Interaction between the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction and lipid membranes: a kinetic investigation
|
|
|
- Emerald Lamb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Design and Nature V 339 Interaction between the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction and lipid membranes: a kinetic investigation F. M. Pulselli1, M. Catalucci1, F. Rossi1,2 & N. Marchettini1 1 2 Department of Chemistry, Siena University, Italy Department of Chemistry, Brandeis University, USA Abstract Far-from-equilibrium oscillating chemical reactions are among the simplest systems showing complex behaviours and emergent properties, when coupled with diffusion they can behave as excitable media and support impulse and wave propagation. The reaction diffusion approach has been widely employed to explain patterns generation in a great array of biological processes, like limb development and skin pattering. During the past years our group has been studying the mechanisms of pattern formation and wave propagation occurring when the well known BelousovZhabotinsky (BZ) reaction is carried out in membranes, i.e. the lamellar phases generated by the. 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocoline (DPPC). Many kinetic parameters of the BZ reaction were found to be influenced by the addition of increasing amounts of DPPC. The aggregates in solution are likely capable of interacting with many of the BZ intermediates, like radicals and molecular bromine. In this paper we will illustrate the results coming from a kinetic study on the temporal and spatio-temporal modifications (increase in amplitude of oscillations, increase of the lifespan of the oscillatory regime, etc.) induced on the BZ reaction by the presence of DPPC. Keyword: Belousov-Zhabotinsky, biomimetics membrane, chemicals oscillators, thermodynamics in nature. 1 Introduction The Belousov-Zhabotinsky (BZ) reaction is the most famous and thoroughly studied chemical oscillator. Initially proposed as a simplified scheme of a doi: /dn100291
2 340 Design and Nature V metabolic pathway (Krebs cycle), it was subsequently adopted as a more general model for certain major nonlinear phenomena, e.g. enzymatic catalysis, biological oscillations and pattern formation. It represents the catalytic oxidation of an organic substrate with active methylenic hydrogens, generally malonic acid CH2(COOH)2,(MA), by bromate ions in a strongly acidic aqueous solution. The general stoichiometry has the form: 2BrO3- + 3MA + 2H+ 2BrMA + 4H2O + 3CO2 (1) where BrMA is bromomalonic acid (BrCH(COOH)2). The most used catalysts are metal redox couples, such as Ce(IV)/Ce(III) or ferriin/ferroin (Fe(phen)3 3+ /Fe(phen)32+). Complexes that show markedly different colour in different oxidation states, like ferroin, are often used to visualize patterns and structures generated by the BZ reaction when coupled with transport phenomena. The BZ reaction mechanism is very complex, and the latest proposed full models for the cerium catalyzed reaction involves more than 80 elemental steps. In the study of chemical systems characterized by nonlinear dynamics, such as the BZ reaction, surfactants are often used as perturbing agents. Surfactants are surface acting agents which belong to the wide class of the amphiphilic compounds, and they are able to form a great variety of self-assembling structures in solution, all of which share the characteristic of compartmentalization between polar and non polar regions, with defined boundary interfaces. Surfactant molecules generally consist of a hydrophilic head of various nature (ionic or non-ionic) and a hydrophobic tail which is usually linear or branched, with or without unsaturated bonds. This dual nature is the origin of the capability of the molecule of self-assembling in aqueous solvents in thermodynamically stable aggregates called micelles. The surfactant concentration at which the reversible association of a certain number of monomers leads to aggregates (micelles) is the critical micellar concentration (cmc). A micelle is therefore characterized by three solubilization sites [6, 7]. They are the hydrophobic core, the palisade layer, with the polar portion in contact with the micellar surface and the hydrophobic portion directed toward the core, and the hydrophilic shell. Figure 1: Structure of the bilayers (on the left) generated by the selfassembly of the DPPC molecules (on the right). The BZ reaction is confined in the water compartment between the polar heads of the lamellar phase.
3 Design and Nature V 341 When a reaction takes place in the presence of surfactant aggregates, the chemical reactivity is obviously dependent on the solubilisation site of the reactants. Among the other surfactants, phospholipids have attracted increasing interest as biomimetic matrices for their close resemblance to biological membranes [8, 9]. The most commonly chosen lipids to build up model membranes consist of a glycerol (propan-1,2,3-triol) backbone linked to two fatty acid chains, to a phosphate group and to a choline end. In particular, in our experiments we used a saturated amphiphile with 16 carbon hydrophobic tails, the 1,2-dipalmitoyl-snglycero-3-phosphocoline (DPPC), which is able to self-assembly in a lamellar structure (Figure 1). In the past we found that BZ reaction is able to generate an interesting array of moving and stationary patterns, when performed in the water phase of a DPPC lamellar stack [4, 5]. The structural changes induced by the BZ reaction to the lipid bilayers were investigated by means of NMR [10] and Small Angle X-Ray Scattering [11] techniques. We are now undertaking a systematic study to understand the modifications of the BZ oscillating mechanism induced by the lipids. In this paper we will illustrate the results coming from a kinetic analysis of the main BZ oscillating parameters. 2 Experimental All experiments were performed in a 20 ml beaker with constant magnetic stirring. The reaction was followed by monitoring the redox potential of the solution as a function of time with a platinum microelectrode (Amel mod. 805/SPG/4) coupled with a saturated calomel reference electrode (Amel mod. 383/SHG/6). The potential was recorded with a personal computer connected to a voltmeter Amel model 338. Both the BZ reagents (SIGMA) and the DPPC (Lipoid) were used as received. A total solution volume of 15 ml and the following initial composition were used for all the experimental runs: Malonic acid 0.30 mol dm-3 NaBrO mol dm-3 H2SO mol dm-3 Ferroin mol dm-3 The recorded time-series were analyzed by means of the software OriginPro 8.0. Table 1 and Figure 2 report the oscillating parameters taken into account in the present study. All parameters are averaged over the first 5 oscillatory cycles for each experiment. 3 Results All of the BZ oscillatory parameters are significantly influenced when DPPC is added to the solution. The most evident changes are induced in the reaction lifespan, as can be seen in the example of Figure 3, where the last hours of two reactions are reported. It is also evident that the oscillatory regime is
4 342 Design and Nature V Table 1: <T> / s <Tautocat> / s <Tinhibit> / s Figure 2: Oscillatory parameters with their units. Average oscillatory period (s): Average period included between a minimum and the following maximum Average period included between a maximum and the following minimum Measured oscillatory parameters. qualitatively different in the sample containing DPPC (Fig.3a)) compared to the water system (Fig. 3b)). The BZ system involves a large number of intermediates with different characteristics (hydrophobic/hydrophilic, neutral/charge, etc.) and the DPPC may likely induce considerable effects on many aspects of the reaction. The polar heads of DPPC form a charged surface, in contact with the water phase, able to interact both with the ions and the solvent. Moreover, the hydrophobic moieties inside the bilayers can trap non-polar species, such as Br2 which is a key intermediate (inhibitor) in many steps of the BZ reaction. Other effects of the presence of lipid aggregates may involve changes in some physical properties of the reaction mixture, such as surface tension, viscosity and ionic strength. At this stage it is difficult to understand how the lipid interacts with the overall chemistry of the BZ reaction and how it influences the total number of the oscillations and their dynamical regime.
