CAnnually, about 3 million patient visits to doctors in the
|
|
|
- Ethan Curtis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UDC : ACTUAL TOPICS The modern approach to intravesical therapy of chronic cystitis O.D. Nikitin Bogomolets National Medical University Kyiv The difficulty of treating patients with chronic recurrent cystitis is caused by various factors like the virulence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli as well as the state of the local resistance of the bladder's mucosa and their interaction. Hyaluronic acid instillations used in the of patients with chronic cystitis led to pronounced positive clinical dynamics in 5% of patients, as well as to more than a 2 fold reduction in the of recurrences of cystitis, which greatly improved the quality of life of patients. The results allow us to recommend the use of intravesical sodium hyaluronate for the of various forms of chronic cystitis. Key words: chronic cystitis, intravesical therapy, sodium hyaluronate. ystitis is one of the most common urological diseases. CAnnually, about 3 million patient visits to doctors in the USA alone are associated with various forms of cystitis. Bacterial infection is the most common cause of chronic cystitis. About 40-50% of women have experienced acute cystitis once in their lifetime, -% of women experience a recurrence within 3-4 months after the first episode of a urinary tract infection. About -% of them suffer from recurrent cystitis throughout their life. The diagnosis of recurrent cystitis involves 2 exacerbations within months or 3 exacerbations during the year, which significantly affects not only the quality of life of patients, but has a large social and economic impact on society as a whole [1]. Recently, there exist experiments confirming the formation of intracellular bacterial communities in urothelium cells, which ensures the persistence of Escherichia coli in the urinary tract [15]. Difficulties in treating patients with chronic recurrent cystitis are caused by various factors like the virulence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli as well as the state of the local resistance of the bladder's mucosa and their interaction. A uropathogenic Escherichia coli is able to simulate the immune response of macroorganisms. There are well-known immunomodulatory roles of sexually-transmitted intracellular pathogens, which create prerequisites for the development of bacterial cystitis in women [2]. Atrophic processes are of great importance in the development and support of chronic cystitis in women during the postmenopause period. The most severe conditions which are also manifestations of chronic cystitis include cystalgia and interstitial cystitis, which are resistant to standard conservative therapy []. In case of interstitial cystitis, changes of phases of the course of inflammatory processes occur, thus leading to a severe pain syndrome and a decrease in bladder capacity with increasing dysuria. This clinical picture and accompanying morphological manifestations indicate the cyclical nature of the disease with frequent changes in episodes of remissions and exacerbations []. Chronic cystitis is a disease characterized by a long-standing inflammatory reaction in the bladder tissue. The reason for inflammatory infiltration in the mucosa and submucosal layers of the bladder wall is due to the damage of the intermediary substance of the connective tissue due to various causes - both of congenital and acquired character. Regardless of these reasons, the result is a violation of the physiological regeneration process of the bladder's epithelium and barrier function of the transitional epithelium [12]. These changes lead to dysregeneratory processes in the urothelium, followed by a change in the physiologically-based distribution of the subpopulations of mononuclear cells. The above changes can be interpreted as the interstitial inflammation with manifestation of glycosaminoglycan deficiency [3]. Glycosaminoglycans and in particular zinc hyaluronate as the biopolymers of the mucopolysaccharide type, are the most important components of connective tissues, skin and mucous membranes. Due to its high hydrophilicity, it readily forms a dispersion matrix with water molecules, which is important in maintaining protective mechanisms as well as the elasticity of the skin and mucous membranes [4, ]. The most important fact is that hyaluronic acid enhances the migration of fibroblasts. The local concentration of hyaluronic acid increases in the process of tissue regeneration: this creates optimal conditions for the activation of the migration and proliferation of cells involved in tissue regeneration. The local microcirculation improves as a result of such angiogenic properties. In cases of pathological processes, the concentration of hyaluronic acid in tissues decreases due to such imbalance and the recovery process slows down. In case of interstitial cystitis, the concentration of hyaluronic acid in the bladder's mucous membrane decreases, thus leading to a decrease in the proliferation and regeneration of epithelium, which can be influenced by the local application of hyaluronic acid. Naturally, hyaluronic acid occurs in the form of sodium salts; it is a homopolymer of M-acetyl-O-glucosamine and D-glucuronic acid, 1-3-beta-linked. The molecular mass ranges from 00 to several million Daltons [13]. Studies conducted in recent years have found that hyaluronic acid binds to a large of molecules in aqueous solutions with the formation of a dense molecular sieve. The dispersion matrix forms canaliculi for selective diffusion of water-soluble molecules. Hydrophobic areas regularly repeat on the molecule, that facilitates the interaction between cellular membranes and hydrophobic type proteins [11]. It should be noted that hyaluronic acid controls the water content in the extracellular fluid, counteracting bacterial penetration. In addition, it binds to cations and significantly affects cell mobility and tissue regeneration [4]. Treating recurrent infections of the lower urinary tract is a great challenge. Prolonged courses of antimicrobial therapy with oral doses give a positive effect only during the, while frequent recurrences of infection are observed again after discontinuation of therapy [5]. Moreover, such tactics lead to the development of microorganisms which are resistant to antimicrobial drugs [, 14]. Vaccination therapy has so far failed to fulfil expectations. Recurrent cystitis is difficult to treat conservatively, thus driving numerous researchers to look for new therapies. Intravesical usage of hyaluronic acid is a promising method, but it requires the carrying out of several randomized trials. All of the above determine the relevance of this topic. MEN'S HEALTH N 4 (55) 15 ISSN
