A. Incorrect! The resistance that an individual acquires during life is known as specific immunity.
|
|
|
- Annabel Strickland
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Microbiology - Problem Drill 13: Innate Immunity No. 1 of Which type of immunity is attributed to the Anatomic, Physiologic, Phagocytic and inflammatory barriers? A. Specific Immunity B. Adaptive Immunity C. Non-specific Immunity D. Acquired Immunity The resistance that an individual acquires during life is known as specific immunity. It is other name of specific immunity. C. Correct! These four types of barriers help to prevent our body from the entrance and establishment of infectious agents. It is the other name of specific immunity. The term, Innate immunity, refers to basic disease resistance that an individual possesses by virtue of his/her birth. It is the first line of defense against infection. Innate immunity is comprised of four types of defensive barriers: anatomic, physiologic, phagocytic and inflammatory barriers. 1. Anatomic barriers tend to prevent the entry of pathogens inside our body and are known as the first line of defense against infection. The skin and mucous membranes are included in this category. 2. The physiologic barriers that contribute to innate immunity include temperature, ph, and various soluble factors. 3. Phagocytes engulf the foreign materials and destroy them; this is known as phagocytic response. 4. Tissue damage caused by a wound or by an invading pathogenic microorganism induces a complex sequence of events collectively known as the inflammatory response.
2 No. 2 of Which components of sebum maintain the ph of the skin between 3 and 5? A. Lactic acid and fatty acids B. Lysine and Histidine C. Glucose and lactose D. ATP and GTP A. Correct! Lactic acid and fatty acid maintains the ph of the skin between 3 & 5, as they are acidic in nature. As they are basic amino acids. Glucose is a monosaccharide and lactose after break down yields glucose and galactose, they are not involved in maintaining the ph of the sebum. They are high energy compounds. The sebaceous glands are associated with the hair follicles and produce an oily secretion called sebum. Sebum consists of lactic acid and fatty acid, which maintains the ph of the skin between 3 and 5, this ph inhibits the growth of most organisms. A few bacteria that metabolize sebum live as commensals on the skin and sometimes cause a severe form of acne.
3 No. 3 of Which process of the cells takes up fluids from the surrounding medium and many molecules contained in it? A. Endocytosis B. Pinocytosis C. Phagosomes D. Vasodilation Process by which macromolecules contained within the extracellular tissue fluid are internalized by cells. B. Correct! Cells take up fluids from the surrounding medium and many molecules contained in it. It involves nonspecific cell invagination. In phagocytosis, a cell s plasma membrane expands around the particulate material to form large vesicles known as phagosomes A process in which there is an increase in the diameter of blood vessels is known as vasodilation. Various cells internalize (endocytose) and break down foreign macromolecules. Specialized cells such as blood monocytes, neutrophils, and tissue macrophages internalize i.e. phagocytose, kill and digest whole microorganisms. Phagocytosis is one type of endocytosis. Other forms of endocytosis are: Receptor Mediated endocytosis Pinocytosis: Cells take up fluid from the surrounding medium and many molecules contained in it. It involves nonspecific cell invagination.
4 No. 4 of Which type of the immune response includes Acute-Phase proteins, histamines, and kinins? A. Phagocytic response B. Physiologic response C. Anatomic response D. Inflammatory response Phagocytes engulf the foreign materials and destroy them; this is known as phagocytic response. The physiologic barriers that contribute to innate immunity include temperature, ph, and various soluble factors. Skin and mucous membrane are the two pillars of anatomic barriers. D. Correct! The events in the inflammatory response are initiated by various soluble chemical mediators listed in the question. Tissue damage caused by a wound or by an invading pathogenic microorganism induces a complex sequence of events collectively known as the inflammatory response. The events in the inflammatory response are initiated by various soluble chemical mediators like acutephase proteins, histamines, & kinins. Acute-phase proteins are the serum proteins; they increase dramatically in tissue damaging infections. Histamine is a chemical released by a variety of cells in response to tissue injury. They can bind to receptors on the near by capillaries and venules, causing vasodilation and increased permeability of capillaries. Kinins are small peptides present in blood plasma in an inactive form. Tissue injury activates this peptides, which then causes vasodilation and increased permeability of capillaries.
5 No. 5 of Which type of barrier is attributed to the Skin and mucous membranes? A. Inflammatory barriers B. Physiological barriers C. Phagocytic barriers D. Anatomical barriers Tissue damage caused by a wound or by an invading pathogenic microorganism induces a complex sequence of events collectively known as the inflammatory response. The physiologic barriers that contribute to innate immunity include temperature, ph, and various soluble factors. Phagocytes engulf the foreign materials and destroy them; this is known as phagocytic response. D. Correct! Anatomic barriers tend to prevent the entry of pathogens inside our body and known as first line of defense against infection. The skin and mucous membrane are included in this category. Anatomic barriers tend to prevent the entry of pathogens inside our body and known as first line of defense against infection. The skin and mucous membrane are included in this category. Skin: It consists of two layers, epidermis and dermis. They acts as mechanical barriers which retards the entry of microbes and also the acidic environment (ph 3-5) retards the growth of microbes. Mucus membranes of Conjunctivae, Alimentary tract, Respiratory tract, Urogenital tract, are lined by mucous membranes. Most pathogens enter the body by binding to and penetrating through mucous membranes.
