Differential expression of rat hippocampal micrornas in two rat models of chronic pain
|
|
|
- Thomasina Wade
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 32: , 2013 Differential expression of rat hippocampal micrornas in two rat models of chronic pain YOKO HORI, GENTARO GOTO, MASAE ARAI-IWASAKI, MASASHI ISHIKAWA and ATSUHIRO SAKAMOTO Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Nippon Medical School, Tokyo, Japan Received June 24, 2013; Accepted September 16, 2013 DOI: /ijmm Abstract. The two most common forms of chronic pain are inflammatory pain and neuropathic pain. Nevertheless, the underlying mechanisms of these pain conditions and their therapeutic responses are poorly understood. MicroRNAs (mirnas) negatively regulate cell genes, and thus control cell proliferation, inflammation and metabolism. In the present study, we examined gene expression in the hippocampus of rats in two models of chronic pain. In addition, we used the left hindpaw procedure to identify differences in the bilateral hippocampus. We divided the rats into the 4 following groups: the group with chronic constriction injury (CCI), the sham-operated group, the group injected with complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) and the group injected with normal saline. mirna expression profiles were analyzed using TaqMan low-density array (TLDA). We observed 54 mirnas (22.7%) in the rats with CCI rats that were differentially expressed, including 7 mirnas that were downregulated compared with the sham-operated rats. In the CFA-injected rats, 40 mirnas (16.8%) were differentially expressed, including 8 mirnas that were downregulated compared with the normal saline-injected rats. Pearson's correlation co-efficient for all detected mirnas in the rat hippocampus failed to identify differences between the hippocampi bilaterally. An unsupervised cluster analysis produced separate clusters between the control and experimental groups. In this study, we demonstrate the differential expression of hippocampal mirnas in two rat models of chronic pain; however, no significant differences were observed bilaterally in hippocampal mirna expression. Further research is required to determine the correlation among mirnas, messenger RNAs (mrnas) and proteins. Introduction Chronic pain that is severe and difficult to manage can degrade the quality of life of patients. The two most common forms Correspondence to: Dr Yoko Hori, Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Nippon Medical School, Sendagi, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo , Japan hori-84@nms.ac.jp Key words: chronic pain, neuroinflammation, neuropathic pain, hippocampus, microrna of chronic pain are inflammatory pain and neuropathic pain. These two conditions show similar clinical symptoms; however, their underlying mechanisms and responses are dissimilar. In general, chronic pain involves changes in the expression of messenger RNAs (mrnas) or proteins that regulate cytokines, receptors and neurotransmitters in the dorsal root ganglia and the brain (1,2). Previous studies have suggested that the differential expression of multiple pain-associated genes plays a key role in the development and maintenance of chronic pain (3-5). The hippocampus, a brain region that participates in learning and memory formation, plays a fundamental role in pain perception (6,7). The association between the hippocampus and pain has been the focus of a number of recent studies. In particular, recent studies have indicated that peripheral neuropathy alters hippocampal gene expression, which suggests that the hippocampus may contribute to neuropathic pain symptoms (8-10). There are a few studies, however, that directly examine the association between the hippocampus and inflammatory or neuropathic pain. Furthermore, few studies have examined the role that hippocampal micrornas (mirnas) may play in chronic pain, particularly for the two different pain models. We hypothesized that hippocampal mirna expression may differ between inflammatory and neuropathic pain models. An improved understanding of the underlying mechanisms for chronic pain may lead to more effective treatment strategies. In this study, we used TaqMan low-density array (TLDA) and quantitative real-time PCR (qrt-pcr) of mirnas to examine mirna expression in the hippocampus in two rat models of chronic pain. The model of neuropathic pain comprised rats with chronic constriction injury (CCI), whereas the model of inflammatory pain comprised rats injected with complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA), as previously described (11,12). In addition, we examined differences in gene expression between the hippocampus bilaterally, as bilateral effects have been observed with unilateral chronic pain models induced by inflammation or by ischemic monomelic neuropathy (13). Materials and methods All experimental procedures were approved by the Institutional Committee on Laboratory Animals of Nippon Medical School, Tokyo, Japan (approval no ) and were performed under the guidelines of the International Association for the Study of Pain.
2 1288 HORI et al: CHANGES IN microrna EXPRESSION UNDER CONDITIONS OF CHRONIC PAIN Male Sprague-Dawley rats (6-7 weeks of age and g in weight; Experimental Animal Center, Saitama, Japan) were used. The rats were housed in clear plastic cages with sawdust bedding at standard room temperature under a 12-h light/dark cycle. All rats received food and water ad libitum. We divided the rats into 4 experimental groups as follows: i) a group of rats with CCI that were sacrificed 7 days after the procedure (CCI group, n=6); ii) a group of sham-cci operated rats (sham-cci group, n=6) [as previously described (11)]; iii) a group of rats injected with CFA that were sacrificed 7 days after the procedure (CFA group, n=6); and iv) a group of normal saline-injected rats (sham-cfa group, n=6) [as previously described (12)]. All surgical procedures were performed under deep anesthesia with sodium pentobarbital [50 mg/kg intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection]. Rat model of neuropathic pain induced by CCI. The CCI model was established according to the methods of Bennett and Xie (11). The left (ipsilateral) common sciatic nerve was exposed and loosely ligated with 4-0 silk thread at 4 regions that were spaced at approximately 1-mm intervals. The sciatic nerve in the sham-operated group was similarly exposed but not ligated. CFA injection for the induction of inflammatory pain. The CFA model was established by injecting CFA (50% in saline, 20 µl) into the plantar surface of the left hindpaw. In the sham- CFA group, normal saline was similarly injected into the left hindpaw as previously described (12). Behavioral assessment. The Plantar Test apparatus (Ugo Basile, Comerio, Italy) was used to examine thermal hyperalgesia, and the von Frey test (Muromachi Kikai, Tokyo, Japan) was used to examine mechanical allodynia. These tests were performed on the day before surgery (day 0), and on post-operative days 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13 and 15, as previously described (14). For the plantar test, each rat was placed on a glass plate with radiant heat equipment (a 50-W halogen reflector bulb) underneath. After the acclimation period, radiation heat was applied to either the contralateral or ipsilateral hindpaw pad. The latency of paw withdrawal from the thermal stimulus was measured 3 times at 5-min intervals, and the average value of these 3 measurements was used as the response latency. For the von Frey test, each rat was placed on a metallic mesh floor, covered with a plastic box, and a von Frey filament with bending forces from 2.0 to 32.0 g was applied from under the mesh floor to the plantar surface of either the contralateral or ipsilateral hindpaw. In individual trials, each paw was stimulated with each filament 5 times at 10-sec intervals. The weakest force (g) that induced the withdrawal of the stimulated paw at least 3 times in each trial was considered the paw withdrawal threshold. mirna profiling. On