PELVIC IMAGING GUIDELINES 2007 MedSolutions, Inc
|
|
|
- Ross Dorsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MedSolutions, Inc. Clinical Decision Support Tool Diagnostic Strategies This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations that are not specifically addressed will require physician review. Consultation with the referring physician, specialist and/or patient s Primary Care Physician (PCP) may provide additional insight. PELVIC IMAGING GUIDELINES 2007 MedSolutions, Inc MedSolutions, Inc. Clinical Decision Support Tool for Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Common symptoms and symptom complexes are addressed by this tool. Imaging requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations that are not specifically addressed will require physician review. Consultation with the referring physician may provide additional insight. This version incorporates MSI accepted revisions prior to 11/30/ MedSolutions, Inc. Pelvic Imaging Guidelines Page 1 of 15
2 ABBREVIATIONS for PELVIC GUIDELINES CA-125: cancer antigen 125 test CT: computed tomography GTN: gestational trophoblastic neoplasia HCG: human chorionic gonadotropin KUB: kidneys, ureters, bladder (plain frontal supine radiograph of the abdomen) MRA: magnetic resonance angiography MRI: magnetic resonance imaging msv: millisievert PA: posteroanterior projection PID: pelvic inflammatory disease TA: transabdominal TV: transvaginal WBC: white blood cell count 2007 MedSolutions, Inc. Pelvic Imaging Guidelines Page 2 of 15
3 PV-1~GENERAL GUIDELINES...4 PV-2~ABNORMAL UTERINE BLEEDING 4 PV-3~ADENOMYOSIS.4 PV-4~SUSPECTED ADNEXAL MASS..5 PV-5~ENDOMETRIOSIS.6 PV-6~PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE (PID)..6 PV-7~PELVIC PAIN, FEMALE 7 PV-8~LEIOMYOMATA.7 PV-9~PERIURETHRAL CYSTS AND URETHRAL DIVERTICULA.8 PV-10~ UTERINE ANOMALIES.8 PV-11~ FETAL MRI..8 PV-12 ~ MOLAR PREGNANCY AND GESTATIONAL..9 PV-13~ PELVIMETRY..9 PV-14~IMPOTENCE/ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION..9 PV-15 PROSTATITIS/PUDENDAL NEURALGIA/CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN.10 PV-16~SCROTAL PATHOLOGY..10 PV-17~UNDESCENDED TESTIS.10 PV-18~FISTULA IN ANO...11 PV-3 ~ ADENOMYOSIS.12 Evidence Based Clinical Support..12 PV-4 ~ SUSPECTED ADNEXAL MASS..12 Evidence Based Clinical Support.. 12 PV-8 ~ LEIOMYOMATA..12 Evidence Based Clinical Support..12 PV-13 ~ PELVIMETRY 13 Evidence Based Clinical Support...13 REFERENCES.14 PEDIATRIC TABLE OF CONTENTS PV-1~GENERAL GUIDELINES...4 PV-11~ FETAL MRI..8 PV-17~UNDESCENDED TESTIS MedSolutions, Inc. Pelvic Imaging Guidelines Page 3 of 15
4 PELVIC IMAGING GUIDELINES PV-1~GENERAL GUIDELINES Abdominal imaging begins at the diaphragm and extends to the umbilicus or iliac crest. Pelvic imaging begins at the umbilicus and extends to the pubis. CT imaging is a more generalized modality. MRI imaging is preferred as a more targeted study, in cases of renal failure, or for patients allergic to iodinated contrast. CT of each body area delivers about 10 msv of ionizing radiation. For each 10 msv of radiation, the risk of developing a future cancer according to the BEIR VII report is 1:1000 to 1:2000 (chest x-ray, PA/Lateral = 0.4 msv; KUB abdomen = 1.5 msv). o Radiation exposure is particularly important in children and women of child bearing age. o To avoid radiation exposure, pediatric imaging should consider the use of ultrasound or MRI where it is a clinical option. o To avoid radiation exposure, pregnant women should be evaluated by ultrasound or MRI where it is a clinical option. Pelvic CT or MRI may be indicated to further evaluate abnormalities seen on other imaging modalities such as plain x-rays, ultrasound, etc. Pediatric guidelines: The Pelvic guidelines are the same for both the pediatric population and the adult population, unless there are specific Pediatric guidelines (highlighted in yellow). PELVIC SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS FEMALE PV-2~ABNORMAL UTERINE BLEEDING Initial evaluation includes ultrasound, saline infusion sonography,* hysteroscopy and possible biopsy. MRI pelvis without contrast (CPT 72195) is indicated only if other tests are equivocal and the MRI results will affect treatment. *Obstet Gynecol 2003;102: Gynecology specialist evaluation is helpful for women with abnormal uterine bleeding.* *Management of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding. Slide presentation modified from: APGO Educational Series on Women s Health Issues PV-3~ADENOMYOSIS Adenomyosis is a histologic diagnosis and imaging has limitations. Adenomyosis is suspected by history and physical examination MedSolutions, Inc. Pelvic Imaging Guidelines Page 4 of 15
5 Pelvic ultrasound is the primary screening modality for imaging the female pelvis. Transvaginal ultrasonography (along with color Doppler ultrasound) is the diagnostic procedure of choice for the initial evaluation of suspected adenomyosis and is useful to evaluate other potential etiologies of the patient s symptoms. If transvaginal ultrasound is inconclusive and a more definitive diagnosis is necessary because invasive treatment is being considered, MRI pelvis without contrast (CPT 72195) can be useful. If hormonal therapy is going to be tried first, then MRI is not indicated in patients with suspected adenomyosis. PV-4~SUSPECTED ADNEXAL MASS Adnexal masses have a long list of diagnostic possibilities and ultrasound results must be correlated with history and laboratory testing. Transabdominal (TA) and transvaginal (TV) ultrasound imaging techniques should be combined for the evaluation of adnexal masses. o Color Doppler ultrasound may be helpful in selected situations. Sonographic identification of a simple cystic mass establishes a benign process in almost 100% of premenopausal women and 95% of postmenopausal women. o Adnexal cysts 5 cm or smaller in postmenopausal women are not considered malignant, although a 3 cm to 5 cm cyst may need correlation with CA-125 and color Doppler findings. Complex adnexal masses are usually ovarian in origin, and in premenopausal women, most commonly represent hemorrhagic cysts or endometriomas. o Ultrasound characteristics usually suggest the diagnosis, and in premenopausal women, a follow up ultrasound can be done in six weeks or following a menstrual cycle to evaluate for resolution. o A pregnancy test is important to narrow the differential diagnosis. In postmenopausal women with a complex adnexal mass by ultrasound, MRI pelvis without and with contrast (CPT 72197) may be indicated for further characterization.* *ACR Appropriateness Criteria for Women s Imaging, 2002 *Radiol. Clin. North Am 2002 May;40(3): MRI pelvis without and with contrast (CPT 72197) is superior to CT scan (CT is useful only when the identification of fat and calcifications is important, such as in benign teratoma) in evaluating whether a complex adnexal mass is ovarian cancer when ultrasound is indeterminate. o The probability that a lesion is ovarian cancer in a premenopausal woman with an indeterminate ovarian mass on ultrasound decreases to less than 2% with a negative MRI.* 2007 MedSolutions, Inc. Pelvic Imaging Guidelines Page 5 of 15
6 *Radiology 2005;236:85-94 Complex or solid ovarian masses may require surgical removal. o With complex or solid ovarian masses, preoperative evaluation of the abdomen and pelvis without and with contrast using CT (CPT and 72194) or MRI (CPT and 72197) can be performed. PV-5~ENDOMETRIOSIS Endometriosis is a surgical diagnosis and imaging is of little value unless the pelvic clinical exam is abnormal. Pelvic ultrasound is the first line diagnostic exam for suspected endometriosis. o Although ultrasound is able to diagnose endometriosis in most locations, it has limited sensitivity for posterior locations such as uterosacral ligaments, cul-de-sac of Douglas, torus uterinus, vagina, rectosigmoid, and occasionally the bladder. In most patients, ultrasound followed by medical treatment or laparoscopy should be considered prior to advanced imaging. o Laparoscopy remains the definitive test for diagnosis and evaluation of endometriosis in most patients.* *Eur Radiol 2006 Feb;16(2): *ACOG Committee Opinion, Number 310, April 2005 MRI has shown high accuracy for both anterior and posterior endometriosis and can enable complete lesion mapping prior to surgery.* o MRI pelvis without and with contrast (CPT 72197) can be considered for preoperative planning. This is the minority of patients and MRI should not, in general, be used for diagnosing endometriosis in women with pelvic pain. *Eur Radiol 2006 Feb;16(2): *Aeby TC, Hiraoka MKY. Endometriosis. Updated May 15, Accessed November 20, 2006 PV-6~PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE (PID) Ultrasound is the initial study for imaging of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) that does not respond well to antibiotic therapy or for complicated PID. In rare cases where there is extensive abscess formation or a percutaneous drainage procedure is planned, CT of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast (CPT and CPT 72193) may be helpful MedSolutions, Inc. Pelvic Imaging Guidelines Page 6 of 15
