications for local and systemic immune homeostasis Ida H. Hiemstra Microbial control of the mucosal barrier function ISBN: 978-94-6182-321-2 Author:
2. Innate immunity 2013
 1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
Innate immunity as a therapeutic target in IBD. Elke Cario Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology University Hospital of Essen Essen, Germany
 Innate immunity as a therapeutic target in IBD Elke Cario Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology University Hospital of Essen Essen, Germany The intestinal mucosa must rapidly recognize luminal pathogens
Innate immunity as a therapeutic target in IBD Elke Cario Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology University Hospital of Essen Essen, Germany The intestinal mucosa must rapidly recognize luminal pathogens
Animal Models to Understand Immunity
 Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction: The Primary Driver of IBD?
 2 Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction: The Primary Driver of IBD? Pieter Hindryckx and Debby Laukens Ghent University Belgium 1. Introduction The healthy gastrointestinal tract is functionally maintained by
2 Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction: The Primary Driver of IBD? Pieter Hindryckx and Debby Laukens Ghent University Belgium 1. Introduction The healthy gastrointestinal tract is functionally maintained by
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 July 2017
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 July 2017 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 July 2017 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Lecture 11: Mucosal Immunity (based on lecture by Dr. Betsy Herold, Einstein)
 Lecture 11: Mucosal Immunity (based on lecture by Dr. Betsy Herold, Einstein) Questions to Consider How is the mucusal immune system different from the systemic immune system? How does the immune system
Lecture 11: Mucosal Immunity (based on lecture by Dr. Betsy Herold, Einstein) Questions to Consider How is the mucusal immune system different from the systemic immune system? How does the immune system
2 االستاذ المساعد الدكتور خالد ياسين الزاملي \ مناعة \ المرحلة الثانية \ التحليالت المرضية \
 Innate Immunity Innate immunity: is the resistance that an individual possesses by birth. Innate immunity may be classified as (a) individual immunity (b) racial immunity (c) species immunity. Factors
Innate Immunity Innate immunity: is the resistance that an individual possesses by birth. Innate immunity may be classified as (a) individual immunity (b) racial immunity (c) species immunity. Factors
THE ROLE OF INTESTINAL EPITHELIAL CELLS AND THE REGULATION OF THE POLYMERIC IMMUNOGLOBULIN RECEPTOR IN HOMEOSTASIS AND INFLAMMATION
 University of Kentucky UKnowledge Theses and Dissertations--Microbiology, Immunology, and Molecular Genetics Microbiology, Immunology, and Molecular Genetics 2012 THE ROLE OF INTESTINAL EPITHELIAL CELLS
University of Kentucky UKnowledge Theses and Dissertations--Microbiology, Immunology, and Molecular Genetics Microbiology, Immunology, and Molecular Genetics 2012 THE ROLE OF INTESTINAL EPITHELIAL CELLS
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Putting it Together. Stephen Canfield Secondary Lymphoid System. Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s
 Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Modeling the Immune System
 An Introduction to Modeling the Immune System School of Computer and Communication Sciences EPFL, SS 2007-08 http://swis.epfl.ch/teaching/modeling_immune_system/ Master Modelling the immune system Aims
An Introduction to Modeling the Immune System School of Computer and Communication Sciences EPFL, SS 2007-08 http://swis.epfl.ch/teaching/modeling_immune_system/ Master Modelling the immune system Aims
Innate Immunity. Lines of defense. Immunity. Innate vs. adaptive immunity 11/24/2017
