RESEARCH COMMUNICATION TISSUE CULTURE STUDIES ON A SUSPECTED LYSOSOMAL STORAGE DISEASE IN ABYSSINIAN CATS
|
|
|
- Joanna McBride
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Onderstepoort f. vet. Res., 47, (1980) RESEARCH COMMUNICATION TISSUE CULTURE STUDIES ON A SUSPECTED LYSOSOMAL STORAGE DISEASE IN ABYSSINIAN CATS A. LUClA LANGE, Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Pretoria, P.O. Box 12580, Onderstepoort 0110 ABSTRACT LANGE, A. LUCIA., Tissue culture studies on a suspected lysosomal storage disease in Abyssinian cats. Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 47, (1980). Cell cultures prepared from the spleen and mesenteric lymph nodes of affected kit!ens were subjected to histochemical and ultrastructural studies. Macrophages m the. cultures contau;te~ hp~d in the cytoplasm and the ultrastructural studies revealed lysosomes contammg lamellae Similar m appearance to phospholipids. Resume ETUDES DE CULTURES DE T!SSUS SUR UN MALAD! LYSOSOM!AL D'EMMAGA SINAGE CHEZ LES CHATS ABYSSINIENS Des cultures de cellules pn!parees a partir de Ia rate et des gang/ions lymphatiques mesenterique de chatons affectes ont ere soumises a des etudes histochimiques et a microscopie electronique. L~s macrophages dans les cultures contenaient du lipide dans le cytoplasme et des etudes en mzcroscop1~ electronique revelerent des lysosomes contenant des lamellae simi/aires en apparence aux phosphoilpides. INTRODUCTION Lange, Bland van den Berg & Baker ( 1977) described a suspected lysosomal storage disease in Abyssinian cats, a disease characterized clinically by incoordination, body tremors and sometimes seizures. It was also found to be genetic, with an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance (Bland van den Berg, Baker & Lange, 1977). Histological lesions included vacuolization of neurones and macrophages, and an ultrastructural examination of these cells showed lamella ted membranous cytoplasmic bodies (Lange eta!., 1977). At the time, the nature of the stored substance in lysosomes could not be determined in formalin-fixed and frozen sections. In an attempt to identify the substance, spleen and lymph node cells of affected kittens were cultured and subjected to histochemical and ultrastructural studie. MATERIALS AND METHODS At various times S affected kittens were killed by the intravenous administration of an overdosage of pentobarbitone sodium. The spleen and mesenteric lymph nodes were removed aseptically within minutes of the kittens being killed. The spleen and lymph nodes were cut into small pieces and the excess blood rinsed off with a calcium- and magnesium-free phosphate-buffered saline solution (PBS) to which penicillin at a concentration of units/f and 200 mg streptomycin/f had been added. The tissues were then stirred in the above solution for 30 minutes and the fluid decanted. The spleen and lymph node tissue were trypsinized in a 0,25% trypsin* solution for 1 hour and the cell suspension centrifuged at 200 rpm. The supernatant was removed and the cells were placed in 30 mf disposable tissue culture flasks containing Hanks-Eagle's medium** to which 10% inactivated bovine serum and I,5 gm/f sodium bicarbonate had been added. The flasks were incubated for 24 hours at 37 oc and the medium was *Trypsin 1 : 250. Difco Laboratories, Detroit, Michigan, USA **50% Hanks balanced salt solution plus 50% Eagle's Minimal Essential Medium Received 11 March 1980-Editor subsequently decanted and the culture~ washed ~w.ice in phosphate buffered saline. Fresh medmm contammg serum was replaced in the flasks which were then returned to the incubator. Daily, after 4-6 days incubation, individual fla~ks were removed from the incubator and the followmg procedures carried out: (i) The medium from a flask was decanted and the cells fixed to the wall o ; the flask by adding Bouin's fixative. After 60 minutes the cells in the flasks were stained with the haematoxylin and eosin (HE), oilred-o (Anon., 1968) and Sudan IV (Lillie, 1944) methods. The top and sides of the flasks were removed and the stained cultures were then examined with the light microscope. (ii) The other flasks containing 4-6-day-old cultures were prepared for electron microscopy. The m~diu~ was decanted and the cultures were washed twice m PBS. The cells were removed with the aid of a trypsin versene solution* and centrifuged for 3 minutes at rpm. The supernatant was removed, the cells fixed in 2% gluteraldehyde in Millonig's phosphate buffer (ph 7,2-7,4) for 1 hour at 4 C, washed on~e in the same buffer and post-fixed for a further hour m 2% osmium tetroxide. This was followed by 2 more washes in buffer, after gentle centrifugation and a resuspension of cellular material. After the final wash, the cells were re-suspended in a small quant!t~ of buffer solution and drawn into non-hepanmzed micro-haematocrit tubes. The tubes were sealed and centrifuged at high speed to create a plug of compressed cellular material. The plugs were removed from the tubes, cut into small blocks with a sharp blade, dehydrated in ethanol and propylene oxide and em bedded in Epon 812 in gelatin capsules for 48 hours at 60 oc. Gold and silver sections were cut with a glass knife on a Reichert OMU 4 Ultracut ultramicrotome, stained in 1% uranyl acetate for 10 minutes and 0,2% lead citrate for 30 seconds and examined in a Philips EM 301 electron microscope. (iii) Semi-thin sections were cut from the ab.ove blocks and stained with toluidine blue for exammation with the light microscope. * 1 % Trypsin and 0, 4% versene solution 121
