Atrophic Vaginitis. Mimi Clarke Secor CHAPTER 23
|
|
|
- Jerome Brown
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Atrophic Vaginitis CHAPTER 23 Mimi Clarke Secor I. Atrophic vaginitis explained. A. Statistics. 1. Statistics indicate that 45 million women are menopausal and that this number is growing as baby boomers reach menopause and beyond. 2. Three years after the onset of menopause, almost 50% of women will experience vaginal dryness. B. Some facts. 1. Symptoms of atrophic vaginitis are commonly associated with menopause as estrogen levels drop causing thinning of the vulvovaginal epithelium. 2. Urogenital atrophy is the most inevitable consequence of menopause. 3. Atrophic changes are reversible with the estrogen therapy. 4. Conditions associated with low estrogen are summarized in Box II. Pathophysiology. A. Urogenital changes occur during perimenopause, often well in advance of cessation of menses. Vaginal mucosal tissues contain many estrogen receptors which are commonly affected by reductions in estrogen. B. As the wall of the vagina become thin, there is a decrease in the 357
2 358 Unit 6: Evaluation of the Menopausal Woman Causes of Urogenital Atrophy Antiestrogen medications Lupron Clomid Provera Synarel Nolvadex Danocrine OBOX 23.1 Postpartum Absence of placental estrogen Breastfeeding Antagonistic action of prolactin on estrogen Premenopausal Premature ovarian failure Extraneous causes Surgery (oophorectomy) Chemotherapy Radiation Menopause Other milder forms Heavy smoking (reduced estrogen absorption) Reduced sexual activity Inadequate systemic estrogen replacement therapy support for the pelvic organs and the muscles that are adjacent to it. C. The drop in estrogen causes a decrease in glycogen reducing lactobacilli which leads to an increase in vaginal ph (from acid to alkaline). This often leads to overgrowth of various pathogenic bacteria such as Gardnerella vaginalis, mycoplasma, streptococci, and others (see Figure 23.1). D. Reduced estrogen may also result in a reduced blood flow, loss of collagen, elasticity, and muscle tone. Thinning of the urogenital epithelium or atrophism leads to various symptoms associated with atrophic vaginitis including dyspareunia and pruritus. E. Similar tissue changes may also occur in the urinary tract contributing to dysuria, incontinence, urinary frequency, and increased risk of urinary tract infections. F. Symptoms and signs of genitourinary atrophy may develop slowly, over many months or years, or may have a more rapid onset. G. Symptoms vary and are affected by many factors such as an individual s estrogen levels and response to these levels.
3 Chapter 23: Atrophic Vaginitis 359 Figure 23.1 Side view of bladder and related structures. III. Indications for evaluation. A. The complaint of urogential symptoms is an indication for a thorough work-up. IV. Assessment. A. A history of symptoms may include the following: 1. Vulvovaginal symptoms. a. Vulvar dryness, lack of lubrication, pruritus, irritation, and vaginal discharge. 2. Vaginal bleeding. a. Due to tissue thinning and friability, vaginal spotting is of-
4 360 Unit 6: Evaluation of the Menopausal Woman ten the first symptom a patient presents with. The source of bleeding must be determined and if necessary, a biopsy and/or ultrasound should be performed. b. Bleeding may be noticed after sex or after wiping with toilet tissue. 3. Dyspareunia. a. Also known as painful intercourse, this condition may result from stretching or tearing of the thin narrowed introital mucosa, or from stretching of the dry, less elastic, shorter vagina causing dyspareunia. b. These changes are less likely to occur if sexual relations are maintained during perimenopause and beyond (the use it or lose it phenomenon). 4. Low libido and other sexual complaints such as lack of lubrication, dyspareunia, and distress related to atrophic and/or sexual complaints. 5. Urinary symptoms. a. The lower urinary tract and pelvic musculature are under the influence of estrogen and share a common embryologic origin with the vagina. b. Squamous epithelium of the trigone and urethra thin and blood flow decreases. c. Urinary symptoms related to low estrogen levels include dysuria, hematuria, frequency, nocturia, urinary incontinence (usually stress type), sensation of a dropped bladder, and history of frequent urinary tract infections. 6. Hematuria is commonly associated with atrophism and must be thoroughly evaluated as it can, uncommonly, be a symptom of bladder cancer. B. Gynecologic history may include: 1. Menstrual history including LMP, FMP, abnormal bleeding, history of hot flashes, night sweats, or flushing. 2. Age of biologic mother or sisters at menopause. 3. Date of last Papanicolaou test (Pap test), results, history of abnormal Pap, and management. 4. Sexual history including dyspareunia, dryness, sexual partner (gender), date of last sex, use of lubricants, distress related to symptoms. 5. Total hysterectomy is associated with atrophic vaginitis and symptoms may be severe due to the sudden reduction in estrogen levels.
5 Chapter 23: Atrophic Vaginitis 361 V. Medical, surgical, and family history, lifestyle, medications including use of AV (vaginal estrogen) over-the-counter preparations. (Box 23.2 summarizes the characteristic symptoms of AV.) A. External genitalia exam. 1. Note thinning of hair and tissues, pallor, erythema, lesions, fissures, loss of architectural landmarks, introital shrinkage, vulvar atrophy, pallor, erythema (diffuse versus focal), and tenderness. 2. Vulvar dryness and/or positive sticky glove sign, which occurs when the examiner s glove adheres temporarily and is thought to be diagnostic for atrophic vaginitis. 3. Urethral caruncle. a. Small friable polyp of urethral mucosa which protrudes from the inferior border of the urethral meatus (Figure 23.2). b. Associated with symptoms of dysuria, frequency, and may be the cause of vaginal bleeding in the menopausal woman. B. Vaginal exam. 1. Cystocele, rectocele, and grade (see Unit 7, chapter 24). 2. Introital laxity, tension, loss of tone with Kegels, or Valsalva maneuver. 3. Tenderness with palpation or during speculum insertion and/or exam. 4. Note vaginal pallor, erythema, loss of rugae (flattening), lesions, shortening of vagina, loss of elasticity, tenderness. 5. Discharge; which may range from scant to copious, be variable in quality ranging from thin white to thick, yellow/ green and malordorous. 6. Abnormal discharge may mimic trichomoniasis or other STI associated discharge. 7. Cervix. a. Erythema, lesions, friability, bleeding, tenderness, flattening and shortening, stenosis of cervical os (small). C. Bimanual exam. 1. Uterus. a. Size, shape especially asymmetry (associated with fibroids that usually shrink in menopause), diffuse enlargement associated with pregnancy or pathology such as hyperplasia, tenderness, sometimes fibroids, etc. 2. Pelvic floor (see chapter 24).
