Cellular Pathology (VPM 152) Lecture 4 (Web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
|
|
|
- Beverly Lloyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Cellular Pathology (VPM 152) Lecture 4 (Web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
3 IRREVERSIBLE CELL INJURY 1) Necrosis describes the range of morphologic changes that follow cell death in living tissue the morphologic appearance is due to 2 concurrent processes: denaturation of proteins (nonproteolytic alteration 2 o or 3 o structure) Raw egg white (albumin protein) is a transparent / clear viscous liquid Adding heat, acid or alkali will denature (misfold) the proteins which results in a change of the color to white / opaque & the texture becomes solid enzymatic digestion autolysis* (self digestion) = endogenous enzymes derived from the lysosomes of the dead cells themselves heterolysis = lysosomes of immigrant leukocytes *autolysis also used for changes that occur in all cells after death, ie postmortem autolysis
4 1) Necrosis distinctive morphologic patterns depending on whether enzyme catabolism or protein denaturation predominates morphologic patterns of necrosis include: Coagulation Necrosis Liquefactive Necrosis Caseous Necrosis *Gangrenous Necrosis *Fat Necrosis
5 a) Coagulation Necrosis most common manifestation of cell death characteristic of hypoxic / ischemic death of cells in all tissues (except brain) on LM, basic outline of the coagulated cell persists at least a few days (protein denaturation predominates over enzymatic digestion) necrotic cells eventually removed by leukocyte proteolysis & phagocytosis
6 a) Coagulation Necrosis Gross Appearance architecture resembles normal tissue, but color and texture are different lighter in color- denatured cytoplasmic proteins and decreased blood flow usually firm necrotic tissue may be swollen or shrunken may see a local vascular / inflammatory reaction to necrotic tissue
7 Figure 01-18A (McGavin & Zachary). Coagulation necrosis, infarcts, kidney, cow. A, Note the pale regions of acute coagulation necrosis surrounded by a red rim of active hyperemia and inflammation (far left). Bovine, kidney, renal infarct, cut surface. Note pyramidal (wedge) shaped area of necrosis with hyperemic border.
8 Bovine, fetus, liver, multifocal hepatic necrosis. Bovine herpesvirus 1 (BoHV-1) causes IBR (infectious bovine rhinotracheitis) in adult cattle and can also cause abortion when a pregnant cow is infected. Often see multifocal hepatic necrosis (necrotizing hepatitis) in the fetus.
9 Bovine, liver: Multifocal hepatic necrosis (coagulative) due to infection with the bacterium Fusobacterium necrophorum. The majority of bacterial infections cause liquefactive necrosis due to the marked infiltration of neutrophils with associated heterolysis; however in this particular bacterial infection there are toxins which result in coagulative necrosis (at least initially).
10 Bovine, heart, myocardial necrosis (coagulative); note irregular area of pallor within myocardium.
11 a) Coagulation Necrosis Microscopic Appearance original cell shape & tissue architecture is preserved (ie eosinophilic "shadow ) cytoplasm: nucleus: increased eosinophilia (H&E stain) usually hyalinized (homogeneous / glassy) may be mineralized karyolysis pyknosis karyorrhexis
12 Figure 01-17B (McGavin & Zachary). Pyknosis and karyolysis, renal cortex, chloroform toxicosis, mouse. Some epithelial cells exhibit hydropic degeneration, whereas others are necrotic. Some necrotic cells exhibit pyknosis (arrow), whereas others have lost the nucleus or have a very pale nucleus, ie karyolysis (arrowheads)
13 Figure 01-17C (McGavin & Zachary) Karyorrhexis, lymphocytes, spleen, dog. Spleen of a dog with parvovirus infection. Lymphocyte nuclei have fragmented because of the infection (arrow). H&E stain.
14 White muscle disease, skeletal muscle, calf. Note coagulation necrosis of myofibers characterized by fragmentation and hyalinization; also note extensive mineralization (blue-purple staining)
15 Ultrastructural Appearance of Irreversible Injury Path Basis of Vet Disease, 8 th ed
16 Irreversible ischemic injury - renal tubular epithelium Disrupted cell membranes Marked mitochondrial swelling with amorphous densities Dense pyknotic nucleus Fig 2-10 (Robbins). C, Proximal tubular cell showing late injury, expected to be irreversible. Note the markedly swollen mitochondria containing electron-dense deposits, expected to contain precipitated calcium and proteins. Higher magnification micrographs of the cell would show disrupted plasma membrane and swelling and fragmentation of organelles.
17 Irreversible Injury Normal human epithelial cell (Scanning EM). Epithelial cell 24 hours after exposure to sulfur mustard (SEM). Note loss of microvilli and perforations / invaginations of the plasma membrane.