2 TISSUE CULTURE STUDIES ON A SUSPECTED LYSOSOMAL STORAGE DISEASE IN ABYSSINIAN CATS Normal feline lung tissue cultures, 4-6 days old were fixed and stained for light microscopy as described above. RESULTS Light microscopy Cell culture from affected kittens The growth of the spleen and lymph node cell cultures varied considerably, though on the whole the cultures of the spleen grew much better than those of the lymph nodes. Two distinct growth phases were noticed in these cultures. In the 4-day-old cultures there were a few fibroblast-like cells which were ove_rlaid by many large macrophage-like cells. The m.:tcrophage-like cells had large vesicular nuclei with 1 or sometimes 2 distinct nucleoli. The cells were usually rounded, but sometimes amoeboid-like projec i )ns were present In cultures stained with HE the cytoplasm of the macrophage-like cells was filled with numerous round to oval reddish-pink "globules" which varied in size from very small to almost the size of the nucleus (Fig. 3). These cytoplasmic structures stained orange-red to dark-red with the oilred-o staining method (Fig. 2 & 3), while they stained less intensely with the Sudan IV method. The cytoplasm of the macrophages was filled with many fine granular structures. A few macrophages showed, in addition, a small number of large yellowish-red structures interspersed between the granules (Fig. 4). The second growth phase was observed in the 6-dayold cultures. The fibroblast-like cell> predominated, but a few macrophage-like c:lls, similar to those described in the 4-day-old cultures, were still preeent. In the older cultures some of these cells showed distinct degenerative changes; the nuclei were small and pyknotic and the plasma membrane of some appeared to have ruptured. Feline lung cell cultures After 4 days the flasks had an even growth of fibroblast-like cells which were of the same size and had very large vesicular nuclei with distinct nucleoli. Many of the cells had mitotic figures and some cells were in telophase. The cytoplasm was stellate in shape and only a few small, light-pink granules were seen in the cells stained with HE. These granules were an even red colour with oil-red-o (Fig. 1) and orange with Sudan IV stains. Semi-thin sections stained with toluidine blue Most of the cells in the pellets prepared for electron microscopy appeared to be macrophages with a round cytoplasm and a few cytoplasmic projections. The cytoplasm contained structures which varied in morphology with the age of the cultures from which they were prepared. Most of the cells from the 4-day-old cultures had small, uniformly round structures in the cytoplasm, which stained navy blue. A few cells from t 1e 4-day-old cultures and more from the 5-day-old cultures had, in addition, round structures of varying size in the cytoplasm. These stained metachromatically with toluidine blue. Furthermore, many of the macrophages in the 6-day-old cultures contained empty vacuoles of varying sizes in the cytoplasm in addition to the navy blue and metachromatic granules. Ultrastructure All the cells examined were round, probably due to the trypsinization pro.:ess required to release them from the tissue culture flasks. These cells appreared to be of 2 basic types: some had very large nuclei and a relatively small cytoplasm which, in addition to the usual cytoplasmic organelles, had a few lipid-lysosomes. These lysosomes were surrounded by a single membrane and had a uniform light grey colour. These cells probably correspond to the fibroblast-like cells mentioned earlier. The other cells, to be described below, were similar to the macrophage-like cells found in the tissue cultures and had lipid-containing lysosomes as well as lamellated membranous cytoplasmic bodies which varied in size and shape (Fig. 5). The lamellae were irregularly spaced and in some there were small electron-lucent areas where the lamellae appeared to have drawn apart or disintegrated. Other cells had lysosomes that were dark-grey in colour and were smaller and more abundant than those described above (Fig. 6). In these cells there were also distinct secondary lysosomes which were surrounded by a trilaminar membrane and which contained regularly spaced lamellae, giving an onion-ring appearance (Fig. 7). Cells with these structures were most common in the 4-day-old tissue cultures. In other macrophage-like cells the regularly lamellated structures had fused to form larger irregular bodies with lamellae in different stages of formation and disintegration surrounded by a trilaminar membrane (Fig. 8). In some of these bodies there were areas of a uniform grey colour partially encapsulated by regular lamellae (Fig. 9). Distinct lamellated patterns may be present in the same body. Vacuoles of different sizes containing a few remnants of lamellae in an electron-lucent background were present in other similar membranous cytoplasmic bodies (Fig. 9). Cells with these bodies were more abundc:nt in the 5- and 6-day-old cultures. In addition to the cells described above, there were also cells with the following characteristic appearance: light-grey lysosomes in the cytoplasm and numerous electron-dense, round, lamellated structures of different sizes in which the lamellae were interspersed with a homogeneous electron-lucent, and a light grey granular substance (Fig. l 0). This entire structure (lamellae, electronlucent and light-grey granular substance) was enclosed in a trilaminar membrane (Fig. 11 & 12). In these cells the other cytoplasmic organelles appeared to be affected by degenerative changes. The granular endoplasmic reticulum was dilated and the mitochondria had disappeared from some cells. The nuclei of some of these cells also appeared to have degenerated. DISCUSSION Lange et a/. (1977) described macrophages and neurons with vacuoles in the cytoplasm but the nature of the substance in the vacuoles could not be determined by histochemical methods. In this study, structures present in the cytoplasm of cultured macrophage-like cells stained positive for lipids with oil-red-o and Sudan IV. Lung cell cultures from normal cats were examined simultaneously with the macrophage cultures to determine the amount of lipid present in them. The fibroblast-like cells in these control cultures contained a few lipid droplets, but these were much smaller and stained more evenly than the lipid accumulated in the lysosomes of the macrophage-like cells from affected kittens. Ultrastructural examination of the cell cultures revealed structures similar to those described previously in the tissues of cats suffering from this disease (Lange eta/., 1977). 122
3 FIG. 1 Normal lung cell culture, 4 days old. Oil-red-O; x 800 FIG. 2 Four-day-old spleen tissue culture from an affected kitten. Oil-red-O positive material in the cytoplasm of a macrophage-like cell; Oil-red-O x 800 FIG. 3 Four-day-old spleen tissue culture from an affected kitten. Oil-red-O positive structures of varying size in the cytoplasm of macrophage" like cells; Oil-red-O x FIG. 4 Six-day-old spleen tissue culture from an affected kitten. One large macrophage-like cell with Sudan IV positive material in the cytoplasm; Sudan IV x 2 000