6 362 Unit 6: Evaluation of the Menopausal Woman Summary of Characteristics of Urogenital Atrophy OBOX 23.2 Labia (majora and minora) Less prominent, flattened Fusion of labia minora Lax and wrinkled (lack of subcutaneous fat) Thinning cell layer Prominent sebaceous glands Positive sticky glove sign Easily traumatized (fissures, excoriations) Irritation due to continuous use of pad for urinary incontinence Clitoris Less prominent Retracts beneath the prepuce Slight atrophy Subcutaneous fat Diminished Pubic hair Thins Less coarse Vaginal wall epithelium Thin (a few layers thick) Friable Shiny Small ulcerations Patches of granulation tissue Petechial spots (resemble trichomoniasis) Fissures Ecchymotic areas from exposed capillaries Loss of rugae Decreased vasularity (pale) Less lubrication (dryness) Loss of distensibility, elasticity Decreased discharge Vagina Introital stenosis (< two fingers) Shortened Shrinkage of fornices Less elasticity Possible cystocele, rectocele or pelvic prolapse
7 Chapter 23: Atrophic Vaginitis 363 Box 23.2 (continued) Discharge Variable Watery to thick and cloudy May be serosanguineous from friable surfaces Maturation Index Preponderance of parabasal cells Cervix Shrinks, flattens into vaginal wall Os becomes tiny Squamo-columnar junction recedes up the cervical canal Atrophied crypts and ducts in canal Uterus Smaller Endometrium thins less glandular, atrophic Uterine stripe < 4mm Fibroids may shrink Perineum Minor laceration at the posterior fourchette Urethra Caruncle red, berry-type protrusion Atrophy Polyps Prolapse/eversion of urethral mucosa Pelvic Floor Muscle tone diminishes Cystocele Rectocele Ligaments and connective tissue Lose strength and tone Bladder mucosa and urethra Decreased tone
8 364 Unit 6: Evaluation of the Menopausal Woman Figure 23.2 Small polyp of urethral mucosa in sagittal section and shown protruding from the inferior border of the urethral meatus. a. Note cystocele, rectocele, introital tone with Kegels, and Valsalva maneuver. 3. Ovaries. a. In menopause, ovaries should not be palpable. b. If ovaries are palpable, a work-up is indicated. VI. Diagnostic testing and differential diagnosis. A. Differential considerations (Table 23.1).
9 Chapter 23: Atrophic Vaginitis 365 Table 23.1 Differential Considerations in the Diagnosis of Atrophic Vaginitis Differential ph KOH Microscopy Atrophic vaginitis 5.0 Negative Few LB, WBCs variable, Immature Epithelial Cells (ECs) Trichomoniasis 5.0 Negative Trich, WBCs, Immature ECs, Few LB BV 4.7 Positive Clue cells, few WBCs, few LB Intermediate Flora ± normal ± positive Grainy epithelial cells, reduced LB Factors That Affect Vaginal ph Menses (ph 7.2) Semen (ph > 7) Cervical mucus, because it is alkaline Lubricant from speculum Intravaginal medications Lubricating jelly Tap water OBOX Vaginal ph. a. Atrophic vaginitis is associated with a significantly elevated vaginal ph, usually above 5. (1) A normal vaginal ph (4.0 to 4.5) indicates normal circulating estrogen levels and rules out atrophic vaginitis. (2) A high ph is due to the lack of lactobacilli which make lactic acid. b. Many factors can alter the ph results (Box 23.3). 2. Amine testing with potassium hydroxide (KOH). a. If negative, BV (bacterial vaginosis) is unlikely, and atrophic vaginitis is possible, especially if vaginal ph is also elevated. 3. Vaginal microscopy (see chapter 10). a. Note reduced or absent lactobacilli (LB). b. Note immature epithelial cells indicating low estrogen.
10 366 Unit 6: Evaluation of the Menopausal Woman c. Rule out trichomoniasis. If microscopy is equivocal for the identification of trichomoniasis, a trich culture should be done. Trichomoniasis may be asymptomatic for decades reactivating in perimenopause or postmenopause. The clinical presentation may mimic that of atrophic vaginitis. d. Rule out genital herpes with herpes select serology IGG type 2 testing. HSV 2 (herpes simplex virus) may be latent and/or asymptomatic for decades, activating in perimenopause or menopause. Genital HSV 2 is very common, and prevalence increases with age, affecting 1 out of 3 women over 30 years of age. Adding to the diagnostic challenge most clinical presentations are atypical, further evading easy diagnosis. e. If WBCs (white blood cells), this is most likely related to atrophic effects resulting in secondary vaginal infection, which will resolve when local estrogen is administered and maintained. Initial treatment daily for 2 to 6 weeks, then may be tapered to 2 to 3 times a week depending on patient response. If symptoms recur, frequency of treatment may need to be increased to daily, then gradually decreased again after 2 to 6 weeks of daily treatment. f. STIs must be ruled out (chapter 21), especially if WBCs are noted. STIs are increasing in older adults, so to assess risk, consider clinical assessment (history and exam) and age of sexual partners. 4. The Maturation Index. a. The presence of estrogen promotes the maturation of the cells lining the vaginal mucosa. b. The Maturation Index monitors the differentiation of the immature squamous cells toward their most evolved forms, from parabasal to intermediate cells, to the mature superficial cells, each representing a cellular layer (Figure 23.3). c. Sample is obtained by scraping the lateral wall of the vagina. d. The index represents the relative number of each kind of cell per hundred cells counted. (See Box 23.4, which compares the type of cell in each cell layer.) e. Expressed in a ratio of parabasal to intermediate to superficial cells and read from left to right. (1) 0:0:100 superficial cells well estrogenized because there are all superficial cells present.