post-operative day 7, the rats were deeply anesthetized with pentobarbital (300 mg/100 g body weight, i.p.) and decapitated immediately. The brains were rapidly removed, and the hippocampi were dissected as previously described (15). The unilateral hippocampi were divided into left and right sections. Each sample was placed in RNA later (Applied Biosystems, LLC, Foster City, CA, USA) and stored at -80 C until use. Total RNA was isolated using a mirvana mirna isolation kit (Applied Biosystems, LLC) according to the manufacturer's instructions. RNA quantity and quality were assessed using the NanoDrop ND 1000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). All RNA samples with an A260/280 nm reading of 1.8 were used for quantitative analysis. Total RNA samples containing mirnas were used for qrt-pcr. The mirna expression profiles were analyzed using TLDA Rodent MicroRNA cards v.3 A and B (Applied Biosystems, LLC). Each card contains 373 pre-loaded rodent mirna targets, which are all catalogued in the mirbase database (16) and 3 endogenous controls. The procedures were performed as previously described (17,18). Briefly, TLDAs were performed using a two-step process. First, 800 ng total RNA per sample was reverse transcribed using Megaplex RT primer pool A and B, which contains up to 381 stem-looped primers per pool, and a TaqMan MicroRNA Reverse Transcription kit (Applied Biosystems, LLC). Second, the resulting complementary DNA was diluted, mixed with TaqMan Universal PCR master mix (Applied Biosystems, LLC), and deionized in distilled water (Wako, Tokyo, Japan) and loaded into 1 of the 8 fill ports on the TLDA microfluidic cards. The cards were briefly centrifuged for 1 min at 1,600 x g to distribute samples to the multiple wells connected to the fill ports, and then sealed to prevent well-to-well contamination. Finally, the cards were processed and analyzed using a 7900 HT Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, LLC). Data analysis was performed using DataAssist software v2.0 (Applied Biosystems, LLC). The data were represented as the threshold cycle (Ct) values, where Ct represents a unitless value defined as the fractional cycle number at which the sample fluorescence signal passes a fixed threshold above baseline. For each mirna, the expression level was calculated using the comparative Ct method (ΔΔCt) and was further analyzed by comparing the fold change to the basal levels in the control samples. ΔCt was the difference in the Ct values derived from the experimental samples and the control, and ΔΔCt represented the difference between paired samples, as calculated by the following formula: ΔΔCt = ΔCt of sample after surgical procedure -ΔCt of the control. The expression ratio shows the relative quantity of the target gene (Xtarget) to the control gene (Xcontrol). The fold change was computed by the formula Xtarget/Xcontrol = 2 -ΔΔCt. For mirnas, graphic displays were visualized as heat map results of hierarchical clustering. Distances between the samples and assays were calculated for hierarchical clustering based on ΔCt values using the Euclidean distance. Statistical analyses. Values are expressed as the means ± standard deviation. A two-tailed paired t-test was used to compare latencies or threshold values in behavioral tests between the ipsilateral and contralateral sides (CCI group; n=6). Dunnett's test for multiple comparisons was used to compare latencies and threshold values obtained in the behavioral tests performed pre-operatively (day 0, n=6) with those obtained post-operatively (days 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13 and 15; n=6). ANOVA followed by Tukey's test were performed using KyPlot 5.0 software (KyensLab Inc., Tokyo, Japan). Using Pearson's correlation, we assessed whether the hippocampal mirnas that showed expression changes in the rat models of chronic pain were differentially expressed between the left and right hippocampus.
3 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 32: , Figure 1. Effects of (A) chronic constriction injury (CCI) (n=6) and (B) complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) injection (n=6) on thermal hypersensitivity. Thresholds for foot withdrawal on the ipsilateral and contralateral sides in response to thermal stimuli applied to the corresponding hindpaw pad in rats with CCI and CFAinjected rats. * P<0.01 compared with values on the contralateral side on the same days by a paired t-test; # P<0.01 compared with the values on the pre-operative day (day 0) by Dunnett's multiple comparisons. Values are the means ± standard error of the mean. Figure 2. Effects of (A) chronic constriction injury (CCI) (n=6) and (B) complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) injection on mechanical allodynia. Thresholds for foot withdrawal on the ipsilateral and contralateral sides in response to mechanical stimuli applied to the corresponding hindpaw pad in rats with CCI and CFA-injected rats. * P<0.01 compared with values on the contralateral side on the same days, by a paired t-test; # P<0.01 compared with the values on the pre-operative day (day 0) by Dunnett's multiple comparisons. Values are the means ± standard error of the mean. Results Behavioral assessment. The rats with CCI showed a significant decrease in the latency of paw withdrawal in the plantar test and threshold values in the von Frey test for the ipsilateral side on post-operative days (1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13 and 15) compared with day 0 (P<0.05). On the contralateral side, significant decreases were not observed (Figs. 1A and 2A). Even though the CFA injection was administered to the left hindpaw, the rats with CFA showed a significant decrease in the latency of paw withdrawal in the plantar test, and a significant decrease in threshold values in the von Frey test for the hindpaws bilaterally. These differences were observed on the post-operative days examined compared with day 0 (P<0.05) (Figs. 1B and 2B). TLDA. Of the 373 rat mirnas, 237 (63.5%) were detected in the rat hippocampus. In the control rats, we observed no difference in mirna expression between the left and right hippocampus (correlation value, 0.99; P<0.0001). Compared with the sham-operated rats, TLDA in the rats with CCI identified 54 mirnas (22.7%) that were differentially expressed, including 7 mirnas that were downregulated (Table I). Compared with the normal saline-injected rats, the CFA-injected rats had 40 mirnas (16.8%) that were differentially expressed, including 25 mirnas that were downregulated (Table II). Twenty mirnas were expressed in both the rats with CCI and the CFA-injected rats, whereas 34 mirnas were expressed in only the rats with CCI, and 22 were expressed in only the CFA-injected rats. There were no significant differences observed in the comparisons between the sham-operated rats and the normal saline-injected rats. We observed no difference between the hippocampi bilaterally for either the CCI group (correlation value, 0.99; P<0.0001) or the CFA group (correlation value, 0.98; P<0.0001). Furthermore, there was no difference bilaterally among the control rats, the rats with CCI or the CFA-injected rats (Fig. 4). A clustergram of the samples and the mirnas that showed significant differences are shown as a heat map in