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS A total of 5 women were examined with a preliminary diagnosis of chronic cystitis, cystalgia, interstitial cystitis. Generally, patients reported the same complaints of constant or periodic dysuria, pollakiuria, urethralgia, lower abdominal pain, heavy weight above the pubis, increasing with the bladder filling and reaching the greatest intensity at the end of urination, a feeling of incomplete urinary bladder emptying, urgency, sometimes, a hyperactive bladder. Based on a complete physical examination, women were selected from the 5 patients, among which 3 groups were distinguished according to the developed examination card (the presence or absence of signs of urinary tract infection, including sexually transmitted infections were taken into account except for complaints, anamnesis, physical examination, laboratory data) as follows: I. Patients with a urinary tract infection, i.e. with recurrent bacterial cystitis and, in particular, with sexually transmitted infections, - (33.3%) patients. II. Patients with dysuria in post-menopause, without laboratory confirmation of a urinary tract infection - 11 (3.%) patients. III. Patients with interstitial cystitis - (%) patients. For the examination of patients, an individual registration card was developed, which included the following: age, sex, nosological entity of the disease, severity of the course of the disease, anamnestic data, complete blood count and urine analysis, bacterial urinalysis on the flora and susceptibility to antimicrobial drugs, microscopy of smears from the urethra, vagina and cervix, PCR-based diagnostics for sexually transmitted infections. Examinations were performed on a gynecological examination chair (according to indications consulted by a gynecologist), ultrasonography of the kidneys and bladder, urodynamic examination and excretory urography (according to indications). Urination diaries and pain visual analogue scale (VAS) were used to assess the severity of dysuria and pain syndrome. Comparative analyses of the quantitative changes which characterize the clinical and laboratory as well as functional states of the urinary system were performed through descriptive statistics using the nonparametric Wilcoxon test. The statistical 2 method of the chi-squared (x ) criterion was used in the analysis of qualitative characteristics. In describing the qualitative characters of the data distribution, the standard error of the proportion (m) was used in the calculations as well as the standard deviation (o) was used to assess the quantitative characteristics. Processing and graphical representation of data were carried out using Statistica.0 and Excel 03 as statistical computer programs. STUDY RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Various states were identified during the complete physical examination of patients with chronic recurrent cystitis. Patients are divided into three nosological groups: џ Group I - patients with chronic recurrent bacterial cystitis. џ џ Group II - patients with post-menopausal chronic cystitis. Group III - patients with nonbacterial forms of chronic cystitis. Despite the different ages of patients in the 3 study groups coupled with the presence or absence of bacterial infection of the urinary tract and sexually transmitted intracellular pathogens, all patients had a fairly similar pronounced clinical symptomatology with frequent recurrences of the disease and a low quality of life. All patients had a fairly long experience of concerning their disease without a satisfactory effect. The consisted in the administration of antimicrobial, non-steroidal antiinflammatory, sedative drugs, antidepressants, antihistamines, etc. In addition to systemic pharmacotherapy, they were given intravesical instillations of various substances, such as collargol, protargol, sea buckthorn oil, antibiotics and local anesthetics. In addition, various physiotherapeutic methods were used in the of our patients. All these surely decreased recurrences of the disease for a certain time, reduced the severity of clinical symptoms and somehow improve the quality of life of patients. While analyzing the possible mechanisms of the etiology and pathogenesis of the disease in the three nosological groups after a thorough study of clinical, cystoscopic and morphological characteristics, we found a of features of the state of bladder wall and its epithelium. Patients of all groups had cystoscopic signs of urothelium lesion. As a result of the endoscopic examination of the patients, hyperemia of the mucous membrane of various degrees in the area of the vesical triangle, neck of the urinary bladder and internal urethral opening were detected in 14 (4.%) of them. In these cases, this symptom was expressed to a greater extent in the groups I and III. Glomeruli were detected during cystoscopy in patients, which accounted for 2.% of all patients. When analyzing this criterion, depending on the nosological group, it was found that this symptom was significantly more frequent in Group ІІІ than in patients from other groups. We detected Hunner's ulcer only in two patients (.%), who all belonged to the third nosological group. Urinary bladder's mucous membrane vascular injection took place in patients, which amounted to 33.3% of patients of all groups. To a lesser extent, this symptom was expressed in the second group of patients. In a small percentage of cases (.