11 Chapter 23: Atrophic Vaginitis 367 Figure 23.3 Layers of the vaginal epithelium. Comparison of the Squamous Epithelial Cells of the Vagina Parabasal Intermediate Superficial OBOX 23.4 Lower layer Smaller, round cells with large nuclei comprising 50% to 75% of the total cell size Sparse cytoplasm Middle layer Smaller nuclei with round cell Surface layer Small nuclei with rectangular cell membrane Nucleus comprises only 10% to 20% of the cell Abundant cytoplasm
12 368 Unit 6: Evaluation of the Menopausal Woman (2) 0:100:0 intermediate cell atrophy minimal atrophic vaginitis. (3) 100:0:0 parabasal cell atrophy marked atrophic vaginitis because there are no mature epithelial cells, only parabasal cells. (4) Note: The presence of any parabasal cells on a wet mount may be considered documentation of atrophic vaginitis. 5. Endometrial biopsy, colposcopy (based on Pap and HPV results) and possibly an ultrasound should be considered for abnormal vaginal bleeding. VII. Treatment considerations. A. Local estrogen is preferred to systemic estrogen as it is more effective for the treatment of atrophic vaginitis and is thought to be safer due to lower systemic absorption compared to oral administration. B. Systemic estrogen is not recommended for treatment of atrophic symptoms and if it is given for VMS (vasomotor symptoms) additional local estrogen may be necessary to adequately treat atrophic symptoms. C. Only the intravaginal estrogen FemRing is effective for the treatment of both hot flashes and atrophic vaginitis. D. Local estrogen therapy starts with daily intravaginal treatment for 2 to 4 weeks then may be tapered to three times weekly then twice a week as needed. E. Applying a small pea-sized amount of local estrogen cream to the introital area may relieve dyspareunia. Daily application is recommended initially, then three or two times weekly as needed. F. Less effective than estrogen, non-prescription over-the-counter (OTC) lubricants may help relieve dyspareunia and vaginal dryness. G. If BV is present with atrophic vaginitis, either local estrogen alone may be used, or BV may be treated followed by treatment with local estrogen. If estrogen has been stopped and BV recurs, local estrogen should be restarted and used for a longer term to prevent BV. Estrogen supports the regrowth and maintenance of lactobacilli, which is thought to be protective against recurrent BV. H. If vulvar skin lesions do not resolve within 6 weeks, a skin biopsy should be considered (see chapter 32). VIII. Follow-up. A. Follow-up visits may range from 2 weeks to 3 months based on the patient s problems, response to therapy, and clinician/patient preference.
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas. Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N
 Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Female Reproductive System
 Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
New Treatments for Vaginal Health. Sarah Azad, MD El Camino Women s Medical Group
 New Treatments for Vaginal Health There s Hope Sarah Azad, MD El Camino Women s Medical Group The Genitrourinary Syndrome of Menopause (GSM) Problems with genital health secondary to the changes that occur
New Treatments for Vaginal Health There s Hope Sarah Azad, MD El Camino Women s Medical Group The Genitrourinary Syndrome of Menopause (GSM) Problems with genital health secondary to the changes that occur
WOMEN'S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY GYNECOLOGICAL EXAM FORM 8
 WOMEN'S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY GYNECOLOGICAL EXAM FORM 8 AFFIX ID LABEL HERE ---> PARTICIPANT ID: (Enter number here only if ID label is not available) - - - WIHS STUDY VISIT #: FORM VERSION: 04/01/99 EXAMINER'S
WOMEN'S INTERAGENCY HIV STUDY GYNECOLOGICAL EXAM FORM 8 AFFIX ID LABEL HERE ---> PARTICIPANT ID: (Enter number here only if ID label is not available) - - - WIHS STUDY VISIT #: FORM VERSION: 04/01/99 EXAMINER'S
Gynecological Cancers
 Gynecological Cancers Outline Ovarian Cancer Uterine (Endometrial) Cancer Cervical Cancer Vulvar Cancer Vaginal Cancer Overian Cancer Ovarian cancer is cancer that forms in the tissue of the ovary and
Gynecological Cancers Outline Ovarian Cancer Uterine (Endometrial) Cancer Cervical Cancer Vulvar Cancer Vaginal Cancer Overian Cancer Ovarian cancer is cancer that forms in the tissue of the ovary and
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Year: Issue 1 Obs/Gyne The silent epidemic: Postmenopausal vaginal atrophy
 Year: 2013 - Issue 1 Obs/Gyne The silent epidemic: Postmenopausal vaginal atrophy By: Dr David W Sturdee, Immediate past President International Menopause Society and Hon Consultant Gynaecologist, Solihull
Year: 2013 - Issue 1 Obs/Gyne The silent epidemic: Postmenopausal vaginal atrophy By: Dr David W Sturdee, Immediate past President International Menopause Society and Hon Consultant Gynaecologist, Solihull
Menopause Symptoms and Management: After Breast Cancer
 Menopause Symptoms and Management: After Breast Cancer An Educational Webinar for Patients and their Caregivers Wen Shen, MD, MPH Division of Gynecologic Specialties July 27, 2018 1 Disclosure I have a
Menopause Symptoms and Management: After Breast Cancer An Educational Webinar for Patients and their Caregivers Wen Shen, MD, MPH Division of Gynecologic Specialties July 27, 2018 1 Disclosure I have a
What Causes Cervical Cancer? Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
 Cervical Health Awareness Month is a chance to raise awareness about how women can protect themselves from HPV (human papillomavirus) and cervical cancer. HPV is a very common infection that spreads through
Cervical Health Awareness Month is a chance to raise awareness about how women can protect themselves from HPV (human papillomavirus) and cervical cancer. HPV is a very common infection that spreads through
Dr. Maliheh Keshvari
 1 Dr. Maliheh Keshvari Assistant professor of Urology Fellowship in Female Urology Mashhad University of Medical Sciences 2 Female Sexual Function and Dysfunction 3 It was not until recently that urologists
1 Dr. Maliheh Keshvari Assistant professor of Urology Fellowship in Female Urology Mashhad University of Medical Sciences 2 Female Sexual Function and Dysfunction 3 It was not until recently that urologists
Investigation and Management of Vaginal Discharge in Adult Women
 Investigation and Management of Vaginal Discharge in Adult Women SUMMARY POINTS A detailed history, including sexual history, should be taken to explore potential causes and guide investigation and management.
