Cellular Injury, Necrosis, Apoptosis
|
|
|
- Eugene McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cellular Injury, Necrosis, Apoptosis
2 Cell injury results when cells are stressed and can no longer adapt Injury may progress through a reversible stage
3 Reversible Cell Injury Reduced oxidative phosphorylation with resultant depletion of energy stores in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) Cellular swelling caused by changes in ion concentrations and water influx
4 Cell Death Necrosis- pathologic Damage to membranes is severe, lysosomal enzymes enter the cytoplasm and digest the cell, and cellular contents leak out Apoptosis- normal and pathologic DNA or proteins are damaged beyond repair, the cell kills itself characterized by nuclear dissolution, fragmentation of the cell without complete loss of membrane integrity Autophagy- normal and pathologic
5 Causes of Cell Injury Oxygen Deprivation Hypoxia is a deficiency of oxygen that can result in a reduction in aerobic oxidative respiration. Extremely important common cause of cell injury/cell death. Causes include reduced blood flow (ischemia), inadequate oxygenation of the blood, decreased blood oxygen-carrying capacity. Physical Agents Mechanical trauma, extremes of temperature (burns and deep cold), sudden changes in atmospheric pressure, radiation, and electric shock. Chemical Agents and Drugs Infectious Agents Immunologic Reactions Genetic Derangements Nutritional Imbalances Protein-calorie and/or vitamin deficiencies. Nutritional excesses (overnutrition)
6 Morphology of Cell Injury
7
8 ble_1_1.gif
9 Normal Kidney h/bioc3800/kidney.jpg l/quizzes/practical/kidney_practical/s20.14.htm
10 Normal kidney tubules Epithelial cells stain evenly pink (eosinophilic) in cytoplasm, with purple, basophilic, nucleic acids confined to the nuclei Apical surfaces are ciliated Interstitia not infiltrated with immune cells nor congested with proteins
11 Swollen kidney tubules Increased eosinophilic staining Decreased basophilic staining (RNA) Plasma membrane rounding, blebbing, loss of cilia, due to loss of connections with cytoskeleton Integrity of tubules degrading, but basement membranes intact Nuclei largely intact, slightly narrowed, pyknotic
12 How much can a cell swell? Boudreault F, Grygorczyk R J Physiol 2004;561: by The Physiological Society
13 Reversible damage cellular swelling Cellular swelling (synonyms: hydropic change, vacuolar degeneration, cellular edema) is an acute reversible change resulting as a response to nonlethal injuries. It is an intracytoplasmic accumulation of water due to incapacity of the cells to maintain the ionic and fluid homeostasis. It is easy to be observed in parenchymal organs : liver (hepatitis, hypoxia), kidney (shock), myocardium (hypoxia, phosphate intoxication). It may be local or diffuse, affecting the whole organ.
14 Reversible damage fatty change Intracellular accumulations of a variety of materials can occur in response to cellular injury. Here is fatty metamorphosis (fatty change) of the liver in which deranged lipoprotein transport from injury (most often alcoholism) leads to accumulation of lipid in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes.
15 Necrotic kidney tubules Cellular fragmentation Loss and fading of nuclei--karyolysis Burst membranes Loss of tissue architecture
16 Necrosis The morphologic appearance of necrosis is the result of denaturation of intracellular proteins and enzymatic digestion. Necrotic cells are unable to maintain membrane integrity and their contents often leak out, a process that may elicit inflammation in the surrounding tissue. The enzymes that digest the necrotic cell are derived from the lysosomes of the dying cells themselves and from the lysosomes of leukocytes that are called in as part of the inflammatory reaction. Digestion of cellular contents and the host response may take hours to develop. The earliest histologic evidence of necrosis may not become apparent until 4 to 12 hours.
17
18
19 Necrosis- cytoplasm Increased eosinophilia in hematoxylin and eosin (H & E) stains, attributable in part to the loss of cytoplasmic RNA (which binds the blue dye, hematoxylin) and in part to denatured cytoplasmic proteins (which bind the red dye, eosin). When enzymes have digested the cytoplasmic organelles, the cytoplasm becomes vacuolated and appears moth-eaten. Dead cells may be replaced by large, whorled phospholipid masses called myelin figures that are derived from damaged cell membranes. These phospholipid precipitates are then either phagocytosed by other cells or further degraded into fatty acids; calcification of such fatty acid residues results in the generation of calcium soaps. Thus, the dead cells may ultimately become calcified.