6 No. 6 of Which is the antimicrobial substance that prevents and also destroys the growth of microorganism in our body? A. Complement B. Interferon C. Cryptidins D. Histamine Is a group of serum proteins that lyses microorganisms or facilitates phagocytes. They circulate in an inactive state in our body & can be activated by a variety of specific & nonspecific immunologic mechanisms. Is produced by virus infected cell, induces antiviral state in uninfected cells. C. Correct! Is an antimicrobial substance. Histamine is a chemical released by a variety of cells in response to tissue injury. It can bind to receptors on the near by capillaries and venules, causing vasodilation and increased permeability of capillaries. Various substances produced by the host body can destroy microorganisms and are known as antimicrobial substances. Anti-microbial substances which directly destroy microorganism are: Cryptidins and a-defensin, produced in the base of crypts of the small intestine, damages cell membranes. b-defensins, produced within skin, respiratory tract - also damages cell membranes. Surfactant proteins A & D, present in lungs, function as opsonins which enhance the efficiency of phagocytosis.
7 No. 7 of Which of the following soluble protein contribute to the physiological barriers of non-specific immunity? A. Sebum B. Interferon C. Histamine D. Acute-Phase proteins It is included under anatomical barriers. B. Correct! It is produced by virus infected cells and induces an antiviral state in uninfected cells. It is included under inflammatory barriers. It is included under inflammatory barriers. A variety of soluble factors contribute to non-specific immunity, among them the soluble proteins lysosome, interferon, & complement. They are the group of molecules involved in signaling between cells of the immune system, and in protection against viral infections. Among the many functions of interferon is the ability to bind to nearby cells and induce a generalized antiviral state.
8 No. 8 of 10 8 A cytoplasmic vesicle containing degradative enzymes is known as a. A. Dermis B. Macrophage C. Phagosomes D. Lysosome Layer of skin containing blood vessels and sebaceous glands. Phagocytic cell found in tissues. Large vesicles containing ingested particulate material. D. Correct! It is the name of the vesicle containing the ingested particulate material. A small cytoplasmic vesicle found in many types of cells that contains hydrolytic enzymes like lysozyme, which play an important role in the degradation of material ingested by phagocytosis and endocytosis.
9 No. 9 of How do phagocytic cells distinguish between Self and Non-Self? A. Microbial patterns B. Diversity C. Memory D. Specificity A. Correct! Our body cells recognize invading microorganisms by recognizing common microbial patterns. It is the attribute of adaptive immunity. It is the attribute of adaptive immunity. It is the attribute of adaptive immunity. Our body cells recognize invading microorganisms by recognizing common microbial patterns like: LPS- lipopolysaccharide (associated with the outer membrane of Gram - bacteria) Mannose, fucose, and other sugar residues (not just absence/presence but also factors like spacing between sugars on the cell surface) Techoid acid (associated with the peptidoglycan cell wall of Gram+ bacteria) N-formyl peptides ( recall that all prokaryotic protein sequences begin with a formyl-methionine) These common microbial patterns are recognized by host proteins which have been termed Pattern Recognition Molecules (PRMs) or Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs).
