Use of anatomic measurement to guide injection of botulinum toxin for the management of chronic lateral epicondylitis: a randomized controlled trial
|
|
|
- Rosaline Singleton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CMAJ Use of anatomic measurement to guide injection of botulinum toxin for the management of chronic lateral epicondylitis: a randomized controlled trial Ramin Espandar MD, Pedram Heidari MD, Mohammad Reza Rasouli MD, Soheil Saadat MD PhD, Mahmood Farzan MD, Mohsen Rostami, Shideh Yazdanian MD, S.M. Javad Mortazavi MD Previously published at See related commentary by Buchbinder and Richards, page 749 DOI: /cmaj Abstract Background: When using botulinum toxin for the management of lateral epicondylitis, injection at a fixed distance from an anatomic landmark could result in inadequate paralysis of the intended muscle. We assessed the effectiveness of injection of botulinum toxin using precise anatomic measurement in individual patients. Methods: In this randomized placebo-controlled trial, 48 patients with chronic refractory lateral epicondylitis were randomly assigned to receive a single injection of either botulinum toxin (60 units) or placebo (normal saline). The site of injection was chosen as a distance one-third the length of the forearm from the tip of the lateral epicondyle on the course of the posterior interosseus nerve. The primary outcome measure was intensity of pain at rest, measured with the use of a 100-mm visual analogue scale, at baseline and at 4, 8 and 16 weeks after injection. Results: Compared with the placebo group, the group given botulinum toxin had significant reductions in pain at rest during follow-up (decrease at 4 weeks 14.1 mm, 95% confidence interval [CI] ; at 8 weeks 11.5 mm, 95% CI ; at 16 weeks 12.6 mm, 95% CI ; p = 0.01). As for the secondary outcomes, the intensity of pain during maximum pinch de creased in the botulinum toxin group; there was no difference in pain during maximum grip or in grip strength between the two groups. All but one of the patients in the intervention group experienced weakness in the extension of the third and fourth fingers at week 4 that resolved by week 16. No serious adverse events were reported. Interpretation: The use of precise anatomic measurement to guide injection of botulinum toxin significantly reduced pain at rest in patients with chronic refractory lateral epicondylitis. However, the transient extensor lag makes this method inappropriate for patients whose job requires finger extension. (ClinicalTrials.gov trial register no. NCT ) Botulinum toxin type A, a potent neuromuscular blocking agent, has been used for a variety of neuromuscular disorders, including cervical dystonia and blepharospasm. 1 Recently, this drug has been used in the management of chronic lateral epicondylitis (tennis el bow). 2 5 The extensor muscles of the wrist are paralyzed with the aim of releasing tension on the common extensor tendon and causing gradual healing of the epicondylitis. This approach is based on the same rationale as surgical release of the extensor carpi radialis brevis tendon. 3 The most important factor in successfully paralyzing any muscle is the site of injection of the botulinum toxin. 1 Injection at a fixed distance from anatomic landmarks, as was performed in previous clinical trials of botulinum toxin for the management of lateral epicondylitis, 2 5 would result in inadequate paralysis of the intended muscle. It has been suggested that the extensor digitorum muscle, which is innervated by deep branches of the radial nerve, plays an important role in the development of lateral epicondylitis. 6 We therefore chose to determine the injection site based on each patient s forearm length and the course of the posterior interosseus nerve to achieve adequate paralysis of the extensor digitorum muscle. We conducted a randomized controlled trial to test whether this approach would be effective in reducing pain and improving grip strength. Methods Study design The study was performed at the Imam Khomeini Hospital Complex, a 1230-bed tertiary care referral hospital affiliated with the Tehran University of Medical Sciences that serves patients from all over Iran. The study protocol was approved by the hospital s ethical committee. The participants of the study were chosen according to our inclusion and exclusion criteria (Box 1) from patients referred to our clinic from August 2007 to March All participants had to have a history of failed previous therapeutic From the Departments of Orthopedic Surgery (Espandar, Heidari, Rasouli, Farzan, Rostami, Mortazavi) and Internal Medicine (Yazdanian), Imam Khomeini Hospital Complex, Tehran University of Medical Sciences; the Sports Medicine Research Center (Mortazavi), Tehran University of Medical Sciences; and the Sina Trauma and Surgery Research Center (Saadat), Sina Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran CMAJ DOI: /cmaj CMAJ MAY 18, (8) 2010 Canadian Medical Association or its licensors
2 interventions. The process and aim of the study as well as possible adverse effects of the drug injection were described to the patients. All of the enrolled patients signed a written informed consent. Patients were randomly assigned to receive an injection of either botulinum toxin or normal saline. A computer- generated sequence with a block size of four patients was used for randomization. The patients were assigned consecutive numbers based on the order of enrolment in the study. A session for a pre-injection evaluation and injection was scheduled with the patients, and their assigned numbers were sent to a research assistant whose only role in this study was to prepare the solutions for the injection date. The research assistant was the only one with access to the randomization list. He prepared the injections according to the numbers received, and he delivered them in numbered envelopes to the clinic one hour before injection. Although both solutions were colorless, syringes were covered using opaque tape to prevent the physician and patients from guessing the contents. Injections were made by a physician who was not aware of the allocation status. Participants receiving botulinum toxin were given a single injection of 60 units of botulinum toxin A reconstituted in 1 ml of normal saline; those in the placebo group received an injection of 1 ml of 0.9% saline. Injections were performed using insulin syringes. The injection site was individualized according to the length of each patient s forearm (i.e., the distance between the lateral epicondyle and the tip of styloid process of radius). A distance of one-third the length of the forearm from the tip of the lateral epicondyle on the course of the posterior inter - osseus nerve (i.e., from the tip of the lateral epicondyle to the posterior midpoint of the wrist) was marked as the injection point. Based on previous cadaveric studies, the motor nerve branch enters the extensor digitorum and extensor carpi ulnaris muscles at a distance of 33% on average of the forearm length from the lateral epicondyle tip (range 17% 51% and 24% 43% of forearm length, respectively). 