7 PV-7~PELVIC PAIN, FEMALE Pelvic ultrasound remains the imaging study of choice for the initial evaluation of pelvic pain, with color Doppler ultrasound where ovarian torsion is a consideration. Advanced imaging is generally not indicated for pelvic pain unless accompanied by fever, elevated WBC or palpable mass, the pelvic ultrasound is nondiagnostic or equivocal, or there is a suspicious pelvic exam. In this setting, CT pelvis with contrast (CPT 72193) can be performed. PV-8~LEIOMYOMATA Transabdominal and transvaginal ultrasound are the preferred screening procedures for leiomyomata. Preoperative ultrasound should be performed prior to myomectomy. o If ultrasound is indeterminate, MRI pelvis without contrast (CPT 72195) may be considered. o MRI pelvis without and with contrast (CPT 72197) can be performed if leiomyoma necrosis is suspected. MRI pelvis without and with contrast (CPT 72197) is warranted in those cases in which arterial embolization is contemplated. MRI accurately assesses the number, location, and size of leiomyomata for pretreatment planning and post treatment response.* *AJR 2003;181: There is no literature support for the addition of MRA pelvis (CPT 72198) to the preoperative evaluation. There are currently no published guidelines regarding follow up MRI in patients who have undergone uterine artery embolization. o Although there are no compelling data to support the need for follow up MRI in asymptomatic patients who are status post uterine artery embolization, consensus opinion suggests that one follow up pelvic MRI (CPT 72197) post embolization will be allowed 3 to 6 months after the procedure. o In patients with persistent or recurrent symptoms, pelvic MRI without and with contrast (CPT 72197) should be performed. o In patients with fever, pain, or other acute symptoms status post embolization, pelvic MRI without and with contrast (CPT 72197) should be performed MedSolutions, Inc. Pelvic Imaging Guidelines Page 7 of 15
8 PV-9~PERIURETHRAL CYSTS AND URETHRAL DIVERTICULA Also see AB-37 Urinary Tract Infection (last bullet). Symptomatic infection of congenital periurethral glands can result in urethral diverticula. Symptoms include pain, urinary urgency, frequency of urination, recurrent urinary tract infection, dribbling after urination, or incontinence. o MRI pelvis without and with contrast (CPT 72197) is superior to transvaginal ultrasound for evaluating these entities but should be reserved for patients in whom ultrasound, voiding cytourethrography, or retrograde urethography are equivocal.* *ACR Appropriateness Criteria, Recurrent Lower Urinary Tract Infections in Women, 2005 PV-10~ UTERINE ANOMALIES In the detection of uterine anomalies, particularly during infertility evaluation, transabdominal and transvaginal ultrasound are the initial imaging modalities of choice. If ultrasound defines a complex anomaly or is not definitive, then pelvic MRI without contrast (CPT 72195) is recommended.* *Radiographics 2003; 23: and PREGNANCY RELATED PV-11~ FETAL MRI Ultrasound (ideally performed at a tertiary care center) remains the predominant modality for evaluating disorders related to the fetus and pregnancy overall. MRI is used as an adjunct to ultrasound in evaluating fetal abnormalities. Most fetal MRI imaging occurs after 18 weeks gestation. Fetal MRI should be performed using sedation. Studies should be coded as noncontrast MRI abdomen and pelvis (CPT and 72195). The most common use of fetal MRI is to evaluate central nervous system abnormalities. Neural tube defects are usually well evaluated by ultrasound. Abnormalities in the fetal thorax, such as congenital diaphragmatic hernia and fetal lung development can also be evaluated by fetal MRI. Fetal MRI can be helpful in detecting fetal genitourinary abnormalities in pregnancies complicated by oligohydramnios. MRI is helpful in the antenatal evaluation of conjoined twins in whom postnatal separation is being anticipated MedSolutions, Inc. Pelvic Imaging Guidelines Page 8 of 15
9 The added utility of fetal MRI in the evaluation of organ systems other than central nervous system, thorax, and urogenital system has not yet been demonstrated.* *Applied Radiology 2004;33:9-25 PV-12 ~ MOLAR PREGNANCY AND GESTATIONAL TROPHOBLASTIC NEOPLASIA (GTN) A recurrent molar pregnancy is called gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN). These cells can metastasize to other organs such as lungs, brain, bone, and vagina. Treatment is usually methotrexate. Patients should have head CT without and with contrast (CPT 70470), CT abdomen and pelvis with contrast (CPT and 72193), and chest x- ray as a metastatic work up. Weekly HCG tests are performed until they fall to zero. PV-13~ PELVIMETRY Pelvimetry for cephalic dystocia (failure to progress in active labor because of a disproportion between the fetal head and the size of the bony pelvis) is investigational. Pelvimetry may be done for breech presentations in which vaginal delivery is anticipated. Pelvimetry is usually done with plain x-ray, low dose CT pelvis without contrast (CPT 72192), or MRI pelvis without contrast (CPT 72195). o Low dose CT is institution specific and if protocol is not followed, the fetus will receive full ionizing radiation dose. References: o Obstet Gynecol 2004;104: o Obstet Gynecol 2003:102: PELVIC SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS MALE PV-14~IMPOTENCE/ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION Brain MRI without and with contrast (CPT 70553) should be restricted to hypogonadism as documented by low bio-available/free testosterone of <20 ng/dl or total serum testosterone of less than 80% of the lower limit of normal (i.e. <150 ng/dl is lower limits for most labs), or patients with elevated prolactin. o Also see HD-28 Male hypogonadism in the Head guidelines Erectile dysfunction is frequently an early symptom of peripheral vascular disease MedSolutions, Inc. Pelvic Imaging Guidelines Page 9 of 15
10 o Also see PVD-1 General Guidelines (Bullet 5) in the Peripheral Vascular Disease guidelines. Functional MRI or PET studies are considered investigational. Reference: o J Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2001:86(6): PV-15 PROSTATITIS/PUDENDAL NEURALGIA/CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN Chronic prostatitis is a clinical diagnosis and advanced imaging is not indicated. Urology consultation is helpful in patients with Pudendal Neuralgia/ Chronic Pelvic Pain. o Confirmatory tests include Pudendal Nerve Terminal Motor Latency Test and Quantitative Sensory Threshold Test. o MRI of the lumbar spine without contrast (CPT 72148) and/or sacral plexus MRI without contrast (CPT 72195) may be requested but are rarely abnormal. * *Antolak SJ, Jr. Male Pelvic Pain. International Pelvic Pain Society, Atlanta, GA, October 2005 PV-16~SCROTAL PATHOLOGY Acute scrotal pain, masses, trauma, inguinal hernia, variocele, or inflammation should be evaluated by ultrasound. MRI in these patients is not supported by evidence-based data.* *ACR Appropriateness Criteria, Acute Onset Scrotal Pain, 2005 PV-17~UNDESCENDED TESTIS Men or boys with a history of cryptorchid (undescended) testes have a several fold risk increase of testicular cancer. Therefore, it is important to diagnose and treat this condition either by bringing the undescended testis into the scrotum, or resecting the testis. o MRI abdomen and pelvis without and with contrast (CPT and 72197) can be performed. MRI pelvis without and with contrast (CPT 72197) can be used to evaluate abnormalities of the scrotum if ultrasound is inconclusive. Children should be evaluated initially with ultrasound, and if inconclusive, MRI pelvis (CPT 72197) can be performed.* CT and MRI have a high false negative rate and in general are not reliable as diagnostic tools. o Urology evaluation is helpful in determining the most appropriate imaging pathway MedSolutions, Inc. Pelvic Imaging Guidelines Page 10 of 15