18 Irreversible Injury after cell death: - cell parts continue to be digested by lysosomal acid hydrolases - leakage of cellular enzymes into ECF (eg muscle CK, liver ALT) - influx of ions (eg Ca 2+ ) and macromolecules from the ECF - cells debris removed by phagocytosis or broken into fatty acid residues
19 b) Liquefactive Necrosis when enzymatic digestion of necrotic cells predominates many bacterial infections; neutrophils contain potent hydrolases in hypoxic damage of the CNS Gross appearance affected tissue is liquefied, ie soft to viscous to fluid mass in inflammation, the liquid is often mostly dead WBC s (pus) Microscopic appearance may see degenerate neutrophils and/or amorphous necrotic material
20 Porcine, abscess in ventral neck / shoulder area. Escape of purulent exudate (pus) when the abscess is lanced. Note, suppurative (= purulent) exudate is a common type of liquefactive necrosis.
21 Cytology of an aspirate from abscess / suppurative exudate. The predominate cell type is neutrophils and there are fewer scattered macrophages. Porcine, kidney, suppurative pyelonephritis, note purulent exudate (again an example of liquefactive necrosis).
22 Figure 01-20A (McGavin & Zachary). Liquefactive necrosis. Acute polioencephalomalacia, brain, goat. A thiamine deficiency has resulted in polioencephalomalacia (ie polio = grey, encephalo = brain and malacia = necrosis). This is liquefaction necrosis with varying degrees of tissue separation (arrows). Scale bar = 2 cm. Note: this same lesion can result from either ischemia, lead poisoning or salt poisoning.
23 c) Caseous Necrosis typical seen with specific bacterial diseases, eg TB, caseous lymphadenitis infections in birds, since heterophils lack myeloperoxidase Gross appearance grey-white, dry, friable to pasty (caseous = cheese like) Microscopic appearance dead cells persist as amorphous, coarsely granular, eosinophilic debris retain cellular outline (coagulative) caseous complete dissolution (liquefactive)
24 Ovine, submandibular lymph node, with caseous lymphadenitis an infectious disease caused by infection with the bacteria Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis; note the type of necrosis in this exudate is caseous (not quite liquefactive, but more broken down than coagulation necrosis, ie it would be a thick pasty texture, if you could cut / feel it)
25 Equine, lung tissue, pyogranulomatous pneumonia due to Rhodococcus equi; note caseous exudate (arrows).
26 Figure Tuberculosis, lymph node, transverse section, ox. A, The lymph has been replaced by a caseating granuloma. Note the caseous necrosis characterized by a pale yellow, crumbly exudate. B, Granulomatous inflammation in caseous necrosis. Cell walls are disrupted and tissue architecture is lost. Mineralization (not seen here) is common in this type of necrosis. H&E stain.
27 d) Gangrenous Necrosis definition = necrosis (usually ischemic) of extremities, eg digits, ear tips dry gangrene = coagulation necrosis of an extremity wet gangrene = when the coagulative necrosis of dry gangrene is modified by liquefactive action of saprophytic / putrefactive bacteria Frostbite of the hand in a person (above). Cat with sloughing of ear tips and paws following dry gangrene due to frostbite.
28 Calf, gangrenous necrosis of distal limbs due to ischemia; this ischemia could result from frostbite or sepsis or a mycotoxin such as ergot. Bovine, calf, gangrenous necrosis / dry gangrene with sloughing of distal limbs, ergot poisoning
29 Fig 1-21A (McGavin & Zachary), Moist gangrene, udder, sheep. The surrounding tissue is well vascularized, which contributes to the wet and bloody nature of the lesion. Often saprophytic bacteria and clostridia contaminate areas of necrosis. Bovine, mammary gland, wet gangrene; tissue starting to slough.
30 Bovine, lung, gangrenous pneumonia following aspiration of rumen content. [Although historically called gangrenous pneumonia, it is probably better called necrotizing pneumonia as a morphologic Dx or aspiration pneumonia as an etiologic Dx]
31 e) Fat Necrosis distinguished by its location within body fat stores etiology: inflammation (eg pancreatitis), Vit E deficiency, trauma, idiopathic
32 Canine, recurrent pancreatic necrosis ( pancreatitis ) with mesenteric fat necrosis
33 Canine, recurrent pancreatic necrosis ( pancreatitis ) with omental fat necrosis.
34 Canine, recurrent pancreatic necrosis ( pancreatitis ) with fat necrosis; note necrosis of fat (larger arrow) and pancreatic tissues (smaller arrow) some areas of coagulative type and other areas with significant enzyme degradation (liquefaction) of necrotic tissue.
35
36 2) Apoptosis Greek = falling off death of single cells through activation of genetically programmed suicide pathways apoptosis indicates selective elimination of cells (either physiologic or pathologic), while necrosis points to widespread tissue injury (severe pathologic stimuli) apoptosis death of single cells / intact membranes / phagocytosed with no inflam. necrosis area of dead cells / damaged membranes / enzyme digest. & 2 o inflam. Figure (Molecular Biolology of the Cell, 4 th ed) Sculpting the digits in the developing mouse paw by apoptosis (A) The paw in this mouse embryo has been stained with a dye that specifically labels cells that have undergone apoptosis. The apoptotic cells appear as bright green dots between the developing digits (arrows). (B) This interdigital cell death eliminates the tissue between the developing digits, as seen one day later, when few, if any, apoptotic cells can be seen.
