CLINICAL STUDY TO EVALUATE THE RIPASA SCORING SYSTEM IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF ACUTE APPENDICITIS
|
|
|
- Kory Shelton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 e - ISSN - XXXX - XXXX American Journal of Advanced Medical & Surgical Research Journal homepage: CLINICAL STUDY TO EVALUATE THE RIPASA SCORING SYSTEM IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF ACUTE APPENDICITIS Sandeep Khadda, Ajay Kumar Yadav, Anwar Ali, Ashok Parmar, Jitender Kumar Sakrani, Hemant Beniwal Department of General Surgery, Sardar patel medical College, Bikaner, Rajasthan, India. Corresponding Author:- Ajay Kumar Yadav drajaykyadav 24@gmail.com Article Info Received 28/10/2015 Revised 07/11/2015 Accepted 17/ Key words: Computed tomography, Radiological modalities, Appendicectomy. ABSTRACT Acute appendicitis is the most common surgical emergencies encountered by surgeons on-call, with emergency appendicectomy making up one in ten of all emergency abdominal surgeries. A quick and correct diagnosis of acute appendicitis leading to early appendicectomy and avoidance of complications arising from perforation can be difficult at times. Radiological modalities such as computed tomography (CT) imaging further aid in making a definite diagnosis and have been reported to have high sensitivity (94%) and specificity (95%) for diagnosing acute appendicitis. Thus, in most large hospitals, it is routine to request for CT imaging in all patients suspected of acute appendicitis. However, such routine practice will inflate the cost of healthcare substantially. Furthermore, the process of arranging for CT imaging may cause further delay for emergency appendicectomy. A recent study has suggested that such indiscriminate use of CT imaging may lead to the detection of early low-grade appendicitis and unnecessary appendicectomies in a condition that would otherwise have resolved spontaneously with antibiotics therapy The present study was conducted in an attempt to evaluate the RIPASA score which is a new scoring system for diagnosis of acute appendicitis in patients presented to emergency department and the surgical wards with comlaint of right iliac fossa pain. INTRODUCTION The vermiform appendix, recognized as a wormlike narrow extension beginning abruptly during the eighth week of embryologic development as a protuberance off the terminal portion of caecum. During both antenatal and postnatal development, the growth rate of the caecum exceeds that of appendix, so that the appendix displaced medially toward the ileocecal valve. The vermiform appendix is present only in humans, certain anthropoid apes and the wombat [1]. About 7% of people in Western countries have appendicitis at some time during their life, with a peak incidence between 10 and 30 years of age. The vermiform appendix is considered by most to be a vestigial organ, its importance in surgery result only from its propensity for inflammation, which results in clinical syndrome known as acute appendicitis. ANATOMY In humans, the vermiform appendix is a small, finger-sized structure, found at the end of small gut at the iliocaecal junction. The adjective "vermiform" literally means "worm-like" and reflects the narrow, elongated shape of this intestinal appendage. The appendix can vary in length from <1 cm to >30 cm, but most appendices are 6 to 9 cm long, with its outside diameter ranging from 3-8 mm and its lumen ranging from 1-3 mm. Embryologically, appendix is a continuation of caecum arising from its inferior tip. The base of the appendix is present at the convergence of the taeniae coli on the inferior aspect of cecum. The most common location is retrocecal but within the peritoneal cavity. The varying location of the tip of the 67
2 appendix likely explains the myriad of symptoms that are attributable to the inflamed appendix. The appendiceal artery, a branch of the ileocolic artery, supplies the appendix. PATHOLOGY Acute appendicitis may occur at any age, although it is relatively rare at the extremes of age. The maximum incidence of the disease occurs in the 2 nd decade; thereafter, disease incidence declines with age. The primary pathogenic event in the majority of patients with acute appendicitis is luminal obstruction. This may result from a variety of causes, which include fecoliths, lymphoid hyperplasia, foreign bodies, parasites, and both primary (carcinoid, adenocarcinoma, Kaposi sarcoma, and lymphoma) and metastatic (colon and breast) tumors. Once appendiceal obstruction occurs, the continued secretion of mucus results in elevated intraluminal pressure and luminal distension. This stimulates the visceral afferent nerve fibres that enter the spinal cord at thoracic levels T8 through T10, which causes referred epigastric and periumbilical pain. This visceral pain is usually mild & poorly localised in 4-6 hours duration. Anorexia, nausea, and vomiting usually follow as the pathophysiology worsens. Increasing intraluminal pressure eventually exceed capillary perfusion pressure, which leads to venous engorgement, arterial compromise, and tissue ischemia. As the epithelial mucosal barrier becomes compromised, luminal bacteria multiply and invade the appendiceal wall, which causes transmural inflammation. All species of bacteria common to intestinal tract can be found and usually multiple organisms can be isolated eg. - Yersinia species, Adenovirus, Cytomegalovirus, Actinomycosis, Mycobacterium species, Histoplasma species, Schistosoma species, Pinworms, Stronglyoides sterocolaris. CLINICAL FEATURES Patients typically experience the classic migration of pain to the right lower quadrant of the abdomen. This somatic pain is continuous and is more severe than the early visceral pain. The patient often gives a history of similar attacks in the past. The attacks commence at any time, but frequently it occurs in the morning hours awakening the patient from sleep. The classic migration of pain need not occur, and the point of maximal tenderness may be distinct from Mcburney's point if the appendix is in an atypical location. Later, a worsening progressive pain along with vomiting, nausea, and anorexia are described by the patient. Usually fever is not present at this stage. This pain increases with the act of coughing (Dunphy sign). With the passage of time, accurate localization of tenderness becomes more difficult as muscular rigidity too becomes evident in addition to tenderness. Tenderness is less marked in retroceacal appendix. Various authors like Bhatnagar [2-68 4] have emphasized that pain is a predominant symptom followed by vomiting.. DIAGNOSIS If the diagnosis is confirmed from the history, physical examination and laboratory studies, taking the patient directly to surgery without imaging is justified. For now the use of imaging modalities in atypical presentation of suspected cases of appendicitis should complement, but not replace, clinical assessment and judgment. IMAGING STUDIES Ultrasonography Ultrasonography (US) is valuable in the diagnosis of suspected cases of appendicitis and is a cost-efficient adjunct to the clinical evaluation. Use of preoperative ultrasonography is associated with overall lower negative appendectomy rate [5]. The inflamed appendix is seen as a blind-ended, aperistaltic, noncompressible, tubular structure that arises from the base of the caecum having a diameter greater than 6 mm. Presence of a fecolith may aid in arriving at a positive diagnosis. Loculated pericecal fluid, phlegmon or abscess, prominent pericecal fat and circumferential loss of the submucosal layer of appendix are associated with appendiceal perforation. Advantages of sonography include its noninvasiveness, short acquisition time, lack of radiation exposure and potential for diagnosis of other causes of abdominal pain, particularly in the subset of women of childbearing age. Computerised Tomography CT is more precise than ultrasonography and more reproducible from hospital to hospital having a diagnostic accuracy rate of 93 to 98%. Abdominal CT has become the most important imaging study in the evaluation of patients with atypical presentations of appendicitis. Abdominal Radiography The kidney-urinary-bladder (KUB) view is typically used. Visualization of an appendicolith in a patient with symptoms consistent with appendicitis is highly suggestive of appendicitis, but this occurs in fewer than 10% of cases. MRI A single retrospective study assessed the accuracy of MRI in 51 pregnant patients with suspected appendicitis in whom ultrasonography was nondiagnostic. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, and accuracy for MRI was 100%, 93.6%, 91.4%, 100% and 94.04% respectively. OTHERS TESTS Scoring systems