11 Undescended Testicle or Cryptorchidism. Cornell University Dept. of Urology, Accessed November 21, 2006 MISCELLANEOUS PV-18~FISTULA IN ANO MRI pelvis without and with contrast (CPT 72197) is indicated for the assessment of complex or recurrent fistulas. Preoperative MRI frequently alters the surgical approach and MRI guided surgery can significantly decrease postoperative recurrence in complex cases by 75%.* * AJR 2004;183: MedSolutions, Inc. Pelvic Imaging Guidelines Page 11 of 15
12 PV-3 ~ ADENOMYOSIS Evidence Based Clinical Support Adenomyosis is characterized by benign invasion of ectopic endometrium into the myometrium with hyperplasia of adjacent smooth muscle. Common symptoms include dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia, and abnormal uterine bleeding, and enlarged uterus. Differentiation of adenomyosis from leiomyoma is important because treatment will differ. Hysterectomy is the only definitive treatment for symptomatic adenomyosis. Embolization of adenomyosis has poor long term results with only 55% of treated patients showing clinical improvement after 2 years.* *Radiology 2005;234: The only way to accurately diagnose adenomyosis is pathologically after hysterectomy. Transvaginal ultrasound has a reported sensitivity of 53%-89% in diagnosing adenomyosis, and a specificity of 67%-98%.* *Radiographics 2005;25:21-40 MRI has a sensitivity of 78%-88% and specificity of 67%-93% in diagnosing adenomyosis.* *Radiographics 2005;25:21-40 PV-4 ~ SUSPECTED ADNEXAL MASS Evidence Based Clinical Support A study of 505 consecutive resected adnexal masses over 3.5 years showed that 457 (90%) were benign. Lesions smaller than 4 cm were benign in 211 of 218 cases (97%). 246 of 287 lesions (86%) larger than 4 cm were benign. Every lesion that did not have a solid component was benign. Every non-benign lesion had some solid component. 244 of 250 (98%) of lesions without Doppler flow were benign, while lesions with flow were benign in 76 of 106 (72%) cases.* *RSNA meeting 2003 PV-8 ~ LEIOMYOMATA Evidence Based Clinical Support For uterine artery embolization, size of the dominant fibroid must be considered. Some studies have reported treatment failure to be more likely with fibroids >8 cm.* *Obstet Gynecol Surv 2002;57: MedSolutions, Inc. Pelvic Imaging Guidelines Page 12 of 15
13 Interventional radiologists have, as part of their protocol, a follow-up MRI post embolization generally 3 to 6 months post procedure in asymptomatic patients. MRI results are used for prediction, and for some, any gadolinium accumulation is followed by another embolization. PV-13 ~ PELVIMETRY Evidence Based Clinical Support Low Dose CT utilizes a single view with 0.25 msv radiation exposure, but most facilities will do multiple views with total exposure of 10 msv (same as a normal CT pelvis) MedSolutions, Inc. Pelvic Imaging Guidelines Page 13 of 15
14 PELVIC GUIDELINE REFERENCES PV-2~Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Breitkopf D, Goldstein SR, Seeds JW. ACOG Committee on Gynecologic Practice. ACOG technology assessment in obstetrics and gynecology. Number 3, September Saline infusion sonohysterography. Obstet Gynecol 2003;102: Management of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding. Slide presentation modified from: APGO Educational Series on Women s Health Issues. PV-4~Suspected Adnexal Mass ACR Appropriateness Criteria for Women's Imaging, 2002 Funt SA, Hann LE. Detection and characterization of adnexal masses. Radiol Clin North Am 2002 May;40(3): Kinkel K, Lu Y, Mehdizade A, et al. Indeterminate ovarian mass at US: incremental value of second imaging test for characterization--meta-analysis and Bayesian analysis. Radiology 2005;236: PV-5~Endometriosis Kinkel K, Frel KA, Balleyguier C, Chapron C. Diagnosis of endometriosis with imaging: a review. Eur Radiol 2006 Feb;16(2): ACOG Committee Opinion, Number 310, Endometriosis in Adolescents. Obstet Gynecol 2005 April;105: Aeby TC, Hiraoka MKY. Endometriosis. Updated May 15, Accessed November 20, PV-8~Leiomyomata Jha RC, Takahoma J, Imaoka I. Adenomyosis: MRI of the uterus treated with uterine artery embolization. AJR 2003;181: PV-9~Periurethral Cysts and Urethral Diverticula ACR Appropriateness Criteria, Recurrent Lower Urinary Tract Infections in Women, 2005 PV-10~Uterine Anomalies Imaoka I, Wada A, Matsuo M, et al. MR imaging of disorders associated with female infertility: use in diagnosis, treatment, and management. Radiographics 2003; 23: Kido A, Togashi K, Koyama T, et al. Diffusely enlarged uterus: evaluation with MR imaging. Radiographics 2003; 23: PV-11~Fetal MRI Brown SD, Estroff JA, Barnewolt CE. Fetal MRI. Applied Radiology 2004; 33: MedSolutions, Inc. Pelvic Imaging Guidelines Page 14 of 15
15 PV-13~Pelvimetry ACOG Committee on Obstetric Practice. ACOG Committee Opinion. Number 299, September 2004 (replaces Number 158, September 1995). Guidelines for diagnostic imaging during pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 2004;104: American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology Committee on Practice Bulletins--Obstetrics. ACOG Practice Bulletin Number 49, December Dystocia and augmentation of labor. Obstet Gynecol 2003:102: PV-14~Impotence/Erectile Dysfunction Cohan P, Korenman SG. Erectile dysfunction. J Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2001:86(6): PV-15~Prostatitis/Pudendal Neuralgia/Chronic Pelvic Pain Antolak SJ, Jr. Male Pelvic Pain. International Pelvic Pain Society, Atlanta, GA, October PV-16~Scrotal Pathology ACR Appropriateness Criteria, Acute Onset of Scrotal Pain, 2005 PV-17~Undescended Testis Undescended Testicle or Cryptorchidism. Cornell University Dept. of Urology, Accessed November 21, PV-18~Fistula in Ano Buchanan GN, Halligan S, Taylor S, et al. MRI of fistula in ano: inter-and intraobserver agreement and effects of directed education. AJR 2004;183: PV-3~Adenomyosis, Evidence Based Clinical Support Pelage JP, Jacob D, Fazel A, et al. Midterm results of uterine artery embolization for symptomatic adenomyosis: initial experience. Radiology 2005;234: Tamai K, Togashi K, Ito T, et al. MR imaging findings of adenomyosis: correlation with histopathologic features and diagnostic pitfalls. Radiographics 2005;25: PV-4~Suspected Adnexal Mass, Evidence Based Clinical Support RSNA meeting 2003 PV-8~Leiomyomata, Evidence Based Clinical Support Al-Fozan H, Tulandi T. Factors affecting early surgical intervention after uterine artery embolization. Obstet Gynecol Surv 2002;57: MedSolutions, Inc. Pelvic Imaging Guidelines Page 15 of 15
PELVIS IMAGING GUIDELINES 2009 MedSolutions, Inc
 MedSolutions, Inc. Clinical Decision Support Tool Diagnostic Strategies This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations
MedSolutions, Inc. Clinical Decision Support Tool Diagnostic Strategies This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations
PELVIS IMAGING GUIDELINES 2010 MedSolutions, Inc
 MedSolutions, Inc. Clinical Decision Support Tool Diagnostic Strategies This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations
MedSolutions, Inc. Clinical Decision Support Tool Diagnostic Strategies This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 2/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 7 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 2/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 7 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
PELVIS IMAGING GUIDELINES 2011 MedSolutions, Inc
 MedSolutions, Inc. Clinical Decision Support Tool Diagnostic Strategies This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations
MedSolutions, Inc. Clinical Decision Support Tool Diagnostic Strategies This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations
Cigna Medical Coverage Policies Radiology Pediatric Pelvis Imaging
 Cigna Medical Coverage Policies Radiology Pediatric Pelvis Imaging Effective February 19, 2016 Instructions for use The following coverage policy applies to health benefit plans administered by Cigna.
