Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis
|
|
|
- Hester Phelps
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Received: 17 December 2016 Accepted: 26 February 2017 DOI: /nau ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis Ömer Gülpınar 1 Barış Esen 1 Aytaç Kayış 2 Mehmet İlker Gökçe 1 Evren Süer 1 1 Department of Urology, Ankara University, Ankara, Turkey 2 Department of Urology, Kars State Hospital, Kars, Turkey Correspondence Ömer Gülpınar, Department of Urology, Ankara University, Ankara 06100, Turkey. omergulpinar@yahoo.com Introduction: Intravesical glucosaminoglycan (GAG) replacement therapies are commonly used in the treatment of bladder pain syndrome (BS)/interstitial cystitis (IC). Different intravesical glucosaminoglycan products are currently available. In this prospective study, clinical efficacy of chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid are compared in patients with BS/IC. Methods: atients were randomized to CS and HA groups. All patients were evaluated for visual analogue pain scale (VAS), interstitial cystitis symptom index (ICSI), interstitial cystitis problem index (ICI), voiding diary for frequency/ nocturia, and mean urine volume per void at the beginning of the therapy and after 6 months. All patients had a potassium sensitivity test (ST) initially. Wilcoxon and Mann-Whitney U tests were used for statistical analysis. Results: There were 21 patients in both groups. Mean age of patients in CS and HA groups were and 48.90, respectively( > 0.05). Before treatment, arson s test was positive in 64.3% of patients (27/42) with no difference between groups. VAS of pain, ICSI, ICI, frequency at 24 h and nocturia results have improved significantly at both treatment arms. Intravesical CS was also found superior to intravesical HA in terms of 24 h frequency, nocturia and ICI ( < 0.05). No severe adverse effects were reported. Conclusions: Data comparing clinical efficiencies of different GAG therapies are very limited. In this study, intravesical CS was found superior to intravesical HA in terms of 24 h frequency, nocturia and ICI in patients with BS/IC in short term follow-up. To provide a definitive conclusion on superiority of one GAG therapy to others, further evaluation with long term follow up is required. 1 INTRODUCTION Bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BS/IC) is the occurrence of persistent or recurrent pain perceived in the Fred Milani led the peer-review process as the Associate Editor responsible for the paper. urinary bladder region, accompanied by at least one other symptom, such as pain worsening with bladder filling and day-time and/or night-time urinary frequency, in the absence of proven urinary infection or other obvious local pathology. 1 Wide variation of prevelance rates have been reported in literature due to different definitions accepted in the studies and different study designs. But recent modern prevelance Neurourology and Urodynamics. 2017;9999:1 6. wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/nau 2017 Wiley eriodicals, Inc. 1
2 2 GÜLІNAR ET AL. studies showed higher rates than previous estimations. A population based epidemiological study revealed prevelance rates in females and males as 2.7% and 1.9%, respectively. 2,3 Although etiology of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis is not clearly identified and probably has a multifactorial cause, it is a widely accepted theory that such clinical conditions may arise from a primary defective urothelium lining or from a damage of its glycosaminoglycan (GAG) component. 4 The loss of the watertight function of the urothelium may allow both the normal and abnormal constituents of urine to directly contact the subepithelial layers, resulting in inflammation and delayed healing of the damaged urothelial layer. Consequently, some noxious substances in urine may activate submucosal nerve filaments, thus accounting for symptoms of pain, urgency, and urinary frequency. 5 To improve the integrity and function of the bladder lining, exogenous intravesical GAG replacement therapies are one of the treatment options for patients with BS/IC, generally refractory to conventional therapy. 6 İntravesical heparin with or without lidocain and sodium bicarbonate, sodium pentosan polysulfate (S), hyaluronic acid (HA), chondroitin suphate (CS), and HA-CS combinations are avaible products currently used as intravesical GAG replacement therapies. In literature, there are some placebo-controlled and uncontrolled studies showing success rates of these products but data comparing these substances in BS/IC patients is very limited. This causes difficulty for physicians to choose optimal GAG replacement therapy for their patients. In this study, we compared the clinical efficacy of HA and CS in patients with BS/IC who had no benefit from previous conservative and medical treatment. 2 METHODS A total of 42 female patients with BS/IC were included to the study. atients with complaints of chronic pelvic pain related to bladder filling accomppanied by voiding frequency 8 times/24 h, nocturia 2 times per night or persistant urge for at least 24 weeks, an average pain score of 4 (VAS; 0 no pain, 10 unbearable pain), a negative pregnancy test, a sterile urine culture and inadequate clinical response after 6 months of conservative and medical treatment were included to the study. atients with positive pregnancy test, current urinary infection or sexually transmitted disease, chemical cystitis, tuberculous or radiation cystitis, urolithiasis, urological malignancy, endometriosis, urethral diverticulum, and breastfeeding women were excluded from the study. Data were collected prospectively and evaluated retrospectively. Hospital ethical committee approval and informed consents of patients were obtained. atients were randomized for intravesical therapy with 50 ml/120 mg sterile sodium HA (HYACYST Molecular weight:152 kda) or 40 ml/80 mg sodium CS (GEAN INSTILL ). Intravesical instillations were administered to patients using 12F hydrophilic Foley catheters. atients were instructed to try not to urinate for the next 60 min. Intravesical instillations were done weekly in first month, once in 15 days in second month and monthly in third and fourth months as a total of eight intravesical doses. atients were evaluated for visual analog scale score (VAS) for pain, 3 day voiding diary (24 h frequency, nocturia, median voided volume), symptom index score (ICSI) and problem index score (ICI) at the beginning of the therapy and after 6 months. A reduction less than two on VAS of pain was considered as non-response to treatment. Among responders; a reduction of more than 50% of VAS score was considered as strong benefit and less than 50% of VAS score was considered as limited benefit. All patients had a potassium sensitivity test (ST) initially. The primary outcome of the study was the change of pain VAS score from baseline compared to week 24. Secondary outcomes included comparison of daily urinary frequency/ nocturia, ICSI, and ICI scores and mean voided volume from baseline to week 24. Baseline factors were compared with the t-test and the Mann-Whitney rank sum test, and differences between treatment outcomes were calculated with the Mann-Whitney rank sum test. roportions of responders were calculated with the Fisher exact test; < 0.05 was considered signicant. Statistical analysis was performed with SSS, v.16.0 statistical software (SAS Institute, Cary, NC). 