Investigation and Management of Vaginal Discharge in Adult Women SUMMARY POINTS A detailed history, including sexual history, should be taken to explore potential causes and guide investigation and management.
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
Innovations in the Management of Dyspareunia
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Vaginitis. Is vaginal discharge ever normal? Women with vaginal discharge. Vaginal symptoms are very common. Patient with chronic vaginal discharge
 Vaginitis Is the wet prep out of the building? No disclosures related to this topic Images are cited with permissions Barbara S. Apgar, MD, MS Professor of Family Medicine University of Michigan Health
Vaginitis Is the wet prep out of the building? No disclosures related to this topic Images are cited with permissions Barbara S. Apgar, MD, MS Professor of Family Medicine University of Michigan Health
Chapter 2. Reproductive system matures and becomes capable of reproduction
 Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Colposcopic Principles. Simon Leeson Consultant Obstetrician/ Gynaecologist Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Board UK
 Colposcopic Principles Simon Leeson Consultant Obstetrician/ Gynaecologist Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Board UK The cervix topics discussed are: original squamous epithelium endocervical epithelium
Colposcopic Principles Simon Leeson Consultant Obstetrician/ Gynaecologist Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Board UK The cervix topics discussed are: original squamous epithelium endocervical epithelium
Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376
 374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
Management of Menopausal Symptoms
 Management of Menopausal Symptoms Tammie Koehler DO, FACOG 1 Menopause Permanent cessation of menstruation that occurs after the loss of ovarian activity Determined to have occurred after 1 full year of
Management of Menopausal Symptoms Tammie Koehler DO, FACOG 1 Menopause Permanent cessation of menstruation that occurs after the loss of ovarian activity Determined to have occurred after 1 full year of
Dr. Mojibian. Menopause
 Dr. Mojibian Menopause I. Introduction - The term menopause is derived from Greek Meno (months) and pause (cessation). The word means cessation of menstruation. - Cliamacteric which is by dictionary definition
Dr. Mojibian Menopause I. Introduction - The term menopause is derived from Greek Meno (months) and pause (cessation). The word means cessation of menstruation. - Cliamacteric which is by dictionary definition
LTASEX.INFO STI SUMMARY SHEETS FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY. COMMERCIAL USE RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 2013, JEROME STUART NICHOLS
 LTASEX.INFO STI SUMMARY SHEETS FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY. COMMERCIAL USE RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 2013, JEROME STUART NICHOLS LTASEX.INFO! IN AIDS is a treatable complication of advanced HIV infection.
LTASEX.INFO STI SUMMARY SHEETS FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY. COMMERCIAL USE RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 2013, JEROME STUART NICHOLS LTASEX.INFO! IN AIDS is a treatable complication of advanced HIV infection.
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks
 1100 Wayne Ave, Suite 825 Silver Spring, MD 20910 301.273.0570 Fax 301.273.0778 info@augs.org www.augs.org Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks ICD 9 ICD 9 Description ICD 10 Code ICD 10 Description
1100 Wayne Ave, Suite 825 Silver Spring, MD 20910 301.273.0570 Fax 301.273.0778 info@augs.org www.augs.org Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks ICD 9 ICD 9 Description ICD 10 Code ICD 10 Description
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Cervical Cancer - Suspected
 Cervical Cancer - Suspected Presentation for patients Asymptomatic presentation Symptomatic presentation History and examination Consider differential diagnoses RED FLAG! Cervix appears normal after examination
Cervical Cancer - Suspected Presentation for patients Asymptomatic presentation Symptomatic presentation History and examination Consider differential diagnoses RED FLAG! Cervix appears normal after examination
4/3/2017 DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY OF RECURRENT VULVOVAGINAL SYMPTOMS BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS EPIDEMIOLOGY OBJECTIVES
 DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY OF RECURRENT VULVOVAGINAL SYMPTOMS KELLY HODGES, MD (NO DISCLOSURES) OBJECTIVES REVIEW THE TWO MOST COMMON CAUSES OF RECURRENT ABNORMAL DISCHARGE (CANDIDA AND BV) REVIEW THE MOST
DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY OF RECURRENT VULVOVAGINAL SYMPTOMS KELLY HODGES, MD (NO DISCLOSURES) OBJECTIVES REVIEW THE TWO MOST COMMON CAUSES OF RECURRENT ABNORMAL DISCHARGE (CANDIDA AND BV) REVIEW THE MOST
Pelvic Prolapse. A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction
 Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
Stop Coping. Start Living. Talk to your doctor about pelvic organ prolapse and sacrocolpopexy
 Stop Coping. Start Living Talk to your doctor about pelvic organ prolapse and sacrocolpopexy Did you know? One in three women will suffer from a pelvic health condition in her lifetime. Four of the most
Stop Coping. Start Living Talk to your doctor about pelvic organ prolapse and sacrocolpopexy Did you know? One in three women will suffer from a pelvic health condition in her lifetime. Four of the most
Process of Aging. Manifestation of Estrogen and/or Androgen Loss: Symptoms Over Time. Estrogen Decrease and Its Impact on Sexual Functioning
 Impact of Vulvovaginal Atrophy on Quality of Life and Sexuality Process of Aging physical health sexual activity Sexual function and aging desire androgen levels Michael L. Krychman MD Executive Director
Impact of Vulvovaginal Atrophy on Quality of Life and Sexuality Process of Aging physical health sexual activity Sexual function and aging desire androgen levels Michael L. Krychman MD Executive Director
Chlamydia, Gardenerella, and Ureaplasma
 Chlamydia, Gardenerella, and Ureaplasma Dr. Hala Al Daghsitani Chlamydia trachomatis is a Gram negative with LPS, obligate intracellular life cycle, associated with sexually transmitted disease (STD).
Chlamydia, Gardenerella, and Ureaplasma Dr. Hala Al Daghsitani Chlamydia trachomatis is a Gram negative with LPS, obligate intracellular life cycle, associated with sexually transmitted disease (STD).