3 Physical examination, laboratory or radiological, clinical suspicion and experience of surgeon can lead to diagnosis. A number of clinical scores have been developed to decrease the number of negative appendicectomies. In the past, various scoring systems had been described for acute appendicitis and the cited studies are either computer based or retrospective. Scoring systems would appear to be ideal as they are accurate, non-invasive and require no special equipment. Clinical scoring systems are attractive because of their simplicity, however, none has been shown prospectively to improve on the physician's judgment in the subset of patients evaluated for abdominal pain suggestive of appendicitis. The various scoring systems are: - The Eskelinen score, The Fenyo-Lindberg score, The Christian scores, The Ohmann score, The Samuel score, The Teicher Cohen score, The Tzanakis score and The Alvarado score, RIPASA Score.(Newer scoring system) Alvarado score is one such scoring system described by Alvarado in 1986 and has been validated in adult surgical practices and is the simplest of all. It is based on three symptoms, three signs and two laboratory investigations with score of 10 [6]. In the year 1994, Kalan gave a slightly modified version of the original Alvarado score in which the laboratory finding of shift to the left of neutrophil maturation (score 1) was not used. This was done because the test is not routinely available in many of the centers. So a Modified Alvarado Score (MAS) with a total score of nine was used after having excluded the score for the left shift of neutrophil maturation. Presence of a high score was found to be an easy and satisfactory aid to early diagnosis of appendicitis in children and men. However, the false positive rate for appendicitis in women was unacceptably high [7-10]. Morbidity and mortality rates associated with appendicitis increased when perforation ensues. Following perforation, the length of stay in hospital increases, wound infection rates may triple, risk of infertility rises, postoperative intra-abdominal collection develops 15 times more frequently and mortality of appendicitis normally quoted as 1% rises to 5-8%.It is therefore, obvious that the aim of the surgeon must be to prevent perforation at any price. Therefore, a high false positive appendicectomy rate has been regarded as acceptable in the light of the severe complications of sitting on a 'hot appendix' and risking perforation. It appears therefore, that surgeons have created for themselves a surgical security zone which allows then to accept a 15-30% false positive appendicectomy rate. The Raja Isteri Pengiran Anak Saleha Appendicitis (RIPASA) score is a new diagnostic scoring system developed for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis and has been shown to have significantly higher sensitivity, 69 specificity and diagnostic accuracy than that reported for the Alvarado or Modified Alvarado scores, particularly when the latter two scores were applied in an Asian or oriental population. Although the RIPASA score is more extensive than the Alvarado score, it is simple to apply and has several parameters that are absent in the Alvarado score, such as age, gender and duration of symptoms prior to presentation. These parameters have been shown to affect the sensitivity and specificity of the Alvarado and Modified Alvarado scores. The RIPASA score consists of 14 fixed generalised parameters, with an additional parameter that is specific to our local population. We prospectively evaluate the RIPASA score by applying score to patients who presented to our Accident and Emergency (A&E) Department with right iliac fossa (RIF) pain and who were suspected of acute appendicitis. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES 1. To study different parameters helpful in diagnosis of acute appendicitis. 2. To evaluate the RIPASA scoring system in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. MATERIALS AND METHODS The present study was conducted in General Surgery Department of S.P. Medical College, Bikaner. A hospital based analytic type of observational study September 2013 to February 2014 the desired sample were covered Sample size was calculated 150 subjects. Every case falling in inclusive criteria till the sample size completed. Patient with pain in RIGHT ILIAC FOSSA getting admitted in Department of General Surgery, PBM Hospital, Bikaner. METHODOLOGY The study was conducted in the general surgery department of PBM hospital and associated group of hospital, Bikaner. The patient presenting with pain in RIF was included in my study.on admission RIPASA was performed by completion of score sheet shown below. The RIPASA score sheet consists of fourteen parameters and the scores were age (less than 40 years is 1 point; greater than 40 years is 0.5 point), gender (male is 1 point; female is 0.5 point), right iliac fossa (RIF) pain (0.5 point), migration of pain to RIF (0.5 point), nausea and vomiting (1 point), anorexia (1 point), duration of symptoms (less than 48 hours is 1 point; more than 48 hours is 0.5 point), RIF tenderness (1 point), guarding (2 points), rebound tenderness (1 point), Rovsing's sign (2 points), fever (1 point), raised white cell count (1 point), negative urinalysis (1 point). After admission to surgical ward scoring carried out by the admitting surgeon. Scoring were performed at every review at the next morning round, if the patient was
4 admitted in early hours of morning until a decision was made for either appendicectomy or continued conservative treatment. All the data regarding patient admission and discharge dates, data of appendicectomy (if performed), name& signature of the confirming surgeon, postoperative complication and radiological investigation used should be record in score sheet. All patients underwent for emergency appendicectomy were confirmed by histopathological examination. Inclusion Criteria Patient with right iliac fossa pain. Consented for study Exclusion Criteria Those patient who had been admitted previously for other complaints but who subsequently develop right iliac fossa pain during their admission episodes. Preoperative Workup: A standardized history was obtained. Past history for TB, Diabetes, Hypertension, Drug Allergy, Bronchial Asthma and Previous Abdominal or Pelvic Surgery was taken. Personal history with regards to his dietary habits, bowels habits, smoking was taken. RIPASA Scoring were done for every patient in study. In our study patients with score 7.5 & more considered positive for RIPASA Score. Routine blood investigations, USG, ECG and Chest X- ray were obtained. Appendicetomy was performed in those cases which were positive for RIPASA Score. Then operative findings were confirmed by histopathology. Follow Up - Histopathology report was obtained and compared with RIPASA Score. Data Collection and Analysis The proforma was filled systematically for each patient. The data collected was subjected to statistical analysis. Statistical Analysis Guidelines for management according to RIPASA Score Score Interpretation < 5 probability of acute appendicitis unlikely 5 7 low probability high probability >12 definite acute appendicitis. The data was tabulated, analyzed and the observations and results of the study were discussed for arriving at conclusions regarding the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of RIPASA Score. OBSERVATIONS Table 1. Distribution of Cases according to age group (years) in relation to sex Age Group (years) Female Male Total No. % No. % No. % < > Total Mean Age SD According to above table, maximum number of patients were males (83) while maximum patients were in age group <30 (n=93). Mean age in females was while mean age in males was According to RIPASA score, 55.3% was males while 44.7% were females. In our study, inclusion criteria was pain in right iliac fossa, so 100% of our patients were present in pain in right iliac fossa. Table 2. Distribution of Cases according to Migratory Pain to Right Iliac Fossa Migratory Pain to Right Iliac Fossa Points Frequency Percent Absent Present Total Migratory pain to right iliac fossa was present in 73(48.7%) while it was absent in 77(51.3%). 70