4 1290 HORI et al: CHANGES IN microrna EXPRESSION UNDER CONDITIONS OF CHRONIC PAIN Table I. The 54 mirnas that were differentially expressed in the CCI group compared with the sham-operated group. Assay Fold change ± SD P-value hsa-mir-324-3p 1.64±0.40 <0.001 mmu-mir-125a-5p 2.10±0.24 <0.001 mmu-mir ±0.46 <0.001 mmu-mir-151-3p 3.51±0.18 <0.001 mmu-mir ±0.13 <0.001 mmu-mir-181c 0.51±0.21 <0.001 mmu-mir ±1.20 <0.001 mmu-mir ±0.44 <0.001 mmu-mir-29c 0.37±0.29 <0.001 mmu-mir ±0.43 <0.001 mmu-mir ±0.54 <0.001 mmu-mir-434-3p 3.35±0.78 <0.001 mmu-mir ±0.68 <0.001 rno-mir-345-3p 2.48±0.37 <0.001 rno-mir ±0.31 <0.001 hsa-mir-30a-3p 1.83±0.51 <0.01 hsa-mir-30e-3p 1.55±0.40 <0.01 mmu-mir-126-3p 1.96±0.28 <0.01 mmu-mir-133a 2.48±1.55 <0.01 mmu-mir ±0.25 <0.01 mmu-mir ±0.98 <0.01 mmu-mir ±0.74 <0.01 mmu-mir-30a 1.42±0.18 <0.01 mmu-mir-323-3p 1.96±0.58 <0.01 mmu-mir-331-3p 1.42±0.14 <0.01 mmu-mir ±1.07 <0.01 mmu-mir ±0.46 <0.01 mmu-mir-487b 1.45±0.36 <0.01 mmu-mir-770-5p 1.82±0.64 <0.01 mmu-mir-872# 1.92±0.50 <0.01 rno-mir-125b# 2.09±0.61 <0.01 rno-mir-146b 1.74±0.41 <0.01 rno-mir-339-3p 3.21±1.57 <0.01 rno-mir-409-3p 1.75±0.51 <0.01 rno-mir ±0.56 <0.01 rno-mir ±0.23 <0.01 rno-mir ±0.50 <0.01 rno-mir-7a# 1.85±0.63 <0.01 hsa-mir-28-3p 2.17±0.43 <0.05 hsa-mir-423-3p 1.65±0.41 <0.05 mmu-mir-128a 1.61±0.23 <0.05 mmu-mir ±0.31 <0.05 mmu-mir ±0.95 <0.05 mmu-mir ±2.32 <0.05 mmu-mir-193b 1.98±1.10 <0.05 mmu-mir ±0.84 <0.05 mmu-mir-23b 1.53±0.19 <0.05 mmu-mir ±0.40 <0.05 mmu-mir-30d 0.63±0.16 <0.05 mmu-mir ±0.44 <0.05 mmu-mir-376b 0.58±0.26 <0.05 mmu-mir-380-5p 1.45±0.41 <0.05 mmu-mir-384-5p 1.62±0.56 <0.05 rno-mir ±0.54 <0.05 Values are the mean fold change ± SD in each group. CFA, complete Freund's adjuvant;; mirna, microrna; mmu, Mus musculus; rno, Rattus norvegicus; P-value, statistical results of Tukey's test. Table II. The 40 mirnas that were differentially expressed in the CFA group compared with the normal saline group. Assay Fold change ± SD P-value hsa-mir-324-3p 1.53±0.30 <0.001 mmu-mir-15b 1.09±0.26 <0.001 mmu-mir ±0.90 <0.001 mmu-mir ±0.50 <0.001 mmu-mir-770-5p 1.85±0.46 <0.001 rno-mir-409-3p 1.63±0.50 <0.001 hsa-mir ±2.23 <0.01 hsa-mir-30a-3p 1.86±1.08 <0.01 mmu-mir-125a-5p 2.10±0.50 <0.01 mmu-mir-126-3p 1.96±0.35 <0.01 mmu-mir-133a 2.48±0.92 <0.01 mmu-mir ±0.38 <0.01 mmu-mir-138# 1.98±0.80 <0.01 mmu-mir-139-5p 1.96±0.51 <0.01 mmu-mir-148b 1.03±0.41 <0.01 mmu-mir ±1.20 <0.01 mmu-mir-296-5p 0.61±0.19 <0.01 mmu-mir ±0.16 <0.01 mmu-mir ±0.23 <0.01 mmu-mir ±0.13 <0.01 rno-mir-146b 1.77±0.62 <0.01 rno-mir p 0.83±0.15 <0.01 rno-mir ±0.55 <0.01 rno-mir-7a# 1.49±0.58 <0.01 hsa-mir-140-3p 1.54±0.45 <0.05 hsa-mir-30e-3p 1.37±0.44 <0.05 mmu-mir-142-3p 0.70±0.06 <0.05 mmu-mir-146a 2.27±0.88 <0.05 mmu-mir ±0.68 <0.05 mmu-mir ±0.23 <0.05 mmu-mir-27a 0.98±0.16 <0.05 mmu-mir-324-5p 0.90±0.08 <0.05 mmu-mir ±0.37 <0.05 mmu-mir ±0.57 <0.05 mmu-mir ±0.64 <0.05 mmu-mir-7a 1.03±0.21 <0.05 mmu-mir-872# 2.40±1.48 <0.05 rno-mir-125b# 2.05±1.02 <0.05 rno-mir-204# 2.52±0.79 <0.05 rno-mir ±0.18 <0.05 Values are the mean fold change ± SD in each group. CFA, complete Freund's adjuvant; mirna, microrna; mmu, Mus musculus; rno, Rattus norvegicus; P-value, statistical results of Tukey's test. Fig. 3. As can be observed in the figure, the heat map indicates 3 main branches (control and experimental) that separate the CCI from the CFA group. Discussion In the present study, we determined that hippocampal mirna expression differed in two pain models that have similar symptoms (CCI and CFA models). Furthermore, we demonstrated
5 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 32: , Figure 4. Pearson's correlation was used to assess hippocampal mirna expression. Left hippocampal sample ΔCt (difference in threshold cycle) is plotted on the abscissa and the right sample ΔCt is plotted on the ordinate. In the control rats, there was no difference in mirna expression between the left and right hippocampus (correlation value, 0.99; P<0.0001), in the chronic constriction injury (CCI) group (correlation value, 0.99; P<0.0001), and in the complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) group (correlation value, 0.98; P<0.0001). Figure 3. Unsupervised hierarchical cluster analysis using Euclidean distance from TaqMan low-density arrays. There were 73 micrornas differentially expressed in the control and chronic pain models. Colors show the level of gene expression; red indicates a higher expression, blue indicates lower expression. Each group is shown separately: control group, chronic constriction injury (CCI) group and complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) group. that mirna expression did not differ between the left and right hippocampus. Pain hypersensitivity and dysesthesia. In both the CCI and CFA models, we observed hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia on the injured side beginning on the first post-operative day (day 1). Pain hypersensitivity continued until day 14, which indicated that a similar chronic pain was induced in the two models. In the CFA model, we observed hyperalgesia and allodynia on the uninjured side beginning on day 3. We suspect that this was due to CFA-mediated inflammation that was caused by systemic inflammation, which led to pain hypersensitivity on the uninjured side. mirna expression. On day 7, when chronic pain was thought to be complete, we investigated hippocampal mirna expression using cluster analysis.
6 1292 HORI et al: CHANGES IN microrna EXPRESSION UNDER CONDITIONS OF CHRONIC PAIN Cluster analysis is a method used for grouping samples same with very similar expression levels; it aids in the identification of group-specific expression patterns. We observed differential mirna expression in the hippocampus. Furthermore, the CCI and CFA group each produced differential mirna expression patterns. The limbic system, which includes the hippocampus, has been reported to be associated with memory and emotional responses (19). Both the cause and persistence of chronic pain is complex and cannot be easily explained. Thus, differences at the mirna level are likely involved, even when the symptoms of chronic pain are identical. Therefore, treatments for the different forms of chronic pain may not be the same. We believe that our findings may lead to the future assessment of treatment methods, and the development of therapeutic agents with greater efficacies. Difference between the left and right hippocampus. Previous studies have indicated a correlation between chronic pain and the hippocampus (20). Although previous studies have examined anatomical differences between the hippocampus bilaterally, as well as the effect of peripheral pain on the hippocampus, the responsible pathways remain unelucidated. Therefore, we in this study, investigated how unilateral chronic pain affects the hippocampus bilaterally. In addition, we examined the hypothesis that a model of inflammatory pain would induce a systemic reaction, but not bilateral differences in the hippocampus. In both the CCI and CFA groups, we searched for bilateral differences in mirna expression that showed significant changes. We found no evidence that indicated a difference between the hippocampus bilaterally. We concluded that the bilateral hippocampal mirna expression is equal in the two chronic pain models. Although the hippocampus functions bilaterally, it is widely known that its asymmetrical nature is an essential feature for high-order brain functioning (21,22). Bilateral differences in hippocampal projections related to chronic pain have not been investigated thus far. Although bilateral differences in mirna expression have been previously demonstrated in the spinal cord, in this study, to our knowledge, we show for the first time that there was no difference in mirna expression between the left and right hippocampus. Symptomatic bilateral differences disappeared in the model of inflammatory pain (CFA group), but remained in the CCI model. In both models, however, we observed no differences between the left and right hippocampus. In the pain pathway, the left and right sides of the hippocampus are thought to be morphologically connected or in a compartment, and thus, symptomatic bilateral differences were not affected. In conclusion, two chronic pain models that show similar pain actions also showed differential changes in hippocampal mirna expression patterns. Such a finding indicates that each model may possess a unique mechanism for regulating mrna and protein expression. We observed no differences in mirna expression between the left and right hippocampus. Thus, we believe that clarifying the mechanisms underlying pain development may lead to improved treatment techniques, as well as to the development of therapeutic agents with greater efficacies. References 1. Lee HL, Lee KM, Son SJ, Hwang SH and Cho HJ: Temporal expression of cytokines and their receptors mrnas in a neuropathic pain model. Neuroreport 15: , Urban MO and Gebhart GF: Supraspinal contributions to hyperalgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: , Kuss AW and Chen W: MicroRNAs in brain function and disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 8: , Farh KK, Grimson A, Jan C, Lewis BP, Johnston WK, et al: The widespread impact of mammalian MicroRNAs on mrna repression and evolution. Science 310: , Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, et al: Microarray analysis shows that some micrornas downregulate large numbers of target mrnas. Nature 433: , Gozzi A, Crestan V, Turrini G, Clemens M and Bifone A: Antagonism at serotonin 5-HT(2A) receptors modulates functional activity of frontohippocampal circuit. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 209: 37-50, Gemma C, Imeri L and Opp MR: Serotonergic activation stimulates the pituitary-adrenal axis and alters interleukin-1 mrna expression in rat brain. Psychoneuroendocrinology 28: , Norman GJ, Karelina K, Zhang N, Walton JC, Morris JS and Devries AC: Stress and IL-1beta contribute to the development of depressive-like behavior following peripheral nerve injury. Mol Psychiatry 15: , Klein AB, Santini MA, Aznar S, Knudsen GM and Rios M: Changes in 5-HT2A-mediated behavior and 5-HT2A- and 5-HT1A receptor binding and expression in conditional brainderived neurotrophic factor knock-out mice. Neuroscience 169: , Bordukalo-Niksic T, Mokrovic G, Stefulj J, Zivin M, Jernej B and Cicin-Sain L: 5HT-1A receptors and anxiety-like behaviours: studies in rats with constitutionally upregulated/downregulated serotonin transporter. Behav Brain Res 213: , Bennett GJ and Xie YK: A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33: , Zhang W, Liu LY and Xu TL: Reduced potassium-chloride co-transporter expression in spinal cord dorsal horn neurons contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity in rats. Neuroscience 152: , Okabe T, Sato C and Sakamoto A: Changes in neuropeptide Y gene expression in the spinal cord of chronic constrictive injury model rats after electroconvulsive stimulation. Biomed Res 31: , Sato C, Sakai A, Ikeda, Y, Suzuki H and Sakamoto A: The prolonged analgesic effect of epidural ropivacaine in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Anesth Analg 106: , Chiu K, Lau WM, Lau HT, So KF and Chang RC: Microdissection of rat brain for RNA or protein extraction from specific brain region. J Vis Exp 7: 269, Wang B, Howel P, Bruheim S, Ju J, Owen LB, Fodstad O and Xi Y: Systematic evaluation of three microrna profiling platforms: microarray, beads array, and quantitative real-time PCR array. PLoS One 6: e17167, Hui AB, Shi W, Boutros PC, et al: Robust global micro-rna profiling with formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded breast cancer tissues. Lab Invest 89: , Ishikawa M, Tanaka S, Arai M, Genda Y and Sakamoto A: Differences in microrna changes of healthy rat liver between sevoflurane and propofol anesthesia. Anesthesiology 117: , Devinsky O, Morrell MJ and Vogt BA: Contributions of anterior cingulate cortex to behavior. Brain 118: , Arai M, Genda Y, Ishikawa M, Shunsuke T, Okabe T and Sakamoto A: The mirna and mrna changes in rat hippocampi after chronic constriction injury. Pain Med 14: , Corballis MC: From mouth to hand: gesture, speech, and the evolution of right-handedness. Behav Brain Sci 26: , Cooke J: Developmental mechanism and evolutionary origin of vertebrate left/right asymmetries. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 79: , 2004.
The Role of micrornas in Pain. Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan
 The Role of micrornas in Pain Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan 1 Motivation for molecular analysis of Pain Chronic pain one of the most common causes for seeking medical treatment Approximate
The Role of micrornas in Pain Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan 1 Motivation for molecular analysis of Pain Chronic pain one of the most common causes for seeking medical treatment Approximate
Enhanced formalin nociceptive responses following L5 nerve ligation in the rat reveals neuropathy-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
 University of Kentucky From the SelectedWorks of Renee R. Donahue 2001 Enhanced formalin nociceptive responses following L5 nerve ligation in the rat reveals neuropathy-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
University of Kentucky From the SelectedWorks of Renee R. Donahue 2001 Enhanced formalin nociceptive responses following L5 nerve ligation in the rat reveals neuropathy-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and. widespread hyperalgesia
 Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo. Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale
 Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale Our research question Can paternal preconceptional exposure to environmental
Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale Our research question Can paternal preconceptional exposure to environmental
Published online October 10, 2016
 Published online October 10, 2016 reviewed by Jim C. Eisenach, Wake Forest University; Ronald Lindsay, Zebra Biologics; Remi Quirion, McGill University; and Tony L. Yaksh, University of California, San
Published online October 10, 2016 reviewed by Jim C. Eisenach, Wake Forest University; Ronald Lindsay, Zebra Biologics; Remi Quirion, McGill University; and Tony L. Yaksh, University of California, San
Spinal Cord Injury Induced Hyperalgesia is Associated with Increased Levels of Let-7 Family of MicroRNAs
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Cellular & Molecular Medicine: Open access Spinal Cord Injury Induced Hyperalgesia is Associated with Increased Levels of Let-7 Family of MicroRNAs
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Cellular & Molecular Medicine: Open access Spinal Cord Injury Induced Hyperalgesia is Associated with Increased Levels of Let-7 Family of MicroRNAs
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
Animal Model of Trigeminal Neuralgia Induced by Chronic Constriction Injury Applied to the Ophthalmic Nerve in the Rat
 Showa Univ. J. Med. Sci. 9(2), 8995, December 1997 Original Animal Model of Trigeminal Neuralgia Induced by Chronic Constriction Injury Applied to the Ophthalmic Nerve in the Rat Kazuo HANAKAWA, Takao
Showa Univ. J. Med. Sci. 9(2), 8995, December 1997 Original Animal Model of Trigeminal Neuralgia Induced by Chronic Constriction Injury Applied to the Ophthalmic Nerve in the Rat Kazuo HANAKAWA, Takao
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Synthesis and Evaluation of Antiallodynic and Anticonvulsant Activity of Novel Amide and Urea Derivatives of Valproic Acid Analogues Dan Kaufmann, Meir Bialer, $, Jakob Avi Shimshoni,
Supporting Information Synthesis and Evaluation of Antiallodynic and Anticonvulsant Activity of Novel Amide and Urea Derivatives of Valproic Acid Analogues Dan Kaufmann, Meir Bialer, $, Jakob Avi Shimshoni,
mirna Biomarkers Seena K. Ajit PhD Pharmacology & Physiology Drexel University College of Medicine October 12, 2017
 mirna Biomarkers Seena K. Ajit PhD Pharmacology & Physiology Drexel University College of Medicine October 12, 2017 Outline Introduction Circulating mirnas as potential biomarkers for pain Complex regional
mirna Biomarkers Seena K. Ajit PhD Pharmacology & Physiology Drexel University College of Medicine October 12, 2017 Outline Introduction Circulating mirnas as potential biomarkers for pain Complex regional
Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical Allodynia in a Rat Model of Postoperative Pain
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2013 April; Vol. 26, No. 2: 125-129 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.2.125 Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical
Original Article Korean J Pain 2013 April; Vol. 26, No. 2: 125-129 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.2.125 Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III
 Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice.
 Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D.,
Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D.,
High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases
 https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
EFFECTS OF Pueraria mirifica ON NEUROPATHIC PAIN IN RATS
 EFFECTS OF Pueraria mirifica ON NEUROPATHIC PAIN IN RATS Kamolchanok Tanchotikul 1, Quankamon Dejativongse Na Ayudhya 1*, Orawan Piyaboon 1 and Supin Chompoopong 2 1 Department of Biology, Mahidol Wittayanusorn
EFFECTS OF Pueraria mirifica ON NEUROPATHIC PAIN IN RATS Kamolchanok Tanchotikul 1, Quankamon Dejativongse Na Ayudhya 1*, Orawan Piyaboon 1 and Supin Chompoopong 2 1 Department of Biology, Mahidol Wittayanusorn
Curcumin Attenuates Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Chronic Constrictive Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain
 Pain Ther (2014) 3:59 69 DOI 10.1007/s40122-014-0024-4 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Curcumin Attenuates Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Chronic Constrictive Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain Yu Xiang Di Cao
Pain Ther (2014) 3:59 69 DOI 10.1007/s40122-014-0024-4 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Curcumin Attenuates Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Chronic Constrictive Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain Yu Xiang Di Cao
The levels of mrna expression in the mouse brain were measured at 52 dpi after the brains were divided into five regions: cortex, hippocampus,
 Supplemental material Supplemental method RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and real-time PCR The levels of mrna expression in the mouse brain were measured at 52 dpi after the brains were divided
Supplemental material Supplemental method RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and real-time PCR The levels of mrna expression in the mouse brain were measured at 52 dpi after the brains were divided
Chronic Inflammatory Pain Induces Maladaptation to Stress in Mice
 日本緩和医療薬学雑誌 (Jpn. J. Pharm. Palliat. Care Sci.)9 : 55 _ 60(2016) 55 [Short Communication] Chronic Inflammatory Pain Induces Maladaptation to Stress in Mice Daisuke ISHII *, Kazuya MIYAGAWA *, Minoru TSUJI,
日本緩和医療薬学雑誌 (Jpn. J. Pharm. Palliat. Care Sci.)9 : 55 _ 60(2016) 55 [Short Communication] Chronic Inflammatory Pain Induces Maladaptation to Stress in Mice Daisuke ISHII *, Kazuya MIYAGAWA *, Minoru TSUJI,
Original Article FEMALE CASTRATED RATS WITH NEUROPATHIC PAIN: BEHAVIOURAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL CORRELATES. Summary. Slavina K.
 J Biomed Clin Res Volume 2 Number 2, 2009 Original Article FEMALE CASTRATED RATS WITH NEUROPATHIC PAIN: BEHAVIOURAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL CORRELATES Slavina K. Surcheva, 2 Milka A. Nashar, 1 Lachezar K. Surchev,
J Biomed Clin Res Volume 2 Number 2, 2009 Original Article FEMALE CASTRATED RATS WITH NEUROPATHIC PAIN: BEHAVIOURAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL CORRELATES Slavina K. Surcheva, 2 Milka A. Nashar, 1 Lachezar K. Surchev,
Behavior of neuropathic pain in mice following chronic constriction injury comparing silk and catgut ligatures
 van der Wal et al. SpringerPlus (2015) 4:225 DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1009-4 a SpringerOpen Journal RESEARCH Open Access Behavior of neuropathic pain in mice following chronic constriction injury comparing
van der Wal et al. SpringerPlus (2015) 4:225 DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1009-4 a SpringerOpen Journal RESEARCH Open Access Behavior of neuropathic pain in mice following chronic constriction injury comparing
Evaluation of Gabapentin and S-( )-3-Isobutylgaba in a Rat Model of Postoperative Pain
 0022-3565/97/2823-1242$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 282, No. 3 Copyright 1997 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
0022-3565/97/2823-1242$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 282, No. 3 Copyright 1997 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat. Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons Hawon Cho, Young Duk Yang, Jesun Lee, Byeongjoon Lee, Tahnbee Kim Yongwoo Jang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons Hawon Cho, Young Duk Yang, Jesun Lee, Byeongjoon Lee, Tahnbee Kim Yongwoo Jang,
GABA B Receptor Agonist Baclofen Has Non-Specific Antinociceptive Effect in the Model of Peripheral Neuropathy in the Rat
 Physiol. Res. 3: 31-3, GABA B Receptor Agonist Baclofen Has Non-Specific Antinociceptive Effect in the Model of Peripheral Neuropathy in the Rat M. FRANĚK, Š. VACULÍN, R. ROKYTA Department of Normal, Pathological
Physiol. Res. 3: 31-3, GABA B Receptor Agonist Baclofen Has Non-Specific Antinociceptive Effect in the Model of Peripheral Neuropathy in the Rat M. FRANĚK, Š. VACULÍN, R. ROKYTA Department of Normal, Pathological
Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy
 Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy David Kendall & Bengt von Mentzer; PharmNovo AB/UK Alex Conibear & Eamonn Kelly, University of Bristol Junaid Asghar,
Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy David Kendall & Bengt von Mentzer; PharmNovo AB/UK Alex Conibear & Eamonn Kelly, University of Bristol Junaid Asghar,
Axotomy increases NADPH-diaphorase activity in the dorsal root ganglia and lumbar spinal cord of the turtle Trachemys dorbigni
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 489-493 NADPH-d after peripheral axotomy in the turtle ISSN 0100-879X 489 Axotomy increases NADPH-diaphorase activity in the dorsal root
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 489-493 NADPH-d after peripheral axotomy in the turtle ISSN 0100-879X 489 Axotomy increases NADPH-diaphorase activity in the dorsal root
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A. Real-Time RT-PCR Detection.
 For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
Vantage Diabetes Panel 1
 Catalog No. AM100050 50 Reactions To be used in conjunction with the Vantage microrna Detection Kit, catalog number AM100091 (50 reactions) or AM100092 (200 reactions). Components included in this kit:
Catalog No. AM100050 50 Reactions To be used in conjunction with the Vantage microrna Detection Kit, catalog number AM100091 (50 reactions) or AM100092 (200 reactions). Components included in this kit:
Risk Factors That Predispose Patients to Orofacial Pain
 Risk Factors That Predispose Patients to Orofacial Pain Paul Durham, PhD Distinguished Professor of Cell Biology Director Center for Biomedical & Life Sciences Missouri State University Cluster Headache
Risk Factors That Predispose Patients to Orofacial Pain Paul Durham, PhD Distinguished Professor of Cell Biology Director Center for Biomedical & Life Sciences Missouri State University Cluster Headache
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
NEUROPATHIC pain afflicts millions of people
 PAIN MEDICINE Effects of Regional and Whole-body Hypothermic Treatment before and after Median Nerve Injury on Neuropathic Pain and Glial Activation in Rat Cuneate Nucleus Yi-Ju Tsai, Ph.D.,* Chun-Ta Huang,
PAIN MEDICINE Effects of Regional and Whole-body Hypothermic Treatment before and after Median Nerve Injury on Neuropathic Pain and Glial Activation in Rat Cuneate Nucleus Yi-Ju Tsai, Ph.D.,* Chun-Ta Huang,
TITLE: Exploration of a Novel Persistent Reversal of Pathological Pain: Mechanisms and Mediators
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-2-0070 TITLE: Exploration of a Novel Persistent Reversal of Pathological Pain: Mechanisms and Mediators PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Distinguished Professor Dr. Linda Watkins CONTRACTING
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-2-0070 TITLE: Exploration of a Novel Persistent Reversal of Pathological Pain: Mechanisms and Mediators PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Distinguished Professor Dr. Linda Watkins CONTRACTING
A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch
 Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
The Effect of Intrathecal Gabapentin on Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Rats Induced by Spinal Nerve Ligation
 J Korean Med Sci 2002; 17: 225-9 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences The Effect of Intrathecal Gabapentin on Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Rats Induced
J Korean Med Sci 2002; 17: 225-9 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences The Effect of Intrathecal Gabapentin on Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Rats Induced