%), we found a pseudopolyposis in the neck of the bladder. This symptom was distributed almost evenly between patients of all groups. It was not possible to detect statistically significant differences. We found signs of atrophy of the urinary bladder's mucous membrane in (%) patients. This symptom prevailed in patients of the second nosological group, i.e. in patients of postmenopausal age; it reached % in this group while in the other groups this indicator did not exceed.3%. The differences observed with this criterion were statistically significant (p <0.05). Also, atony of the bladder internal sphincter was reported in the second nosological group with a high statistical significance (p <0.05). In the course of the study, we investigated the efficacy, safety and tolerability of the intravesical istillations of sodium hyaluronate (Instylan 0 mg/50 ml, Yuria-Pharm, Ukraine) in the of patients with chronic recurrent bacterial cystitis, chronic postmenopausal cystitis and in patients with nonbacterial forms of chronic cystitis, i.e. in patients with confirmed deficiency of the glucosaminoglycan layer of the bladder. The inclusion criteria for the study group, in addition to the results of the morphological study, also include the requirement of non-participation in other studies, and non-receipt of by intravesical instillations for months before inclusion in to the study group. All patients were prescribed a course of intravesical instillations of 50 ml (0 mg) of sodium hyaluronate solution once a week. individual urinary bladder emptying and external genitalia preparation with 0.2% chlorhexidine bi-gluconate solution, bladder catheterization was carried out with a sterile urethral catheter. the administration of Instylan, patients were advised not to empty the bladder for one or more hours to increase exposure. Within a year after the end of, the indicator of the of cystitis recurrences decreased significantly by more than 2 folds for all groups of patients, which improved the quality of life of our patients. The of exacerbations decreased by.4 times in all three groups: in Group I - by 5.; in Group II - by 4.5 and in Group III - by.4 exacerbations per year (Table 1). 1 MEN'S HEALTH N 4 (55) 15 ISSN 2-500
3 Cystitis recurrence rate before and after the (p <0.01) Table 1 Results (М±а) All patients, n= n=11 n= The average of cystitic recurrences (per year) before the, of cases.± ±.5.3± ±5. the, of cases 4.5±5.* 5.3±4. 4.±3.*.1±4.* Note. * The difference is statistically significant before and after the. The analysis of the nature of complaints of patients in the nosological groups with regards to their dynamics, before and after the, revealed the following: the frequency of pollakiuria in the study groups decreased by 3. times (by 3.%); while in group I, the indicator decreased by 4 times, in group II - by 5 times, and in group III - by 3 times. The frequency of nocturnal pollakiuria decreased by 3.1 times (i.e. by 50%): in group I - by 4 times, in group II - by times, and in group III, the frequency of night pollakiuria decreased by 2. times. The frequency of urgency to urinate decreased by 5 times (by 53.4%) in the three groups after. This indicator decreased by times for by times - for Group II and by 2.5 times - for the nosological Group III patients. All patients from the three nosological groups complained of pain above the pubis before the initiation of. This indicator decreased by 3.1 times (by 3.3%) after. Pain episodes above the pubis decreased by 3.3 times in by 5 times in Group II and by 2.5 times in Group III. the start of, pain during bladder filing affected 22 (3.3%) patients while at the end of, this indicator decreased by 2. times (by 4.%). This indicator decreased by 3.3 times in by 3.5 times in Group II and by 2.5 times in Group III. The frequency of discomfort and burning with urination decreased by 3.5 times (by 50%) in the three groups after the initiation. This indicator decreased by times in Group I, by 2. times in Group II and by 3.5 times in Group III. The frequency of dyspareunia after decreased in all three groups and by 2. times (by 40%) for groups I and II, the frequency of pain during sexual intercourse decreased by 3 times, and by 2.3 times in Group III. The duration and intensity of the above complaints caused emotional distress of patients with chronic cystitis in 0% of cases. Most often, they did not believe in the success of the proposed at the beginning, having had an unfavorable long-term experience of previous therapy. Emotional distress was clearly pronounced in all three groups though no statistically significant differences were found. However, the frequency of this indicator decreased by 2. times (by 40%) for all three groups after the initiation of. This indicator decreased by 3 times in by 2.3 times in Group II and by 3 times in Group III (Table 2). Cystitis recurrence rate before and after the (p <0.01) Table 2 Complaints of patients before and after All groups, n= % Pollakiuria 2 0 * Nocturnal pollakiuria 22 3,3 * Urgency, 5 13,3 Note. * The difference is statistically significant before and after the. MEN'S HEALTH N 4 (55) 15 ISSN
4 Cystitis recurrence rate before and after the (p <0.01) Table 2 Complaints of patients before and after All groups, n= % Pain above the pubis 2 3,3 * Pain during bladder filling 22 3,3 * 2, Discomfort and burning sensation with urination 21 0 * Dyspareuria 1 3,3 * Emotional distress 1 3,3 * Note. * The difference is statistically significant before and after the. While analyzing the complaints that patients with chronic cystitis of all three nosological groups presented before and after the end of, attention was drawn to the fact that the average volume of urination (in ml) increased by 45.4 ml in general; in Group I by 34.2 ml, in Group II by 0.3 ml, in Group III by 1.2ml. The frequency of urination per day decreased by 2. times in general: by 2. times in by 2. times in Group II and by 2.1 times in Group III. The frequency of nocturnal urination decreased by 2.35 times in general; by 2.45 times in by 2.2 times in Group II and by 2.3 times in Group III (Table 3). Index Dynamics of urination diary data in patients before and after (p <0.05) Output data (М ± а) All groups, n= n=11 The average volume of urination, ml Table 3 n= 13.3± ±3.1 13±51.4.3± ±1. 1.1±.* 1.3±4. 1.5±4. The frequency of urination per day 15.1± ± ±.3 5.±2. 5.3±1.* 5.2±2..±3. The of nocturnal urination 4.±0. 5.4±2. 3.3±1.5.4±1. 2.0±0. 2.2±0.* 1.5±0. 2.±1. MEN'S HEALTH N 4 (55) 15 ISSN 2-500