3 RESULTS Between January 2012 and February 2014, a total of 42 patients were randomized. Twenty-one patients with a mean age of randomized for CS group and 21 patients with a mean age of randomized for HA group ( > 0.05). ST was positive for 14 patients (66.7%) and 13 patients (61.9%) in CS and HA groups respectively ( > 0.05). Total positiveness rate of ST was 64.3% (27/42). There was no statistically significant difference between the pretreatment findings of the two groups (Table 1). Former treatments in CS group were dietary restrictions and analgesics (n = 10), dietary restrictions and hydroxyzine hydrochloride (n = 5), dietary restrictions and amitriptyline (n = 3) and oral pentosanpolysulfate (n = 3). Dietary restrictions and analgesics (n = 12), dietary restrictions and amitriptyline (n = 4), and oral pentosanpolysulfate (n = 5) were the former treatments of the HA group. We compared results at baseline and 6 months. In both groups VAS of pain decreased significantly at both groups (nine to four in HA group and eight to five in CS group,
3 GÜLІNAR ET AL. 3 TABLE 1 retreatment characteristics of the two groups arameters Hyaluronic acide (HA), n =21 Chondroitin sulfate (CS), n =21 value Age ± ± VAS of pain 9 (min:4-max:10) 8 (min:5-max:10) Micturition frequency (24 h) ± ± Nocturia 2 (min:0- max:12) 3 (min:1-max:6) Mean voided volume (ml) 148 (min:26-max:369) 136 (min:29-max:355) ICSI 16 (min:4-max:20) 17 (min:11-max:20) ICI 13 (min:6-max:16) 14 (min:8-max:16) ST positivity rate 61.9% 66.7% HA, hyaluronic acid; CS, chondroitin sulfate; VAS, visual analog scale; ICSI, interstitial cystitis symptom index; ICI, interstitial cystitis problem index; ST, potassium sensitivity test. < 0.05). According to changes in VAS scores, patients were categorized into three groups such as non-response, limited benefit and strong benefit. No statistically significant difference was found between treatment arms (Table 2) ICSI, ICI, frequency at 24 h, nocturia results have improved significantly at both treatment arms. CS was also found to increase mean urine volume per void, but not for HA (Fig. 1). Intravesical CS was also found superior to intravesical HA in terms of 24 h frequency, nocturia, and ICI ( < 0.05) (Fig. 2). But there was no statistically significant difference between treatment arms in VAS scores and mean urine volume per void ( > 0.05) (Table 3). No severe adverse effects were reported. 4 DISCUSSION Hursts purposal, defects of glucosaminoglycan layer can cause symptoms of BS/IC, is a widely accepted theory. 7 Intravesical GAG replacement therapy is indicated in patients who have poor or inadequate response to conventional therapy. 6 Intravesical heparin with or without lidocain and sodium bicarbonate, sodium pentosan polysulfate (S), HA, CS, and HA-CS combinations are avaible products currently used as intravesical GAG replacement therapies. Exogenous intravesical HA was the first GAG used to treat BS/IC. First study evaluating HA use for BS/IC TABLE 2 Treatment response groups according to VAS score changes Treatment response HA CS value No response 23.8% (5/21) 28.5% (6/21) Limited benefit 38.1% (8/21) 19% (4/21) 0.38 Strong benefit 38.1% (8/21) 52.4% (11/21) symptoms was published in 1996 by Morales and collegues, and they found 71% complete or partial response by week Since than studies reported wide range of response rates, from 30% to 85% Best results reported by Riedl and collegues. They have studied on 126 BS/IC patients with positive modified potassium chloride test and found 85% had symptom improvement ( 2 VAS units) and 84% had significant improvement of their quality of life. 11 In contrast to previously mentioned studies, in 2003 and 2004, two industry sponsored randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled studies of different HA preparations (40 or 200 mg per ml) were completed. No significant efficacy of HA compared with placebo for BS/IC patients was shown. However, further details, including patient selection, inclusion/exclusion criteria, definition of improvement/success, are not available. 12 revious studies has shown a deficit of chondroitin sulfate from lumenal surface may play a role in the pathophysiology of BS/IC. 13 Based on this point, intravesical CS treatment has been suggested to be effective in BS/IC patients. Steinhoff et al evaluated intravesical CS therapy efficiency in an open label 12-month study. In this study, 40-mL instillations of CS 0.2% were administered to 18 patients with interstitial cystitis and positive potassium chloride test. They found a response rate for symptom improvement of 67%. 14 An uncontrolled open multicenter study of 53 IC patients, found 60% response rate to CS 2% at 6 months. 15 In contrast to previous results, a prospective randomized and controlled 12 week trial (6 weeks treatment period, 6 weeks follow up) by Nickel et al failed to show superiority of CS 2% over control. In this study, twice as many patients reported a clinically significant benefit with intravesical chondroitin sulfate treatment compared with control treatment, but difference was not enough to maintain statistical significance. 16 In a latter study by Nickel et al, minor improvements in BS/IC related symptoms and pain were
