Case Report: Burns Reid Sadoway PGY1 Emergency Medicine, Dalhousie
|
|
|
- Berniece Terry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Report: Burns Reid Sadoway PGY1 Emergency Medicine, Dalhousie
2 History 3 yo boy, presents to pediatric ED with mother Child can be heard crying inside waiting/patient room, has both hands bandaged and wrapped According to mother, unwitnessed event but child likely grabbed grates on an old wood burning stove. Child immediately screamed out, parents grabbed him, and flushed hands under cool water. Wrapped child s hands in towels and brought to ED No other injuries noted
3 Case cont d PMHx: Had orchidopexy for an undescended testicle at 15 months of age, otherwise healthy. Meds: None Allergies: Penicillin Rash Immunizations: UTD Development: All normal for fine motor, gross motor, and speech
4 Vitals Temp: 36.4 HR: 154 RR: 28 O2: 99% on RA BP: 96/52 Weight: 14.5 kg Glucose: Not Done
5 Physical Exam H+N: Normal, no obvious burns or singe to oropharynx or nares Cardiac: N S1S2, no murmurs noted Resp: AE=AE, no wheeze, no stridor, no obvious increased work of breathing Abdo: Soft, non tender with N bowel sounds Hands look as follows
6
7 Hand exam CR: 1-2 seconds in all digits Radial pulses: N Still moving all fingers and wrists Mom able to convince child to give a thumbs up
8 Disposition Child s hands covered in ointment containing lidocaine/tetracaine + vaseline Wrapped in gauze, mother advised to change daily with daily application of ointment Given follow up appointment with plastics because of location of burn Child happy and eating popsicle on way out of the department.
9 Introduction to Burns Relatively common injuries caused by direct or indirect contact with heat, electrical current, radiation, or chemical agents With thermal burns, the severity of injury is dependent on length of exposure, the temp, and the intrinsic tissue structure leading to heat conductivity Common denominator in burn injuries is protein denaturation and cell death (either by necrosis or apoptosis)
10 Epidemiology In the U.S. there are approx medical visits per year related to burns, with 3500 deaths and admissions. The majority of burns occur from fire or flame (44%), scalds (33%), contact with hot objects (9%), electricity (4%), or chemical agents (3%) More than 1/3 of admissions have >10% TBSA affected. Other admission typically involve severe burns to vital areas such as the hands, face, or feet, or there has been other trauma involved Half of patients are between 19 and 44 years of age. Most commonly affected are the upper extremities (44%), lower ext (26%) and H & N (17%)
11 Pathophysiology Unique, dynamic injuries in that there tends to be progression in depth and size occurring AFTER the time of injury. Temperatures below 44 0 C are generally tolerated without injury. However as temperature rises there is an exponential decrease in the time to injury. Traditionally burns are separated into 3 concentric zones: Coagulation, Stasis/Ischemia, and Hyperemia
12 Pathophysiology Cont d The cont d progression of burn injuries is multifactorial and not completely understood at this time. The initial inflammatory response triggers a cascade that seems to cause further injury There is an occlusion of the dermal microcirculation with a combination of red blood cells, neutrophils, and microthrombi that results in reduced perfusion.
13 Pathophysiology Cont d Inhalation injury: Exposure to heat can cause rapid and extensive upper airway edema in burn patients. Components of smoke such as incomplete combustion materials (ie CO, cyanide, aldehydes, and oxides) can result in further pulmonary edema and V/Q mismatch Necrosis in the airway leads to de-epitheliazation and formation of pseudomembranous casts that cause further airway obstruction Reduced ability to clear secretions causing further exacerbation
14 Classification of Burns Burns are classified by mechanism of injury, depth, extent, and associated injuries and comorbidities. First Degree: Limited to the epidermis, characterized by erythema and pain Second Degree/Partial Thickness: Can be further subdivided into superficial and deep. Superficial thickness burns are limited to the papillary dermis while Deep extend to the reticular dermis Important to distinguish between the two as Deep partial thickness burns will often will not heal in 2-3 weeks and can lead to scarring and contractures.
15 Classification of Burns Third Degree: Also referred to as full thickness burns Appear thick, white, or tan. Also appear dry with possible charred appearance. Non-blanching, and because of nerve destruction are not painful Fourth Degree: Extend through the skin into muscle and bone. Appear stiff, charred, with visibly thrombosed vessels
16 1 st Degree Burn
17 2 nd Degree Burn
18 2 nd Degree Burns
19 3 rd Degree Burn
20 4 th Degree Burn
21 Burn Assessment Various tools and modalities to assess the depth and healing capacity of burns. In the emergency department however one must use clinical assessment and estimation, which can be unreliable. The extent of the burned area or total body surface area (TBSA) burned is also critical in assessment. Helps guide the fluid resuscitation management in the patients. Also helps convey criteria for admittance to the hospital/burn ward. Only second degree or deeper burns are used when assessing TBSA affected.
22 Burn Assessment A useful tool for assessment of smaller burns or scattered areas of burn is that the area of a patient s palm and fingers is approximately 1% TBSA For larger burns the rule of 9 s is frequently employed. The rule of nines should not be used for children as their head is larger and, in proportion, their extremities are smaller than those of adults. Finally, burns are classified by severity into minor, moderate, and severe based on the TBSA burned, the percentage of full-thickness injury, and the involvement of specific areas such as the face, hands, feet, or perineum.
