Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Sjögren s Syndrome Complicated by Conversion Disorder: a Case Report
|
|
|
- Roy Norris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Report This is Advance Publication Article Kurume Medical Journal, 64, , 2017 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Sjögren s Syndrome Complicated by Conversion Disorder: a Case Report MISA NAKAMURA, SEIJI TANAKA, TADASHI INOUE, YASUTO MAEDA, KIYOHITO OKUMIYA, TAKUYA ESAKI, GO SHIMOMURA, KENJI MASUNAGA, SHINICHIRO NAGAMITSU AND YUSHIRO YAMASHITA Department of Pediatrics and Child Health, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume, Japan Received 2 May 2017, accepted 20 November 2017 J-STAGE advance publication 21 May 2018 Edited by TAKAYUKI TANIWAKI Summary: Conversion disorder (CD) is sometimes accompanied by motor and sensory impairments, such as muscle weakness, paralysis, sensory hypersensitivity, and sensory loss. Sjögren s syndrome (SS) complicates 5-10% of cases of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Patients with SS or SLE present with various neurological symptoms and psychiatric manifestations. When neurological symptoms are present, it is important to distinguish whether the symptoms are caused by a neurological or a mental disorder because the former requires early intensive intervention, such as methylprednisolone pulse therapy (MPT), whereas psychotherapy or antidepressant drugs are recommended for mental disorders. We noticed SS- and SLE-like symptoms just after a diagnosis of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in a 14-year-old girl. At approximately the same time, paralysis started in her lower limbs and subsequently spread to her upper limbs. An examination for neurological symptoms revealed no abnormalities. Because of the conversion reaction between her neurological symptoms and her disease state, CD was suspected as the etiology of her physical symptoms. Nevertheless, because of the progressive nature of the neurological symptoms, MPT was initiated with concurrent administration of intravenous immunoglobulin, but it failed to achieve a good outcome. The patient s symptoms eventually improved after she underwent psychotherapy treatment for a few months. Because early diagnosis of the cause of neurological symptoms accompanying SS and SLE is difficult, it may be necessary to combine the two lines of treatment in the early stages. However, when a mental disorder is suspected, psychotherapy should be started early to minimize the use of unnecessary neurological treatment. Key words Sjögren s syndrome, neurological symptoms, psychiatric manifestation, Conversion Disorder, Psychotherapy INTRODUCTION Conversion disorder (CD), also known as functional neurological symptom disorder, is classified as a somatic symptom and related disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition [1]. CD may be accompanied by sensory/motor symptoms, such as weakness or partial paralysis, sensory loss, and motor deficits. Sjögren s syndrome (SS) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are complicated by a wide spectrum of neurological disorders and present abnormalities on brain and spinal cord mag- Corresponding Author: Seiji Tanaka, Department of Pediatrics and Child Health, Kurume University School of Medicine, 67 Asahi-machi, Kurume City, Fukuoka, , Japan. Tel , Fax , tanaka_seiji@kurume-u.ac.jp Abbreviations: CD, conversion disorder; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; SS, Sjögren s syndrome; MPT, methylprednisolone pulse therapy; CNS, central nervous system; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; ISN, International Society of Nephrology; ITP, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura; IVIG, intravenous immunoglobulin; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; SSEP, short latency somatosensory evoked potentials.
2 98 NAKAMURA ET AL. netic resonance imaging (MRI) and in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) [2-4]. The levels of interleukin-6 in CSF are also elevated in cases of central nervous system (CNS) lupus [5]. Corticosteroid therapy is a basic approach for the treatment of SLE, but treatment is intensified when severe CNS symptoms are present. In a previous study of neurological symptoms in SS, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) therapy was more effective than methylprednisolone pulse therapy [6]. Approximately 30% of SS patients present with psychiatric manifestations [7], while 46% of SLE patients present with neuropsychiatric manifestations [8]. Reports of SLE and SS cases accompanied by CD are very rare, possibly because the symptoms of the two disorders are indistinguishable and can lead to an ambiguous diagnosis. CASE PRESENTATION SS and SLE A 14-year-old girl was admitted to our hospital for the treatment of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) because her platelet count dropped to 19,000/μL two weeks after an upper respiratory infection. The patient had experienced dry mouth and hypohidrosis for the previous two years. A butterfly rash was observed 20 days after the decrease in platelet count. There was no abnormality in the iris. Some antinuclear antibodies, such as anti-ro/ssa and La/SSB antibodies, and rheumatoid factor were positive, while other related antibodies were negative. Urine test results were all negative. While Schirmer s test showed normal tear production, the Saxon test and salivary scintigraphy revealed impaired salivary secretion. Other clinical findings were bilateral knee pain, an elevated serum matrix metalloproteinase-3 level, and a small amount of effusion in the knee on contrast-enhanced MRI. No abnormalities were observed on chest X-ray, echocardiography, brain perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography, or gallium scintigraphy. After SLE was diagnosed, we performed a biopsy to evaluate the patient s stage of SLE. Kidney biopsy findings were consistent with stage 1 pathology in accordance with the International Society of Nephrology (ISN) classification. Based on the test results and symptoms, we diagnosed concomitant SS and SLE. After starting corticosteroid therapy for ITP, the patient experienced neurological symptoms starting in her lower limbs, and treatment was delayed due to the difficulty encountered in determining whether the symptoms were attributable to a neurological or mental disorder. Two cycles of methylprednisolone pulse therapy were completed one month after the onset of the neurological symptoms. Subsequently, the joint pain and erythema disappeared. Oral corticosteroids 20 mg/day and tacrolimus 3 mg/day alleviated the joint pain. Neurological symptoms Two days after the patient began corticosteroid therapy for ITP, we observed muscle weakness in her lower limbs (Fig. 1). The weakness gradually spread throughout the length of her lower limbs and to the upper limbs, leading to a loss of muscle strength in all four limbs and increased tendon reflexes. Despite mildly reduced muscle strength in her four limbs, no muscle atrophy, spastic paralysis, or bladder/rectal disorder was observed. Tests for pathological reflexes, such as Babinski reflex, were also negative, with no findings indicating pyramidal tract lesions besides her increased tendon reflexes. The patient could not lift her lower limbs but was able to hold them in a raised position. Hoover s sign was positive. The anatomical sites of sensory impairment varied from day to day. Hypersensitivities to tactile, temperature, and pain stimuli were observed on the right side of her face. While her left lower limb and right upper limb had normal sensory perception, her right lower limb and left upper limb were hypersensitive to tactile and temperature stimuli. There were no signs of impairment in position sense, cranial neuropathy, or cerebellar ataxia. Although nociception and temperature perception returned to normal, hyperalgesia persisted in the soles of both feet on the third day of treatment; this symptom eventually decreased and disappeared completely 15 days later. Blood and CSF analysis, brain and spinal cord MRI, nerve conduction velocity, and electroencephalography revealed no abnormalities. We started physical therapy 14 days after the onset of muscle weakness. The first cycle of three-day methylprednisolone pulse therapy (500 mg) began after 7 days of corticosteroid therapy, but no improvement in the patient s condition was observed, even after the second cycle. The first and second cycles lasted four weeks. IVIG therapy was performed because, in addition to methylprednisolone pulse therapy, IVIG therapy was found to be effective for neurological symptoms caused by SS in a previous study [9]. Therefore, five-day IVIG therapy (400 mg/kg/dose) was initiated 44 days after the onset of muscle weakness. A few days after the first five-day IVIG administration, spontaneous motor activity was observed in the lower limbs. In the upper limbs, only the fingers showed improvement. However, no clear improvement was observed after the second five-day IVIG administration (Fig. 1).