 Immunity Innate Immunity Chapter 16 BIO 220 The ability to ward off disease caused by microbes or their products and to protect against environmental agents such as pollen, chemicals, and pet dander Innate
Immunity Innate Immunity Chapter 16 BIO 220 The ability to ward off disease caused by microbes or their products and to protect against environmental agents such as pollen, chemicals, and pet dander Innate
Dysbiosis & Inflammation
 MASTERING THE MICROBIOME: Dysbiosis & Inflammation 2017 Tom Fabian, PhD It is reasonable to propose that the composition of the microbiome and its activities are involved in most, if not all, of the biological
MASTERING THE MICROBIOME: Dysbiosis & Inflammation 2017 Tom Fabian, PhD It is reasonable to propose that the composition of the microbiome and its activities are involved in most, if not all, of the biological
1. Overview of Innate Immunity
 Chapter 15: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity Chapter Reading pp. 449-456 The Body s Defenses The
Chapter 15: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity Chapter Reading pp. 449-456 The Body s Defenses The
1. The scavenger receptor, CD36, functions as a coreceptor for which TLR? a. TLR ½ b. TLR 3 c. TLR 4 d. TLR 2/6
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
11/25/2017. THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS BARRIER DEFENSES INNATE IMMUNITY OF VERTEBRATES
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
Immunology Part II. Innate Immunity. 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters,
 Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Mucosal immunity Reddy April Deveshni Reddy Allergy Meeting 13 April 2012
 Deveshni Reddy Allergy Meeting 13 April First recorded by Hippocrates over 2000 years ago. 1921: Prausnitz and Kustner demonstrated that substance responsible for Kustner s fish allergy was present in
Deveshni Reddy Allergy Meeting 13 April First recorded by Hippocrates over 2000 years ago. 1921: Prausnitz and Kustner demonstrated that substance responsible for Kustner s fish allergy was present in
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
Anatomy of the Intes.ne: Epithelium, Lympha.cs, Vessels and Nerves
 Master Course Gastroenterology 2015 Anatomy of the Intes.ne: Epithelium, Lympha.cs, Vessels and Nerves Dr. Stephanie Ganal Department Klinische Forschung University of Bern stephanie.ganal@dkf.unibe.ch
Master Course Gastroenterology 2015 Anatomy of the Intes.ne: Epithelium, Lympha.cs, Vessels and Nerves Dr. Stephanie Ganal Department Klinische Forschung University of Bern stephanie.ganal@dkf.unibe.ch
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response. Physiology Unit 3
 INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation. Innate Immunity: An Evolutionary View
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Differential responses of human colonic ILCs to gut commensal bacteria altered during HIV infection
 Differential responses of human colonic ILCs to gut commensal bacteria altered during HIV infection Moriah J. Castleman, Ph.D. Laboratory of Dr. Cara Wilson University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
Differential responses of human colonic ILCs to gut commensal bacteria altered during HIV infection Moriah J. Castleman, Ph.D. Laboratory of Dr. Cara Wilson University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
Chapter 2 Intestinal Permeability and Transport of Food Antigens
 Chapter 2 Intestinal Permeability and Transport of Food Antigens Contents 2.1 Intestinal Permeability of Antigens... 31 2.1.1 Paracellular Transport Pathways... 31 2.1.2 Transcellular Transport Pathways...
Chapter 2 Intestinal Permeability and Transport of Food Antigens Contents 2.1 Intestinal Permeability of Antigens... 31 2.1.1 Paracellular Transport Pathways... 31 2.1.2 Transcellular Transport Pathways...
