Station 1. Topic 1.1 Introduction to cells
|
|
|
- Jordan Stephens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Station 1 Topic 1.1 Introduction to cells Cell Theory 1. Outline the components of the cell theory with evidence: o All cells come from pre-existing cells: o Cells are the basic unit of life: o All living organisms are made of one or more cells: 2. Discuss possible exceptions to the cell theory o Large single-celled organisms (amoebas): o Fungal Hyphae: o Muscle Cells: o Viruses: 3. Compare and contrast unicellular vs. multicellular organisms 4. What are the functions of Life: 5. Magnification/Actual size problems (Memorize these equations!!) o Mag = Measured length of Scale Bar/Scale bar label o Actual Size = Measured length of image/magnification 6. General Sizes of molecules/organisms (know this chart!) Plant Animal Nucleus Bacteria Mitochondria Virus Ribosome Membrane Molecules 100 µm µm 3-6 µm 1-5 µm 3 µm 100nm 20nm 10nm 1nm 7. Surface Area : Volume ratio o How does it limit cell size? What do cells do to maximize SA:V? Benefits of Large SA:V? 8. Define emergent properties. 9. Process of Cell differentiation: o Cell Differentiation is the process of cells becoming specialized to perform specific functions o All cells have same DNA & come from fertilized egg cell o Expression/Inexpression of certain genes causes specialization o Genes expressed based on location of cell, hormones/chemicals presents, or cell-tocell communication 10. Stem Cells o Define: o Outline one therapeutic use of stem cells:
2 Topic 1.1 Answers: Cell Theory 1. Outline the components of the cell theory with evidence: o All cells come from pre-existing cells: All cells descent from common ancestor. Cells multiply by division to form new cells. Remak discovered cell division. Pasteur disproved spontaneous generation. o Cells are the basic unit of life: Cells perform the functions of life. No organelles can survive outside the cell membrane on their own. o All living organisms are made of one or more cells: Hooke first observed cells. Van Leeuwenhoek first observed living cells. No living entity found not made of cells. 2 types of organisms: Unicellular single celled organisms perform the function of life. Multicellular made up of many specialized cells w/specific functions. 2. Discuss possible exceptions to the cell theory o Large single-celled organisms (amoebas): Single cell capable of all life processes. If there is only one cell is it made of cells? o Fungal Hyphae: Extremely large and multinucleated w/ continuous cytoplasm o Muscle Cells: Very long and mutinucleated o Viruses: do not perform functions of life. Only reproduce w/host cell. 3. Compare and Contrast Unicellular vs. Multicellular organisms Unicellular single celled organisms perform the function of life. Multicellular made up of many specialized cells w/specific functions. 4. What are the Functions of Life: Respiration/metabolic reactions, Require nutrition, respond to environment, experience growth and development, maintain homeostasis, reproduce 5. Magnification/Actual size problems o Mag = Measured length of Scale Bar/Scale bar label o Actual Size = Measured length of image/magnification Plant Animal Nucleus Bacteria Mitochondria Virus Ribosome Membrane Molecules 100 µm µm 3-6 µm 1-5 µm 3 µm 100nm 20nm 10nm 1nm 6. General Sizes of molecules/organisms 7. Surface Area : Volume ratio o How does it limit cell size? What do cells do to maximize SA:V? Benefits of Large SA:V? As cells increase in size, the surface area to volume ratio decreases, so large cells have a small surface area to volume ratio, and small cells have a large surface area to volume ratio. A larger surface area to volume ratio makes diffusion pathways shorter, increases area for metabolic reactions, and makes the cell more efficient at removing waste. As a cell increases to the point where the surface area to volume ratio makes the cell inefficient, it will divide to make two small cells with large surface area to volume ratio. Cells divide, compartmentalize, and have infoldings and outfoldings to increase suface area to volume ratio. 8. Define emergent properties. The whole is greater than the sum of the parts. A multicellular organism is more than the specific cells/organs/tissues that make it. 9. Process of Cell differentiation: o Cell Differentiation is the process of cells becoming specialized to perform specific functions o All cells have same DNA & come from fertilized egg cell
3 o Expression/Inexpression of certain genes causes specialization o Genes expressed based on location of cell, hormones/chemicals presents, or cell-to-cell communication 10. Stem Cells o Define: cells that retain the capacity to divide and can differentiate along different pathways o Outline one therapeutic use of stem cells: Treatment for Leukemia Problem Cancer of the blood or bone marrow, resulting in abnormally high levels of poorly-functioning white blood cells. Treatment Role of Stem Cells Chemotherapy and radiotherapy can be used to destroy the white blood cells, but these need to be replaced with healthy cells. Bone marrow transplants are often used for this. Hematopoetic Stem Cells (HSCs) can be harvested from bone marrow, peripheral blood or umbilical cord blood. As these can differentiate to form any type of white blood cell, they can be used to repopulate the bone marrow and produce new, healthy blood cells. The use of a patient s own HSCs means there is far less risk of immune rejection than with a traditional bone marrow transplant.