Cigna Medical Coverage Policies Radiology Pediatric Pelvis Imaging Effective February 19, 2016 Instructions for use The following coverage policy applies to health benefit plans administered by Cigna.
CLEAR COVERAGE HYSTERECTOMY CHECKLISTS
 CLEAR COVERAGE HYSTERECTOMY CHECKLISTS Click on the link below to access the checklist sheet. Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Adenomyosis Chronic Abdominal or Pelvic Pain Endometriosis Fibroids General Guidelines
CLEAR COVERAGE HYSTERECTOMY CHECKLISTS Click on the link below to access the checklist sheet. Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Adenomyosis Chronic Abdominal or Pelvic Pain Endometriosis Fibroids General Guidelines
A Practical Approach to Adnexal Masses
 A Practical Approach to Adnexal Masses Darcy J. Wolfman, MD Section Chief of Genitourinary Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Clinical Associate Johns Hopkins Community Radiology Division
A Practical Approach to Adnexal Masses Darcy J. Wolfman, MD Section Chief of Genitourinary Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Clinical Associate Johns Hopkins Community Radiology Division
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
FDG-PET Findings in an Ovarian Endometrioma: A Case Report
 FDG-PET Findings in an Ovarian Endometrioma: A Case Report Jia-Huei Lin 1, Victor Chit-kheng Kok 2, Jian-Chiou Su 3 1 Department of Nuclear medicine, Kuang Tien General Hospital, Sha-Lu, Taichung, Taiwan
FDG-PET Findings in an Ovarian Endometrioma: A Case Report Jia-Huei Lin 1, Victor Chit-kheng Kok 2, Jian-Chiou Su 3 1 Department of Nuclear medicine, Kuang Tien General Hospital, Sha-Lu, Taichung, Taiwan
FDG-PET value in deep endometriosis
 Gynecol Surg (2011) 8:305 309 DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0652-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE FDG-PET value in deep endometriosis A. Setubal & S. Maia & C. Lowenthal & Z. Sidiropoulou Received: 3 December 2010 / Accepted:
Gynecol Surg (2011) 8:305 309 DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0652-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE FDG-PET value in deep endometriosis A. Setubal & S. Maia & C. Lowenthal & Z. Sidiropoulou Received: 3 December 2010 / Accepted:
The many faces of Endometriosis
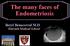 The many faces of Endometriosis Beryl Benacerraf M.D Harvard Medical School What is Endometriosis? Endometriosis is defined as the presence of normal endometrial tissue occurring outside of the endometrial
The many faces of Endometriosis Beryl Benacerraf M.D Harvard Medical School What is Endometriosis? Endometriosis is defined as the presence of normal endometrial tissue occurring outside of the endometrial
 INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
PELVIS IMAGING GUIDELINES Version 17.0; Effective
 MedSolutions, Inc. Clinical Decision Support Tool Diagnostic Strategies This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations
MedSolutions, Inc. Clinical Decision Support Tool Diagnostic Strategies This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations
ADENOMYOSIS CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN IMAGING CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN ADENOMYOSIS: PATHOLOGY ADENOMYOSIS
 CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN IMAGING CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN MOSTAFA ATRI, MD Dipl. Epid. UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Non-menstrual pain of 6 months Prevalence 15%: 18-50 years of age 10-40% of gynecology
CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN IMAGING CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN IN WOMEN MOSTAFA ATRI, MD Dipl. Epid. UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Non-menstrual pain of 6 months Prevalence 15%: 18-50 years of age 10-40% of gynecology
Chronic Pelvic Pain. Bridget Kamen, MD Obstetrics and Gynecology, Confluence Health. I have no disclosures
 Chronic Pelvic Pain Bridget Kamen, MD Obstetrics and Gynecology, Confluence Health I have no disclosures Objectives A little epidemiology Understand there are both gynecologic and non-gynecologic causes
Chronic Pelvic Pain Bridget Kamen, MD Obstetrics and Gynecology, Confluence Health I have no disclosures Objectives A little epidemiology Understand there are both gynecologic and non-gynecologic causes
Pelvic Pain: Overlooked
 EDUCATION EXHIBIT 3 Pelvic Pain: Overlooked and Underdiagnosed Gynecologic Conditions 1 CME FEATURE See accompanying test at http:// www.rsna.org /education /rg_cme.html LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR TEST 1
EDUCATION EXHIBIT 3 Pelvic Pain: Overlooked and Underdiagnosed Gynecologic Conditions 1 CME FEATURE See accompanying test at http:// www.rsna.org /education /rg_cme.html LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR TEST 1
My Patient Has Pelvic Pain. David A. Kenny DO
 My Patient Has Pelvic Pain David A. Kenny DO Definition Of apparent pelvic origin Present most of the time for at least six months Severe enough to cause functional disability Requiring surgical or medical
My Patient Has Pelvic Pain David A. Kenny DO Definition Of apparent pelvic origin Present most of the time for at least six months Severe enough to cause functional disability Requiring surgical or medical
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 2/5/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 6 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 2/5/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 6 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology
 American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr ULTRASONOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF ADNEXAL MASSES Nageswar Rao* Professor,
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr ULTRASONOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF ADNEXAL MASSES Nageswar Rao* Professor,
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Gynecologic Decision Making Based on Sonographic Findings
 Gynecologic Decision Making Based on Sonographic Findings Mindy Goldman, MD Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology & Vickie A. Feldstein, MD Department of Radiology University of California, San Francisco
Gynecologic Decision Making Based on Sonographic Findings Mindy Goldman, MD Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology & Vickie A. Feldstein, MD Department of Radiology University of California, San Francisco
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
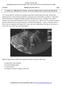 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/20/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 34 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/20/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 34 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Endometriosis - MRI findings with anatomic-pathologic correlation
 Endometriosis - MRI findings with anatomic-pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2551 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Matos, A. T. Almeida, A. Sanches; Vila Nova de Gaia/PT Keywords:
Endometriosis - MRI findings with anatomic-pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2551 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Matos, A. T. Almeida, A. Sanches; Vila Nova de Gaia/PT Keywords:
Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation
 Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation Poster No.: C-0909 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit N. Ramesh 1, T. Simelane 2 ; 1 Portlaoise/IE,
Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation Poster No.: C-0909 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit N. Ramesh 1, T. Simelane 2 ; 1 Portlaoise/IE,
Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation
 Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation Poster No.: C-0909 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit N. Ramesh 1, T. Simelane 2 ; 1 Portlaoise/IE,
Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation Poster No.: C-0909 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit N. Ramesh 1, T. Simelane 2 ; 1 Portlaoise/IE,
Effective Utilization of Imaging. John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging
 Effective Utilization of Imaging John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging Safety Contrast and Radiation What to order Abdomen/Pelvis Brain/Spine Chest Musculoskeletal Ob/Gyn Head and Neck
Effective Utilization of Imaging John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging Safety Contrast and Radiation What to order Abdomen/Pelvis Brain/Spine Chest Musculoskeletal Ob/Gyn Head and Neck
reproductive organs. Malignant neoplasms. 4. Inflammatory disorders of female reproductive organs 2 5. Infertility. Family planning.