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 METHODS Mice and rats. Behavioural experiments were performed in male and female 7 12 week old mice or in male 7 10 week old Wistar rats. Permissions for the animal experiments have been obtained from
METHODS Mice and rats. Behavioural experiments were performed in male and female 7 12 week old mice or in male 7 10 week old Wistar rats. Permissions for the animal experiments have been obtained from
Mechanical sensitization of cutaneous sensory fibers in the spared nerve injury mouse model
 Smith et al. Molecular Pain 2013, 9:61 MOLECULAR PAIN SHORT REPORT Open Access Mechanical sensitization of cutaneous sensory fibers in the spared nerve injury mouse model Amanda K Smith, Crystal L O Hara
Smith et al. Molecular Pain 2013, 9:61 MOLECULAR PAIN SHORT REPORT Open Access Mechanical sensitization of cutaneous sensory fibers in the spared nerve injury mouse model Amanda K Smith, Crystal L O Hara
Circulating Microrna Expression As A Biomarker For Early Diagnosis Of Severity In Spinal Cord Injury
 Circulating Microrna Expression As A Biomarker For Early Diagnosis Of Severity In Spinal Cord Injury Susumu Hachisuka 1, Naosuke Kamei, MD, PhD 2, Satoshi Ujigo 3, Shigeru Miyaki 3, Mitsuo Ochi 3. 1 Hiroshima
Circulating Microrna Expression As A Biomarker For Early Diagnosis Of Severity In Spinal Cord Injury Susumu Hachisuka 1, Naosuke Kamei, MD, PhD 2, Satoshi Ujigo 3, Shigeru Miyaki 3, Mitsuo Ochi 3. 1 Hiroshima
Entrainment of the mouse circadian clock by sub-acute physical and psychological
 Supplementary Information Entrainment of the mouse circadian clock by sub-acute physical and psychological Yu Tahara 1, Takuya Shiraishi 1, Yosuke Kikuchi 1, Atsushi Haraguchi 1, Daisuke Kuriki 1, Hiroyuki
Supplementary Information Entrainment of the mouse circadian clock by sub-acute physical and psychological Yu Tahara 1, Takuya Shiraishi 1, Yosuke Kikuchi 1, Atsushi Haraguchi 1, Daisuke Kuriki 1, Hiroyuki
Original Article Upregulation of neuregulin-1 reverses signs of neuropathic pain in rats
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(9):5916-5921 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001263 Original Article Upregulation of neuregulin-1 reverses signs of neuropathic pain in rats Guojun Wang 1,2*, Dawei Dai
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(9):5916-5921 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001263 Original Article Upregulation of neuregulin-1 reverses signs of neuropathic pain in rats Guojun Wang 1,2*, Dawei Dai
Research Article Contralateral Metabolic Activation Related to Plastic Changes in the Spinal Cord after Peripheral Nerve Injury in Rats
 Neural Plasticity Volume 2015, Article ID 438319, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/438319 Research Article Contralateral Metabolic Activation Related to Plastic Changes in the Spinal Cord after Peripheral
Neural Plasticity Volume 2015, Article ID 438319, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/438319 Research Article Contralateral Metabolic Activation Related to Plastic Changes in the Spinal Cord after Peripheral
Electronic Supplementary Information. Direct chemiluminescence detection of circulating. micrornas in serum samples using a single-strand specific
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Direct chemiluminescence detection of circulating
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Direct chemiluminescence detection of circulating
Genome wide identification and functional analyses of microrna signatures associated with cancer pain
 OPEN ACCESS TRANSPARENT PROCESS Genome wide identification and functional analyses of microrna signatures associated with cancer pain Kiran Kumar Bali 1,2, Deepitha Selvaraj 1,2, Venkata P. Satagopam 3,4,
OPEN ACCESS TRANSPARENT PROCESS Genome wide identification and functional analyses of microrna signatures associated with cancer pain Kiran Kumar Bali 1,2, Deepitha Selvaraj 1,2, Venkata P. Satagopam 3,4,
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Sendai, Japan, 2
 Low-energy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Promotes VEGF Expression and Angiogenesis and Improve Locomotor and Sensory Functions after spinal cord injury Kenichiro Yahata 1, Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D.
Low-energy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Promotes VEGF Expression and Angiogenesis and Improve Locomotor and Sensory Functions after spinal cord injury Kenichiro Yahata 1, Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D.
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Assessment of sample purity and quality.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Supplementary information to. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reversed Morphine Tolerance and Opioid-induced Hyperalgesia
 Supplementary information to Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reversed Morphine Tolerance and Opioid-induced Hyperalgesia Zhen Hua 1,2 *, LiPing Liu 1 *, Jun Shen 1, Katherine Cheng 1, Aijun Liu 1, Jing Yang 1,
Supplementary information to Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reversed Morphine Tolerance and Opioid-induced Hyperalgesia Zhen Hua 1,2 *, LiPing Liu 1 *, Jun Shen 1, Katherine Cheng 1, Aijun Liu 1, Jing Yang 1,
A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization
 A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle 4 th International qpcr Symposium Weihenstephan, March 1,
A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle 4 th International qpcr Symposium Weihenstephan, March 1,
NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions as Related to Analgesia and Tolerance
 Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S7 Proceedings Supplement NDMA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions
Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S7 Proceedings Supplement NDMA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions
Chapter 2. Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit
 15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
TITLE: Exploration of a Novel Persistent Reversal of Pathological Pain: Mechanisms and Mediators
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-2-0070 TITLE: Exploration of a Novel Persistent Reversal of Pathological Pain: Mechanisms and Mediators PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Linda Watkins CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: REPORT
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-2-0070 TITLE: Exploration of a Novel Persistent Reversal of Pathological Pain: Mechanisms and Mediators PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Linda Watkins CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: REPORT
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna targets were found in exosomes and absent in free-floating supernatant. Serum exosomes and exosome-free supernatant were
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna targets were found in exosomes and absent in free-floating supernatant. Serum exosomes and exosome-free supernatant were separated via ultracentrifugation and lysed to analyze
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna targets were found in exosomes and absent in free-floating supernatant. Serum exosomes and exosome-free supernatant were separated via ultracentrifugation and lysed to analyze
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
MOLECULAR PAIN. Josée Guindon 1,3*, Liting Deng 1,2,3, Baochang Fan 1, Jim Wager-Miller 1 and Andrea G Hohmann 1,2,3*
 Guindon et al. Molecular Pain 2014, 10:56 MOLECULAR PAIN RESEARCH Open Access Optimization of a cisplatin model of chemotherapyinduced peripheral neuropathy in mice: use of vitamin C and sodium bicarbonate
Guindon et al. Molecular Pain 2014, 10:56 MOLECULAR PAIN RESEARCH Open Access Optimization of a cisplatin model of chemotherapyinduced peripheral neuropathy in mice: use of vitamin C and sodium bicarbonate
Preclinical evaluation of pain in endometriosis
 receptor antagonism reduces peripheral and central hyperalgesia in a preclinical mouse model of endometriosis Erin Greaves, Andrew W Horne, Helen Jerina, arta ikolajczak, Lisa Hilferty, Rory itchell, Sue
receptor antagonism reduces peripheral and central hyperalgesia in a preclinical mouse model of endometriosis Erin Greaves, Andrew W Horne, Helen Jerina, arta ikolajczak, Lisa Hilferty, Rory itchell, Sue
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016)
 International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) Analgesic Contrast of Diverse Administrations of Botulinum Neurotoxin A (BoTN/A) Using Rat Neuropathic Pain Model Qiong-Fang YANG1,3,