7,8 Therefore, if one assumes an average forearm length of 27 cm, 9 the site of injection should be 9 cm from the tip of the lateral epicondyle. Considering the range of anatomic variation for motor points 7 and a diffusion radius of 3.5 cm for botulinum toxin, 1 injection at this point should effectively paralyze the extensor digitorum muscle in 87.3% of patients and the extensor carpi ulnaris muscle in 94.1%. Patients were allowed to take acetaminophen tablets (500 mg every four hours) for 48 hours after injection if they had any pain or discomfort associated with the injection. They were asked to avoid activities that required repetitive supination or forceful grasp. Outcome measures General characteristics of each participant, including age, sex, dominant hand, affected hand, duration of symptoms and forearm length, were recorded before the baseline evaluation. The primary outcome measure was pain at rest at four weeks after injection. Patients were asked to evaluate the intensity of pain using a 100-mm visual analogue scale, on which 0 represented no pain and 100 signified the most intense pain ever experienced. Box 1: Inclusion and exclusion criteria Inclusion criteria Feeling pain on lateral epicondyle or on the course of extensor muscles in the forearm in at least two of the following situations: - lateral epicondyle is pressed by physician - passive flexion of wrist by physician - active extension of wrist against counterforce applied by physician - extension of third finger against counterforce applied by physician Age years Duration of symptoms > 6 months Previous complete course of physiotherapy or corticosteroid injection, or both Exclusion criteria Previous serious reaction to botulinum toxin injected for any purpose Coexisting arthritis or arthralgia Coexisting medial epicondylitis (golf elbow) Bilateral lateral epicondylitis Neurologic deficits* Depression Previous history of hand surgery Use of any medicine or product containing corticosteroid in past 30 days Current use of analgesic medications other than acetaminophen (especially nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) Current enrolment in physiotherapy course Pregnancy Breastfeeding Having a hobby or job that requires extension of fingers or wrist Systemic disease (e.g., diabetes mellitus, collagen vascular disease) *Includes entrapment of radial nerve, signs of compression of nerve root, decreased muscle force other than grip strength, multiple sclerosis and history of seizure. Secondary outcome measures were pain reported by the patients during maximum grip and maximum pinch (pinching their index finger and thumb together with their elbow resting on a table), and the patient s grip strength. Grip strength was recorded in kilograms using a calibrated hydraulic Jamar Hand Dyna mometer (Sammons Preston, Bolingbrook, USA), according to the manufacturer s instructions. The middle position of the dynamometer s handle was used for all measurements. The physician recorded the average of three consecutive readings for data analysis. During each evaluation session, a research assistant evaluated the patient for the presence of extensor lag of the third and fourth fingers and asked if he or she had experienced any adverse reactions since the past follow-up. Open-ended questions with spontaneous reporting were used to detect adverse effects; all reports were evaluated for a possible association with the injection of botulinum toxin. The research assistant was not aware of the design of CMAJ MAY 18, (8) 769
3 the study and was not involved in recording of other major and minor outcome measures of the study in order to preserve blinding. The patients were evaluated at baseline and at 4 weeks, 8 weeks and 16 weeks after injection. We calculated the sample size using Stata software (version 8; StataCorp LP, College Station, USA). Wong and colleagues showed a decrease in intensity of pain at rest of 16 mm on a 100-mm visual analogue scale in the placebo group at week four compared with baseline. 5 Because a generally accepted scale for the measurement of clinical outcomes in patients with lateral epicondylitis has not yet been reported, we considered results for patients with other rheumatologic diseases. 10 From these data, we defined a clinically important therapeutic response in our study to be an improvement in pain intensity scores on a visual analogue scale of at least 20% in the treatment group over the improvement in the placebo group. By considering the standard deviation of four, we included 24 patients in each group to achieve a statistical power of 0.80 with a type I error of 0.01 for comparison of pain at rest between two groups four weeks after injections. Statistical analysis We report 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for differences between the botulinum toxin and placebo groups at baseline and p values for differences in primary and secondary outcome measures between the two groups over the study period. Assessed for eligibility n = 87 Eligible n = 48 R Excluded n = 39 Did not meet inclusion criteria n = 14 Did not agree to participate n =10 Met 1 exclusion criteria n = 15 We used the Student t test and repeated-measurement analyses accordingly. The level of significance was set at a p value of 0.01 or less. Funding This study was funded by a contribution of the Vice Chancellor of Research at the Tehran University of Medical Sciences. Neither the vice chancellor nor the university had a role in the design, conduct of the study, data analysis or reporting of the results. Results During the study period, all 87 patients with lateral epicondylitis who had been referred to our clinic were assessed for eligibility. We excluded 39 patients because they did not meet the inclusion criteria (n = 14), they did not wish to participate in the study (n = 10) or they met at least one of the exclusion criteria (n = 15). The remaining 48 patients were randomly assigned equally to the botulinum toxin group and the placebo group according to the randomization list. None of the patients were lost during follow-up, and the data for all 48 patients were included in the final analysis (Figure 1). The characteristics of the pa - tients are provided in Table 1. Pain At baseline, the intensity of pain at rest was similar in the botulinum toxin and placebo groups (between-group difference in mean visual analogue score 2.3 mm, 95% CI 9.5 to 14.2). The intensity decreased significantly during follow-up in the botulinum toxin group compared with the placebo group (p = 0.01) (Table 2). The intensity of pain during maximum grip was also similar in the two groups at baseline (between-group difference in mean visual analogue score 0.8 mm, 95% CI 10.9 to 12.6). It decreased more in the botulinum toxin group than in the placebo group during follow-up; however, the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.22) (Table 2). Injection of normal saline Follow-up at: 4 weeks, 8 weeks, 16 weeks, Included in final analysis Injection of botulinum toxin Follow-up at: 4 weeks, 8 weeks, 16 weeks, Included in final analysis Figure 1: Flow of participants through the study. R = randomization. Table 1: Characteristics of 48 patients with chronic lateral epicondylitis randomly assigned to receive injection of either botulinum toxin or placebo (saline) Characteristic Botulinum toxin group Placebo group Age, yr, mean (SD) 43.3 (7.8) 44.2 (7.7) Female sex, no. (%) 22 (92) 22 (92) Right-hand dominant, no. (%) 20 (83) 18 (75) Epicondylitis on right side, 8 (33) 10 (42) no. (%) Length of forearm, cm, 21.2 (1.8) 21.5 (1.7) mean (SD) Duration of symptoms, mo, mean (SD) 12.5 (9.5) 14.0 (8.4) Note: SD = standard deviation. 770 CMAJ MAY 18, (8)