REVIEWS. The impact of perinatal immune development on mucosal homeostasis and chronic inflammation
 The impact of perinatal immune development on mucosal homeostasis and chronic inflammation Harald Renz 1, Per Brandtzaeg 2 and Mathias Hornef 3 Abstract The mucosal surfaces of the gut and airways have
The impact of perinatal immune development on mucosal homeostasis and chronic inflammation Harald Renz 1, Per Brandtzaeg 2 and Mathias Hornef 3 Abstract The mucosal surfaces of the gut and airways have
Basic immunology. Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Innate Immunity. By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik
 Innate Immunity By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Types of immunity Immunity Innate / inborn Non-specific Acquired / adaptive Specific 3rd line of defense Physical barriers Skin, Saliva, Mucous, Stomach acid,
Innate Immunity By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Types of immunity Immunity Innate / inborn Non-specific Acquired / adaptive Specific 3rd line of defense Physical barriers Skin, Saliva, Mucous, Stomach acid,
Grup de fisiologia digestiva i adaptacions nutricionals Institut de Nutrició i Seguretat Alimentaria
 Grup de fisiologia digestiva i adaptacions nutricionals Institut de Nutrició i Seguretat Alimentaria 1 Outline Weaning and the consequences of stress Animal blood plasma Spray-drying SDP SDP in a model
Grup de fisiologia digestiva i adaptacions nutricionals Institut de Nutrició i Seguretat Alimentaria 1 Outline Weaning and the consequences of stress Animal blood plasma Spray-drying SDP SDP in a model
Chapter 24 The Immune System
 Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Human Immune Response. Part 1: innate immunity
 Human Immune Response Part 1: innate immunity Our bodies are under constant attack from pathogens A pathogen is an organism that can cause disease Pathogens include: Bacteria Viruses Protists Fungi 6.3.1
Human Immune Response Part 1: innate immunity Our bodies are under constant attack from pathogens A pathogen is an organism that can cause disease Pathogens include: Bacteria Viruses Protists Fungi 6.3.1
SUBDIVISIONS OF THE MUCOSA Distinct features of type I and type II mucosal surfaces
 Alessandra Pernis P&S 9-435 X53763 abp1@columbia.edu CHALLENGES FACED BY THE MUCOSAL SYSTEM SPECIALIZATION OF CELLS INVOLVED IN MUCOSAL IMMUNITY ORGANIZATION OF THE MUCOSAL IMMUNE SYSTEM CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS
Alessandra Pernis P&S 9-435 X53763 abp1@columbia.edu CHALLENGES FACED BY THE MUCOSAL SYSTEM SPECIALIZATION OF CELLS INVOLVED IN MUCOSAL IMMUNITY ORGANIZATION OF THE MUCOSAL IMMUNE SYSTEM CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS
Anti-infectious Immunity
 Anti-infectious Immunity innate immunity barrier structures Secretory molecules Phagocytes NK cells Anatomical barriers 1. Skin and mucosa barrier 2.hemo-Spinal Fluid barrier 3. placental barrier Phagocytic
Anti-infectious Immunity innate immunity barrier structures Secretory molecules Phagocytes NK cells Anatomical barriers 1. Skin and mucosa barrier 2.hemo-Spinal Fluid barrier 3. placental barrier Phagocytic
4b. Innate (nonspecific) Immunity
 4b. Innate (nonspecific) Immunity Chapter 16: Innate (nonspecific) Immunity! Some terms:! Susceptibility: Lack of immunity to a disease.! Immunity: Ability to ward off disease.! Innate immunity: Defenses
4b. Innate (nonspecific) Immunity Chapter 16: Innate (nonspecific) Immunity! Some terms:! Susceptibility: Lack of immunity to a disease.! Immunity: Ability to ward off disease.! Innate immunity: Defenses
Unit 9 New life College faculty: Ramesh Kumar Subject: Life Sciences date: 15jan 2016
 Unit 9 New life College faculty: Ramesh Kumar Subject: Life Sciences date: 15jan 2016 History and impact The types and functions of cells in the immune system. How cells communicate and recognize antigen
Unit 9 New life College faculty: Ramesh Kumar Subject: Life Sciences date: 15jan 2016 History and impact The types and functions of cells in the immune system. How cells communicate and recognize antigen
Chapter 17. The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Role of the gut microbiota in immunity and inflammatory disease
 Role of the gut microbiota in immunity and inflammatory disease Nobuhiko Kamada 1, Sang Uk Seo 1, Grace Y. Chen 2 and Gabriel Núñez 1 Abstract The mammalian intestine is colonized by trillions of microorganisms,
Role of the gut microbiota in immunity and inflammatory disease Nobuhiko Kamada 1, Sang Uk Seo 1, Grace Y. Chen 2 and Gabriel Núñez 1 Abstract The mammalian intestine is colonized by trillions of microorganisms,