All referrals for out-patient appointments can also be discussed with the Obstetrics and Gynaecology registrar as necessary. Presence of ascites
 Gynaecology Referral Pathway for GPs to Aid Triage for Gynaecology Services in the Rotunda For acute gynaecology (suspected torsion, acute PID, etc..) or acute early pregnancy referrals please consider
Gynaecology Referral Pathway for GPs to Aid Triage for Gynaecology Services in the Rotunda For acute gynaecology (suspected torsion, acute PID, etc..) or acute early pregnancy referrals please consider
Voiding Diary. Begin recording upon rising in the morning and continue for a full 24 hours.
 Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Interactive Questions & Exercises
 Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Gynaecology Cancer Red Flags. Dr Dina Bisson Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Southmead Hospital North Bristol NHS Trust 27 April 2017
 Gynaecology Cancer Red Flags Dr Dina Bisson Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Southmead Hospital North Bristol NHS Trust 27 April 2017 Gynaecological Cancers Endometrial Cancer Ovarian Cancer Cervical
Gynaecology Cancer Red Flags Dr Dina Bisson Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Southmead Hospital North Bristol NHS Trust 27 April 2017 Gynaecological Cancers Endometrial Cancer Ovarian Cancer Cervical
MTN-026 Clinical Management Overview
 MTN-026 Clinical Management Overview Overview of Topics Physical and Genital Exams Medical and Menstrual History STI Management Concomitant Medications Prohibited Medications and Practices Physical Examination:
MTN-026 Clinical Management Overview Overview of Topics Physical and Genital Exams Medical and Menstrual History STI Management Concomitant Medications Prohibited Medications and Practices Physical Examination:
STI Review. CALM: STI/HIV - Lesson One (Handout 3) Bacteria/ Transmission. Symptoms. Disease. Virus
 STI Review Bacteria/ Virus? Transmission Chlamydia Bacteria Unprotected vaginal or anal sex with a person who has Chlamydia Genital Herpes Virus By direct contact with the sores or blisters of an infected
STI Review Bacteria/ Virus? Transmission Chlamydia Bacteria Unprotected vaginal or anal sex with a person who has Chlamydia Genital Herpes Virus By direct contact with the sores or blisters of an infected
Pelvic Support Problems
 AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
Vaginitis. Antibiotics Changes in hormone levels due to pregnancy, breastfeeding, or menopause Douching Spermicides Sexual intercourse Infection
 WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Vaginitis Vaginitis is an inflammation of a woman s vagina. It is one of the most common reasons why women see their health care providers.
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Vaginitis Vaginitis is an inflammation of a woman s vagina. It is one of the most common reasons why women see their health care providers.
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 06 Page June 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i6.07 Study of Cervical Cytology (Pap
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i6.07 Study of Cervical Cytology (Pap
FemTouch Clinical Treatment Guide
 Contributing Medical Expert: Darush L. Mohyi MD Obstetrics and Gynecology & Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility PB-2005717 rev B Epidemiology of vulvo vaginal atrophy (VVA) Vulvo vaginal atrophy
Contributing Medical Expert: Darush L. Mohyi MD Obstetrics and Gynecology & Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility PB-2005717 rev B Epidemiology of vulvo vaginal atrophy (VVA) Vulvo vaginal atrophy
Molly A. Brewer DVM, MD, MS Chair and Professor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Connecticut School of Medicine
 Molly A. Brewer DVM, MD, MS Chair and Professor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Connecticut School of Medicine Review causes of abnormal uterine bleeding: Adolescent Reproductive
Molly A. Brewer DVM, MD, MS Chair and Professor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Connecticut School of Medicine Review causes of abnormal uterine bleeding: Adolescent Reproductive
Learning Objectives. Peri menopause. Menopause Overview. Recommendation grading categories
 Learning Objectives Identify common symptoms of the menopause transition Understand the risks and benefits of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) Be able to choose an appropriate hormone replacement regimen
Learning Objectives Identify common symptoms of the menopause transition Understand the risks and benefits of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) Be able to choose an appropriate hormone replacement regimen
Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376
 374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
Chapter 11. Culturally competent communication key to empowering women to feel confident abut her ability to care for herself and her family
 Chapter 11 The Nurse s Role in Women s Health Care Goals of Healthy People 2020 Culturally competent communication key to empowering women to feel confident abut her ability to care for herself and her
Chapter 11 The Nurse s Role in Women s Health Care Goals of Healthy People 2020 Culturally competent communication key to empowering women to feel confident abut her ability to care for herself and her
Bursting Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.