23 Burn Assessment
24 Burn Assessment
25 Burn Assessment
26 Pre-Hospital Management First priority is to stop the burning process and prevent further injury Following this, one should assess the airway, cardiac, and peripheral perfusion status Prehospital administration of fluids is warranted in extensive burns if IV access can be established effectively and expeditiously in non-burned skin Ringers Lactate is the fluid of choice as it reduces the chance of developing hyperchloremeic acidosis compared to NS. Parkland formula can be used for dosing Burn should be covered with a clean sterile dressing. Minimize hypothermia
27 ER Management People tend to focus on the burns when patients come in, it is important to look for other injuries and do proper ABC assessment. Airway injury and compromise warrants intubation, possibly fiberoptically. If RSI isn t possible, consider surgical airway If IV hasn t been established then do so. May need central line if peripheral line not possible. Humidified O2 should be done to keep sats high (>92%) Full monitors should be in place, and a catheter may be placed in order to monitor U/O
28 Inhalation Injury Smoke inhalation affects 5-35% of burn patients. Presence of inhalation injury more than doubles the mortality rate in adults. Traditional methods for assessment of inhalational injury were/are external physical exam, however now it is felt that direct visualization via laryngoscopy (fiberoptic) or bronchoscopy is best. Mechanical ventilation helps provide support, can help with secretion control and help in the recruitment of alveoli. Aerosolized NAC and Heparin can help with breakdown of thick secretions while suctioning and chest physio augment their removal
29 Inhalational Injury
30 Fluid Resuscitation Prior to WWII many burn patients died of hypovolemic shock and renal failure. Following combat as well as other fires there began to be fluid regimens. The massive amounts of inflammatory mediators lead to increased permeability of the local and systemic vasculature and extravasation of intravascular fluids Patients with small burns can usually be treated with oral fluids (if they can tolerate oral fluids). Patients with severe burns require IV fluids in order to prevent shock and increase intravascular volume
31 Fluid Resuscitation Parkland Formula: TBSA x weight (kg) x 4 (ml) Gives the amount of fluid to give in 24 hours. First ½ should be given in the first 8 hours while the second ½ should be given over the following 16. Other formulas can also be used including rule of 10 This formula states that the estimated burn size (percent of TBSA) is multiplied by 10 to derive the initial fluid rate in milliliters per hour. For every 10 kg above 80 kg, 100 ml is added to this rate These regimens are guidelines and fluids should be adjusted according to tissue/organ perfusion
32 Fluid Resuscitation
33 Fluid Resuscitation Special Considerations: Children have a larger TBSA relative to weight when compared with adults and therefore have larger fluid requirements Fluid needs often calculated on TBSA rather than weight, using things such as the Galveston Formula. Colloids: Since leakage of proteins through capillaries lasts hours, colloids are not generally recommended in the initial resuscitation unless the burn is very deep. ABA guidelines consider the possible addition of colloids AFTER the hr mark to decrease fluid requirements
34 Local Wound Care Burns should be considered contaminated and have gentle cleansing with soap and cool water. Necrotic tissue should be carefully removed as needed (analgesia will most likely be warranted in these scenarios) Tetanus booster should be given if patient has not had booster in the last 5 years. Ice water should generally be avoided as it has been associated with increased tissue injury and hypothermia
35 Local Wound Care Burn Blister Management: Remains a topic of debate. Some evidence that there is less infection with intact blisters, however tends to be less pain with ruptured blisters. With blisters that have already ruptured, any necrotic epidermis should be gently removed while adherent epidermis is left intact. With large or tense blisters, the unruptured blister may be aspirated with a sterile needle
36 Burn Dressings Purpose is to protect the wound, to reduce pain, to absorb wound exudate, and to reduce evaporative heat loss First degree wounds can generally be managed with topical anesthetics, aloe vera gels, and NSAIDS Second degree wounds can be managed with dressings with the main principle being CLEAN AND GREASY!
37 Burn Dressings Open: Appropriate for large, contaminated burns with exudate. The wound can then be covered by a non-occlusive dressing with daily cleansing and dressing changes. Closed: Use of occlusive dressings for a moist environment in a wound that has little to mild exudate. Saran Wrap can be used as it seals in heat, acts as a barrier and also allows you to visualize the wound.
38 Pain Management Burn injuries are among the most painful experienced and pain control should be among the highest priorities for physicians Pain, especially in the emergent phase can be divided into three categories: background, breakthrough, and procedural. Pharmacologic agents used to treat burn pain include opioid analgesics, nonopioid analgesics, anxiolytics, and anesthetics. The type of medication used is determined by the severity of pain, the anticipated duration of pain, and intravenous (IV) access
39 Pain Management Minor burns can be managed with Tylenol and NSAIDS In the emergent setting moderate to severe burn pain is generally managed with parenteral opioids titrated to effect. Fentanyl (with a short half life) can be used for short breakthrough and procedural pain for things like debridement and dressing changes Intravenous infusion of lidocaine (1 mg/kg followed by 40 μg/kg/min infusion) has also been shown to reduce the pain in burn patients. In large severe burns or pediatric burns consider sedation and regional nerve blocks
40 Thank You!! References: Rosen s Guide to Emergency Medicine UpToDate American Burn Association Guidelines
Wisecracks 1. What are the indications for an escharotomy 2. What are the primary considerations in mechanical ventilation of burn patients
 Chapter 63 Thermal Burns Episode Overview Questions 1. List zones of burns 2. List 6 indications for intubation in the burn patient 3. List and describe 2 formulas for fluid resuscitation 4. Describe depth
Chapter 63 Thermal Burns Episode Overview Questions 1. List zones of burns 2. List 6 indications for intubation in the burn patient 3. List and describe 2 formulas for fluid resuscitation 4. Describe depth
Burn Priorities of Care: Triage/Treatment/Transfer. Via Christi Regional Burn Center Sarah Fischer, MSN, RN
 Burn Priorities of Care: Triage/Treatment/Transfer Via Christi Regional Burn Center Sarah Fischer, MSN, RN Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Identify American Burn Association referral criteria
Burn Priorities of Care: Triage/Treatment/Transfer Via Christi Regional Burn Center Sarah Fischer, MSN, RN Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Identify American Burn Association referral criteria
Dóra Ujvárosy MD. Medical University of Debrecen Oxyology and Emergency Department
 Dóra Ujvárosy MD. Medical University of Debrecen Oxyology and Emergency Department Functions Definition A burn is a type of injury to the skin caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, light, radiation or
Dóra Ujvárosy MD. Medical University of Debrecen Oxyology and Emergency Department Functions Definition A burn is a type of injury to the skin caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, light, radiation or
BLS, ILS, ALS OTEP BURNS BURN INTRODUCTION TYPES OF BURNS
 BURNS BLS, ILS, ALS OTEP While we do understand this presentation is an instructional tool for all levels of certification, taking this into consideration everyone taking this class must remember that
BURNS BLS, ILS, ALS OTEP While we do understand this presentation is an instructional tool for all levels of certification, taking this into consideration everyone taking this class must remember that
EmergencyKT: Management of Thermal Injury in Adult Patients
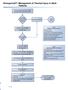 EmergencyKT: Management of Thermal Injury in Adult Patients Remove patient from source of injury, including burned clothing and jewelry Does patient appear to have minor burns? (See Box A) No Notify Burn
EmergencyKT: Management of Thermal Injury in Adult Patients Remove patient from source of injury, including burned clothing and jewelry Does patient appear to have minor burns? (See Box A) No Notify Burn
BURNS MODULE. In the paediatric population consider non-accidental injury as a mechanism for burn injuries.