4 A. LUCIA LANGE FIG. 5 A macrophage-like cell from a 4-day-old lymph node tissue culture from an affected kitten. The cytoplasm contains large, light-grey, lipid-containing lysosomes and lamellated membranous cytoplasmic bodies; X FIG. 6 A macrophage-like cell with many dark-grey lysosomes as well as secondary lysosomes with a lamellated appearance (A); X
5 TISSUE CULTURE STUDIES ON A SUSPECTED LYSOSOMAL STORAGE DISEASE IN ABYSSINIAN CATS FIG. 7 A membranous cytoplasmic body surrounded by a trilaminar membrane and containing regularly spaced lamellae; x FIG. 8 A macrophage-like cell illustrating fusion of regularly lamellated structures to form large irregular bodies; x
6 A. LUCIA LANGE FIG. 9 A macrophage-like cell from 5-day-old spleen tissue culture, with large membranous cytoplasmic bodies. Small vacuolated structures surrounded by regular lamellae can also be seen; x FIG. 10 A cell from a 6-day-old spleen tissue culture containing light-grey lipid lysosomes and numerous electron-dense, round, lamellated structures of different sizes. The lamellae are interspersed with a homogeneous electron-lucent and a light-grey granular substance; x
7 TISSUE CULTURE STUDIES ON A SUSPECTED LYSOSOMAL STORAGE DISEASE IN ABYSSINIAN CATS FIG. 11 & 12 Cytoplasmic structures with electron-dense lamellated areas interspersed with electron-lucent and light-grey granular substance. These structures as a whole are surrounded by a trilaminar membrane; x and x
8 A. LUCIA LANGE Light microscopic examination of semi-thin sections stained with toluidine blue revealed the sequential development of the cytoplasmic structures in the macrophages. In the 4-day-old cultures the cell cytoplasm contained small uniformly round navy blue granules, while in the 5-day-old cultures uneven round metachromatic structures were present. In the 6-dayold cultures both these structures were present to a lesser extent, and there were also empty round vacuoles in the cytoplasm. Ultrastructural studies confirmed this pattern of development. Cells in the 4-day-old cultures had lipid-lysosomes in the cytoplasm. In the 5-day-old cultures cells with dark-grey lysosomes were more numerous and more conspicuous than in the former cells. It was also in these cells that the regularly lamellated structures became visible (Fig. 6 & 7). These lysosomes probably correspond to the navy blue granules in the cells of the toluidine blue stained 4- and 5-day-old cultures. As the cells matured, the lamellated membranous bodies fused and started showing signs of disintegration (Fig. 8). At this stage the cells would be comparable to the metachromatic granules mentioned above, since they consist of substances with different electron density. Most of the cells in the 6-day-old cultures had numerous rounded electron-dense lamellated structures of different sizes in the cytoplasm (Fig. 9 & 10). Some of these lamellated bodies appeared dilated and sometimes round electron-lucent areas were seen in these structures. This could be correlated with the vacuoles seen in the cells of 6-day-old cultures stained with toluidine blue. Similar structures were found by Aubert-Tulkens, Van Hoof & Tulkens (1979), when lysosomal phospholipidosis was induced by gentamicin in cultured rat fibroblasts. The histochemical results and ultrastructural studies of affected cells indicate that the storage disease of Abyssinian cats under investigation is caused by an enzyme deficiency which results in the accumulation of lipid in lysosomes. When the ultrastructural appearance of the lysosomes is compared with those described by Aubert-Tulkens eta!. (1979), it would appear that the accumulated lipid could be a phospholipid, but final confirmation of this can only be obtained by biochemical analyses. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I am much indebted to the technical staff of the Departments of Pathology and Infectious Diseases for their able assistance, to Messrs A. M. du Bruyn, J. Soley and R. Watermeyer for the photography and to Professors R. C. Tustin and P. G. Howell and Dr A. J. M. Verster for reading the manuscript. Mrs V. K. A. Kaber is thanked for typing the manuscript. This study was supported by a grant from the University of Pretoria. REFERENCES ANON., Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. Manual of histologic staining methods. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw Hill. AUBERT-TULKENS, G., VAN HOOF, F. & TULKENS, P., Gentamicin-induced lysosomal phospholipidosis in cultured rat fibroblasts. Quantitative, ultrastructural and biochemical study. Laboratory Investigation, 40, BLAND VAN DEN BERG, P., BAKER, MAUREEN K. & LANGE, A. LUCIA, A suspected lysosomal storage disease in Abyssinian cats. Part I. Genetic, clinical and clinical pathological aspects. Journal of the South African Veterinary Association, 48, LANGE, A. LUCIA, BLAND VAN DEN BERG, P. & BAKER, MAUREEN K., A suspected lysosomal storage disease in Abyssinian cats. Part II. Histopathological and ultrastructural aspects. Journal of the South African Veterinary Association, 48, LILLIE, R. D., Study of certain oil-soluble dyes for use as fat stains. Journal of Technical Methods, 24,
Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*)
 Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
Intercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida
 JouRNAL OF BAcTEROLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 1139-1143 Vol. 123, No. 3 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ntercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida K. R. JOSH, J. B. GAVN,*
JouRNAL OF BAcTEROLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 1139-1143 Vol. 123, No. 3 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ntercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida K. R. JOSH, J. B. GAVN,*
Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich)
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS
 Onderstepoort]. vet. Res. 40 (2), 53-58 (1973) ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS G. LECATSAS, B. J. ERASMUS and H. J. ELS, Veterinary Research Institute, Onderstepoort ABSTRACT
Onderstepoort]. vet. Res. 40 (2), 53-58 (1973) ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS G. LECATSAS, B. J. ERASMUS and H. J. ELS, Veterinary Research Institute, Onderstepoort ABSTRACT