37 Incomplete tissue sculpting (ie incomplete apoptosis) of the digits results in syndactyly (from Greek syn = "together" + dactyly = digits ) It can be partial, as in the web toes (above left) or complete as seen in the childs hand (above right) and calves hooves (below left)
38 2) Apoptosis seen in many physiologic, adaptive and pathologic events: Physiologic causes: Cells undergoing programmed cell death during embryogenesis Cells undergoing normal turnover - hormone-dependent involution - cell deletion in proliferating population Immune System - deletion of autoreactive T cell in thymus - immune regulation
39 2) Apoptosis Pathologic causes: DNA damaged beyond repair eg radiation, toxins Misfolded proteins ER stress Specific infectious agents esp viruses Specific immune responses via cytotoxic T cells Pathologic atrophy of organs after duct obstruction
40 2) Apoptosis d) Morphology considerable apoptosis may occur in tissues before it is evident on histology Cell shrinkage - cytoplasm has packed organelles Chromatin condensation - dense aggregates of chromatin ± fragmentation Formation of cytoplasmic blebs / apoptotic bodies - with intact membranes (± nuclear fragments) Phagocytosis of apoptotic cells / bodies - usually by macrophages with no inflammation
41 Fig 1-8 (Robbins) Schematic illustration of morphologic changes in cell injury culminating in necrosis or apoptosis. Note: with necrosis cells swell, lose membrane integrity and incite an inflammatory response VS apoptosis where cells shrink (condense), membranes remain intact in forming apoptotic bodies and are removed with minimal inflammation.
42 SEM showing showing cytoplasmic blebbing / apoptotic body formation. Figure 3 23 (Junqueira s Basic Histology) Late apoptosis-formation of apoptotic bodies. TEM of a cell in late apoptosis shows that during this process the cell s shape changes radically and large cytoplasmic vesicles (blebs) are formed. These detach from the cell and often separate one from another, but remain contained within plasma membrane so that no cytoplasmic contents are released into the extracellular space.
43 Note, arrows indicate apoptotic epidermal keratinocytes ( sunburn cells ) due to UV-B radiation. These can be induced within 30 minutes of sun exposure.
44 Figure (McGavin & Zachary). Apoptosis, cytoarchitecture of cells, pancreas, rat. Individual acinar cells are shrunken and their chromatin condensed and fragmented (arrows). Cytoplasmic blebs are found in adjacent cells. Inflammation is absent. H&E. (note: blockage of glandular ducts typically results in apoptosis within the gland)
45 Biochemical Mechanisms Signaling pathways that initiate apoptosis ( Death Signals ) stimulate targets on cell surface or within the cell
46 Biochemical Mechanisms Control and integration balance of +ve / -ve regulatory molecules determines outcome of the affected cell
47 Biochemical Mechanisms Common execution phase actual death program accomplished by endonucleases & proteases (esp caspases)
48 Biochemical Mechanisms Removal of dead cells apoptotic bodies have ligands for phagocytic cells (efficient / no inflammation)
49 e) Consequences of too much or too little apoptosis Disorders associated with defective apoptosis (increased cell survival) increased survival of abnormal cells with neoplasia increased survival of autoreactive lymphocytes causing autoimmune disorder Disorders associated with increased apoptosis (excessive cell death) increased loss of cells in: neurodegenerative diseases ischemic injured cells viral infected cells
50
PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Heyam Awad
 number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one
 Necrosis Necrosis Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one or more, small, clearly defined areas of necrosis. Diffuse necrosis- term used
Necrosis Necrosis Necrosis is death of cells and tissues in the living animal. Focal/ Multifocal necrosis- terms used for one or more, small, clearly defined areas of necrosis. Diffuse necrosis- term used
Cellular responses to stress
 Cellular responses to stress (Adaptations, injury and death) (2 of 5) Most injurious stimuli are grouped into: Oxygen deprivation Chemical agents Infectious agents Immunologic reactions Genetic factors
Cellular responses to stress (Adaptations, injury and death) (2 of 5) Most injurious stimuli are grouped into: Oxygen deprivation Chemical agents Infectious agents Immunologic reactions Genetic factors
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations
 Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Mechanisms of Cell Injury
 Causes of Cell Injury 1- oxygen deprivation (anoxia) 2- physical agents 3- chemical agents 4- infections agents 5- immunologic reactions 6- genetic defects 7- nutritional imbalances Mechanisms of Cell
Causes of Cell Injury 1- oxygen deprivation (anoxia) 2- physical agents 3- chemical agents 4- infections agents 5- immunologic reactions 6- genetic defects 7- nutritional imbalances Mechanisms of Cell
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis. Dr H Awad 2017/18
 Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
INTRODUCTION TO HEALTH AND DISEASE BLOCK
 MBBS 1 st Yr. Lecture Dr. Annie Cheung September 25, 2002, 8:30AM 9:30 AM LT1, G/F, Academic and Administration Block Faculty of Medicine Building INTRODUCTION TO HEALTH AND DISEASE BLOCK CELL INJURY AND
MBBS 1 st Yr. Lecture Dr. Annie Cheung September 25, 2002, 8:30AM 9:30 AM LT1, G/F, Academic and Administration Block Faculty of Medicine Building INTRODUCTION TO HEALTH AND DISEASE BLOCK CELL INJURY AND
SECTION 2 CELL INJURY
 Adapted myocyte Normal myocyte Reversibly-injured myocyte SECTION 2 CELL INJURY Cell death 5/4/2014 1 5/4/2014 2 Reversible Degeneration Irreversible Cellular Swelling Fatty Change Hyaline Change Amyloid
Adapted myocyte Normal myocyte Reversibly-injured myocyte SECTION 2 CELL INJURY Cell death 5/4/2014 1 5/4/2014 2 Reversible Degeneration Irreversible Cellular Swelling Fatty Change Hyaline Change Amyloid
Cellular Injury, Necrosis, Apoptosis
 Cellular Injury, Necrosis, Apoptosis Cell injury results when cells are stressed and can no longer adapt Injury may progress through a reversible stage Reversible Cell Injury Reduced oxidative phosphorylation
Cellular Injury, Necrosis, Apoptosis Cell injury results when cells are stressed and can no longer adapt Injury may progress through a reversible stage Reversible Cell Injury Reduced oxidative phosphorylation
APOPTOSIS, NECROSIS AND CANCER. Dr. S. P. Pattanayak
 APOPTOSIS, NECROSIS AND CANCER Dr. S. P. Pattanayak LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Know the importance of cell death. Define various modes of cell death. Identify
APOPTOSIS, NECROSIS AND CANCER Dr. S. P. Pattanayak LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Know the importance of cell death. Define various modes of cell death. Identify
Quiz 1 Review. More Cowbell
 Quiz 1 Review More Cowbell Quiz 1 review Inflamma7on Repair Cell Injury and Adapta7on Quiz 1 review Inflamma7on Injury Acute inflammation Chronic inflammation Abscess Resolution Repair Time course Inflammation
Quiz 1 Review More Cowbell Quiz 1 review Inflamma7on Repair Cell Injury and Adapta7on Quiz 1 review Inflamma7on Injury Acute inflammation Chronic inflammation Abscess Resolution Repair Time course Inflammation
Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury. VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016
 Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016 Gross Specimens The following slides consist of images from the specimens presented
Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016 Gross Specimens The following slides consist of images from the specimens presented
The basis of Disease
 General Curriculum The basis of Disease ZHOU REN 周韧 Prof., M.D., Ph.D. Institute of Pathology & Forensic Medicine Department of Pathology & Patho-physiology Zhenjiang University Judicial Evidence & Evaluation
General Curriculum The basis of Disease ZHOU REN 周韧 Prof., M.D., Ph.D. Institute of Pathology & Forensic Medicine Department of Pathology & Patho-physiology Zhenjiang University Judicial Evidence & Evaluation
Lecture-2 / Dr Hussain Abady Aljebori Over view of cell injury and cell death; Cell injury results when: a. cells are stressed so severely that they
 Lecture-2 / Dr Hussain Abady Aljebori Over view of cell injury and cell death; Cell injury results when: a. cells are stressed so severely that they are no longer able to adapt or b. when cells are exposed
Lecture-2 / Dr Hussain Abady Aljebori Over view of cell injury and cell death; Cell injury results when: a. cells are stressed so severely that they are no longer able to adapt or b. when cells are exposed
NECROSIS, GANGRENE. I. practical training 2 rd year Dentistry
 NECROSIS, GANGRENE. I. practical training 2 rd year Dentistry Signs of death Cardiac arrest (no pulse) Pallor mortis, paleness which happens in the 15 120 minutes after death Livor mortis, a settling of
NECROSIS, GANGRENE. I. practical training 2 rd year Dentistry Signs of death Cardiac arrest (no pulse) Pallor mortis, paleness which happens in the 15 120 minutes after death Livor mortis, a settling of
Cell Adaptation, Cell Injury and Cell Death
 Cell Adaptation, Cell Injury and Cell Death Pathology:- is the study of structural and functional abnormalities that are expressed as diseases of organs and systems. Modern pathology, proposed that injury
Cell Adaptation, Cell Injury and Cell Death Pathology:- is the study of structural and functional abnormalities that are expressed as diseases of organs and systems. Modern pathology, proposed that injury
Chapter 1 CELL INJURY CELL DEATH CELL ADAPTATIONS. M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University.
 Chapter 1 CELL INJURY CELL DEATH CELL ADAPTATIONS M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. CONCEPTS IN CELL INJURY The clinical signs and symptoms are several
Chapter 1 CELL INJURY CELL DEATH CELL ADAPTATIONS M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. CONCEPTS IN CELL INJURY The clinical signs and symptoms are several
Cell injury, adaptation and death. Unite one Second Lab.