5 Table 3. Distribution of cases according to Total RIPASA Score group Total RIPASA Score Frequency Percent > Total Table 15 shows distribution of cases according to total RIPASA score. Out of total 150 patients 50 patients scored 5-7 RIPASA score, 71 patients scored RIPASA score while 29 patients scored >11.5 RIPASA score. Table 4. Different variables in RIPASA Score Variable According to RIPASA Score True Positive 86 True Negative 48 False Positive 14 False Negative 2 Total 150 In present study, out of total 150 patients, according to RIPASA Score 86 patients had true positive results, 48 patients had true negative results, 14 patients had false positive results while 2 patients had false negative results. Table 5. Diagnostic Effectivity of RIPASA Score Diagnostic Effectivity RIPASA Score (%) Sensitivity Specificity Positive Predictive Value Negative Predictive Value According to diagnostic effectivity of RIPASA Score sensitivity was found in 97.73% of patients, specificity was found in 77.42%, positive predictive value was 86% while negative predictive value was 96%. Table 6. Negative appendicectomy rate Total Cases % False Positive True Positive 86 False Negative 2 Total 102 According to above table 14 patients had false positive results, 86 patients had true positive values while 2 patients had false negative results. DISCUSSION The present study was conducted in an attempt to evaluate the RIPASA score new scoring system for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in patients presented to emergency department and the surgical wards with right iliac fossa pain. Total 150 patients recruited for our study by applying inclusion and exclusion criteria. This new appendicitis scoring system includes the three parameters mentioned above as well as four other new parameters deemed important in our local settings, including clinical signs of RIF guarding, Rovsing s sign, negative urinalysis and foreign NRIC status. Guarding and Rovsing s sign are earlier indicators of a local inflammatory process such as acute appendicitis, while rebound tenderness is a much later sign when the peritoneum is involved with peritonism. Negative urinalysis was also included to exclude urinary causes of RIF pain. The RIPASA scoring system which is more extensive yet simple additive scoring system consists of 14 fixed parameters i.e. sex (male 1.00; female 0.50), age (<39.9 = 1.00; >40 = 0.50, RIF pain (Present 0.5), Migratory pain to right iliac fossa (Present 0.5), Anorexia (present 1), Nausea/vomiting (present 1), Duration of symptoms (<48hrs = 1; >48 hrs = 0.50), RIF Tenderness (Present 1), Guarding (Present 2), Rebound tenderness (Present 1), Rovsing s Sign (Present 2), Fever (Present 1), Raised WBC (Present 1) and Negative urinalysis (Present 1). All these 14 parameters were easily obtainable from a good clinical history examination and investigations. The minimum and maximum total scores achievable with RIPASA scoring system were 2 and 16, respectively. This new appendicitis scoring system is easy and simple to apply as the majority of the parameters can be obtained from a routine history and clinical examination. 71
6 Out of 150 patients in our study, 86 patients were true positive according to RIPASA score those had total RIPASA score 7.5 or more then 7.5 and positive appendicitis on HPE, 14 patients were false positive according to RIPASA score, those had total RIPASA score 7.5 or more than 7.5 and negative appendicitis or HPE. Forty Eight patients were true negative according to RIPASA score those had total RIPASA score <7.5. Two patients were false negative according to RIPASA score those had total RIPASA score <7.5 but appendicitis positive on HPE. Using the RIPASA score, at the optimal cut-off threshold score of 7.5 for the RIPASA score, the calculated sensitivity and specificity were 97.73% and 77.42% respectively. This was a definite improvement from the Alvardo Score (sensitivity %; specificity %) and modified Alvardo score (sensitivity 53.8% and specificity 80%) when applied to Middle-Eastern Asian or oriental population. The positive predictive value and negative predictive value for RIPASA score were 86% and 96%. In our study, 48 patients out of 150 were managed conservatively that is consisting 32% while 102 out of 150 were managed by surgical management. Our study showed that out of 102 surgically managed patients, 88 patients were histopathologically positive for acute appendicitis and 14 patients were histopathologically negative for acute appendicitis. According to our study, overall negative appendicectomy were 13.7%. This reduction in unnecessary negative appendicectomy would translate to significant healthcare cost saving as well as unnecessary morbidity subjected to the patients. Furthermore, the sensitivity and specificity achieved by the RIPASA score is equivalent to those achieved with CT scan for acute appendicitis. Hence by applying the RIPASA score, the number of costly CT scans performed to exclude acute appendicitis can be reduced. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION This study was conducted in the Department of General Surgery, S.P. Medical College and Associated group of Hospitals, Bikaner during September 2013 to February In present study, maximum number of patients were males (83) while maximum patients were in age group <30 (n=93). Mean age in females was while mean age in males was In Present study, according to RIPASA score, 55.3% was males while 44.7% were females. In all the patients (100%) right iliac fossa pain was present. Migratory pain to right iliac fossa was present in 73(48.7%). Anorexia was present in 106 patients. Nausea/Vomiting was present 117 (78%) of patients According to RIPASA score, duration of symptoms >48 hours was found in 48(32%) of patients while remaining 68% cases were in duration of symptoms <48 hours. According to RIPASA, RIF tenderness was present in 121(80.7%) of cases. Guarding was present in 82(54.7%) of patients and in 45.3% of cases guarding was not present. Rebound Tenderness was present in 72(48%) of cases while it was absent in 52% of patients. According to RIPASA score, Rovsing s Sign was present in only 33(22%) of patients. Fever was present in 49(32.7%) of patients according to RIPASA Score while 101 patients had no fever. Out of total 150 patients, according to RIPASA score 98(65.3%) patients had raised WBC. Urinalysis was negative in 118 patients according to RIPASA Score while urinalysis was positive in 32(21.3%) of patients. In present study, out of total 150 patients 50 patients scored 5-7 RIPASA Score, 71 patients scored RIPASA Score while 29 patients scored >11.5 RIPASA Score. In present study, out of total 150 patients, according to RIPASA Score 86 patients had true positive results, 48 patients had true negative results, 14 patients had false positive results while 2 patients had false negative results. According to diagnostic effectivity of RIPASA Score sensitivity was found in 97.73% of patients, specificity was found in 77.42%, positive predictive value was 86.00% while negative predictive value was 96.00%. According to our study, overall negative appendicectomy were 13.7%. We concluded that that RIPASA score is currently a much better diagnostic scoring system for acute appendicitis with significantly higher sensitivity and negative predictive value, particularly in our population setting. The 14 fixed parameters can be easily and rapidly obtained in any population setting by taking a complete history, and conducting a clinical examination and two simple investigations. In terms of healthcare cost savings, the use of RIPASA score may help to reduce unnecessary inpatient admissions and expensive radiological investigations. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT None CONFLICT OF INTEREST No interest 72
7 REFERENCES 1. Hardin DM. (1999). Acute Appendicitis: Review and Update. Am Fam Physician, 60, Connel P. (2000). The vermiform appendix. Baily and Loves Short practice of Surgery, 23rd Ed, London, UK, 11, Kozar RMA, Roshyn J. (1992). The Appendix, Principle of surgery. 7th international Edition. McGraw Hill Health Profession Division, Fawcett DW, Raviola E.(1994). Bloom and Fawcett: A textbook of histology Chapman and Hall: New York, NY. 5. Maa J, Kirkwood KS. (2013). The Appendix. In : Sabiston Text Book of Surgery The biological Basis of Modern Surgical Practice 19 th edi. Beauchamp, Evers, Mattox, Bukhari SAH, Rana SH. (2002). Alvardo Score : A new approach to acute appendicitis. Pak Armed Forces Med J, 52(1), Tschuor C, Raptis DA, Limani P, Bachler T, Obekofler CE, Breitenstein S, Graf R. (2012). The value of pancreatic stone protein in predicting acute appendicitis in patients presenting at the emergency department with abdominal pain. Gastroenterology, 12, a Naveen K, Sareesh NN, Satheesha BN, Murlimanju BV, Suhani S, Mamatha H, Sampath PK. (2013). Appendicitis and appendectomy: A retrospective survey in South Indian pouplation. J Surg academia, 3(2),
Role of Alvarado Score in Diagnosis and Management of Acute Appendicitis
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/510 Role of Alvarado Score in Diagnosis and Management of Acute Appendicitis Chhari Akash Singh 1, Ashish Pratap Singh
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/510 Role of Alvarado Score in Diagnosis and Management of Acute Appendicitis Chhari Akash Singh 1, Ashish Pratap Singh
CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2016; 2:1
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2016; 2:1 Editor-in-Chief: Olufemi E. Idowu. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria. MANAGEMENT OF APPENDICITIS Ibrahim NA, Njokanma
CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2016; 2:1 Editor-in-Chief: Olufemi E. Idowu. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria. MANAGEMENT OF APPENDICITIS Ibrahim NA, Njokanma
APPENDICITIS AND ITS APPEARANCES ON CT
 APPENDICITIS AND ITS APPEARANCES ON CT APPENDICITIS Results from acute inflammation of the appendix. Most common abdominal surgical emergencies. Diagnosis usually clinical based on physical exam and lab
APPENDICITIS AND ITS APPEARANCES ON CT APPENDICITIS Results from acute inflammation of the appendix. Most common abdominal surgical emergencies. Diagnosis usually clinical based on physical exam and lab