4 4 GÜLІNAR ET AL. FIGURE 1 Increased mean voided volume in CS group achieved with intravesical CS treatment. But again, these differences were found statistically insignificant. 17 CS-HA combination (2% CS- low molecular weight 1.6% HA) is the latest available substance for intravesical treatment and good results have been reported in uncontrolled studies. In an open-label, single arm study, orru et al evaluated efficiency of CS/HA combination therapy in 20 patients with BS/IC. After treatment, weekly for 8 weeks, then once every 2 weeks for the next 6 months, results showed statistically significant improvement in all parameters including VAS for pain and urgency, mean voiding volume, average number of voids in 24 h, ICSI, and ain Urgency Score (UF). 18 Cervigni et al reported long term outcomes of intravesical CS/HA combination therapy in 12 patients with BS/IC. They found improvements in symptoms and quality of life evaluation were still apperent at 3-year follow up. 19 In the most recent study, statistically significant decreases in ICSI, ICI and UF questionnaire scores in 20 women with BS/IC were obtained by Giberti and colleagues. 20 lacebo-controlled and uncontrolled studies showing success rates of these products were mentioned above. But info comparing these substances to each other is very limited. reviously, intravesical HA/CS combination and intravesical HA were compared in 53 patients with BS/IC who had inadequate clinical response after 6 months of conservative treatment. Improvements in parameters such as VAS for pain, 24-h frequency/nocturia, ICSI and ICI were observed in both treatment arms. However no statistically significant difference in any parameter was found between CS/HA combination therapy and HA therapy at the 6-month evaluation. 21 Our study is the first study in the literature comparing intravesical CS and HA therapies and the first study finding statistically significant difference between two intravesical GAG substances in the treatment of BS/IC. We compared intravesical CS and HA in patients with BS/IC who had inadequate response after 6 months of conservative treatment. Statistically significant TABLE 3 retreatment and 6 months findings of the patients treated with CS and HA Hyaluronic acide (HA) Chondroitin sulfate (CS) HA versus CS Initial visit 6 months value Initial visit 6 months value value VAS of pain 9 (min:4- max:10) 4 (min:0-max:9) < (min:5-max:10) 5 (min:0-max:8) h frequency ± ± ± ± 3.61 <0.001 <0.001 Nocturia 2 (min:0-max:12) 1 (min:0-max:5) (min:1-max:6) 1 (min:0-max:4) < Mean voided volume (ml) 148 (min:26- max:369) 168 (min:20- max:333) (min:29- max:355) 155 (min:64- max:369) < ICSI 16 (min:4-max:20) 10 (min:4-max:19) (min:11-max:20) 9 (min:4-max:18) < ICI 13 (min:6-max:16) 8 (min:2-max:16) < (min:8-max:16) 7 (min:1-max:13) < HA, hyaluronic acid; CS, chondroitin sulfate; VAS, visual analog scale, ICSI, interstitial cystitis symptom index; ICI, interstitial cystitis problem index.
5 GÜLІNAR ET AL. 5 FIGURE 2 Results of parameters; pretreatment and 6 months after treatment improvements in parameters including VAS for pain, average number of voids in 24 h, nocturia, ICSI and ICI scores were obtained in both treatment arms. CS was found to increase in urine volume per void unlike HA. Intravesical CS was also found superior to intravesical HA in terms of 24 h frequency, nocturia, and ICI in patients with BS/IC in short term period. Natural GAG layer consists sulfated GAGs like chondroitin suphate, dermatan sulfate and non-sulfated GAGs such as hyaluronic acid. About 80-90% of the total surface GAG is bound as integral membrane proteins, with 55% of the protein bound GAG being heparan sulfate, 26% being CS, and the remainder either not identified or dermatan sulfates. 22 revious studies also demostrated that a deficit of chondroitin sulfate from lumenal surface may play a role in the pathophysiology of BS/IC. 13 Considering relative abundance of CS compared to HA in the natural GAG layer of bladder surface and results of previously mentioned studies showing the possible role of CS deficit in the pathophysiology of BS/IC, it can be reasonable to suggest that CS may be more efficient than HA in the treatment of IC/BC. To have a definitive conclusion on whether there is a superiority of intravesical CS to other intravesical GAG therapies, we need further research with large prospective RCTs with long-term follow up. Cost-effectiveness of intravesical GAG therapies is certainly an important aspect for physicians to choose optimal treatment for their patients and should be mentioned. In a recently published meta-analysis; cost efficacy was found less than 25% for CS compared with HA. In this meta-analysis; mostly results of CS 2% and HMW (high molecular weight) HA were compared. Number needed to treat for a treatment response was found 1.31 for HMW-HA and 5.51 for CS 2%. 23 But our results showed similar response rates for both therapies and also similar costs. Further studies comparing cost efficacies of LMW-HA and CS 0.2% are required to have a conclusion on the issue. Lack of control group is the important limitation of our study. But it was difficult to form a control group since patients with BS/IC were suffering from severe pain and were desperate for treatment. The duration of the follow-up period and number of patients included to our study were also limited, but comparable to other series in literature. 5 CONCLUSION Intravesical GAG replacement therapy is a standard treatment in patients with inadequate response to conservative treatment. Both CS and HA are shown as effective treatments in patients with BS/IC. Data comparing intravesical GAG therapies are very limited. To our knowledge, this is the first study in literature finding statistically significant difference between two intravesical GAG substances in the treatment of BS/IC. Further research with large prospective RCTs with long-term follow up is required to have a definitive conclusion on any possible superiority of CS to other intravesical GAG replacement therapies. REFERENCES 1. Engeler Engeler D, Baranowski A, Borovicka J, et al. EAU Guidelines on Chronic elvic ain Available online at: 2. Berry SH, Elliott MN, Suttorp M, et al. revalence of symptoms of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis among adult females in the United States. J Urol. 2011;186: Konkle KS, Berry SH, Elliott MN, et al. Comparison of an interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome clinical cohort with symptomatic community women from the RAND Interstitial Cystitis Epidemiology study. J Urol. 2012;187: Hurst RE. Structure, function, and pathology of proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans in the urinary tract. World J Urol. 1994;12:3. 5. Han XM, Wu XH, Li B, et al. The effects of intravesical therapy with hyaluronic acid for painful bladder syndrome: preliminary Chinese experience and systematic review. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;54:240.