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) Analgesic Contrast of Diverse Administrations of Botulinum Neurotoxin A (BoTN/A) Using Rat Neuropathic Pain Model Qiong-Fang YANG1,3,
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Pathophysiology of Pain. Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC
 Pathophysiology of Pain Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC Learning Objectives Anatomic pathway of nociception Discuss the multiple target sites of pharmacological
Pathophysiology of Pain Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC Learning Objectives Anatomic pathway of nociception Discuss the multiple target sites of pharmacological
Analgesic roles of peripheral intrinsic met-enkephalin and dynorphin A in long-lasting inflammatory pain induced by complete Freund's adjuvant in rats
 2344 Analgesic roles of peripheral intrinsic met-enkephalin and dynorphin A in long-lasting inflammatory pain induced by complete Freund's adjuvant in rats YONG LIANG JIANG, XIAO FEN HE, YA FANG SHEN,
2344 Analgesic roles of peripheral intrinsic met-enkephalin and dynorphin A in long-lasting inflammatory pain induced by complete Freund's adjuvant in rats YONG LIANG JIANG, XIAO FEN HE, YA FANG SHEN,
Supplementary Figure 1: Experimental design. DISCOVERY PHASE VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) (N = 20) Healthy = 20. Healthy = 6. Endometriosis = 33
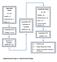 DISCOVERY PHASE (N = 20) Healthy = 6 Endometriosis = 7 EAOC = 7 Quantitative PCR (mirnas = 1113) a Quantitative PCR Verification of Candidate mirnas (N = 24) VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) Healthy = 20 Endometriosis
DISCOVERY PHASE (N = 20) Healthy = 6 Endometriosis = 7 EAOC = 7 Quantitative PCR (mirnas = 1113) a Quantitative PCR Verification of Candidate mirnas (N = 24) VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) Healthy = 20 Endometriosis
ONLINE. F.M. Teixeira*, L.L. Castro*, R.T. Ferreira, P.A. Pires, F.A. Vanderlinde and M.A. Medeiros
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research Online Provisional Version ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research Online Provisional Version ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully
# of Normal brain # of controls Upregulated Downregulated Normalizer # of mirnas in Platform profile
 Profiling studies comparing mirna expression in glioblastoma or glioblastoma cell lines to normal brain. MiRNAs were only included if fold change was greater than or equal to twofold Author Year Type of
Profiling studies comparing mirna expression in glioblastoma or glioblastoma cell lines to normal brain. MiRNAs were only included if fold change was greater than or equal to twofold Author Year Type of
A role for uninjured afferents in neuropathic pain
 Acta Physiologica Sinica, October 25, 2008, 60 (5): 605-609 http://www.actaps.com.cn 605 Review A role for uninjured afferents in neuropathic pain Richard A. Meyer 1,2,3,*, Matthias Ringkamp 1 Departments
Acta Physiologica Sinica, October 25, 2008, 60 (5): 605-609 http://www.actaps.com.cn 605 Review A role for uninjured afferents in neuropathic pain Richard A. Meyer 1,2,3,*, Matthias Ringkamp 1 Departments
IK01400: non-opioid preclinical drug candidate for pain treatment
 IK01400: non-opioid preclinical drug candidate for pain treatment Introduction Bio-Link presents a valuable licensing opportunity for the development of novel nonopioid drug candidates to manage acute
IK01400: non-opioid preclinical drug candidate for pain treatment Introduction Bio-Link presents a valuable licensing opportunity for the development of novel nonopioid drug candidates to manage acute
processes in the central nervous system (CNS), affecting many of the during the course of ethanol treatment. Ethanol stimulates the release of
 INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION Neuroscience research is essential for understanding the biological basis of ethanol-related brain alterations and for identifying the molecular targets for therapeutic compounds
INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION Neuroscience research is essential for understanding the biological basis of ethanol-related brain alterations and for identifying the molecular targets for therapeutic compounds
Epigenetics and trauma
 Epigenetics and trauma Influence of trauma on mental health Patrick McGowan, PhD Biological Sciences, UTSC Cell and Systems Biology, Psychology University of Toronto patrick.mcgowan@utoronto.ca Leuven,
Epigenetics and trauma Influence of trauma on mental health Patrick McGowan, PhD Biological Sciences, UTSC Cell and Systems Biology, Psychology University of Toronto patrick.mcgowan@utoronto.ca Leuven,
211MDS Pain theories
 211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers
 micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in the rat
 Cheppudira et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2016) 16:73 DOI 10.1186/s12871-016-0242-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in
Cheppudira et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2016) 16:73 DOI 10.1186/s12871-016-0242-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in
Microglial Inhibition Influences XCL1/XCR1 Expression and Causes Analgesic Effects in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Neuropathy
 Microglial Inhibition Influences XCL1/XCR1 Expression and Causes Analgesic Effects in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Magdalena Zychowska, M.D., Ewelina Rojewska, Ph.D., Anna Piotrowska, M.D., Grzegorz
Microglial Inhibition Influences XCL1/XCR1 Expression and Causes Analgesic Effects in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Magdalena Zychowska, M.D., Ewelina Rojewska, Ph.D., Anna Piotrowska, M.D., Grzegorz
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
CXCL13 drives spinal astrocyte activation and neuropathic pain via CXCR5
 The Journal of Clinical Investigation CXCL13 drives spinal astrocyte activation and neuropathic pain via CXCR5 Bao-Chun Jiang, 1 De-Li Cao, 1 Xin Zhang, 1 Zhi-Jun Zhang, 1,2 Li-Na He, 1 Chun-Hua Li, 1
The Journal of Clinical Investigation CXCL13 drives spinal astrocyte activation and neuropathic pain via CXCR5 Bao-Chun Jiang, 1 De-Li Cao, 1 Xin Zhang, 1 Zhi-Jun Zhang, 1,2 Li-Na He, 1 Chun-Hua Li, 1
Dissected tissues were minced and lysed in lysis buffer (1x Tris buffered saline (TBS), 1% NP-40,
 Data Supplement for Dincheva et al., Effect of Early-Life Fluoxetine on Anxiety-Like Behaviors in BDNF Val66Met Mice. Am J Psychiatry (doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.15121592) Contents Supplemental Methods
Data Supplement for Dincheva et al., Effect of Early-Life Fluoxetine on Anxiety-Like Behaviors in BDNF Val66Met Mice. Am J Psychiatry (doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.15121592) Contents Supplemental Methods
Original Article Paeoniflorin attenuates neuropathic pain through the regulation of Sirt1 in rats
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(3):4678-4686 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0045899 Original Article Paeoniflorin attenuates neuropathic pain through the regulation of Sirt1 in rats Tao Tao, Hui Zheng,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(3):4678-4686 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0045899 Original Article Paeoniflorin attenuates neuropathic pain through the regulation of Sirt1 in rats Tao Tao, Hui Zheng,
Cannabinoid Agonists Inhibit Neuropathic Pain Induced by Brachial Plexus Avulsion in Mice by Affecting Glial Cells and MAP Kinases
 Cannabinoid Agonists Inhibit Neuropathic Pain Induced by Brachial Plexus Avulsion in Mice by Affecting Glial Cells and MAP Kinases Ana F. Paszcuk 1, Rafael C. Dutra 1, Kathryn A. B. S. da Silva 1, Nara
Cannabinoid Agonists Inhibit Neuropathic Pain Induced by Brachial Plexus Avulsion in Mice by Affecting Glial Cells and MAP Kinases Ana F. Paszcuk 1, Rafael C. Dutra 1, Kathryn A. B. S. da Silva 1, Nara
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Neuropathic Pain Symptom Palliation. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2007 March 26.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Neuropathic Pain Symptom Palliation. 2005 ; 1(1): 19 23. Sympathetic Fiber Sprouting in Chronically Compressed Dorsal Root Ganglia
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Neuropathic Pain Symptom Palliation. 2005 ; 1(1): 19 23. Sympathetic Fiber Sprouting in Chronically Compressed Dorsal Root Ganglia
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me. Agenda. What We Know About Pain 9/7/2012