3 CONVERSION DISORDER WITH SLE AND SS 99 Fig. 1. Symptoms and treatment course PSL, corticosteroid therapy with prednisolone; TAC, tacrolimus; MPT, methylprednisolone pulse therapy (500 mg, three days/cycle, two cycles); IVIG, intravenous immunoglobulin (400 mg/kg, five days/cycle, two cycles); MMT, manual muscle test. Blood and CSF analysis, brain and spinal cord MRI, and nerve conduction velocity tests were repeated but revealed no abnormalities. We made no changes to the patient s oral medicine and started psychotherapy 85 days after the onset of muscle weakness. Spontaneous motor activity in the upper limbs resumed after hospital discharge. One month after discharge, spontaneous motor activity in all four limbs had returned to normal. However, the increased tendon reflexes in all four limbs remained. Psychiatric manifestations The patient had past medical history relevant to psychiatric manifestations, such as epilepsy; additionally, she had stopped attending school because of bullying and anorexia. The patient had no voluntary movement of her upper limbs but did move them upon painful stimulation, leading to a diagnosis of dissociation. After eliminating other causes of neurological symptoms, we made the diagnosis of CD with sensory and motor impairments. We recommended psychiatric counseling for her, but she refused it. We performed mental supportive care that attended to her needs without denying her wishes and gradually promoted independence. DISCUSSION It is of great importance to determine whether paralysis in all four limbs is caused by a neurological or mental disorder because the former urgently requires an intensive intervention, such as methylprednisolone pulse therapy or IVIG therapy [4], whereas psychotherapy and/or antidepressant drug therapy are recommended for psychiatric manifestations. Previous studies have shown that SS can accompany various types of neuropathy: 1 sensory ataxic neuropathy (40% of previous cases), 2 painful neuropathy without sensory ataxia (20%), 3 multiple mononeuropathy, 4 autonomic neuropathy, and 5 radiculopathy. In the present study, the above pathologies were ruled out for several reasons. 1 Despite the presence of cutaneous sensory impairment and dyshidrosis in our patient, sensory ataxic neuropathy was ruled out because of the lack of impaired proprioception and ataxic gait, the presence of muscle weakness, and the lack of abnormalities on the spinal cord MRI or nerve conduction velocity tests. We did not measure short latency somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEP). 2 Despite normal nerve conduction velocity and spinal cord MRI and the fact that the patient s first symptom was dysesthesia in the distal portions of all four limbs, painful
4 100 NAKAMURA ET AL. neuropathy without sensory ataxia was ruled out because of the lack of aggravation of sensory impairment and the presence of muscle weakness. Hypersensitivity, a symptom of small fiber neuropathy, was observed, but the area of hypersensitivity varied from examination to examination and disappeared after a few days. Reduced thermal nociception or autonomic symptoms were absent. 3 Multiple mononeuropathy, which involves sensory and motor disorders in the anatomical area innervated by a single nerve, was ruled out because the anatomical sites of sensory and motor disorders differed from day to day in this patient. 4 Autonomic neuropathy, such as orthostatic hypotension and bladder rectal disorder, was unlikely because of the presence of muscle weakness and the lack of symptoms indicative of autonomic neuropathy (other than dyshidrosis) in the patient. 5 Radiculopathy was ruled out because of normal nerve conduction velocity and no F-wave conduction delay (25.1/24.8 ms in the left/ right bilateral median nerve, 23.8/23.9 ms in the left/ right ulnar nerve, and 46.6/46.9 ms in the left/right tibial nerve) and because of normal MRI and CSF [9] findings, despite the presence of muscle weakness. There were day-to-day variations in neurological symptoms, and the patient s activities of daily living did not match the objective muscle strength findings. Moreover, the findings of sensory impairment appearing for only a few days varied from examination to examination, and the patient could not raise her lower limbs but could hold them in place. These inconsistencies in clinical findings and the positive Hoover s sign were the reasons for suspecting CD. Similarly, in a previous study, CD was diagnosed because of a lack of abnormal findings in a patient who developed paralysis in all four limbs while undergoing steroid therapy for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis [10]. In our case, the patient also developed neurological symptoms while undergoing steroid therapy, suggesting that her pathological condition was unresponsive to steroids. Clinical testing and imaging showed no abnormality, but because it could not be completely ruled out, methylprednisolone pulse therapy was performed as a diagnostic/therapeutic regimen. The fact that psychiatric manifestations are uncommon in SS and SLE and that intensive methylprednisolone pulse therapy and IVIG therapy, which were performed to prevent any delay in treating neurological disorder, were not clearly effective in the present case led us to suspect that psychiatric manifestations were the cause of the patient s symptoms. Because we did not believe that the neurological symptoms were due to the SLE, we did not strengthen the patient s steroid therapy. Corticosteroid therapy with prednisolone (PSL) and tacrolimus are less effective against SLE without neurological symptoms. In our case, we started physical therapy 14 days after the appearance of symptoms and started mental supportive care 85 days after the appearance of symptoms. The patient s condition gradually improved. We could not reduce tacrolimus, but were able to reduce PSL rapidly to 1/4 within half a year. There has been no recurrence. In a similar case, Yamaguchi et al reported that conversion symptoms of a rheumatic patient improved with physical therapy, occupational therapy, and antidepressant drug therapy [10]. CONCLUSION We encountered a patient with no abnormal test findings whose symptoms could not be explained by medical evaluation. Based on the present findings and the patient s history, we determined that CD was responsible for her neurological symptoms. Because early diagnosis of the cause of neurological symptoms accompanying SS and SLE is difficult, in the early stages it is often necessary to provide two lines of treatment: one for a neurological disorder and another for a mental disorder. However, when a mental disorder is suspected, treatment for neurological disorder can be minimized with early psychotherapeutic intervention. REFERENCES 1. American Psychiatric Association. Conversion disorder (functional neurological symptom disorder). In Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th ed. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association; pp Kurz C, Wunderlich S, Spieler D, Schwaiger BJ, Andres C et al. Acute transverse myelitis and psoriasiform dermatitis associated with Sjoegren s syndrome: a case report. BMC Res Notes 2014; 7: Delalande S, de Seze J, Fauchais AL, Hachulla E, Stojkovic T et al. Neurologic manifestations in primary Sjögren syndrome: a study of 82 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2004; 83: Chai J and Logigian EL. Neurological manifestations of primary Sjögren s syndrome. Curr Opin Neurol 2010; 23: Hirohata S and Miyamoto T. Elevated levels of interleukin-6 in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and central nervous system involvement. Arthritis Rheum 1990; 33: Mori K, Iijima M, Koike H, Hattori N, Tanaka F et al. The wide spectrum of clinical manifestations in Sjögren s syndrome-associated neuropathy. Brain 2005; 128: Sagawa A, Tanimura K, Shinohara M, and Warabi T. Neuro-psychiatric involvement in primary Sjögren s syndrome. Nihon Rinsho. 1995; 53:
5 CONVERSION DISORDER WITH SLE AND SS Ainiala H, Loukkola J, Peltola J, Korpela M, and Hietaharju A. The prevalence of neuropsychiatric syndromes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Neurology 2001; 57: Koike H and Sobue G. [Sjogren s syndrome-associated neuropathy]. Brain Nerve 2013; 65: Yamaguchi T, Yahata T, Ikenaga Y, Tateno K, Someya F et al. Rehabilitation experience of a patient with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis who presented quadriplegia due to conversion disorder. J Clin Rehabil 1999; 8:
Severe Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy Ameliorated following High-dose (3 g/kg) Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1723-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Severe Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy Ameliorated following High-dose (3 g/kg) Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1723-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Severe Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy Ameliorated following High-dose (3 g/kg) Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy
PMH: No medications; Immunizations UTD No hospitalizations or surgeries Speech Delay. Birth Hx: 24 WGA, NICU x6 months
 HPI: 6 months of weakness and parathesias- originally in both feet x 2-3 months, then resolved. Now with parathesias and weakness in fingers x 1 week. Seen by podiatrist and given custom in-soles 1 month
HPI: 6 months of weakness and parathesias- originally in both feet x 2-3 months, then resolved. Now with parathesias and weakness in fingers x 1 week. Seen by podiatrist and given custom in-soles 1 month
A Case of Acute Sensory Neuropathy Associated with Contrast Enhancement of the Cauda Equina on Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 61 Case Report St. Marianna Med. J. Vol. 33, pp. 61 66, 2005 A Case of Acute Sensory Neuropathy Associated with Contrast Enhancement of the Cauda Equina on Magnetic Resonance Imaging Toshinari Kobayashi
61 Case Report St. Marianna Med. J. Vol. 33, pp. 61 66, 2005 A Case of Acute Sensory Neuropathy Associated with Contrast Enhancement of the Cauda Equina on Magnetic Resonance Imaging Toshinari Kobayashi
Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (NPSLE) Case presentations and topic discussion The Rheumatology Unit UMMC experience
 Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (NPSLE) Case presentations and topic discussion The Rheumatology Unit UMMC experience References Sanna G, Bertolaccini ML. Neuropsychiatric manifestations
Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (NPSLE) Case presentations and topic discussion The Rheumatology Unit UMMC experience References Sanna G, Bertolaccini ML. Neuropsychiatric manifestations
Symptomatic pain treatments (carbamazepine and gabapentin) were tried and had only a transient and incomplete effect on the severe pain syndrome.
 Laurencin 1 Appendix e-1 Supplementary Material: Clinical observations Patient 1 (48-year-old man) This patient, who was without a notable medical history, presented with thoracic pain and cough, which
Laurencin 1 Appendix e-1 Supplementary Material: Clinical observations Patient 1 (48-year-old man) This patient, who was without a notable medical history, presented with thoracic pain and cough, which
COPYRIGHT 2012 THE TRANSVERSE MYELITIS ASSOCIATION. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
 The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL
 A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL CASE HISTORY Nine year old male child Second born Born
A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL CASE HISTORY Nine year old male child Second born Born
AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING
 AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING Diagnosis and Treatment Goals Aimee Borazanci, MD BNI Neuroimmunology Objectives Give an update on the causes for admission, clinical features, and outcomes of
AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING Diagnosis and Treatment Goals Aimee Borazanci, MD BNI Neuroimmunology Objectives Give an update on the causes for admission, clinical features, and outcomes of
A RARE NEUROLOGICAL PRESENTATION OF SLE. Dr Yoganand M N Dr Prithvi P Nayak
 A RARE NEUROLOGICAL PRESENTATION OF SLE Dr Jayachandra Dr Yoganand M N Dr Prithvi P Nayak Presenter: Dr Shambhavi K R CHIEF COMPLAINTS A 30 year old lady hailing from Nepal presented to OPD with complaints
A RARE NEUROLOGICAL PRESENTATION OF SLE Dr Jayachandra Dr Yoganand M N Dr Prithvi P Nayak Presenter: Dr Shambhavi K R CHIEF COMPLAINTS A 30 year old lady hailing from Nepal presented to OPD with complaints
Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression. Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre
 Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre Outline of talk Mononeuropathies median and anterior interosseous nerve ulnar nerve
Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre Outline of talk Mononeuropathies median and anterior interosseous nerve ulnar nerve
Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers
 Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers NICE guidance link: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121 Clinical presentation of brain tumours History and Examination Consider immediate referral Management
Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers NICE guidance link: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121 Clinical presentation of brain tumours History and Examination Consider immediate referral Management
Immune Mediated Neuropathies
 Immune Mediated Neuropathies Hernan Gatuslao, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Neurology Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine AIDP and CIDP Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
Immune Mediated Neuropathies Hernan Gatuslao, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Neurology Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine AIDP and CIDP Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS PROFILE
 MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS PROFILE What is Multiple Sclerosis? Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, inflammatory disease of unknown etiology that involves an immune-mediated attack on the central nervous system
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS PROFILE What is Multiple Sclerosis? Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, inflammatory disease of unknown etiology that involves an immune-mediated attack on the central nervous system
PNS and ANS Flashcards
 1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
S (18) doi: /j.ensci Reference: ENSCI 122
 Accepted Manuscript A case of cerebellar ataxia associated with VZV infection Hirofumi Matsuyama, Takekazu Ohi PII: S2405-6502(18)30012-1 DOI: doi:10.1016/j.ensci.2018.04.003 Reference: ENSCI 122 To appear
Accepted Manuscript A case of cerebellar ataxia associated with VZV infection Hirofumi Matsuyama, Takekazu Ohi PII: S2405-6502(18)30012-1 DOI: doi:10.1016/j.ensci.2018.04.003 Reference: ENSCI 122 To appear
CIDP + MMN - how to diagnose and treat. Dr Hadi Manji
 CIDP + MMN - how to diagnose and treat Dr Hadi Manji Outline Introduction CIDP Diagnosis Clinical features MRI Nerve conduction tests Lumbar puncture Nerve biopsy Treatment IV Ig Steroids Plasma Exchnage
CIDP + MMN - how to diagnose and treat Dr Hadi Manji Outline Introduction CIDP Diagnosis Clinical features MRI Nerve conduction tests Lumbar puncture Nerve biopsy Treatment IV Ig Steroids Plasma Exchnage
American Board of Physical Therapy Residency and Fellowship Education
 American Board of Physical Therapy Residency and Fellowship Education Description of Residency Practice Clinical Electrophysiology February 2017 American Physical Therapy Association 1111 North Fairfax
American Board of Physical Therapy Residency and Fellowship Education Description of Residency Practice Clinical Electrophysiology February 2017 American Physical Therapy Association 1111 North Fairfax
Spinal Cord Injury Transection Injury, Spinal Shock, and Hermiated Disc. Copyright 2014, 2011, 2006 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc.