10 No. 10 of Within a species, different races may show differences in susceptibility to infections; this is known as. A. Species immunity B. Acquired immunity C. Racial immunity D. Individual immunity Species immunity refers to the total refractoriness to a pathogen, shown by all the members of a species obtained as their birthright. The resistance that an individual acquires during life is known as specific immunity. C. Correct! Different races show differences in susceptibility to infections is known as racial immunity. The differences in innate immunity exhibited by different individuals in a race are known as individual immunity. It is genetic in origin.. Within a species, different races may show differences in susceptibility to infections. This is known as racial immunity, it is genetic in origin. By selection and inbreeding it is possible to develop races that possess high degrees of resistance or susceptibility to pathogens. Example: Genetic resistance to plasmodium falciparum malaria is seen in some parts of Africa & Mediterranean coast. This occurs due to the hereditary abnormality of red blood cells (sickling), prevalent in those areas. Which confers immunity to infection by the malarial parasite & may have evolved from the survival advantage conferred by it in a malarial environment? Solution
2 االستاذ المساعد الدكتور خالد ياسين الزاملي \ مناعة \ المرحلة الثانية \ التحليالت المرضية \
 Innate Immunity Innate immunity: is the resistance that an individual possesses by birth. Innate immunity may be classified as (a) individual immunity (b) racial immunity (c) species immunity. Factors
Innate Immunity Innate immunity: is the resistance that an individual possesses by birth. Innate immunity may be classified as (a) individual immunity (b) racial immunity (c) species immunity. Factors
Chapter 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
 Module 10 Chapter 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host The concept of immunity Immunity: ability to protect against from microbes and their o Aka, Susceptibility: vulnerability or lack
Module 10 Chapter 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host The concept of immunity Immunity: ability to protect against from microbes and their o Aka, Susceptibility: vulnerability or lack
1. Overview of Innate Immunity
 Chapter 15: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity Chapter Reading pp. 449-456 The Body s Defenses The
Chapter 15: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity Chapter Reading pp. 449-456 The Body s Defenses The
Ch 12. Host Defenses I: Nonspecific Defenses
 Ch 12 Host Defenses I: Nonspecific Defenses SLOs Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity. Define and explain PRRs and PAMPs Differentiate physical from chemical factors, and list examples of
Ch 12 Host Defenses I: Nonspecific Defenses SLOs Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity. Define and explain PRRs and PAMPs Differentiate physical from chemical factors, and list examples of
PATHOGENS AND DEFENCE AGAINST INFECTIOUS DISEASE. By: Stephanie, Emily, Cem, and Julie
 PATHOGENS AND DEFENCE AGAINST INFECTIOUS DISEASE By: Stephanie, Emily, Cem, and Julie Pathogen Pathogen: an organism or virus that causes a disease. Examples: bacteria, fungi, protozoa, virus Disease Cause
PATHOGENS AND DEFENCE AGAINST INFECTIOUS DISEASE By: Stephanie, Emily, Cem, and Julie Pathogen Pathogen: an organism or virus that causes a disease. Examples: bacteria, fungi, protozoa, virus Disease Cause
Human Immune Response. Part 1: innate immunity
 Human Immune Response Part 1: innate immunity Our bodies are under constant attack from pathogens A pathogen is an organism that can cause disease Pathogens include: Bacteria Viruses Protists Fungi 6.3.1
Human Immune Response Part 1: innate immunity Our bodies are under constant attack from pathogens A pathogen is an organism that can cause disease Pathogens include: Bacteria Viruses Protists Fungi 6.3.1
Module 10 Innate Immunity
 Module 10 Innate Immunity Chapter 16 Innate Immunity Lectures Lectures prepared prepared by by Christine HelmutL.Kae Case The Concept of Immunity Immunity: ability to protect against disease from microbes
Module 10 Innate Immunity Chapter 16 Innate Immunity Lectures Lectures prepared prepared by by Christine HelmutL.Kae Case The Concept of Immunity Immunity: ability to protect against disease from microbes
Overview of the immune system
 Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
The Lymphatic System. Innate Immunity
 The Lymphatic System Innate Immunity 1 Types of Immunity Innate (non-specific) immunity Adaptive (specific) immunity The human body has several different ways that it defends itself against infection by
The Lymphatic System Innate Immunity 1 Types of Immunity Innate (non-specific) immunity Adaptive (specific) immunity The human body has several different ways that it defends itself against infection by
Nonspecific Defenses of the Host. Chapter 16
 Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Chapter 16 I. Introduction: Overview of host defenses A. Resistance Ability to ward off disease through body defenses 1. Nonspecific All body defenses that protect one
Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Chapter 16 I. Introduction: Overview of host defenses A. Resistance Ability to ward off disease through body defenses 1. Nonspecific All body defenses that protect one
Chapter 37 Section 1: Protecting Against Disease. Key Vocabulary Terms 9
 Chapter 37 Section 1: Protecting Against Disease Key Vocabulary Terms 9 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Pathogen A microorganism, another organism, a virus, or a protein that causes disease; an infectious
Chapter 37 Section 1: Protecting Against Disease Key Vocabulary Terms 9 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Pathogen A microorganism, another organism, a virus, or a protein that causes disease; an infectious
Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Host Response to Disease Resistance- ability
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Host Response to Disease Resistance- ability
4b. Innate (nonspecific) Immunity
 4b. Innate (nonspecific) Immunity Chapter 16: Innate (nonspecific) Immunity! Some terms:! Susceptibility: Lack of immunity to a disease.! Immunity: Ability to ward off disease.! Innate immunity: Defenses
4b. Innate (nonspecific) Immunity Chapter 16: Innate (nonspecific) Immunity! Some terms:! Susceptibility: Lack of immunity to a disease.! Immunity: Ability to ward off disease.! Innate immunity: Defenses
16 Innate Immunity: M I C R O B I O L O G Y. Nonspecific Defenses of the Host. a n i n t r o d u c t i o n
 ninth edition TORTORA FUNKE CASE M I C R O B I O L O G Y a n i n t r o d u c t i o n 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation prepared by Christine L.
ninth edition TORTORA FUNKE CASE M I C R O B I O L O G Y a n i n t r o d u c t i o n 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation prepared by Christine L.
Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity & Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity & Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Pathogenicity: Virulence: The extent of pathogenicity. - function of: - infectivity
Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity & Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Pathogenicity: Virulence: The extent of pathogenicity. - function of: - infectivity
Defense mechanism against pathogens
 Defense mechanism against pathogens Immune System What is immune system? Cells and organs within an animal s body that contribute to immune defenses against pathogens ( ) Bacteria -Major entry points ;open
Defense mechanism against pathogens Immune System What is immune system? Cells and organs within an animal s body that contribute to immune defenses against pathogens ( ) Bacteria -Major entry points ;open
BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS
 BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS A pathogen is a microorganism that is able to cause disease. Pathogenicity is the ability to produce disease in a host organism. Virulence a term which refers to the degree of pathogenicity
BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS A pathogen is a microorganism that is able to cause disease. Pathogenicity is the ability to produce disease in a host organism. Virulence a term which refers to the degree of pathogenicity
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response. Physiology Unit 3
 INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity
 Part 1 Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity Bacteria Most common pathogens Anthrax Cholera Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria Bacterial diseases Tuberculosis Cholera Bubonic Plague Tetanus Effects
Part 1 Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity Bacteria Most common pathogens Anthrax Cholera Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria Bacterial diseases Tuberculosis Cholera Bubonic Plague Tetanus Effects
primary : thymus, bone marrow lymphoid tissue secondary : lymph nodes, MALT, spleen spleen: there are 2 main types of tissues in the spleen :
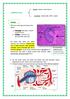 primary : thymus, bone marrow lymphoid tissue secondary : lymph nodes, MALT, spleen spleen: there are 2 main types of tissues in the spleen : 1. white pulp (gray area) : contains lymphoid tissue 2. red
primary : thymus, bone marrow lymphoid tissue secondary : lymph nodes, MALT, spleen spleen: there are 2 main types of tissues in the spleen : 1. white pulp (gray area) : contains lymphoid tissue 2. red
Innate Immunity. Natural or native immunity
 Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Natural Defense Mechanisms
 Color code: Important in red Extra in blue For team error adjustments, click here Natural Defense Mechanisms Objectives To know First (non-specific immunity) and second (adaptive immunity) lines of defense
Color code: Important in red Extra in blue For team error adjustments, click here Natural Defense Mechanisms Objectives To know First (non-specific immunity) and second (adaptive immunity) lines of defense
Innate Immunity. Natural or native immunity
 Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
11/25/2017. THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS BARRIER DEFENSES INNATE IMMUNITY OF VERTEBRATES
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
By Lucy Simpson and Taylor Meyers
 By Lucy Simpson and Taylor Meyers Two Types of Immunity Innate immunity- Innate immunity consists of external barriers formed by the skin and mucous membranes, plus a set of internal cellular and chemical
By Lucy Simpson and Taylor Meyers Two Types of Immunity Innate immunity- Innate immunity consists of external barriers formed by the skin and mucous membranes, plus a set of internal cellular and chemical
Immune System AP SBI4UP
 Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Unit 5 The Human Immune Response to Infection
 Unit 5 The Human Immune Response to Infection Unit 5-page 1 FOM Chapter 21 Resistance and the Immune System: Innate Immunity Preview: In Chapter 21, we will learn about the branch of the immune system
Unit 5 The Human Immune Response to Infection Unit 5-page 1 FOM Chapter 21 Resistance and the Immune System: Innate Immunity Preview: In Chapter 21, we will learn about the branch of the immune system
Where are we heading?
 Unit 5: Where are we heading? Unit 5: Introduction Unit 1: Why should we care about infectious diseases? Unit 2: What does it mean to have an infectious disease? Unit 3: When does a microbe become a pathogen?
Unit 5: Where are we heading? Unit 5: Introduction Unit 1: Why should we care about infectious diseases? Unit 2: What does it mean to have an infectious disease? Unit 3: When does a microbe become a pathogen?