5 Design and Nature V Figure 3: 343 Last hours of the oscillatory regime of two BZ reactions in a) DPPC 3% w/w and b) water system. Figure 4: Metric oscillations.
6 344 Design and Nature V Figure 5: Average period and average period of inhibition. Nevertheless, we can focus our attention on other parameters which are regulated by relatively simpler mechanisms. A nonlinear response of <T> to the increasing concentration of DPPC was found. In fact, after an initial decrease, the average oscillation period starts to grow when [DPPC] > 2.5%, even if it never reaches the initial value (Figures 4 and 5). A similar behavior has been found in the past for other surfactants [12, 13]. Any oscillation cycle is composed by a part in which the concentration of the oxidized form of the catalyst (ferriin) increases (autocatalytic process) and by a second one in which it is consumed (inhibitory process). One of the processes responsible for the ferriin consumption is its reaction with the bromomalonic acid during the reaction [11, 13] 2Fe(phen) BrMA fbr- + 2Fe(phen)32+ + other products (2) According to Edelson [14], reaction (2) is the most important step in determining the length of <T>. In fact, in Figure 4 we see that, if we split <T> in <Tautocat> and <Tinhibit>, the contribution of the latter to the total length of <T> is predominant. The initial decrease of the oscillation period, it is possibly due to the role of the lipid as a radical scavenger. The same behavior was observed for the zwitterionic surfactant CHAPS 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1 propanesulfonate] [13]. It is interesting to note from Figures 4-6, that both <Tautocat> and <Tinhibit> have the same threshold behavior at [DPPC] = 2.5%. Since the length of the autocatalytic and the inhibitory parts are regulated by different chemical
7 Design and Nature V Figure 6: 345 Average period of autocatalysis. processes, it is hard to attribute these trends to the same chemical interaction mechanism. Most probably, by increasing the lipid concentration the aggregates structure undergoes to a physical transition (e.g. vesicles to bilayers). In this case, several physical properties (viscosity, ionic strength, surface tension, etc.) can be affected and their effect can be fundamental in determining the oscillatory behavior. Further studies in this direction are already planned. 4 Conclusions The oscillating Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction has been shown to respond in a peculiar way to addition of increasing amounts of DPPC in batch reactors under stirring. It can be concluded that DPPC acts as a catalyst for the reaction, increasing the average oscillation frequency, though with a nonlinear trend. At this stage it is very difficult to understand the interaction mechanism between the BZ intermediates and the lipids, nevertheless our kinetic measurements provide an interesting starting point to be extended with further studies. Acknowledgements This research was supported by a Marie Curie International Outgoing Fellowship (crossdiffusionrossi ) within the 7th European Community Framework Programme. Thanks are due to Dr. Sandra Ristori for helpful discussions.
8 346 Design and Nature V References [1] E. Tiezzi, Steps Towards an Evolutionary Physics, Wit Press, Southampton (UK), pp. 157, [2] V.K. Vanag and I.R. Epstein, Pattern formation mechanisms in reactiondiffusion systems, International Journal of Developmental Biology, vol. 53, 2009, pp [3] J.D. Murray, Mathematical Biology, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, [4] A. Magnani, N. Marchettini, S. Ristori, C. Rossi, F. Rossi, M. Rustici, O. Spalla, and E. Tiezzi, Chemical waves and pattern formation in the 1,2dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine/water lamellar system, Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 126, 2004, pp [5] F. Rossi, S. Ristori, M. Rustici, N. Marchettini, and E. Tiezzi, Dynamics of pattern formation in biomimetic systems, Journal of Theoretical Biology, vol. 255, 2008, pp [6] J.H. Fendler, Membrane Mimetic Chemistry, New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc, [7] J.H. Fendler, Interactions and Kinetics in Membrane Mimetic Systems, Annual Review of Physical Chemistry, vol. 35, 1984, pp [8] J.K. Parrish and L. Edelstein-Keshet, Complexity, Pattern, and Evolutionary Trade-Offs in Animal Aggregation, Science, vol. 284, Apr. 1999, pp [9] P. Walde, Prebiotic Chemistry: From Simple Amphiphiles to Protocell Models, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, [10] N. Marchettini, S. Ristori, F. Rossi, and M. Rustici, An experimental model for mimicking biological systems the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction in lipid membranes, International Journal of Ecodynamics, vol. 1, 2006, pp [11] S. Ristori, F. Rossi, G. Biosa, N. Marchettini, M. Rustici, and E. Tiezzi, Interplay between the Belousov-Zhabotinsky reaction-diffusion system and biomimetic matrices, Chemical Physics Letters, vol. 436, 2007, pp [12] F. Rossi, R. Lombardo, L. Sciascia, C. Sbriziolo, and M.L.T. Liveri, Spatio-Temporal Perturbation of the Dynamics of the Ferroin Catalyzed Belousov Zhabotinsky Reaction in a Batch Reactor Caused by Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Micelles., Journal of Physical Chemistry B, vol. 112, 2008, pp [13] A. Paul, Observations of the Effect of Anionic, Cationic, Neutral, and Zwitterionic Surfactants on the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction, Journal of Physical Chemistry B, vol. 109, 2005, pp [14] D. Edelson and V.M. Thomas, Sensitivity analysis of oscillating reactions. 1. The period of the Oregonator, Journal of Physical Chemistry, vol. 85, 1981, pp
AN EXPERIMENTAL MODEL FOR MIMICKING BIOLOGICAL SYSTEMS: THE BELOUSOV ZHABOTINSKY REACTION IN LIPID MEMBRANES
 P a g e 321 AN EXPERIMENTAL MODEL FOR MIMICKING BIOLOGICAL SYSTEMS: THE BELOUSOV ZHABOTINSKY REACTION IN LIPID MEMBRANES N. MARCHETTINI 1, S. RISTORI 2, F. ROSSI 1 & M. RUSTICI 3 1 Department of Chemical
P a g e 321 AN EXPERIMENTAL MODEL FOR MIMICKING BIOLOGICAL SYSTEMS: THE BELOUSOV ZHABOTINSKY REACTION IN LIPID MEMBRANES N. MARCHETTINI 1, S. RISTORI 2, F. ROSSI 1 & M. RUSTICI 3 1 Department of Chemical
Surfactants. The Basic Theory. Surfactants (or surface active agents ): are organic compounds with at least one lyophilic. Paints and Adhesives
 Surfactants Surfactants (or surface active agents ): are organic compounds with at least one lyophilic ( solvent-loving ) group and one lyophobic ( solvent-fearing ) group in the molecule. In the simplest
Surfactants Surfactants (or surface active agents ): are organic compounds with at least one lyophilic ( solvent-loving ) group and one lyophobic ( solvent-fearing ) group in the molecule. In the simplest
Biology Chapter 2 Review
 Biology Chapter 2 Review Vocabulary: Define the following words on a separate piece of paper. Element Compound Ion Ionic Bond Covalent Bond Molecule Hydrogen Bon Cohesion Adhesion Solution Solute Solvent
Biology Chapter 2 Review Vocabulary: Define the following words on a separate piece of paper. Element Compound Ion Ionic Bond Covalent Bond Molecule Hydrogen Bon Cohesion Adhesion Solution Solute Solvent
Self-Assembly. Lecture 3 Lecture 3 Surfactants Self-Assembly