 Spinal Cord Injury Transection Injury, Spinal Shock, and Hermiated Disc 1 Spinal Cord Injury Results from fracture and/or dislocation of vertebrae // Compresses, stretches, or tears spinal cord Cervical
Spinal Cord Injury Transection Injury, Spinal Shock, and Hermiated Disc 1 Spinal Cord Injury Results from fracture and/or dislocation of vertebrae // Compresses, stretches, or tears spinal cord Cervical
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Multifocal inflammatory leukoencephalopathy induced by accidental consumption of levamisole: A case report
 Iranian Journal of Neurology Case Report Ir J neurol 2012; 11(2): 65-69 Multifocal inflammatory leukoencephalopathy induced by accidental consumption of levamisole: A case report Received: 25 Oct 2011
Iranian Journal of Neurology Case Report Ir J neurol 2012; 11(2): 65-69 Multifocal inflammatory leukoencephalopathy induced by accidental consumption of levamisole: A case report Received: 25 Oct 2011
Acute Motor-dominant Polyneuropathy as Guillain-Barré Syndrome and Multiple Mononeuropathies in a Patient with Sjögren s Syndrome
 CASE REPORT Acute Motor-dominant Polyneuropathy as Guillain-Barré Syndrome and Multiple Mononeuropathies in a Patient with Sjögren s Syndrome Kenichiro Tanaka 1, Hiroyuki Nakayasu 1, Yutaka Suto 1, Shotaro
CASE REPORT Acute Motor-dominant Polyneuropathy as Guillain-Barré Syndrome and Multiple Mononeuropathies in a Patient with Sjögren s Syndrome Kenichiro Tanaka 1, Hiroyuki Nakayasu 1, Yutaka Suto 1, Shotaro
American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. Part I Curriculum & Weights
 American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Part I Curriculum & Weights Neurologic Disorders 30% Stroke Spinal Cord Injury Traumatic Brain Injury Neuropathies a) Mononeuropathies b) Polyneuropathies
American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Part I Curriculum & Weights Neurologic Disorders 30% Stroke Spinal Cord Injury Traumatic Brain Injury Neuropathies a) Mononeuropathies b) Polyneuropathies
Myelitis. Case 2. History. Examination. Mahtab Ghadiri
 Case 2 Myelitis Mahtab Ghadiri History A 42-year-old man presented to the emergency department with altered sensation in the lower limbs and difficulty ambulating. He first noted paresthesia in his feet
Case 2 Myelitis Mahtab Ghadiri History A 42-year-old man presented to the emergency department with altered sensation in the lower limbs and difficulty ambulating. He first noted paresthesia in his feet
Chronic Lymphocytic Inflammation with Pontine Perivascular Enhancement Responsive to Steroids (CLIPPERS) with Limbic Encephalitis
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8533-16 Intern Med Advance Publication http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Chronic Lymphocytic Inflammation with Pontine Perivascular Enhancement Responsive to Steroids (CLIPPERS)
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8533-16 Intern Med Advance Publication http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Chronic Lymphocytic Inflammation with Pontine Perivascular Enhancement Responsive to Steroids (CLIPPERS)
Title. CitationInternal Medicine, 46(8): Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information
 Title Scapular Winging as a Symptom of Cervical Flexion My Author(s)Yaguchi, Hiroaki; Takahashi, Ikuko; Tashiro, Jun; Ts CitationInternal Medicine, 46(8): 511-514 Issue Date 2007-04-17 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/20467
Title Scapular Winging as a Symptom of Cervical Flexion My Author(s)Yaguchi, Hiroaki; Takahashi, Ikuko; Tashiro, Jun; Ts CitationInternal Medicine, 46(8): 511-514 Issue Date 2007-04-17 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/20467
Nervous system Reflexes and Senses
 Nervous system Reflexes and Senses Physiology Lab-4 Wrood Slaim, MSc Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology University of Al-Mustansyria 2017-2018 Nervous System The nervous system is the part of an
Nervous system Reflexes and Senses Physiology Lab-4 Wrood Slaim, MSc Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology University of Al-Mustansyria 2017-2018 Nervous System The nervous system is the part of an
Bryan Andresen MD Advances in Clinical Neuroscience Practice /2/11
 Bryan Andresen MD Advances in Clinical Neuroscience Practice 2011 5/2/11 Intro/History Definition Differential Diagnosis Clinical Characteristics Exam Findings Treatment Outcomes 46 yo female admitted
Bryan Andresen MD Advances in Clinical Neuroscience Practice 2011 5/2/11 Intro/History Definition Differential Diagnosis Clinical Characteristics Exam Findings Treatment Outcomes 46 yo female admitted
Seema Sikka, MD January 18, 2014 TRANSVERSE MYELITIS: A CLINICAL OVERVIEW
 Seema Sikka, MD January 18, 2014 TRANSVERSE MYELITIS: A CLINICAL OVERVIEW DISCLOSURES I have no industry relationships to disclose. I will not discuss off-label use. OBJECTIVES: TRANSVERSE MYELITIS Review
Seema Sikka, MD January 18, 2014 TRANSVERSE MYELITIS: A CLINICAL OVERVIEW DISCLOSURES I have no industry relationships to disclose. I will not discuss off-label use. OBJECTIVES: TRANSVERSE MYELITIS Review
Monocular Oculomotor Nerve Disorder Manifesting as Cranial Neuropathy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1106-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Monocular Oculomotor Nerve Disorder Manifesting as Cranial Neuropathy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Kiyotaka Nakamagoe 1, Hisami
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1106-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Monocular Oculomotor Nerve Disorder Manifesting as Cranial Neuropathy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Kiyotaka Nakamagoe 1, Hisami
Committee Approval Date: May 9, 2014 Next Review Date: May 2015
 Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru248 Topic: Benlysta, belimumab Date of Origin: May 13, 2011 Committee Approval Date: May 9, 2014 Next Review Date: May 2015 Effective Date: June 1, 2014 IMPORTANT
Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru248 Topic: Benlysta, belimumab Date of Origin: May 13, 2011 Committee Approval Date: May 9, 2014 Next Review Date: May 2015 Effective Date: June 1, 2014 IMPORTANT
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
The Internist s Approach to Neuropathy
 The Internist s Approach to Neuropathy VOLKAN GRANIT, MD, MSC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY NEUROMUSCU LAR DIVISION UNIVERSITY OF MIAMI, MILLER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE RELEVANT DECLARATIONS Financial disclosures:
The Internist s Approach to Neuropathy VOLKAN GRANIT, MD, MSC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY NEUROMUSCU LAR DIVISION UNIVERSITY OF MIAMI, MILLER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE RELEVANT DECLARATIONS Financial disclosures:
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Bell Work What s your reaction time? Go to this website and check it out: https://www.justpark.com/creative/reaction-timetest/ Read the following brief article and summarize
DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Bell Work What s your reaction time? Go to this website and check it out: https://www.justpark.com/creative/reaction-timetest/ Read the following brief article and summarize
Central Nervous System (CNS) and Lupus: Learn from the Experts. Betty Diamond, M.D. Feinstein Institute for Medical Research
 Central Nervous System (CNS) and Lupus: Learn from the Experts Betty Diamond, M.D. Feinstein Institute for Medical Research Stages in SLE Pathogenesis Crow MK, Arth Res & Tx. 2009 ACR Criteria for the
Central Nervous System (CNS) and Lupus: Learn from the Experts Betty Diamond, M.D. Feinstein Institute for Medical Research Stages in SLE Pathogenesis Crow MK, Arth Res & Tx. 2009 ACR Criteria for the
Situaciones estresantes en el lupus
 Situaciones estresantes en el lupus Munther A Khamashta MD FRCP PhD Director: Lupus Research Unit Barcelona, Noviembre 2008 What is Lupus? Lupus is a neurological disease and sometimes affects other organs
Situaciones estresantes en el lupus Munther A Khamashta MD FRCP PhD Director: Lupus Research Unit Barcelona, Noviembre 2008 What is Lupus? Lupus is a neurological disease and sometimes affects other organs
Minami-Hori M, Tsuji H, Takahashi H, Hanada K, Iizuka H
 The Journal of Dermatology (2013.Jan) :. Optic neuritis in a psoriatic arthritis patient treated by infliximab Minami-Hori M, Tsuji H, Takahashi H, Hanada K, Iizuka H 1 Optic neuritis in a psoriatic arthritis
The Journal of Dermatology (2013.Jan) :. Optic neuritis in a psoriatic arthritis patient treated by infliximab Minami-Hori M, Tsuji H, Takahashi H, Hanada K, Iizuka H 1 Optic neuritis in a psoriatic arthritis
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Stevens O, Claeys KG, Poesen K, Veroniek S, Van Damme P. Diagnostic challenges and clinical characteristics of hepatitis E virus associated Guillain- Barré syndrome. JAMA Neurol.
Supplementary Online Content Stevens O, Claeys KG, Poesen K, Veroniek S, Van Damme P. Diagnostic challenges and clinical characteristics of hepatitis E virus associated Guillain- Barré syndrome. JAMA Neurol.
Subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord following recreational nitrous oxide use
 Subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord following recreational nitrous oxide use Jae Park Hui Mei Cheng Royal Perth Hospital, Perth Western Australia Australia Background and aim Subacute combined
Subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord following recreational nitrous oxide use Jae Park Hui Mei Cheng Royal Perth Hospital, Perth Western Australia Australia Background and aim Subacute combined
Unilateral Trigeminal Mandibular Motor Neuropathy Caused by Tumor in the Foramen Ovale
 Journal of Clinical Neurology / Volume 2 / September, 2006 Unilateral Trigeminal Mandibular Motor Neuropathy Caused by Tumor in the Foramen Ovale Kyung Seok Park, M.D., Jae-Myun Chung, M.D., Beom S. Jeon,
Journal of Clinical Neurology / Volume 2 / September, 2006 Unilateral Trigeminal Mandibular Motor Neuropathy Caused by Tumor in the Foramen Ovale Kyung Seok Park, M.D., Jae-Myun Chung, M.D., Beom S. Jeon,
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis
 Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
Intracranial hypotension secondary to spinal CSF leak: diagnosis Spinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is an important and underdiagnosed cause of new onset headache that is treatable. Cerebrospinal fluid
This is a repository copy of Anti-MAG negative distal acquired demyelinating symmetric neuropathy in association with a neuroendocrine tumor..
 This is a repository copy of Anti-MAG negative distal acquired demyelinating symmetric neuropathy in association with a neuroendocrine tumor.. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk//
This is a repository copy of Anti-MAG negative distal acquired demyelinating symmetric neuropathy in association with a neuroendocrine tumor.. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk//
Lecturer. Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014
 Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Epilepsy: diagnosis and treatment. Sergiusz Jóźwiak Klinika Neurologii Dziecięcej WUM
 Epilepsy: diagnosis and treatment Sergiusz Jóźwiak Klinika Neurologii Dziecięcej WUM Definition: the clinical manifestation of an excessive excitation of a population of cortical neurons Neurotransmitters:
Epilepsy: diagnosis and treatment Sergiusz Jóźwiak Klinika Neurologii Dziecięcej WUM Definition: the clinical manifestation of an excessive excitation of a population of cortical neurons Neurotransmitters:
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Name Date Period. Human Reflexes Lab
 Name Date Period Introduction: Human Reflexes Lab Neurons communicate in many ways, but much of what the body must do every day is programmed as reflexes. Reflexes are rapid, predictable, involuntary motor
Name Date Period Introduction: Human Reflexes Lab Neurons communicate in many ways, but much of what the body must do every day is programmed as reflexes. Reflexes are rapid, predictable, involuntary motor
Done By: manar aljebreen Abdulrahman alsharidah
 Female Side Male side Done By: manar aljebreen Abdulrahman alsharidah Revised By: Nour Al-Khawajah Mohammed Asiri 2 Slide No.( 1 ) Slide No.( 2 ) 3 Slide No.( 3 ) Slide No.( 4 ) Upper motor neurons are
Female Side Male side Done By: manar aljebreen Abdulrahman alsharidah Revised By: Nour Al-Khawajah Mohammed Asiri 2 Slide No.( 1 ) Slide No.( 2 ) 3 Slide No.( 3 ) Slide No.( 4 ) Upper motor neurons are
A Patient s Guide to Dropped Head Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Dropped Head Syndrome 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It
A Patient s Guide to Dropped Head Syndrome 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
Neuropsychiatric SLE (NPSLE) Dr. MTL NYO FCP(SA), Cert Rheum (Phys) Division of Rheumatology Department of Internal Medicine DGMAH / SMU
 Neuropsychiatric SLE (NPSLE) Dr. MTL NYO FCP(SA), Cert Rheum (Phys) Division of Rheumatology Department of Internal Medicine DGMAH / SMU NPSLE represents a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge Wide range
Neuropsychiatric SLE (NPSLE) Dr. MTL NYO FCP(SA), Cert Rheum (Phys) Division of Rheumatology Department of Internal Medicine DGMAH / SMU NPSLE represents a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge Wide range
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be?
 Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
Making headway: problem-oriented approaches to neurological disease
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Making headway: problem-oriented approaches to neurological disease Author : Mark Lowrie Categories : Vets Date : July 4,
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Making headway: problem-oriented approaches to neurological disease Author : Mark Lowrie Categories : Vets Date : July 4,
Diffuse myelitis in a 9-month-old infant: case report and review of the literature
 230 La Revue de Santé de la Méditerranée orientale, Vol. 15, N 1, 2009 Case report Diffuse myelitis in a 9-month-old infant: case report and review of the literature O. Hüdaoglu,¹ U. Yis,¹ S. Kurul,¹ H.
230 La Revue de Santé de la Méditerranée orientale, Vol. 15, N 1, 2009 Case report Diffuse myelitis in a 9-month-old infant: case report and review of the literature O. Hüdaoglu,¹ U. Yis,¹ S. Kurul,¹ H.
A Practical Approach to Polyneuropathy SLOCUM DICKSON ANNUAL TEACHING DAY NOVEMBER 4, 2017
 A Practical Approach to Polyneuropathy SLOCUM DICKSON ANNUAL TEACHING DAY NOVEMBER 4, 2017 Disclosures Research support from Cytokinetics, Inc Catalyst, Inc Editorial fees from UptoDate. Objectives Describe
A Practical Approach to Polyneuropathy SLOCUM DICKSON ANNUAL TEACHING DAY NOVEMBER 4, 2017 Disclosures Research support from Cytokinetics, Inc Catalyst, Inc Editorial fees from UptoDate. Objectives Describe
The Spinal Cord. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord. The Spinal Cord 1/2/2016. Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum.
 The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
A Hypothesis Driven Approach to the Neurological Exam
 A Hypothesis Driven Approach to the Neurological Exam Vanja Douglas, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Department of Neurology Disclosures None 1 Purpose of Neuro Exam Screen asymptomatic patients Screen
A Hypothesis Driven Approach to the Neurological Exam Vanja Douglas, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Department of Neurology Disclosures None 1 Purpose of Neuro Exam Screen asymptomatic patients Screen
Sawada J, Orimoto R, Misu T, Katayama T, Aizawa H, Asanome A, Takahashi K, Saito T, Anei R, Kamada K, Miyokawa N, Takahashi T, Fujihara K, Hasebe N.
 Mult Scler (2014.9) 20(10):1413-1416. A case of pathology-proven neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder with Sjögren syndrome manifesting aphasia and apraxia due to a localized cerebral white matter lesion.
Mult Scler (2014.9) 20(10):1413-1416. A case of pathology-proven neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder with Sjögren syndrome manifesting aphasia and apraxia due to a localized cerebral white matter lesion.
IVIG (intravenous immunoglobulin) Bivigam, Carimune NF, Flebogamma, Gammagard, Gammagard S/D, Gammaked, Gammaplex, Gamunex-C, Octagam, Privigen
 Pre - PA Allowance None Prior-Approval Requirements Diagnoses Patient must have ONE of the following documented indications: 1. Primary Immunodeficiency Disease (PID) with ONE of the a. Hypogammaglobulinemia,
Pre - PA Allowance None Prior-Approval Requirements Diagnoses Patient must have ONE of the following documented indications: 1. Primary Immunodeficiency Disease (PID) with ONE of the a. Hypogammaglobulinemia,
Spinal cord. We have extension of the pia mater below L1-L2 called filum terminale
 Spinal cord Part of the CNS extend from foramen magnum to the level of L1-L2 (it is shorter than the vertebral column) it is covered by spinal meninges. It is cylindrical in shape. It s lower end become
Spinal cord Part of the CNS extend from foramen magnum to the level of L1-L2 (it is shorter than the vertebral column) it is covered by spinal meninges. It is cylindrical in shape. It s lower end become
MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
 MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS There are a wide variety of Neurologic and Musculoskeletal disorders which can impact driving safety. Impairment may be the result of altered muscular, skeletal,
MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS There are a wide variety of Neurologic and Musculoskeletal disorders which can impact driving safety. Impairment may be the result of altered muscular, skeletal,
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists
 Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Brain Stem. Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies
 Objectives A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies Tahseen Mozaffar, MD FAAN Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, UC Irvine-MDA ALS and Neuromuscular Center Director, Neurology Residency Training
Objectives A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies Tahseen Mozaffar, MD FAAN Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, UC Irvine-MDA ALS and Neuromuscular Center Director, Neurology Residency Training
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases
 Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
doi: /j.jns
 doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2014.05.055 Title: Sixth nerve palsy associated with obstruction in Dorello s canal, accompanied by nodular type muscular sarcoidosis Author: Ayako Shioya 1), Hiroshi Takuma 1), Masanari
doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2014.05.055 Title: Sixth nerve palsy associated with obstruction in Dorello s canal, accompanied by nodular type muscular sarcoidosis Author: Ayako Shioya 1), Hiroshi Takuma 1), Masanari
SCLERODERMA OVERLAP SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT Diwakar K. Singh 1, Nataraju H. V 2
 SCLERODERMA OVERLAP SYNDROME: A Diwakar K. Singh 1, Nataraju H. V 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Diwakar K. Singh, Nataraju H. V. Scleroderma Overlap Syndrome: A Case Report. Journal of Evolution of Medical
SCLERODERMA OVERLAP SYNDROME: A Diwakar K. Singh 1, Nataraju H. V 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Diwakar K. Singh, Nataraju H. V. Scleroderma Overlap Syndrome: A Case Report. Journal of Evolution of Medical
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS
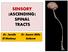 SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
High Yield Neurological Examination
 High Yield Neurological Examination Vanja Douglas, MD Sara & Evan Williams Foundation Endowed Neurohospitalist Chair Director, Neurohospitalist Division Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF Department
High Yield Neurological Examination Vanja Douglas, MD Sara & Evan Williams Foundation Endowed Neurohospitalist Chair Director, Neurohospitalist Division Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF Department
Infection-Associated Neurological Syndromes
 Infection-Associated Neurological Syndromes Anand P, MD PhD Medical Director, BloodCenter of Wisconsin Assistant Professor, Medical College of Wisconsin ASFA Annual Meeting San Antonio, TX, May 8th, 2015
Infection-Associated Neurological Syndromes Anand P, MD PhD Medical Director, BloodCenter of Wisconsin Assistant Professor, Medical College of Wisconsin ASFA Annual Meeting San Antonio, TX, May 8th, 2015
AMERICAN BOARD OF PHYSICAL THERAPY RESIDENCY AND FELLOWSHIP EDUCATION
 AMERICAN BOARD OF PHYSICAL THERAPY RESIDENCY AND FELLOWSHIP EDUCATION June 2017 American Physical Therapy Association 1111 North Fairfax Street Alexandria, VA 22314-1488 resfel@apta.org 703/706-3152 www.abptrfe.org