Role of modified Alvarado scoring system and USG abdomen in acute appendicitis: an overview
 International Surgery Journal http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20175404 Role of modified Alvarado scoring
International Surgery Journal http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20175404 Role of modified Alvarado scoring
Appendicitis USG vs CT
 Appendicitis USG vs CT Dr Sateesh Kumar Kailasam MBBS Dip EM (RCGP, UK) MRCEM (UK) Group Head Maxcure Group of Hospitals National Treasurer Society for Emergency Medicine India (SEMI) My Talk includes
Appendicitis USG vs CT Dr Sateesh Kumar Kailasam MBBS Dip EM (RCGP, UK) MRCEM (UK) Group Head Maxcure Group of Hospitals National Treasurer Society for Emergency Medicine India (SEMI) My Talk includes
To Evaluate the Efficacy of Alvarado Score and Ultrasonography in Acute Appendicitis
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. XI (September). 16), PP 14-18 www.iosrjournals.org To Evaluate the Efficacy of Alvarado
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. XI (September). 16), PP 14-18 www.iosrjournals.org To Evaluate the Efficacy of Alvarado
Always keep it in the differential
 Acute Appendicitis Lissa C. Sakata and Lindsey Perea 2 Always keep it in the differential Learning Objectives 1. The learner should be able to describe the etiology of acute appendicitis. 2. The learner
Acute Appendicitis Lissa C. Sakata and Lindsey Perea 2 Always keep it in the differential Learning Objectives 1. The learner should be able to describe the etiology of acute appendicitis. 2. The learner
Alvarado vs Lintula Scoring Systems in Acute Appendicitis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Alvarado vs Lintula Scoring Systems in Acute Appendicitis Daniel Ojuka, Mike Sangoro School of Medicine, University of Nairobi Correspondence to: Dr. Daniel Ojuka, P.O. Box 19762 00202,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Alvarado vs Lintula Scoring Systems in Acute Appendicitis Daniel Ojuka, Mike Sangoro School of Medicine, University of Nairobi Correspondence to: Dr. Daniel Ojuka, P.O. Box 19762 00202,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Evaluation Of Alvarado Score And CRP In Diagnosis Of Acute Appendicitis And Correlation With Histopathological Examination
 IJCMR 509 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Evaluation Of Alvarado Score And CRP In Diagnosis Of Acute Appendicitis And Correlation With Histopathological Examination Vinay Sagar Cheeti 1, P. Mallikarjun 2, D.Venkateshwar
IJCMR 509 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Evaluation Of Alvarado Score And CRP In Diagnosis Of Acute Appendicitis And Correlation With Histopathological Examination Vinay Sagar Cheeti 1, P. Mallikarjun 2, D.Venkateshwar
Development of the RI PASA score: a new appendicitis scoring system for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis
 220 Original Article Development of the RI PASA score: a new appendicitis scoring system for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis Chong C F, Adi M I W, Thien A, Suyoi A, Mackie A J, Tin A S, Tripathi S,
220 Original Article Development of the RI PASA score: a new appendicitis scoring system for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis Chong C F, Adi M I W, Thien A, Suyoi A, Mackie A J, Tin A S, Tripathi S,
Evaluation of accuracy of four clinical scores and comparison with ultrasonography for diagnosis of acute appendicitis
 International Surgery Journal Subramaniyan P et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Jun;4(6):1940-1944 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20172108
International Surgery Journal Subramaniyan P et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Jun;4(6):1940-1944 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20172108
Pitfalls in Paediatric Appendicitis: Highlighting Common Clinical Features of Missed Cases
 Original Article Pitfalls in Paediatric Appendicitis: Highlighting Common Clinical Features of Missed Cases Melanie D.W. Seah and Kee-Chong Ng, Department of Emergency Medicine, KK Women s and Children
Original Article Pitfalls in Paediatric Appendicitis: Highlighting Common Clinical Features of Missed Cases Melanie D.W. Seah and Kee-Chong Ng, Department of Emergency Medicine, KK Women s and Children
Significance of Ripasa Scoring System in Diagnosis of Acute Appendicitis
 Significance of Ripasa Scoring System in Diagnosis of Acute Appendicitis 1 Marwah Karan, 2 Maheshwari Kumar Mukesh, 3 Krishna Atul, 4 Agarwal Vijay, 5 Kumar Deepak, 6 Jain Atul, 7 Prasad Akshay 1,6,7 Resident,
Significance of Ripasa Scoring System in Diagnosis of Acute Appendicitis 1 Marwah Karan, 2 Maheshwari Kumar Mukesh, 3 Krishna Atul, 4 Agarwal Vijay, 5 Kumar Deepak, 6 Jain Atul, 7 Prasad Akshay 1,6,7 Resident,
Introduction Diagnosis of acute appendicitis is basically a clinical matter. Many patients present with a typical history and physical examination fin
 Modified Clinical Score of Acute Appendicitis Surgical Department College Of Medicine Karballa University. Abstract B ackground Suspected acute appendicitis is the most common non traumatic admissions
Modified Clinical Score of Acute Appendicitis Surgical Department College Of Medicine Karballa University. Abstract B ackground Suspected acute appendicitis is the most common non traumatic admissions
The appendix is a small, tube-like structure attached to the first part of the large intestine, also called the colon. The appendix.
 The appendix is a small, tube-like structure attached to the first part of the large intestine, also called the colon. The appendix is located in the lower right portion of the abdomen. It has no known
The appendix is a small, tube-like structure attached to the first part of the large intestine, also called the colon. The appendix is located in the lower right portion of the abdomen. It has no known
Original Research Article
 International Surgery Journal Regar MK et al. Int Surg J. 2017 May;4(5):1755-1761 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20171634
International Surgery Journal Regar MK et al. Int Surg J. 2017 May;4(5):1755-1761 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20171634
Evaluation of the of the sensitivity, accuracy and positive predictive value of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of Appendicitis.
 West African Journal of Ultrasound Vol 17 Number 2 (2016) Evaluation of the of the sensitivity, accuracy and positive predictive value of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of Appendicitis. 1 2 3 Oguntola
West African Journal of Ultrasound Vol 17 Number 2 (2016) Evaluation of the of the sensitivity, accuracy and positive predictive value of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of Appendicitis. 1 2 3 Oguntola
Appendicitis: When Simple Becomes not so Simple
 Wright State University CORE Scholar Department of Surgery Faculty Publications Surgery 1-26-2010 Appendicitis: When Simple Becomes not so Simple Elizabeth H. Ey Wright State University, elizabeth.ey@wright.edu
Wright State University CORE Scholar Department of Surgery Faculty Publications Surgery 1-26-2010 Appendicitis: When Simple Becomes not so Simple Elizabeth H. Ey Wright State University, elizabeth.ey@wright.edu
Original Research Article A clinicopathological study of acute appendicitis in eastern India Ekka NMP 1, Singh PR 2, Kumar V 3
 Original Research Article A clinicopathological study of acute appendicitis in eastern India Ekka NMP 1, Singh PR 2, Kumar V 3 1 Dr Nishith M Paul Ekka Senior Resident drnmpekka@gmail.com 2 Dr Pritesh
Original Research Article A clinicopathological study of acute appendicitis in eastern India Ekka NMP 1, Singh PR 2, Kumar V 3 1 Dr Nishith M Paul Ekka Senior Resident drnmpekka@gmail.com 2 Dr Pritesh
Right Iliac Fossa Pain
 Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Right Iliac Fossa Pain Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should
Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Right Iliac Fossa Pain Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72(2), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72(2), Page 3904-3908 Comparative Study between Alvarado Score and Appendicitis Inflammatory Response Score in Diagnosis of Acute Appendicitis
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72(2), Page 3904-3908 Comparative Study between Alvarado Score and Appendicitis Inflammatory Response Score in Diagnosis of Acute Appendicitis
Clinical, Diagnostic, and Operative Correlation of Acute Abdomen
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/163 Clinical, Diagnostic, and Operative Correlation of Acute Abdomen Madipeddi Venkanna 1, Doolam Srinivas 2, Budida
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/163 Clinical, Diagnostic, and Operative Correlation of Acute Abdomen Madipeddi Venkanna 1, Doolam Srinivas 2, Budida
Is Pediatric Appendicitis Score Sufficient to Make the Diagnosis of Acute Appendicitis Among Children?