 Self-Assembly Lecture 3 Lecture 3 Surfactants Self-Assembly Anionic surfactants unsaturated omega-3 3 fatty acids rd carbon from the metyl end has double bond saturated Non-ionic surfactants Cationic surfactants
Self-Assembly Lecture 3 Lecture 3 Surfactants Self-Assembly Anionic surfactants unsaturated omega-3 3 fatty acids rd carbon from the metyl end has double bond saturated Non-ionic surfactants Cationic surfactants
Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 22: Aggregates of lipids: micelles, liposomes and their applications OBJECTIVE
 Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 22: Aggregates of lipids: micelles, liposomes and their applications OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module is to introduce the students to the types
Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 22: Aggregates of lipids: micelles, liposomes and their applications OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module is to introduce the students to the types
Physical Pharmacy. Interfacial phenomena. Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department
 Physical Pharmacy Interfacial phenomena Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department 1 Introduction The boundary between two phases is generally described as
Physical Pharmacy Interfacial phenomena Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department 1 Introduction The boundary between two phases is generally described as
2.2 Properties of Water
 2.2 Properties of Water I. Water s unique properties allow life to exist on Earth. A. Life depends on hydrogen bonds in water. B. Water is a polar molecule. 1. Polar molecules have slightly charged regions
2.2 Properties of Water I. Water s unique properties allow life to exist on Earth. A. Life depends on hydrogen bonds in water. B. Water is a polar molecule. 1. Polar molecules have slightly charged regions
Colloid chemistry. Lecture 10: Surfactants
 Colloid chemistry Lecture 10: Surfactants Applications of surfactants: cleaning/detergents (40%); textiles; cosmetics; pharmacy; paint; food; etc. Etymology Surfactant micelles surfactant molecule spherical
Colloid chemistry Lecture 10: Surfactants Applications of surfactants: cleaning/detergents (40%); textiles; cosmetics; pharmacy; paint; food; etc. Etymology Surfactant micelles surfactant molecule spherical
Due in class on Thursday Sept. 8 th
 Problem Set #1 Chem 391 Due in class on Thursday Sept. 8 th Name Solutions 1. For the following processes, identify whether G, H and S are positive (+), negative (-) or about zero (~0) at the standard
Problem Set #1 Chem 391 Due in class on Thursday Sept. 8 th Name Solutions 1. For the following processes, identify whether G, H and S are positive (+), negative (-) or about zero (~0) at the standard
Chapter Three (Biochemistry)
 Chapter Three (Biochemistry) 1 SECTION ONE: CARBON COMPOUNDS CARBON BONDING All compounds can be classified in two broad categories: organic compounds and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are made
Chapter Three (Biochemistry) 1 SECTION ONE: CARBON COMPOUNDS CARBON BONDING All compounds can be classified in two broad categories: organic compounds and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are made
3.1.3 Lipids. Source: AQA Spec
 alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Triglycerides and phospholipids are two groups of lipid. Triglycerides are formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. A
alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Triglycerides and phospholipids are two groups of lipid. Triglycerides are formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. A
Self-assembled nanostructures soft and hard matter
 Hands-On Nano-Technology course Nano-Science Center University of Copenhagen Self-assembled nanostructures soft and hard matter One-day workshop, August 12, 2004 Division of Physical Chemistry 1, Center
Hands-On Nano-Technology course Nano-Science Center University of Copenhagen Self-assembled nanostructures soft and hard matter One-day workshop, August 12, 2004 Division of Physical Chemistry 1, Center
Inorganic compounds: Usually do not contain carbon H 2 O Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 NaCl Carbon containing molecules not considered organic: CO 2
 Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties. Biochemistry: Made by living things All contain the elements carbon and hydrogen Inorganic: Inorganic compounds: All other
Organic Chemistry The study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties. Biochemistry: Made by living things All contain the elements carbon and hydrogen Inorganic: Inorganic compounds: All other
Chemistry 212 Fall Semester 1996 Examination #2
 Chemistry 212 Fall Semester 1996 Examination #2 University of Missouri Columbia Prof. Rainer Glaser Wednesday, October 16, 1996 103 Schlundt Hall, 8:40-9:30 featuring Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid
Chemistry 212 Fall Semester 1996 Examination #2 University of Missouri Columbia Prof. Rainer Glaser Wednesday, October 16, 1996 103 Schlundt Hall, 8:40-9:30 featuring Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid
Interactions between Bisphosphate. Geminis and Sodium Lauryl Ether
 Chapter 5 Interactions between Bisphosphate Geminis and Sodium Lauryl Ether Sulphate 110 5.1 Introduction The physiochemical and surface active properties of mixed surfactants are of more interest and
Chapter 5 Interactions between Bisphosphate Geminis and Sodium Lauryl Ether Sulphate 110 5.1 Introduction The physiochemical and surface active properties of mixed surfactants are of more interest and
Membrane Structure and Membrane Transport of Small Molecules. Assist. Prof. Pinar Tulay Faculty of Medicine
 Membrane Structure and Membrane Transport of Small Molecules Assist. Prof. Pinar Tulay Faculty of Medicine Introduction Cell membranes define compartments of different compositions. Membranes are composed
Membrane Structure and Membrane Transport of Small Molecules Assist. Prof. Pinar Tulay Faculty of Medicine Introduction Cell membranes define compartments of different compositions. Membranes are composed
OCR (A) Biology A-level
 OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 2.2: Biological molecules Notes Water Water is a very important molecule which is a major component of cells, for instance: Water is a polar molecule due to uneven distribution
OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 2.2: Biological molecules Notes Water Water is a very important molecule which is a major component of cells, for instance: Water is a polar molecule due to uneven distribution
Supporting Information. with Phospholipid Engineered Membranes
 Supporting Information Interaction of the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction with Phospholipid Engineered Membranes Kristian Torbensen, a Federico Rossi, b Ottorino L. Pantani, c Sandra Ristori, d * and Ali
Supporting Information Interaction of the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction with Phospholipid Engineered Membranes Kristian Torbensen, a Federico Rossi, b Ottorino L. Pantani, c Sandra Ristori, d * and Ali
Biochemical Techniques 06 Salt Fractionation of Proteins. Biochemistry
 . 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name 12 Module Name/Title 2 1. Objectives Understanding the concept of protein fractionation Understanding protein fractionation with salt 2. Concept Map 3.