4 The intensity of pain during maximum pinch was similar in the two groups at baseline (between-group difference 2.4 mm, 95% CI 11.0 to 15.9). As with pain at rest, it decreased significantly during follow-up in the botulinum toxin group compared with the placebo group (p = 0.004) (Table 2). Grip strength The mean maximum grip strength was similar in the two groups at baseline (between-group difference 1.4 mm, 95% CI 1.5 to 4.4). Although this value decreased in the botulinum toxin group during follow-up, the between-group differences were not significant (p = 0.02) (Table 2). Extensor lag Of the patients in the botulinum toxin group, all but one experienced weakness in the extension of the third and fourth fingers at week 4 that interfered with functioning at work. However, the paralysis resolved at week 8 in one patient and at week 16 in the rest of the patients. None of the patients in the placebo group experienced extensor lag. Adverse reactions The reported adverse reactions and their frequency in each group are summarized in Table 3. Interpretation We found that the intensity of pain at rest decreased significantly among patients with lateral epicondylitis after botulinum toxin was injected at a site based on precise anatomic measurement of each patient s forearm length. The same was true for intensity of pain during maximum pinch. However, this treatment method caused a decline in grip strength and resulted in extensor lag. If a 20% reduction in pain intensity is considered a clinically significant response in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, 10 injection of botulinum toxin in our study provoked such a response. Plazeck and colleagues 4 and Wong and colleagues 5 reported a reduction in pain intensity similar to that in our study; however, they did not measure the intensity of pain during maximum grip or maximum pinch. Reports of pain in the extensor muscles of the forearm while the flexor muscles are used are common among patients with lateral epicondylitis; 11 some patients experience intense pain during gripping while feeling minimal or no pain at rest. Therefore, we felt that measuring pain intensity during gripping would be a more precise measure of treatment. However, we did not observe a significant reduction in pain intensity during gripping in the botulinum toxin group. This might be be - cause the participants in our study had chronic refractory Table 2: Mean pain intensity scores on 100-mm visual analogue scale and handgrip strength in botulinum toxin and placebo groups at baseline and at 4, 8 and 16 weeks after injection Outcome measure Botulinum toxin Group; mean (SD) Placebo Difference in mean (95% CI) p value (repeated measurement) Pain score at rest, mm Baseline 48.8 (23.7) 46.4 (16.2) 2.3 ( 9.5 to 14.2) Week (15.9) 34.5 (12.2) 14.1 (5.8 to 22.3) Week (18.0) 29.4 (14.5) 11.5 (2.0 to 21.4) Week (6.0) 16.7 (10.5) 12.6 (7.7 to 17.8) Pain score during maximum grip, mm Baseline 65.8 (22.0) 65.0 (18.3) 0.8 ( 10.9 to 12.6) Week (23.3) 57.4 (18.2) 5.3 ( 6.8 to 17.5) Week (23.1) 51.5 (20.1) 7.8 ( 4.8 to 20.4) Week (10.0) 30.6 (15.6) 11.8 (4.2 to 19.4) Pain score during maximum pinch, mm Baseline 42.6 (26.5) 45.1 (19.0) 2.4 ( 11.0 to 15.9) Week (16.8) 32.7 (12.6) 15.4 (6.8 to 24.1) Week (14.9) 26.6 (11.3) 14.4 (6.8 to 22.2) Week (9.7) 13.6 (8.3) 8.5 (3.1 to 13.9) Maximum grip strength, kg Baseline 17.4 (5.2) 18.8 (5.0) 1.4 ( 1.5 to 4.4) Week (4.5) 19.0 (4.6) 4.5 (1.8 to 7.1) Week (4.4) 18.4 (4.8) 5.3 (2.6 to 8.0) Week (5.4) 18.8 (4.8) 1.7 ( 1.2 to 4.7) 0.010* * 0.02 Note: CI = confidence interval, SD = standard deviation. *Statistically significant difference. CMAJ MAY 18, (8) 771
5 epicondylitis, or because pain intensity following gripping could be more resistant to therapy and would generally take longer to respond to management. 4 We did find a significant reduction in pain during maximum pinch in the botulinum toxin group. The decrease in grip strength observed in the botulinum toxin group was greater than in the placebo group; however, the difference was not statistically significant and grip strength returned to its baseline level at week 16. Our findings were similar to those of Wong and colleagues, 5 who reported no significant difference in grip strength between the botulinum toxin and placebo groups during the course of their study. Hayton and colleagues proposed that grip strength can be used as a precise objective measure indicative of pain intensity perceived by the patients. 2 However, the reduction of grip strength in our study could not be explained only by the degree of pain experienced by the patient. We observed a high rate of extensor paralysis, which can result in decreased stabilization of the wrist during gripping 12 and transient re - duced grip strength in turn. 13 Electrodiagnostically guided injection of botulinum toxin for the management of lateral epicondylitis has been reported to show high rates of success in producing paralysis and favourable clinical outcomes. 14 However, this technique has limitations, including the need for local expertise and equipment, discomfort and pain during its application, and the multi plicity of motor points of a single muscle (only one of the nerve branches to the muscle may be detected with electrodiagnostic studies; if it is not the main Table 3: Reported adverse reactions immediately after injection and during time frames between follow-up assessments Adverse reaction; time frame Group; no. of patients Botulinum toxin Placebo Pain at injection site After injection 3 2 Weeks Weeks Weeks Tingling sensation around injection site After injection 0 0 Weeks Weeks Weeks Subjective feeling of muscle spasm around injection site After injection 0 0 Weeks Weeks Weeks Total 23 4 branch to the muscle, the paralysis induced by botulinum toxin injection is not adequate). To overcome these limitations, we devised an anatomically based approach to determine the site of injection in individual patients that can easily be used in routine practice. The success rate of inducing paralysis in our study was 96%, as compared with less than 60% in previous studies, even in those that used considerably higher doses of botulinum toxin. 