Acid phosphatase activity in the neutral red granules of mouse exocrine pancreas cells
 343 Acid phosphatase activity in the neutral red granules of mouse exocrine pancreas cells By JENNIFER M. BYRNE (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology, University Museum, Oxford) With
343 Acid phosphatase activity in the neutral red granules of mouse exocrine pancreas cells By JENNIFER M. BYRNE (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology, University Museum, Oxford) With
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS*
 Onderstepoort J. vet. Res. (1968), 35 (1), 139-150 Printed in the Repub. of S. Afr. by The Government Printer, Pretoria ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS* G. LECATSAS, Veterinary
Onderstepoort J. vet. Res. (1968), 35 (1), 139-150 Printed in the Repub. of S. Afr. by The Government Printer, Pretoria ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS* G. LECATSAS, Veterinary
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
ataxia, head tremors and mild inappentence, was given palliative care
 2013-5-2 Cerebellum, Spleen-Raccoon Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION :College of Veterinary Medicine UC Davies Signalment: Wild-caught juvenile male raccoon, ( Procyon lotor)
2013-5-2 Cerebellum, Spleen-Raccoon Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION :College of Veterinary Medicine UC Davies Signalment: Wild-caught juvenile male raccoon, ( Procyon lotor)
CELLS CONTAINING LANGERHANS GRANULES IN HUMAN LYMPH NODES OF DERMATOPATHIC LYMPHADENOPATHY*
 THS JOURNAL OF INVEBTIOATIVR DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 93, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. CELLS CONTAINING LANGERHANS GRANULES IN HUMAN LYMPH NODES OF DERMATOPATHIC LYMPHADENOPATHY*
THS JOURNAL OF INVEBTIOATIVR DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 93, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. CELLS CONTAINING LANGERHANS GRANULES IN HUMAN LYMPH NODES OF DERMATOPATHIC LYMPHADENOPATHY*
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Heyam Awad
 number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
(From The Rockefeller Institute) Materials and Methods. Observations with the Electron Microscope
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE
 ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE by D. L. Lee ABSTRACT Infective stage larvae of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis are immobilized within
ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE by D. L. Lee ABSTRACT Infective stage larvae of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis are immobilized within
ALAEZI CM 1 *, ADISA JO 2, OKOROCHI EC 3 and OKECHI OO 4
 Global Journal of Scientific Researches Available online at gjsr.blue-ap.org 2014 GJSR Journal. Vol. 2(2), pp. 51-55, 28 February, 2014 E-ISSN: 2311-732X METHYL GREEN PYRONIN: A PROGRESSIVE NUCLEAR STAIN
Global Journal of Scientific Researches Available online at gjsr.blue-ap.org 2014 GJSR Journal. Vol. 2(2), pp. 51-55, 28 February, 2014 E-ISSN: 2311-732X METHYL GREEN PYRONIN: A PROGRESSIVE NUCLEAR STAIN
7'cA 5P 'Z /' IA.N 5 '7S abra'ry TECHNiCAL F:-'.. THE INSTITUTE OF PAPER CHEMISTRY, APPLETON, WISCONSIN IPC TECHNICAL PAPER SERIES NUMBER 16
 7'cA 5P 'Z /' IA.N 5 '7S abra'ry TECHNiCAL F:-'.. THE INSTITUTE OF PAPER CHEMISTRY, APPLETON, WISCONSIN IPC TECHNICAL PAPER SERIES NUMBER 16 DIFFERENTIATION OF TANNIN, LIPID, AND STARCH IN CULTURED PLANT
7'cA 5P 'Z /' IA.N 5 '7S abra'ry TECHNiCAL F:-'.. THE INSTITUTE OF PAPER CHEMISTRY, APPLETON, WISCONSIN IPC TECHNICAL PAPER SERIES NUMBER 16 DIFFERENTIATION OF TANNIN, LIPID, AND STARCH IN CULTURED PLANT
Title. Author(s)SONODA, Mitsuo; KOBAYASHI, Kosaku. CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 18(3): 125- Issue Date DOI. Doc URL.
 Title PLASMACYTOID CELLS OF CANINE PERIPHERAL BLOOD IN ELE Author(s)SONODA, Mitsuo; KOBAYASHI, Kosaku CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 18(3): 125- Issue Date 1970-09 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.18.3.125
Title PLASMACYTOID CELLS OF CANINE PERIPHERAL BLOOD IN ELE Author(s)SONODA, Mitsuo; KOBAYASHI, Kosaku CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 18(3): 125- Issue Date 1970-09 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.18.3.125
STUDIES OF THE HUMAN UNFERTILIZED TUBAL OVUM*t
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright @ 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, No.8, August 1973 Printed in U.S.A. STUDIES OF THE HUMAN UNFERTILIZED TUBAL OVUM*t C. NORIEGA, M.D., AND C. OBERTI, M.D.
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright @ 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, No.8, August 1973 Printed in U.S.A. STUDIES OF THE HUMAN UNFERTILIZED TUBAL OVUM*t C. NORIEGA, M.D., AND C. OBERTI, M.D.
Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells. Special Reference to the Well-Developed Agranular Endoplasmic Reticulum
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Biol110L-Cell Biology Lab Spring Quarter 2012 Module 1-4 Friday April 13, 2012 (Start promptly; work fast; the protocols take ~4 h)
 Biol110L-Cell Biology Lab Spring Quarter 2012 Module 1-4 Friday April 13, 2012 (Start promptly; work fast; the protocols take ~4 h) A. Microscopic Examination of the Plasma Membrane and Its Properties
Biol110L-Cell Biology Lab Spring Quarter 2012 Module 1-4 Friday April 13, 2012 (Start promptly; work fast; the protocols take ~4 h) A. Microscopic Examination of the Plasma Membrane and Its Properties
Epstein-Barr Virus: Stimulation By 5 '-Iododeoxy uridine or 5 '-Brom odeoxy uridine in Human Lymphoblastoid Cells F ro m a Rhabdom yosarcom a*
 A n n a ls o f C l i n i c a l L a b o r a t o r y S c i e n c e, Vol. 3, No. 6 Copyright 1973, Institute for Clinical Science Epstein-Barr Virus: Stimulation By 5 '-Iododeoxy uridine or 5 '-Brom odeoxy
A n n a ls o f C l i n i c a l L a b o r a t o r y S c i e n c e, Vol. 3, No. 6 Copyright 1973, Institute for Clinical Science Epstein-Barr Virus: Stimulation By 5 '-Iododeoxy uridine or 5 '-Brom odeoxy
New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis
 J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
Lysosomes. Gr: lysis solution, soma body. Membrane bounded vesicles. Usually round ovoid or irregular electron dense bodies m.