20 Nuclear changes Necrosis- nucleus Pyknosis, characterized by nuclear shrinkage and increased basophilia. Karyorrhexis, the pyknotic nucleus undergoes fragmentation. With the passage of time (a day or two), the nucleus in the necrotic cell totally disappears. Karyolysis, the basophilia of the chromatin fades which appears to reflect loss of DNA because of enzymatic degradation by due to endonucleases. 4/vet%20pathology/CASES/CELLINJURY2/karyorrhexd iag%20copy.jpg
21 Patterns of Tissue Necrosis When large numbers of cells die the tissue or organ is said to be necrotic Necrosis of tissues has several morphologically distinct patterns, which are important to recognize because they may provide clues about the underlying cause. The terms that describe these patterns are somewhat outmoded, they are used often and their implications are understood by pathologists and clinicians.
22 Types of Tissue necrosis Coagulative Liquefactive Gangrenous Caseous Fat Fibrinoid
23 Coagulative Necrosis Architecture of dead tissues is preserved for a span of at least some days. Tissues exhibit a firm texture Injury denatures proteins and enzymes blocking proteolysis of the dead cells; Eosinophilic, anucleate cells may persist for days or weeks. Ultimately the necrotic cells are removed by phagocytosis of the cellular debris by infiltrating leukocytes.
24 Coagulative necrosis kidney infarction This is the typical pattern with ischemia and infarction (loss of blood supply and resultant tissue anoxia). Here, there is a wedgeshaped pale area of coagulative necrosis (infarction) in the renal cortex of the kidney. Microscopically, the renal cortex has undergone anoxic injury at the left so that the cells appear pale and ghost-like. There is a hemorrhagic zone in the middle where the cells are dying or have not quite died, and then normal renal parenchyma at the far right.
25
26 Coagulative necrosis myocardial infarction Here is myocardium in which the cells are dying as a result of ischemic injury from coronary artery occlusion. This is early in the process of necrosis. The nuclei of the myocardial fibers are being lost. The cytoplasm is losing its structure, because no well-defined cross-striations are seen. 1.preview.jpg ML/CINJ013.html
27 Liquefactive Necrosis Digestion of the dead Transformation of the tissue into a liquid viscous mass. The necrotic material is frequently creamy yellow because of the presence of dead leukocytes and is called pus. osis_lung_7.jpg
28 Gangrenous Necrosis Not a specific pattern. Term is commonly used in clinical practice. Sepsis induced DIC has led to extensive arterial thrombosis, resulting in profound tissue death. Usually applied to a limb, generally the lower leg, that has lost its blood supply and has undergone, typically, coagulative necrosis WebPath/CINJHTML/CINJ051.htm
29 Caseous Necrosis Caseous (cheeselike) is derived from the friable white appearance of the area of necrosis Necrotic area appears as a collection of fragmented or lysed cells and amorphous granular debris enclosed within a distinctive inflammatory border; this appearance is characteristic of a focus of inflammation known as a granuloma. d.nus.edu.sg/ path/images/t b-myco.jpg estead.com/files/gran uloma_apoptotic2.jpg
30 Fat Necrosis Not a specific pattern Focal areas of fat destruction, typically resulting from release of activated pancreatic lipases into the substance of the pancreas and the peritoneal cavity. Lipases split the triglyceride esters contained within fat cells. Free fatty acids can combine with calcium to produce grossly visible chalky-white areas (fat saponification).
31 Fibrinoid Necrosis Usually seen in immune reactions involving blood vessels. Deposits of immune complexes, together with fibrin that has leaked out of vessels. Bright pink and amorphous appearance in H&E stains, called fibrinoid (fibrin-like) by pathologists.
32 Mechanisms leading to necrotic cells
33 S gr2.jpg
34 Calcium Flux Intracellular, cytosolic [Ca++] as many as 4 orders of magnitude lower than extracellular or organellar (ER, SR, Mt) Mitochondrial damage and ER swelling releases Ca++ to cytosol Hydrolytic enzymes activated Apoptosis may be activated Necrosis occurs
35
36 ROS and free radicals Hydroxyl radicals and hydrogen may be split from water by ionizing radiation Superoxide radicals, hydrogen peroxide, lipid peroxides normally present in small amounts Neutralized by catalase or glutathione peroxidase ROS created and released by neutrophils in response to microbial infection Toxic chemicals natively, or after activation by P450 redox in liver or kidney, may result in free radicals ROS initiate chain reaction of lipid peroxidation in membranes
37 Inflammation Radiation Chemicals Reperfusion Injury
38
39 Loss of ER Homeostasis
40
41
42 Apoptosis Programmed cell death Especially during fetal development In response to hormonal cycles (e.g. endometrium) Normal turnover in proliferating tissues (e.g. intestinal epithelium) Cells shrink, not swell Nuclei condense and DNA fragments Cells fragment into membrane-bound bits Bits are phagocytosed by macrophages
43
44 Apoptotic fetal thymus In this fetal thymus there is involution of thymic lymphocytes by the mechanism of apoptosis. In this case, it is an orderly process and part of normal immune system maturation. Individual cells fragment and are consumed by phagocytes to give the appearance of clear spaces filled with cellular debris. Apoptosis is controlled by many mechanisms. Genes such as BCL-2 are turned off and Bax genes turned on. Intracellular proteolytic enzymes called caspases produce much cellular breakdown.