 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Possible Involvement of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Analgesic Effects of 4-Methylcatechol on Neuropathic Pain
 49 Bull Yamaguchi Med School 57 3-4 :49-56, 2010 Possible Involvement of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Analgesic Effects of 4-Methylcatechol on Neuropathic Pain Kozo Ishikawa 2 Department of Emergency
49 Bull Yamaguchi Med School 57 3-4 :49-56, 2010 Possible Involvement of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Analgesic Effects of 4-Methylcatechol on Neuropathic Pain Kozo Ishikawa 2 Department of Emergency
The Nervous System. Anatomy of a Neuron
 The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
Involvement of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted from chromosome 10 in rodent model of neuropathic pain
 Huang et al. Journal of Neuroinflammation (2015) 12:59 DOI 10.1186/s12974-015-0280-1 JOURNAL OF NEUROINFLAMMATION RESEARCH Open Access Involvement of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted from chromosome
Huang et al. Journal of Neuroinflammation (2015) 12:59 DOI 10.1186/s12974-015-0280-1 JOURNAL OF NEUROINFLAMMATION RESEARCH Open Access Involvement of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted from chromosome
Serum mirna signature diagnoses and discriminates murine colitis subtypes and predicts ulcerative colitis in humans
 Serum mirna signature diagnoses and discriminates murine colitis subtypes and predicts ulcerative colitis in humans Emilie Viennois 1*, Yuan Zhao 1, 2, Moon Kwon Han 1, Bo Xiao 1, 3, Mingzhen Zhang 1,
Serum mirna signature diagnoses and discriminates murine colitis subtypes and predicts ulcerative colitis in humans Emilie Viennois 1*, Yuan Zhao 1, 2, Moon Kwon Han 1, Bo Xiao 1, 3, Mingzhen Zhang 1,
microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions. In brief, 10ng of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
Transcriptional and Epigenetic Mechanisms of Addiction
 Transcriptional and Epigenetic Mechanisms of Addiction Eric J. Nestler Mount Sinai School of Medicine New York, NY Dr. Ray Fuller There is every reason to be optimistic that in the future we will find
Transcriptional and Epigenetic Mechanisms of Addiction Eric J. Nestler Mount Sinai School of Medicine New York, NY Dr. Ray Fuller There is every reason to be optimistic that in the future we will find
Cancer-induced bone pain
 Cancer-induced bone pain Common Prevalent in particular cancers: breast (73%), prostate (68%), thyroid (42%), lung (36%), renal (35%), colon (5%) Correlates with an increased morbidity Reduced performance
Cancer-induced bone pain Common Prevalent in particular cancers: breast (73%), prostate (68%), thyroid (42%), lung (36%), renal (35%), colon (5%) Correlates with an increased morbidity Reduced performance
EVALUATION OF ANTI-NOCICEPTIVE EFFECT OF TOLPERISONE BY COMPARING ITS EFFECT WITH TRAMADOL IN NEUROPATHIC PAIN
 Journal of Pharmaceutical Biology www.jpbjournal.com e-issn - 2249-7560 Print ISSN - 2249-7579 EVALUATION OF ANTI-NOCICEPTIVE EFFECT OF TOLPERISONE BY COMPARING ITS EFFECT WITH TRAMADOL IN NEUROPATHIC
Journal of Pharmaceutical Biology www.jpbjournal.com e-issn - 2249-7560 Print ISSN - 2249-7579 EVALUATION OF ANTI-NOCICEPTIVE EFFECT OF TOLPERISONE BY COMPARING ITS EFFECT WITH TRAMADOL IN NEUROPATHIC
Materials and Methods
 Anesthesiology 2004; 100:1258 62 2004 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Spinal Adenosine Receptor Activation Reduces Hypersensitivity after Surgery by a Different
Anesthesiology 2004; 100:1258 62 2004 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Spinal Adenosine Receptor Activation Reduces Hypersensitivity after Surgery by a Different
RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays
 Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Single Cell Quantitative Polymer Chain Reaction (sc-qpcr)
 Single Cell Quantitative Polymer Chain Reaction (sc-qpcr) Analyzing gene expression profiles from a bulk population of cells provides an average profile which may obscure important biological differences
Single Cell Quantitative Polymer Chain Reaction (sc-qpcr) Analyzing gene expression profiles from a bulk population of cells provides an average profile which may obscure important biological differences
Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture
 Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture Nanna Goldman *, Michael Chen *, Takumi Fujita *, Qiwu Xu, Weiguo Peng, Wei Liu, Tina K. Jensen, Yong Pei, Fushun Wang, Xiaoning
Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture Nanna Goldman *, Michael Chen *, Takumi Fujita *, Qiwu Xu, Weiguo Peng, Wei Liu, Tina K. Jensen, Yong Pei, Fushun Wang, Xiaoning
mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons
 Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Interaction of Morphine and Selective Serotonin Receptor Inhibitors in Rats Experiencing Inflammatory Pain
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anesthesiology & Pain http://dx.doi.org/10.336/jkms.01.7..30 J Korean Med Sci 01; 7: 30-36 Interaction of Morphine and Selective Serotonin Receptor Inhibitors in Rats Experiencing Inflammatory
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anesthesiology & Pain http://dx.doi.org/10.336/jkms.01.7..30 J Korean Med Sci 01; 7: 30-36 Interaction of Morphine and Selective Serotonin Receptor Inhibitors in Rats Experiencing Inflammatory
Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA
 Contribution of Calcium Channel α 2 δ Binding Sites to the Pharmacology of Gabapentin and Pregabalin Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA Disclosure Information Charlie Taylor, PhD
Contribution of Calcium Channel α 2 δ Binding Sites to the Pharmacology of Gabapentin and Pregabalin Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA Disclosure Information Charlie Taylor, PhD
Randomized Experimental Trial. Pain Physician 2018; 21:33-40 ISSN
 Pain Physician 2018; 21:33-40 ISSN 1533-3159 Randomized Experimental Trial Pulsed Radiofrequency Improves Neuropathic Pain in Chronic Constriction Injury Rats through the Upregulation of the Transcription
Pain Physician 2018; 21:33-40 ISSN 1533-3159 Randomized Experimental Trial Pulsed Radiofrequency Improves Neuropathic Pain in Chronic Constriction Injury Rats through the Upregulation of the Transcription
Cognitive Function Test. NOR & spatial NOR task. Introduction. Novel Object Recognition (NOR) Estrogen Receptor (ER) in Brain
 Cognitive Function Test Human Rodent Sutcliffe JS, Marshall KM, Neill JC. Behavioral Brain Research 177(2007) 117-125. Radial Arm maze Morris Water maze Siriporn Vongsaiyat 16 th Feb 2007 Novel Object
Cognitive Function Test Human Rodent Sutcliffe JS, Marshall KM, Neill JC. Behavioral Brain Research 177(2007) 117-125. Radial Arm maze Morris Water maze Siriporn Vongsaiyat 16 th Feb 2007 Novel Object
Opioid Receptor Trafficking in Pain States
 Encyclopedia of Pain Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2007 10.1007/978-3-540-29805-2_2962 Robert F. Schmidt and William D. Willis Opioid Receptor Trafficking in Pain States Catherine M. Cahill 3, Anne
Encyclopedia of Pain Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2007 10.1007/978-3-540-29805-2_2962 Robert F. Schmidt and William D. Willis Opioid Receptor Trafficking in Pain States Catherine M. Cahill 3, Anne
he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003)
 MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
Pain Pathways. Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH
 Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
microrna analysis for the detection of autologous blood transfusion in doping control
 microrna analysis for the detection of autologous blood transfusion in doping control Application note Doping Control Authors Francesco Donati*, Fiorella Boccia, Xavier de la Torre, Alessandra Stampella,
microrna analysis for the detection of autologous blood transfusion in doping control Application note Doping Control Authors Francesco Donati*, Fiorella Boccia, Xavier de la Torre, Alessandra Stampella,
Analgesic effects of the COX-2 inhibitor parecoxib on surgical pain through suppression of spinal ERK signaling
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 275-279, 2013 Analgesic effects of the COX-2 inhibitor parecoxib on surgical pain through suppression of spinal ERK signaling YA-JING GUO 1, XU-DAN SHI 2, DI FU
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 275-279, 2013 Analgesic effects of the COX-2 inhibitor parecoxib on surgical pain through suppression of spinal ERK signaling YA-JING GUO 1, XU-DAN SHI 2, DI FU
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