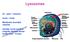 Lysosomes Gr: lysis solution, soma body Membrane bounded vesicles Usually round ovoid or irregular electron dense bodies 0.05 0.5 m. Lysosomes No. varies from a few to several hundred per cell, in different
Lysosomes Gr: lysis solution, soma body Membrane bounded vesicles Usually round ovoid or irregular electron dense bodies 0.05 0.5 m. Lysosomes No. varies from a few to several hundred per cell, in different
Basophilic. Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue
 Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
and glycoprotein in human bronchial glands
 Thorax, 1981, 36, 108-115 Ultrastructural localisation of lactoferrin and glycoprotein in human bronchial glands DENISE BOWES, A E CLARK, AND B CORRIN From Midhurst Medical Research Institute, Midhurst,
Thorax, 1981, 36, 108-115 Ultrastructural localisation of lactoferrin and glycoprotein in human bronchial glands DENISE BOWES, A E CLARK, AND B CORRIN From Midhurst Medical Research Institute, Midhurst,
Laboratory diagnosis of parasitic diseases. (Amoebiasis)
 Laboratory diagnosis of parasitic diseases (Amoebiasis) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University This document contains materials modified or
Laboratory diagnosis of parasitic diseases (Amoebiasis) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University This document contains materials modified or
PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
Exercise 6. Procedure
 Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF MELANIN-PHAGOCYTOSIS BY CUTANEOUS VESSELS IN CELLULAR BLUE NEVUS*
 THE JOURNAL 05' INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkinl Co. Vol. 62, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF MELANIN-PHAGOCYTOSIS BY CUTANEOUS VESSELS IN CELLULAR
THE JOURNAL 05' INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkinl Co. Vol. 62, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF MELANIN-PHAGOCYTOSIS BY CUTANEOUS VESSELS IN CELLULAR
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1
 ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ab CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit
 ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
COMPARATIVE DISTRIBUTION OF CARBOHYDRATES AND LIPID DROPLETS IN THE GOLGI APPARATUS OF INTESTINAL ABSORPTIVE CELLS
 COMPARATIVE DISTRIBUTION OF CARBOHYDRATES AND LIPID DROPLETS IN THE GOLGI APPARATUS OF INTESTINAL ABSORPTIVE CELLS JEAN A. SAGE and RALPH A. JERSILD, JR. Medical Center, Indianapolis, Indiana 46202 From
COMPARATIVE DISTRIBUTION OF CARBOHYDRATES AND LIPID DROPLETS IN THE GOLGI APPARATUS OF INTESTINAL ABSORPTIVE CELLS JEAN A. SAGE and RALPH A. JERSILD, JR. Medical Center, Indianapolis, Indiana 46202 From
IT has been shown (Chou, 1957 a, b) that there are three kinds of lipid
 279 The Ultra-fine Structure of Lipid Globules in the Neurones of Helix aspersa By J. T. Y. CHOU and G. A. MEEK (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology; and Department of Human Anatomy,
279 The Ultra-fine Structure of Lipid Globules in the Neurones of Helix aspersa By J. T. Y. CHOU and G. A. MEEK (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology; and Department of Human Anatomy,
Evaluation of Chromatin Clumping and Myelination of the Spinal Cord of Pigs with Congenital Tremor
 Vet. Pathol. 12: 1-5 (1975) Evaluation of Chromatin Clumping and Myelination of the Spinal Cord of Pigs with Congenital Tremor C.H. LAMAR and D.C. VAN SICKLE School of Veterinary Medicine, Purdue University,
Vet. Pathol. 12: 1-5 (1975) Evaluation of Chromatin Clumping and Myelination of the Spinal Cord of Pigs with Congenital Tremor C.H. LAMAR and D.C. VAN SICKLE School of Veterinary Medicine, Purdue University,
FINE STRUCTURE STUDY OF POLLEN DEVELOPMENT IN HAEMANTHUS KATHERINAE BAKER
 J. Cell Sci. 8, 289-301 (1971) 289 Printed in Great Britain FINE STRUCTURE STUDY OF POLLEN DEVELOPMENT IN HAEMANTHUS KATHERINAE BAKER I. FORMATION OF VEGETATIVE AND GENERATIVE CELLS JEAN M. SANGER AND
J. Cell Sci. 8, 289-301 (1971) 289 Printed in Great Britain FINE STRUCTURE STUDY OF POLLEN DEVELOPMENT IN HAEMANTHUS KATHERINAE BAKER I. FORMATION OF VEGETATIVE AND GENERATIVE CELLS JEAN M. SANGER AND
Contributions to Anatomic Pathology, over the years
 Contributions to Anatomic Pathology, over the years Anatomic Pathology, part 1 G.B. Morgagni Xavier Bichat Rudolf Wirchow Anatomic Pathology, part 1 Anatomic pathology materials: morphological samples
Contributions to Anatomic Pathology, over the years Anatomic Pathology, part 1 G.B. Morgagni Xavier Bichat Rudolf Wirchow Anatomic Pathology, part 1 Anatomic pathology materials: morphological samples
Microscopic Examination of Urine
 Download http://www.vetlab.com/kova.htm Definition of urine sediment: all solid materials suspended in the urine - a semiquantative evaluation of the urine sediment Significance of formed elements in the
Download http://www.vetlab.com/kova.htm Definition of urine sediment: all solid materials suspended in the urine - a semiquantative evaluation of the urine sediment Significance of formed elements in the
AN ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE STARCH-CONTAINING PLASTIDS IN THE FERN TODEA BARBARA
 J. Cell Sci. 4, 211-221 (1969) 211 Printed in Great Britain AN ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE STARCH-CONTAINING PLASTIDS IN THE FERN TODEA BARBARA H. M. SMITH* AND D. S. SMITHf Department of Biology,
J. Cell Sci. 4, 211-221 (1969) 211 Printed in Great Britain AN ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE STARCH-CONTAINING PLASTIDS IN THE FERN TODEA BARBARA H. M. SMITH* AND D. S. SMITHf Department of Biology,
A Histological and Histochemical Study of the Brown and Yellow Adipose Tissue of the Bat, Hipposideros speoris
 369 A Histological and Histochemical Study of the Brown and Yellow Adipose Tissue of the Bat, Hipposideros speoris By J. C. GEORGE and J. EAPEN {From the Laboratories of Animal Physiology and Histochemistry,
369 A Histological and Histochemical Study of the Brown and Yellow Adipose Tissue of the Bat, Hipposideros speoris By J. C. GEORGE and J. EAPEN {From the Laboratories of Animal Physiology and Histochemistry,
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Electron Microscope Studies of HeLa Cells Infected with Herpes Virus
 244 STOKER, M. G. P., SMITH, K. M. & Ross, R. W. (1958). J. gen. Microbiol. 19,244-249 Electron Microscope Studies of HeLa Cells Infected with Herpes Virus BY M: G. P. STOKER, K. M. SMITH AND R. W. ROSS
244 STOKER, M. G. P., SMITH, K. M. & Ross, R. W. (1958). J. gen. Microbiol. 19,244-249 Electron Microscope Studies of HeLa Cells Infected with Herpes Virus BY M: G. P. STOKER, K. M. SMITH AND R. W. ROSS
Morphogenesis of the residual body of the mouse testis
 93 Morphogenesis of the residual body of the mouse testis By CASIMIR F. FIRLIT and JOSEPH R. DAVIS (From the Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Stritch School of Medicine, and Graduate School,
93 Morphogenesis of the residual body of the mouse testis By CASIMIR F. FIRLIT and JOSEPH R. DAVIS (From the Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Stritch School of Medicine, and Graduate School,
Cell Physiology
 Cell Physiology 21-10-2018 1 The two major parts of a typical cell are the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane, and the cytoplasm is separated from
Cell Physiology 21-10-2018 1 The two major parts of a typical cell are the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane, and the cytoplasm is separated from
POLLEN-WALL PROTEINS: ELECTRON- MICROSCOPIC LOCALIZATION OF ACID PHOSPHATASE IN THE INTINE OF CROCUS VERNUS
 J. Cell Sci. 8, 727-733 (197O 727 Printed in Great Britain POLLEN-WALL PROTEINS: ELECTRON- MICROSCOPIC LOCALIZATION OF ACID PHOSPHATASE IN THE INTINE OF CROCUS VERNUS R.B. KNOX* AND J. HESLOP-HARRISONf
J. Cell Sci. 8, 727-733 (197O 727 Printed in Great Britain POLLEN-WALL PROTEINS: ELECTRON- MICROSCOPIC LOCALIZATION OF ACID PHOSPHATASE IN THE INTINE OF CROCUS VERNUS R.B. KNOX* AND J. HESLOP-HARRISONf