. 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name 12 Module Name/Title 2 1. Objectives Understanding the concept of protein fractionation Understanding protein fractionation with salt 2. Concept Map 3.
BIOPHYSICS II. By Prof. Xiang Yang Liu Department of Physics,
 BIOPHYSICS II By Prof. Xiang Yang Liu Department of Physics, NUS 1 Hydrogen bond and the stability of macromolecular structure Membrane Model Amphiphilic molecule self-assembly at the surface and din the
BIOPHYSICS II By Prof. Xiang Yang Liu Department of Physics, NUS 1 Hydrogen bond and the stability of macromolecular structure Membrane Model Amphiphilic molecule self-assembly at the surface and din the
CH 3. Lipids CHAPTER SUMMARY
 H 3 C H 3 C 15 H 3 C H Views of Cholesterol APTER SUMMARY 15.1 The Nature of can best be defined as biomolecules which are soluble to a great extent in solvents. In contrast to carbohydrates, proteins
H 3 C H 3 C 15 H 3 C H Views of Cholesterol APTER SUMMARY 15.1 The Nature of can best be defined as biomolecules which are soluble to a great extent in solvents. In contrast to carbohydrates, proteins
Synthesis of Cationic Novel Bolaform Surfactant and Effect of Alkyl Group Chain Length on Polar Head Group
 Synthesis of Cationic Novel Bolaform Surfactant and Effect of Alkyl Group Chain Length on Polar Head Group 1. Propane-1,3-bis(trimethylammonium bromide) and Propane-1,3-bis(triethylammonium bromide) V.
Synthesis of Cationic Novel Bolaform Surfactant and Effect of Alkyl Group Chain Length on Polar Head Group 1. Propane-1,3-bis(trimethylammonium bromide) and Propane-1,3-bis(triethylammonium bromide) V.
NOTE: For studying for the final, you only have to worry about those with an asterix (*)
 NOTE: For studying for the final, you only have to worry about those with an asterix (*) (*)1. An organic compound is one that: a. contains carbon b. is slightly acidic c. forms long chains d. is soluble
NOTE: For studying for the final, you only have to worry about those with an asterix (*) (*)1. An organic compound is one that: a. contains carbon b. is slightly acidic c. forms long chains d. is soluble
Emulsification. An Introduction to the Emulsification of Lipids within a Watery Environment. By Noel Ways
 Emulsification An Introduction to the Emulsification of Lipids within a Watery Environment By Noel Ways To begin the process of understanding emulsification, let's start with water. First, we note that
Emulsification An Introduction to the Emulsification of Lipids within a Watery Environment By Noel Ways To begin the process of understanding emulsification, let's start with water. First, we note that
Colloid Chemistry. Lecture #2 Association colloid
 Colloid Chemistry Lecture #2 Association colloid 1 https://ilustracionmedica.wordpress.com/2014/08/27/fisicos-haciendo-medicina-john-tyndall/ Solution Classical vs. Colloid solution Tyndall effect Increased
Colloid Chemistry Lecture #2 Association colloid 1 https://ilustracionmedica.wordpress.com/2014/08/27/fisicos-haciendo-medicina-john-tyndall/ Solution Classical vs. Colloid solution Tyndall effect Increased
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Part 2
 Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Part 2 Carbohydrates are Polymers of Monosaccharides Three different ways to represent a monosaccharide Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are sugars and starches and provide
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Part 2 Carbohydrates are Polymers of Monosaccharides Three different ways to represent a monosaccharide Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are sugars and starches and provide
The main biological functions of the many varied types of lipids include: energy storage protection insulation regulation of physiological processes
 Big Idea In the biological sciences, a dehydration synthesis (condensation reaction) is typically defined as a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecules. This reaction
Big Idea In the biological sciences, a dehydration synthesis (condensation reaction) is typically defined as a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecules. This reaction
Carbohydrates and Lipids
 Carbohydrates and Lipids Chapter 5: Macromolecules Macromolecules Smaller organic molecules join together to form larger molecules o macromolecules 4 major classes of macromolecules: o Carbohydrates o
Carbohydrates and Lipids Chapter 5: Macromolecules Macromolecules Smaller organic molecules join together to form larger molecules o macromolecules 4 major classes of macromolecules: o Carbohydrates o
Self-assembly and phase behavior
 Self-assembly and phase behavior Amphiphiles and surface tension Lyotropic phases Micelles Key parameters for micellisation Critical packing parameter Other lyotropic phases Special lyotropic phases: vesicles
Self-assembly and phase behavior Amphiphiles and surface tension Lyotropic phases Micelles Key parameters for micellisation Critical packing parameter Other lyotropic phases Special lyotropic phases: vesicles
Chapter 7: Membranes
 Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
From Atoms to Cells: Fundamental Building Blocks. Models of atoms. A chemical connection
 From Atoms to Cells: A chemical connection Fundamental Building Blocks Matter - all materials that occupy space & have mass Matter is composed of atoms Atom simplest form of matter not divisible into simpler
From Atoms to Cells: A chemical connection Fundamental Building Blocks Matter - all materials that occupy space & have mass Matter is composed of atoms Atom simplest form of matter not divisible into simpler
Millicient A. Firestone, Amanda C. Wolf, and Sonke Seifert. Chris Bianchi 4/30/12
 Small-Angle X-ray Scattering of the Interaction of Poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(propylene oxide)-b- Poly(ethylene oxide)triblock Copolymers with Lipid Bilayers Millicient A. Firestone, Amanda C. Wolf, and
Small-Angle X-ray Scattering of the Interaction of Poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(propylene oxide)-b- Poly(ethylene oxide)triblock Copolymers with Lipid Bilayers Millicient A. Firestone, Amanda C. Wolf, and
Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds.