 Cell injury, adaptation and death Unite one Second Lab. The two lung abscesses seen here are examples of liquefactive necrosis in which there is a liquid center in an area of tissue injury. One abscess
Cell injury, adaptation and death Unite one Second Lab. The two lung abscesses seen here are examples of liquefactive necrosis in which there is a liquid center in an area of tissue injury. One abscess
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
shehab Moh Tarek ... ManarHajeer
 3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
3 shehab Moh Tarek... ManarHajeer In the previous lecture we discussed the accumulation of oxygen- derived free radicals as a mechanism of cell injury, we covered their production and their pathologic
CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH
 CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH INTRODUCTION Cell Injury is a result of the sequence of events that occur if the limits of the adaptive capability of cells are exceeded or there is no adaptive response is possible,
CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH INTRODUCTION Cell Injury is a result of the sequence of events that occur if the limits of the adaptive capability of cells are exceeded or there is no adaptive response is possible,
Types of insult - hypoxia
 Introduction This presentation will be a guide to cell injury and cell death outline causes and pathogenesis of cell injury/death describe the morphological changes of cell injury/death Describe the process
Introduction This presentation will be a guide to cell injury and cell death outline causes and pathogenesis of cell injury/death describe the morphological changes of cell injury/death Describe the process
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing. Shannon Martinson: VPM 152: April 2013
 Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: April 2013 Example A Reproductive tract and colon/rectum from a sheep Previous
Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: April 2013 Example A Reproductive tract and colon/rectum from a sheep Previous
Cellular Injury. Intracellular degeneration. By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall /20/2018 1
 Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
Cellular Injury Intracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2018 10/20/2018 1 Types of cell injury Cell injury is divided into: 1. Reversible cell injury 2. Irreversible cell
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY
 Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
Cellular response to stress
 Cellular pathology - cell injury, death and adaptations Pathology Göran Andersson Cellular response to stress Cells differ in their capacity to tolerate changes in their microenvironment Acute, severe
Cellular pathology - cell injury, death and adaptations Pathology Göran Andersson Cellular response to stress Cells differ in their capacity to tolerate changes in their microenvironment Acute, severe
[General Pathology] Introduction to Pathology
![[General Pathology] Introduction to Pathology [General Pathology] Introduction to Pathology](/thumbs/73/69585662.jpg) Introduction to Pathology Pathology: Literally translated, pathology is the study (logos) of disease (pathos, suffering). It involves the investigation of the causes of disease and the associated changes
Introduction to Pathology Pathology: Literally translated, pathology is the study (logos) of disease (pathos, suffering). It involves the investigation of the causes of disease and the associated changes
7 NECROSIS, GANGRENE AND POST-MORTEM CHANGES
 7 NECROSIS, GANGRENE AND POST-MORTEM CHANGES Necrosis Coagulative Necrosis Caseative Necrosis Liquifactive Necrosis Fat Necrosis Apoptosis Gangrene Post Mortem Changes Autolysis Putrefaction Rigor Mortis
7 NECROSIS, GANGRENE AND POST-MORTEM CHANGES Necrosis Coagulative Necrosis Caseative Necrosis Liquifactive Necrosis Fat Necrosis Apoptosis Gangrene Post Mortem Changes Autolysis Putrefaction Rigor Mortis
HISTOPATHOLOGY. Shannon Martinson
 HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
Disturbances of Circulation. Histopathology Lab #2 (Web)
 Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
Extracellular degeneration
 Extracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1/17/2017 1 Extracellular Degenerations I / Hyaline Degeneration (Hyalinization): The ward hyaline is derived from the Latin
Extracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1/17/2017 1 Extracellular Degenerations I / Hyaline Degeneration (Hyalinization): The ward hyaline is derived from the Latin
Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity
 Part 1 Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity Bacteria Most common pathogens Anthrax Cholera Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria Bacterial diseases Tuberculosis Cholera Bubonic Plague Tetanus Effects
Part 1 Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity Bacteria Most common pathogens Anthrax Cholera Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria Bacterial diseases Tuberculosis Cholera Bubonic Plague Tetanus Effects
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR
 Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
Pathology of the Hematopoietic System - Lab.
 Pathology of the Hematopoietic System - Lab http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Shannon Martinson, September 2015 Case #1 Signalment: 96 kg gilt History: Pig from minimal disease herd. Sudden death Case
Pathology of the Hematopoietic System - Lab http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Shannon Martinson, September 2015 Case #1 Signalment: 96 kg gilt History: Pig from minimal disease herd. Sudden death Case
Mechanisms of disease
 PP Mechanisms of disease Stress and disease Homeostasis - Responsible for maintaining a constant, safe internal environment - Controlled by feedback loops o Negative feedback loop: temperature, blood glucose
PP Mechanisms of disease Stress and disease Homeostasis - Responsible for maintaining a constant, safe internal environment - Controlled by feedback loops o Negative feedback loop: temperature, blood glucose
Pathology of the Alimentary Tract
 Pathology of the Alimentary Tract Lab 2: Lower alimentary tract SI, LI, cecum, and peritoneum GIST in the cecum of a dog Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 221: November, 2011 3 year
Pathology of the Alimentary Tract Lab 2: Lower alimentary tract SI, LI, cecum, and peritoneum GIST in the cecum of a dog Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 221: November, 2011 3 year
Blood: Functions. Liquid connective tissue 3 general functions 1. Transportation. 2. Regulation. 3. Protection
 Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
Stages in the cellular response to stress & injurious stimuli
 Blok BBS 2 Departemen Patologi Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera Utara Medan -2011 Stages in the cellular response to stress & injurious stimuli 3/28/2011 2 1 Table 1-1.Cellular Responses
Blok BBS 2 Departemen Patologi Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera Utara Medan -2011 Stages in the cellular response to stress & injurious stimuli 3/28/2011 2 1 Table 1-1.Cellular Responses
Avian Pathology. Bacterial diseases: histo slides. ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN
 Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Inflammation Laboratory 1
 Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
INFLAMMATION. 5. Which are the main phases of inflammation in their "sequence": 1. Initiation, promotion, progression.