 Iraqi JMS Published by AlNahrain College of Medicine ISSN 686579 Email: iraqijms@colmedalnahrain.edu.iq http://www.colmednahrain.edu.iq Is Pediatric Appendicitis Score Sufficient to Make the Diagnosis
Iraqi JMS Published by AlNahrain College of Medicine ISSN 686579 Email: iraqijms@colmedalnahrain.edu.iq http://www.colmednahrain.edu.iq Is Pediatric Appendicitis Score Sufficient to Make the Diagnosis
Chapter 93 Appendicitis
 Chapter 93 Appendicitis Episode Overview: 1) List 8 ddx for appendicitis 2) List 5 causes of acute appendiceal obstruction and describe the pathophysiology of appendicitis including pain location 3) List
Chapter 93 Appendicitis Episode Overview: 1) List 8 ddx for appendicitis 2) List 5 causes of acute appendiceal obstruction and describe the pathophysiology of appendicitis including pain location 3) List
Paediatric appendicitis scoring: a useful guide to diagnose acute appendicitis in children
 International Surgery Journal Dhruv KK et al. Int Surg J. 2016 Feb;3(1):84-89 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20151534
International Surgery Journal Dhruv KK et al. Int Surg J. 2016 Feb;3(1):84-89 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20151534
GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT INFECTIONS - ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT
 GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT INFECTIONS - ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT Name & Title Of Author: Dr Linda Jewes, Consultant Microbiologist Date Amended: December 2016 Approved by Committee/Group: Drugs & Therapeutics
GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT INFECTIONS - ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT Name & Title Of Author: Dr Linda Jewes, Consultant Microbiologist Date Amended: December 2016 Approved by Committee/Group: Drugs & Therapeutics
Gastrointestinal Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%)
 Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
Small Bowel and Colon Surgery
 Small Bowel and Colon Surgery Why Do I Need a Small Bowel Resection? A variety of conditions can damage your small bowel. In severe cases, your doctor may recommend removing part of your small bowel. Conditions
Small Bowel and Colon Surgery Why Do I Need a Small Bowel Resection? A variety of conditions can damage your small bowel. In severe cases, your doctor may recommend removing part of your small bowel. Conditions
Comparative study of management of acute appendicitis with special consideration of Alvarado Score
 Original Research Article Comparative study of management of acute appendicitis with special consideration of Alvarado Score Jayesh Gohel, Hiren Parmar *, Balraj Solanki 2 Associate Professor, Department
Original Research Article Comparative study of management of acute appendicitis with special consideration of Alvarado Score Jayesh Gohel, Hiren Parmar *, Balraj Solanki 2 Associate Professor, Department
ISPUB.COM. A Clinical Study Of Right Iliac Fossa Mass. S K Shetty, M Shankar INTRODUCTION AIMS AND OBJECTIVES
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 30 Number 4 S K Shetty, M Shankar Citation S K Shetty, M Shankar.. The Internet Journal of Surgery. 2013 Volume 30 Number 4. Abstract Background and Objectives
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 30 Number 4 S K Shetty, M Shankar Citation S K Shetty, M Shankar.. The Internet Journal of Surgery. 2013 Volume 30 Number 4. Abstract Background and Objectives
ALVARADO SCORE IN DIAGNOSIS OF ACUTE APPENDICITIS
 ALVARADO SCORE IN DIAGNOSIS OF ACUTE APPENDICITIS *Md. Zikrullah Tamanna 1, Uzma Eram 2, Abdul Muthalib Hussain 3, ShafkatUllahKhateeb 4 and Badurudeen Mahmood Buhary 5 1 Emergency Department, King Fahad
ALVARADO SCORE IN DIAGNOSIS OF ACUTE APPENDICITIS *Md. Zikrullah Tamanna 1, Uzma Eram 2, Abdul Muthalib Hussain 3, ShafkatUllahKhateeb 4 and Badurudeen Mahmood Buhary 5 1 Emergency Department, King Fahad
FHS Appendicitis US Protocol
 FHS Appendicitis US Protocol Reviewed By: Shireen Khan, MD; Sarah Farley, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: May 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible
FHS Appendicitis US Protocol Reviewed By: Shireen Khan, MD; Sarah Farley, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: May 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible
Prospective validation of the APPEND clinical prediction rule within a pathway dedicated to right iliac fossa pain
 Prospective validation of the APPEND clinical prediction rule within a pathway dedicated to right iliac fossa pain A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the Degree of Master
Prospective validation of the APPEND clinical prediction rule within a pathway dedicated to right iliac fossa pain A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the Degree of Master
Retrospective study analyzing the data on non-traumatic abdominal emergency surgeries done tertiary care hospital, Chennai
 Original Research Article Retrospective study analyzing the data on non-traumatic abdominal emergency surgeries done tertiary care hospital, Chennai S. Vijayalakshmi 1, Sriramchristopher M 2* 1 Associate
Original Research Article Retrospective study analyzing the data on non-traumatic abdominal emergency surgeries done tertiary care hospital, Chennai S. Vijayalakshmi 1, Sriramchristopher M 2* 1 Associate
The role of abdominal X-rays in the investigation of suspected acute appendicitis
 Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol. 2(11) pp. 1216-1220, November 2011 Available online@ http://www.interesjournals.org/jmms Copyright 2011 International Research Journals Full Length Research
Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol. 2(11) pp. 1216-1220, November 2011 Available online@ http://www.interesjournals.org/jmms Copyright 2011 International Research Journals Full Length Research
Case Report An Unusual Cause of Right Lower Quadrant Pain: The Caecum Diverticulitis
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2012, Article ID 789397, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/789397 Case Report An Unusual Cause of Right Lower Quadrant Pain: The Caecum Diverticulitis Murat Yildar, 1 Omer Faruk Ozkan,
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2012, Article ID 789397, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/789397 Case Report An Unusual Cause of Right Lower Quadrant Pain: The Caecum Diverticulitis Murat Yildar, 1 Omer Faruk Ozkan,
Surgical Education Series
 Surgical Education Series The Acute Abdomen Ahmad kachooei, MD MPH Assistant Professor Division of General Surgery Department of Surgery University of Qom Outline Definitions What causes an acute abdomen
Surgical Education Series The Acute Abdomen Ahmad kachooei, MD MPH Assistant Professor Division of General Surgery Department of Surgery University of Qom Outline Definitions What causes an acute abdomen
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 05 Page May 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i5.198 Role of C Reactive Protein and WBC Count
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i5.198 Role of C Reactive Protein and WBC Count
Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum. Elective Student S. C.
 Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum 2008 4 Elective Student S. C. Case History An elderly male presented to the Emergency Department with abdominal pain. Chief Complaint: Worsening, diffuse abdominal
Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum 2008 4 Elective Student S. C. Case History An elderly male presented to the Emergency Department with abdominal pain. Chief Complaint: Worsening, diffuse abdominal
Perforation: An Unusual Presentation of Enteric Fever. J Pharm Biomed Sci 2015; 05(05): S1-S4.
 JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES Khadda S, Parmar A, Ali A, Yadav AK, Sakhrani JK, Kapoor A. Gall bladder Perforation: An Unusual Presentation of Enteric Fever. J Pharm Biomed Sci 2015;
JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES Khadda S, Parmar A, Ali A, Yadav AK, Sakhrani JK, Kapoor A. Gall bladder Perforation: An Unusual Presentation of Enteric Fever. J Pharm Biomed Sci 2015;
Summary and conclusions
 Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
ACUTE APPENDICITIS IN THE
 Age and Ageing 87;:2-2 JAMES McCAUJON* Registrar GORDON P. CANNMGt Senior Registrar ACUTE APPENDICITIS IN THE Registrar Department of Pathology Stobhill General Hospital, Glasgow G2 Summary Acute appendicitis
Age and Ageing 87;:2-2 JAMES McCAUJON* Registrar GORDON P. CANNMGt Senior Registrar ACUTE APPENDICITIS IN THE Registrar Department of Pathology Stobhill General Hospital, Glasgow G2 Summary Acute appendicitis
LAPAROSCOPIC APPENDICECTOMY
 LAPAROSCOPIC APPENDICECTOMY WHAT IS THE APPENDIX? The appendix is a small, fingerlike pouch of the intestinal tract located where the small and large join. It has no known use. It is postulated that the
LAPAROSCOPIC APPENDICECTOMY WHAT IS THE APPENDIX? The appendix is a small, fingerlike pouch of the intestinal tract located where the small and large join. It has no known use. It is postulated that the
A Case Report of Acute Renal Artery Occlusion Mimicking Acute Appendicitis
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 7 Number 1 A Case Report of Acute Renal Artery Occlusion Mimicking Acute Appendicitis S Abouel-Enin, A Douglas, R Morgan Citation S Abouel-Enin, A Douglas,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 7 Number 1 A Case Report of Acute Renal Artery Occlusion Mimicking Acute Appendicitis S Abouel-Enin, A Douglas, R Morgan Citation S Abouel-Enin, A Douglas,
Anatomy of the Large Intestine
 Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
The nontraumatic acute abdomen
 CT features of acute appendicitis: pictorial review Marco ntonio Cura, MD The nontraumatic acute abdomen is one of the most common presentations to the emergency room, with appendicitis being one of the
CT features of acute appendicitis: pictorial review Marco ntonio Cura, MD The nontraumatic acute abdomen is one of the most common presentations to the emergency room, with appendicitis being one of the
Comparative Analysis of Alvarado and Teicher Scores in the Diagnosis of Acute Appendicitis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparative Analysis of Alvarado and Teicher s in the Diagnosis of Acute ABSTRACT Objective Study design Place & Duration of study Methodology Results Conclusion Key words Faran Kiani,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparative Analysis of Alvarado and Teicher s in the Diagnosis of Acute ABSTRACT Objective Study design Place & Duration of study Methodology Results Conclusion Key words Faran Kiani,
Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Role of (Non Gynaecological Causes) Kaleem Ahmad 1, Rishav Kumar Jain 2, Ashok Yadav 3, Shilpa Vahikar 4 1 Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, 2 Professor, Department
Original Research Article Role of (Non Gynaecological Causes) Kaleem Ahmad 1, Rishav Kumar Jain 2, Ashok Yadav 3, Shilpa Vahikar 4 1 Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, 2 Professor, Department
Clinical Scoring System: A Valuable Tool for Decision Making in cases of Acute Appendicitis
 Clinical Scoring System: A Valuable Tool for Decision Making in cases of Acute Appendicitis Pages with reference to book, From 254 To 259 Ambreen Jawaid,Ansul Asad,Arashk Motiei,Asma Munir,Erum Bhutto,Haroon
Clinical Scoring System: A Valuable Tool for Decision Making in cases of Acute Appendicitis Pages with reference to book, From 254 To 259 Ambreen Jawaid,Ansul Asad,Arashk Motiei,Asma Munir,Erum Bhutto,Haroon
CASE SCENARIO EXERCISE
 påçííáëü=pìêîéáää~ååé=çñ=eé~äíüå~êé ^ëëçåá~íéç=fåñéåíáçå=mêçöê~ããé CASE SCENARIO EXERCISE CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION SURVEILLANCE SCOTTISH SURVEILLANCE OF HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED INFECTION
påçííáëü=pìêîéáää~ååé=çñ=eé~äíüå~êé ^ëëçåá~íéç=fåñéåíáçå=mêçöê~ããé CASE SCENARIO EXERCISE CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTION SURVEILLANCE SCOTTISH SURVEILLANCE OF HEALTHCARE ASSOCIATED INFECTION
NON OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF ACUTE APPENDICITIS - IS THIS APPROPRIATE IN SOUTH AFRICA O.D MONTWEDI
 NON OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF ACUTE APPENDICITIS - IS THIS APPROPRIATE IN SOUTH AFRICA O.D MONTWEDI Acute appendicitis is the commonest surgical emergency. About 300000 appendectomies are performed in the
NON OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF ACUTE APPENDICITIS - IS THIS APPROPRIATE IN SOUTH AFRICA O.D MONTWEDI Acute appendicitis is the commonest surgical emergency. About 300000 appendectomies are performed in the
Caeco-colic Intussusception Simulating an Appendicular Mass
 Article ID: WMC003206 ISSN 2046-1690 Caeco-colic Intussusception Simulating an Appendicular Mass Corresponding Author: Dr. Matthew O Adelekan, Surgeon, North manchester General Hospital - United Kingdom
Article ID: WMC003206 ISSN 2046-1690 Caeco-colic Intussusception Simulating an Appendicular Mass Corresponding Author: Dr. Matthew O Adelekan, Surgeon, North manchester General Hospital - United Kingdom
Diverticular Disease Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.
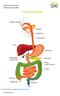 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Diverticular Disease Diverticulum refers to a side-branch or pouch which sticks outwards from the wall
Appendicitis inflammatory response score: a novel scoring system for acute appendicitis
 International Surgery Journal Patil S et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Mar;4(3):1065-1070 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20170863
International Surgery Journal Patil S et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Mar;4(3):1065-1070 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20170863
Original article A Prospective Study of Christian Scoring System and its Co- Relation with Ultrasound in diagnosing Acute Appendicitis
 Original article A Prospective Study of Christian Scoring System and its Co- Relation with Ultrasound in diagnosing Acute Appendicitis Abhinandan. B. Vandakudri*, Sanjay N Koppad*, Arunkumar. Jeedi,*,
Original article A Prospective Study of Christian Scoring System and its Co- Relation with Ultrasound in diagnosing Acute Appendicitis Abhinandan. B. Vandakudri*, Sanjay N Koppad*, Arunkumar. Jeedi,*,
Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases. Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT)
 Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT) Role of ultrasound to rule out Appendicitis Overview: Ultrasound is relatively inexpensive, safe and quick solution to rule
Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT) Role of ultrasound to rule out Appendicitis Overview: Ultrasound is relatively inexpensive, safe and quick solution to rule
Alvarado scores and pain onset in relation to multislice CT findings in acute appendicitis
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2008; 14:14-18 Turkish Society of Radiology 2008 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Alvarado scores and pain onset in relation to multislice CT findings in acute appendicitis Erkan
Diagn Interv Radiol 2008; 14:14-18 Turkish Society of Radiology 2008 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Alvarado scores and pain onset in relation to multislice CT findings in acute appendicitis Erkan
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN
 UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
The Role of Ultrasound in the Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 The Role of Ultrasound in the Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Dr. Richard A. Beable Consultant Gastrointestinal Radiologist Queen Alexandra Hospital Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Topics for Discussion
The Role of Ultrasound in the Assessment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Dr. Richard A. Beable Consultant Gastrointestinal Radiologist Queen Alexandra Hospital Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Topics for Discussion
Management of an Appendiceal Mass - Approach to acute presentation of appendiceal neoplasms
 Management of an Appendiceal Mass - Approach to acute presentation of appendiceal neoplasms Dr. Claudia LY WONG, Department of Surgery, Kwong Wah Hospital Joint Hospital Surgical Grand Round Presentation,
Management of an Appendiceal Mass - Approach to acute presentation of appendiceal neoplasms Dr. Claudia LY WONG, Department of Surgery, Kwong Wah Hospital Joint Hospital Surgical Grand Round Presentation,
Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis
 The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
DIVERTICULOSIS MEDICAL AND SURGICAL MANAGEMENT. Simon Radley Consultant Surgeon March 2013
 DIVERTICULOSIS MEDICAL AND SURGICAL MANAGEMENT Simon Radley Consultant Surgeon March 2013 Definitions Diverticulosis: presence of diverticulae Diverticular disease: diverticulae associated with symptoms
DIVERTICULOSIS MEDICAL AND SURGICAL MANAGEMENT Simon Radley Consultant Surgeon March 2013 Definitions Diverticulosis: presence of diverticulae Diverticular disease: diverticulae associated with symptoms
12 Blueprints Q&A Step 2 Surgery
 12 Blueprints Q&A Step 2 Surgery 34. A 40-year-old female has been referred to you for a recent ER and hospital admission, from which she was given a diagnosis of acute diverticulitis. Treatment at that
12 Blueprints Q&A Step 2 Surgery 34. A 40-year-old female has been referred to you for a recent ER and hospital admission, from which she was given a diagnosis of acute diverticulitis. Treatment at that
IV and Oral contrast vs. IV contrast alone computed tomography for the visualization of appendix and diagnosis of appendicitis in adult ED patients
 IV and Oral contrast vs. IV contrast alone computed tomography for the visualization of appendix and diagnosis of appendicitis in adult ED patients Aman Wadhwani, MD/MSc-Candidate Lancia Guo, MD Erik Saude,
IV and Oral contrast vs. IV contrast alone computed tomography for the visualization of appendix and diagnosis of appendicitis in adult ED patients Aman Wadhwani, MD/MSc-Candidate Lancia Guo, MD Erik Saude,
DESPITE advances in diagnostic technics the early recognition of appendicitis
 'MISSED' APPENDICITIS: A CONTINUING DIAGNOSTIC CHALLENGE Report of a Case RICHARD G. FARMER, M.D., Department of Gastroenterology and RUPERT B. TURNBULL, JR., M.D. Department of General Surgery DESPITE
'MISSED' APPENDICITIS: A CONTINUING DIAGNOSTIC CHALLENGE Report of a Case RICHARD G. FARMER, M.D., Department of Gastroenterology and RUPERT B. TURNBULL, JR., M.D. Department of General Surgery DESPITE
Alvarado score: can it reduce unnecessary interventions for acute appendicitis in children?