Initially, the patients did not receive extra vitamin E except for a very
 EFFECT OF VITAMIN E ON MEMBRANES OF THE INTESTINAL CELL BY I. MOLENAAR, F. A. HOMMES, W. G. BRAAMS, AND H. A. POLMAN CENTER FOR MEDICAL ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AND DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS, UNIVERSITY OF GRONINGEN,
EFFECT OF VITAMIN E ON MEMBRANES OF THE INTESTINAL CELL BY I. MOLENAAR, F. A. HOMMES, W. G. BRAAMS, AND H. A. POLMAN CENTER FOR MEDICAL ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AND DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS, UNIVERSITY OF GRONINGEN,
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
FOCUS SubCell. For the Enrichment of Subcellular Fractions. (Cat. # ) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
 169PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name FOCUS SubCell For the Enrichment of Subcellular Fractions (Cat. # 786 260) think
169PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name FOCUS SubCell For the Enrichment of Subcellular Fractions (Cat. # 786 260) think
Blood: Functions. Liquid connective tissue 3 general functions 1. Transportation. 2. Regulation. 3. Protection
 Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
Blood Elements Lecture Objectives List blood components. Classify formed elements of blood. Discuss the scientific basis of the above classification. Describe the basic structure of erythrocytes and criteria
Lipid Histochemistry of Surgically Resected Adrenal. Glands in Hyperadrenocorticism
 Lipid Histochemistry of Surgically Resected Adrenal Glands in Hyperadrenocorticism Hideo TSUCHIYAMA Department of Pathology, Nagasaki University School of Medicine, Nagasaki Recently, fresh adrenal tissue
Lipid Histochemistry of Surgically Resected Adrenal Glands in Hyperadrenocorticism Hideo TSUCHIYAMA Department of Pathology, Nagasaki University School of Medicine, Nagasaki Recently, fresh adrenal tissue
Blood Cells. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Blood Cells Dr. Sami Zaqout Blood Blood Blood cells (45%) Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Plasma (55%) Hematocrit tubes with blood Composition of Plasma Plasma Aqueous solution (90%) Substances (10%)
Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s)
 Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
SECTION 2 CELL INJURY
 Adapted myocyte Normal myocyte Reversibly-injured myocyte SECTION 2 CELL INJURY Cell death 5/4/2014 1 5/4/2014 2 Reversible Degeneration Irreversible Cellular Swelling Fatty Change Hyaline Change Amyloid
Adapted myocyte Normal myocyte Reversibly-injured myocyte SECTION 2 CELL INJURY Cell death 5/4/2014 1 5/4/2014 2 Reversible Degeneration Irreversible Cellular Swelling Fatty Change Hyaline Change Amyloid
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISTINGUISHING MORPHOLOGIC LOOK-ALIKES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Histological and Ultrastructural studies of Caecal tonsil in Chicken (Gallus domesticus)
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 6 (2015) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Histological and Ultrastructural studies of Caecal tonsil in Chicken (Gallus domesticus) T.A.Kannan 1*,
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 6 (2015) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Histological and Ultrastructural studies of Caecal tonsil in Chicken (Gallus domesticus) T.A.Kannan 1*,
Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit
 Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit Catalog Number KA0895 50 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit Catalog Number KA0895 50 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Individual cells Extracellular matrix
 Connective Tissue Connective Tissue Elements Individual cells Extracellular matrix»fibers» Collagen» Elastic» Reticular»Ground Substance» PG (proteoglycans)» GAG (glycosaminoglycan)» GP (glycoprotein)
Connective Tissue Connective Tissue Elements Individual cells Extracellular matrix»fibers» Collagen» Elastic» Reticular»Ground Substance» PG (proteoglycans)» GAG (glycosaminoglycan)» GP (glycoprotein)
Cell Basics. Basic Unit of Life. Prokaryotic. Eukaryotic. Plant Cell. Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Bacteria. Very Complex.
 Basic Unit of Life It is Cell Basics Type Type Prokaryotic (before the nucleus) Examples Eukaryotic (true nucleus) Characteristics Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Examples Bacteria Plant Cell Characteristics
Basic Unit of Life It is Cell Basics Type Type Prokaryotic (before the nucleus) Examples Eukaryotic (true nucleus) Characteristics Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Examples Bacteria Plant Cell Characteristics
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal 1 0.
 Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Product Use HPSC-CC are for research use only. It is not approved for human or animal use, or for application in in vitro diagnostic procedures.
 HPSC-derived Cardiomyocyte Cells (HPSC-CC) Catalog #6240 Cell Specification Human primary cardiomyocytes and cardiac tissue are superior modeling systems for heart disease studies, drug discovery and toxicity
HPSC-derived Cardiomyocyte Cells (HPSC-CC) Catalog #6240 Cell Specification Human primary cardiomyocytes and cardiac tissue are superior modeling systems for heart disease studies, drug discovery and toxicity
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES IN PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
THE GOLGI APPARATUS IN SMALL LYMPHOCYTES AND IN
 THE GOLG APPARATUS N SMALL LYMPHOCYTES AND N TRANSFORMED BLAST CELLS. By A. S. COULSON. From the Department of Pathology, Cambridge University. (Received for publication 23rd December 1964) The Golgi apparatus
THE GOLG APPARATUS N SMALL LYMPHOCYTES AND N TRANSFORMED BLAST CELLS. By A. S. COULSON. From the Department of Pathology, Cambridge University. (Received for publication 23rd December 1964) The Golgi apparatus
Tissue Reaction to Root Canal Filling Material Embedded Subcutaneously in Rats
 11 Chapter 2 Tissue Reaction to Root Canal Filling Material Embedded Subcutaneously in Rats Takanaga Ochiai Keisuke Nakano Hiromasa Hasegawa Toshiyuki Kawakami Abstract The reaction of subcutaneous connective
11 Chapter 2 Tissue Reaction to Root Canal Filling Material Embedded Subcutaneously in Rats Takanaga Ochiai Keisuke Nakano Hiromasa Hasegawa Toshiyuki Kawakami Abstract The reaction of subcutaneous connective
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE
 TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE PAUL F. PARAKKAL. From the Department of Dermatology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02118 INTRODUCTION
TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE PAUL F. PARAKKAL. From the Department of Dermatology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02118 INTRODUCTION
Standard 2 Exam Biology. 2. This macromolecule is responsible for short term energy storage and structural support in plants
 1. This macromolecule is responsible for structural support, movement, enzymatic activity, cell communication, and is made of amino acids. a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Nucleic Acids e. ATP
1. This macromolecule is responsible for structural support, movement, enzymatic activity, cell communication, and is made of amino acids. a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Nucleic Acids e. ATP
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
psittaci by Silver-Methenamine Staining and
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, July 1972, p. 267-271 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 111, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Location of Polysaccharide on Chlamydia psittaci by Silver-Methenamine
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, July 1972, p. 267-271 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 111, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Location of Polysaccharide on Chlamydia psittaci by Silver-Methenamine
Chairman: Dr H. L. Israel, M.D.