Chapter 16/17: Immune system
 Chapter 16/17: Immune system Lecture Chapter 16: Nonspecific defenses First line of defense Formed elements Second line of defense Complement system Chapter 17: Specific defenses Antibodies Humoral response
Chapter 16/17: Immune system Lecture Chapter 16: Nonspecific defenses First line of defense Formed elements Second line of defense Complement system Chapter 17: Specific defenses Antibodies Humoral response
Immunology Lecture- 1
 Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Chapter Pages Transmission
 Chapter 19.2 Pages 442-448 Transmission Immunity There are three lines of defense: 1 The skin and mucous membranes are a nonspecific barrier to infection. 2 Macrophages attack pathogens that enter the
Chapter 19.2 Pages 442-448 Transmission Immunity There are three lines of defense: 1 The skin and mucous membranes are a nonspecific barrier to infection. 2 Macrophages attack pathogens that enter the
I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms. Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense
 I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense Innate Immunity involves nonspecific physical & chemical barriers that are adapted for
I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense Innate Immunity involves nonspecific physical & chemical barriers that are adapted for
Innate Immunity. By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik
 Innate Immunity By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Types of immunity Immunity Innate / inborn Non-specific Acquired / adaptive Specific 3rd line of defense Physical barriers Skin, Saliva, Mucous, Stomach acid,
Innate Immunity By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Types of immunity Immunity Innate / inborn Non-specific Acquired / adaptive Specific 3rd line of defense Physical barriers Skin, Saliva, Mucous, Stomach acid,
ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
lysosomes Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types:
 lysosomes Digests Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types: Proteins Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Lipids Single membrane bound vesicle, contains up to 50 digestive
lysosomes Digests Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types: Proteins Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Lipids Single membrane bound vesicle, contains up to 50 digestive
Immunology. Prof. Nagwa Mohamed Aref (Molecular Virologist & Immunology)
 Host Defenses Overview and Nonspecific Defenses I Immunology Prof. Nagwa Mohamed Aref (Molecular Virologist & Immunology) The Nature of Host Defenses 2 3 4 1st line of defense - intact skin mucous membranes
Host Defenses Overview and Nonspecific Defenses I Immunology Prof. Nagwa Mohamed Aref (Molecular Virologist & Immunology) The Nature of Host Defenses 2 3 4 1st line of defense - intact skin mucous membranes
Components of the innate immune system
 Components of the innate immune system Before our discussion about innate immunity Differences between innate and adaptive systems: Innate immune system = natural = native -Germline: prepared before exposure
Components of the innate immune system Before our discussion about innate immunity Differences between innate and adaptive systems: Innate immune system = natural = native -Germline: prepared before exposure
Innate Immunity. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Innate Immunity Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The vertebrate, including human, immune system is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. The
Innate Immunity Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The vertebrate, including human, immune system is a complex multilayered system for defending against external and internal threats to the integrity of the body. The
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
Resisting infection. Cellular Defenses: Leukocytes. Chapter 16: Innate host defenses Phagocytosis Lymph Inflammation Complement
 Resisting infection Chapter 16: Innate host defenses Lymph Inflammation Complement Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Innate defenses (ch. 16) Physical & chemical barriers; cellular defenses; inflammation, fever;
Resisting infection Chapter 16: Innate host defenses Lymph Inflammation Complement Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Innate defenses (ch. 16) Physical & chemical barriers; cellular defenses; inflammation, fever;
Nonspecific External Barriers skin, mucous membranes
 Immune system Chapter 36 BI 103 Plant-Animal A&P Levels of Defense Against Disease Nonspecific External Barriers skin, mucous membranes Physical barriers? Brainstorm with a partner If these barriers are
Immune system Chapter 36 BI 103 Plant-Animal A&P Levels of Defense Against Disease Nonspecific External Barriers skin, mucous membranes Physical barriers? Brainstorm with a partner If these barriers are
BIOH122 Session 8 Non-Specific Disease Resistance
 BIOH122 Session 8 Non-Specific Disease Resistance To complete this worksheet, select: Module: Disease Resistance Activity: Animations Title: Non-Specific Disease Resistance Introduction 1. Name five general
BIOH122 Session 8 Non-Specific Disease Resistance To complete this worksheet, select: Module: Disease Resistance Activity: Animations Title: Non-Specific Disease Resistance Introduction 1. Name five general
Acquired Immunity Cells are initially and require before they can work Responds to individual microbes
 1 of 10 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM CHAPTER 43; PAGES 898 921 WHY DO WE NEED AN IMMUNE SYSTEM? It s a dirty, dirty world out there and we are vastly outnumbered Bacteria and parasites are everywhere The body has
1 of 10 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM CHAPTER 43; PAGES 898 921 WHY DO WE NEED AN IMMUNE SYSTEM? It s a dirty, dirty world out there and we are vastly outnumbered Bacteria and parasites are everywhere The body has
Chapter 17. The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Unit 9 New life College faculty: Ramesh Kumar Subject: Life Sciences date: 15jan 2016
 Unit 9 New life College faculty: Ramesh Kumar Subject: Life Sciences date: 15jan 2016 History and impact The types and functions of cells in the immune system. How cells communicate and recognize antigen
Unit 9 New life College faculty: Ramesh Kumar Subject: Life Sciences date: 15jan 2016 History and impact The types and functions of cells in the immune system. How cells communicate and recognize antigen
Chapter 38- Immune System