45
46
47 Getting TRAIL back on track for cancer therapy Article Literature Review (PDF Available) in Cell Death and Differentiation 21(9) June 2014 with 301 ReadsDOI: /cdd Source: PubMed
48
49
50 Neuronal caspase-3 signaling: not only cell death M D'Amelio, V Cavallucci & F Cecconi Cell Death and Differentiation 17, (2010) doi: /cdd Download Citation
Cellular responses to stress
 Cellular responses to stress (Adaptations, injury and death) (2 of 5) Most injurious stimuli are grouped into: Oxygen deprivation Chemical agents Infectious agents Immunologic reactions Genetic factors
Cellular responses to stress (Adaptations, injury and death) (2 of 5) Most injurious stimuli are grouped into: Oxygen deprivation Chemical agents Infectious agents Immunologic reactions Genetic factors
PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Heyam Awad
 number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
Mechanisms of Cell Injury
 Causes of Cell Injury 1- oxygen deprivation (anoxia) 2- physical agents 3- chemical agents 4- infections agents 5- immunologic reactions 6- genetic defects 7- nutritional imbalances Mechanisms of Cell
Causes of Cell Injury 1- oxygen deprivation (anoxia) 2- physical agents 3- chemical agents 4- infections agents 5- immunologic reactions 6- genetic defects 7- nutritional imbalances Mechanisms of Cell
Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one
 Necrosis Necrosis Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one or more, small, clearly defined areas of necrosis. Diffuse necrosis- term used
Necrosis Necrosis Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one or more, small, clearly defined areas of necrosis. Diffuse necrosis- term used
Lecture-2 / Dr Hussain Abady Aljebori Over view of cell injury and cell death; Cell injury results when: a. cells are stressed so severely that they
 Lecture-2 / Dr Hussain Abady Aljebori Over view of cell injury and cell death; Cell injury results when: a. cells are stressed so severely that they are no longer able to adapt or b. when cells are exposed
Lecture-2 / Dr Hussain Abady Aljebori Over view of cell injury and cell death; Cell injury results when: a. cells are stressed so severely that they are no longer able to adapt or b. when cells are exposed
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations
 Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
INTRODUCTION TO HEALTH AND DISEASE BLOCK
 MBBS 1 st Yr. Lecture Dr. Annie Cheung September 25, 2002, 8:30AM 9:30 AM LT1, G/F, Academic and Administration Block Faculty of Medicine Building INTRODUCTION TO HEALTH AND DISEASE BLOCK CELL INJURY AND
MBBS 1 st Yr. Lecture Dr. Annie Cheung September 25, 2002, 8:30AM 9:30 AM LT1, G/F, Academic and Administration Block Faculty of Medicine Building INTRODUCTION TO HEALTH AND DISEASE BLOCK CELL INJURY AND
The basis of Disease
 General Curriculum The basis of Disease ZHOU REN 周韧 Prof., M.D., Ph.D. Institute of Pathology & Forensic Medicine Department of Pathology & Patho-physiology Zhenjiang University Judicial Evidence & Evaluation
General Curriculum The basis of Disease ZHOU REN 周韧 Prof., M.D., Ph.D. Institute of Pathology & Forensic Medicine Department of Pathology & Patho-physiology Zhenjiang University Judicial Evidence & Evaluation
Cellular response to stress
 Cellular pathology - cell injury, death and adaptations Pathology Göran Andersson Cellular response to stress Cells differ in their capacity to tolerate changes in their microenvironment Acute, severe
Cellular pathology - cell injury, death and adaptations Pathology Göran Andersson Cellular response to stress Cells differ in their capacity to tolerate changes in their microenvironment Acute, severe
Cell Adaptation, Cell Injury and Cell Death
 Cell Adaptation, Cell Injury and Cell Death Pathology:- is the study of structural and functional abnormalities that are expressed as diseases of organs and systems. Modern pathology, proposed that injury
Cell Adaptation, Cell Injury and Cell Death Pathology:- is the study of structural and functional abnormalities that are expressed as diseases of organs and systems. Modern pathology, proposed that injury
Quiz 1 Review. More Cowbell
 Quiz 1 Review More Cowbell Quiz 1 review Inflamma7on Repair Cell Injury and Adapta7on Quiz 1 review Inflamma7on Injury Acute inflammation Chronic inflammation Abscess Resolution Repair Time course Inflammation
Quiz 1 Review More Cowbell Quiz 1 review Inflamma7on Repair Cell Injury and Adapta7on Quiz 1 review Inflamma7on Injury Acute inflammation Chronic inflammation Abscess Resolution Repair Time course Inflammation
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis. Dr H Awad 2017/18
 Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
SECTION 2 CELL INJURY
 Adapted myocyte Normal myocyte Reversibly-injured myocyte SECTION 2 CELL INJURY Cell death 5/4/2014 1 5/4/2014 2 Reversible Degeneration Irreversible Cellular Swelling Fatty Change Hyaline Change Amyloid