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (August 1970) 46, 496-500. SESSION III Chairman: Dr H. L. Israel, M.D. The fine structure of sarcoid and tuberculous granulomas W. JONES WILLIAMS E. M. VALERIE JAMES D. A.
Postgraduate Medical Journal (August 1970) 46, 496-500. SESSION III Chairman: Dr H. L. Israel, M.D. The fine structure of sarcoid and tuberculous granulomas W. JONES WILLIAMS E. M. VALERIE JAMES D. A.
Chapter 4. Cartilage and Bone. Li Shu-Lei instructor. Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University
 Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
Instructions. Fuse-It-mRNA easy. Shipping and Storage. Overview. Kit Contents. Specifications. Note: Important Guidelines
 Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
Yara shwabkeh. Osama Alkhader. Heba Kalbouneh
 2 Yara shwabkeh Osama Alkhader Heba Kalbouneh CELL OVERVIEW -Note ; the important thing is to know how the organelles appear under the microscope - the stains we usually use in Histology are composed of
2 Yara shwabkeh Osama Alkhader Heba Kalbouneh CELL OVERVIEW -Note ; the important thing is to know how the organelles appear under the microscope - the stains we usually use in Histology are composed of
ULTRASTRUCTURE OF THE ADRENAL CORTEX IN FROZEN THIN SECTIONS
 J. Cell Set. 27, 3C3-3" (i977) 303 Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited ULTRASTRUCTURE OF THE ADRENAL CORTEX IN FROZEN THIN SECTIONS M. M. MAGALHAES Laboratory of Histology and Embryology,
J. Cell Set. 27, 3C3-3" (i977) 303 Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited ULTRASTRUCTURE OF THE ADRENAL CORTEX IN FROZEN THIN SECTIONS M. M. MAGALHAES Laboratory of Histology and Embryology,
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DIFFERENTIATING IMMATURE PERIPHERAL BLOOD CELLS
 Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Continuing Education on the left side of the
Thursday, October 16 th
 Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
ISOLATION OF A SARCOMA VIRUS FROM A SPONTANEOUS CHICKEN TUMOR
 ISOLATION OF A SARCOMA VIRUS FROM A SPONTANEOUS CHICKEN TUMOR Shigeyoshi ITOHARA, Kouichi HIRATA, Makoto INOUE, Masanori Veterinary Pathology, Faculty of Agriculture, Yamaguchi University* HATSUOKA, and
ISOLATION OF A SARCOMA VIRUS FROM A SPONTANEOUS CHICKEN TUMOR Shigeyoshi ITOHARA, Kouichi HIRATA, Makoto INOUE, Masanori Veterinary Pathology, Faculty of Agriculture, Yamaguchi University* HATSUOKA, and
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Mansoura university Faculty of medicine Histology and cell Biology Department Curriculum Content And Logbook
 Mansoura university Faculty of medicine Histology and cell Biology Department Curriculum Content And Logbook For the 1 st year Medical Student s In Histology and cell Biology Mansoura university Faculty
Mansoura university Faculty of medicine Histology and cell Biology Department Curriculum Content And Logbook For the 1 st year Medical Student s In Histology and cell Biology Mansoura university Faculty
ASSAY OF SPHINGOMYELINASE ACTIVITY
 ASSAY OF SPHINGOMYELINASE ACTIVITY Protocol for Protein Extraction Stock Solution 1. Leupeptin/hydrochloride (FW 463.0,
ASSAY OF SPHINGOMYELINASE ACTIVITY Protocol for Protein Extraction Stock Solution 1. Leupeptin/hydrochloride (FW 463.0,
CONNECTIVE TISSUE (C.T.)
 CONNECTIVE TISSUE (C.T.) Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Enumerate the general characteristics of C.T. 2. Classify C.T into C.T. proper and special types of C.T.
CONNECTIVE TISSUE (C.T.) Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Enumerate the general characteristics of C.T. 2. Classify C.T into C.T. proper and special types of C.T.