AMERICAN BOARD OF PHYSICAL THERAPY RESIDENCY AND FELLOWSHIP EDUCATION June 2017 American Physical Therapy Association 1111 North Fairfax Street Alexandria, VA 22314-1488 resfel@apta.org 703/706-3152 www.abptrfe.org
BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII
 463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
Professor Michael Kossove
 Professor Michael Kossove Is this a new disease? No, but doctors only began noticing it in 2014. That s when dozens of children began showing up in hospitals unable to move their arms or legs. Ultimately,
Professor Michael Kossove Is this a new disease? No, but doctors only began noticing it in 2014. That s when dozens of children began showing up in hospitals unable to move their arms or legs. Ultimately,
WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
Lumbosacral plexus lesion Lumbosacral plexus disorders G54.1 Neuralgic amyotrophy Neuralgic amyotrophy G
 ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM NEUROMUSCULAR DIAGNOSIS CODES Focal Neuropathy ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM Mononeuropathy G56.00 Carpal tunnel syndrome 354.00 Other median nerve lesion 354.10 Lesion of ulnar nerve 354.20
ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM NEUROMUSCULAR DIAGNOSIS CODES Focal Neuropathy ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM Mononeuropathy G56.00 Carpal tunnel syndrome 354.00 Other median nerve lesion 354.10 Lesion of ulnar nerve 354.20
Clinical and electrophysiologic features of childhood Guillain-Barré syndrome in Northeast China
 Journal of the Formosan Medical Association (2014) 113, 634e639 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.jfma-online.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and electrophysiologic features
Journal of the Formosan Medical Association (2014) 113, 634e639 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.jfma-online.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and electrophysiologic features
AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer
 AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer ( )1. Choose one best answer for the following pathologic pictures. A. choroid cyst B. choroid papilloma C. pontine glioma D. ependymoma E. metastatic tumor
AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer ( )1. Choose one best answer for the following pathologic pictures. A. choroid cyst B. choroid papilloma C. pontine glioma D. ependymoma E. metastatic tumor
V1-ophthalmic. V2-maxillary. V3-mandibular. motor
 4. Trigeminal Nerve I. Objectives:. Understand the types of sensory information transmitted by the trigeminal system.. Describe the major peripheral divisions of the trigeminal nerve and how they innervate
4. Trigeminal Nerve I. Objectives:. Understand the types of sensory information transmitted by the trigeminal system.. Describe the major peripheral divisions of the trigeminal nerve and how they innervate
Reflexes. Dr. Baizer
 Reflexes Dr. Baizer 1 Learning objectives: reflexes Students will be able to describe: 1. The clinical importance of testing reflexes. 2. The essential components of spinal reflexes. 3.The stretch reflex.
Reflexes Dr. Baizer 1 Learning objectives: reflexes Students will be able to describe: 1. The clinical importance of testing reflexes. 2. The essential components of spinal reflexes. 3.The stretch reflex.
Anxiety disorders part II
 Anxiety disorders part II OBSESSIVE-COMPULSIVE DISORDER obsession a recurrent and intrusive thought, feeling, idea, or sensation compulsion a conscious, standarized, recurring pattern of behavior, such
Anxiety disorders part II OBSESSIVE-COMPULSIVE DISORDER obsession a recurrent and intrusive thought, feeling, idea, or sensation compulsion a conscious, standarized, recurring pattern of behavior, such
Multifocal motor neuropathy: diagnostic criteria that predict the response to immunoglobulin treatment
 Multifocal motor neuropathy: diagnostic criteria that predict the response to immunoglobulin treatment 7 MMN RM Van den Berg-Vos, H Franssen, JHJ Wokke, HW Van Es, LH Van den Berg Annals of Neurology 2000;
Multifocal motor neuropathy: diagnostic criteria that predict the response to immunoglobulin treatment 7 MMN RM Van den Berg-Vos, H Franssen, JHJ Wokke, HW Van Es, LH Van den Berg Annals of Neurology 2000;
Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Associate Professor Head of Pediatric Department Rawalpindi Medical College
 Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Associate Professor Head of Pediatric Department Rawalpindi Medical College AN APPROACH TO BLEEDING DISORDERS NORMAL HEMOSTASIS After injury, 3 processes halt bleeding Vasoconstriction
Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Associate Professor Head of Pediatric Department Rawalpindi Medical College AN APPROACH TO BLEEDING DISORDERS NORMAL HEMOSTASIS After injury, 3 processes halt bleeding Vasoconstriction
Case Report Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma with 2-Stage Total en bloc Spondylectomy after Marked Response to Molecular Target Drugs
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 916501, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/916501 Case Report Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma with 2-Stage Total en bloc Spondylectomy after Marked
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 916501, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/916501 Case Report Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma with 2-Stage Total en bloc Spondylectomy after Marked
New Insights on Optic Neuritis in Young People
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Case Study New Insights on Optic Neuritis in Young People Sergio Carmona 1, Sandra Barbosa 1 and Maria Laura Ortube 2 * 1 Department of Neuro-ophthalmology, Hospital
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Case Study New Insights on Optic Neuritis in Young People Sergio Carmona 1, Sandra Barbosa 1 and Maria Laura Ortube 2 * 1 Department of Neuro-ophthalmology, Hospital
Reporting Autoimmune Diseases in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
 Reporting Autoimmune Diseases in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Marcelo C. Pasquini, MD, MSc HVD05_1.ppt Outline Review of autoimmune diseases (AID). Role of transplantation for AID Data collection:
Reporting Autoimmune Diseases in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Marcelo C. Pasquini, MD, MSc HVD05_1.ppt Outline Review of autoimmune diseases (AID). Role of transplantation for AID Data collection:
Meyers' A&P February 15, Unit 7. The Nervous System. I. Functions of the Nervous System. Monitors body's internal and external enviornments
 Unit 7 The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System Monitors body's internal and external enviornments Integrates sensory information Coordinates voluntary & involuntary responses of many other
Unit 7 The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System Monitors body's internal and external enviornments Integrates sensory information Coordinates voluntary & involuntary responses of many other
Syllabus. Questions may appear on any of the topics below: I. Multidimensional Nature of Pain
 Questions may appear on any of the topics below: I. Multidimensional Nature of Pain Syllabus A. Epidemiology 1. Pain as a public health problem with social, ethical, legal and economic consequences 2.