4 Prokaryotic/Eukaryotic Cells Station 2 Topic 2.2 Ultrastructure of Cells 1. Draw, label, and annotate a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell (both plant and animal) 2. Functions of Cell Components/Organelles: (What is an organelle?) o Cell membrane: o Cell wall(prokaryotic & plant cell): o Nucleoid (prokaryotic): o Pili (prokaryotic): o Flagella (prokaryotic): o Ribosomes: o Endoplasmic Reticulum (smooth & rough): o Golgi Apparatus: o Lysosomes: o Mitochondria: o Nucleus: o Chloroplasts (plant): o Vacuoles (plant): 3. Prokaryotic cells divide by Binary Fission 4. Compare/Contrast Plant & Animal Cells 5. Compare/Contrast Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cell
5 Topic 1.2 Answers Prokaryotic/Eukaryotic Cells 1. Draw, label, and annotate a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell (both plant and animal) 2. Functions of Cell Components/Organelles: discrete structures inside cell w/specific functions a. Cell membrane: selectively permeable, controls entry/exit of materials in cell b. Cell wall(prokaryotic & plant cell): protection and shape of cells c. Nucleoid (prokaryotic): region of closed loop DNA in prokaryotic cells, controls cell functions d. Pili (prokaryotic): attach cells to one another and sexual reproduction e. Flagella (prokaryotic): movement f. Ribosomes: protein synthesis g. Endoplasmic Reticulum (smooth & rough): Rough synthesis, packaging, and transport of proteins. Smooth production and transportation of molecules in cells, detox of drugs, etc.
6 h. Golgi Apparatus: collection, modification, distribution/transportation of materials made in cell to outside. i. Lysosomes: digestive centers of cell j. Mitochondria: provides energy to cell by converting glucose into usable energy ATP k. Nucleus: contains DNA in nuclear membrane. Controls the functions of cells and protein production l. Chloroplasts (plant): Absorbs sunlight in plants and converts it into glucose. m. Vacuoles (plant): large storage of nutrients and water 3. Prokaryotic cells divide by Binary Fission 4. Compare/Contrast Plant & Animal Cells Plant Cells Contain plasma membrane and CELL WALL Chloroplasts & Mitochondria Large central vacuole Do not contain centrioles Store starch (carb) Rigid cell wall Animal Cells Plasma membrane, no cell wall Mitochondria Vacuoles typically not present or small Do contain centrioles with centrosome area Stores glycogen Flexible cell 5. Compare/Contrast Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cell Both have cell membranes, cytoplasm, ribosomes. Prokaryotic cells have 70 s ribosomes, Euk have 80 s. Pro has nucleoid, Euk has nucleus, All Pro have cell wall, only plants have cell wall, Pro no
7 membrane bound organelles. Euk has membrane bound organelles (can mention up to 2 specific organelles for points). Pro has pili, euk does not. Pro has flagella, euk does not. Etc
8 Station 3 Topic 1.3 Membrane Structure Cell Membrane Structure & Function of Cell membrane o Draw and label a diagram of cell membrane (phospholipids, phospholipid bilayer, glycoproteins, integral proteins, peripheral proteins, & cholesterol) o Outline hydrophobic/hydrophilic properties of membrane and how they maintain structure of cell o Functions of membrane proteins: Cell-to-Cell Adhesion: Cell-to-Cell Communication: Enzymatic Action: Hormone Binding Cites: Passive Transport: Active Transport: o Label the parts of the membrane:
9 Answers 1.3 Cell Membrane Structure & Function of Cell membrane o o Draw and label a diagram of cell membrane (phospholipids, phospholipid bilayer, glycoproteins, integral proteins, peripheral proteins, & cholesterol) o Outline hydrophobic/hydrophilic properties of membrane and how they maintain structure of cell. Hydrophobic properties created hydrophobic section of cell membrane that separates internal components from exterior components and make it difficult for all materials to pass through membrane. Hydrophilic properties are oriented toward aqueous solutions inside and outside of cell, helping to create barrier between internal and external environnents. o o Functions of membrane proteins: Cell-to-Cell Adhesion: Cell-to-Cell Communication: Enzymatic Action: Hormone Binding Cites: Passive Transport: Active Transport: Label the parts of the membrane: A is phospholipid A1 is hydrophilic head A2 is hydrophobic tail B: SKIP C is glycoprotein D: skip E is Cholesterol F is peripheral protein G is integral protein H I is phospholipid bilayer
10 o
11 Station 4 Topic 1.4 Membrane Transport 1. Passive Transport: o Define: o Diffusion: o Facilitated Diffusion: o Osmosis: Different solutions (hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic) 2. Active Transport: o Define/Discuss: o Outline steps of Na + /K - pump and how it maintains different internal and external environments. 3. Endocytosis: o Define: o How does it occur? o 3 Types: Phagocytosis: Pinocytosis Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis 4. Exocytosis: o Define: o How does it occur? o Outline 4 steps of protein production to excretion using exocytosis: 5. Discuss how endocytosis and Exocytosis rely on the fluidity of the phospholipids and the stability of the membrane that results from the hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions of the membrane. 6. Match the definition with the title a. Osmosis c. Facilitated Diffusion b. Diffusion d. Active Transport I. Net movement of molecules across a cell membrane down a concentration gradient. II. When a cell expends energy in order to transfer molecules across a membrane. III. A type of passive transport that allows substances to cross membranes with the assistance of special transport proteins. IV. Movement of water down a concentration gradient across a membrane. 7. Explain how vesicles are use to transport materials within a cell between the rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and plasma membrane. Using the vocab above explain the order of protein synthesis: 1. Synthesized by 2. Modified by 3. If vesicle carries protein it moves to to be shipped out 4. The vesicle fuses with the and moves outside the cell. 5. The pinching off of a vesicle to the outside of the cell is called 6. The pinching off of a substance to the inside of the cell (pulling on the plasma membrane) is called.
12 Topic 1.4 Answers 1. Passive Transport: o Define: Movement of molecules across a cell membrane w/out use of energy, but requiring use of concentration gradient. o o Diffusion: tendency of molecules to move down gradient from high to low concentration across a cell membrane w/out use of energy or proteins Facilitated Diffusion: molecules to move down gradient from high to low concentration across a cell membrane w/out use of energy but require the use of membrane proteins as channels for transport. o Osmosis: passive movement of water from areas of low solute concentration to high solute concentratoin Different solutions (hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic) Hypertonic high solute concentration, water moves into hypertonic solutions Hypotonic low solute concentration, water leaves hypotonic solution and enters hypertonic. Isostonic equal solute concentration, water enters and leaves w/eas 1. Active Transport: a. Define/Discuss: movement of molecules against gradient (low to high concentrations) w/use of proteins and energy (ATP) b. Outline steps of Na + /K - pump and how it maintains different internal and external environments. Sodium binds to pump, ATP phosphorylates and gives energy to protein, causing change in conformation and exposing protein to exterior. Sodium ions leave, potassium ions bind. Phosphate group is released, protein changes shape and opens to interior, potassium leaves protein pump.