 Thematic plan of lectures module iii. Diseases of female reproductive system. Family planning. Topic No of hours 1. Disturbances of menstrual function. Neuroendocrinological 2 syndromes in gynecology 1.
Thematic plan of lectures module iii. Diseases of female reproductive system. Family planning. Topic No of hours 1. Disturbances of menstrual function. Neuroendocrinological 2 syndromes in gynecology 1.
Pelvic Pain. What you need to know. 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone Fax
 Pelvic Pain What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 PELVIC PAIN This is a common problem and most women experience some form
Pelvic Pain What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 PELVIC PAIN This is a common problem and most women experience some form
Ultrasound - Pelvis. What is Pelvic Ultrasound Imaging?
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Pelvis Ultrasound imaging of the pelvis uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures and organs in the lower abdomen and pelvis. There are three types of pelvic
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Pelvis Ultrasound imaging of the pelvis uses sound waves to produce pictures of the structures and organs in the lower abdomen and pelvis. There are three types of pelvic
ENDOMETRIOSIS AS A COMMON CAUSE OF PELVIC PAIN
 ENDOMETRIOSIS AS A COMMON CAUSE OF PELVIC PAIN M.Basta Nikolić, S. Stojanović, O. Nikolić, T. Mrđanin, D. Donat, V. Žigić Center for Radiology, Clinical Center of Vojvodina Novi Sad Chronic pelvic pain
ENDOMETRIOSIS AS A COMMON CAUSE OF PELVIC PAIN M.Basta Nikolić, S. Stojanović, O. Nikolić, T. Mrđanin, D. Donat, V. Žigić Center for Radiology, Clinical Center of Vojvodina Novi Sad Chronic pelvic pain
Female Genital Tract Lab. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan
 Female Genital Tract Lab Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan Ovarian Pathology A 20-year-old female presented with vague left pelvic pain. Pelvic exam revealed
Female Genital Tract Lab Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan Ovarian Pathology A 20-year-old female presented with vague left pelvic pain. Pelvic exam revealed
3 Summary of clinical applications and limitations of measurements
 CA125 (serum) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Cancer Antigen 125 (CA125) 1.2 Alternative names Mucin-16 1.3 NLMC code To follow 1.4 Description of analyte CA125 is an antigenic determinant
CA125 (serum) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Cancer Antigen 125 (CA125) 1.2 Alternative names Mucin-16 1.3 NLMC code To follow 1.4 Description of analyte CA125 is an antigenic determinant
Continuing Professional Development
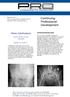 Volume 15.4.1 This Lecture Serties qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Continuing Professional Development Pelvic Calcifications By Dr Kristin Grace (DACBR) WHAT IS THAT??? Calcifications in
Volume 15.4.1 This Lecture Serties qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Continuing Professional Development Pelvic Calcifications By Dr Kristin Grace (DACBR) WHAT IS THAT??? Calcifications in
Introduction to GYN Specialties
 Outline Introduction to GYN Specialties Gynecologic Oncology* Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery* Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility* Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology** Family
Outline Introduction to GYN Specialties Gynecologic Oncology* Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery* Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility* Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology** Family
PALM-COEIN: Your AUB Counseling Guide
 PALM-COEIN: Your AUB Counseling Guide 10 million+ Treat the cause, not the symptom In the U.S, more than 10 million women between the ages of 35 and 49 are affected by AUB 1 Diagnosis Cause Structural
PALM-COEIN: Your AUB Counseling Guide 10 million+ Treat the cause, not the symptom In the U.S, more than 10 million women between the ages of 35 and 49 are affected by AUB 1 Diagnosis Cause Structural
PREAMBLE GENERAL DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY
 PREAMBLE The General Diagnostic Radiology category is intended to cover the body of knowledge a practicing board certified Diagnostic Radiologist should know. Since the range of content relevant to the
PREAMBLE The General Diagnostic Radiology category is intended to cover the body of knowledge a practicing board certified Diagnostic Radiologist should know. Since the range of content relevant to the
CNGOF Guidelines for the Management of Endometriosis
 CNGOF Guidelines for the Management of Endometriosis Anatomoclinical forms of endometriosis Definitions Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue containing both glands and stroma
CNGOF Guidelines for the Management of Endometriosis Anatomoclinical forms of endometriosis Definitions Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue containing both glands and stroma
What is endometrial cancer?
 Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Endometriosis د. نجمه محمود كلية الطب جامعة بغداد فرع النسائية والتوليد
 Endometriosis د. نجمه محمود كلية الطب جامعة بغداد فرع النسائية والتوليد Objectives:- To know what is endometriosis The sites where it occur To explain its itiology & pathogenesis To know the clinical features
Endometriosis د. نجمه محمود كلية الطب جامعة بغداد فرع النسائية والتوليد Objectives:- To know what is endometriosis The sites where it occur To explain its itiology & pathogenesis To know the clinical features
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
Cervical Cancer 3/25/2019. Abnormal vaginal bleeding
 Cervical Cancer Abnormal vaginal bleeding Postcoital, intermenstrual or postmenopausal Vaginal discharge Pelvic pain or pressure Asymptomatic In most patients who are not sexually active due to symptoms
Cervical Cancer Abnormal vaginal bleeding Postcoital, intermenstrual or postmenopausal Vaginal discharge Pelvic pain or pressure Asymptomatic In most patients who are not sexually active due to symptoms
STAGING AND FOLLOW-UP STRATEGIES
 ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology STAGING AND FOLLOW-UP STRATEGIES Ahmet Tuncay Turgut, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University, Faculty of Medicine Ankara 2nd ESUR
ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology STAGING AND FOLLOW-UP STRATEGIES Ahmet Tuncay Turgut, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University, Faculty of Medicine Ankara 2nd ESUR
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
 J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Partial or complete mole based on pathology, morphology and karyotype Pathology Complete mole Absent
J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Partial or complete mole based on pathology, morphology and karyotype Pathology Complete mole Absent
Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma
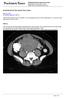 May 26, 2011 By Sushila Ladumor, MD [1] Endometrial stromal sarcoma (ESS) is a rare malignant tumor of the endometrium, occurring in the age group of 40-50 years. History The 50-year-old, female patient
May 26, 2011 By Sushila Ladumor, MD [1] Endometrial stromal sarcoma (ESS) is a rare malignant tumor of the endometrium, occurring in the age group of 40-50 years. History The 50-year-old, female patient
Adenomyosis by myometrial Invasion of endometriosis: Comparison with typical adenomyosis
 Adenomyosis by myometrial Invasion of endometriosis: Comparison with typical adenomyosis Poster No.: C-1294 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary Authors: S. Moon, H. K. Lim,
Adenomyosis by myometrial Invasion of endometriosis: Comparison with typical adenomyosis Poster No.: C-1294 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary Authors: S. Moon, H. K. Lim,
7/2/15. Approach to imaging of pelvic pain. Acute pelvic pain. Chronic pelvic pain. Dysmenorrhea
 I have no financial rela.onships to disclose. Approach to imaging of pelvic pain To emphasize the importance of ultrasound as the imaging modality of choice for the most commonly presen6ng diagnoses in