 www.infertiltysolutionsng.info/blog Disclaimer The information in this book is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to treat, diagnose or prevent any disease. The information in this
www.infertiltysolutionsng.info/blog Disclaimer The information in this book is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to treat, diagnose or prevent any disease. The information in this
Renewing Intimacy & Sexuality after Gynecologic Cancer
 Renewing Intimacy & Sexuality after Gynecologic Cancer foundationforwomenscancer.org Over 90,000 women are diagnosed with a gynecologic cancer each year. The challenge for a woman with cancer and her healthcare
Renewing Intimacy & Sexuality after Gynecologic Cancer foundationforwomenscancer.org Over 90,000 women are diagnosed with a gynecologic cancer each year. The challenge for a woman with cancer and her healthcare
Passport to Health Preventing and Recognizing Gynecologic Cancers
 Passport to Health Preventing and Recognizing Gynecologic Cancers Presented by: Obstetrician/Gynecologist Leigh Bauer, M.D. They can sneak up on you. 2 Gynecologic cancers, that is. Knowing the facts can
Passport to Health Preventing and Recognizing Gynecologic Cancers Presented by: Obstetrician/Gynecologist Leigh Bauer, M.D. They can sneak up on you. 2 Gynecologic cancers, that is. Knowing the facts can
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
FEMININE INTIMATE CARE
 FEMININE INTIMATE CARE The role of the pharmacist Dr Trudy Smith Vaginal Health Vagina sensitive area Just like GIT, also contain flora Vaginal flora Maintain healthy ph (4.5) Lactobacilli (aerobic) Automatic
FEMININE INTIMATE CARE The role of the pharmacist Dr Trudy Smith Vaginal Health Vagina sensitive area Just like GIT, also contain flora Vaginal flora Maintain healthy ph (4.5) Lactobacilli (aerobic) Automatic
Parasitology. The genus Trichomonas
 Parasitology Lecture: 2 د. هيفاء The genus Trichomonas -These are common flagellates of the tropical areas,. -They exist only in trophozoite stage. -They are pear-shaped body and measures 10-12 microns
Parasitology Lecture: 2 د. هيفاء The genus Trichomonas -These are common flagellates of the tropical areas,. -They exist only in trophozoite stage. -They are pear-shaped body and measures 10-12 microns
Case Study 1. Cervical Cancer Screening and Sexually Transmitted Infections Case Studies
 Case Study 1 Cervical Cancer Screening and Sexually Transmitted Infections Case Studies Joyce, a 32 year old returning veteran, comes in for a Well Woman visit. She has a history of an abnormal Pap before
Case Study 1 Cervical Cancer Screening and Sexually Transmitted Infections Case Studies Joyce, a 32 year old returning veteran, comes in for a Well Woman visit. She has a history of an abnormal Pap before
STI s. (Sexually Transmitted Infections)
 STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
41a Pathology: Reproductive System
 41a Pathology: Reproductive System 41a Pathology: Reproductive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
41a Pathology: Reproductive System 41a Pathology: Reproductive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
Reproductive System: Male
 Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Chapter 11. The Nurse s Role in Women s Health Care
 Chapter 11 The Nurse s Role in Women s Health Care Objectives Explain aspects of preventive health care for women. Describe each menstrual disorder and its care. Explain each gynecological infection in
Chapter 11 The Nurse s Role in Women s Health Care Objectives Explain aspects of preventive health care for women. Describe each menstrual disorder and its care. Explain each gynecological infection in
Sexually Transmissible Infections (STI) and Blood-borne Viruses (BBV) A guide for health promotion workers
 Sexually Transmissible Infections (STI) and Blood-borne Viruses (BBV) A guide for health promotion workers Sexual & Reproductive Health Western Australia Chlamydia (bacterial infection) Unprotected vaginal
Sexually Transmissible Infections (STI) and Blood-borne Viruses (BBV) A guide for health promotion workers Sexual & Reproductive Health Western Australia Chlamydia (bacterial infection) Unprotected vaginal
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Vaginal atrophy is a common condition
 original article Oman Medical Journal [2017], Vol. 32, No. 1: 15 19 Treatment of Vaginal Atrophy with Vaginal Estrogen Cream in Menopausal Indian Women Maitri Shah 1 *, Zalak Karena 1, Sangita V. Patel
original article Oman Medical Journal [2017], Vol. 32, No. 1: 15 19 Treatment of Vaginal Atrophy with Vaginal Estrogen Cream in Menopausal Indian Women Maitri Shah 1 *, Zalak Karena 1, Sangita V. Patel
Personal Data. Present Symptoms
 Chris A. Pate, MD 2280 Hwy 70 West, Suite B 265 Racine Drive, Suite 102 Goldsboro, NC 27530 Wilmington, NC 28403 (919) 988-9332 Fx(919) 581-0353 (910) 399-6661 Fx(910) 399-6667 Name Personal Data Address
Chris A. Pate, MD 2280 Hwy 70 West, Suite B 265 Racine Drive, Suite 102 Goldsboro, NC 27530 Wilmington, NC 28403 (919) 988-9332 Fx(919) 581-0353 (910) 399-6661 Fx(910) 399-6667 Name Personal Data Address
The Case of Mrs. Virginia Jones* Asst. Professor Division of Gyne-Oncology University of British Columbia, Department of Gynecology Vancouver, Canada
 Case title: Case authors: Case synopsis: The Case of Mrs. Virginia Jones* Dr. Leslie A. Sadownik Asst. Professor Division of Gyne-Oncology University of British Columbia, Department of Gynecology Vancouver,
Case title: Case authors: Case synopsis: The Case of Mrs. Virginia Jones* Dr. Leslie A. Sadownik Asst. Professor Division of Gyne-Oncology University of British Columbia, Department of Gynecology Vancouver,
Gynecology Dr. Sallama Lecture 3 Genital Prolapse
 Gynecology Dr. Sallama Lecture 3 Genital Prolapse Genital(utero-vaginal )prolapse is extremely common, with an estimated 11% of women undergoing at least one operation for this condition. Definition: A
Gynecology Dr. Sallama Lecture 3 Genital Prolapse Genital(utero-vaginal )prolapse is extremely common, with an estimated 11% of women undergoing at least one operation for this condition. Definition: A
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are the nurse providing care for a client reporting symptoms of bloating, irritability,
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are the nurse providing care for a client reporting symptoms of bloating, irritability,
2/28/2018. This presentation contains images of a graphic nature and are presented for medical education only. New Terminology Old Problem!