6 6 GÜLІNAR ET AL. 6. Engeler DS, Baranowski A, Dinis-Oliveira, et al. The 2013 EAU guidelines on chronic pelvic pain: is management of chronic pelvic pain a habit, a philosophy, or a science? 10 years of development. Eur Urol. 2013;64: arsons CL, Lilly JD, Stein. Epithelial dysfunction in nonbacterial cystitis (interstitial cystitis). J Urol. 1991;145: Morales A, Emerson L, Nickel JC, et al. Intravesical hyaluronic acid in the treatment of refractory interstitial cystitis. JUrol. 1996;156: Gupta SK, idcock L, arr NJ. The potassium sensitivity test: a predictor of treatment response in interstitial cystitis. BJU Int. 2005;96: Kallestrup EB, Jorgensen SS, Nordling J, et al. Treatment of interstitial cystitis with Cystistat: a hyaluronic acid product. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2005;39: Riedl CR, Engelhardt F, Daha KL, et al. Hyaluronan treatment of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Int Urogynecol J elvic Floor Dysfunct. 2008;19: Hanno, Baranowski A, Fall M, et al. ainful bladder syndrome (including interstitial cystitis). In: Abrams H, Wein AJ, Cardozo L, eds. Incontinence (3rd ed.) aris: Health ublications Limited; 2005: Hurst RE, Roy JB, Min KW, et al. A deficit of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans on the bladder uroepithelium in interstitial cystitis. Urology. 1996;48: Steinhoff G, Ittah B, Rowan S. The efficacy of chondroitin sulfate 0.2% in treating interstitial cystitis. Can J Urol. 2002;9: Nickel JC, Egerdie B, Downey J, et al. A real-life multicentre clinical practice study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of intravesical chondroitin sulphate for the treatment of interstitial cystitis. BJU Int. 2009;103: Nickel JC, Egerdie RB, Steinhoff G, et al. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel group pilot evaluation of the efficacy and safety of intravesical sodium chondroitin sulfate versus vehicle control in patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Urology. 2010;76: Nickel JC, Hanno, Kumar K, et al. Second multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group evaluation of effectiveness and safety of intravesical sodium chondroitin sulfate compared with inactive vehicle control in subjects with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Urology. 2012;79: orru D, Leva F, armigiani A, et al. Impact of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate on bladder pain syndrome/ interstitial cystitis. Int Urogynecol J. 2012;23: Cervigni M, Natale F, Nasta L, et al. Intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulphate for bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis: long-term treatment results. Int Urogynecol J. 2012; 23: Giberti C, Gallo F, Cortese, et al. Combined intravesical sodium hyaluronate/chondroitin sulfate therapy for interstitial cystitis/ bladder pain syndrome: a prospective study. Ther Adv Urol. 2013;5: Gulpinar O, Kayis A, Suer E, et al. Clinical comparision of intravesical hyaluronic acid and hyaluronic acid-chondroitin sulphate therapy for patients with bladder pain syndrome/ interstitital cystitis. Can Urol Assoc J. 2014;8:E Hurst RE, Zebrowski R. Identification of proteoglycans present at high density on bovine and human bladder luminal surface. J Urol. 1994;152: Barua JM, Arance I, Angulo JC, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the efficacy of intravesical therapy for bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int Urogynecol J. 2016; 27:1137. How to cite this article: Gülpınar Ö, Esen B, Kayış A, Gökçe Mİ, Süer E. Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment of bladder pain syndrome/ interstitial cystitis. Neurourology and Urodynamics. 2017;9999:1 6.
Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Interstitial and chronic cystitis. Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall?
 Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
In evaluating a patient with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), urologists
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW?
 NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW? *Massimo Lazzeri, 1 Philip Van Kerrebroeck 2 1. Department of Urology, Istituto Clinico Humanitas IRCCS, Humanitas
NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW? *Massimo Lazzeri, 1 Philip Van Kerrebroeck 2 1. Department of Urology, Istituto Clinico Humanitas IRCCS, Humanitas
The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
Original Article - Infection/Inflammation. Ömer Gülpınar, Ahmet Hakan Haliloğlu 1, Mehmet İlker Gökce, Nihat Arıkan
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.5.354 Original Article - Infection/Inflammation http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.4111/kju.2014.55.5.354&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2014-05-16
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.5.354 Original Article - Infection/Inflammation http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.4111/kju.2014.55.5.354&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2014-05-16
Introduction. For further information please contact:
 Product Monograph Introduction Teva UK Limited is one of the biggest pharmaceutical companies in the UK. We re proud to be part of the Teva Pharmaceutical Industries group, and we make medicines that help
Product Monograph Introduction Teva UK Limited is one of the biggest pharmaceutical companies in the UK. We re proud to be part of the Teva Pharmaceutical Industries group, and we make medicines that help
In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective?
 Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS. Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >60%
 DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_
 207 Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_2542 207..212 C. Lowell Parsons, MD,* Paul Zupkas, PhD,* Jeffrey Proctor, MD,
207 Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_2542 207..212 C. Lowell Parsons, MD,* Paul Zupkas, PhD,* Jeffrey Proctor, MD,
BJU International EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME
 EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME Journal: Manuscript ID: Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author: BJU-2007-1373
EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME Journal: Manuscript ID: Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author: BJU-2007-1373
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
PRACTICAL APPLICATION INSTYLAN MODERN PROTECTOR OF URINARY BLADDER MUCOSA
 PRACTICAL APPLICATION INSTYLAN MODERN PROTECTOR OF URINARY BLADDER MUCOSA E.O. Stakhovsky, PhD, MD, Professor, Head of the Scientific and Research Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Oncourology,
PRACTICAL APPLICATION INSTYLAN MODERN PROTECTOR OF URINARY BLADDER MUCOSA E.O. Stakhovsky, PhD, MD, Professor, Head of the Scientific and Research Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Oncourology,
Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy Tanya Ha, Jie Hua Xu Urology Department, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II) Administrative
Review Article Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy Tanya Ha, Jie Hua Xu Urology Department, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II) Administrative
Addendum 1: International Consultation
 Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
Review of intravesical therapies for bladder pain syndrome/ interstitial cystitis
 Review Article Review of intravesical therapies for bladder pain syndrome/ interstitial cystitis Kristina Cvach 1, Anna Rosamilia 2 1 Mercy Hospital for Women, Melbourne, Australia; 2 Monash Medical Centre,
Review Article Review of intravesical therapies for bladder pain syndrome/ interstitial cystitis Kristina Cvach 1, Anna Rosamilia 2 1 Mercy Hospital for Women, Melbourne, Australia; 2 Monash Medical Centre,
WHAT IS INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS?