I have no financial rela.onships to disclose. Approach to imaging of pelvic pain To emphasize the importance of ultrasound as the imaging modality of choice for the most commonly presen6ng diagnoses in
Accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis and extension of pelvic endometriosis
 Accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis and extension of pelvic endometriosis A.Salem, Kh. Fakhfakh, S. Mehiri, Y. Ben Brahim, F. Ben Amara, H. Rajhi, R. Hamza,
Accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis and extension of pelvic endometriosis A.Salem, Kh. Fakhfakh, S. Mehiri, Y. Ben Brahim, F. Ben Amara, H. Rajhi, R. Hamza,
n Make tremendous difference in patients lives: n Diagnosing or excluding disease and injury n Evaluating response to therapy
 Imaging: Choosing the Appropriate Exam Rob Milman, MD Austin Radiological Association What is a Radiologist? A physician who specializes in diagnosing and treating disease and injury by using medical imaging
Imaging: Choosing the Appropriate Exam Rob Milman, MD Austin Radiological Association What is a Radiologist? A physician who specializes in diagnosing and treating disease and injury by using medical imaging
Case 9539 Endometriosis in the canal of Nuck
 Case 9539 Endometriosis in the canal of Nuck Monteiro V, Cunha TM Section: Genital (Female) Imaging Published: 2011, Sep. 27 Patient: 26 year(s), female Authors' Institution V Monteiro 1 TM Cunha 2 1 Unidade
Case 9539 Endometriosis in the canal of Nuck Monteiro V, Cunha TM Section: Genital (Female) Imaging Published: 2011, Sep. 27 Patient: 26 year(s), female Authors' Institution V Monteiro 1 TM Cunha 2 1 Unidade
Pelvic Pain: Diagnosis and Management
 Pelvic Pain: Diagnosis and Management Mr N Pisal Consultant Gynaecologist Advanced Laparoscopic Surgeon www.london-gynaecology.com History LMP Dysmenorrhoea / Dyspareunia Cyclical pain related to menstrual
Pelvic Pain: Diagnosis and Management Mr N Pisal Consultant Gynaecologist Advanced Laparoscopic Surgeon www.london-gynaecology.com History LMP Dysmenorrhoea / Dyspareunia Cyclical pain related to menstrual
Endometriosis of the Appendix Resulting in Perforated Appendicitis
 27 Endometriosis of the Appendix Resulting in Perforated Appendicitis Toru Hasegawa a Koichi Yoshida b Kazuhiro Matsui c a Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toyama,
27 Endometriosis of the Appendix Resulting in Perforated Appendicitis Toru Hasegawa a Koichi Yoshida b Kazuhiro Matsui c a Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toyama,
Genitourinary. Common Clinical Scenarios Protocoling Module. Patty Ojeda & Mariam Shehata
 The following training module was developed as a quality improvement project to serve as an educational tool for junior radiology residents. The following diagnostic radiology protocoling modules were
The following training module was developed as a quality improvement project to serve as an educational tool for junior radiology residents. The following diagnostic radiology protocoling modules were
RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (526)
 RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (526) 526-133 DMS General Procedures 2 Radiologic Technology (526) 1 526-130 Introduction to Diagnostic Medical Sonography This course introduces the student to the history of ultrasound
RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (526) 526-133 DMS General Procedures 2 Radiologic Technology (526) 1 526-130 Introduction to Diagnostic Medical Sonography This course introduces the student to the history of ultrasound
R-SCAN: Engaging Clinicians in Value-based Care
 R-SCAN: Engaging Clinicians in Value-based Care Nancy Fredericks, MBA R-SCAN Director rscan.org What is R-SCAN? A collaborative between referring clinicians and radiologists to improve patient care R-SCAN
R-SCAN: Engaging Clinicians in Value-based Care Nancy Fredericks, MBA R-SCAN Director rscan.org What is R-SCAN? A collaborative between referring clinicians and radiologists to improve patient care R-SCAN
Log Title: OBRES Gynecologic Case Log
 Log Title: OBRES Gynecologic Case Log Hospital/Institution: (Lookup) Attending Physician (Lookup) Is Patient Pregnant? ( Y or N) MEDRECNO: (text) Date (encounter) (Date) Diagnosis DX GYN Acute Pelvic Pain
Log Title: OBRES Gynecologic Case Log Hospital/Institution: (Lookup) Attending Physician (Lookup) Is Patient Pregnant? ( Y or N) MEDRECNO: (text) Date (encounter) (Date) Diagnosis DX GYN Acute Pelvic Pain
Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE
 Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES PHYSICAL EXAMINATION CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE 3/5 Patient presents through the emergency room with
Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES PHYSICAL EXAMINATION CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE 3/5 Patient presents through the emergency room with
PELVIC PAIN IN GYNECOLOGY
 PELVIC PAIN IN GYNECOLOGY Pelvic pain is an important part of clinical practice for who any clinician who provides health care for women. It can be acute, recurrent or chronic. Differential Diagnosis:
PELVIC PAIN IN GYNECOLOGY Pelvic pain is an important part of clinical practice for who any clinician who provides health care for women. It can be acute, recurrent or chronic. Differential Diagnosis:
Chronic Pelvic Pain. AP099, December 2010
 AP099, December 2010 Chronic Pelvic Pain Pain in the pelvic area that lasts for 6 months or longer is called chronic pelvic pain. An estimated 15 20% of women aged 18 50 years have chronic pelvic pain
AP099, December 2010 Chronic Pelvic Pain Pain in the pelvic area that lasts for 6 months or longer is called chronic pelvic pain. An estimated 15 20% of women aged 18 50 years have chronic pelvic pain
The Role of Imaging for Gynecologic Emergencies
 Objectives The Role of Imaging for Gynecologic Emergencies M. Jonathon Solnik, MD, FACOG FACS Associate Professor of Obstetrics & Gynaecology Head of Gynaecology & Minimally Invasive Surgery University
Objectives The Role of Imaging for Gynecologic Emergencies M. Jonathon Solnik, MD, FACOG FACS Associate Professor of Obstetrics & Gynaecology Head of Gynaecology & Minimally Invasive Surgery University
A Case Report Hydronephrosis and Hydrodureter due to Ureteral Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis mimic Ureteral Stricture Suryamanggala SI 1, Satria ML 2
 A Case Report Hydronephrosis and Hydrodureter due to Ureteral Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis mimic Ureteral Stricture Suryamanggala SI 1, Satria ML 2 1 Departement of Obstetric and Gynecology Faculty
A Case Report Hydronephrosis and Hydrodureter due to Ureteral Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis mimic Ureteral Stricture Suryamanggala SI 1, Satria ML 2 1 Departement of Obstetric and Gynecology Faculty
Hysterectomy : A Clinicopathologic Correlation
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No.2, June 2006 Hysterectomy : A Clinicopathologic Correlation Layla S Abdullah, FRCPC* Objective : To study the most common pathologies identified in hysterectomy specimens
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No.2, June 2006 Hysterectomy : A Clinicopathologic Correlation Layla S Abdullah, FRCPC* Objective : To study the most common pathologies identified in hysterectomy specimens
Revision Date(s): In children under the age of 14, ultrasound should be the initial study performed for evaluation of abdominal pain.
 Subject: MRI Pelvis Policy Number: MCR: 618 Revision Date(s): MHW Original Effective Date: 11/7/2017 Review Date: 8/23/2017 DISCLAIMER This Molina Clinical Review (MCR) is intended to facilitate the Utilization
Subject: MRI Pelvis Policy Number: MCR: 618 Revision Date(s): MHW Original Effective Date: 11/7/2017 Review Date: 8/23/2017 DISCLAIMER This Molina Clinical Review (MCR) is intended to facilitate the Utilization
Top Tips for Gynaecological Ultrasound. Catherine Kirkpatrick Consultant Sonographer Dublin Oct 2018
 Top Tips for Gynaecological Ultrasound Catherine Kirkpatrick Consultant Sonographer Dublin Oct 2018 We can all scan a pelvis so what can we do to improve? Uterus, endometrium and ovaries, got it covered!