13 2. Endocytosis: a. Define: taking in macromolecules by pinching off a vesicle from cell membrane. b. How does it occur? pinches off from cell membrane to form vesiscle c. 3 Types: i. Phagocytosis: cell eating ii. Pinocytosis cell drinking iii. Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis specific to bring in bulk quantities of one molecules 3. Exocytosis: a. Define: fusion of vesicles w/ cell membrane to secrete molecule out of cell. b. How does it occur? Vesicles fuse w/ cell membranes c. Outline 4 steps of protein production to excretion using exocytosis: Proteins made in ER/ribosomes. Transported to golgi apparatus, modified/packaged into vesicle. Vesicle fuses w/ membrane to secret molecules. 4. Discuss how endocytosis and Exocytosis rely on the fluidity of the phospholipids and the stability of the membrane that results from the hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions of the membrane. Fluidity of membranes allow for membranes to fuse together while maintaining a barrier between the two environments. 6. Match the definition with the title a. Osmosis (IV) b. Diffusion (I) c. Facilitated Diffusion (III) d. Active Transport (II) 7. Explain how vesicles are used to transport materials within a cell between the rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and plasma membrane. Using the vocab above explain the order of protein synthesis: 1. Synthesized by ribosomes 2. Modified by endoplasmic reticulum 3. If vesicle carries protein it moves to golgi apparatus to be shipped out 4. The vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane and moves outside the cell. 5. The pinching off of a vesicle to the outside of the cell is called exocytosis 6. The pinching off of a substance to the inside of the cell (pulling on the plasma membrane) is called endocytosis.
14 Station 5 Topic 1.5 The origin of cells 1. Define spontaneous generation. 2. How did the following scientist help to discover how cells evolved? a. Pasteur b. Miller and Urey 3. Discuss the endosymbiotic theory.
15 Answers Define spontaneous generation. a. Life could arise from nonliving things. Meat spontaneously produced magots. 2. How did the following scientist help to discover how cells evolved? a. Pasteur b. Miller and Urey i. Produced organic compounds from nonorganic compounds.
16 3. Discuss the endosymbiotic theory.
17 Station 6 Topic 1.6: Cell Division 1. List the stages of the cell cycle 2. List and describe what happens during each phase of interphase 3. Label the parts of the cell cycle below:
18 4. Describe mitosis 5. Label the parts of mitosis below: 6. Describe the process of cytokinesis in plant and animal cells. 7. Discuss the involvement of cyclins in the cell cycle. 8. Contrast benign and malignant tumors. 9. Discuss mutations and how they can lead to the development of cancer.
19 Topic 1.6 Answers 1. List the stages of the cell cycle a. Interphase, mitosis, cytokinesis 2. List and describe what happens during each phase of interphase a. G1: cell grows, mitochondria replicate, increase in size b. S: cell replicates all the genetic material in its nucleus c. G2: Get ready for cell division 3. Label the parts of the cell cycle below: a. A: G1 b. B: S c. C: G2 d. D: mitosis 4. Describe mitosis: Division of the nucleus. Consists of 4 phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. 5. Label the parts of mitosis below: a. Prophase b. Metaphase c. Anaphase d. Telophase e. Interpase 1. Centriole 2. Spindle fiber 3. Sister chromatids 4. 2 new cells 5. Chromatin 6. Plasma membrane 7. Nucleolus 8. Centriole 9. Choromosomes 10. Nuclear membrane 6. Describe the process of cytokinesis in plant and animal cells.
20 7. Discuss the involvement of cyclins in the cell cycle. a. Group of proteins that ensure that task are performed at eh correct time and that the cell only moves on to the next stage at the correct time. 8. Contrast benign and malignant tumors.
21 9. Discuss mutations and how they can lead to the development of cancer.
22
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Theory. Cells are the basic unit of life.