 BURNS MODULE INTRODUCTION Burns are a common cause of trauma. Most burn injuries are a result of flame burns, with scalds also occurring commonly. Electrical and chemical burns are less common. 1 Concurrent
BURNS MODULE INTRODUCTION Burns are a common cause of trauma. Most burn injuries are a result of flame burns, with scalds also occurring commonly. Electrical and chemical burns are less common. 1 Concurrent
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 46 Caring for Clients with Burns Types of Burns Thermal Dry heat flame Moist heat steam or hot liquid
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 46 Caring for Clients with Burns Types of Burns Thermal Dry heat flame Moist heat steam or hot liquid
Burn Injuries & Its Management M JARI.MD
 Burn Injuries & Its Management M JARI.MD 1 BURNS Wounds caused by exposure to: 1. excessive heat 2. Chemicals 3. fire/steam 4. radiation 5. electricity 2 BURNS Results in 10-20 thousand deaths annually
Burn Injuries & Its Management M JARI.MD 1 BURNS Wounds caused by exposure to: 1. excessive heat 2. Chemicals 3. fire/steam 4. radiation 5. electricity 2 BURNS Results in 10-20 thousand deaths annually
EMERGENCYROOM BURN MANAGEMENT
 EMERGENCYROOM INITIAL ASSESSMENT PRIMARY SURVEY A = Airway and C-spine immobilization B = Breathing and Ventilation C = Circulation D = Disability, Neurologic Deficit E = Expose (remove all clothing and
EMERGENCYROOM INITIAL ASSESSMENT PRIMARY SURVEY A = Airway and C-spine immobilization B = Breathing and Ventilation C = Circulation D = Disability, Neurologic Deficit E = Expose (remove all clothing and
PEDIATRIC TRAUMA I: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA BURNS. December 19, 2012
 PEDIATRIC TRAUMA I: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA BURNS Niel F. Miele,, M.D. December 19, 2012 EPIDEMIOLOGY Major Trauma responsible for
PEDIATRIC TRAUMA I: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA BURNS Niel F. Miele,, M.D. December 19, 2012 EPIDEMIOLOGY Major Trauma responsible for
Burn injury. A : patent airway with smoking inhalation, stridor. D: E4V5M6,pupil 2mm RTLBE
 Burn injury Pinyong Uthaitas Emergency Department Faculty of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital A Thai man 52 year old came to the hospital due to flam burn ½ hr ago at his house. He gain conscious but hoarseness
Burn injury Pinyong Uthaitas Emergency Department Faculty of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital A Thai man 52 year old came to the hospital due to flam burn ½ hr ago at his house. He gain conscious but hoarseness
At the conclusion of this course the learner will be able to
 Objectives At the conclusion of this course the learner will be able to 1. Discuss basic anatomy and pathophysiology of burns 2. Describe burn injuries in terms of size, depth, coloration and characteristics
Objectives At the conclusion of this course the learner will be able to 1. Discuss basic anatomy and pathophysiology of burns 2. Describe burn injuries in terms of size, depth, coloration and characteristics
Chapter 29. Objectives. Objectives 01/09/2013. Burns
 Chapter 29 Burns Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 1. Define key terms introduced in
Chapter 29 Burns Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 1. Define key terms introduced in
Children's National Medical Center The Division of Trauma and Burn Burn Education Module Post-test
 Children's National Medical Center The Division of Trauma and Burn Burn Education Module Post-test Purpose: To provide nurses with on overview of burn injuries in pediatric patients. Learning Objectives:
Children's National Medical Center The Division of Trauma and Burn Burn Education Module Post-test Purpose: To provide nurses with on overview of burn injuries in pediatric patients. Learning Objectives:
Pediatric Burn Management Justin D. Klein, MD Associate Burn Director Lisa C. Vitale, RN Burn Program Coordinator
 Pediatric Burn Management Justin D. Klein, MD Associate Burn Director Lisa C. Vitale, RN Burn Program Coordinator Lecture Overview Burn statistics and etiologies Pre-hospital evaluation Anatomy of a burn
Pediatric Burn Management Justin D. Klein, MD Associate Burn Director Lisa C. Vitale, RN Burn Program Coordinator Lecture Overview Burn statistics and etiologies Pre-hospital evaluation Anatomy of a burn
Burns. A Comprehensive Review Assessment & Management
 Burns A Comprehensive Review Assessment & Management 1 Objectives Understand types of Burns Understand the pathophysiology of the Burns Understand Rule of Nine Understand Classification of Burns Identify
Burns A Comprehensive Review Assessment & Management 1 Objectives Understand types of Burns Understand the pathophysiology of the Burns Understand Rule of Nine Understand Classification of Burns Identify
IMMEDIATE EMERGENCY BURN CARE » THERMAL BURNS » ELECTRICAL BURNS » CHEMICAL BURNS FIRST AID FOR THE THREE MAJOR CATEGORIES
 IMMEDIATE EMERGENCY BURN CARE 1. Treat according to BLS or ACLS Protocol 2. Use airway and C-Spine precautions. 3. Stop the burning process. FIRST AID FOR THE THREE MAJOR CATEGORIES» THERMAL BURNS + Stop
IMMEDIATE EMERGENCY BURN CARE 1. Treat according to BLS or ACLS Protocol 2. Use airway and C-Spine precautions. 3. Stop the burning process. FIRST AID FOR THE THREE MAJOR CATEGORIES» THERMAL BURNS + Stop
Responsibility This guideline applies to teams of health professions caring for burn patients.