2,3 Strengths and limitations To preserve blinding of the physician who gave the injections and assessed pain and grip strength, extensor lag was assessed by a research assistant who was not aware of the study de - sign. Also, the patients were asked to hold the dynamometer before the physician entered the room so he would not realize the existence of extensor lag. As for the limitations of our study, we could not ensure that participants were blinded to the drug they received because of the high rate of extensor lag in the botulinum toxin group. Another limitation was that more than 90% of the participants were women. Most of the male participants did not meet the inclusion criteria, had at least one of the exclusion criteria or did not consent to participate in the study because they thought that development of extensor lag would affect their ability to work. Small sample size was another limitation. We calculated the sample size according to the primary outcome. The differences in secondary outcome measures between the two groups may have been significant with larger samples. Finally, our follow-up period was only 4 months. We are unable to draw conclusions about whether the effect of botulinum toxin injection would persist beyond that time. Conclusion Our trial showed that the use of anatomic measurement to guide injection of botulinum toxin can be effective in the management of chronic lateral epicondylitis. This approach is easily implemented and does not require complex methods. However, because of the high rate of transient extensor lag, it should be reserved for patients whose job does not require finger extension. Further research is needed to determine whether the pain-relieving effects of the treatment remain or diminish after four months. This article has been peer reviewed. Competing interests: None declared. Contributors: Ramin Espandar and Javad Mortazavi contributed to the study concept and, with Mahmood Farzan, the study design. Pedram Heidari, Mohsen Rostami and Shideh Yazdanian were responsible for the acquisition of data. Mohammad Reza Rasouli and Soheil Saadat contributed to the analysis and interpretation of the data. Pedram Heidari, Mohammad Reza Rasouli, Mohsen Rostami and Shideh Yazdanian drafted the manuscript. Ramin Espandar, Soheil Saadat, Mahmood Farzan and Javad Mortazavi critically revised the manucript. All of the authors approved the final version of the manuscript submitted for publication. Funding: This study was funded by a contribution of the Vice Chancellor of Research at the Tehran University of Medical Sciences. Neither the vice chancellor nor the university had a role in the design, conduct of the study, data analysis or reporting of the results. 772 CMAJ MAY 18, (8)
6 REFERENCES 1. Seyler TM, Smith BP, Marker DR, et al. Botulinum neurotoxin as a therapeutic modality in orthopaedic surgery: more than twenty years of experience. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2008;90(Suppl 4): Hayton MJ, Santini AJA, Hughes PJ, et al. Botulinum toxin injection in the treatment of tennis elbow: a double-blind, randomized, controlled, pilot study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2005;87: Keizer SB, Rutten HP, Pilot P, et al. Botulinum toxin injection versus surgical treatment for tennis elbow: a randomized pilot study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2002; Placzek R, Drescher W, Deuretzbacher G, et al. Treatment of chronic radial epicondylitis with botulinum toxin A: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized multicenter study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2007;89: Wong SM, Hui AC, Tong PY, et al. Treatment of lateral epicondylitis with botulinum toxin: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 2005;143: Fairbank SM, Corlett RJ. The role of the extensor digitorum communis muscle in lateral epicondylitis. J Hand Surg [Br] 2002;27: Liu J, Pho RWH, Pereira BP, et al. Distribution of primary motor nerve branches and terminal nerve entry points to the forearm muscles. Anat Rec 1997;248: Linell EA. The distribution of nerves in the upper limb, with reference to variabilities and their clinical significance. J Anat 1921;55: Karwowski W, Marras WS. The occupational ergonomics handbook. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press; Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, et al.; American College of Rheumatology. Preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1995; 38: Ranney D, Wells R, Moore A. Upper limb musculoskeletal disorders in highly repetitive industries: precise anatomical physical findings. Ergonomics 1995; 38: Snijders CJ, Volkers AC, Mechelse K, et al. Provocation of epicondylalgia lateralis (tennis elbow) by power grip or pinching. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1987;19: Mogk JP, Keir PJ. The effects of posture on forearm muscle loading during gripping. Ergonomics 2003;46: Morre HH, Keizer SB, van Os JJ. Treatment of chronic tennis elbow with botulinum toxin [letter]. Lancet 1997;349:1746. Correspondence to: Dr. S.M. Javad Mortazavi, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Imam Khomeini Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Keshavarz Blvd., Tehran , Iran; smjmort@yahoo.com The marriage is over. Custody might not be the only thing on his mind. For some men, separation can trigger domestic violence or even femicide. Studies have shown that actual or impending separation is a key risk factor for domestic violence, femicide and femicide-suicide. What s more, unemployment, depression and prior domestic violence increase the risk. And that s not all. Stalking and harassment are also strongly associated with lethal violence. In most cases of intimate femicide, there is a history of partner violence. As family physicians, you can help. There are ways to recognize when your patient may be abusive. There are things you can do and say. And theree are ways to respond when both he and his partner are your patients. You can learn more about domestic violence and, at the same time, earn valuable CME credits from the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada and the College of Family Physicians of Canada. Visit us on-line at CMAJ MAY 18, (8) 773
Management of upper limb in cerebral palsy. Dr Sameer Desai Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon KEM, Ruby Hall, Sahyadri Hospital, Unique Childrens Hospital
 Management of upper limb in cerebral palsy Dr Sameer Desai Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon KEM, Ruby Hall, Sahyadri Hospital, Unique Childrens Hospital Importance of upper limb in CP Activities of daily living
Management of upper limb in cerebral palsy Dr Sameer Desai Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon KEM, Ruby Hall, Sahyadri Hospital, Unique Childrens Hospital Importance of upper limb in CP Activities of daily living
Elbow Muscle Power Deficits
 1 Elbow Muscle Power Deficits ICD-9-CM code: 726.32 Lateral epicondylitis ICF codes: Activities and Participation code: d4300 Lifting, d4452 Reaching, d4401 Grasping Body Structure code: s73012 Muscles
1 Elbow Muscle Power Deficits ICD-9-CM code: 726.32 Lateral epicondylitis ICF codes: Activities and Participation code: d4300 Lifting, d4452 Reaching, d4401 Grasping Body Structure code: s73012 Muscles
Interesting Case Series. Radial Tunnel Syndrome Complicated by Lateral Epicondylitis in a Middle-Aged Female
 Interesting Case Series Radial Tunnel Syndrome Complicated by Lateral Epicondylitis in a Middle-Aged Female Sumesh Kaswan, MD, a Olivier Deigni, MD, MPH, a Kashyap K. Tadisina, BS, b Michael Totten, BS,
Interesting Case Series Radial Tunnel Syndrome Complicated by Lateral Epicondylitis in a Middle-Aged Female Sumesh Kaswan, MD, a Olivier Deigni, MD, MPH, a Kashyap K. Tadisina, BS, b Michael Totten, BS,
Evaluating concomitant lateral epicondylitis and cervical radiculopathy
 Evaluating concomitant lateral epicondylitis and cervical radiculopathy March 06, 2010 This article describes a study of the prevalence of lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow among patients with neck
Evaluating concomitant lateral epicondylitis and cervical radiculopathy March 06, 2010 This article describes a study of the prevalence of lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow among patients with neck
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