 Patient Information WHAT IS INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS? Interstitial Cystitis (IC) is a condition resulting in recurring discomfort or pain in the bladder and the surrounding pelvic region. Its cause is unknown,
Patient Information WHAT IS INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS? Interstitial Cystitis (IC) is a condition resulting in recurring discomfort or pain in the bladder and the surrounding pelvic region. Its cause is unknown,
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 59 (2011)
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 59 (2011) 645 651 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Infections Prevention of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections by Intravesical Administration
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 59 (2011) 645 651 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Infections Prevention of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections by Intravesical Administration
A systematic review and meta-analysis on the efficacy of intravesical therapy for bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis
 Int Urogynecol J (2016) 27:1137 1147 DOI 10.1007/s00192-015-2890-7 REVIEW ARTICLE A systematic review and meta-analysis on the efficacy of intravesical therapy for bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis
Int Urogynecol J (2016) 27:1137 1147 DOI 10.1007/s00192-015-2890-7 REVIEW ARTICLE A systematic review and meta-analysis on the efficacy of intravesical therapy for bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Menke H. Hazewinkel & Lukas J. A. Stalpers & Marcel G. Dijkgraaf & Jan-Paul W. R. Roovers
 Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:725 730 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1357-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prophylactic vesical instillations with 0.2% chondroitin sulfate may reduce symptoms of acute radiation cystitis in patients
Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:725 730 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1357-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prophylactic vesical instillations with 0.2% chondroitin sulfate may reduce symptoms of acute radiation cystitis in patients
Treatment effectiveness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines?
 original research Treatment ness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines? Avril Lusty, MD; Elizabeth Kavaler, MD; Kay Zakariasen; Victoria
original research Treatment ness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines? Avril Lusty, MD; Elizabeth Kavaler, MD; Kay Zakariasen; Victoria
USE OF MEDICAL PRODUCTS WITH HYALURONIC ACID IN CHRONIC CYSTITIS TREATMENT
 USE OF MEDICAL PRODUCTS WITH HYALURONIC ACID IN CHRONIC CYSTITIS TREATMENT Ivanov D.D., M.D., Professor Dombrowski Ya.A. National Academy of Postgraduate Education named after P.L. Shupik, Kiev, Kyiv City
USE OF MEDICAL PRODUCTS WITH HYALURONIC ACID IN CHRONIC CYSTITIS TREATMENT Ivanov D.D., M.D., Professor Dombrowski Ya.A. National Academy of Postgraduate Education named after P.L. Shupik, Kiev, Kyiv City
Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2
 Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2 1 The Male Health Centre, Oakville, Ontario, Canada 2 Humber River Regional Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto,
Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2 1 The Male Health Centre, Oakville, Ontario, Canada 2 Humber River Regional Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto,
How does interstitial cystitis begin?
 Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective. Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado
 Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis
 Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis R. J. Evans,*, R. M. Moldwin, N. Cossons, A. Darekar, I. W. Mills and D. Scholfield From the Department
Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis R. J. Evans,*, R. M. Moldwin, N. Cossons, A. Darekar, I. W. Mills and D. Scholfield From the Department
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
CYSTISTAT. Hyaluronan Training
 CYSTISTAT Hyaluronan Training HISTORICAL ASPECTS In 1934, Karl Meyer and his assistant, John Palmer, described for the first time the process to isolate a new Glucosa- Amino-Glycan (GAG) from the cows
CYSTISTAT Hyaluronan Training HISTORICAL ASPECTS In 1934, Karl Meyer and his assistant, John Palmer, described for the first time the process to isolate a new Glucosa- Amino-Glycan (GAG) from the cows
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis
 Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence
 BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O. Talbott,* Josephine Davis and Lisa J. Regan
 Safety and Efficacy of the Use of Intravesical and Oral Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium for Interstitial Cystitis: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O.
Safety and Efficacy of the Use of Intravesical and Oral Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium for Interstitial Cystitis: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O.
Interstitial Cystitis. Dr. Gerard Testa
 Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
Interstitial Cystitis:
 Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
INTRODUCTION. Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction. Aram Kim 1, Kyeong-Ok Hoe 2, Jung Hyun Shin 2, Myung-Soo Choo 2 1
 Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
The Evidence for Antimuscarinic Agents in Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence
 european urology supplements 5 (2006) 849 853 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com The Evidence for Antimuscarinic Agents in Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence Stefano
european urology supplements 5 (2006) 849 853 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com The Evidence for Antimuscarinic Agents in Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence Stefano
Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
REVIEW OF THE 27TH ANNUAL CONGRESS OF THE EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF UROLOGY (EAU), HELD IN PARIS, FRANCE, FEBRUARY 2012
 REVIEW OF THE 27TH ANNUAL CONGRESS OF THE EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF UROLOGY (EAU), HELD IN PARIS, FRANCE, 24-28 FEBRUARY 2012 Reviewed by Jane Meijlink The EAU Annual Congress 2012 in Paris began with a
REVIEW OF THE 27TH ANNUAL CONGRESS OF THE EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF UROLOGY (EAU), HELD IN PARIS, FRANCE, 24-28 FEBRUARY 2012 Reviewed by Jane Meijlink The EAU Annual Congress 2012 in Paris began with a
Intravesical Drug Delivery for Dysfunctional Bladder
 Intravesical Drug Delivery for Dysfunctional Bladder Yao-Chi Chuang Professor and Chief, Division of Urology, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan 成長於台南 建興國中 台南一中 2 Yao-Chi Chuang In connection
Intravesical Drug Delivery for Dysfunctional Bladder Yao-Chi Chuang Professor and Chief, Division of Urology, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan 成長於台南 建興國中 台南一中 2 Yao-Chi Chuang In connection
Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines
 Review Article Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines Amita Jain To cite: Jain A. Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines. Pan Asian J Obs Gyn 2018;1(1):18-23.