 Page 1 of 9 Guideline: Initial Assessment & Management of Burn Injuries Purpose This document provides a guideline for the initial assessment and management of burn patients. It is not intended as a full
Page 1 of 9 Guideline: Initial Assessment & Management of Burn Injuries Purpose This document provides a guideline for the initial assessment and management of burn patients. It is not intended as a full
Frostbite. Jessica Cardona PGY1 Jackson Memorial Hospital Pediatrics Department
 Frostbite Jessica Cardona PGY1 Jackson Memorial Hospital Pediatrics Department Question 1 An 8 year old male is brought in by EMS from an icy mountain. He was with his family skiing but was separated from
Frostbite Jessica Cardona PGY1 Jackson Memorial Hospital Pediatrics Department Question 1 An 8 year old male is brought in by EMS from an icy mountain. He was with his family skiing but was separated from
Mr Zachary Moaveni Plastic Surgeon, Middlemore Hospital. Mr Adam Bialostocki Plastic Surgeon, Tauranga
 Mr Zachary Moaveni Plastic Surgeon, Middlemore Hospital Mr Adam Bialostocki Plastic Surgeon, Tauranga Mr. Adam Bialostocki Plastic Surgeon Minor Burns First Aid Remove the burning agent / wet clothes
Mr Zachary Moaveni Plastic Surgeon, Middlemore Hospital Mr Adam Bialostocki Plastic Surgeon, Tauranga Mr. Adam Bialostocki Plastic Surgeon Minor Burns First Aid Remove the burning agent / wet clothes
Objectives. Initial Burn Care and Fluid Resuscitation 6/5/2015 INITIAL MANAGEMENT
 Initial Burn Care and Fluid Resuscitation Sarah Taylor MSN, RN, ACNS-BC Clinical Nurse Specialist Trauma Burn Center University of Michigan Health System Ann Arbor, MI Objectives Discuss the initial assessment
Initial Burn Care and Fluid Resuscitation Sarah Taylor MSN, RN, ACNS-BC Clinical Nurse Specialist Trauma Burn Center University of Michigan Health System Ann Arbor, MI Objectives Discuss the initial assessment
Management of Acute Burn Injuries: The First 24 Hours
 Speaker Disclosure I, Debbie Harrell, MSN, RN, NE BC, have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss off label uses of any pharmaceutical products or medical devices. Management of Acute
Speaker Disclosure I, Debbie Harrell, MSN, RN, NE BC, have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss off label uses of any pharmaceutical products or medical devices. Management of Acute
Chapter 23 Caring for Clients with Burns
 Chapter 23 Caring for Clients with Burns Burn Injuries 4500 people die from burns each year High risk group ~ children and the elderly The most common cause of burns Smoking material Scalding Lighting
Chapter 23 Caring for Clients with Burns Burn Injuries 4500 people die from burns each year High risk group ~ children and the elderly The most common cause of burns Smoking material Scalding Lighting
Approved By: Airway and Breathing A. Initially give humidified high flow oxygen at 15 L (100%) using a nonrebreather
 Subject: BURN CARE CLINICAL GUIDELINE Originator: Approval Date: 2015 Approved By: Policy: All burn patients presenting to XXXXXX Hospital will have appropriate assessment, stabilization and evaluation
Subject: BURN CARE CLINICAL GUIDELINE Originator: Approval Date: 2015 Approved By: Policy: All burn patients presenting to XXXXXX Hospital will have appropriate assessment, stabilization and evaluation
INITIAL CARE AND TREATMENT OF BURN INJURIES. November 10,
 INITIAL CARE AND TREATMENT OF BURN INJURIES 2 11/10/2012 November 10, 2012 2 Oregon Burn Center Only burn center in Oregon and SW Washington New unit 16 beds, 20,000 square feet Opened in February 2002
INITIAL CARE AND TREATMENT OF BURN INJURIES 2 11/10/2012 November 10, 2012 2 Oregon Burn Center Only burn center in Oregon and SW Washington New unit 16 beds, 20,000 square feet Opened in February 2002
Pediatrics Grand Rounds 1 June University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. Management of Burn Wounds. Management of Burn Wounds
 Management of Burn Wounds Management of Burn Wounds History of Burn Care Pathophysiology of Burn Lillian F. Liao, MD, MPH Division of Trauma and Emergency Surgery Department of Surgery UTHSCSA Acute burn
Management of Burn Wounds Management of Burn Wounds History of Burn Care Pathophysiology of Burn Lillian F. Liao, MD, MPH Division of Trauma and Emergency Surgery Department of Surgery UTHSCSA Acute burn
INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES. When the student has finished this module, he/she will be able to:
 Burn Care and Management WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
Burn Care and Management WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
Burns and electrical injuries. Shelley Westwood, RN, BSN
 Burns and electrical injuries Shelley Westwood, RN, BSN Burns A burn is an injury caused by fire, heat, chemicals, radiation, or electricity. Burns are traumatic in that they can cause extreme pain, permanent
Burns and electrical injuries Shelley Westwood, RN, BSN Burns A burn is an injury caused by fire, heat, chemicals, radiation, or electricity. Burns are traumatic in that they can cause extreme pain, permanent
Advanced Paediatric Nursing. Burn Trauma. 26 April Wong Tze Wing NC (Burns), Burns Centre, Surgery, PWH
 Advanced Paediatric Nursing Burn Trauma 26 April 2016 Wong Tze Wing NC (Burns), Burns Centre, Surgery, PWH Objective: Understand burn trauma in children Understand Important nursing interventions in burn
Advanced Paediatric Nursing Burn Trauma 26 April 2016 Wong Tze Wing NC (Burns), Burns Centre, Surgery, PWH Objective: Understand burn trauma in children Understand Important nursing interventions in burn
Thermal Injuries. Manika Bhandari, Malika Bhola, Rucha Desai, Dhruvika Joshi, Abir Shamim Life Science 4M03
 Thermal Injuries Manika Bhandari, Malika Bhola, Rucha Desai, Dhruvika Joshi, Abir Shamim Life Science 4M03 INTRODUCTION Anatomy of the skin The skin has three anatomical layers Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous
Thermal Injuries Manika Bhandari, Malika Bhola, Rucha Desai, Dhruvika Joshi, Abir Shamim Life Science 4M03 INTRODUCTION Anatomy of the skin The skin has three anatomical layers Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous
Thermal Burns PFN: SOMEML07. Terminal Learning Objective. References. Hours: 3.0 Instructor: Action: Communicate knowledge of thermal burns