Top Tips for Gynaecological Ultrasound Catherine Kirkpatrick Consultant Sonographer Dublin Oct 2018 We can all scan a pelvis so what can we do to improve? Uterus, endometrium and ovaries, got it covered!
January Dear Medical Director:
 January 2010 Dear Medical Director: It is the position of the American Urological Association (AUA) that urologists are appropriately trained in the performance of sonographic procedures. In spite of this,
January 2010 Dear Medical Director: It is the position of the American Urological Association (AUA) that urologists are appropriately trained in the performance of sonographic procedures. In spite of this,
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablation in uterine leiomyoma management, 719 723 Adnexal masses diagnosis of, 664 667 imaging in, 664 665 laboratory studies in, 665
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablation in uterine leiomyoma management, 719 723 Adnexal masses diagnosis of, 664 667 imaging in, 664 665 laboratory studies in, 665
Clinical aspects in urogenital injuries
 Clinical aspects in urogenital injuries Rolf Wahlqvist Oslo Urological University Clinic Aker University Hospital Nordic Rad.2008 1 Urogenital injuries in trauma patients Renal injury Ureteral injury (infrequent/iatrogenic)
Clinical aspects in urogenital injuries Rolf Wahlqvist Oslo Urological University Clinic Aker University Hospital Nordic Rad.2008 1 Urogenital injuries in trauma patients Renal injury Ureteral injury (infrequent/iatrogenic)
Chapter 100 Gynecologic Disorders
 Chapter 100 Gynecologic Disorders Episode Overview: 1. Describe the presentation and RF for Adnexal torsion 2. List the imaging findings of adnexal torsion (US vs CT) 3. What is the management of adnexal
Chapter 100 Gynecologic Disorders Episode Overview: 1. Describe the presentation and RF for Adnexal torsion 2. List the imaging findings of adnexal torsion (US vs CT) 3. What is the management of adnexal
Basic Training Programme. 16 Februrary 2018, ROTTERDAM. Pre and Post-Course Test Answers
 Basic Training Programme 16 Februrary 2018, ROTTERDAM Pre and Post-Course Test Answers Your details: Name: Conference registration number/ BT delegate number: Email address: Are you already performing
Basic Training Programme 16 Februrary 2018, ROTTERDAM Pre and Post-Course Test Answers Your details: Name: Conference registration number/ BT delegate number: Email address: Are you already performing
URINARY TRACT IMAGING - BASIC PRINCIPLES
 URINARY TRACT IMAGING - BASIC PRINCIPLES Clinical Radiology Every physician needs a basic understanding of diagnostic imaging to understand how to order the appropriate studies and to understand the resulting
URINARY TRACT IMAGING - BASIC PRINCIPLES Clinical Radiology Every physician needs a basic understanding of diagnostic imaging to understand how to order the appropriate studies and to understand the resulting
RADIOLOGIC AND IMAGING SCIENCE (RIS)
 Kent State University Catalog 2017-2018 1 RADIOLOGIC AND IMAGING SCIENCE (RIS) RIS 34001 INTRODUCTION TO DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY 1 Credit Provides an introduction to diagnostic medical sonography.
Kent State University Catalog 2017-2018 1 RADIOLOGIC AND IMAGING SCIENCE (RIS) RIS 34001 INTRODUCTION TO DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY 1 Credit Provides an introduction to diagnostic medical sonography.
Rad Lab 4 Unknowns: Genitourinary!
 Rad Lab 4 Unknowns: Genitourinary! Peter Clarke MD! Don Di Salvo, MD! Clerkship Directors for Radiology! Harvard Medical School! Brigham and Women s Hospital! Dana Farber Cancer Institute! Case 1: 69 year
Rad Lab 4 Unknowns: Genitourinary! Peter Clarke MD! Don Di Salvo, MD! Clerkship Directors for Radiology! Harvard Medical School! Brigham and Women s Hospital! Dana Farber Cancer Institute! Case 1: 69 year
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL. PHD THESIS UNDESCENDED TESTICLE IN CHILD CLINICAL AND THERAPEUTIC ASPECTS - Abstract -
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL PHD THESIS UNDESCENDED TESTICLE IN CHILD CLINICAL AND THERAPEUTIC ASPECTS - Abstract - SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: Prof. Dr. Ion GEORGESCU PHD
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL PHD THESIS UNDESCENDED TESTICLE IN CHILD CLINICAL AND THERAPEUTIC ASPECTS - Abstract - SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: Prof. Dr. Ion GEORGESCU PHD
Program Schedule. Update in Gynecology and Minimally Invasive Surgery 2018
 Program Schedule Update in Gynecology and Minimally Invasive Surgery 2018 Wednesday, February 7, 2018 6:00 a.m. Registration & Breakfast with Exhibitors 6:55 a.m. Welcome Announcements SESSION: Practical
Program Schedule Update in Gynecology and Minimally Invasive Surgery 2018 Wednesday, February 7, 2018 6:00 a.m. Registration & Breakfast with Exhibitors 6:55 a.m. Welcome Announcements SESSION: Practical
Adnexal Masses and Problem Solving Pelvic MRI
 28th Congress of the Hungarian Society of Radiologists RCR Session Budapest June 2016 Adnexal Masses and Problem Solving Pelvic MRI DrSarah Swift St James s University Hospital Leeds, UK Objectives Characterisation
28th Congress of the Hungarian Society of Radiologists RCR Session Budapest June 2016 Adnexal Masses and Problem Solving Pelvic MRI DrSarah Swift St James s University Hospital Leeds, UK Objectives Characterisation
Fibroid mapping. Haitham Hamoda MD FRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist, Subspecialist in Reproductive Medicine & Surgery King s College Hospital
 Fibroid mapping Haitham Hamoda MD FRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist, Subspecialist in Reproductive Medicine & Surgery King s College Hospital Fibroids Common condition >70% of women by onset of menopause.
Fibroid mapping Haitham Hamoda MD FRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist, Subspecialist in Reproductive Medicine & Surgery King s College Hospital Fibroids Common condition >70% of women by onset of menopause.