Adapted myocyte Normal myocyte Reversibly-injured myocyte SECTION 2 CELL INJURY Cell death 5/4/2014 1 5/4/2014 2 Reversible Degeneration Irreversible Cellular Swelling Fatty Change Hyaline Change Amyloid
APOPTOSIS, NECROSIS AND CANCER. Dr. S. P. Pattanayak
 APOPTOSIS, NECROSIS AND CANCER Dr. S. P. Pattanayak LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Know the importance of cell death. Define various modes of cell death. Identify
APOPTOSIS, NECROSIS AND CANCER Dr. S. P. Pattanayak LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Know the importance of cell death. Define various modes of cell death. Identify
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury.
 Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
Chapter 1 CELL INJURY CELL DEATH CELL ADAPTATIONS. M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University.
 Chapter 1 CELL INJURY CELL DEATH CELL ADAPTATIONS M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. CONCEPTS IN CELL INJURY The clinical signs and symptoms are several
Chapter 1 CELL INJURY CELL DEATH CELL ADAPTATIONS M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. CONCEPTS IN CELL INJURY The clinical signs and symptoms are several
Types of insult - hypoxia
 Introduction This presentation will be a guide to cell injury and cell death outline causes and pathogenesis of cell injury/death describe the morphological changes of cell injury/death Describe the process
Introduction This presentation will be a guide to cell injury and cell death outline causes and pathogenesis of cell injury/death describe the morphological changes of cell injury/death Describe the process
Cellular Injury. Intracellular degeneration. By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall /20/2018 1
 Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
Cell injury, adaptation and death. Unite one Second Lab.
 Cell injury, adaptation and death Unite one Second Lab. The two lung abscesses seen here are examples of liquefactive necrosis in which there is a liquid center in an area of tissue injury. One abscess
Cell injury, adaptation and death Unite one Second Lab. The two lung abscesses seen here are examples of liquefactive necrosis in which there is a liquid center in an area of tissue injury. One abscess
shehab Moh Tarek ... ManarHajeer
 3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
[General Pathology] Introduction to Pathology
![[General Pathology] Introduction to Pathology [General Pathology] Introduction to Pathology](/thumbs/73/69585662.jpg) Introduction to Pathology Pathology: Literally translated, pathology is the study (logos) of disease (pathos, suffering). It involves the investigation of the causes of disease and the associated changes
Introduction to Pathology Pathology: Literally translated, pathology is the study (logos) of disease (pathos, suffering). It involves the investigation of the causes of disease and the associated changes
NECROSIS, GANGRENE. I. practical training 2 rd year Dentistry
 NECROSIS, GANGRENE. I. practical training 2 rd year Dentistry Signs of death Cardiac arrest (no pulse) Pallor mortis, paleness which happens in the 15 120 minutes after death Livor mortis, a settling of
NECROSIS, GANGRENE. I. practical training 2 rd year Dentistry Signs of death Cardiac arrest (no pulse) Pallor mortis, paleness which happens in the 15 120 minutes after death Livor mortis, a settling of
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY
 Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH
 CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH INTRODUCTION Cell Injury is a result of the sequence of events that occur if the limits of the adaptive capability of cells are exceeded or there is no adaptive response is possible,
CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH INTRODUCTION Cell Injury is a result of the sequence of events that occur if the limits of the adaptive capability of cells are exceeded or there is no adaptive response is possible,
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
Coagulative Necrosis of Myocardium. Dr Rodney Itaki Division of Pathology
 Coagulative Necrosis of Myocardium Dr Rodney Itaki Division of Pathology Coagulative Necrosis Gross pathology: 3 day old infarct: Yellow necrosis surrounded by hyperemic borders. Arrow points to a transmural
Coagulative Necrosis of Myocardium Dr Rodney Itaki Division of Pathology Coagulative Necrosis Gross pathology: 3 day old infarct: Yellow necrosis surrounded by hyperemic borders. Arrow points to a transmural
CELL INJURY. Severity of Cell Injury
 GENERAL PATHOLOGY LECTURE - 3 DR. M. TARIQ JAVED Professor Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. 9/11/2009 1 CELL INJURY No adaptive response
GENERAL PATHOLOGY LECTURE - 3 DR. M. TARIQ JAVED Professor Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. 9/11/2009 1 CELL INJURY No adaptive response