 Lipids Lipids Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds. u long hydrocarbon chain u composed of CHO Diverse group u fats u oils u waxes u steroids Do not form polymers u big molecules made
Lipids Lipids Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds. u long hydrocarbon chain u composed of CHO Diverse group u fats u oils u waxes u steroids Do not form polymers u big molecules made
Quiz 8 Introduction to Polymers (Chemistry)
 051117 Quiz 8 Introduction to Polymers (Chemistry) (Figures from Heimenz Colloid Sci.) 1) Surfactants are amphiphilic molecules (molecules having one end hydrophobic and the other hydrophilic) and are
051117 Quiz 8 Introduction to Polymers (Chemistry) (Figures from Heimenz Colloid Sci.) 1) Surfactants are amphiphilic molecules (molecules having one end hydrophobic and the other hydrophilic) and are
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at Lipids.
 Lipids Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Topic Sub-Topic Booklet International A Level Biology Edexcel Molecules, Transport and Health Lipids Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 63 minutes Score: /52 Percentage:
Lipids Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Topic Sub-Topic Booklet International A Level Biology Edexcel Molecules, Transport and Health Lipids Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 63 minutes Score: /52 Percentage:
Bio 12 Chapter 2 Test Review
 Bio 12 Chapter 2 Test Review 1.Know the difference between ionic and covalent bonds In order to complete outer shells in electrons bonds can be Ionic; one atom donates or receives electrons Covalent; atoms
Bio 12 Chapter 2 Test Review 1.Know the difference between ionic and covalent bonds In order to complete outer shells in electrons bonds can be Ionic; one atom donates or receives electrons Covalent; atoms
TA Instruments Applications Note. Thermodynamics of Micelle Formation
 Thermodynamics of Micelle Formation Angélica Román Guerrero 1, E. Jaime Vernon Carter 1 and Neil A. Demarse 2 1 DIPH and DBT, Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana Iztapalapa, San Rafael Atlixco #186, Col.
Thermodynamics of Micelle Formation Angélica Román Guerrero 1, E. Jaime Vernon Carter 1 and Neil A. Demarse 2 1 DIPH and DBT, Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana Iztapalapa, San Rafael Atlixco #186, Col.
Cellular Neurophysiology I Membranes and Ion Channels
 Cellular Neurophysiology I Membranes and Ion Channels Reading: BCP Chapter 3 www.bioelectriclab All living cells maintain an electrical potential (voltage) across their membranes (V m ). Resting Potential
Cellular Neurophysiology I Membranes and Ion Channels Reading: BCP Chapter 3 www.bioelectriclab All living cells maintain an electrical potential (voltage) across their membranes (V m ). Resting Potential
/ The following functional group is a. Aldehyde c. Carboxyl b. Ketone d. Amino
 Section A: Multiple Choice Select the answer that best answers the following questions. Please write your selected choice on the line provided, in addition to circling the answer. /25 1. The following
Section A: Multiple Choice Select the answer that best answers the following questions. Please write your selected choice on the line provided, in addition to circling the answer. /25 1. The following
Reading. Learning Objectives. How are macromolecules assembled? 8. Macromolecules I. Contents
 Contents 1 Reading 2 Learning Objectives 3 How are macromolecules assembled? 4 Carbohydrates 4.1 Structural Carbohydrates 5 Lipids 5.1 Fats/Triglycerides 5.1.1 Saturated versus Unsaturated fats 5.2 Phospholipids
Contents 1 Reading 2 Learning Objectives 3 How are macromolecules assembled? 4 Carbohydrates 4.1 Structural Carbohydrates 5 Lipids 5.1 Fats/Triglycerides 5.1.1 Saturated versus Unsaturated fats 5.2 Phospholipids
H 2 O. Liquid, solid, and vapor coexist in the same environment
 Water H 2 O Liquid, solid, and vapor coexist in the same environment WATER MOLECULES FORM HYDROGEN BONDS Water is a fundamental requirement for life, so it is important to understand the structural and
Water H 2 O Liquid, solid, and vapor coexist in the same environment WATER MOLECULES FORM HYDROGEN BONDS Water is a fundamental requirement for life, so it is important to understand the structural and
Micellar and Phase Transfer Catalyses
 Micellar and Phase Transfer Catalyses Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati 781039 India Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD 1/17 Table
Micellar and Phase Transfer Catalyses Dr. Pallab Ghosh Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering IIT Guwahati, Guwahati 781039 India Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD 1/17 Table
John Lenyo Corrina Perez Hazel Owens. Cell Membrane.
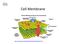 John Lenyo Corrina Perez Hazel Owens Cell Membrane http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/plasmamembrane/plasmamembrane.html Cell membranes are composed of proteins and lipids. Since they are made up of mostly
John Lenyo Corrina Perez Hazel Owens Cell Membrane http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/plasmamembrane/plasmamembrane.html Cell membranes are composed of proteins and lipids. Since they are made up of mostly
Liquid-Liquid Extraction Prof. Mukesh Doble Department Of Biotechnology Indian Institute Of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 19
 Liquid-Liquid Extraction Prof. Mukesh Doble Department Of Biotechnology Indian Institute Of Technology, Madras Lecture - 19 Liquid-Liquid Extraction Let us continue with the Liquid- Liquid Extraction.
Liquid-Liquid Extraction Prof. Mukesh Doble Department Of Biotechnology Indian Institute Of Technology, Madras Lecture - 19 Liquid-Liquid Extraction Let us continue with the Liquid- Liquid Extraction.
Membranes. Chapter 5
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Biomolecules. Unit 3
 Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membranes
 Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Acid/Base chemistry. NESA Biochemistry Fall 2001 Review problems for the first exam. Complete the following sentences
 1 NESA Biochemistry Fall 2001 eview problems for the first exam Acid/Base chemistry 1. 2 3 is a weak acid. 2. The anion of a weak acid is a weak base 3. p is the measure of a solutions acidity. 4. 3 and
1 NESA Biochemistry Fall 2001 eview problems for the first exam Acid/Base chemistry 1. 2 3 is a weak acid. 2. The anion of a weak acid is a weak base 3. p is the measure of a solutions acidity. 4. 3 and
EH1008 Biomolecules. Inorganic & Organic Chemistry. Water. Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry.