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2017; 3(23): 115-120 10.1515/arsm-2017-0020 Chisalau V.1, Tica C.2, Chirila S.2, Ionescu C.2 Alvarado score: can it reduce unnecessary interventions for acute appendicitis in children?
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2017; 3(23): 115-120 10.1515/arsm-2017-0020 Chisalau V.1, Tica C.2, Chirila S.2, Ionescu C.2 Alvarado score: can it reduce unnecessary interventions for acute appendicitis in children?
The vermiform appendix is a small vermain tube of length
 Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2395-1893 DOI: 10.17354/SUR/2018/155 Original Article Retrospective Study of Single Dose of Antibiotic in Laparoscopic Appendectomy O Siddharth, B Ramakrishna Assistant
Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2395-1893 DOI: 10.17354/SUR/2018/155 Original Article Retrospective Study of Single Dose of Antibiotic in Laparoscopic Appendectomy O Siddharth, B Ramakrishna Assistant
General Data. 王 X 村 78 y/o 男性
 General Data 王 X 村 78 y/o 男性 Chief Complaint Vomiting twice this early morning Fever up to 38.9ºC was noted Present Illness (1) Old CVA with left side weakness for more than 10 years and with bed ridden
General Data 王 X 村 78 y/o 男性 Chief Complaint Vomiting twice this early morning Fever up to 38.9ºC was noted Present Illness (1) Old CVA with left side weakness for more than 10 years and with bed ridden
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ROLE OF ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN PRE-OPERATIVE EVALUATION OF RIGHT ILIAC FOSSA MASS
 ROLE OF ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN PRE-OPERATIVE EVALUATION OF RIGHT ILIAC FOSSA MASS Madhushankar L 1, Satish Kumar R 2, Sanjay S.C 3, Laxmikanta. L 4, Hemanth V 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Madhushankar L, Satish
ROLE OF ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN PRE-OPERATIVE EVALUATION OF RIGHT ILIAC FOSSA MASS Madhushankar L 1, Satish Kumar R 2, Sanjay S.C 3, Laxmikanta. L 4, Hemanth V 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Madhushankar L, Satish
Khanal BR, Ansari MA, Pradhan S Department of Radiology and Imaging, Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital, Maharajgunj, Kathmandu, Nepal.
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2008), Vol. 6, No. 1, Issue 21, 70-74 Original Article Accuracy of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis Khanal BR, Ansari MA, Pradhan S Department
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2008), Vol. 6, No. 1, Issue 21, 70-74 Original Article Accuracy of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis Khanal BR, Ansari MA, Pradhan S Department
2. Blunt abdominal Trauma
 Abdominal Trauma 1. Evaluation and management depends on: a. Mechanism (Blunt versus Penetrating) b. Injury complex in addition to abdomen c. Haemodynamic stability assessment: i. Classically patient s
Abdominal Trauma 1. Evaluation and management depends on: a. Mechanism (Blunt versus Penetrating) b. Injury complex in addition to abdomen c. Haemodynamic stability assessment: i. Classically patient s
SIMPLE GUIDE FOR SONOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF APPENDICITIS
 SIMPLE GUIDE FOR SONOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF APPENDICITIS A Case Study by Dr. Avni K P Skandhan, India (Consultant Radio Diagnosis, Malabar Institute of Medical Science, Malappuram, Kerala) Email: avniskandhan@gmail.com
SIMPLE GUIDE FOR SONOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF APPENDICITIS A Case Study by Dr. Avni K P Skandhan, India (Consultant Radio Diagnosis, Malabar Institute of Medical Science, Malappuram, Kerala) Email: avniskandhan@gmail.com
Ruptured Acute Appendicitis With Calcified Appendicolith Mimicking Acute Gastroenteritis
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 12 Number 1 Ruptured Acute Appendicitis With Calcified Appendicolith Mimicking Acute Gastroenteritis M Akinkunmi, O Fadiran Citation M Akinkunmi, O Fadiran.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 12 Number 1 Ruptured Acute Appendicitis With Calcified Appendicolith Mimicking Acute Gastroenteritis M Akinkunmi, O Fadiran Citation M Akinkunmi, O Fadiran.
Laparoscopy for diagnosing equivocal appendicitis. Oscar Duffy Surgical Intern Cork University Hospital
 Laparoscopy for diagnosing equivocal appendicitis Oscar Duffy Surgical Intern Cork University Hospital Treatment is straightforward diagnosis is not Negative appendicectomy rate 15-33% but can be as high
Laparoscopy for diagnosing equivocal appendicitis Oscar Duffy Surgical Intern Cork University Hospital Treatment is straightforward diagnosis is not Negative appendicectomy rate 15-33% but can be as high
The Epidemiology of Appendicitis and Appendectomy in India: An Observational Study
 The Epidemiology of Appendicitis and Appendectomy in India: An Observational Study Raj Kumar Mishra 1, Prateek Goel 2*, Rajeev Sharma 3, A C Sharma 4 1Assistant Professor, 2* Senior Resident, 4 Associate
The Epidemiology of Appendicitis and Appendectomy in India: An Observational Study Raj Kumar Mishra 1, Prateek Goel 2*, Rajeev Sharma 3, A C Sharma 4 1Assistant Professor, 2* Senior Resident, 4 Associate
Ct Of The Acute Abdomen Medical Radiology
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with ct of the acute abdomen
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with ct of the acute abdomen
Clinical Anatomy of the Biliary Apparatus: Relations & Variations
 Clinical Anatomy of the Biliary Apparatus: Relations & Variations Handout download: http://www.oucom.ohiou.edu/dbms-witmer/gs-rpac.htm 27 March 2007 Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Professor of Anatomy Department
Clinical Anatomy of the Biliary Apparatus: Relations & Variations Handout download: http://www.oucom.ohiou.edu/dbms-witmer/gs-rpac.htm 27 March 2007 Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Professor of Anatomy Department
Investigating the Impact of the Amount of Contrast Material used in Abdominal CT Examinations Regarding the Diagnosis of Appendicolith
 Research Article Investigating the Impact of the Amount of Contrast Material used in Abdominal CT Examinations Regarding the Diagnosis of Appendicolith Eleftherios Lavdas 1,2, Nadia Boci 2, Lia Sarantaenna
Research Article Investigating the Impact of the Amount of Contrast Material used in Abdominal CT Examinations Regarding the Diagnosis of Appendicolith Eleftherios Lavdas 1,2, Nadia Boci 2, Lia Sarantaenna
Pediatric Surgical Emergencies Veronica Victorian, PA-C
 Pediatric Surgical Emergencies Veronica Victorian, PA-C Texas Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric General Surgery Assistant Professor, Baylor College of Medicine Objectives 1. Define Pediatric Surgical
Pediatric Surgical Emergencies Veronica Victorian, PA-C Texas Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric General Surgery Assistant Professor, Baylor College of Medicine Objectives 1. Define Pediatric Surgical
Original Article Validity of Modified Alvarado Scoring System Pak Armed Forces Med J 2017; 67 (5):
 Open Access Original Article Validity of Modified Alvarado Scoring System Pak Armed Forces Med J 2017; 67 (5): 813-18 VALIDITY OF MODIFIED ALVARADO SCORING SYSTEM (MASS) IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF ACUTE APPENDICITIS
Open Access Original Article Validity of Modified Alvarado Scoring System Pak Armed Forces Med J 2017; 67 (5): 813-18 VALIDITY OF MODIFIED ALVARADO SCORING SYSTEM (MASS) IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF ACUTE APPENDICITIS
PATH Inflammation Module - Student Worksheet
 PATH2220 - Inflammation Module - Student Worksheet Prof Jennet Harvey Dr Ben Dessauvagie Learning Outcomes By the end of the class, students will be able to: Learning Outcome 1: describe the inflammatory