 Thermal Burns PFN: SOMEML07 Hours: 3.0 Instructor: Slide 1 Terminal Learning Objective Action: Communicate knowledge of thermal burns Condition: Given a lecture in a classroom environment Standard: Received
Thermal Burns PFN: SOMEML07 Hours: 3.0 Instructor: Slide 1 Terminal Learning Objective Action: Communicate knowledge of thermal burns Condition: Given a lecture in a classroom environment Standard: Received
Current Trends in Burn Care
 Objectives Current Trends in Burn Care Jordan Murphy, BSN, CFRN Clinical Educator-KY/FL PHI Air Medical Describes normal skin anatomy. Differentiates pathophysiology related to etiology of injury. Identify
Objectives Current Trends in Burn Care Jordan Murphy, BSN, CFRN Clinical Educator-KY/FL PHI Air Medical Describes normal skin anatomy. Differentiates pathophysiology related to etiology of injury. Identify
Wound Care in the Community. Lisa Sutherland MSc Tissue Viability Senior Lead Ipswich Hospital & Community NHS Trusts
 Wound Care in the Community Lisa Sutherland MSc Tissue Viability Senior Lead Ipswich Hospital & Community NHS Trusts What are the key elements? What is the patient s goal or aim for the wound? What are
Wound Care in the Community Lisa Sutherland MSc Tissue Viability Senior Lead Ipswich Hospital & Community NHS Trusts What are the key elements? What is the patient s goal or aim for the wound? What are
Skin Anatomy and Physiology
 Skin Anatomy and Physiology Body s largest organ Three layers: Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous tissue 1 2 Skin Anatomy and Physiology Complex system, variety of functions Sensation Control of water loss
Skin Anatomy and Physiology Body s largest organ Three layers: Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous tissue 1 2 Skin Anatomy and Physiology Complex system, variety of functions Sensation Control of water loss
The immediate management of burns patients should be similar to management of trauma.
 CATS Clinical Guideline Burns The National Burn Care Review recommends that children with burns should be treated in a Burn Centre. Chelsea and Westminster may take non-ventilated children, Broomfield
CATS Clinical Guideline Burns The National Burn Care Review recommends that children with burns should be treated in a Burn Centre. Chelsea and Westminster may take non-ventilated children, Broomfield
Burn Management. Praz Patcha, MD 13 March 2014
 Burn Management Praz Patcha, MD 13 March 2014 Epidemiology 500,000 / yr 40,000 to 60,000 requiring admission < 1% total injuries in US but $10.4 billion Risk Factors Age Location Demographics Socioeconomics
Burn Management Praz Patcha, MD 13 March 2014 Epidemiology 500,000 / yr 40,000 to 60,000 requiring admission < 1% total injuries in US but $10.4 billion Risk Factors Age Location Demographics Socioeconomics
Hemostasis Inflammatory Phase Proliferative/rebuilding Phase Maturation Phase
 The presenters are staff members of the CHI Health St. Elizabeth Burn and Wound Center. Many of the products discussed are used in our current practice but we have no conflict of interest to disclose.
The presenters are staff members of the CHI Health St. Elizabeth Burn and Wound Center. Many of the products discussed are used in our current practice but we have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Outpatient Burn Care for Primary Care: Who needs a referral?
 Outpatient Burn Care for Primary Care: Who needs a referral? J. Kevin Bailey, MD Associate Professor Department of Surgery Division of Trauma, Critical Care and Burn The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Outpatient Burn Care for Primary Care: Who needs a referral? J. Kevin Bailey, MD Associate Professor Department of Surgery Division of Trauma, Critical Care and Burn The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Burns and Scalds. Treatment and Management. Accident and Emergency Department. Royal Surrey County Hospital. Patient information leaflet
 Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Burns and Scalds Treatment and Management Accident and Emergency Department A Burn is an injury caused to the skin by thermal
Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Burns and Scalds Treatment and Management Accident and Emergency Department A Burn is an injury caused to the skin by thermal
Guidelines for the management of paediatric burns
 Guidelines for the management of paediatric burns Are there signs of airway injury? If yes contact anaesthetist! Is burn TBSA >10% If appropriate COOL THE BURN! Heat room. Insert IVC. Obtain FBC, U&,E
Guidelines for the management of paediatric burns Are there signs of airway injury? If yes contact anaesthetist! Is burn TBSA >10% If appropriate COOL THE BURN! Heat room. Insert IVC. Obtain FBC, U&,E
Aviation Rescue Swimmer Course
 Aviation Rescue Swimmer Course Primary Survey LT 5.4 December 2003 1 Objectives List the procedures used in a primary survey. Demonstrate primary survey procedures used in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario
Aviation Rescue Swimmer Course Primary Survey LT 5.4 December 2003 1 Objectives List the procedures used in a primary survey. Demonstrate primary survey procedures used in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of WSAVA http://www.ivis.org 14(Fri)
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of WSAVA http://www.ivis.org 14(Fri)
Cellular and Tissue Effects. Pathophysiology of the Burn Wound. Special Topics: Thermal Burns & Smoke Inhalation
 Special Topics: Thermal Burns & Smoke Inhalation MEDICAL RESPONDER AND RECEIVER SEMINAR; EXPLOSION AND BLAST INJURIES Pathophysiology of the Burn Wound The burn wound is the source of virtually all ill
Special Topics: Thermal Burns & Smoke Inhalation MEDICAL RESPONDER AND RECEIVER SEMINAR; EXPLOSION AND BLAST INJURIES Pathophysiology of the Burn Wound The burn wound is the source of virtually all ill
LRI Emergency Department. Burn injuries management in adults
 LRI Emergency Department Clinical guideline for: Burn injuries management in adults Authors: Approved by: Martin Wiese Reena Agarwal Claire Porter EF guidelines committee Approval date: 21 Sep 16 Approval
LRI Emergency Department Clinical guideline for: Burn injuries management in adults Authors: Approved by: Martin Wiese Reena Agarwal Claire Porter EF guidelines committee Approval date: 21 Sep 16 Approval
Purpose To outline the pre-hospital and inter-hospital assessment and management of patients with major burns.