 EH1008 Biomolecules Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Inorganic & Organic Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry: generally, substances that do not contain carbon Inorganic molecules:
EH1008 Biomolecules Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Inorganic & Organic Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry: generally, substances that do not contain carbon Inorganic molecules:
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE (SF298) (Continuation Sheet)
 REPRT DCUMENTATIN PAGE (SF298) (Continuation Sheet) Key Features of the Report: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) We have synthesized a polymer that could form both unimolecular micelles and inverse micelles, depending
REPRT DCUMENTATIN PAGE (SF298) (Continuation Sheet) Key Features of the Report: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) We have synthesized a polymer that could form both unimolecular micelles and inverse micelles, depending
Coarse grained simulations of Lipid Bilayer Membranes
 Coarse grained simulations of Lipid Bilayer Membranes P. B. Sunil Kumar Department of Physics IIT Madras, Chennai 600036 sunil@iitm.ac.in Atomistic MD: time scales ~ 10 ns length scales ~100 nm 2 To study
Coarse grained simulations of Lipid Bilayer Membranes P. B. Sunil Kumar Department of Physics IIT Madras, Chennai 600036 sunil@iitm.ac.in Atomistic MD: time scales ~ 10 ns length scales ~100 nm 2 To study
Will s Pre-Test. (4) A collection of cells that work together to perform a function is termed a(n): a) Organelle b) Organ c) Cell d) Tissue e) Prison
 Will s Pre-Test This is a representative of Exam I that you will take Tuesday September 18, 2007. The actual exam will be 50 multiple choice questions. (1) The basic structural and functional unit of the
Will s Pre-Test This is a representative of Exam I that you will take Tuesday September 18, 2007. The actual exam will be 50 multiple choice questions. (1) The basic structural and functional unit of the
Biochemistry Worksheet
 Biology 138 Name Section 3.1 Properties of Water Biochemistry Worksheet 1. Why is water such an important molecule to living things? 2. Describe the chemical make up and type of bonding found in water
Biology 138 Name Section 3.1 Properties of Water Biochemistry Worksheet 1. Why is water such an important molecule to living things? 2. Describe the chemical make up and type of bonding found in water
Biological Molecules B Lipids, Proteins and Enzymes. Triglycerides. Glycerol
 Glycerol www.biologymicro.wordpress.com Biological Molecules B Lipids, Proteins and Enzymes Lipids - Lipids are fats/oils and are present in all cells- they have different properties for different functions
Glycerol www.biologymicro.wordpress.com Biological Molecules B Lipids, Proteins and Enzymes Lipids - Lipids are fats/oils and are present in all cells- they have different properties for different functions
Developing Reagents for Membrane Protein Studies
 Developing Reagents for Membrane Protein Studies Qinghai Zhang In collaboration with JCIMPT-TSRI Labs NIH Roadmap Membrane Protein Production & Technologies Meeting La Jolla, CA, USA Nov. 1-2, 2007 Detergents
Developing Reagents for Membrane Protein Studies Qinghai Zhang In collaboration with JCIMPT-TSRI Labs NIH Roadmap Membrane Protein Production & Technologies Meeting La Jolla, CA, USA Nov. 1-2, 2007 Detergents
Macromolecules. The four groups of biomolecules or macromolecules found in living things which are essential to life are: 1. PROTEINS 1.
 Macromolecules The four groups of biomolecules or macromolecules found in living things which are essential to life are: 1. PROTEINS 1. CARBOHYDRATES 1. LIPIDS 1. NUCLEIC ACIDS Carbon Compounds All compounds
Macromolecules The four groups of biomolecules or macromolecules found in living things which are essential to life are: 1. PROTEINS 1. CARBOHYDRATES 1. LIPIDS 1. NUCLEIC ACIDS Carbon Compounds All compounds
BIOCHEMISTRY. How Are Macromolecules Formed? Dehydration Synthesis or condensation reaction Polymers formed by combining monomers and removing water.
 BIOCHEMISTRY Organic compounds Compounds that contain carbon are called organic. Inorganic compounds do not contain carbon. Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent bonds with as
BIOCHEMISTRY Organic compounds Compounds that contain carbon are called organic. Inorganic compounds do not contain carbon. Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent bonds with as
Chapter 2 Transport Systems
 Chapter 2 Transport Systems The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier between the cell and the extracellular environment. It permeability properties ensure that essential molecules such as
Chapter 2 Transport Systems The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier between the cell and the extracellular environment. It permeability properties ensure that essential molecules such as
Main Functions maintain homeostasis
 The Cell Membrane Main Functions The main goal is to maintain homeostasis. Regulates materials moving in and out of the cell. Provides a large surface area on which specific chemical reactions can occur.
The Cell Membrane Main Functions The main goal is to maintain homeostasis. Regulates materials moving in and out of the cell. Provides a large surface area on which specific chemical reactions can occur.
Chemical Surface Transformation 1
 Chemical Surface Transformation 1 Chemical reactions at Si H surfaces (inorganic and organic) can generate very thin films (sub nm thickness up to µm): inorganic layer formation by: thermal conversion:
Chemical Surface Transformation 1 Chemical reactions at Si H surfaces (inorganic and organic) can generate very thin films (sub nm thickness up to µm): inorganic layer formation by: thermal conversion:
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
A. Membrane Composition and Structure. B. Animal Cell Adhesion. C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport. D. Active Transport
 Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Membranes. Chapter 5. Membrane Structure
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
Membranes & Membrane Proteins
 School on Biomolecular Simulations Membranes & Membrane Proteins Vani Vemparala The Institute of Mathematical Sciences Chennai November 13 2007 JNCASR, Bangalore Cellular Environment Plasma membrane extracellular
School on Biomolecular Simulations Membranes & Membrane Proteins Vani Vemparala The Institute of Mathematical Sciences Chennai November 13 2007 JNCASR, Bangalore Cellular Environment Plasma membrane extracellular
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Name the ester produced when methanol and pentanoic acid react. methyl pentanoate. Name the type of reaction used to make an ester
 1 Name the ester produced when methanol and pentanoic acid react methyl pentanoate 2 Name the type of reaction used to make an ester condensation reaction 3 Name the by-product of the reaction used to
1 Name the ester produced when methanol and pentanoic acid react methyl pentanoate 2 Name the type of reaction used to make an ester condensation reaction 3 Name the by-product of the reaction used to
A Novel Sulfonated Alkyl Ester Surfactant to Reduce Oil-Water Interfacial Tensions in Wide Range Salinity with Monovalent and Divalent Ions
 Modern Applied Science; Vol. 10, No. 1; 2016 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education A Novel Sulfonated Alkyl Ester Surfactant to Reduce Oil-Water Interfacial
Modern Applied Science; Vol. 10, No. 1; 2016 ISSN 1913-1844 E-ISSN 1913-1852 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education A Novel Sulfonated Alkyl Ester Surfactant to Reduce Oil-Water Interfacial
Biological Membranes. Lipid Membranes. Bilayer Permeability. Common Features of Biological Membranes. A highly selective permeability barrier
 Biological Membranes Structure Function Composition Physicochemical properties Self-assembly Molecular models Lipid Membranes Receptors, detecting the signals from outside: Light Odorant Taste Chemicals
Biological Membranes Structure Function Composition Physicochemical properties Self-assembly Molecular models Lipid Membranes Receptors, detecting the signals from outside: Light Odorant Taste Chemicals
The phosphate group replaces the fatty acid on C number 3 of a triacylglycerol molecule O O CH 2 O C R CH 2 O P O X OH.