Avian Pathology. Bacterial diseases: histo slides. ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN
 Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Cellular Pathology (VPM 152) Lecture 4 (Web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology (VPM 152) Lecture 4 (Web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 IRREVERSIBLE CELL INJURY 1) Necrosis describes the range of morphologic changes that follow cell death in living tissue the morphologic
Cellular Pathology (VPM 152) Lecture 4 (Web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 IRREVERSIBLE CELL INJURY 1) Necrosis describes the range of morphologic changes that follow cell death in living tissue the morphologic
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis
 Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Cellular Injury and Adaptation
 General pathology Introduction to pathology Literal translation of the word pathology is the study (logos) of suffering (Pathos). It is a discipline that bridges clinical practice and basic sciences. Pathology
General pathology Introduction to pathology Literal translation of the word pathology is the study (logos) of suffering (Pathos). It is a discipline that bridges clinical practice and basic sciences. Pathology
Hashem Al-Dujaily. Tamer Barakat. Manar Hajeer
 1 Hashem Al-Dujaily Tamer Barakat... Manar Hajeer Introduction Pathology comes from Patho: disease/suffering and Logy: study. Therefore, Pathology is the study of disease. Pathology is the bridge between
1 Hashem Al-Dujaily Tamer Barakat... Manar Hajeer Introduction Pathology comes from Patho: disease/suffering and Logy: study. Therefore, Pathology is the study of disease. Pathology is the bridge between
Consultant Medical Laboratory Scientist Assistant Professor of Histopathology & Cytopathology
 بسم اهلل الرحمن الرحيم By: PhD (Histopathology & Cytopathology), M.BA (Total Quality Management) Consultant Medical Laboratory Scientist Assistant Professor of Histopathology & Cytopathology Introduction
بسم اهلل الرحمن الرحيم By: PhD (Histopathology & Cytopathology), M.BA (Total Quality Management) Consultant Medical Laboratory Scientist Assistant Professor of Histopathology & Cytopathology Introduction
Disturbances of Circulation. Histopathology Lab #2 (Web)
 Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
Mechanisms of disease
 PP Mechanisms of disease Stress and disease Homeostasis - Responsible for maintaining a constant, safe internal environment - Controlled by feedback loops o Negative feedback loop: temperature, blood glucose
PP Mechanisms of disease Stress and disease Homeostasis - Responsible for maintaining a constant, safe internal environment - Controlled by feedback loops o Negative feedback loop: temperature, blood glucose
Extracellular degeneration
 Extracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1/17/2017 1 Extracellular Degenerations I / Hyaline Degeneration (Hyalinization): The ward hyaline is derived from the Latin
Extracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1/17/2017 1 Extracellular Degenerations I / Hyaline Degeneration (Hyalinization): The ward hyaline is derived from the Latin
Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury. VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016
 Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016 Gross Specimens The following slides consist of images from the specimens presented
Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016 Gross Specimens The following slides consist of images from the specimens presented
DEGENERATION NECROSIS AND INFILTRATION
 DEGENERATION NECROSIS AND INFILTRATION Cellular Degenerations and Infiltrations 1. Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration occur when the regulatory mechanisms
DEGENERATION NECROSIS AND INFILTRATION Cellular Degenerations and Infiltrations 1. Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration occur when the regulatory mechanisms
Functions of Blood. Transport. Transport. Defense. Regulation. Unit 6 Cardiovascular System: Blood
 Unit 6 Cardiovascular System: Blood Functions of Blood With each beat of the heart, approximately 75 ml of blood is pumped On average, the heart beats 70 times per minute Every minute, the heart pumps
Unit 6 Cardiovascular System: Blood Functions of Blood With each beat of the heart, approximately 75 ml of blood is pumped On average, the heart beats 70 times per minute Every minute, the heart pumps
Cell Physiology
 Cell Physiology 21-10-2018 1 The two major parts of a typical cell are the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane, and the cytoplasm is separated from
Cell Physiology 21-10-2018 1 The two major parts of a typical cell are the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane, and the cytoplasm is separated from
lysosomes Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types:
 lysosomes Digests Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types: Proteins Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Lipids Single membrane bound vesicle, contains up to 50 digestive
lysosomes Digests Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types: Proteins Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Lipids Single membrane bound vesicle, contains up to 50 digestive
Pathology MCQs. lipid. protein. glycogen. lipofuscin. water. Karyolysis. Cellular swelling. Involvement of a large number of cells
 Pathology MCQs 1. In hypoxic cell injury, cell swelling occurs because of increased intracellular: lipid protein glycogen lipofuscin water 2. Which of the following is a feature of apoptosis? Karyolysis
Pathology MCQs 1. In hypoxic cell injury, cell swelling occurs because of increased intracellular: lipid protein glycogen lipofuscin water 2. Which of the following is a feature of apoptosis? Karyolysis
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi
 number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
I. ADAPTATION TO ENVIRONMENTAL STRESS. A. Hypertrophy:
 د.جواهر محي الدين Lec:2&3 Cellular Reaction to Injury I. ADAPTATION TO ENVIRONMENTAL STRESS II. HYPOXIC CELL INJURY III. FREE RADICAL INJURY IV. CHEMICAL CELL INJURY V. NECROSIS VI. APOPTOSIS VII. REVERSIBLE
د.جواهر محي الدين Lec:2&3 Cellular Reaction to Injury I. ADAPTATION TO ENVIRONMENTAL STRESS II. HYPOXIC CELL INJURY III. FREE RADICAL INJURY IV. CHEMICAL CELL INJURY V. NECROSIS VI. APOPTOSIS VII. REVERSIBLE
The basis of Disease
 General Curriculum The basis of Disease ZHOU REN 周韧 Prof., M.D., Ph.D. Institute of Pathology & Forensic Medicine Department of Pathology & Patho-physiology Zhenjiang University Judicial Evidence & Evaluation
General Curriculum The basis of Disease ZHOU REN 周韧 Prof., M.D., Ph.D. Institute of Pathology & Forensic Medicine Department of Pathology & Patho-physiology Zhenjiang University Judicial Evidence & Evaluation
Histopathology: healing
 Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Blood: Functions. Liquid connective tissue 3 general functions 1. Transportation. 2. Regulation. 3. Protection
 Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.
 المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
A Tour of the Cell. reference: Chapter 6. Reference: Chapter 2
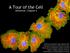 A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
ECVP/ESVP Summer School in Veterinary Pathology Summer School 2015 Histology Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney.
 Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport
 Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
Blood & Blood Formation
 Module IB Blood & Blood Formation Histology and Embryology Martin Špaček, MD (m.spacek@centrum.cz) http://www.lf3.cuni.cz/histologie Approximately 7% of a person's weight is blood (about 5 L) Blood consists
Module IB Blood & Blood Formation Histology and Embryology Martin Špaček, MD (m.spacek@centrum.cz) http://www.lf3.cuni.cz/histologie Approximately 7% of a person's weight is blood (about 5 L) Blood consists
Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity
 Part 1 Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity Bacteria Most common pathogens Anthrax Cholera Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria Bacterial diseases Tuberculosis Cholera Bubonic Plague Tetanus Effects
Part 1 Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity Bacteria Most common pathogens Anthrax Cholera Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria Bacterial diseases Tuberculosis Cholera Bubonic Plague Tetanus Effects
Stages in the cellular response to stress & injurious stimuli
 Blok BBS 2 Departemen Patologi Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera Utara Medan -2011 Stages in the cellular response to stress & injurious stimuli 3/28/2011 2 1 Table 1-1.Cellular Responses
Blok BBS 2 Departemen Patologi Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera Utara Medan -2011 Stages in the cellular response to stress & injurious stimuli 3/28/2011 2 1 Table 1-1.Cellular Responses
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Liver: Hepatitis, necrotizing, multifocal to coalescing, severe, with numerous trichomonads. (3 pt)
 Case 1. Tissue from a pelican. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Liver: Approximately 80% (1 pt) of the liver is replaced by multifocal to coalescing areas of coagulative and lytic necrosis. Centrally, within these
Case 1. Tissue from a pelican. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Liver: Approximately 80% (1 pt) of the liver is replaced by multifocal to coalescing areas of coagulative and lytic necrosis. Centrally, within these
ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
Immunity Learning objectives Explain what triggers an immune response and where in the body the immune response occurs. Understand how the immune system handles exogenous and endogenous antigen differently.
CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION TO PATHOLOGY
 Dr. Nabeel Abdulwadood Rasheed 1 CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION TO PATHOLOGY The literal translation of the word pathology is the study (logos) of suffering (pathos). It is a discipline that bridges clinical
Dr. Nabeel Abdulwadood Rasheed 1 CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION TO PATHOLOGY The literal translation of the word pathology is the study (logos) of suffering (pathos). It is a discipline that bridges clinical
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cells and Tissues. Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues
 2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
34 Apoptosis Programmed cell death is vital to the health and development of multicellular organisms.
 Principles of Biology contents 34 Apoptosis Programmed cell death is vital to the health and development of multicellular organisms. Apoptosis is the reason we have separate fingers and toes. During embryonic
Principles of Biology contents 34 Apoptosis Programmed cell death is vital to the health and development of multicellular organisms. Apoptosis is the reason we have separate fingers and toes. During embryonic
INFLAMMATION. 5. Which are the main phases of inflammation in their "sequence": 1. Initiation, promotion, progression.
 INFLAMMATION 1. What is inflammation: 1. Selective anti-infective pathological reaction. 2. Pathological process, typical for vascularized tissues. 3. Self-sustained pathological condition. 4. Disease
INFLAMMATION 1. What is inflammation: 1. Selective anti-infective pathological reaction. 2. Pathological process, typical for vascularized tissues. 3. Self-sustained pathological condition. 4. Disease
I. Concepts: Fill in the following sections with information from the text and lecture.
 Name: Period: 10 Blood Study Guide I. Concepts: Fill in the following sections with information from the text and lecture. 1. Composition and Function of Blood: 2. Hematopoiesis: 1 Miss School, Miss Out
Name: Period: 10 Blood Study Guide I. Concepts: Fill in the following sections with information from the text and lecture. 1. Composition and Function of Blood: 2. Hematopoiesis: 1 Miss School, Miss Out
2 nd Practice. Cell injury, adaptation, storage disorders. Semmelweis University 2nd Department of Pathology
 2 nd Practice Cell injury, adaptation, storage disorders Semmelweis University 2nd Department of Pathology Cell and tissue injury Cellular response to injury depends on the type, the duration and the severity
2 nd Practice Cell injury, adaptation, storage disorders Semmelweis University 2nd Department of Pathology Cell and tissue injury Cellular response to injury depends on the type, the duration and the severity
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5
 AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
Cells. Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function. Cells. Plasma Membrane
 Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function Cells Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of life The cells of all living things exhibit the seven characteristics of life All living things are made of cells Cells
Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function Cells Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of life The cells of all living things exhibit the seven characteristics of life All living things are made of cells Cells
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structure & Function of Cells
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell. reference: Chapter 6. Reference: Chapter 2
 A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
A Tour of the Cell reference: Chapter 6 Reference: Chapter 2 Monkey Fibroblast Cells stained with fluorescent dyes to show the nucleus (blue) and cytoskeleton (yellow and red fibers), image courtesy of
PLATES 24 TO 26. (Received for publication, December 4, 1935)
 Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
HEMOTOLOGY. B. Helps stabilize body temperature -heats up and cools down slowly which moderates body temp
 I. Body H 2 O = HEMOTOLOGY A. Variable quantities 1. sweating and urination ( ) decreases H 2 O 2. drinking H 2 O increases B. Water is found in two compartments 1. contains 2/3 of all water in your body
I. Body H 2 O = HEMOTOLOGY A. Variable quantities 1. sweating and urination ( ) decreases H 2 O 2. drinking H 2 O increases B. Water is found in two compartments 1. contains 2/3 of all water in your body
Pathophysiology and treatment of focal cerebral ischemia
 J Neurosurg 77: 169-184, 1992 Review Article Pathophysiology and treatment of focal cerebral ischemia Part I: Pathophysiology Bo K. SIESJO, M.D. Laborutory for Experimental Bruin Reseurch, Experrmc~ntul
J Neurosurg 77: 169-184, 1992 Review Article Pathophysiology and treatment of focal cerebral ischemia Part I: Pathophysiology Bo K. SIESJO, M.D. Laborutory for Experimental Bruin Reseurch, Experrmc~ntul
HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION
 HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION Learning Objectives Define congestion and hyperemia Differentiate between the two with regard to: Mechanisms / underlying causes Appearance (gross and histologic) Effects Differentiate
HYPEREMIA AND CONGESTION Learning Objectives Define congestion and hyperemia Differentiate between the two with regard to: Mechanisms / underlying causes Appearance (gross and histologic) Effects Differentiate
BIOSC 041. v Today s lecture. v Today s lab. v Note- Monday is a holiday good time to do some reading!