5 During bladder filling, the pain visual analogue scale (VAS) and analyzing the data obtained, it was found that pain disturbed more or less patients from all three nosological groups. There was ACTUAL TOPICS a pronounced positive dynamic after the : in some patients the pain completely disappeared, while a significant reduction in pain syndrome was noted in other patients (Table 4). Severity of pain syndrome in nosological groups before and after, scores (p <0.05) Table 4 Severity of pain Insignificant n=11 n= Average * 40 * 40 * Intense * * Severe * Note.* - The difference is statistically significant. In the post- examination phase, attention was drawn to the reduction in the of samples with -relevant bacilluria, i.e. by 4 times (by %) based on all three nosological groups. Leukocyturia decreased by 3.5 times (by 33.4%) in all three groups. The most significant changes were in the parameters of patients of nosological Group I. In the first group of patients with bacterial cystitis, the most common pathogen was Escherichia coli (.5%) while Enterobacter spp., Enterococcus spp., K. Pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa were detected in a small percentage of cases (1.%). Patients of this group underwent antimicrobial therapy according to the sensitivity data of pathogens. 25 (3.33%) patients noted a significant improvement in their state of health, reduction in complaints; a decrease in the frequency of urgency as well as increase in the intervals between cystitis exacerbations. 5 patients (1.%) had no improvement in their clinical status. The drug showed good safety and tolerability. Only one patient (3.33%) refused to administer the drug due to the burning. Side effects, allergic reactions during the study period have not been reported. CONCLUSIONS 1. The use of Instylan instillations in the complex therapy of patients with chronic cystitis showed pronounced positive clinical dynamics in 5% of patients. 2. The use of Instylan showed decrease in the of cystitis recurrences by more than 2 folds, which significantly improved the quality of life of patients. 3. The results obtained allows us to recommend the administration of intravesical sodium hyaluronate in the therapeutic plan for various forms of chronic cystitis accompanied by a deficiency of the glucosaminoglycan layer. Information about the author Nikitin Oleg Dmitrievich - Bogomolets National Medical University, 01 Kyiv 3/1 Shovkovychna Str. nikitin@bigmir.net LIST OF REFERENCES 1. Moldwin RM, Sant GR. I n t e r s t i t i a l c y s t i t i s : a p a t h o p h y s i o l o g y a n d update. Clin Obstet Gynecol 02;45: Oravisto KJ. Epidemiology of interstitial cystitis. Ann Chir Gynaecol Fenn 15; 4:5. 3. Jones CA, Nyberg L. Epidemiology of interstitial cystitis. Urology 1; 4 (5A Suppl):2. 4. Parsons CL, Stein PC, Bidair M, L e b o w D. A b n o r m a l sensitivity to intravesical potassium in interstitial cystitis a n d r a d i a t i o n c y s t i t i s. N e u r o u r o l U r o d y n 14;13: P a rs o n s C L. C h ro n i c cystitis: epidemiology and clinical presentation. Clin Obstet Gynecol 02;45:242.. Parsons CL, Lilly JD, Stein P. E p i t h e l i a l d y s f u n c t i o n i n nonbacterial cystitis (interstitial cystitis). J Urol 11;145: 32.. D a h a L K, R i e d l C R, Hohlbrugger G, Knoll M, Engelhardt PF, Pfluger H. Comparative assessment of maximal bladder capacity, (0.) NaCl versus 0.2M KCl, for the diagnosis of interstitial c y s t i t i s : a p r o s p e c t i v e c o n t ro l l e d s t u d y. J U ro l 03;10: 0.. Ruggieri MR, Chelsky MJ, Rosen SI, Shickley TJ, Hanno PM. Current find ings and future research avenues in the study of interstitial cystitis. Urol Clin North Am 14; 21: 13.. Ratliff TL, Klutke CG, McDougall EM. The etiology of interstitial cystitis. Urol Clin North Am 14; 21:21.. Parsons CL, Housley T, S c h m i d t J D, L e b o w D. Treatmentof interstitial cystitis with intravesical heparin. Br J Urol 14; 3: Hanno PM. Analysis of long-term Elmiron therapy for interstitial cystitis. Urology 1; 4 (5A Suppl): Morales A, Emerson L, N i c k e l J C. I n t r a v e s i c a l hyaluronic acid in the of refractory cystitis. Urology 1;4 (5A Suppl): W e i n A J, H a n n o P, Gillenwater JY. An introduction to the problem. In: Hanno P, Staskin DR, Krane RJ, Wein AJ, editors. Cystitis. London: Springer-Verlag; 10. p Fall M, Johansson SL, Aldenborg F. Chronic cystitis: a heterogeneous syndrome. J Urol 1;13: Peeker R, Haghsheno MA, Holmang S, Fall M. Intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin and dimethyl sulfoxide for the of classic and nonulcer interstitial cystitis: a prospective, randomized double-blind study. J Urol 00; 14:112. MEN'S HEALTH N 4 (55) 15 ISSN
In evaluating a patient with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), urologists
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
PRACTICAL APPLICATION INSTYLAN MODERN PROTECTOR OF URINARY BLADDER MUCOSA
 PRACTICAL APPLICATION INSTYLAN MODERN PROTECTOR OF URINARY BLADDER MUCOSA E.O. Stakhovsky, PhD, MD, Professor, Head of the Scientific and Research Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Oncourology,
PRACTICAL APPLICATION INSTYLAN MODERN PROTECTOR OF URINARY BLADDER MUCOSA E.O. Stakhovsky, PhD, MD, Professor, Head of the Scientific and Research Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Oncourology,
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS. Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >60%
 DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective?
 Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Interstitial and chronic cystitis. Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall?
 Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Interstitial Cystitis
 Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis
 Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence
 BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
WHAT IS INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS?
 Patient Information WHAT IS INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS? Interstitial Cystitis (IC) is a condition resulting in recurring discomfort or pain in the bladder and the surrounding pelvic region. Its cause is unknown,
Patient Information WHAT IS INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS? Interstitial Cystitis (IC) is a condition resulting in recurring discomfort or pain in the bladder and the surrounding pelvic region. Its cause is unknown,
RECURRENT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS: WHAT AN INTERNIST
 RECURRENT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS: WHAT AN INTERNIST MUST KNOW PROF. MD. ENAMUL KARIM Professor of Medicine Green Life Medical College INTRODUCTION Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the commonest
RECURRENT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS: WHAT AN INTERNIST MUST KNOW PROF. MD. ENAMUL KARIM Professor of Medicine Green Life Medical College INTRODUCTION Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the commonest
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
How does interstitial cystitis begin?
 Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
USE OF MEDICAL PRODUCTS WITH HYALURONIC ACID IN CHRONIC CYSTITIS TREATMENT
 USE OF MEDICAL PRODUCTS WITH HYALURONIC ACID IN CHRONIC CYSTITIS TREATMENT Ivanov D.D., M.D., Professor Dombrowski Ya.A. National Academy of Postgraduate Education named after P.L. Shupik, Kiev, Kyiv City
USE OF MEDICAL PRODUCTS WITH HYALURONIC ACID IN CHRONIC CYSTITIS TREATMENT Ivanov D.D., M.D., Professor Dombrowski Ya.A. National Academy of Postgraduate Education named after P.L. Shupik, Kiev, Kyiv City
32 OBG Management July 2010 Vol. 22 No. 7 obgmanagement.com
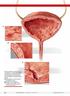 A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
6/4/2018. Conflicts Disclosure. Objectives. Introduction. Classifications of UTI. Host Defenses. Management of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
 Conflicts Disclosure Presenter has no conflicts of interest to disclose Management of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections COLIN M. GOUDELOCKE, M.D. JUNE 14, 2018 Objectives Attendees will review the identification
Conflicts Disclosure Presenter has no conflicts of interest to disclose Management of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections COLIN M. GOUDELOCKE, M.D. JUNE 14, 2018 Objectives Attendees will review the identification
A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS)
 31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
UTI IN ELDERLY. Zeinab Naderpour
 UTI IN ELDERLY Zeinab Naderpour Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most frequent bacterial infection in elderly populations. While urinary infection in the elderly person is usually asymptomatic, symptomatic
UTI IN ELDERLY Zeinab Naderpour Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most frequent bacterial infection in elderly populations. While urinary infection in the elderly person is usually asymptomatic, symptomatic
BLADDER HEALTH. Painful Bladder AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
 BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Learning Objectives Identify signs and symptoms that may indicate presence of UTI (both complicated and uncomplicated) List common causative organisms and risk factors for UTIs
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Learning Objectives Identify signs and symptoms that may indicate presence of UTI (both complicated and uncomplicated) List common causative organisms and risk factors for UTIs
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students. Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile.. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile.. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products,
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC)
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS): THE BASIC FACTS ANDREW L. SIEGEL, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Specialty: Male and Female Incontinence, Voiding Dysfunction,
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS): THE BASIC FACTS ANDREW L. SIEGEL, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Specialty: Male and Female Incontinence, Voiding Dysfunction,
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
Interstitial Cystitis:
 Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Voiding Diary. Begin recording upon rising in the morning and continue for a full 24 hours.
 Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys.
 UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys. 1-3% of Below 1 yr. male: female ratio is 4:1 especially among uncircumcised males,
UTI are the most common genitourinary disease of childhood. The prevalence of UTI at all ages is girls and 1% of boys. 1-3% of Below 1 yr. male: female ratio is 4:1 especially among uncircumcised males,
Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks
 1100 Wayne Ave, Suite 825 Silver Spring, MD 20910 301.273.0570 Fax 301.273.0778 info@augs.org www.augs.org Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks ICD 9 ICD 9 Description ICD 10 Code ICD 10 Description
1100 Wayne Ave, Suite 825 Silver Spring, MD 20910 301.273.0570 Fax 301.273.0778 info@augs.org www.augs.org Urogynecology ICD-9 to ICD-10 Crosswalks ICD 9 ICD 9 Description ICD 10 Code ICD 10 Description
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students. Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile in urinary bladder.. It contains fluids,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile in urinary bladder.. It contains fluids,
Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis
 n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Information for patients Leeds Centre for Women s Health Welcome to the Department of Urogynaecology Your consultant
n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Information for patients Leeds Centre for Women s Health Welcome to the Department of Urogynaecology Your consultant
Dr. Aso Urinary Symptoms
 Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
-Almost one third of cases admitted to medical centers are related to urinary tract infection
 Urinary tract infections: -Almost one third of cases admitted to medical centers are related to urinary tract infection -Urinary tract infection and respiratory infection together encompass about fifty
Urinary tract infections: -Almost one third of cases admitted to medical centers are related to urinary tract infection -Urinary tract infection and respiratory infection together encompass about fifty
NEOSPORIN G.U. Irrigant Sterile (neomycin sulfate polymyxin B sulfate solution for irrigation)
 NEOSPORIN G.U. Irrigant Sterile (neomycin sulfate polymyxin B sulfate solution for irrigation) NEOSPORIN G.U.SOLUTION NOT FOR INJECTION DESCRIPTION NEOSPORIN G.U. Irrigant is a concentrated sterile antibiotic
NEOSPORIN G.U. Irrigant Sterile (neomycin sulfate polymyxin B sulfate solution for irrigation) NEOSPORIN G.U.SOLUTION NOT FOR INJECTION DESCRIPTION NEOSPORIN G.U. Irrigant is a concentrated sterile antibiotic
Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER
 GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER (Limited text update December 21) M. Babjuk, W. Oosterlinck, R. Sylvester, E. Kaasinen, A. Böhle, J. Palou, M. Rouprêt Eur Urol 211 Apr;59(4):584-94 Introduction
GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER (Limited text update December 21) M. Babjuk, W. Oosterlinck, R. Sylvester, E. Kaasinen, A. Böhle, J. Palou, M. Rouprêt Eur Urol 211 Apr;59(4):584-94 Introduction
Anatomy kidney ureters bladder urethra upper lower
 Urinary tract Anatomy The urinary tract consists of the kidney, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Urinary tract infections can be either: upper or lower based primarily on the anatomic location of the infection.
Urinary tract Anatomy The urinary tract consists of the kidney, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Urinary tract infections can be either: upper or lower based primarily on the anatomic location of the infection.
Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome
 page 1 Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome Q: What is interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS)? A: Interstitial cystitis (int-uhr-stishuhl siss-tyt-uhss) (IC), is a chronic pain condition
page 1 Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome Q: What is interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS)? A: Interstitial cystitis (int-uhr-stishuhl siss-tyt-uhss) (IC), is a chronic pain condition
Urinary tract infections
 بسم رلاهللا Urinary tract infections This sheet will only contain extra notes said by the dr. UTIs: - is the second most common type of infections in community(second only to RTIs) - Incidence=20-30% of
بسم رلاهللا Urinary tract infections This sheet will only contain extra notes said by the dr. UTIs: - is the second most common type of infections in community(second only to RTIs) - Incidence=20-30% of
Interstitial Cystitis. Dr. Gerard Testa
 Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
Cystoscopic and Histopathologic Patterns in Iraqi Patients with Chronic Cystitis /Painful Bladder Syndrome
 CHRONIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE CYSTITIS /PAINFUL MEDICAL BLADDER JOURNAL SYNDROME VOL., NO., Cystoscopic and Histopathologic Patterns in Iraqi Patients with Chronic Cystitis /Painful Bladder Syndrome Issam
CHRONIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE CYSTITIS /PAINFUL MEDICAL BLADDER JOURNAL SYNDROME VOL., NO., Cystoscopic and Histopathologic Patterns in Iraqi Patients with Chronic Cystitis /Painful Bladder Syndrome Issam
Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.10.682 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.10.682 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
Urinary tract infection. Mohamed Ahmed Fouad Lecturer of pediatrics Jazan faculty of medicine
 Urinary tract infection Mohamed Ahmed Fouad Lecturer of pediatrics Jazan faculty of medicine Objectives To differentiate between types of urinary tract infections To recognize the epidemiology of UTI in
Urinary tract infection Mohamed Ahmed Fouad Lecturer of pediatrics Jazan faculty of medicine Objectives To differentiate between types of urinary tract infections To recognize the epidemiology of UTI in
BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION
 BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION The bladder is the balloon like organ located in the pelvis that stores and empties urine. Urine is produced by the kidneys, is conducted to the bladder by the ureters,
BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION The bladder is the balloon like organ located in the pelvis that stores and empties urine. Urine is produced by the kidneys, is conducted to the bladder by the ureters,
Lecture 1: Genito-urinary system. ISK
 Urinary Tract Infections Lecture 1: Genito-urinary system. ISK 07 08 2009. Getting Clear on the Terminology UTI Cystitis Urosepsis Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Asymptomatic UTI Pyuria Symptomatic UTI Pylonephritis
Urinary Tract Infections Lecture 1: Genito-urinary system. ISK 07 08 2009. Getting Clear on the Terminology UTI Cystitis Urosepsis Asymptomatic Bacteriuria Asymptomatic UTI Pyuria Symptomatic UTI Pylonephritis
Effects of Local EstrogenTherapy on Recurrent UrinaryTract Infections inyoung Females under Oral Contraceptives
 European Urology European Urology 47 (2005) 243 249 Effects of Local EstrogenTherapy on Recurrent UrinaryTract Infections inyoung Females under Oral Contraceptives Germar-M. Pinggera a, *, Gudrun Feuchtner
European Urology European Urology 47 (2005) 243 249 Effects of Local EstrogenTherapy on Recurrent UrinaryTract Infections inyoung Females under Oral Contraceptives Germar-M. Pinggera a, *, Gudrun Feuchtner
CYSTISTAT. Hyaluronan Training
 CYSTISTAT Hyaluronan Training HISTORICAL ASPECTS In 1934, Karl Meyer and his assistant, John Palmer, described for the first time the process to isolate a new Glucosa- Amino-Glycan (GAG) from the cows
CYSTISTAT Hyaluronan Training HISTORICAL ASPECTS In 1934, Karl Meyer and his assistant, John Palmer, described for the first time the process to isolate a new Glucosa- Amino-Glycan (GAG) from the cows
Interstitial Cystitis
 J Obstet Gynecol India Vol. 58, No. 1 : January/February 2008 pg 24-31 Review Article Interstitial Cystitis Satpathy Hemant K, Taylor Richert Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, CUMC, Omaha, NE, USA,
J Obstet Gynecol India Vol. 58, No. 1 : January/February 2008 pg 24-31 Review Article Interstitial Cystitis Satpathy Hemant K, Taylor Richert Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, CUMC, Omaha, NE, USA,
Treatment Regimens for Bacterial Urinary Tract Infections. Characteristic Pathogen. E. coli, S.saprophyticus P.mirabilis, K.
 HEALTHSPAN URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (ADULT FEMALE) Methodology: Evidence-Based Issue Date: 1-98 Champion: Internal Medicine Most Recent Review: 4-10, 4-12, 4-14 Key Stakeholders: IM, Urology, Next Review:
HEALTHSPAN URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (ADULT FEMALE) Methodology: Evidence-Based Issue Date: 1-98 Champion: Internal Medicine Most Recent Review: 4-10, 4-12, 4-14 Key Stakeholders: IM, Urology, Next Review:
Bladder Instillation Therapy (BCG) Department of Urology Information for patients
 Bladder Instillation Therapy (BCG) Department of Urology Information for patients i Introduction Your consultant has prescribed a course of treatment for you called bladder instillation therapy. What is
Bladder Instillation Therapy (BCG) Department of Urology Information for patients i Introduction Your consultant has prescribed a course of treatment for you called bladder instillation therapy. What is
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence. Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations
 The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_
 207 Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_2542 207..212 C. Lowell Parsons, MD,* Paul Zupkas, PhD,* Jeffrey Proctor, MD,
207 Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_2542 207..212 C. Lowell Parsons, MD,* Paul Zupkas, PhD,* Jeffrey Proctor, MD,
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 59 (2011)
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 59 (2011) 645 651 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Infections Prevention of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections by Intravesical Administration
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 59 (2011) 645 651 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Infections Prevention of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections by Intravesical Administration
Introduction. For further information please contact:
 Product Monograph Introduction Teva UK Limited is one of the biggest pharmaceutical companies in the UK. We re proud to be part of the Teva Pharmaceutical Industries group, and we make medicines that help
Product Monograph Introduction Teva UK Limited is one of the biggest pharmaceutical companies in the UK. We re proud to be part of the Teva Pharmaceutical Industries group, and we make medicines that help
VAGINAL REJUVENATION
 VAGINAL REJUVENATION FOR ULTIMATE COMFORT AND CONFIDENCE LOTUS GYNOLASER ADVANCED AND RELIABLE Ageing, childbirth, illness and medication can affect you in many ways, but hidden problems can often be the
VAGINAL REJUVENATION FOR ULTIMATE COMFORT AND CONFIDENCE LOTUS GYNOLASER ADVANCED AND RELIABLE Ageing, childbirth, illness and medication can affect you in many ways, but hidden problems can often be the
THE UROLOGY GROUP
 THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
Definition/Epidemiology Approach to premenopausal and postmenopausal women A couple tricky cases DISCLOSURES. No financial relationships to disclose.