 Phosphoacylglycerols (Phospholipids) Phosphoacylglycerols are fatty acid esters of glycerol which also contain a phosphate group and other specific groups The phosphate group replaces the fatty acid on
Phosphoacylglycerols (Phospholipids) Phosphoacylglycerols are fatty acid esters of glycerol which also contain a phosphate group and other specific groups The phosphate group replaces the fatty acid on
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2.
 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2. A possible explanation for an event that occurs in nature is
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2. A possible explanation for an event that occurs in nature is
Transport through membranes
 Transport through membranes Membrane transport refers to solute and solvent transfer across both cell membranes, epithelial and capillary membranes. Biological membranes are composed of phospholipids stabilised
Transport through membranes Membrane transport refers to solute and solvent transfer across both cell membranes, epithelial and capillary membranes. Biological membranes are composed of phospholipids stabilised
PROCEEDINGS OF THE YEREVAN STATE UNIVERSITY
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE YEREVAN STATE UNIVERSITY Physical and Mathematical Sciences 2018, 52(3), p. 217 221 P h y s i c s STUDY OF THE SWELLING OF THE PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER, DEPENDING ON THE ANGLE BETWEEN THE
PROCEEDINGS OF THE YEREVAN STATE UNIVERSITY Physical and Mathematical Sciences 2018, 52(3), p. 217 221 P h y s i c s STUDY OF THE SWELLING OF THE PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER, DEPENDING ON THE ANGLE BETWEEN THE
BIOMOLECULES. (AKA MACROMOLECULES) Name: Block:
 BIOMOLECULES (AKA MACROMOLECULES) Name: Block: BIOMOLECULES POGIL All living things share the same chemical building blocks and depend on chemical processes for survival. Life without carbon (C) would
BIOMOLECULES (AKA MACROMOLECULES) Name: Block: BIOMOLECULES POGIL All living things share the same chemical building blocks and depend on chemical processes for survival. Life without carbon (C) would
Chapter 3. Table of Contents. Section 1 Carbon Compounds. Section 2 Molecules of Life. Biochemistry
 Biochemistry Table of Contents Section 1 Carbon Compounds Section 2 Molecules of Life Section 1 Carbon Compounds Objectives Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Explain the importance of
Biochemistry Table of Contents Section 1 Carbon Compounds Section 2 Molecules of Life Section 1 Carbon Compounds Objectives Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Explain the importance of
The Carbon Atom (cont.)
 Organic Molecules Organic Chemistry The chemistry of the living world. Organic Molecule a molecule containing carbon and hydrogen Carbon has 4 electrons in its outer shell and can share electrons with
Organic Molecules Organic Chemistry The chemistry of the living world. Organic Molecule a molecule containing carbon and hydrogen Carbon has 4 electrons in its outer shell and can share electrons with
Reading for lecture 6
 Reading for lecture 6 1. Lipids and Lipid Bilayers 2. Membrane Proteins Voet and Voet, Chapter 11 Alberts et al Chapter 6 Jones, R.A.L, Soft Condensed Matter 195pp Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-850590-6
Reading for lecture 6 1. Lipids and Lipid Bilayers 2. Membrane Proteins Voet and Voet, Chapter 11 Alberts et al Chapter 6 Jones, R.A.L, Soft Condensed Matter 195pp Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-850590-6
Good Afternoon! 11/30/18
 Good Afternoon! 11/30/18 1. The term polar refers to a molecule that. A. Is cold B. Has two of the same charges C. Has two opposing charges D. Contains a hydrogen bond 2. Electrons on a water molecule
Good Afternoon! 11/30/18 1. The term polar refers to a molecule that. A. Is cold B. Has two of the same charges C. Has two opposing charges D. Contains a hydrogen bond 2. Electrons on a water molecule
Life Sciences 1a. Practice Problems 4
 Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 4 1. KcsA, a channel that allows K + ions to pass through the membrane, is a protein with four identical subunits that form a channel through the center of the tetramer.
Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 4 1. KcsA, a channel that allows K + ions to pass through the membrane, is a protein with four identical subunits that form a channel through the center of the tetramer.
Lecture-3. Water and Phospholipid
 Lecture-3 Water and Phospholipid Life on earth began in water and evolved there for three billion years before spreading onto land. Although most of the water in liquid form, it is also in solid form and
Lecture-3 Water and Phospholipid Life on earth began in water and evolved there for three billion years before spreading onto land. Although most of the water in liquid form, it is also in solid form and
Unit 1: Biochemistry
 Unit 1: Biochemistry Chapter 1: The Biochemical Basis of Life Section 1.1: The Fundamental Chemistry of Life, pp. 2 5 1. Table 1: Atomic Structure Element Symbol Atomic Number 12 carbon 6 C 6 nitrogen
Unit 1: Biochemistry Chapter 1: The Biochemical Basis of Life Section 1.1: The Fundamental Chemistry of Life, pp. 2 5 1. Table 1: Atomic Structure Element Symbol Atomic Number 12 carbon 6 C 6 nitrogen
The further from the nucleus, the higher the electron s energy Valence shell electrons participate in biological reactions
 Chemistry of Life Revision: The further from the nucleus, the higher the electron s energy Valence shell electrons participate in biological reactions Atoms exchange electrons with other elements to form
Chemistry of Life Revision: The further from the nucleus, the higher the electron s energy Valence shell electrons participate in biological reactions Atoms exchange electrons with other elements to form
Life s molecular diversity is based on the. properties of carbon. Chain Ring Branching chain
 Carbon Compounds Life s molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon Chain Ring Branching chain The Chemistry of Carbon : carbon based Carbon can make 4 covalent bonds The foundation of organic
Carbon Compounds Life s molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon Chain Ring Branching chain The Chemistry of Carbon : carbon based Carbon can make 4 covalent bonds The foundation of organic
Efficiency of Amphoteric Surfactants as Flow Improvers and Pour Point Depressants
 Journal of Power and Energy Engineering, 13, 1, 90-94 http://dx.doi.org/.4236/jpee.13.0 Published Online October 13 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jpee) Efficiency of Amphoteric Surfactants as Flow Improvers
Journal of Power and Energy Engineering, 13, 1, 90-94 http://dx.doi.org/.4236/jpee.13.0 Published Online October 13 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jpee) Efficiency of Amphoteric Surfactants as Flow Improvers
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
Basic Biochemistry. Classes of Biomolecules
 Basic Biochemistry ABE 580 Classes of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Amino Acids Nucleic Acids Other 1 Carbohydrates Sugars Composed of C, H, O (C n H 2n O n ) Biological Uses Energy source/storage