 INFLAMMATION 1. What is inflammation: 1. Selective anti-infective pathological reaction. 2. Pathological process, typical for vascularized tissues. 3. Self-sustained pathological condition. 4. Disease
INFLAMMATION 1. What is inflammation: 1. Selective anti-infective pathological reaction. 2. Pathological process, typical for vascularized tissues. 3. Self-sustained pathological condition. 4. Disease
Coagulative Necrosis of Myocardium. Dr Rodney Itaki Division of Pathology
 Coagulative Necrosis of Myocardium Dr Rodney Itaki Division of Pathology Coagulative Necrosis Gross pathology: 3 day old infarct: Yellow necrosis surrounded by hyperemic borders. Arrow points to a transmural
Coagulative Necrosis of Myocardium Dr Rodney Itaki Division of Pathology Coagulative Necrosis Gross pathology: 3 day old infarct: Yellow necrosis surrounded by hyperemic borders. Arrow points to a transmural
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System
 37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System 1 Blood Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs,
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System 1 Blood Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs,
DEGENERATION NECROSIS AND INFILTRATION
 DEGENERATION NECROSIS AND INFILTRATION Cellular Degenerations and Infiltrations 1. Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration occur when the regulatory mechanisms
DEGENERATION NECROSIS AND INFILTRATION Cellular Degenerations and Infiltrations 1. Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration occur when the regulatory mechanisms
Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology
 2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.
 المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
Histopathology: healing
 Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Injurious stimuli cause a protective vascular connective tissue reaction called inflammation Acute and chronic forms o Inflame
Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Injurious stimuli cause a protective vascular connective tissue reaction called inflammation Acute and chronic forms o Inflame
34 Apoptosis Programmed cell death is vital to the health and development of multicellular organisms.
 Principles of Biology contents 34 Apoptosis Programmed cell death is vital to the health and development of multicellular organisms. Apoptosis is the reason we have separate fingers and toes. During embryonic
Principles of Biology contents 34 Apoptosis Programmed cell death is vital to the health and development of multicellular organisms. Apoptosis is the reason we have separate fingers and toes. During embryonic
ECVP/ESVP Summer School in Veterinary Pathology Summer School 2015 Histology Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney.
 Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
The basis of Disease
 General Curriculum The basis of Disease ZHOU REN 周韧 Prof., M.D., Ph.D. Institute of Pathology & Forensic Medicine Department of Pathology & Patho-physiology Zhenjiang University Judicial Evidence & Evaluation
General Curriculum The basis of Disease ZHOU REN 周韧 Prof., M.D., Ph.D. Institute of Pathology & Forensic Medicine Department of Pathology & Patho-physiology Zhenjiang University Judicial Evidence & Evaluation
Inflammation Laboratory 1
 Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2013 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2013 Describing Lesions
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course. Histo Exam #3 KEY
 2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
CELL INJURY, DEATH, AND ADAPTATION
 CELL INJURY, DEATH, AND ADAPTATION Definitons Pathology is a dicipline bridging clinical practice and basic sience To render diagnosis and guide therapy - Identity changes in gross - Morphology ( microscopy
CELL INJURY, DEATH, AND ADAPTATION Definitons Pathology is a dicipline bridging clinical practice and basic sience To render diagnosis and guide therapy - Identity changes in gross - Morphology ( microscopy
Inflammation Laboratory 2. Shannon Martinson: VPM 152: March 2012
 Inflammation Laboratory 2 Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2012 Reminder - Creating a Morphologic Diagnosis for Inflammatory Lesions Organ and Process Exudate Distribution
Inflammation Laboratory 2 Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2012 Reminder - Creating a Morphologic Diagnosis for Inflammatory Lesions Organ and Process Exudate Distribution
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis
 Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
ataxia, head tremors and mild inappentence, was given palliative care
 2013-5-2 Cerebellum, Spleen-Raccoon Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION :College of Veterinary Medicine UC Davies Signalment: Wild-caught juvenile male raccoon, ( Procyon lotor)
2013-5-2 Cerebellum, Spleen-Raccoon Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION :College of Veterinary Medicine UC Davies Signalment: Wild-caught juvenile male raccoon, ( Procyon lotor)
Pathology MCQs. lipid. protein. glycogen. lipofuscin. water. Karyolysis. Cellular swelling. Involvement of a large number of cells
 Pathology MCQs 1. In hypoxic cell injury, cell swelling occurs because of increased intracellular: lipid protein glycogen lipofuscin water 2. Which of the following is a feature of apoptosis? Karyolysis
Pathology MCQs 1. In hypoxic cell injury, cell swelling occurs because of increased intracellular: lipid protein glycogen lipofuscin water 2. Which of the following is a feature of apoptosis? Karyolysis
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi
 number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
Histopathology: pulmonary pathology
 Histopathology: pulmonary pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: pulmonary pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very
 This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
Histopathology: chronic inflammation
 Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
I. ADAPTATION TO ENVIRONMENTAL STRESS. A. Hypertrophy:
 د.جواهر محي الدين Lec:2&3 Cellular Reaction to Injury I. ADAPTATION TO ENVIRONMENTAL STRESS II. HYPOXIC CELL INJURY III. FREE RADICAL INJURY IV. CHEMICAL CELL INJURY V. NECROSIS VI. APOPTOSIS VII. REVERSIBLE
د.جواهر محي الدين Lec:2&3 Cellular Reaction to Injury I. ADAPTATION TO ENVIRONMENTAL STRESS II. HYPOXIC CELL INJURY III. FREE RADICAL INJURY IV. CHEMICAL CELL INJURY V. NECROSIS VI. APOPTOSIS VII. REVERSIBLE
Pathophysiology lab 2. Cellular injury and adaptation
 Pathophysiology lab 2 Cellular injury and adaptation Adaptation Cellular changes that aim to preserve cell viability and prevent cell injury. The adaptive responses include: 1. Atrophy 2. Hypertrophy 3.