 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
Cell Theory. Eukaryote Cells. Prokaryote Cells 8/18/16
 Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
CH 7 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 1 Review What is a cell Explain What three statements make up the cell theory Infer How did the invention of the microscope help the development of the cell theory 2 Review How do microscopes work Apply
1 Review What is a cell Explain What three statements make up the cell theory Infer How did the invention of the microscope help the development of the cell theory 2 Review How do microscopes work Apply
Questions in Cell Biology
 Name: Questions in Cell Biology Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on the subject of cell biology. Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the
Name: Questions in Cell Biology Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on the subject of cell biology. Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. Chapter 7
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
Chapter Seven. A View of the Cell
 Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells?
 Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
Topic 1 (Old Curriculum) Past Exam Questions Extended Response SOLUTIONS
 1. skeletal muscle fibres are larger / have many nuclei / are not typical cells; fungal hyphae are (sometimes) not divided up into individual cells; unicellular organisms can be considered acellular; because
1. skeletal muscle fibres are larger / have many nuclei / are not typical cells; fungal hyphae are (sometimes) not divided up into individual cells; unicellular organisms can be considered acellular; because
Chapter 3: Cytology. Cytology is the study of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. We are made up of trillions of cells.
 PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
Chapter Seven. A View of the Cell
 Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Lesson 1. Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions. Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Cell Structure & Interactions
 Cells Structures & Interactions Overview 1830s-Botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann were studying tissues and proposed the unified cell theory All living things are composed of one
Cells Structures & Interactions Overview 1830s-Botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann were studying tissues and proposed the unified cell theory All living things are composed of one
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS. All living things are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all of the processes of life.
 CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1
 Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided.
 Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided. 1. The type of electron microscope that gives 2 dimensional images. a) Scanning b) Condensing c) Transmission d) Multidimensional
Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided. 1. The type of electron microscope that gives 2 dimensional images. a) Scanning b) Condensing c) Transmission d) Multidimensional
Delve AP Biology Lecture 4: 10/9/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang
 Today s Agenda: I. Review of organelles II. More important organelles III. Plasma membrane structure IV. Diffusion and transport Delve AP Biology Lecture 4: 10/9/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang I. Review
Today s Agenda: I. Review of organelles II. More important organelles III. Plasma membrane structure IV. Diffusion and transport Delve AP Biology Lecture 4: 10/9/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang I. Review
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Cells. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Euakryotic cells are generally one to one hundred times bigger than prokaryotic cells
 Cell Theory Cells 1. All living things are composed of one or more cell 2. Cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division of pre-existing cells Cells are divided into 2 categories:
Cell Theory Cells 1. All living things are composed of one or more cell 2. Cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division of pre-existing cells Cells are divided into 2 categories:
Cell Structure and Function Cell Structure and function
 Cell Structure and Cell Structure and function Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Cells Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw
Cell Structure and Cell Structure and function Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Cells Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw
Chapter 7 Notes. Section 1
 Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Cell Structure and Function C H A P T E R 7
 Cell Structure and Function C H A P T E R 7 EQ: What Scientists and inventions helped aid in creating Cell Theory? 7.1 Cell Theory (Cells and Living Things) Cells are the basic building block of all life
Cell Structure and Function C H A P T E R 7 EQ: What Scientists and inventions helped aid in creating Cell Theory? 7.1 Cell Theory (Cells and Living Things) Cells are the basic building block of all life
1 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of an animal plasma membrane?
 1 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of an animal plasma membrane? A) separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment B) helps the cell maintain homeostasis C)
1 Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of an animal plasma membrane? A) separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment B) helps the cell maintain homeostasis C)
1.3 - Cells. Chapter 3 - Cells
 1.3 - Cells Chapter 3 - Cells Cells Cytology = the study of cells All animal cells have 3 main parts: Nucleus Cell Membrane Cell membrane is semipermeable Cytoplasm (cytosol): where remaining organelles
1.3 - Cells Chapter 3 - Cells Cells Cytology = the study of cells All animal cells have 3 main parts: Nucleus Cell Membrane Cell membrane is semipermeable Cytoplasm (cytosol): where remaining organelles
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function
 Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Biology Study Guide Answers. Cells/Cell Transport
 Biology Study Guide Answers Cells/Cell Transport 1 1.) All living things are made of cells. 2.) Cells are the most basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3.) Cells come from pre-existing
Biology Study Guide Answers Cells/Cell Transport 1 1.) All living things are made of cells. 2.) Cells are the most basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3.) Cells come from pre-existing
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport
 Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
The Cell. The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes.