Basic Biochemistry ABE 580 Classes of Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Amino Acids Nucleic Acids Other 1 Carbohydrates Sugars Composed of C, H, O (C n H 2n O n ) Biological Uses Energy source/storage
AP BIOLOGY: READING ASSIGNMENT FOR CHAPTER 5
 1) Complete the following table: Class Monomer Functions Carbohydrates 1. 3. Lipids 1. 3. Proteins 1. 3. 4. 5. 6. Nucleic Acids 1. 2) Circle the atoms of these two glucose molecules that will be removed
1) Complete the following table: Class Monomer Functions Carbohydrates 1. 3. Lipids 1. 3. Proteins 1. 3. 4. 5. 6. Nucleic Acids 1. 2) Circle the atoms of these two glucose molecules that will be removed
9/11/18. Cell Function & Chemistry. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell
 Molecular and Cellular Biology Cell Function & Chemistry 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Interaction Molecular Bonds Define Cellular Functions Water H 2 O Interactions
Molecular and Cellular Biology Cell Function & Chemistry 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Interaction Molecular Bonds Define Cellular Functions Water H 2 O Interactions
Lipids: Fats, Oils & Waxes: AP Biology
 Lipids: Fats, Oils & Waxes: Lipids long term energy storage concentrated energy *9 Cal/gram Lipids: Triglycerides Lipids are composed of C, H, O u long hydrocarbon chains (H-C) Family groups u fats u phospholipids
Lipids: Fats, Oils & Waxes: Lipids long term energy storage concentrated energy *9 Cal/gram Lipids: Triglycerides Lipids are composed of C, H, O u long hydrocarbon chains (H-C) Family groups u fats u phospholipids
Membrane transport. Pharmacy Dr. Szilvia Barkó
 Membrane transport Pharmacy 04.10.2017 Dr. Szilvia Barkó Cell Membranes Cell Membrane Functions Protection Communication Import and and export of molecules Movement of the cell General Structure A lipid
Membrane transport Pharmacy 04.10.2017 Dr. Szilvia Barkó Cell Membranes Cell Membrane Functions Protection Communication Import and and export of molecules Movement of the cell General Structure A lipid
WHAT IS A LIPID? OBJECTIVE The objective of this worksheet is to understand the structure and function of lipids
 WHAT IS A LIPID? OBJECTIVE The objective of this worksheet is to understand the structure and function of lipids PART A: Understanding Lipids Lipids are more commonly known as fats and include triglycerides,
WHAT IS A LIPID? OBJECTIVE The objective of this worksheet is to understand the structure and function of lipids PART A: Understanding Lipids Lipids are more commonly known as fats and include triglycerides,
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
Cell membrane & Transport. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Ebneshahidi
 Cell membrane & Transport Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Cell Membrane To enclose organelles and other contents in cytoplasm. To protect the cell. To allow substances into and out of the cell. To have metabolic reactions
Cell membrane & Transport Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Cell Membrane To enclose organelles and other contents in cytoplasm. To protect the cell. To allow substances into and out of the cell. To have metabolic reactions
Unit 3: Chemistry of Life Mr. Nagel Meade High School
 Unit 3: Chemistry of Life Mr. Nagel Meade High School IB Syllabus Statements 3.2.1 Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. 3.2.2 Identify amino acids, glucose, ribose and fatty acids from
Unit 3: Chemistry of Life Mr. Nagel Meade High School IB Syllabus Statements 3.2.1 Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. 3.2.2 Identify amino acids, glucose, ribose and fatty acids from
Molecules of Life. Chapter 22. Great Idea: A cell s major parts are constructed from a few simple molecular building blocks 1
 Molecules of Life Chapter 22 Great Idea: A cell s major parts are constructed from a few simple molecular building blocks 1 Chapter Outline Organic Molecules Organic Chemistry Proteins: The Workhorses
Molecules of Life Chapter 22 Great Idea: A cell s major parts are constructed from a few simple molecular building blocks 1 Chapter Outline Organic Molecules Organic Chemistry Proteins: The Workhorses
1. Describe the difference between covalent and ionic bonds. What are the electrons doing?
 Exam 1 Review Bio 212: 1. Describe the difference between covalent and ionic bonds. What are the electrons doing? 2. Label each picture either a Carbohydrate, Protein, Nucleic Acid, or Fats(Lipid). a.
Exam 1 Review Bio 212: 1. Describe the difference between covalent and ionic bonds. What are the electrons doing? 2. Label each picture either a Carbohydrate, Protein, Nucleic Acid, or Fats(Lipid). a.
Biology. Membranes.
 1 Biology Membranes 2015 10 28 www.njctl.org 2 Vocabulary active transport carrier protein channel protein concentration gradient diffusion enzymatic activity facilitated diffusion fluid mosaic hypertonic
1 Biology Membranes 2015 10 28 www.njctl.org 2 Vocabulary active transport carrier protein channel protein concentration gradient diffusion enzymatic activity facilitated diffusion fluid mosaic hypertonic
Chem Lecture 8 Lipids and Cell Membranes
 Chem 452 - Lecture 8 Lipids and Cell Membranes 111114 Like carbohydrates, lipids are one of the four major classes of biomolecules, which also include the proteins, carbohydrates and nucleic acids. Lipids
Chem 452 - Lecture 8 Lipids and Cell Membranes 111114 Like carbohydrates, lipids are one of the four major classes of biomolecules, which also include the proteins, carbohydrates and nucleic acids. Lipids
7/11/17. Cell Function & Chemistry. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell
 Molecular and Cellular Biology Cell Function & Chemistry 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Interaction Molecular Bonds Define Cellular Functions Water H 2 O Interactions
Molecular and Cellular Biology Cell Function & Chemistry 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Interaction Molecular Bonds Define Cellular Functions Water H 2 O Interactions
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE. Lecture 8. Biology Department Concordia University. Dr. S. Azam BIOL 266/
 1 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 8 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Plasma Membrane 2 Plasma membrane: The outer boundary of the cell that separates it from the world
1 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 8 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Plasma Membrane 2 Plasma membrane: The outer boundary of the cell that separates it from the world
Biochemistry. 2. Besides carbon, name 3 other elements that make up most organic compounds.
 Biochemistry Carbon compounds Section 3-1 1. What is an organic compound? 2. Besides carbon, name 3 other elements that make up most organic compounds. 3. Carbon dioxide, CO 2, is NOT an organic compound.
Biochemistry Carbon compounds Section 3-1 1. What is an organic compound? 2. Besides carbon, name 3 other elements that make up most organic compounds. 3. Carbon dioxide, CO 2, is NOT an organic compound.