A. Incorrect! The resistance that an individual acquires during life is known as specific immunity.
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 13: Innate Immunity No. 1 of 10 1. Which type of immunity is attributed to the Anatomic, Physiologic, Phagocytic and inflammatory barriers? A. Specific Immunity B. Adaptive
Microbiology - Problem Drill 13: Innate Immunity No. 1 of 10 1. Which type of immunity is attributed to the Anatomic, Physiologic, Phagocytic and inflammatory barriers? A. Specific Immunity B. Adaptive
Molecular and Cellular Basis of Immune Protection of Mucosal Surfaces
 Molecular and Cellular Basis of Immune Protection of Mucosal Surfaces Department of Biologic & Materials Sciences School of Dentistry University of Michigan Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109-1078 1 Image quality
Molecular and Cellular Basis of Immune Protection of Mucosal Surfaces Department of Biologic & Materials Sciences School of Dentistry University of Michigan Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109-1078 1 Image quality
Overview of Immunology. Evolution CORE CONCEPTS IN IMMUNOLOGY. Cliona O Farrelly
 Overview of Immunology Cliona O Farrelly Professor Comparative Immunology, School of Biochemistry & Immunology & School of Health Sciences cliona.ofarrelly@tcd.ie CORE CONCEPTS IN IMMUNOLOGY 1. Identification
Overview of Immunology Cliona O Farrelly Professor Comparative Immunology, School of Biochemistry & Immunology & School of Health Sciences cliona.ofarrelly@tcd.ie CORE CONCEPTS IN IMMUNOLOGY 1. Identification
Nutrition & Gut Immunity
 Nutrition & Gut Immunity Kenneth A. Kudsk, MD FACS Professor of Surgery University of Wisconsin - Madison Madison, Wisconsin No conflicts of interest to disclose % Survival Survival vs. Malnutrition (after
Nutrition & Gut Immunity Kenneth A. Kudsk, MD FACS Professor of Surgery University of Wisconsin - Madison Madison, Wisconsin No conflicts of interest to disclose % Survival Survival vs. Malnutrition (after
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Identification of Microbes
 Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
primary : thymus, bone marrow lymphoid tissue secondary : lymph nodes, MALT, spleen spleen: there are 2 main types of tissues in the spleen :
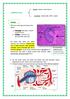 primary : thymus, bone marrow lymphoid tissue secondary : lymph nodes, MALT, spleen spleen: there are 2 main types of tissues in the spleen : 1. white pulp (gray area) : contains lymphoid tissue 2. red
primary : thymus, bone marrow lymphoid tissue secondary : lymph nodes, MALT, spleen spleen: there are 2 main types of tissues in the spleen : 1. white pulp (gray area) : contains lymphoid tissue 2. red
Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury. Journal Club December 16, 2004
 Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury Journal Club December 16, 2004 Gut-Commensal Interactions Nutrient metabolism Tissue development Resistance to colonization with pathogens
Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury Journal Club December 16, 2004 Gut-Commensal Interactions Nutrient metabolism Tissue development Resistance to colonization with pathogens
NASPGHAN Physiology Education Series Immunology in the gastrointestinal tract
 NASPGHAN Physiology Education Series Immunology in the gastrointestinal tract Esi Lamousé-Smith, MD, PhD Morgan Stanley Children s Hospital of New York Columbia University enl2118@columbia.edu Content
NASPGHAN Physiology Education Series Immunology in the gastrointestinal tract Esi Lamousé-Smith, MD, PhD Morgan Stanley Children s Hospital of New York Columbia University enl2118@columbia.edu Content
Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease
 Nature Reviews Immunology AOP, published online 22 April 2014; doi:10.1038/nri3661 REVIEWS Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease Markus F. Neurath Abstract Cytokines have a crucial role in the pathogenesis
Nature Reviews Immunology AOP, published online 22 April 2014; doi:10.1038/nri3661 REVIEWS Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease Markus F. Neurath Abstract Cytokines have a crucial role in the pathogenesis
16 Innate Immunity: M I C R O B I O L O G Y. Nonspecific Defenses of the Host. a n i n t r o d u c t i o n
 ninth edition TORTORA FUNKE CASE M I C R O B I O L O G Y a n i n t r o d u c t i o n 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation prepared by Christine L.
ninth edition TORTORA FUNKE CASE M I C R O B I O L O G Y a n i n t r o d u c t i o n 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation prepared by Christine L.