 Chapter 38- Immune System First Line of Defense: Barriers Nonspecific defenses, such as the skin and mucous membranes, are barriers to potential pathogens. In addition to being a physical barrier to pathogens,
Chapter 38- Immune System First Line of Defense: Barriers Nonspecific defenses, such as the skin and mucous membranes, are barriers to potential pathogens. In addition to being a physical barrier to pathogens,
Independent Study Guide The Innate Immune Response (Chapter 15)
 Independent Study Guide The Innate Immune Response (Chapter 15) I. General types of immunity (Chapter 15 introduction) a. Innate i. inborn ii. pattern recognition b. Adaptive i. "learned" through exposure
Independent Study Guide The Innate Immune Response (Chapter 15) I. General types of immunity (Chapter 15 introduction) a. Innate i. inborn ii. pattern recognition b. Adaptive i. "learned" through exposure
Immune System. Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka
 Immune System Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka Content Standards 35.1 In innate immunity, recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens 35.2
Immune System Presented by Kazzandra Anton, Rhea Chung, Lea Sado, and Raymond Tanaka Content Standards 35.1 In innate immunity, recognition and response rely on traits common to groups of pathogens 35.2
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Universiti Malaysia Kelantan. Immunology and Serology (DVT2153)
 Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Universiti Malaysia Kelantan Immunology and Serology (DVT2153) By Dr. Erkihun Aklilu 1 Immune Response AgAinst Various infectious agents Immunology and Serology (DVT2153)
Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Universiti Malaysia Kelantan Immunology and Serology (DVT2153) By Dr. Erkihun Aklilu 1 Immune Response AgAinst Various infectious agents Immunology and Serology (DVT2153)
KEY CONCEPT Germs cause many diseases in humans.
 31.1 40.1 Pathogens Infectious Diseases and Human Illness KEY CONCEPT Germs cause many diseases in humans. 31.1 40.1 Pathogens Infectious Diseases and Human Illness Germ theory states that microorganisms
31.1 40.1 Pathogens Infectious Diseases and Human Illness KEY CONCEPT Germs cause many diseases in humans. 31.1 40.1 Pathogens Infectious Diseases and Human Illness Germ theory states that microorganisms
3/28/2012. Immune System. Activation of Innate Immunity. Innate (non-specific) Immunity
 Chapter 5 Outline Defense Mechansims Functions of B Lymphocytes Functions of T Lymphocytes Active and Passive Immunity Tumor Immunology Diseases Caused By Immune System Immune System Anatomy - Lymphoid
Chapter 5 Outline Defense Mechansims Functions of B Lymphocytes Functions of T Lymphocytes Active and Passive Immunity Tumor Immunology Diseases Caused By Immune System Immune System Anatomy - Lymphoid
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
AP Biology. Why an immune system? Chapter 43. Immune System. Lines of defense. 1st: External defense. 2nd: Internal, broad range patrol
 Chapter 43. Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph phagocytic leukocyte Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against
Chapter 43. Immune System lymphocytes attacking cancer cell lymph phagocytic leukocyte Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against
Innate Immunity. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter 3. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Immune System. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 Immune System 37 section 2 The Immune System Biology/Life Sciences 10.b Students know the role of antibodies in the body s response to infection. Also covers: Biology/Life Sciences 10.a, 10.e, 10.f Components
Immune System 37 section 2 The Immune System Biology/Life Sciences 10.b Students know the role of antibodies in the body s response to infection. Also covers: Biology/Life Sciences 10.a, 10.e, 10.f Components
The Immune System it protects your health. Who are the invaders? Viruses tiny protein shells filled with DNA or RNA
 The Immune System it protects your health Who are the invaders? Bacteria Viruses Pathogens Bacteria are very small and mostly harmless Single-celled organisms Only a few cause disease Extremely small,
The Immune System it protects your health Who are the invaders? Bacteria Viruses Pathogens Bacteria are very small and mostly harmless Single-celled organisms Only a few cause disease Extremely small,
Immunity. Chapter 38 Part 1
 Immunity Chapter 38 Part 1 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1
Immunity Chapter 38 Part 1 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System
 Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
OpenStax-CNX module: m Innate Immunity. OpenStax College. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m45542 1 Innate Immunity OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m45542 1 Innate Immunity OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology
 Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses ( )
 NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses (43.1-43.2) The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system. LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS Lymphatic capillaries
NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses (43.1-43.2) The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system. LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS Lymphatic capillaries
Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
Warm-up. Parts of the Immune system. Disease transmission. Disease transmission. Why an immune system? Chapter 43 3/9/2012.
 Warm-up Objective: Explain how antigens react with specific lymphocytes to induce immune response and immunological memory. Warm-up: Which of the following would normally contain blood with the least amount
Warm-up Objective: Explain how antigens react with specific lymphocytes to induce immune response and immunological memory. Warm-up: Which of the following would normally contain blood with the least amount
Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Big Picture: Immunity Big Picture: Immunity
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host Big Picture: Immunity Big Picture: Immunity
The Immune System. These are classified as the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Innate Immunity
 The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM. There are specific defense mechanisms and nonspecific defense mechanisms also known as innate immune response.