 BIOSC 041 v Today s lecture Review questions Chapter 6, Cells More review questions v Today s lab Quick review of lab safety The Scientific Method start thinking about which environments you might want
BIOSC 041 v Today s lecture Review questions Chapter 6, Cells More review questions v Today s lab Quick review of lab safety The Scientific Method start thinking about which environments you might want
Modern Cell Theory. Plasma Membrane. Generalized Cell Structures. Cellular Form and Function. Three principle parts of a cell
 Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system. Answer Sheet
 Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
CH 11 Blood OUTLINE: Functions of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Cell Disorders Blood Types Blood Clotting Functions of Blood Transportation
 1 CH 11 Blood OUTLINE: Functions of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Cell Disorders Blood Types Functions of Blood Transportation Protection Regulation ph Temperature Composition of Blood Plasma: liquid
1 CH 11 Blood OUTLINE: Functions of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Cell Disorders Blood Types Functions of Blood Transportation Protection Regulation ph Temperature Composition of Blood Plasma: liquid
Basophilic. Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue
 Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Unit Seven Blood and Immunity
 Unit Seven Blood and Immunity I. Introduction A. Definition Blood is a sticky fluid that is heavier and thicker than water. Blood is a type of, whose cells and suspended in a liquid intercellular material.
Unit Seven Blood and Immunity I. Introduction A. Definition Blood is a sticky fluid that is heavier and thicker than water. Blood is a type of, whose cells and suspended in a liquid intercellular material.
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Overview. Chapter 3: Cells and Their Functions. The Cell. Key Terms. Microscopes. Microscopes. Cytology The study of cells
 Overview Chapter 3: Cells and Their Functions Key Terms The Cell active transport filtration mitochondria cancer gene mitosis carcinogen hemolysis mutation chromosome hypertonic nucleus cytology hypotonic
Overview Chapter 3: Cells and Their Functions Key Terms The Cell active transport filtration mitochondria cancer gene mitosis carcinogen hemolysis mutation chromosome hypertonic nucleus cytology hypotonic
CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES By: Shifaa AlQa qa Cerebrovascular diseases Brain disorders caused by pathologic processes involving blood vessels 3 pathogenic mechanisms (1) thrombotic occlusion, (2) embolic
CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES By: Shifaa AlQa qa Cerebrovascular diseases Brain disorders caused by pathologic processes involving blood vessels 3 pathogenic mechanisms (1) thrombotic occlusion, (2) embolic
CELL INJURY, DEATH, AND ADAPTATION
 CELL INJURY, DEATH, AND ADAPTATION Definitons Pathology is a dicipline bridging clinical practice and basic sience To render diagnosis and guide therapy - Identity changes in gross - Morphology ( microscopy
CELL INJURY, DEATH, AND ADAPTATION Definitons Pathology is a dicipline bridging clinical practice and basic sience To render diagnosis and guide therapy - Identity changes in gross - Morphology ( microscopy
Cells & Cell Transport. Cells
 Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
Cell Quality Control. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
Pathophysiology lab 2. Cellular injury and adaptation
 Pathophysiology lab 2 Cellular injury and adaptation Adaptation Cellular changes that aim to preserve cell viability and prevent cell injury. The adaptive responses include: 1. Atrophy 2. Hypertrophy 3.
Pathophysiology lab 2 Cellular injury and adaptation Adaptation Cellular changes that aim to preserve cell viability and prevent cell injury. The adaptive responses include: 1. Atrophy 2. Hypertrophy 3.
Pigments and accumulations
 Pigments and accumulations Intracellular Accumulations Normal cellular constituent vs. abnormal substance Transient vs. permanent Harmless vs. toxic Cytoplasm vs. nucleus Cell produced vs. produced other
Pigments and accumulations Intracellular Accumulations Normal cellular constituent vs. abnormal substance Transient vs. permanent Harmless vs. toxic Cytoplasm vs. nucleus Cell produced vs. produced other
POST-INJURY INTERVALS 1
 POST-INJURY INTERVALS 1 Introduction 1 Contusion dating 2 Skin 2 Brain 5 Hypoxic/ischemic injury and increased intracranial pressure 18 Brain incidentals (non-injurious) 21 Sexual violence 27 INTRODUCTION
POST-INJURY INTERVALS 1 Introduction 1 Contusion dating 2 Skin 2 Brain 5 Hypoxic/ischemic injury and increased intracranial pressure 18 Brain incidentals (non-injurious) 21 Sexual violence 27 INTRODUCTION