Adnexal Torsion in Post-Menopausal Women: An Even More Challenging Diagnosis
 ISSN- O: 2458-868X, ISSN P: 2458 8687 Index Copernicus Value: 49. 23 PubMed - National Library of Medicine - ID: 101731606 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.956 International Journal of Medical Science and Innovative
ISSN- O: 2458-868X, ISSN P: 2458 8687 Index Copernicus Value: 49. 23 PubMed - National Library of Medicine - ID: 101731606 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.956 International Journal of Medical Science and Innovative
MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Policy Number: PA.017.MH Last Review Date: 08/04/2016 Effective Date: 01/01/2016
 MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL PA.017.MH Infertility- Diagnosis This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar MA DSNP CSNP (Not Covered) MedStar
MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL PA.017.MH Infertility- Diagnosis This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar MA DSNP CSNP (Not Covered) MedStar
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis
 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
Prenatal and Neonatal MRI of Sacrococcygeal Teratoma With Surgical Correlation
 Prenatal and Neonatal MRI of Sacrococcygeal Teratoma With Surgical Correlation Ali Mahmood, M.D., and Nadia F. Mahmood, M.D. Citation: Mahmood A, Mahmood NF. Prenatal and Neonatal MRI of Sacrococcygeal
Prenatal and Neonatal MRI of Sacrococcygeal Teratoma With Surgical Correlation Ali Mahmood, M.D., and Nadia F. Mahmood, M.D. Citation: Mahmood A, Mahmood NF. Prenatal and Neonatal MRI of Sacrococcygeal
GENERAL DATA. Sex : female Age : 40 years old Marriage status : married
 GENERAL DATA Sex : female Age : 40 years old Marriage status : married CHIEF COMPLAINT Bilateral ovarian tumors discovered by sonography accidentally PRESENT ILLNESS 2003-06-26 :bilateral ovarian tumors
GENERAL DATA Sex : female Age : 40 years old Marriage status : married CHIEF COMPLAINT Bilateral ovarian tumors discovered by sonography accidentally PRESENT ILLNESS 2003-06-26 :bilateral ovarian tumors
Value of MRI in Characterizing Adnexal Masses
 The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India (July August 2015) 65(4):259 266 DOI 10.1007/s13224-015-0730-9 PHOTO ESSAY Value of MRI in Characterizing Adnexal Masses Alpana Karnik 1 Raina Anil Tembey
The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India (July August 2015) 65(4):259 266 DOI 10.1007/s13224-015-0730-9 PHOTO ESSAY Value of MRI in Characterizing Adnexal Masses Alpana Karnik 1 Raina Anil Tembey
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings
 Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 10 Reproductive Systems 1 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Objectives Define, understand and correctly pronounce medical terms related to
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 10 Reproductive Systems 1 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Objectives Define, understand and correctly pronounce medical terms related to
Contents: Benign Diseases of the Uterus
 COLLEGE OF MEDICINE DEPT. OF OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY Benign Diseases of the Uterus Dr.Ayman Hussien Shaamash MBBCH, MSc., MD. (Egypt) Professor of OB./Gyn. Faculty of Medicine. King khalid University
COLLEGE OF MEDICINE DEPT. OF OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY Benign Diseases of the Uterus Dr.Ayman Hussien Shaamash MBBCH, MSc., MD. (Egypt) Professor of OB./Gyn. Faculty of Medicine. King khalid University
Table 2. First Generated List of Expert Responses. Likert-Type Scale. Category or Criterion. Rationale or Comments (1) (2) (3) (4)
 Table 2. First Generated List of Expert Responses. Likert-Type Scale Category or Criterion Anatomical Structures and Features Skeletal Structures and Features (1) (2) (3) (4) Rationale or Comments 1. Bones
Table 2. First Generated List of Expert Responses. Likert-Type Scale Category or Criterion Anatomical Structures and Features Skeletal Structures and Features (1) (2) (3) (4) Rationale or Comments 1. Bones
Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay
 rown et al. MRI of the Female Pelvis Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.41 on 12/17/17 from IP address 37.44.202.41. Copyright RRS. For personal use only;
rown et al. MRI of the Female Pelvis Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.41 on 12/17/17 from IP address 37.44.202.41. Copyright RRS. For personal use only;
General history. Basic Data : Age :62y/o Date of admitted: Married status : Married
 General history Basic Data : Age :62y/o Date of admitted:940510 Married status : Married General history Chief Complain : bilateral ovarian cyst incidentally being found out during pap smear. Present Illness
General history Basic Data : Age :62y/o Date of admitted:940510 Married status : Married General history Chief Complain : bilateral ovarian cyst incidentally being found out during pap smear. Present Illness
Case Fibrothecoma of the ovary
 Case 10646 Fibrothecoma of the ovary Elisa Melo Abreu, Teresa Margarida Cunha Section: Genital (Female) Imaging Published: 2015, Jan. 2 Patient: 70 year(s), female Authors' Institution Department of Radiology,
Case 10646 Fibrothecoma of the ovary Elisa Melo Abreu, Teresa Margarida Cunha Section: Genital (Female) Imaging Published: 2015, Jan. 2 Patient: 70 year(s), female Authors' Institution Department of Radiology,
Imaging Ejaculatory Disorders and Hematospermia
 ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology Imaging Ejaculatory Disorders and Hematospermia Parvati Ramchandani, MD Professor, Radiology and Surgery University of Pennsylvania Medical
ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology Imaging Ejaculatory Disorders and Hematospermia Parvati Ramchandani, MD Professor, Radiology and Surgery University of Pennsylvania Medical
Endometrial line thickness in different conditions.
 Endometrial line thickness in different conditions 1 Endometrial thickens in response to Rising estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle and then shedding endometrial at the times of menses 2 The thickens
Endometrial line thickness in different conditions 1 Endometrial thickens in response to Rising estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle and then shedding endometrial at the times of menses 2 The thickens
Asyntomatic bacteriuria, Urinary Tract Infection
 Asyntomatic bacteriuria, Urinary Tract Infection C. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asyntomatic Bacteriuria in Adults (2005) Pyuria accompanying asymptomatic
Asyntomatic bacteriuria, Urinary Tract Infection C. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Asyntomatic Bacteriuria in Adults (2005) Pyuria accompanying asymptomatic
Unexpected Gynecologic Findings at Laparotomy. Susan A. Davidson, MD University of Colorado, Denver School of Medicine
 Unexpected Gynecologic Findings at Laparotomy Susan A. Davidson, MD University of Colorado, Denver School of Medicine Adnexal Mass: Gyn Etiologies Uterine Leiomyomas Pregnancy Malignancy Tubal Pregnancy
Unexpected Gynecologic Findings at Laparotomy Susan A. Davidson, MD University of Colorado, Denver School of Medicine Adnexal Mass: Gyn Etiologies Uterine Leiomyomas Pregnancy Malignancy Tubal Pregnancy
CASE STUDY. Presented by: Jessica Pizzo. CFCC Sonography student Class of 2018
 CASE STUDY Presented by: Jessica Pizzo CFCC Sonography student Class of 2018 Case Presentation April 4, 2017 56 yr old woman presented to ED with lower abdominal pain & swelling, along with constipation.
CASE STUDY Presented by: Jessica Pizzo CFCC Sonography student Class of 2018 Case Presentation April 4, 2017 56 yr old woman presented to ED with lower abdominal pain & swelling, along with constipation.
performed to help sway the clinician in what the appropriate diagnosis is, which can substantially alter the treatment of management.
 Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Barnet Hospital Royal Free NHS Trust
 Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Barnet Hospital Royal Free NHS Trust Endometriosis one of the most common conditions requiring treatment Growth of endometrial like tissue outside
Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Barnet Hospital Royal Free NHS Trust Endometriosis one of the most common conditions requiring treatment Growth of endometrial like tissue outside
Children's (Pediatric) Ultrasound - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) Ultrasound - Abdomen Children s (pediatric) ultrasound imaging of the abdomen is a safe, noninvasive test that uses sound waves to produce a clear picture of
Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) Ultrasound - Abdomen Children s (pediatric) ultrasound imaging of the abdomen is a safe, noninvasive test that uses sound waves to produce a clear picture of
Frequency of menses. Duration of menses 3 days to 7 days. Flow/amount of menses Average blood loss with menstruation is 60-80cc.
 Frequency of menses 24 days (0.5%) to 35 days (0.9%) Age 25, 40% are between 25 and 28 days Age 25-35, 60% are between 25 and 28 days Teens and women over 40 s cycles may be longer apart Duration of menses
Frequency of menses 24 days (0.5%) to 35 days (0.9%) Age 25, 40% are between 25 and 28 days Age 25-35, 60% are between 25 and 28 days Teens and women over 40 s cycles may be longer apart Duration of menses
Clinical evaluation of infertility
 Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 2/19/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 8 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 2/19/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 8 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
COLOR DOPPLER ULTRASOUND IN EVALUATION OF SCROTAL LESIONS
 COLOR DOPPLER ULTRASOUND IN EVALUATION OF SCROTAL LESIONS Desai Sanjay D Associate Professor, Department of Radiology, RCSM Govt. Medical College, Kolhapur. ABSTRACT: Color Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive,
COLOR DOPPLER ULTRASOUND IN EVALUATION OF SCROTAL LESIONS Desai Sanjay D Associate Professor, Department of Radiology, RCSM Govt. Medical College, Kolhapur. ABSTRACT: Color Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive,