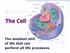 The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
Think About it. Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells. The Discovery of the Cell. The cell theory states: Exploring the Cell 10/10/2016
 Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
A small, membrane-bound compartment capable of performing all the basic functions of life
 AP Biology The Cell The Cell Cell: A small, membrane-bound compartment capable of performing all the basic functions of life Discovery of Cells: - 17 th century - A Dutch clothing dealer named Antonie
AP Biology The Cell The Cell Cell: A small, membrane-bound compartment capable of performing all the basic functions of life Discovery of Cells: - 17 th century - A Dutch clothing dealer named Antonie
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7
 Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY
 Biology 12 Name: Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY Cell parts and Function 1. Identify each part of the cell indicated and give one role for each structure in the secretion and/or synthesis
Biology 12 Name: Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY Cell parts and Function 1. Identify each part of the cell indicated and give one role for each structure in the secretion and/or synthesis
Unit 2 Notes: Cells. What you need to know:
 1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head
 CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Hydrophobic regions of protein Hydrophilic regions of protein
CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Hydrophobic regions of protein Hydrophilic regions of protein
Cell Category? Prokaryote
 CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
The Study of Cells The diversity of the cells of the body The following figure shows the proportion of cell size of the variety of cells in the body
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20
 Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Exam 2 spring 2016 Page 1
 xam 2 spring 2016 Page 1 Name: ate: 1 ll of the following are composed of eukaryotic cells XPT animals plants fungi bacteria 2 The function of the cytoplasm is to keep the cell contents wet provide a medium
xam 2 spring 2016 Page 1 Name: ate: 1 ll of the following are composed of eukaryotic cells XPT animals plants fungi bacteria 2 The function of the cytoplasm is to keep the cell contents wet provide a medium
Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions
 Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 62-107 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 527) 1. 2. 3. 4. 9. What
Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 62-107 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 527) 1. 2. 3. 4. 9. What
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment
 Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Biology Structures in Cells. 1.3 Structures in Cells
 Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems. Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells
 IN: Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells Where are cells on the biological scale? Sub-Atomic Particles Atoms Molecules Macromolecules (proteins, lipids, nucleic
IN: Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells Where are cells on the biological scale? Sub-Atomic Particles Atoms Molecules Macromolecules (proteins, lipids, nucleic
Cells and Homeostasis Vocabulary Key. Unicellular organism: An organism having only one cell but carries out all life functions
 Cells and Homeostasis Vocabulary Key Unicellular organism: An organism having only one cell but carries out all life functions Multicellular: An organism with many cells, each of which is specialized to
Cells and Homeostasis Vocabulary Key Unicellular organism: An organism having only one cell but carries out all life functions Multicellular: An organism with many cells, each of which is specialized to
Cells 2/2/2019. Cell Theory. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. Life on Earth. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. Bacterial Cell. Structure and Function
 Cell Theory Cells Structure and Function All living things are made of cells New cells come from pre-existing cells NO Spontaneous Generation Francesco Redi Italian 17 th century Louis Pasteur French 19
Cell Theory Cells Structure and Function All living things are made of cells New cells come from pre-existing cells NO Spontaneous Generation Francesco Redi Italian 17 th century Louis Pasteur French 19
Chapter 1 Plasma membranes
 1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function The Discovery of the Cell - microscopes invented in 1600 s - Robert Hooke observed cork in 1665 and described them as little boxes he called cells - Hooke did not
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function The Discovery of the Cell - microscopes invented in 1600 s - Robert Hooke observed cork in 1665 and described them as little boxes he called cells - Hooke did not
The Discovery of the Cell
 The Discovery of the Cell 7-1 Life Is Cellular Review the cell in relation to: - Its definition - The origin of life - The characteristics of life - The hierarchy of biological organization - The science
The Discovery of the Cell 7-1 Life Is Cellular Review the cell in relation to: - Its definition - The origin of life - The characteristics of life - The hierarchy of biological organization - The science
Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane. Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5
 Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5 Unit 5: Lecture 1 Topic: The Cell Membrane Covers: Chapter 5, pages 95-96 Chapter 4, pages 73-75 The Cell Membrane The chemistry
Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5 Unit 5: Lecture 1 Topic: The Cell Membrane Covers: Chapter 5, pages 95-96 Chapter 4, pages 73-75 The Cell Membrane The chemistry
Anatomy Chapter 2 - Cells
 Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
1. Structure A is the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Vacuole d. Lysosome
 Figure 1 Use Figure 1 to answer the following questions: 1. Structure A is the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Vacuole d. Lysosome 2. Structure E controls cellular functions. It is the a. Nucleolus b.