Questions may appear on any of the topics below: I. Multidimensional Nature of Pain Syllabus A. Epidemiology 1. Pain as a public health problem with social, ethical, legal and economic consequences 2.
Adult Neurology Residency Training Program McGill University Objectives of Training and Training Requirements. For Outpatient Neurology Clinics
 Neurology Residency Program Department of Neurology & Neurosurgery Postal address: Montreal Neurological Institute 3801 University Street Montreal, PQ, Canada H3A 2B4 Tel.: (514) 398-1904 Fax: (514) 398-4621
Neurology Residency Program Department of Neurology & Neurosurgery Postal address: Montreal Neurological Institute 3801 University Street Montreal, PQ, Canada H3A 2B4 Tel.: (514) 398-1904 Fax: (514) 398-4621
The Neurology of HIV Infection. Carolyn Barley Britton, MD, MS Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology Columbia University
 The Neurology of HIV Infection Carolyn Barley Britton, MD, MS Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology Columbia University HIV/AIDS Epidemiology World-wide pandemic, 40 million affected U.S.- Disproportionate
The Neurology of HIV Infection Carolyn Barley Britton, MD, MS Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology Columbia University HIV/AIDS Epidemiology World-wide pandemic, 40 million affected U.S.- Disproportionate
InterQual Level of Care 2018 Index
 InterQual Level of Care 2018 Index Rehabilitation Criteria Index Words by Subset The Index is an alphabetical listing of conditions and/or diagnoses designed to guide the user to the criteria subset where
InterQual Level of Care 2018 Index Rehabilitation Criteria Index Words by Subset The Index is an alphabetical listing of conditions and/or diagnoses designed to guide the user to the criteria subset where
Spring Semester OST 571 Neuromusculoskeletal Lecture-Lab Schedule Revised
 Revised 1-07-16 Week 1: Monday, January 11, 2016 9:00-9:50 a.m. 001 - Principles of Neurobiology/Orientation Lovell Online 10:00-10:50 a.m. 002 - Cells, synapses & neurotransmitter systems Nazaroff Online
Revised 1-07-16 Week 1: Monday, January 11, 2016 9:00-9:50 a.m. 001 - Principles of Neurobiology/Orientation Lovell Online 10:00-10:50 a.m. 002 - Cells, synapses & neurotransmitter systems Nazaroff Online
What is the role for neurophysiology in the evaluation of patients with uro-genito-anal dysfunction?
 London, 2016 What is the role for neurophysiology in the evaluation of patients with uro-genito-anal dysfunction? David B. Vodušek Medical Faculty, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia vodusek.david.b@gmail.com
London, 2016 What is the role for neurophysiology in the evaluation of patients with uro-genito-anal dysfunction? David B. Vodušek Medical Faculty, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia vodusek.david.b@gmail.com
2/23/18. Disclosures. Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood. Making Room for Rheumatology. I have nothing to disclose. James J.
 Making Room for Rheumatology James J. Nocton, MD Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Making Room for Rheumatology James J. Nocton, MD Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Neurophysiology Lab (Adapted From the Joy of Lab )
 Neurophysiology Lab (Adapted From the Joy of Lab ) Introduction: The nervous system operates by receiving input, processing information, and then providing output. The input is detected by structures called
Neurophysiology Lab (Adapted From the Joy of Lab ) Introduction: The nervous system operates by receiving input, processing information, and then providing output. The input is detected by structures called
X-Plain Muscles Reference Summary
 X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
AGE RELATED CHANGES 2. Dr. Rehab gwada
 AGE RELATED CHANGES 2 Dr. Rehab gwada Objectives of lecture At the end of this lecture the student will be able to: Determine Age-related sensory, proprioceptive, vestibular Changes in addition to nervous
AGE RELATED CHANGES 2 Dr. Rehab gwada Objectives of lecture At the end of this lecture the student will be able to: Determine Age-related sensory, proprioceptive, vestibular Changes in addition to nervous
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Neuromyelitis Optica (Devic s Syndrome)
 J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 45-50 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Neuromyelitis Optica (Devic s Syndrome) Chien-Chuan Huang Tai-Yuan Chen Tai-Ching Wu Yu-Kun Tsui Te-Chang Wu Wen-Sheng Tzeng Chien-Jen Lin Department
J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 45-50 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Neuromyelitis Optica (Devic s Syndrome) Chien-Chuan Huang Tai-Yuan Chen Tai-Ching Wu Yu-Kun Tsui Te-Chang Wu Wen-Sheng Tzeng Chien-Jen Lin Department
Common Pitfalls in Multiple Sclerosis and CNS Demyelinating Diseases
 Common Pitfalls in Multiple Sclerosis and CNS Demyelinating Diseases Case-Based Learning Common Pitfalls in Multiple Sclerosis and CNS Demyelinating Diseases Case-Based Learning Mayo Clinic College of
Common Pitfalls in Multiple Sclerosis and CNS Demyelinating Diseases Case-Based Learning Common Pitfalls in Multiple Sclerosis and CNS Demyelinating Diseases Case-Based Learning Mayo Clinic College of
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Arthritis & Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas PATIENT EDUCATION SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
 Arthritis & Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas PATIENT EDUCATION SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Introduction: There is perhaps no rheumatic disease that evokes so much fear and confusion among both patients
Arthritis & Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas PATIENT EDUCATION SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Introduction: There is perhaps no rheumatic disease that evokes so much fear and confusion among both patients
Index SLEEP MEDICINE CLINICS. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis, for Kleine-Levin syndrome,
 165 SLEEP MEDICINE CLINICS Index Sleep Med Clin 1 (2006) 165 170 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Academic performance, effects of sleepiness in children on, 112 Accidents,
165 SLEEP MEDICINE CLINICS Index Sleep Med Clin 1 (2006) 165 170 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Academic performance, effects of sleepiness in children on, 112 Accidents,