 This presentation contains images of a graphic nature and are presented for medical education only. New Terminology Old Problem! Dr. Chevelta A. Smith Adjunct Professor of LECOM - OB/Gyn March 3, 2018
This presentation contains images of a graphic nature and are presented for medical education only. New Terminology Old Problem! Dr. Chevelta A. Smith Adjunct Professor of LECOM - OB/Gyn March 3, 2018
Natural and Holistic Medicine Approach in Evaluation and Treatment of Vaginal and Urinary Tract Health
 Natural and Holistic Medicine Approach in Evaluation and Treatment of Vaginal and Urinary Tract Health By Dr. Michael John Badanek, BS, DC, CNS, CTTP, DACBN, DCBCN, MSGR./CHEV While the gut has an estimated
Natural and Holistic Medicine Approach in Evaluation and Treatment of Vaginal and Urinary Tract Health By Dr. Michael John Badanek, BS, DC, CNS, CTTP, DACBN, DCBCN, MSGR./CHEV While the gut has an estimated
Community Gynaecology. Top Tips for GPs
 Community Gynaecology Top Tips for GPs Top Tips for GPs Case Scenarios- common referral themes 6 topics What you can do in Primary Care to avoid or before referral. What we don t need to see Triage ensures
Community Gynaecology Top Tips for GPs Top Tips for GPs Case Scenarios- common referral themes 6 topics What you can do in Primary Care to avoid or before referral. What we don t need to see Triage ensures
bleeding Studies naar de diagnostiek van endom triumcarcinoom bij vrouwen met postm nopauzaal bloedverlies. Studies on the
 Studies on the diagnosis of endometria cancer in women with postmenopausal bleeding. Studies naar de diagnostiek va endometriumcarcinoom bij vrouwen m postmenopauzaal bloedverlies. Studies on the diagnosis
Studies on the diagnosis of endometria cancer in women with postmenopausal bleeding. Studies naar de diagnostiek va endometriumcarcinoom bij vrouwen m postmenopauzaal bloedverlies. Studies on the diagnosis
Menopause & HRT. Matt McKenna Elliot Davis
 Menopause & HRT Matt McKenna Elliot Davis Menopause Before age 40: Premature Menopause After 12 months clinical diagnosis made Depletion of Ovarian Follicles Oestrogen Progesterone LH FSH Spontaneous Amemorrhoea
Menopause & HRT Matt McKenna Elliot Davis Menopause Before age 40: Premature Menopause After 12 months clinical diagnosis made Depletion of Ovarian Follicles Oestrogen Progesterone LH FSH Spontaneous Amemorrhoea
Cervical cancer presentation
 Carcinoma of the cervix: Carcinoma of the cervix is the second commonest cancer among women worldwide, with only breast cancer occurring more commonly. Worldwide, cervical cancer accounts for about 500,000
Carcinoma of the cervix: Carcinoma of the cervix is the second commonest cancer among women worldwide, with only breast cancer occurring more commonly. Worldwide, cervical cancer accounts for about 500,000
Dr Lilianne Scholtz (MBBCh)
 Dr Lilianne Scholtz (MBBCh) I have a discharge. It s itchy and it burns. My urine burns too. Diagnosis based on symptoms alone is accurate in ~34 % of women because symptoms are very non-specific Sobel
Dr Lilianne Scholtz (MBBCh) I have a discharge. It s itchy and it burns. My urine burns too. Diagnosis based on symptoms alone is accurate in ~34 % of women because symptoms are very non-specific Sobel
Understanding Women's Sexuality after Bladder Cancer webinar. Part I: The Physical Impact
 Understanding Women's Sexuality after Bladder Cancer webinar Tuesday, December 1, 2015 Part I: The Physical Impact Presented by LaShon Day received her Masters of Science as a Physician s Assistant at
Understanding Women's Sexuality after Bladder Cancer webinar Tuesday, December 1, 2015 Part I: The Physical Impact Presented by LaShon Day received her Masters of Science as a Physician s Assistant at
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF STDS
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF STDS Diana Torres-Burgos MD, MPH NYC STD/HIV Prevention Training Center STD/HIV Update Conference Grand Rapids, MI 3/11/2014 Outline Essential components of STD care management Sexual
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF STDS Diana Torres-Burgos MD, MPH NYC STD/HIV Prevention Training Center STD/HIV Update Conference Grand Rapids, MI 3/11/2014 Outline Essential components of STD care management Sexual
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
MYTHS OF STIs True or False
 MYTHS OF STIs True or False 1. Most people with an STD experience painful symptoms. 2. Birth control pills prevent the spread of STDs. 3. Douching will cure and STD. 4. Abstinence is the best way to prevent
MYTHS OF STIs True or False 1. Most people with an STD experience painful symptoms. 2. Birth control pills prevent the spread of STDs. 3. Douching will cure and STD. 4. Abstinence is the best way to prevent
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
PAINFUL URINATION CAUSES & NATURAL REMEDY. Dr. Bestman Anyatonwu
 LIBRACIN NATURAL MEDICINE IND. LTD PAINFUL URINATION CAUSES & NATURAL REMEDY Dr. Bestman Anyatonwu MEANING Painful urination is a broad term that describes discomfort during urination. This pain may originate
LIBRACIN NATURAL MEDICINE IND. LTD PAINFUL URINATION CAUSES & NATURAL REMEDY Dr. Bestman Anyatonwu MEANING Painful urination is a broad term that describes discomfort during urination. This pain may originate
Endometrial line thickness in different conditions.
 Endometrial line thickness in different conditions 1 Endometrial thickens in response to Rising estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle and then shedding endometrial at the times of menses 2 The thickens
Endometrial line thickness in different conditions 1 Endometrial thickens in response to Rising estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle and then shedding endometrial at the times of menses 2 The thickens
Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence. Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes
 Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes 66 year old woman with incontinence PC: 7 year Hx of urgency, frequency, nocturia (incl. incontinence at night), and stress incontinence
Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes 66 year old woman with incontinence PC: 7 year Hx of urgency, frequency, nocturia (incl. incontinence at night), and stress incontinence
Cytoplasmic changes Nuclear changes
 The presence of infection in the female genital tract may procure certain cellular changes in the epithelium. Such changes are seen in nucleus and cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus. Cytoplasmic changes
The presence of infection in the female genital tract may procure certain cellular changes in the epithelium. Such changes are seen in nucleus and cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus. Cytoplasmic changes
The Female Reproductive System
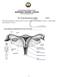 The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
Types of vaginal yeast
 Types of vaginal yeast You should seek medical care any time if you have pain. Although vaginal infections may cause unpleasant itching, they should not cause pain. Call for an appointment with your healthcare
Types of vaginal yeast You should seek medical care any time if you have pain. Although vaginal infections may cause unpleasant itching, they should not cause pain. Call for an appointment with your healthcare
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 15 AND 16
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 15 AND 16 Name Identify the following: 1) The ureter is indicated by letter 2) The renal pyramid is indicated by letter 3) The fibrous capsule is indicated by letter
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 15 AND 16 Name Identify the following: 1) The ureter is indicated by letter 2) The renal pyramid is indicated by letter 3) The fibrous capsule is indicated by letter
Menopause and HRT. John Smiddy and Alistair Ledsam
 Menopause and HRT John Smiddy and Alistair Ledsam Menopause The cessation of menstruation Diagnosed retrospectively after 1 year of amenorrhoea Average age 51 in the UK Normal physiology - Menstruation
Menopause and HRT John Smiddy and Alistair Ledsam Menopause The cessation of menstruation Diagnosed retrospectively after 1 year of amenorrhoea Average age 51 in the UK Normal physiology - Menstruation
Cervical Cancer. Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year.
 Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
Ackers, JP (2003) Trichomonas. In: The Oxford Textbook of Medicine. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1:783-4.
 Ackers, JP (2003) Trichomonas. In: The Oxford Textbook of Medicine. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1:783-4. Downloaded from: http://researchonline.lshtm.ac.uk/15085/ DOI: Usage Guidelines Please refer
Ackers, JP (2003) Trichomonas. In: The Oxford Textbook of Medicine. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1:783-4. Downloaded from: http://researchonline.lshtm.ac.uk/15085/ DOI: Usage Guidelines Please refer
Rejuvenating the Vagina A GUIDE TO LABIAPLASTY. Your guide to the female form and treatments for vaginal ageing & rejuvenation
 A GUIDE TO LABIAPLASTY Your guide to the female form and treatments for vaginal ageing & rejuvenation THE VAGINA Every woman should know about the vagina, and the changes that can occur with age, but first,
A GUIDE TO LABIAPLASTY Your guide to the female form and treatments for vaginal ageing & rejuvenation THE VAGINA Every woman should know about the vagina, and the changes that can occur with age, but first,
What is endometrial cancer?
 Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Microscopy Competency/Training For Clinic-Based Providers
 Microscopy Competency/Training For Clinic-Based Providers OSBHCN October 11, 2013 Diane Avenoso, MPH, MT(ASCP)SBB, CQA(ASQ) Clinical Laboratory Inspector/Compliance Specialist OHA, Oregon State Public
Microscopy Competency/Training For Clinic-Based Providers OSBHCN October 11, 2013 Diane Avenoso, MPH, MT(ASCP)SBB, CQA(ASQ) Clinical Laboratory Inspector/Compliance Specialist OHA, Oregon State Public
reproductive organs. Malignant neoplasms. 4. Inflammatory disorders of female reproductive organs 2 5. Infertility. Family planning.
 Thematic plan of lectures module iii. Diseases of female reproductive system. Family planning. Topic No of hours 1. Disturbances of menstrual function. Neuroendocrinological 2 syndromes in gynecology 1.
Thematic plan of lectures module iii. Diseases of female reproductive system. Family planning. Topic No of hours 1. Disturbances of menstrual function. Neuroendocrinological 2 syndromes in gynecology 1.
Clinically Microscopically Pathogenesis: autoimmune not lifetime
 Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
FemTouch Treatment for Improving Vulvovaginal Health
 FemTouch Treatment for Improving Vulvovaginal Health Dr. M. Marziali MD PhD in Gynecology and Obstetric Introduction Vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) accompanies the natural aging of the vagina and affects up
FemTouch Treatment for Improving Vulvovaginal Health Dr. M. Marziali MD PhD in Gynecology and Obstetric Introduction Vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) accompanies the natural aging of the vagina and affects up
Management of Urogenital Prolapse of Women in Primary Care. Lizzie McManus MBE RGN RMN Practice nurse Womens health practitioner
 Management of Urogenital Prolapse of Women in Primary Care Lizzie McManus MBE RGN RMN Practice nurse Womens health practitioner Primary Care Womens Health Forum www.pcwhf.org.uk Useful websites RCN genital
Management of Urogenital Prolapse of Women in Primary Care Lizzie McManus MBE RGN RMN Practice nurse Womens health practitioner Primary Care Womens Health Forum www.pcwhf.org.uk Useful websites RCN genital
Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Ch 24
 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Ch 24 Statistics THERE ARE CURRENTLY 65 MILLION PEOPLE LIVING WITH INCURABLE STDs IN THE U.S. THERE ARE 15 MILLION NEW CASES REPORTED EACH YEAR SOURCE: CDC, 2000 REPORTS WHY
Sexually Transmitted Diseases Ch 24 Statistics THERE ARE CURRENTLY 65 MILLION PEOPLE LIVING WITH INCURABLE STDs IN THE U.S. THERE ARE 15 MILLION NEW CASES REPORTED EACH YEAR SOURCE: CDC, 2000 REPORTS WHY
LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR
 LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR Dr. R. K. Mishra Elements comprising the Pelvis Bones Ilium, ischium and pubis fusion Ligaments Muscles Obturator internis muscle Arcus tendineus levator ani or white
LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR Dr. R. K. Mishra Elements comprising the Pelvis Bones Ilium, ischium and pubis fusion Ligaments Muscles Obturator internis muscle Arcus tendineus levator ani or white
Getting ready for and recovering from Gynecological Surgery. Island Health Surgery Resources
 Getting ready for and recovering from Gynecological Surgery Island Health Surgery Resources 1 Printing number # 9-90598 Rev05/20/2017 Surgical Services, Island Health About these materials This booklet
Getting ready for and recovering from Gynecological Surgery Island Health Surgery Resources 1 Printing number # 9-90598 Rev05/20/2017 Surgical Services, Island Health About these materials This booklet
Pap Smears Pelvic Examinations Well Woman Examinations. When should you have them performed???
 Pap Smears Pelvic Examinations Well Woman Examinations. When should you have them performed??? Arlene Evans-DeBeverly, PA-C Copyright 2012 There are always ongoing changes in gynecology, including the
Pap Smears Pelvic Examinations Well Woman Examinations. When should you have them performed??? Arlene Evans-DeBeverly, PA-C Copyright 2012 There are always ongoing changes in gynecology, including the
Coding for Fitting and Insertion of a Pessary
 Coding for Fitting and Insertion of a Pessary A pessary is a device worn in the vagina for the treatment of pelvic organ prolapse or stress urinary incontinence. The pessary provides support of the vaginal
Coding for Fitting and Insertion of a Pessary A pessary is a device worn in the vagina for the treatment of pelvic organ prolapse or stress urinary incontinence. The pessary provides support of the vaginal
Sexually Transmi/ed Diseases
 Sexually Transmi/ed Diseases Chapter Fourteen 2013 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. Also known as sexually transmitted infections The Major STDs (STIs) HIV/AIDS Chlamydia Gonorrhea Human
Sexually Transmi/ed Diseases Chapter Fourteen 2013 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. Also known as sexually transmitted infections The Major STDs (STIs) HIV/AIDS Chlamydia Gonorrhea Human