 DISCLOSURES RECURRENT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS No financial relationships to disclose. Anna C. Kirby, MD, MAS Acting Assistant Professor University of Washington Division of Urogynecology Department of
DISCLOSURES RECURRENT URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS No financial relationships to disclose. Anna C. Kirby, MD, MAS Acting Assistant Professor University of Washington Division of Urogynecology Department of
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and Nurse-Led Clinics. Sean Diver Urology Advanced Nurse Practitioner candidate Letterkenny University Hospital
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and Nurse-Led Clinics Sean Diver Urology Advanced Nurse Practitioner candidate Letterkenny University Hospital 01/02/2018 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms LUTS - one of
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and Nurse-Led Clinics Sean Diver Urology Advanced Nurse Practitioner candidate Letterkenny University Hospital 01/02/2018 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms LUTS - one of
BJU International EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME
 EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME Journal: Manuscript ID: Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author: BJU-2007-1373
EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME Journal: Manuscript ID: Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author: BJU-2007-1373
PAINFUL URINATION CAUSES & NATURAL REMEDY. Dr. Bestman Anyatonwu
 LIBRACIN NATURAL MEDICINE IND. LTD PAINFUL URINATION CAUSES & NATURAL REMEDY Dr. Bestman Anyatonwu MEANING Painful urination is a broad term that describes discomfort during urination. This pain may originate
LIBRACIN NATURAL MEDICINE IND. LTD PAINFUL URINATION CAUSES & NATURAL REMEDY Dr. Bestman Anyatonwu MEANING Painful urination is a broad term that describes discomfort during urination. This pain may originate
Chronic urinary infection.
 Chronic urinary infection. These figures are drawn from experiments conducted on (1) mouse models of chronic cystitis and (2) more recent work done in our own laboratories using human bladder cells, or
Chronic urinary infection. These figures are drawn from experiments conducted on (1) mouse models of chronic cystitis and (2) more recent work done in our own laboratories using human bladder cells, or
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Mini-Reviews. Interstitial Cystitis in Adolescents and Children: A Review
 J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol (2004) 17:7 11 Mini-Reviews Interstitial Cystitis in Adolescents and Children: A Review T.F. Mattox, MD, FACOG Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Division of Urogynecology,
J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol (2004) 17:7 11 Mini-Reviews Interstitial Cystitis in Adolescents and Children: A Review T.F. Mattox, MD, FACOG Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Division of Urogynecology,
Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis
 Received: 17 December 2016 Accepted: 26 February 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23284 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment
Received: 17 December 2016 Accepted: 26 February 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23284 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment
Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines
 Review Article Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines Amita Jain To cite: Jain A. Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines. Pan Asian J Obs Gyn 2018;1(1):18-23.
Review Article Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines Amita Jain To cite: Jain A. Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines. Pan Asian J Obs Gyn 2018;1(1):18-23.
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective. Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado
 Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer
 Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Intravesical (Bladder) Chemotherapy Urology Patient information Leaflet
 Intravesical (Bladder) Chemotherapy Urology Patient information Leaflet Page 1 This leaflet should be used in conjunction with the cancerbackup booklet entitled Early (superficial bladder) cancer Please
Intravesical (Bladder) Chemotherapy Urology Patient information Leaflet Page 1 This leaflet should be used in conjunction with the cancerbackup booklet entitled Early (superficial bladder) cancer Please
IAUN Conference Dublin, January Helen Forristal Cancer Nurse Co- Ordinator Jonathan Borwell Bladder Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist
 IAUN Conference Dublin, January 2014 Helen Forristal Cancer Nurse Co- Ordinator Jonathan Borwell Bladder Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist Theoretical component Observation Supervised practice Assessment
IAUN Conference Dublin, January 2014 Helen Forristal Cancer Nurse Co- Ordinator Jonathan Borwell Bladder Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist Theoretical component Observation Supervised practice Assessment
Interstitial Cystitis
 Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence
 Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
The Urinary System 15PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (ADULT FEMALE)
 KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (ADULT FEMALE) Methodology: Evidence-Based Issue Date: 1-98 Champion: Internal Medicine Most Recent Review: 4-10, 4-12 Key Stakeholders: IM, Urology, Next
KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (ADULT FEMALE) Methodology: Evidence-Based Issue Date: 1-98 Champion: Internal Medicine Most Recent Review: 4-10, 4-12 Key Stakeholders: IM, Urology, Next
Urinary tract infections, renal malformations and scarring
 Urinary tract infections, renal malformations and scarring Yaacov Frishberg, MD Division of Pediatric Nephrology Shaare Zedek Medical Center Jerusalem, ISRAEL UTI - definitions UTI = growth of bacteria
Urinary tract infections, renal malformations and scarring Yaacov Frishberg, MD Division of Pediatric Nephrology Shaare Zedek Medical Center Jerusalem, ISRAEL UTI - definitions UTI = growth of bacteria
Urogynecology Associates of Philadelphia URODYNAMIC TESTING
 URODYNAMIC TESTING Urogynecology Associates of Philadelphia Most women with urinary incontinence will need to complete a few simple tests, performed in the office, to help your doctor assess your symptoms
URODYNAMIC TESTING Urogynecology Associates of Philadelphia Most women with urinary incontinence will need to complete a few simple tests, performed in the office, to help your doctor assess your symptoms
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA LEARNING OBJECTIVES DEFINITION. KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer
 MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function
 Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
11/15/2010. Asymptomatic Bacteriuria UTI. Symptomatic UTI. Asymptomatic UTI. Cystitis. Pylonephritis. Pyuria. Urosepsis