A randomised controlled trial to study the efficacy of mobilization with movement combined with low level laser therapy in lateral epicondylitis
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2013, 4(5):381-386 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC A randomised controlled trial to study the efficacy of mobilization
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2013, 4(5):381-386 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC A randomised controlled trial to study the efficacy of mobilization
Interesting Case Series. Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression
 Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS. Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran
 TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
Proximal wrist extensor tendinopathy
 Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med (2008) 1:48 52 DOI 10.1007/s12178-007-9005-0 Proximal wrist extensor tendinopathy Joseph Ihm Published online: 2 November 2007 Ó Humana Press 2007 Abstract Proximal wrist extensor
Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med (2008) 1:48 52 DOI 10.1007/s12178-007-9005-0 Proximal wrist extensor tendinopathy Joseph Ihm Published online: 2 November 2007 Ó Humana Press 2007 Abstract Proximal wrist extensor
Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity RADIUS AND ULNA right
 11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
Referral Criteria: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Feb
 Referral Criteria: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Feb 2019 1 5.2. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Background Carpal tunnel syndrome present with non-traumatic tingling of the fingers due to compression of the median nerve
Referral Criteria: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Feb 2019 1 5.2. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Background Carpal tunnel syndrome present with non-traumatic tingling of the fingers due to compression of the median nerve
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Mashad University of Medical Sciences, Mashad, Iran
 Arch Iranian Med 2003; 6 (3): 196 199 ORIGINAL ARTICLE INJECTION OF METHYLPREDNISOLONE AND LIDOCAINE IN THE TREATMENT OF MEDIAL EPICONDYLITIS: A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL Mahmood Bahari MD, Mohammad Gharehdaghi
Arch Iranian Med 2003; 6 (3): 196 199 ORIGINAL ARTICLE INJECTION OF METHYLPREDNISOLONE AND LIDOCAINE IN THE TREATMENT OF MEDIAL EPICONDYLITIS: A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL Mahmood Bahari MD, Mohammad Gharehdaghi
An Investigation of Hand Force Distribution, Hand Posture and Surface Orientation
 An Investigation of Hand Force Distribution, Hand Posture and Surface Orientation R. FIGUEROA and T. ARMSTRONG Department of Industrial and Operations Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
An Investigation of Hand Force Distribution, Hand Posture and Surface Orientation R. FIGUEROA and T. ARMSTRONG Department of Industrial and Operations Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
Limb Pain (Tendonitis, Osteoarthritis, Plantar Fasciitis, Piriformis Syndrome)
 Limb Pain (Tendonitis, Osteoarthritis, Plantar Fasciitis, Piriformis Syndrome) Martin Taylor, DO, PhD Neurology / OrthoNeuro Clinical Associate Professor, Neurology Ohio University College of Osteopathic
Limb Pain (Tendonitis, Osteoarthritis, Plantar Fasciitis, Piriformis Syndrome) Martin Taylor, DO, PhD Neurology / OrthoNeuro Clinical Associate Professor, Neurology Ohio University College of Osteopathic
The Reasons We Experience Pain
 Pain signals can originate in the skin, bone, muscles or nerves. We have all experienced aches and pains from daily activities, work activities, sports activities or accidents and trauma. Our bodies have
Pain signals can originate in the skin, bone, muscles or nerves. We have all experienced aches and pains from daily activities, work activities, sports activities or accidents and trauma. Our bodies have
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
ANATOMICAL STUDY OF THE RADIAL TUNNEL BY CADAVERIC DISSECTION, FOR POSSIBLE SITES OF THE POSTERIOR INTEROSSEOUS NERVE ENTRAPMENT
 Int. J. Pharm. Med. & Bio. Sc. 2014 Bhavana Sunil Junagade and Aruna Mukherjee, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2278 5221 www.ijpmbs.com Vol. 3, No. 2, April 2014 2014 IJPMBS. All Rights Reserved ANATOMICAL STUDY
Int. J. Pharm. Med. & Bio. Sc. 2014 Bhavana Sunil Junagade and Aruna Mukherjee, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2278 5221 www.ijpmbs.com Vol. 3, No. 2, April 2014 2014 IJPMBS. All Rights Reserved ANATOMICAL STUDY
1/13/2013. Anatomy Guy Dissection Sheet Extensor Forearm and Hand. Eastern Virginia Medical School
 Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Restoration of Reaching and Grasping Functions in Hemiplegic Patients with Severe Arm Paralysis
 Restoration of Reaching and Grasping Functions in Hemiplegic Patients with Severe Arm Paralysis Milos R. Popovic* 1,2, Vlasta Hajek 2, Jenifer Takaki 2, AbdulKadir Bulsen 2 and Vera Zivanovic 1,2 1 Institute
Restoration of Reaching and Grasping Functions in Hemiplegic Patients with Severe Arm Paralysis Milos R. Popovic* 1,2, Vlasta Hajek 2, Jenifer Takaki 2, AbdulKadir Bulsen 2 and Vera Zivanovic 1,2 1 Institute
Biceps Brachii. Muscles of the Arm and Hand 4/4/2017 MR. S. KELLY
 Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Treatment of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions
 APPENDIX G Treatment of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions The purpose of this document is to provide information for physiotherapists of common medical and surgical interventions
APPENDIX G Treatment of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions The purpose of this document is to provide information for physiotherapists of common medical and surgical interventions
Anatomic Landmarks for the Radial Tunnel
 Anatomic Landmarks for the Radial Tunnel Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Arian Mowlavi, MD, Michael Neumeister, MD, W.P. Andrew Lee, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive
Anatomic Landmarks for the Radial Tunnel Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Arian Mowlavi, MD, Michael Neumeister, MD, W.P. Andrew Lee, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow)
 EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow) Description Expected Outcome Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is the most common painful condition of the elbow. Inflammation and pain occur on the outer side
EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow) Description Expected Outcome Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is the most common painful condition of the elbow. Inflammation and pain occur on the outer side
Incidence, Prevalence and Consequences of work-related musculoskeletal disorders: Current Canadian Evidence
 Incidence, Prevalence and Consequences of work-related musculoskeletal disorders: Current Canadian Evidence Cam Mustard, ScD President, Institute for Work & Health JASP Conference Montreal, October 2006
Incidence, Prevalence and Consequences of work-related musculoskeletal disorders: Current Canadian Evidence Cam Mustard, ScD President, Institute for Work & Health JASP Conference Montreal, October 2006
MCQWeek2. All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin.
 MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
Therapeutic Exercise Program for Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow / Golfer s Elbow)
 Prepared for: Prepared by: Therapeutic (Tennis Elbow / Golfer s Elbow) To ensure that this exercise program is safe and effective for you, it should be performed under your doctor's supervision. Talk to
Prepared for: Prepared by: Therapeutic (Tennis Elbow / Golfer s Elbow) To ensure that this exercise program is safe and effective for you, it should be performed under your doctor's supervision. Talk to
A new computer mouse called Horse
 A new computer mouse called Horse Anatomy and technology; The computer mouse as extension of the human body C.J. Snijders and P.C. Helder Department of Biomedical Physics and Technology, Erasmus MC, University
A new computer mouse called Horse Anatomy and technology; The computer mouse as extension of the human body C.J. Snijders and P.C. Helder Department of Biomedical Physics and Technology, Erasmus MC, University
Physical examination protocol in the study of VPT and nerve conduction in working women with and without chronic pain
 Physical examination protocol in the study of VPT and nerve conduction in working women with and without chronic pain ID number General health OK Affected Height cm Weight kg Heart OK Arrhythmia Murmurs
Physical examination protocol in the study of VPT and nerve conduction in working women with and without chronic pain ID number General health OK Affected Height cm Weight kg Heart OK Arrhythmia Murmurs
Upper limb injuries II. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Upper limb injuries II Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Capsulitis = inflammatory lesion of the glenohumeral joint capsule leading to: thickening and loss of joint volume painful stiffness of the
Upper limb injuries II Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Capsulitis = inflammatory lesion of the glenohumeral joint capsule leading to: thickening and loss of joint volume painful stiffness of the
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity
 Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request
 Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Surgery Criteria Based Access Policy Date Adopted: 6 th February 2017 Version: 1617.1.02 Individual Funding Request Team Bristol,
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Surgery Criteria Based Access Policy Date Adopted: 6 th February 2017 Version: 1617.1.02 Individual Funding Request Team Bristol,
WEEKEND 2 Elbow. Elbow Range of Motion Assessment
 Virginia Orthopedic Manual Physical Therapy Institute - 2016 Technique Manual WEEKEND 2 Elbow Elbow Range of Motion Assessment - Patient Positioning: Sitting or supine towards the edge of the bed - Indications:
Virginia Orthopedic Manual Physical Therapy Institute - 2016 Technique Manual WEEKEND 2 Elbow Elbow Range of Motion Assessment - Patient Positioning: Sitting or supine towards the edge of the bed - Indications:
WRIST SPRAIN. Description
 WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View
 Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
We performed a prospective, randomised trial on
 LOCAL CORTICOSTEROID INJECTION VERSUS CYRIAX-TYPE PHYSIOTHERAPY FOR TENNIS ELBOW J. A. N. VERHAAR, G. H. I. M. WALENKAMP, H. VAN MAMEREN, A. D. M. KESTER, A. J. VAN DER LINDEN From the University Hospital,
LOCAL CORTICOSTEROID INJECTION VERSUS CYRIAX-TYPE PHYSIOTHERAPY FOR TENNIS ELBOW J. A. N. VERHAAR, G. H. I. M. WALENKAMP, H. VAN MAMEREN, A. D. M. KESTER, A. J. VAN DER LINDEN From the University Hospital,
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2
 Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles
 Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
The Handmaster NMS1 surface FES neuroprosthesis in hemiplegic patients
 The Handmaster NMS1 surface FES neuroprosthesis in hemiplegic patients R. H. Nathan 1,2, H. P. Weingarden 1,3, A. Dar 1,2, A. Prager 1 1 NESS Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation Systems Ltd. 2 Biomedical
The Handmaster NMS1 surface FES neuroprosthesis in hemiplegic patients R. H. Nathan 1,2, H. P. Weingarden 1,3, A. Dar 1,2, A. Prager 1 1 NESS Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation Systems Ltd. 2 Biomedical
1-Apley scratch test.
 1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
Common Tendon Disorders of the Upper Extremity. Mark Tait MD
 Common Tendon Disorders of the Upper Extremity Mark Tait MD Tendonitis History Pain and swelling (any tendon, any location) Overuse Physical examination findings Localized swelling Pain with resistance
Common Tendon Disorders of the Upper Extremity Mark Tait MD Tendonitis History Pain and swelling (any tendon, any location) Overuse Physical examination findings Localized swelling Pain with resistance
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology. Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
Main Menu. Wrist and Hand Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
Traditional Thai Acupressure Points. The anterior aspect of the body THE ANATOMICAL ATLAS
 Traditional Thai Acupressure Points The anterior aspect of the body THE ANATOMICAL ATLAS lines of the SHOULDER BLADES AND POSTERIOR ARM Scapula Line This line runs through landmarks: 1. Above the midpoint
Traditional Thai Acupressure Points The anterior aspect of the body THE ANATOMICAL ATLAS lines of the SHOULDER BLADES AND POSTERIOR ARM Scapula Line This line runs through landmarks: 1. Above the midpoint
N. Bigorre a,, G. Raimbeau b, P.-A. Fouque b, Y. Saint Cast b, F. Rabarin b, B. Cesari b ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2011) 97, 159 163 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lateral epicondylitis treatment by extensor carpi radialis fasciotomy and radial nerve decompression: Is outcome influenced
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2011) 97, 159 163 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lateral epicondylitis treatment by extensor carpi radialis fasciotomy and radial nerve decompression: Is outcome influenced
Treatment Framework patient tracker
 Treatment Framework patient tracker Utilize the BOTOX Treatment Framework when evaluating your Focal Spasticity patients to establish The right goals The right muscles/dose The right plan Use the following
Treatment Framework patient tracker Utilize the BOTOX Treatment Framework when evaluating your Focal Spasticity patients to establish The right goals The right muscles/dose The right plan Use the following
Key Points for Success:
 SELF WRIST & HAND 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Sit comfortably in a position where you can straighten or fully extend
SELF WRIST & HAND 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Sit comfortably in a position where you can straighten or fully extend
EFFECTIVENESS OF MICROCURRENT THERAPY IN A PILOT STUDY THE MANAGEMENT OF LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS: Introduction. Research Report
 Research Report EFFECTIVENESS OF MICROCURRENT THERAPY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS: A PILOT STUDY Lydie O.L. Ho, 1 MMedSc; Wai Lun Kwong, 2 MSc; Gladys L.Y. Cheing, 2 PhD Abstract: Lateral
Research Report EFFECTIVENESS OF MICROCURRENT THERAPY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS: A PILOT STUDY Lydie O.L. Ho, 1 MMedSc; Wai Lun Kwong, 2 MSc; Gladys L.Y. Cheing, 2 PhD Abstract: Lateral
Sick Call Screener Course
 Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: review and recommendations.
 Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2014 Nov;93(11 Suppl 3):S108-21. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000115. Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: review and recommendations.
Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2014 Nov;93(11 Suppl 3):S108-21. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000115. Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: review and recommendations.
Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer's elbow)
 Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer's elbow) Golfer's elbow is the term used to describe pain arising from the tendons on the inside of your elbow. The tendons insert onto the medial epicondyle of the humerus
Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer's elbow) Golfer's elbow is the term used to describe pain arising from the tendons on the inside of your elbow. The tendons insert onto the medial epicondyle of the humerus
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Treatment of the Child with Cerebral Palsy Post Surgical Rehabilitation
 Treatment of the Child with Cerebral Palsy Post Surgical Rehabilitation Sheelah Cochran OTR/L, CPAM, CKTP Objectives Perform an initial evaluation of post-surgical conditions Identify appropriate splinting
Treatment of the Child with Cerebral Palsy Post Surgical Rehabilitation Sheelah Cochran OTR/L, CPAM, CKTP Objectives Perform an initial evaluation of post-surgical conditions Identify appropriate splinting
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7
 Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
DECISION OF THE WORKERS COMPENSATION APPEAL TRIBUNAL
 Decision Number: A1801732 (September 11, 2018) DECISION OF THE WORKERS COMPENSATION APPEAL TRIBUNAL Decision Number: A1801732 Decision Date: September 11, 2018 Introduction [1] The worker has appealed
Decision Number: A1801732 (September 11, 2018) DECISION OF THE WORKERS COMPENSATION APPEAL TRIBUNAL Decision Number: A1801732 Decision Date: September 11, 2018 Introduction [1] The worker has appealed
Effectiveness of Corticosteroids in the Treatment of Lateral Epicondylosis
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2012, 21, 83-88 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. Effectiveness of Corticosteroids in the Treatment of Lateral Epicondylosis Kelli R. Snyder and Todd A. Evans Clinical Scenario
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2012, 21, 83-88 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. Effectiveness of Corticosteroids in the Treatment of Lateral Epicondylosis Kelli R. Snyder and Todd A. Evans Clinical Scenario
INTRODUCTION Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
 INTRODUCTION Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Diagram of the ulnar nerve supplying the muscles of forearm and hand Cubital Tunnel is a condition that refers to the ulnar nerve being compressed around the elbow.