 Major Burns HELI.CLI.08 Purpose To outline the pre-hospital and inter-hospital assessment and management of patients with major burns. Procedure Management of Severe Burns For Review Aug 2015 1. Introduction
Major Burns HELI.CLI.08 Purpose To outline the pre-hospital and inter-hospital assessment and management of patients with major burns. Procedure Management of Severe Burns For Review Aug 2015 1. Introduction
Speaker Disclosure Emergent Burn Care I, Debbie Harrell, MSN, RN, NE BC, have no financial relationships to disclose.
 Speaker Disclosure Emergent Burn Care I, Debbie Harrell, MSN, RN, NE BC, have no financial relationships to disclose. Debbie Harrell RN, MSN, Shriners Hospitals for Children Cincinnati Cincinnati, Ohio
Speaker Disclosure Emergent Burn Care I, Debbie Harrell, MSN, RN, NE BC, have no financial relationships to disclose. Debbie Harrell RN, MSN, Shriners Hospitals for Children Cincinnati Cincinnati, Ohio
Daniel A. Beals MD, FACS, FAAP Pediatric Surgery and Urology Community Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics University of
 Daniel A. Beals MD, FACS, FAAP Pediatric Surgery and Urology Community Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics University of Washington Seattle Children s Hospital Objectives Define
Daniel A. Beals MD, FACS, FAAP Pediatric Surgery and Urology Community Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics University of Washington Seattle Children s Hospital Objectives Define
SN Visit Note. Vital Signs. Blood Sugar. Oxygen. Allergies. Pain Assessment. Visit Date: Episode Date: Patient Name: Patient ID:
 Patient Name: Patient ID: Visit Date: Episode Date: SN Visit Note Vital Signs Not ed Temperature: Pulse Apical: Reg Irreg Resp: / min Pulse Radial: Reg Irreg B/P (L) B/P (R) Sitting: / Sitting: / Standing:
Patient Name: Patient ID: Visit Date: Episode Date: SN Visit Note Vital Signs Not ed Temperature: Pulse Apical: Reg Irreg Resp: / min Pulse Radial: Reg Irreg B/P (L) B/P (R) Sitting: / Sitting: / Standing:
WOUNDS. Emergency Procedures in PT
 WOUNDS Emergency Procedures in PT Types of Wounds Abrasions uppermost layer scraped away, minor capillary bleeding occurs, nerve endings exposed Lacerations skin tear with edges jagged and uneven Incisions
WOUNDS Emergency Procedures in PT Types of Wounds Abrasions uppermost layer scraped away, minor capillary bleeding occurs, nerve endings exposed Lacerations skin tear with edges jagged and uneven Incisions
Applicable to. Team Members Performing
 Protocol: Pediatric Burn Inhalation Injury Category Clinical Practice Protocol Number Approval Date November 1, 2016 Due for review November 1, 2018 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations
Protocol: Pediatric Burn Inhalation Injury Category Clinical Practice Protocol Number Approval Date November 1, 2016 Due for review November 1, 2018 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations
Current Concepts in Burn Rehabilitation
 Current Concepts in Burn Rehabilitation 7 th Congress of the Baltic Association of Rehabilitation Tallinn, Estonia September 2010 R. Scott Ward, PT, PhD Professor and Chair Department of Physical Therapy
Current Concepts in Burn Rehabilitation 7 th Congress of the Baltic Association of Rehabilitation Tallinn, Estonia September 2010 R. Scott Ward, PT, PhD Professor and Chair Department of Physical Therapy
Dr. Muhammad Shamim. FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA), MHPE (Nl & Eg)
 Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA), MHPE (Nl & Eg) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Salman bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com Web: surgeonshamim.com
Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA), MHPE (Nl & Eg) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Salman bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com Web: surgeonshamim.com
MANAGING THE BURN WOUND
 MANAGING THE BURN WOUND Robert H. Demling, M.D. Leslie DeSanti R.N., Brigham and Women s Hospital Burn Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA TABLE OF CONTENTS Section I: Section II: Section III: Section
MANAGING THE BURN WOUND Robert H. Demling, M.D. Leslie DeSanti R.N., Brigham and Women s Hospital Burn Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA TABLE OF CONTENTS Section I: Section II: Section III: Section
Review. A. abrasion B. contusion C. hematoma D. avulsion
 Chapter 24 Review Review 1. A young male was struck in the forearm with a baseball and complains of pain to the area. Slight swelling and ecchymosis are present, but no external bleeding. What type of
Chapter 24 Review Review 1. A young male was struck in the forearm with a baseball and complains of pain to the area. Slight swelling and ecchymosis are present, but no external bleeding. What type of
INSTRUCTOR GUIDE FOR TACTICAL FIELD CARE 3B BURNS AND FRACTURES
 INSTRUCTOR GUIDE FOR TACTICAL FIELD CARE 3B BURNS AND FRACTURES 180801 1 Tactical Combat Casualty Care for Medical Personnel 1. August 2017 (Based on TCCC-MP Guidelines 180801 In this presentation, we