 Chapter 43 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Disease-causing microorganisms are called pathogens. They include bacteria, viruses, protozoans and fungi. Immunology is the study of specific defense mechanisms. Two major
Chapter 43 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Disease-causing microorganisms are called pathogens. They include bacteria, viruses, protozoans and fungi. Immunology is the study of specific defense mechanisms. Two major
Chapter 43. Immune System. phagocytosis. lymphocytes. AP Biology
 Chapter 43. Immune System phagocytosis lymphocytes 1 Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against unwelcome invaders viruses protists
Chapter 43. Immune System phagocytosis lymphocytes 1 Why an immune system? Attack from outside lots of organisms want you for lunch! animals must defend themselves against unwelcome invaders viruses protists
Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
 Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 8 Immune System 1 Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan
Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 8 Immune System 1 Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan
CH. 24. The Immune System
 CH. 24 The Immune System The immune systems consists of organs, cells, and molecules that fight infections and protect us from invaders. Pathogens: Bacteria, Viruses, Parasites, Fungi 1. Innate (nonspecific)
CH. 24 The Immune System The immune systems consists of organs, cells, and molecules that fight infections and protect us from invaders. Pathogens: Bacteria, Viruses, Parasites, Fungi 1. Innate (nonspecific)
Internal Defense Notes
 Internal environment of animals provides attractive area for growth of bacteria, viruses, fungi Harm via: 1. destruction of cells 2. production of toxic chemicals To protect against foreign invaders, humans
Internal environment of animals provides attractive area for growth of bacteria, viruses, fungi Harm via: 1. destruction of cells 2. production of toxic chemicals To protect against foreign invaders, humans
The immune system is made up of a complex and vital network of cells and organs that protect the body from infection.
 IMMUNE SYSTEM Viruses, bacteria and other germs are all around us. Most of the time, a healthy immune system keeps us well. The purpose of the immune system is to keep infectious micro-organisms, such
IMMUNE SYSTEM Viruses, bacteria and other germs are all around us. Most of the time, a healthy immune system keeps us well. The purpose of the immune system is to keep infectious micro-organisms, such
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and. Specific. (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell
 There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
~ons~ecific Bod~ Defenses and Immunity
 ~ons~ecific Bod~ Defenses and Immunity The human body continually attempts to maintain homeostasis by counteracting harmful or disease-producing organisms called pathoqens or the toxins they produce. The
~ons~ecific Bod~ Defenses and Immunity The human body continually attempts to maintain homeostasis by counteracting harmful or disease-producing organisms called pathoqens or the toxins they produce. The
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
Outline. Animals: Immunity. Defenses Against Disease. Key Concepts:
 Animals: Immunity Defenses Against Disease Outline 1. Key concepts 2. Physical barriers: Skin, Mucus and HCL in stomach 3. Non-specific 4. Specific responses Immune System a. Components of Immune system
Animals: Immunity Defenses Against Disease Outline 1. Key concepts 2. Physical barriers: Skin, Mucus and HCL in stomach 3. Non-specific 4. Specific responses Immune System a. Components of Immune system
Questions on Disease and Immunity
 Name: Questions on Disease and Immunity Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.3 (Defence against infectious disease). Answer all questions. This will serve
Name: Questions on Disease and Immunity Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.3 (Defence against infectious disease). Answer all questions. This will serve
4/28/2016. Host Defenses. Unit 8 Microorganisms & The Immune System. Types of Innate Defenses. Defensive Cells Leukocytes
 Host Defenses Unit 8 Microorganisms & The Immune System CH 16-18 Host defenses that produce resistance can be either innate or adaptive: Innate: those that protect against any type of invading agent Adaptive:
Host Defenses Unit 8 Microorganisms & The Immune System CH 16-18 Host defenses that produce resistance can be either innate or adaptive: Innate: those that protect against any type of invading agent Adaptive:
How and Why do we get sick? The Non-specific Lines of defense
 How and Why do we get sick? The Non-specific Lines of defense Disease A possible disruption in homeostasis A lack of stability within the body May be caused by heredity, microorganism, macroorganism, pollutants,
How and Why do we get sick? The Non-specific Lines of defense Disease A possible disruption in homeostasis A lack of stability within the body May be caused by heredity, microorganism, macroorganism, pollutants,
All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
Immune System. Biol 105 Chapter 13
 Immune System Biol 105 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
Immune System Biol 105 Chapter 13 Outline Immune System I. Function of the Immune system II. Barrier Defenses III. Nonspecific Defenses A. Immune system cells B. Inflammatory response C. Complementary
The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately
 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 INNATE IMMUNITY (all animals) Recognition of traits shared
The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 INNATE IMMUNITY (all animals) Recognition of traits shared
Body Defense Mechanisms
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 13 Body Defense Mechanisms Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 13 Body Defense Mechanisms Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of
The Innate Immune Response
 The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
Lines of defense. Innate Immunity. Immunity. First line of defense: Skin and mucous membranes 11/20/2016. Chapter 16 BIO 220
 Lines of defense Innate Immunity Chapter 16 BIO 220 Immunity The ability to ward off disease caused by microbes or their products and to protect against environmental agents such as pollen, chemicals,
Lines of defense Innate Immunity Chapter 16 BIO 220 Immunity The ability to ward off disease caused by microbes or their products and to protect against environmental agents such as pollen, chemicals,
محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases
 محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases Immunity to infection depends on a combination of innate mechanisms (phagocytosis, complement, etc.) and antigen
محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases Immunity to infection depends on a combination of innate mechanisms (phagocytosis, complement, etc.) and antigen
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
What are bacteria? Microbes are microscopic(bacteria, viruses, prions, & some fungi etc.) How do the sizes of our cells, bacteria and viruses compare?