PATH2220 - Inflammation Module - Student Worksheet Prof Jennet Harvey Dr Ben Dessauvagie Learning Outcomes By the end of the class, students will be able to: Learning Outcome 1: describe the inflammatory
Case Report Urachal Cyst Causing Small Bowel Obstruction in an Adult with a Virgin Abdomen
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 3247087, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3247087 Case Report Urachal Cyst Causing Small Bowel Obstruction in an Adult with a Virgin Abdomen Michael
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 3247087, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3247087 Case Report Urachal Cyst Causing Small Bowel Obstruction in an Adult with a Virgin Abdomen Michael
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Alison Douglass Gillian Lieberman, MD. November. Colon Cancer. Alison Douglass, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD
 November Colon Cancer Alison Douglass, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient Mr. K. is a 67 year old man with no prior medical problems other than hemorrhoids which have caused occasional rectal
November Colon Cancer Alison Douglass, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient Mr. K. is a 67 year old man with no prior medical problems other than hemorrhoids which have caused occasional rectal
Endometriosis of the Appendix Resulting in Perforated Appendicitis
 27 Endometriosis of the Appendix Resulting in Perforated Appendicitis Toru Hasegawa a Koichi Yoshida b Kazuhiro Matsui c a Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toyama,
27 Endometriosis of the Appendix Resulting in Perforated Appendicitis Toru Hasegawa a Koichi Yoshida b Kazuhiro Matsui c a Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toyama,
Specialespecifikt kursus i Patologisk Anatomi 2009: Fordøjelseskanalens patologi APPENDIX
 Specialespecifikt kursus i Patologisk Anatomi 2009: Fordøjelseskanalens patologi APPENDIX Appendix Occurrence of lesions (%) Acute appendicitis 72 Normal 16 Fibrosis 3 (Cyst-)Adenoma 3 Diverticulitis
Specialespecifikt kursus i Patologisk Anatomi 2009: Fordøjelseskanalens patologi APPENDIX Appendix Occurrence of lesions (%) Acute appendicitis 72 Normal 16 Fibrosis 3 (Cyst-)Adenoma 3 Diverticulitis
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v5i6.1 Clinical-Epidemiological Study of Abdominal
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v5i6.1 Clinical-Epidemiological Study of Abdominal
Appendicitis Care Map. Go directly to Care Map Flowchart
 Appendicitis Care Map Go directly to Care Map Flowchart How to Use Reference Icons Go directly to Care Map Flowchart When accessing a document, please use the browser return arrow (upper left-hand corner)
Appendicitis Care Map Go directly to Care Map Flowchart How to Use Reference Icons Go directly to Care Map Flowchart When accessing a document, please use the browser return arrow (upper left-hand corner)
Intestinal Obstruction Clinical Presentation & Causes
 Intestinal Obstruction Clinical Presentation & Causes V Chidambaram-Nathan Consultant Transplant and General Surgeon Sheffield Kidney Institute Northern General Hospital Intestinal Obstruction One of the
Intestinal Obstruction Clinical Presentation & Causes V Chidambaram-Nathan Consultant Transplant and General Surgeon Sheffield Kidney Institute Northern General Hospital Intestinal Obstruction One of the
Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1-
 Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1- Objectives To know radiology modalities used in abdomen imaging mainly GI tract. To know advantages and disadvantages of each modality. To know indications and contraindications
Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1- Objectives To know radiology modalities used in abdomen imaging mainly GI tract. To know advantages and disadvantages of each modality. To know indications and contraindications
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
US diagnosis of acute appendicitis
 US diagnosis of acute appendicitis Poster No.: C-1496 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: GI Tract Authors: A. Gligorievski; Skopje/MK Keywords: Ultrasound, Acute appendicitis, Diagnosis
US diagnosis of acute appendicitis Poster No.: C-1496 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: GI Tract Authors: A. Gligorievski; Skopje/MK Keywords: Ultrasound, Acute appendicitis, Diagnosis
Acute Pancreatitis: Role of Imaging Modalities
 International Journal of Interdisciplinary and Multidisciplinary Studies (IJIMS), 2015, Vol 2, No.9,109-114. 109 Available online at http://www.ijims.com ISSN: 2348 0343 Abstract Acute Pancreatitis: Role
International Journal of Interdisciplinary and Multidisciplinary Studies (IJIMS), 2015, Vol 2, No.9,109-114. 109 Available online at http://www.ijims.com ISSN: 2348 0343 Abstract Acute Pancreatitis: Role
Children's (Pediatric) Ultrasound - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) Ultrasound - Abdomen Children s (pediatric) ultrasound imaging of the abdomen is a safe, noninvasive test that uses sound waves to produce a clear picture of
Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) Ultrasound - Abdomen Children s (pediatric) ultrasound imaging of the abdomen is a safe, noninvasive test that uses sound waves to produce a clear picture of
Study of post cholecystectomy biliary leakage and its management
 Original Research Article Study of post cholecystectomy biliary leakage and its management P. Krishna Kishore 1*, B. Manju Sruthi 2, G. Obulesu 3 1 Assistant Professor, Departmentment of General Surgery,
Original Research Article Study of post cholecystectomy biliary leakage and its management P. Krishna Kishore 1*, B. Manju Sruthi 2, G. Obulesu 3 1 Assistant Professor, Departmentment of General Surgery,
HKCEM JCM OSCE. 06 March 3013 AED POH
 HKCEM JCM OSCE 06 March 3013 AED POH 1 Case 1 M/52 Walk unaided to AED c/o left foot sprain few days ago during working P/E swelling, tender over dorsum of foot 2 3 Questions What were the X ray findings
HKCEM JCM OSCE 06 March 3013 AED POH 1 Case 1 M/52 Walk unaided to AED c/o left foot sprain few days ago during working P/E swelling, tender over dorsum of foot 2 3 Questions What were the X ray findings
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery
 World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 2 2013 Article 18 Revenge of the Christmas Turkey; Unusual Presentation of Colonic Perforation Secondary to Foreign Body. Mashuk Khan Sudeep Thomas Warwick
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 2 2013 Article 18 Revenge of the Christmas Turkey; Unusual Presentation of Colonic Perforation Secondary to Foreign Body. Mashuk Khan Sudeep Thomas Warwick
Management of acute abdomen: Study of 110 cases
 Original Research Article Management of acute abdomen: Study of 110 cases Samir Ray 1, Manthan Patel 2, Hiren Parmar 3* 1 Associate Professor, Department of Surgery, GMERS Medical College, Gotri, Vadodara,
Original Research Article Management of acute abdomen: Study of 110 cases Samir Ray 1, Manthan Patel 2, Hiren Parmar 3* 1 Associate Professor, Department of Surgery, GMERS Medical College, Gotri, Vadodara,
Appendiceal diverticular disease
 Formosan Journal of Surgery (2013) 46, 4e9 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-fjs.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Appendiceal diverticular disease Yun-Wu Deng a, Hsiao-Bai Yang b,e,
Formosan Journal of Surgery (2013) 46, 4e9 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-fjs.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Appendiceal diverticular disease Yun-Wu Deng a, Hsiao-Bai Yang b,e,