Review Article Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines Amita Jain To cite: Jain A. Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines. Pan Asian J Obs Gyn 2018;1(1):18-23.
IAUN Conference Dublin, January Helen Forristal Cancer Nurse Co- Ordinator Jonathan Borwell Bladder Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist
 IAUN Conference Dublin, January 2014 Helen Forristal Cancer Nurse Co- Ordinator Jonathan Borwell Bladder Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist Theoretical component Observation Supervised practice Assessment
IAUN Conference Dublin, January 2014 Helen Forristal Cancer Nurse Co- Ordinator Jonathan Borwell Bladder Cancer Clinical Nurse Specialist Theoretical component Observation Supervised practice Assessment
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website:
 Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology
 Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
Is Urethral Pain Syndrome Really Part of Bladder Pain Syndrome?
 Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.22 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):22-27 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.22 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):22-27 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Interstitial Cystitis
 Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
Inflammation Pathways
 Inflammation Pathways Siam Oottamasathien, MD FAAP FACS Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatric Urology Research Associate Professor of Medicinal Chemistry Director of Pediatric Urology Basic Science
Inflammation Pathways Siam Oottamasathien, MD FAAP FACS Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatric Urology Research Associate Professor of Medicinal Chemistry Director of Pediatric Urology Basic Science
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease. June 2017
 Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2017 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2017 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh Repair: A Prospective Study of 105 Cases
 International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
Urinary Incontinence in Women: Never an Acceptable Consequence of Aging
 Urinary Incontinence in Women: Never an Acceptable Consequence of Aging Catherine A. Matthews, MD Associate Professor Chief, Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery University of North Carolina,
Urinary Incontinence in Women: Never an Acceptable Consequence of Aging Catherine A. Matthews, MD Associate Professor Chief, Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery University of North Carolina,
Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis
 n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Information for patients Leeds Centre for Women s Health Welcome to the Department of Urogynaecology Your consultant
n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Information for patients Leeds Centre for Women s Health Welcome to the Department of Urogynaecology Your consultant
Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
 Int Urogynecol J (2012) 23:1147 1153 DOI 10.1007/s00192-012-1686-2 REVIEW ARTICLE Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis P. K. Matsuoka & J. M. Haddad
Int Urogynecol J (2012) 23:1147 1153 DOI 10.1007/s00192-012-1686-2 REVIEW ARTICLE Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis P. K. Matsuoka & J. M. Haddad
5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France
 A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
INCONTINENCE. Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation TYPES OF INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE 11/08/2015
 INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
CAnnually, about 3 million patient visits to doctors in the
 UDC 1.2 002.2:15.032.2 ACTUAL TOPICS The modern approach to intravesical therapy of chronic cystitis O.D. Nikitin Bogomolets National Medical University Kyiv The difficulty of treating patients with chronic
UDC 1.2 002.2:15.032.2 ACTUAL TOPICS The modern approach to intravesical therapy of chronic cystitis O.D. Nikitin Bogomolets National Medical University Kyiv The difficulty of treating patients with chronic
Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium
 Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium Excerpts from: Drugdex Monograph on Pentosan Edition: online URL: www.thomsonhc.com/home/dispatch Date Added: 29/04/2010 17:42:55 Source Notes:Evidence
Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium Excerpts from: Drugdex Monograph on Pentosan Edition: online URL: www.thomsonhc.com/home/dispatch Date Added: 29/04/2010 17:42:55 Source Notes:Evidence
Managing urinary morbidity after brachytherapy. Kieran O Flynn Department of Urology, Salford Royal Foundation Trust, Manchester
 Managing urinary morbidity after brachytherapy Kieran O Flynn Department of Urology, Salford Royal Foundation Trust, Manchester Themes Can we predict urinary morbidity? Prevention of urinary morbidity
Managing urinary morbidity after brachytherapy Kieran O Flynn Department of Urology, Salford Royal Foundation Trust, Manchester Themes Can we predict urinary morbidity? Prevention of urinary morbidity
32 OBG Management July 2010 Vol. 22 No. 7 obgmanagement.com
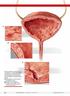 A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
Urinary tract disorders
 Urinary tract disorders Medicines Formulary Contents: 1. Urinary retention 1 2. Urinary incontinence 2 3. Urethral pain prevention during catheterisation 3 4. Indwelling catheters maintenance of patency
Urinary tract disorders Medicines Formulary Contents: 1. Urinary retention 1 2. Urinary incontinence 2 3. Urethral pain prevention during catheterisation 3 4. Indwelling catheters maintenance of patency
Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Clinical Presentation of Visceral Urological Pain
 Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Clinical Presentation of Visceral Urological Pain Prof Dr K. Everaert Functional urology Department of Urology Ghent University Hospital Gent, Belgium Chronic pelvic pain
Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Clinical Presentation of Visceral Urological Pain Prof Dr K. Everaert Functional urology Department of Urology Ghent University Hospital Gent, Belgium Chronic pelvic pain