Defense mechanism against pathogens
 Defense mechanism against pathogens Immune System What is immune system? Cells and organs within an animal s body that contribute to immune defenses against pathogens ( ) Bacteria -Major entry points ;open
Defense mechanism against pathogens Immune System What is immune system? Cells and organs within an animal s body that contribute to immune defenses against pathogens ( ) Bacteria -Major entry points ;open
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel
 Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
review Innate immune signalling at the intestinal epithelium in homeostasis and disease Johanna Pott 1,2 & Mathias Hornef 2+ review
 Innate immune signalling at the intestinal epithelium in homeostasis and disease Johanna Pott 1,2 & Mathias Hornef 2+ 1 Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK, 2 Institute
Innate immune signalling at the intestinal epithelium in homeostasis and disease Johanna Pott 1,2 & Mathias Hornef 2+ 1 Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK, 2 Institute
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Innate Immunity. Jan 8 th Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1
 Innate Immunity Jan 8 th 2018. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Adaptive Innate 2 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid
Innate Immunity Jan 8 th 2018. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Adaptive Innate 2 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid
Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity & Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity & Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Pathogenicity: Virulence: The extent of pathogenicity. - function of: - infectivity
Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity & Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Pathogenicity: Virulence: The extent of pathogenicity. - function of: - infectivity
Interactions between epithelial cells and leukocytes in immunity and tissue homeostasis
 Interactions between epithelial cells and leukocytes in immunity and tissue homeostasis Renat Shaykhiev and Robert Bals 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Division for Pulmonary Diseases, Philipps-Universtät
Interactions between epithelial cells and leukocytes in immunity and tissue homeostasis Renat Shaykhiev and Robert Bals 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Division for Pulmonary Diseases, Philipps-Universtät
Immunology. Prof. Nagwa Mohamed Aref (Molecular Virologist & Immunology)
 Host Defenses Overview and Nonspecific Defenses I Immunology Prof. Nagwa Mohamed Aref (Molecular Virologist & Immunology) The Nature of Host Defenses 2 3 4 1st line of defense - intact skin mucous membranes
Host Defenses Overview and Nonspecific Defenses I Immunology Prof. Nagwa Mohamed Aref (Molecular Virologist & Immunology) The Nature of Host Defenses 2 3 4 1st line of defense - intact skin mucous membranes
Innate Immunity. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Innate Immunity Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The vertebrate, including human, immune system is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. The
Innate Immunity Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The vertebrate, including human, immune system is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. The
Accepted Manuscript. Title: The role of barrier function, autophagy, and cytokines in maintaining intestinal homeostasis
 Accepted Manuscript Title: The role of barrier function, autophagy, and cytokines in maintaining intestinal homeostasis Author: Dana Elshaer Jakob Begun PII: S1084-9521(16)30256-7 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.08.018
Accepted Manuscript Title: The role of barrier function, autophagy, and cytokines in maintaining intestinal homeostasis Author: Dana Elshaer Jakob Begun PII: S1084-9521(16)30256-7 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.08.018
Immune System. Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka
 Immune System Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka Content Standards 35.1 In innate immunity, recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens 35.2
Immune System Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka Content Standards 35.1 In innate immunity, recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens 35.2