INSTRUCTOR GUIDE FOR TACTICAL FIELD CARE 3B BURNS AND FRACTURES 180801 1 Tactical Combat Casualty Care for Medical Personnel 1. August 2017 (Based on TCCC-MP Guidelines 180801 In this presentation, we
Update on Burn Care and Resuscitation
 Niknam Eshraghi, M.D., F.A.C.S General and Burn Surgery; The Oregon Clinic Director; Oregon Burn Center, Legacy Emanuel Medical Center Affiliate Professor of Surgery, Oregon Health Sciences University
Niknam Eshraghi, M.D., F.A.C.S General and Burn Surgery; The Oregon Clinic Director; Oregon Burn Center, Legacy Emanuel Medical Center Affiliate Professor of Surgery, Oregon Health Sciences University
Burn Resuscitation Formulas. John P. Sabra, MD Seton Surgical Group Department of Surgery Dell Medical School Austin, TX
 Burn Resuscitation Formulas John P. Sabra, MD Seton Surgical Group Department of Surgery Dell Medical School Austin, TX BURN INJURY % Physiologic Change % TBSA burn Stasis BURN VASCULAR PERMEABILITY
Burn Resuscitation Formulas John P. Sabra, MD Seton Surgical Group Department of Surgery Dell Medical School Austin, TX BURN INJURY % Physiologic Change % TBSA burn Stasis BURN VASCULAR PERMEABILITY
Lecture Notes. Chapter 9: Smoke Inhalation Injury and Burns
 Lecture Notes Chapter 9: Smoke Inhalation Injury and Burns Objectives List the factors that influence mortality rate Describe the nature of smoke inhalation and the fire environment Recognize the pulmonary
Lecture Notes Chapter 9: Smoke Inhalation Injury and Burns Objectives List the factors that influence mortality rate Describe the nature of smoke inhalation and the fire environment Recognize the pulmonary
Acute And perioperative care of the burn-injured patient. Anesthesiology, V 122, No 2
 Acute And perioperative care of the burn-injured patient Anesthesiology, V 122, No 2 Reporter:R4 沈士鈞 Supervisor: 蔡欣怡醫師 Pathophysiology Initial evaluation and management Anesthetic managemen nt Pathophysiology
Acute And perioperative care of the burn-injured patient Anesthesiology, V 122, No 2 Reporter:R4 沈士鈞 Supervisor: 蔡欣怡醫師 Pathophysiology Initial evaluation and management Anesthetic managemen nt Pathophysiology
NOTE If it is necessary to perform abdominal thrusts, expose the abdominal area prior to pressing on the abdomen.
 ENABLING OBJECTIVES: 4.7 List the procedures used in a primary survey. 4.8 Demonstrate primary survey procedures used in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario without injury to personnel or damage to equipment.
ENABLING OBJECTIVES: 4.7 List the procedures used in a primary survey. 4.8 Demonstrate primary survey procedures used in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario without injury to personnel or damage to equipment.
Subtle Signs of Child Abuse Child s Protection Office MOH Presented by Dr.Fatoumah Alabdulrazzaq M.D,FRCPC,FAAP,PEM(C)
 Subtle Signs of Child Abuse Child s Protection Office MOH Presented by Dr.Fatoumah Alabdulrazzaq M.D,FRCPC,FAAP,PEM(C) Cutaneous Injuries Bruise : injury to soft tissues in which skin is not broken, characterized
Subtle Signs of Child Abuse Child s Protection Office MOH Presented by Dr.Fatoumah Alabdulrazzaq M.D,FRCPC,FAAP,PEM(C) Cutaneous Injuries Bruise : injury to soft tissues in which skin is not broken, characterized
Skin Integrity and Wound Care
 Skin Integrity and Wound Care By Dr. Amer Hasanien & Dr. Ali Saleh Skin Integrity and Wound Care Skin integrity: the presence of normal Skin & Uninterrupted skin layers by wounds. Factors affecting appearance
Skin Integrity and Wound Care By Dr. Amer Hasanien & Dr. Ali Saleh Skin Integrity and Wound Care Skin integrity: the presence of normal Skin & Uninterrupted skin layers by wounds. Factors affecting appearance
Sidney Miller, MD, FACS Professor of Surgery Director of Research and Development Ohio State University Burn Center
 Management of the Burn Patient Sidney Miller, MD, FACS Professor of Surgery Director of Research and Development Ohio State University Burn Center American Burn Association Transfer Criteria Burn > 10%
Management of the Burn Patient Sidney Miller, MD, FACS Professor of Surgery Director of Research and Development Ohio State University Burn Center American Burn Association Transfer Criteria Burn > 10%
Student Guide Module 4: Pediatric Trauma
 Student Guide Module 4: Pediatric Trauma Problem based learning exercise objectives Understand how to manage traumatic injuries in mass casualty events. Discuss the features and the approach to pediatric
Student Guide Module 4: Pediatric Trauma Problem based learning exercise objectives Understand how to manage traumatic injuries in mass casualty events. Discuss the features and the approach to pediatric
OUTLINE SHEET 5.4 PRIMARY SURVEY
 ENABLING OBJECTIVES: 4.7 List the procedures used in a primary survey. 4.8 Demonstrate primary survey procedures used in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario without injury to personnel or damage to equipment.
ENABLING OBJECTIVES: 4.7 List the procedures used in a primary survey. 4.8 Demonstrate primary survey procedures used in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario without injury to personnel or damage to equipment.