 7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
Anti-infectious Immunity
 Anti-infectious Immunity innate immunity barrier structures Secretory molecules Phagocytes NK cells Anatomical barriers 1. Skin and mucosa barrier 2.hemo-Spinal Fluid barrier 3. placental barrier Phagocytic
Anti-infectious Immunity innate immunity barrier structures Secretory molecules Phagocytes NK cells Anatomical barriers 1. Skin and mucosa barrier 2.hemo-Spinal Fluid barrier 3. placental barrier Phagocytic
Topics in Parasitology BLY Vertebrate Immune System
 Topics in Parasitology BLY 533-2008 Vertebrate Immune System V. Vertebrate Immune System A. Non-specific defenses against pathogens 1. Skin - physical barrier a. Tough armor protein KERATIN b. Surface
Topics in Parasitology BLY 533-2008 Vertebrate Immune System V. Vertebrate Immune System A. Non-specific defenses against pathogens 1. Skin - physical barrier a. Tough armor protein KERATIN b. Surface
Innate vs Adaptive Response
 General Immunology Innate vs Adaptive Response Innate- non-specific (4 types of barriers) anatomic- ato mechanical ca (skin), ph, mucous, normal flora Physiologic- temperature, ph, chemicals (lysozyme,
General Immunology Innate vs Adaptive Response Innate- non-specific (4 types of barriers) anatomic- ato mechanical ca (skin), ph, mucous, normal flora Physiologic- temperature, ph, chemicals (lysozyme,
Fluid movement in capillaries. Not all fluid is reclaimed at the venous end of the capillaries; that is the job of the lymphatic system
 Capillary exchange Fluid movement in capillaries Not all fluid is reclaimed at the venous end of the capillaries; that is the job of the lymphatic system Lymphatic vessels Lymphatic capillaries permeate
Capillary exchange Fluid movement in capillaries Not all fluid is reclaimed at the venous end of the capillaries; that is the job of the lymphatic system Lymphatic vessels Lymphatic capillaries permeate
(b) fluid returns to venous end of capillary due to hydrostatic pressure and osmotic pressure
 (Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Lymphatic System and Immunity (Body Defenses) I. (Slide 2) Introduction A) General 1) Lymphatic System performs 2 basic functions: 2) Organs of the Lymphatic System (a) lymphatic
(Slide 1) Lecture Notes: Lymphatic System and Immunity (Body Defenses) I. (Slide 2) Introduction A) General 1) Lymphatic System performs 2 basic functions: 2) Organs of the Lymphatic System (a) lymphatic
3/17/2014. The Lymphatic System. Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs
 The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep
 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep invaders out of the body (pp. 772 773; Fig. 21.1; Table
The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep invaders out of the body (pp. 772 773; Fig. 21.1; Table
Immune System Notes Innate immunity Acquired immunity lymphocytes, humoral response Skin lysozyme, mucus membrane
 Immune System Notes I. The immune system consists of innate and acquired immunity. A. An animal must defend itself against unwelcome intruders the many potentially dangerous viruses, bacteria, and other
Immune System Notes I. The immune system consists of innate and acquired immunity. A. An animal must defend itself against unwelcome intruders the many potentially dangerous viruses, bacteria, and other
Chapter 24 The Immune System
 Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Defense & the Immune System. Immune System Agenda 4/28/2010. Overview. The bigger picture Non specific defenses Specific defenses (Immunity)
 Defense &The Immune System Overview Immune System Agenda The bigger picture Non specific defenses Specific defenses (Immunity) Defense & the Immune System Big Picture Defense Any means of preventing or
Defense &The Immune System Overview Immune System Agenda The bigger picture Non specific defenses Specific defenses (Immunity) Defense & the Immune System Big Picture Defense Any means of preventing or