Natural Defense Mechanisms
 Color code: Important in red Extra in blue For team error adjustments, click here Natural Defense Mechanisms Objectives To know First (non-specific immunity) and second (adaptive immunity) lines of defense
Color code: Important in red Extra in blue For team error adjustments, click here Natural Defense Mechanisms Objectives To know First (non-specific immunity) and second (adaptive immunity) lines of defense
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity
 Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
The Impact of Bifidobacterium bifidum and its Surface Protein BopA on the Murine Intestinal Barrier and Endogenous Microbiota Composition
 The Impact of Bifidobacterium bifidum and its Surface Protein BopA on the Murine Intestinal Barrier and Endogenous Microbiota Composition By Christopher Ross Villa A thesis submitted in conformity with
The Impact of Bifidobacterium bifidum and its Surface Protein BopA on the Murine Intestinal Barrier and Endogenous Microbiota Composition By Christopher Ross Villa A thesis submitted in conformity with
Exosomes as a. Novel Therapeutic Approach to Gastrointestinal Diseases Rebecca Murray APRN, FNP, CDE
 Exosomes as a Novel Therapeutic Approach to Gastrointestinal Diseases Rebecca Murray APRN, FNP, CDE Endocrine Nurse Practitioner Institute for Hormonal Balance Orlando, FL Medical Director Ward-Murray
Exosomes as a Novel Therapeutic Approach to Gastrointestinal Diseases Rebecca Murray APRN, FNP, CDE Endocrine Nurse Practitioner Institute for Hormonal Balance Orlando, FL Medical Director Ward-Murray
Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Universiti Malaysia Kelantan. Immunology and Serology (DVT2153)
 Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Universiti Malaysia Kelantan Immunology and Serology (DVT2153) By Dr. Erkihun Aklilu 1 Immune Response AgAinst Various infectious agents Immunology and Serology (DVT2153)
Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Universiti Malaysia Kelantan Immunology and Serology (DVT2153) By Dr. Erkihun Aklilu 1 Immune Response AgAinst Various infectious agents Immunology and Serology (DVT2153)
Part III Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction
 Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
Diabetes and the Microbiome Structure, Function, and Terminology
 Diabetes and the Microbiome Structure, Function, and Terminology Kim L. Kelly, PharmD, BCPS, FCCP, CDTC, CPC, CEC Kelly Diabetes Associates, LLC Cupertino, CA Patricia Davidson, DCN, RDN, CDE, LDN, FAND
Diabetes and the Microbiome Structure, Function, and Terminology Kim L. Kelly, PharmD, BCPS, FCCP, CDTC, CPC, CEC Kelly Diabetes Associates, LLC Cupertino, CA Patricia Davidson, DCN, RDN, CDE, LDN, FAND
Chapter 1. Chapter 1 Concepts. MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally!
 MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
XV Jornada de Avances en Hepatología Málaga 20 y 21 de Mayo de Barrera intestinal en la cirrosis. Agustín Albillos
 XV Jornada de Avances en Hepatología Málaga 20 y 21 de Mayo de 2016 Barrera intestinal en la cirrosis Agustín Albillos Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal Universidad de Alcalá, Ciberehd Madrid, Spain
XV Jornada de Avances en Hepatología Málaga 20 y 21 de Mayo de 2016 Barrera intestinal en la cirrosis Agustín Albillos Hospital Universitario Ramón y Cajal Universidad de Alcalá, Ciberehd Madrid, Spain
محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases
 محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases Immunity to infection depends on a combination of innate mechanisms (phagocytosis, complement, etc.) and antigen
محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases Immunity to infection depends on a combination of innate mechanisms (phagocytosis, complement, etc.) and antigen
Mucosal Immunology. Cathryn Nagler University of Chicago Department of Pathology/Committee on Immunology
 Mucosal Immunology Cathryn Nagler University of Chicago Department of Pathology/Committee on Immunology cnagler@bsd.uchicago.edu Mucosal surfaces are the major portals of entry for antigen Largest area
Mucosal Immunology Cathryn Nagler University of Chicago Department of Pathology/Committee on Immunology cnagler@bsd.uchicago.edu Mucosal surfaces are the major portals of entry for antigen Largest area