Figure 1 Use Figure 1 to answer the following questions: 1. Structure A is the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Vacuole d. Lysosome 2. Structure E controls cellular functions. It is the a. Nucleolus b.
MY BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM WORKBOOK
 NAME PER DATE MY BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM WORKBOOK DIRECTIONS: This study work book is due on the day of your final exam. Start now! After you have completed this study guide, you need to memorize it! 1. Look
NAME PER DATE MY BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM WORKBOOK DIRECTIONS: This study work book is due on the day of your final exam. Start now! After you have completed this study guide, you need to memorize it! 1. Look
Chapter 3 Review Assignment
 Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
History of the Cell. History of the Cell 10/24/2013. Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function. Robert Hooke (1665) Robert Hooke (1665)
 Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
Exam 2 fall 2015 Page 1
 xam 2 fall 2015 Page 1 Name: 1 ll of the following are composed of eukaryotic cells XPT animals plants fungi bacteria 2 The function of the cytoplasm is to keep the cell contents wet provide a medium for
xam 2 fall 2015 Page 1 Name: 1 ll of the following are composed of eukaryotic cells XPT animals plants fungi bacteria 2 The function of the cytoplasm is to keep the cell contents wet provide a medium for
Cell Theory. Passive Transport
 Cell Theory 4 basic concepts of cell theory are: Cells are the units of structure (building blocks) of all animals and plants. Cells are the smallest unit of function in all animals and plants. Cells originate
Cell Theory 4 basic concepts of cell theory are: Cells are the units of structure (building blocks) of all animals and plants. Cells are the smallest unit of function in all animals and plants. Cells originate
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam
 Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
Name Class Date. cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell. MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell theory.
 Section 1: Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell
Section 1: Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell
CELLS CELL THEORY. There are two types of cells: 9/26/2016 CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES. Which is more complicated? REMEMBER YOU ARE EUKARYOTIC!
 CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells
 What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
What did Robert Hooke call the boxes that he observed in cork? Cells Why should I care? So, what is a cell? Smallest functional unit that can support life A bacterium is only one self-sustaining cell You
The Cell and Cellular transport
 Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
Objectives. By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles
 Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle
 What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
(impermeable; freely permeable; selectively permeable)
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
Modern Cell Theory. Plasma Membrane. Generalized Cell Structures. Cellular Form and Function. Three principle parts of a cell
 Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cells & Transport. Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4
 Cells & Transport Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4 Do Now How big is a cell? How many cells are we made of? How many cells is the smallest living organism made of? Objectives Describe how cells were discovered
Cells & Transport Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4 Do Now How big is a cell? How many cells are we made of? How many cells is the smallest living organism made of? Objectives Describe how cells were discovered
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
Unit 2 Cell Structure and Function
 Unit 2 Cell Structure and Function Biology 30 Mr. Oosterom Development of the Cell Theory People have known about the existence of cells for approximately 300 yrs Early microscopes allowed scientists to
Unit 2 Cell Structure and Function Biology 30 Mr. Oosterom Development of the Cell Theory People have known about the existence of cells for approximately 300 yrs Early microscopes allowed scientists to
Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell
 CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
Plant Cells. Chapter 3
 Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell
 Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell Cell basic unit of life o Small o Self-sufficient o Self-replicating Cell Theory organisms are composed of cells and all cells come from the division of other cells Cells
Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell Cell basic unit of life o Small o Self-sufficient o Self-replicating Cell Theory organisms are composed of cells and all cells come from the division of other cells Cells
Cell Structure and Function. The Basic Unit of Life
 Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke The word " cell was first used in late 1665 by Robert Hooke. He looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under
Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke The word " cell was first used in late 1665 by Robert Hooke. He looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under
Biology 120 Mock Midterm Examination Student Learning Services and Bio 120 SSS Peer Mentors
 Name: Tuesday, October 13 th, 2015 Time: 5:30-6:20 (50 mins) Location: HLTH 1150 Biology 120 Mock Midterm Examination Student Learning Services and Bio 120 SSS Peer Mentors Important note: This mock midterm
Name: Tuesday, October 13 th, 2015 Time: 5:30-6:20 (50 mins) Location: HLTH 1150 Biology 120 Mock Midterm Examination Student Learning Services and Bio 120 SSS Peer Mentors Important note: This mock midterm
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the
 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles Use the diagrams to answer the question.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles Use the diagrams to answer the question.
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 3 The Cellular Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Introduce the parts of a cell 2. Discuss the importance
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 3 The Cellular Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Introduce the parts of a cell 2. Discuss the importance
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
Unit 2 Warm Ups. Equilibrium
 Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
8/7/18. UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function. I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory
 8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized
 Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
 CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2010, 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Cells Most basic unit of living system Arise by cell division from existing cell Make up
CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2010, 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Cells Most basic unit of living system Arise by cell division from existing cell Make up
Ch3: Cellular Transport Review KEY
 Ch3: Cellular Transport Review KEY OSMOSIS Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic environments) hypotonic hypertonic isotonic hypertonic means there is a GREATER concentration of
Ch3: Cellular Transport Review KEY OSMOSIS Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic environments) hypotonic hypertonic isotonic hypertonic means there is a GREATER concentration of
COMMON ASSESSMENT
 1. The diagram above is a model of a cellular process called transcription. What class of biological molecules is represented in the diagram? A. Carbohydrates B. Nucleic acids C. Proteins D. Lipids B.9.A.R
1. The diagram above is a model of a cellular process called transcription. What class of biological molecules is represented in the diagram? A. Carbohydrates B. Nucleic acids C. Proteins D. Lipids B.9.A.R
Warm Up (Discussion )
 Unit 3: Cells! Warm Up (Discussion ) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is a cell? Where do we find cells? What are cells made up of? What happens in a cell? How are plant and animal cells different? Cell Theory 1. Cells
Unit 3: Cells! Warm Up (Discussion ) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is a cell? Where do we find cells? What are cells made up of? What happens in a cell? How are plant and animal cells different? Cell Theory 1. Cells
Cytoskeleton. Provide shape and support for the cell. Other functions of the cytoskeleton. Nucleolus. Nucleus
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
The Fundamental Unit of Life. Intext Exercise 1
 Intext Exercise 1 Who discovered cells and how? Cells were discovered in 1665 by an English Botanist, Robert Hooke. He used a primitive microscope to observe cells in a cork slice. Why is the cell called
Intext Exercise 1 Who discovered cells and how? Cells were discovered in 1665 by an English Botanist, Robert Hooke. He used a primitive microscope to observe cells in a cork slice. Why is the cell called
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Cells and Cell Transport
 Cells and Cell Transport Use the list below to answer question 1. Functions of a Cell Structure 1. The functions of which cell structure are described in this list? A. a lysosome B. a mitochondrion C.
Cells and Cell Transport Use the list below to answer question 1. Functions of a Cell Structure 1. The functions of which cell structure are described in this list? A. a lysosome B. a mitochondrion C.
Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per:
 Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per: 1. Put the following in order according to blood flow through the body, starting with the lungs: Lungs, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta,
Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per: 1. Put the following in order according to blood flow through the body, starting with the lungs: Lungs, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta,