Pathophysiology lab 2 Cellular injury and adaptation Adaptation Cellular changes that aim to preserve cell viability and prevent cell injury. The adaptive responses include: 1. Atrophy 2. Hypertrophy 3.
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system. Answer Sheet
 Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
This is Learning Component 6 in Learning Module 1. We will show examples of features ( things ) including mineral deposits, urates, pigments, dust,
 This is Learning Component 6 in Learning Module 1. We will show examples of features ( things ) including mineral deposits, urates, pigments, dust, plant material, and amyloid. 1 Calcium salts are the
This is Learning Component 6 in Learning Module 1. We will show examples of features ( things ) including mineral deposits, urates, pigments, dust, plant material, and amyloid. 1 Calcium salts are the
Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood. Functions:
 Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood Functions: Transports nutrients, oxygen, cellular waste products, and hormones Aids in distribution of heat Regulates acid-base balance Helps protect against infection
Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood Functions: Transports nutrients, oxygen, cellular waste products, and hormones Aids in distribution of heat Regulates acid-base balance Helps protect against infection
Chapter 11. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 11 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 11 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Practical Histology. Lab 3: Connective tissue
 Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
CONNECTIVE TISSUE (C.T.)
 CONNECTIVE TISSUE (C.T.) Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Enumerate the general characteristics of C.T. 2. Classify C.T into C.T. proper and special types of C.T.
CONNECTIVE TISSUE (C.T.) Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Enumerate the general characteristics of C.T. 2. Classify C.T into C.T. proper and special types of C.T.
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, April 2016
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Liver: Hepatitis, necrotizing, multifocal to coalescing, severe, with numerous trichomonads. (3 pt)
 Case 1. Tissue from a pelican. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Liver: Approximately 80% (1 pt) of the liver is replaced by multifocal to coalescing areas of coagulative and lytic necrosis. Centrally, within these
Case 1. Tissue from a pelican. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Liver: Approximately 80% (1 pt) of the liver is replaced by multifocal to coalescing areas of coagulative and lytic necrosis. Centrally, within these
Pathology of the Hematopoietic System GROSS/HISTO LAB
 Pathology of the Hematopoietic System GROSS/HISTO LAB Paul Hanna (thanks to Dr s Aburto, Martinson & Fenton) Fall 2014 Slide 1 Spleen from a Beaver Give a morphologic diagnosis and possible etiology &
Pathology of the Hematopoietic System GROSS/HISTO LAB Paul Hanna (thanks to Dr s Aburto, Martinson & Fenton) Fall 2014 Slide 1 Spleen from a Beaver Give a morphologic diagnosis and possible etiology &
Figure 2: Lymph node Cortical follicular (F) and paracortical (PC) atrophy, with narrowing of the cortex relative to the medulla (M).
 Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO
 HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
Lymphatic System. Where s your immunity idol?
 Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
7/9/2008. Hypoxic cell injury. Consequences of hypoxia depend on cell type. Significance of hypoxia depends on:
 Cellular Adaptation and Cell Injury CLDavis Foundation On the Beach Lecture 2 Hypoxia, reperfusion, free radicals, and apoptosis R K Myers 2008 Hypoxic cell injury Hypoxia: any state of reduction of O
Cellular Adaptation and Cell Injury CLDavis Foundation On the Beach Lecture 2 Hypoxia, reperfusion, free radicals, and apoptosis R K Myers 2008 Hypoxic cell injury Hypoxia: any state of reduction of O
Introduction. 23 rd Annual Seminar in Pathology. FLUIDS, Part 1. Pittsburgh, PA Gladwyn Leiman UVMMC, VT
 23 rd Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh, PA Gladwyn Leiman UVMMC, VT FLUIDS, Part 1 "Blue walls", Claudia Hansen, 2009 Introduction o Challenging to everyone o Almost any benign or malignant process
23 rd Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh, PA Gladwyn Leiman UVMMC, VT FLUIDS, Part 1 "Blue walls", Claudia Hansen, 2009 Introduction o Challenging to everyone o Almost any benign or malignant process
Hashem Al-Dujaily. Tamer Barakat. Manar Hajeer
 1 Hashem Al-Dujaily Tamer Barakat... Manar Hajeer Introduction Pathology comes from Patho: disease/suffering and Logy: study. Therefore, Pathology is the study of disease. Pathology is the bridge between
1 Hashem Al-Dujaily Tamer Barakat... Manar Hajeer Introduction Pathology comes from Patho: disease/suffering and Logy: study. Therefore, Pathology is the study of disease. Pathology is the bridge between
TOXIC CONDITIONS OF ANIMALS
 TOXIC CONDITIONS OF ANIMALS Prof. R. S. Chauhan Joint Director () Indian Veterinary Research Institute Izatnagar 243 122 (UP) AFLATOXICOSIS Aflatoxicosis is a toxic condition of poultry widely prevalent
TOXIC CONDITIONS OF ANIMALS Prof. R. S. Chauhan Joint Director () Indian Veterinary Research Institute Izatnagar 243 122 (UP) AFLATOXICOSIS Aflatoxicosis is a toxic condition of poultry widely prevalent
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
While corps examination it was noticed: turbid cornea, dry skin integument with yellowbrownish spots of
 While corps examination it was noticed: turbid cornea, dry skin integument with yellowbrownish spots of parchment-like look. Indicate the kind of postmortal changes. + putrid drying out - redistribution
While corps examination it was noticed: turbid cornea, dry skin integument with yellowbrownish spots of parchment-like look. Indicate the kind of postmortal changes. + putrid drying out - redistribution
African Trypanosomes
 African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
CELL INJURY. Severity of Cell Injury
 GENERAL PATHOLOGY LECTURE - 3 DR. M. TARIQ JAVED Professor Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. 9/11/2009 1 CELL INJURY No adaptive response
GENERAL PATHOLOGY LECTURE - 3 DR. M. TARIQ JAVED Professor Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. 9/11/2009 1 CELL INJURY No adaptive response
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury.
 Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
lysosomes Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types:
 lysosomes Digests Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types: Proteins Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Lipids Single membrane bound vesicle, contains up to 50 digestive
lysosomes Digests Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types: Proteins Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Lipids Single membrane bound vesicle, contains up to 50 digestive
WSC , Conference 9. Case 1. Tissue from a rhesus macaque.
 Case 1. Tissue from a rhesus macaque. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Esophagus: There is multifocal loss of the mucosal lining (1 pt). In these areas, the denuded subepithelial fibrous connective tissue is infiltrated
Case 1. Tissue from a rhesus macaque. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Esophagus: There is multifocal loss of the mucosal lining (1 pt). In these areas, the denuded subepithelial fibrous connective tissue is infiltrated
Blood Cells. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Reticuloendothelial System (RES) & Spleen Dr. Nervana Bayoumy
 Haematology Lectures Reticuloendothelial System (RES) & Spleen Dr. Nervana Bayoumy 1 Objectives 1. Define the term Reticuloendothelial system (RES). 2. Describe the cellular components of RES. 3. Describe
Haematology Lectures Reticuloendothelial System (RES) & Spleen Dr. Nervana Bayoumy 1 Objectives 1. Define the term Reticuloendothelial system (RES). 2. Describe the cellular components of RES. 3. Describe
Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase
 Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase Dog Spayed Female LABRADOR RETRIEVER 3 Years old VACCINATIONS ANTIPARASITIC COMMERCIAL DIET VOMITING FOR A MONTH DULLNESS WEIGHT LOSS INAPPETANCE
Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase Dog Spayed Female LABRADOR RETRIEVER 3 Years old VACCINATIONS ANTIPARASITIC COMMERCIAL DIET VOMITING FOR A MONTH DULLNESS WEIGHT LOSS INAPPETANCE
Lysosomes. Gr: lysis solution, soma body. Membrane bounded vesicles. Usually round ovoid or irregular electron dense bodies m.
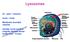 Lysosomes Gr: lysis solution, soma body Membrane bounded vesicles Usually round ovoid or irregular electron dense bodies 0.05 0.5 m. Lysosomes No. varies from a few to several hundred per cell, in different
Lysosomes Gr: lysis solution, soma body Membrane bounded vesicles Usually round ovoid or irregular electron dense bodies 0.05 0.5 m. Lysosomes No. varies from a few to several hundred per cell, in different
HEMOTOLOGY. B. Helps stabilize body temperature -heats up and cools down slowly which moderates body temp
 I. Body H 2 O = HEMOTOLOGY A. Variable quantities 1. sweating and urination ( ) decreases H 2 O 2. drinking H 2 O increases B. Water is found in two compartments 1. contains 2/3 of all water in your body
I. Body H 2 O = HEMOTOLOGY A. Variable quantities 1. sweating and urination ( ) decreases H 2 O 2. drinking H 2 O increases B. Water is found in two compartments 1. contains 2/3 of all water in your body