 Urinary Tract Infections Renal vein Inferior vena cava Urinary bladder Urethra Renal artery Kidney Aorta Ureter Lecture 1: Genito-urinary system. 06 08 2010. (a) Sherwood Fig. 12-6a, p.530 An introduction
Urinary Tract Infections Renal vein Inferior vena cava Urinary bladder Urethra Renal artery Kidney Aorta Ureter Lecture 1: Genito-urinary system. 06 08 2010. (a) Sherwood Fig. 12-6a, p.530 An introduction
Objectives. Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
 URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment
 Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Evaluation of efficacy and safety of fixed dose combination of Cefixime and Oflaxacin in the management of Urinary tract infection
 American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com Vol-1: No-2: 2013 Original Research Article Evaluation of efficacy and safety of fixed dose combination of Cefixime and Oflaxacin in the management
American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com Vol-1: No-2: 2013 Original Research Article Evaluation of efficacy and safety of fixed dose combination of Cefixime and Oflaxacin in the management
You have been booked for a. Flexible Cystoscopy. Under Local Anaesthetic
 You have been booked for a Flexible Cystoscopy Under Local Anaesthetic 1 WHAT IS A FLEXIBLE CYSTOSCOPY A flexible cystoscopy is a test to examine the uretha (waterpipe) and bladder using a thin, lighted
You have been booked for a Flexible Cystoscopy Under Local Anaesthetic 1 WHAT IS A FLEXIBLE CYSTOSCOPY A flexible cystoscopy is a test to examine the uretha (waterpipe) and bladder using a thin, lighted
The Enlarged Prostate Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
 The Enlarged Prostate Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment MAC00031-01 Rev G Financial support for this seminar has been provided by NeoTract, Inc., the manufacturer of the UroLift System. 1 Today s Agenda
The Enlarged Prostate Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment MAC00031-01 Rev G Financial support for this seminar has been provided by NeoTract, Inc., the manufacturer of the UroLift System. 1 Today s Agenda
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis. Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017
 320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France
 A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
Understanding Women's Sexuality after Bladder Cancer webinar. Part I: The Physical Impact
 Understanding Women's Sexuality after Bladder Cancer webinar Tuesday, December 1, 2015 Part I: The Physical Impact Presented by LaShon Day received her Masters of Science as a Physician s Assistant at
Understanding Women's Sexuality after Bladder Cancer webinar Tuesday, December 1, 2015 Part I: The Physical Impact Presented by LaShon Day received her Masters of Science as a Physician s Assistant at
ATLAS OF URODYNAMICS. Bladder. Pure. Pves. Pabd. Pdet EMG. Bladder. volume. Cough Strain IDC. Filling. Pure. Pves. Pabd. Pdet EMG
 2 Normal Micturition The micturition cycle (urine storage and voiding) is a nearly subconscious process that is under complete voluntary control. Bladder filling is accomplished without sensation and without
2 Normal Micturition The micturition cycle (urine storage and voiding) is a nearly subconscious process that is under complete voluntary control. Bladder filling is accomplished without sensation and without
Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela
 Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela Microbiology Department Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia Urinary Tract Infection
Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela Microbiology Department Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia Urinary Tract Infection
How do I prepare for treatment? What happens afterwards? Where can I get more information? Cancerbackup The Prostate Cancer Charity
 How do I prepare for treatment? Do not drink fluids for at least two hours before treatment so that your bladder will be empty. Tell your doctor or nurse about any medicines you take regularly and any
How do I prepare for treatment? Do not drink fluids for at least two hours before treatment so that your bladder will be empty. Tell your doctor or nurse about any medicines you take regularly and any
CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN OF BLADDER ORIGIN:
 ACCREDITATION This activity has been planned and implemented in accordance with the Essential Areas and policies of the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education through the joint sponsorship
ACCREDITATION This activity has been planned and implemented in accordance with the Essential Areas and policies of the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education through the joint sponsorship
Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O. Talbott,* Josephine Davis and Lisa J. Regan
 Safety and Efficacy of the Use of Intravesical and Oral Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium for Interstitial Cystitis: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O.
Safety and Efficacy of the Use of Intravesical and Oral Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium for Interstitial Cystitis: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O.
UTI. Monica Tegeler, MD
 4 UTI Monica Tegeler, MD 2 Diagnosis Stone criteria >100,000 colonies of bacteria growing in urine with no more than 2 species of microorganisms Dysuria OR Fever AND 1 of following: Frequency Urgency Suprapubic
4 UTI Monica Tegeler, MD 2 Diagnosis Stone criteria >100,000 colonies of bacteria growing in urine with no more than 2 species of microorganisms Dysuria OR Fever AND 1 of following: Frequency Urgency Suprapubic
DOWNLOAD OR READ : URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 urinary tract infections in children urinary tract infections in pdf urinary tract infections in children MID 11
DOWNLOAD OR READ : URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 urinary tract infections in children urinary tract infections in pdf urinary tract infections in children MID 11
C. Lowell Parsons UC San Diego Medical Center, Department of Surgery/Urology, La Jolla, CA, USA
 ; 2010 Mini Reviews BLADDER SYMPTOMS CAUSED BY LEAKY EPITHELIUM AND POTASSIUM PARSONS ET AL. BJUI The role of a leaky epithelium and potassium in the generation of bladder symptoms in interstitial cystitis/overactive
; 2010 Mini Reviews BLADDER SYMPTOMS CAUSED BY LEAKY EPITHELIUM AND POTASSIUM PARSONS ET AL. BJUI The role of a leaky epithelium and potassium in the generation of bladder symptoms in interstitial cystitis/overactive
Bacterial urinary tract infections
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Bacterial urinary tract infections Author : CATHERINE F LE BARS Categories : Vets Date : February 11, 2008 CATHERINE F LE
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Bacterial urinary tract infections Author : CATHERINE F LE BARS Categories : Vets Date : February 11, 2008 CATHERINE F LE