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PERCUTANEOUS POSTERIOR TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION (PPTNS) POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Technology Assessment
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PERCUTANEOUS POSTERIOR Clinical criteria used to make utilization review decisions are based on credible scientific evidence published in peer reviewed medical literature generally
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PERCUTANEOUS POSTERIOR Clinical criteria used to make utilization review decisions are based on credible scientific evidence published in peer reviewed medical literature generally
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
A review of the 23 rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, March 2008, Milan, Italy
 A review of the 23 rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, 26-29 March 2008, Milan, Italy by Jane Meijlink The 23 rd congress of the EAU was an unprecedented success with some 14,000 participants,
A review of the 23 rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, 26-29 March 2008, Milan, Italy by Jane Meijlink The 23 rd congress of the EAU was an unprecedented success with some 14,000 participants,
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation
 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.025 01/01/2015 Lines of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2015 Section: Medicine Place(s)
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.025 01/01/2015 Lines of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2015 Section: Medicine Place(s)
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: PERCUTANEOUS POSTERIOR TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION (PPTNS)
 MEDICAL POLICY 03/19/15, 05/17/16 PAGE: 1 OF: 6 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria
MEDICAL POLICY 03/19/15, 05/17/16 PAGE: 1 OF: 6 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease. June 2018
 Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Diagnostic approach to LUTS in men. Prof Dato Dr. Zulkifli Md Zainuddin Consultant Urologist / Head Of Urology Unit UKM Medical Center
 Diagnostic approach to LUTS in men Prof Dato Dr. Zulkifli Md Zainuddin Consultant Urologist / Head Of Urology Unit UKM Medical Center Classification of LUTS Storage symptoms Voiding symptoms Post micturition
Diagnostic approach to LUTS in men Prof Dato Dr. Zulkifli Md Zainuddin Consultant Urologist / Head Of Urology Unit UKM Medical Center Classification of LUTS Storage symptoms Voiding symptoms Post micturition
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC)
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS): THE BASIC FACTS ANDREW L. SIEGEL, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Specialty: Male and Female Incontinence, Voiding Dysfunction,
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS): THE BASIC FACTS ANDREW L. SIEGEL, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Specialty: Male and Female Incontinence, Voiding Dysfunction,
Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome
 page 1 Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome Q: What is interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS)? A: Interstitial cystitis (int-uhr-stishuhl siss-tyt-uhss) (IC), is a chronic pain condition
page 1 Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome Q: What is interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS)? A: Interstitial cystitis (int-uhr-stishuhl siss-tyt-uhss) (IC), is a chronic pain condition
Voiding Dysfunction. Yao-Chi Chuang,* Jonathan H. Kaufmann, David D. Chancellor, Michael B. Chancellor and Hann-Chorng Kuo,k
 Voiding Dysfunction Bladder Instillation of Liposome Encapsulated OnabotulinumtoxinA Improves Overactive Bladder Symptoms: A Prospective, Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized Trial Yao-Chi Chuang,* Jonathan
Voiding Dysfunction Bladder Instillation of Liposome Encapsulated OnabotulinumtoxinA Improves Overactive Bladder Symptoms: A Prospective, Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized Trial Yao-Chi Chuang,* Jonathan
Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011
 Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 Treatment, Urinary Stress Incontinence, Transurethral Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0359 Revision Date: Code(s): 53860 Transurethral
Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 Treatment, Urinary Stress Incontinence, Transurethral Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0359 Revision Date: Code(s): 53860 Transurethral
2/9/2008. Men Women. Prevalence of OAB. Men: 16.0% Women: 16.9% Prevalence (%) < Age (years)
 Definition Botox for Overactive Bladder Donna Y. Deng Assistant Professor UCSF Department of Urology Urinary urgency With or without urge incontinence Usually with frequency & nocturia International Continence
Definition Botox for Overactive Bladder Donna Y. Deng Assistant Professor UCSF Department of Urology Urinary urgency With or without urge incontinence Usually with frequency & nocturia International Continence
Possible Effect of Carbamazepine A Sodium Channel Blocker on Urinary Bladder Dysfunction in Type-1 Diabetic Patients
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 1, March: 85-90, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Possible Effect of Carbamazepine A Sodium Channel Blocker on Urinary Bladder Dysfunction in Type-1 Diabetic
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 1, March: 85-90, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Possible Effect of Carbamazepine A Sodium Channel Blocker on Urinary Bladder Dysfunction in Type-1 Diabetic
Comparison of Intravesical Application of Chondroitin Sulphate and Colchicine in Rat Protamine/Lipopolysaccharide Induced Cystitis Model
 Comparison of Intravesical Application of Chondroitin Sulphate and Colchicine in Rat Protamine/Lipopolysaccharide Induced Cystitis Model Orhun Sinanoglu, 1 Isin Dogan Ekici, 2 Sinan Ekici 1 MISCELLANEOUS
Comparison of Intravesical Application of Chondroitin Sulphate and Colchicine in Rat Protamine/Lipopolysaccharide Induced Cystitis Model Orhun Sinanoglu, 1 Isin Dogan Ekici, 2 Sinan Ekici 1 MISCELLANEOUS
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment
 Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
D-MANNOSE, CRANBERRY AND VITAMIN C (CYSTOMAN 100MG) ARE EFFECTIVE IN PREVENTING URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SUBJECTS.