INTRODUCTION Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Diagram of the ulnar nerve supplying the muscles of forearm and hand Cubital Tunnel is a condition that refers to the ulnar nerve being compressed around the elbow.
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome)
 A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
Efficacy of injection of steroids for lateral epicondylitis
 34 Original article Efficacy of injection of steroids for lateral epicondylitis Department of Orthopaedics, National Academy of Medical Sciences, Bir Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal. Correspondence to : Dr.
34 Original article Efficacy of injection of steroids for lateral epicondylitis Department of Orthopaedics, National Academy of Medical Sciences, Bir Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal. Correspondence to : Dr.
Difference Between Angle You Can Bend Your Left Wrist Back vs Your Right Wrist Jenna Priest Science Department Altoona High School January 25, 2017
 Difference Between Angle You Can Bend Your Left Wrist Back vs Your Right Wrist Jenna Priest Science Department Altoona High School January 25, 2017 Background 1- The wrist joint (also known as the radiocarpal
Difference Between Angle You Can Bend Your Left Wrist Back vs Your Right Wrist Jenna Priest Science Department Altoona High School January 25, 2017 Background 1- The wrist joint (also known as the radiocarpal
SUMMARY DECISION NO. 715/95. Benefit of the doubt; Nerve entrapment (ulnar).
 SUMMARY DECISION NO. 715/95 Benefit of the doubt; Nerve entrapment (ulnar). The worker appealed a decision of the Hearings Officer denying entitlement for left ulnar neuritis. The worker claimed that a
SUMMARY DECISION NO. 715/95 Benefit of the doubt; Nerve entrapment (ulnar). The worker appealed a decision of the Hearings Officer denying entitlement for left ulnar neuritis. The worker claimed that a
MSK Imaging Conference. 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology
 MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
Structure and Function of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand Some say it takes a village to raise a child, but it takes 19 bones and 19 joints in the hand for it to function smoothly. The Hand Dorsal aspect 2 3 4 The digits are
Structure and Function of the Hand Some say it takes a village to raise a child, but it takes 19 bones and 19 joints in the hand for it to function smoothly. The Hand Dorsal aspect 2 3 4 The digits are
Advanced Ergonomic Benefits of Pneumatic Scissors
 Advanced Ergonomic Benefits of Pneumatic Scissors Abstract While a certain of automation within the poultry industry has been reached, there will always be an interaction between the product, individual,
Advanced Ergonomic Benefits of Pneumatic Scissors Abstract While a certain of automation within the poultry industry has been reached, there will always be an interaction between the product, individual,
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME (CTS)
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME (CTS) CTS: why does it matter? Fairly prevalent Early detection may prevent permanent impairment 1 To review: Learning Objectives Signs/symptoms Causes Management prevention treatment
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME (CTS) CTS: why does it matter? Fairly prevalent Early detection may prevent permanent impairment 1 To review: Learning Objectives Signs/symptoms Causes Management prevention treatment
Platelet-Rich Plasma Compared With Other Common Injection Therapies in the Treatment of Chronic Lateral Epicondylitis
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2016, 25, 77-82 http://dx.doi.org/10.1123/jsr.2014-0198 2016 Human Kinetics, Inc. CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC Platelet-Rich Plasma Compared With Other Common Injection Therapies
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2016, 25, 77-82 http://dx.doi.org/10.1123/jsr.2014-0198 2016 Human Kinetics, Inc. CRITICALLY APPRAISED TOPIC Platelet-Rich Plasma Compared With Other Common Injection Therapies
What you need to know about Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 What you need to know about Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Disorders of the Neck, Shoulder, Elbow, Wrist and Hands It is my mission to empower patients with knowledge and care so that they can enjoy
What you need to know about Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Disorders of the Neck, Shoulder, Elbow, Wrist and Hands It is my mission to empower patients with knowledge and care so that they can enjoy
Golfers elbow. Physiotherapy of Department
 Golfers elbow Physiotherapy of Department Image copied from http://www.arthritisresearchuk.org/arthritis-information/conditions/elbow-pain/ specific-conditions.aspx This document can be provided in different
Golfers elbow Physiotherapy of Department Image copied from http://www.arthritisresearchuk.org/arthritis-information/conditions/elbow-pain/ specific-conditions.aspx This document can be provided in different
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH
 COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION For stroke patients, in what ways does robot-assisted therapy improve upper extremity performance in the areas of motor impairment, muscle power, and strength?
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION For stroke patients, in what ways does robot-assisted therapy improve upper extremity performance in the areas of motor impairment, muscle power, and strength?
The Effects of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome on the Kinematics of Reach-to-Pinch Function
 The Effects of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome on the Kinematics of Reach-to-Pinch Function Raviraj Nataraj, Peter J. Evans, MD, PhD, William H. Seitz, MD, Zong-Ming Li. Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA. Disclosures:
The Effects of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome on the Kinematics of Reach-to-Pinch Function Raviraj Nataraj, Peter J. Evans, MD, PhD, William H. Seitz, MD, Zong-Ming Li. Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA. Disclosures:
Lab Activity 11: Group II
 Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
13/02/2011. Ergonomics
 13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation.
 Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Common Injuries to the Elbow, Wrist, Hand & Fingers Lateral epicondylitis tennis elbow Medial epicondylitis golfer s s elbow, little league elbow
Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Common Injuries to the Elbow, Wrist, Hand & Fingers Lateral epicondylitis tennis elbow Medial epicondylitis golfer s s elbow, little league elbow
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
Total distal radioulnar joint replacement for symptomatic joint instability or arthritis
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Total distal radioulnar joint replacement for symptomatic joint instability or arthritis Instability of
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Total distal radioulnar joint replacement for symptomatic joint instability or arthritis Instability of
Anatomical Considerations Regarding the Posterior Interosseous Nerve During Posterolateral Approaches to the Proximal Part of the Radius *
 Anatomical Considerations Regarding the Posterior Interosseous Nerve During Posterolateral Approaches to the Proximal Part of the Radius * BY THOMAS DILIBERTI, M.D., MICHAEL J. BOTTE, M.D., AND REID A.