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION
 ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
Special Staining (I)
 Special Staining (I) Carbohydrates 1- PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF'S (PAS ) Purpose: Glycogen is present in liver, kidney, skeletal and cardiac muscle. The PAS stain is used to demonstrate neutral polysaccharides
Special Staining (I) Carbohydrates 1- PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF'S (PAS ) Purpose: Glycogen is present in liver, kidney, skeletal and cardiac muscle. The PAS stain is used to demonstrate neutral polysaccharides
:1c.c :& Preliminary and Short Report GRANULE FORMATION IN THE LANGERHANS CELL* structure with rounded ends and a striated lamella
 THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1566 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 7, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Preliminary and Short Report GRANULE FORMATION IN THE LANGERHANS CELL* ALVIN S. ZELICKSON,
THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1566 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 7, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Preliminary and Short Report GRANULE FORMATION IN THE LANGERHANS CELL* ALVIN S. ZELICKSON,
8. Ultrastructural examination of the liver of the rainbow trout
 Józef Szarek, Izabella Babińska, Beata Szynaka, Anna Andrzejewska, Emilia Strzyżewska, Joanna Wojtacka, Krzysztof Wąsowicz, Anna Wiśniewska, Magdalena Szweda, Krystyna Dublan 8. Ultrastructural examination
Józef Szarek, Izabella Babińska, Beata Szynaka, Anna Andrzejewska, Emilia Strzyżewska, Joanna Wojtacka, Krzysztof Wąsowicz, Anna Wiśniewska, Magdalena Szweda, Krystyna Dublan 8. Ultrastructural examination
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues. Short Answer. Figure 3.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
The Cytoplasm Li Shulei Department of Histology & Embryology
 The Cytoplasm Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Cell components Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Organelles Cytoplasmic deposits Cytoskeleton Cytosol ( Matrix ) Nucleus Plasma membrane
The Cytoplasm Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Cell components Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Organelles Cytoplasmic deposits Cytoskeleton Cytosol ( Matrix ) Nucleus Plasma membrane
Trident Membrane Protein Extraction Kit
 Cat. No. Size Shelf life GTX16373 5/ 20 tests 12 months at the appropriate storage temperatures (see below) Contents Component Storage Amount for 5 tests Amount for 20 tests Buffer A -20 o C 2.5 ml 10
Cat. No. Size Shelf life GTX16373 5/ 20 tests 12 months at the appropriate storage temperatures (see below) Contents Component Storage Amount for 5 tests Amount for 20 tests Buffer A -20 o C 2.5 ml 10
Development of the myelin sheath of the hypogastric nerves in a human foetus aged 23 weeks
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 63, No. 3, pp. 289 301 Copyright 2004 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Development of the myelin sheath of the hypogastric nerves in a human
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 63, No. 3, pp. 289 301 Copyright 2004 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Development of the myelin sheath of the hypogastric nerves in a human
THE EFFECT OF ROENTGEN RADIATION ON SPINAL GANGLIA OF ALBINO RATS
 THE EFFECT OF ROENTGEN RADIATION ON SPINAL GANGLIA OF ALBINO RATS W. C. MA AND CHIEN-LIANG HSU (From the Departmt-nts of Anatomy and Radiology, Peiping Union M~dical College, Peiping, China) From the extensive
THE EFFECT OF ROENTGEN RADIATION ON SPINAL GANGLIA OF ALBINO RATS W. C. MA AND CHIEN-LIANG HSU (From the Departmt-nts of Anatomy and Radiology, Peiping Union M~dical College, Peiping, China) From the extensive
Occurrence of Ciliated Vesicle-Containing Reticular Cells in the Mouse Thymus
 Occurrence of Ciliated Vesicle-Containing Reticular Cells in the Mouse Thymus By Takeshi Hoshino Department of Anatomy, Hokkaido University School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan (Director : Prof. Takashi
Occurrence of Ciliated Vesicle-Containing Reticular Cells in the Mouse Thymus By Takeshi Hoshino Department of Anatomy, Hokkaido University School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan (Director : Prof. Takashi
Cell Structure and Function. Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells
 Cell Structure and Function Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells Common Features of All Cells All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features. Common Features of All
Cell Structure and Function Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells Common Features of All Cells All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features. Common Features of All
SAMPLE LITERATURE Please refer to included weblink for correct version. Morphology of Cancer Cells. Edvo-Kit #990. Experiment Objective:
 Edvo-Kit #990 Morphology of Cancer Cells Experiment Objective: 990 In this lab, students will explore the morphology of normal and cancerous cells by staining pre-fi xed cells with methylene blue and eosin.
Edvo-Kit #990 Morphology of Cancer Cells Experiment Objective: 990 In this lab, students will explore the morphology of normal and cancerous cells by staining pre-fi xed cells with methylene blue and eosin.
Lipid content of malignant lymphomas
 J. clin. Path. (1968), 1, 6-69 Lipid content of malignant lymphomas D. H. WRIGHT1 From Makerere University College Medical School, Kampala, Uganda SYNOPSIS Lipid staining, using oil red 0 and Sudan black
J. clin. Path. (1968), 1, 6-69 Lipid content of malignant lymphomas D. H. WRIGHT1 From Makerere University College Medical School, Kampala, Uganda SYNOPSIS Lipid staining, using oil red 0 and Sudan black
KARYOTYPE OF A SEI WHALE
 KARYOTYPE OF A SEI WHALE TOSHIO KASUYA The chromosomes of the Mammalia have been studied for a long period, and many species of mammals except those belonging to the Lemures, Proboscidea, Hyracoidea and
KARYOTYPE OF A SEI WHALE TOSHIO KASUYA The chromosomes of the Mammalia have been studied for a long period, and many species of mammals except those belonging to the Lemures, Proboscidea, Hyracoidea and
The Neuron. Consists Of: - cell body. - Dendrites - axon - axon terminal - myelin. dendrites Axon terminal. Cell body. nucleus. axon.
 The Neuron Consists Of: - cell body - Dendrites - axon - axon terminal - myelin dendrites Axon terminal Cell body nucleus myelin axon THE SYNAPSE Definition: It is a point of contact between the axon of
The Neuron Consists Of: - cell body - Dendrites - axon - axon terminal - myelin dendrites Axon terminal Cell body nucleus myelin axon THE SYNAPSE Definition: It is a point of contact between the axon of
Mucoprotein-containing histiocytes (muciphages)
 J. clin. Path. (1966), 19, 368 Mucoprotein-containing histiocytes (muciphages) in the rectum J. G. AZZOPARDI AND D. J. EVANS' From the Department of Morbid Anatomy, Postgraduate Medical School, London
J. clin. Path. (1966), 19, 368 Mucoprotein-containing histiocytes (muciphages) in the rectum J. G. AZZOPARDI AND D. J. EVANS' From the Department of Morbid Anatomy, Postgraduate Medical School, London
Histology Review Can you identify the Cell Structures? Can you identify the Stain? Can you identify the Cell type?
 Histology Review Can you identify the Cell Structures? Can you identify the Stain? Can you identify the Cell type? 2.01 Border of Epithelia (fluorescence) M A: lamina basalis B: epithelium C: other tissues
Histology Review Can you identify the Cell Structures? Can you identify the Stain? Can you identify the Cell type? 2.01 Border of Epithelia (fluorescence) M A: lamina basalis B: epithelium C: other tissues
The Physical Nature of the Lipid Globules in the Living Neurones of Helix aspersa as indicated by Measurements of Refractive Index By K. F. A.
 The Physical Nature of the Lipid Globules in the Living Neurones of Helix aspersa as indicated by Measurements of Refractive Index By K. F. A. ROSS (Department of Biological Science, Wye College (University
The Physical Nature of the Lipid Globules in the Living Neurones of Helix aspersa as indicated by Measurements of Refractive Index By K. F. A. ROSS (Department of Biological Science, Wye College (University
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology
 The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