 D-MANNOSE, CRANBERRY AND VITAMIN C (CYSTOMAN 100MG) ARE EFFECTIVE IN PREVENTING URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SUBJECTS. Maria Laura Lopes De Carvalho, MD Guido Francavilla, MD Roberta
D-MANNOSE, CRANBERRY AND VITAMIN C (CYSTOMAN 100MG) ARE EFFECTIVE IN PREVENTING URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SUBJECTS. Maria Laura Lopes De Carvalho, MD Guido Francavilla, MD Roberta
Interstitial Cystitis
 Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive Bladder
 Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 328364, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/328364 Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive
Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 328364, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/328364 Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive
I-STOP TOMS Transobturator Male Sling
 I-STOP TOMS Transobturator Male Sling The CL Medical I-STOP TOMS sling for male stress urinary incontinence was developed in France where it is widely used and is the market leader. It is constructed with
I-STOP TOMS Transobturator Male Sling The CL Medical I-STOP TOMS sling for male stress urinary incontinence was developed in France where it is widely used and is the market leader. It is constructed with
SOCIETY FOR URODYNAMICS & FEMALE UROLOGY (SUFU)
 SOCIETY FOR URODYNAMICS & FEMALE UROLOGY (SUFU) SUFU 2010 Winter Meeting, 23-27 February 2010 Tampa-St. Petersburg, Florida, USA Reviewer: Jane Meijlink This year s SUFU Winter Meeting included many interesting
SOCIETY FOR URODYNAMICS & FEMALE UROLOGY (SUFU) SUFU 2010 Winter Meeting, 23-27 February 2010 Tampa-St. Petersburg, Florida, USA Reviewer: Jane Meijlink This year s SUFU Winter Meeting included many interesting
URINARY INCONTINENCE. Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond
 Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond Review 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Presentation 4. Other invasive approaches 5. Conclusion 6. Expert opinion Theoharis C Theoharides, Kristine Whitmore,
Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond Review 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Presentation 4. Other invasive approaches 5. Conclusion 6. Expert opinion Theoharis C Theoharides, Kristine Whitmore,
The diagnostic strength of the 24-h pad test for self-reported symptoms of urinary incontinence in pregnancy and after childbirth
 Int Urogynecol J (8) 19:525 53 DOI.7/s192-7-472-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE The diagnostic strength of the 24-h pad test for self-reported symptoms of urinary incontinence in pregnancy and after childbirth Jacobus
Int Urogynecol J (8) 19:525 53 DOI.7/s192-7-472-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE The diagnostic strength of the 24-h pad test for self-reported symptoms of urinary incontinence in pregnancy and after childbirth Jacobus
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease. February 2018
 Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease February 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease February 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC
 PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC STUDIES: IS THERE VALUE IN PREDICTING POST-OPERATIVE STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN UNDERGOING PROLAPSE SURGERY? Dr K Janse van Rensburg Dr JA van Rensburg INTRODUCTION POP
PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC STUDIES: IS THERE VALUE IN PREDICTING POST-OPERATIVE STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN UNDERGOING PROLAPSE SURGERY? Dr K Janse van Rensburg Dr JA van Rensburg INTRODUCTION POP
Mr. GIT KAH ANN. Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur.
 Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
The urethral support system during pregnancy and after childbirth Wijma, Jacobus
 University of Groningen The urethral support system during pregnancy and after childbirth Wijma, Jacobus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen The urethral support system during pregnancy and after childbirth Wijma, Jacobus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS)
 31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores
 DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0587-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores Richard L. Heaton
DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0587-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores Richard L. Heaton
C. Lowell Parsons UC San Diego Medical Center, Department of Surgery/Urology, La Jolla, CA, USA
 ; 2010 Mini Reviews BLADDER SYMPTOMS CAUSED BY LEAKY EPITHELIUM AND POTASSIUM PARSONS ET AL. BJUI The role of a leaky epithelium and potassium in the generation of bladder symptoms in interstitial cystitis/overactive
; 2010 Mini Reviews BLADDER SYMPTOMS CAUSED BY LEAKY EPITHELIUM AND POTASSIUM PARSONS ET AL. BJUI The role of a leaky epithelium and potassium in the generation of bladder symptoms in interstitial cystitis/overactive
Duloxetine in women awaiting surgery
 DOI: 1.1111/j.1471-528.6.879.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Review article H Drutz Ontario Power Generation Building, Toronto, Ontario, Canada Correspondence: Prof. Dr H Drutz, Mount Sinai Hospital,
DOI: 1.1111/j.1471-528.6.879.x www.blackwellpublishing.com/bjog Review article H Drutz Ontario Power Generation Building, Toronto, Ontario, Canada Correspondence: Prof. Dr H Drutz, Mount Sinai Hospital,
Urinary Nerve Growth Factor Could Be a Biomarker for Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis
 Urinary Nerve Growth Factor Could Be a Biomarker for Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis Hong-Chen Qu 1, Wei Zhang 2, Shi Yan 3, Yi-Li Liu 1, Ping Wang 1 * 1 Department of Urological
Urinary Nerve Growth Factor Could Be a Biomarker for Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis Hong-Chen Qu 1, Wei Zhang 2, Shi Yan 3, Yi-Li Liu 1, Ping Wang 1 * 1 Department of Urological
ABNORMAL EXPRESSION OF MOLECULAR MARKERS FOR BLADDER IMPERMEABILITY AND DIFFERENTIATION IN THE UROTHELIUM OF PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS
 0022-5347/04/1714-1554/0 Vol. 171, 1554 1558, April 2004 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION DOI: 10.1097/01.ju.0000118938.09119.a5 ABNORMAL EXPRESSION
0022-5347/04/1714-1554/0 Vol. 171, 1554 1558, April 2004 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION DOI: 10.1097/01.ju.0000118938.09119.a5 ABNORMAL EXPRESSION
Management of OAB. Lynsey McHugh. Consultant Urological Surgeon. Lancashire Teaching Hospitals
 Management of OAB Lynsey McHugh Consultant Urological Surgeon Lancashire Teaching Hospitals Summary Physiology Epidemiology Definitions NICE guidelines Evaluation Conservative management Medical management
Management of OAB Lynsey McHugh Consultant Urological Surgeon Lancashire Teaching Hospitals Summary Physiology Epidemiology Definitions NICE guidelines Evaluation Conservative management Medical management
Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.10.682 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.10.682 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
Updates in the nonpharmacological. treatment on overactive bladder
 Updates in the nonpharmacological treatment on overactive bladder Overactive Bladder Also known as urgency-frequency syndrome Symptoms Urgency Daytime frequency Nocturia Urge urinary incontinence Sudden
Updates in the nonpharmacological treatment on overactive bladder Overactive Bladder Also known as urgency-frequency syndrome Symptoms Urgency Daytime frequency Nocturia Urge urinary incontinence Sudden
BJUI. Validity and reliability of the patient s perception of intensity of urgency scale in overactive bladder
 ; 2010 Lower Urinary Tract PATIENT S PERCEPTION OF INTENSITY OF URGENCY SCALE IN OAB CARTWRIGHT ET AL. BJUI Validity and reliability of the patient s perception of intensity of urgency scale in overactive
; 2010 Lower Urinary Tract PATIENT S PERCEPTION OF INTENSITY OF URGENCY SCALE IN OAB CARTWRIGHT ET AL. BJUI Validity and reliability of the patient s perception of intensity of urgency scale in overactive