Anatomical Considerations Regarding the Posterior Interosseous Nerve During Posterolateral Approaches to the Proximal Part of the Radius * BY THOMAS DILIBERTI, M.D., MICHAEL J. BOTTE, M.D., AND REID A.
Overuse Injuries of the Upper Extremity. Overuse Injuries 7/23/2018. Peadiatric Overuse Sports Injuries. Al Hess, MD
 Overuse Injuries of the Upper Extremity Al Hess, MD 7/21/2018 1 Overuse Injuries Everything? Not Trauma, infection, tumor, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis Onset of pain associated with repetitive
Overuse Injuries of the Upper Extremity Al Hess, MD 7/21/2018 1 Overuse Injuries Everything? Not Trauma, infection, tumor, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis Onset of pain associated with repetitive
10/10/2014. Structure and Function of the Hand. The Hand. Osteology of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
SHOULDER PAIN. A Real Pain in the Neck. Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017
 SHOULDER PAIN A Real Pain in the Neck Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017 THE SHOULDER JOINT (S) 1. glenohumeral 2. suprahumeral 3. acromioclavicular 4. scapulocostal
SHOULDER PAIN A Real Pain in the Neck Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017 THE SHOULDER JOINT (S) 1. glenohumeral 2. suprahumeral 3. acromioclavicular 4. scapulocostal
Common Upper Extremity Neuropathies (Not Carpal Tunnel Syndrome)
 Common Upper Extremity Neuropathies (Not Carpal Tunnel Syndrome) Nerve Compressions Common in adults, rare in children Frequently cause missed days of work and sleepless nights CDC 2001 26,794 cases of
Common Upper Extremity Neuropathies (Not Carpal Tunnel Syndrome) Nerve Compressions Common in adults, rare in children Frequently cause missed days of work and sleepless nights CDC 2001 26,794 cases of
Grundkurs SGSM-SSMS Sion Sports Elbow. Dr Stéphane Kämpfen
 Grundkurs SGSM-SSMS Sion 2015 Sports Elbow Dr Stéphane Kämpfen Type of pathologies! Acute:! Fractures - dislocation! Sprain! Chronic:! Overload syndrome Fractures - Radial head: Mason classification Mason
Grundkurs SGSM-SSMS Sion 2015 Sports Elbow Dr Stéphane Kämpfen Type of pathologies! Acute:! Fractures - dislocation! Sprain! Chronic:! Overload syndrome Fractures - Radial head: Mason classification Mason
Ulnar Neuropathy in the Distal Ulnar Tunnel
 Ulnar Neuropathy in the Distal Ulnar Tunnel DAVID W. SHUPE, PT, ATC' Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy A brief anatomical review of the ulnar nerve and areas of ulnar nerve entrapment is
Ulnar Neuropathy in the Distal Ulnar Tunnel DAVID W. SHUPE, PT, ATC' Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy A brief anatomical review of the ulnar nerve and areas of ulnar nerve entrapment is
SUSPECTS THE UNUSUAL. Often-Overlooked Muscles. Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis. Flexor pollicis longus.
 THE UNUSUAL SUSPECTS Often-Overlooked Muscles By Joseph E. Muscolino, DC Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis Flexor pollicis longus Quadratus femoris 52 massage & bodywork november/december 2016
THE UNUSUAL SUSPECTS Often-Overlooked Muscles By Joseph E. Muscolino, DC Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis Flexor pollicis longus Quadratus femoris 52 massage & bodywork november/december 2016
The Elbow. The Elbow. The Elbow 12/11/2017. Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas. Compose of three bones. Ligaments of the Elbow
 Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Compose of three bones The humerus The radius The ulna Ligaments of the Elbow Ulnar collateral ligament Radial collateral ligament Annular ligament 1 The elbow is considered
Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Compose of three bones The humerus The radius The ulna Ligaments of the Elbow Ulnar collateral ligament Radial collateral ligament Annular ligament 1 The elbow is considered
Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow, radial epicondylitis,
 EPICONDYLITIS Injection of Botulinum Toxin for Treatment of Chronic Lateral Epicondylitis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Leonid Kalichman, PT, PhD,* Raveendhara R. Bannuru, MD, Marianne Severin,
EPICONDYLITIS Injection of Botulinum Toxin for Treatment of Chronic Lateral Epicondylitis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Leonid Kalichman, PT, PhD,* Raveendhara R. Bannuru, MD, Marianne Severin,
Carpal tunnel syndrome
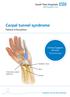 Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
The Biomechanics of the Human Upper Extremity-The Elbow Joint C. Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 The Biomechanics of the Human Upper Extremity-The Elbow Joint C. Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Structure of The Elbow Joint A simple hinge joint, actually categorized as a trochoginglymus joint
The Biomechanics of the Human Upper Extremity-The Elbow Joint C. Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Structure of The Elbow Joint A simple hinge joint, actually categorized as a trochoginglymus joint
Management of Hand Palsies in Isolated C7 to T1 or C8, T1 Root Avulsions
 12(3):156 160, 2008 T E C H N I Q U E Management of Hand Palsies in Isolated C7 to T1 or C8, T1 Root Avulsions Jean-Noel Goubier, PhD and Frédéric Teboul, MD Centre International de Chirurgie de la Main
12(3):156 160, 2008 T E C H N I Q U E Management of Hand Palsies in Isolated C7 to T1 or C8, T1 Root Avulsions Jean-Noel Goubier, PhD and Frédéric Teboul, MD Centre International de Chirurgie de la Main
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings. ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders. Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
Disclosure. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 11/9/15
 Michael S. Bednar, M.D. Chief, Hand Surgery Professor, Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery and Rehab Loyola University - Chicago Disclosure No conflicts for this talk Carpal Tunnel Syndrome AKA Corporal tunnel
Michael S. Bednar, M.D. Chief, Hand Surgery Professor, Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery and Rehab Loyola University - Chicago Disclosure No conflicts for this talk Carpal Tunnel Syndrome AKA Corporal tunnel
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL
 2004 ONWSIAT 502 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 58/04 [1] The appeal was held in Toronto on January 14, 2004 before Vice-Chair, T. Carroll. THE APPEAL PROCEEDINGS [2] The
2004 ONWSIAT 502 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 58/04 [1] The appeal was held in Toronto on January 14, 2004 before Vice-Chair, T. Carroll. THE APPEAL PROCEEDINGS [2] The
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver
 Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
BRACHIAL PLEXUS. DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae
 THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
Carpal Tunnel Release
 Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