Burn wounds - Determining the size and type degree
 1 Burn wounds - Determining the size and type degree Determining surface area of burn (Open hand only for small burns) 1 2 Burn depth Most burns are a combination of superficial and deeper burns and the
1 Burn wounds - Determining the size and type degree Determining surface area of burn (Open hand only for small burns) 1 2 Burn depth Most burns are a combination of superficial and deeper burns and the
the bleeding won t stop? Liane Manz RN, BScN, CNCC(c) Royal Alexandra Hospital
 What do you do when the bleeding won t stop? Teddie Tanguay RN, MN, NP, CNCC(c) Teddie Tanguay RN, MN, NP, CNCC(c) Liane Manz RN, BScN, CNCC(c) Royal Alexandra Hospital Outline Case study Normal coagulation
What do you do when the bleeding won t stop? Teddie Tanguay RN, MN, NP, CNCC(c) Teddie Tanguay RN, MN, NP, CNCC(c) Liane Manz RN, BScN, CNCC(c) Royal Alexandra Hospital Outline Case study Normal coagulation
Chapter 24 Soft Tissue Injuries Presentation Notes
 Names: Chapter 24 Soft Tissue Injuries Presentation Notes Anatomy of the Skin - Function of the Skin control Soft-Tissue Injuries injuries Soft-tissue damage the skin injuries Break in the of the skin
Names: Chapter 24 Soft Tissue Injuries Presentation Notes Anatomy of the Skin - Function of the Skin control Soft-Tissue Injuries injuries Soft-tissue damage the skin injuries Break in the of the skin
The Affects of Music Therapy on Management of Pain and Anxiety During Burn Dressing Changes
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 The Affects of Music Therapy on Management
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 The Affects of Music Therapy on Management
Frontline First Aid 2012 Emergency Care Manual Treatments
 Heart Attack/Angina (p. 132) 1. Recognize signals of a heart attack 2. Assist with Nitroglycerin 3. Assist with ASA 4. Rest and Comfort 6. More advanced medical care Breathing Emergencies (p. 105) Anaphylaxis
Heart Attack/Angina (p. 132) 1. Recognize signals of a heart attack 2. Assist with Nitroglycerin 3. Assist with ASA 4. Rest and Comfort 6. More advanced medical care Breathing Emergencies (p. 105) Anaphylaxis
Fire Deaths. Dr Julie McAdam Consultant Forensic Pathologist Glasgow University
 Fire Deaths Dr Julie McAdam Consultant Forensic Pathologist Glasgow University Forensic investigation multidisciplinary fire officers, police officers, scientists, photographers, pathologist, procurator
Fire Deaths Dr Julie McAdam Consultant Forensic Pathologist Glasgow University Forensic investigation multidisciplinary fire officers, police officers, scientists, photographers, pathologist, procurator
Chapter 21: Burns Introduction to Burn Injuries (1 of 2) Introduction to Burn Injuries (2 of 2) Reduction in Burn Injuries Pathophysiology of Burns
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Chapter 21: Burns Introduction to Burn Injuries (1 of 2) 1.25-2 million Americans treated for burns annually 50,000 require 3-5% considered life threatening leading cause of death for children
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Chapter 21: Burns Introduction to Burn Injuries (1 of 2) 1.25-2 million Americans treated for burns annually 50,000 require 3-5% considered life threatening leading cause of death for children
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Advanced Pre-Test
 ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Advanced Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle crash and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Advanced Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle crash and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I. A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin.
 EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
Surgical Management of wounds, flaps, grafts, and scars
 Disclosures Surgical Management of wounds, flaps, grafts, and scars I have no financial disclosures Cherrie Heinrich, MD, FACS Department of Plastic Surgery Regions Hospital Assistant Professor University
Disclosures Surgical Management of wounds, flaps, grafts, and scars I have no financial disclosures Cherrie Heinrich, MD, FACS Department of Plastic Surgery Regions Hospital Assistant Professor University
SKIN INTEGRITY & WOUND CARE
 SKIN INTEGRITY & WOUND CARE Chapter 34 1 skin integrity: intact skin refers to the presence of normal skin layer uninterrupted by wound 2 WOUNDS DISRUPTION IN THE INTEGRITY OF BODY TISSUE CLASSIFIED AS:
SKIN INTEGRITY & WOUND CARE Chapter 34 1 skin integrity: intact skin refers to the presence of normal skin layer uninterrupted by wound 2 WOUNDS DISRUPTION IN THE INTEGRITY OF BODY TISSUE CLASSIFIED AS:
Patient Details Hospital number NHS number. Surname First name DOB. Permanent address. Post code. Mobile No. Temporary. Mother DOB. Father.
 Burns Unit Page 12 Paediatric Burn Injuries - Assessment & Admission Burns Unit Page 1 Discharge Patient Details Hospital number NHS number Admission date Injury date Hospital Use time time Time: Discharge
Burns Unit Page 12 Paediatric Burn Injuries - Assessment & Admission Burns Unit Page 1 Discharge Patient Details Hospital number NHS number Admission date Injury date Hospital Use time time Time: Discharge
Not All That Blisters Is a Burn! Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD CHAMP Webinar December 6, 2012
 Not All That Blisters Is a Burn! Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD CHAMP Webinar December 6, 2012 Objectives To review the epidemiology of burns in children including burns caused by abuse To review the steps
Not All That Blisters Is a Burn! Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD CHAMP Webinar December 6, 2012 Objectives To review the epidemiology of burns in children including burns caused by abuse To review the steps
Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy)
 Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy) Basic Information: The insertion and placement of a chest tube into the pleural cavity for the purpose of removing air, blood, purulent drainage, or
Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy) Basic Information: The insertion and placement of a chest tube into the pleural cavity for the purpose of removing air, blood, purulent drainage, or
Objectives. Case Presentation. Respiratory Emergencies
 Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
Septic Shock. Kathryn Sims, PGY I
 Septic Shock Kathryn Sims, PGY I A 6 y.o. previously healthy boy presents to the ED with 7 days of fever accompanied by chills. Further history reveals the patient has also been experiencing dysuria for
Septic Shock Kathryn Sims, PGY I A 6 y.o. previously healthy boy presents to the ED with 7 days of fever accompanied by chills. Further history reveals the patient has also been experiencing dysuria for
January Adult Burn Injured patients
 Guideline Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review date (when this version goes out of date): Explicit definition
Guideline Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review date (when this version goes out of date): Explicit definition
Presented by: Indah Dwi Pratiwi
 Presented by: Indah Dwi Pratiwi Normal Fluid Requirements Resuscitation Fluids Goals of Resuscitation Maintain normal body temperature In most cases, elevate the feet and legs above the level of the heart
Presented by: Indah Dwi Pratiwi Normal Fluid Requirements Resuscitation Fluids Goals of Resuscitation Maintain normal body temperature In most cases, elevate the feet and legs above the level of the heart
Basic First Aid. Sue Fisher Emergency Management Coordinator CSUF University Police
 Basic First Aid Sue Fisher Emergency Management Coordinator CSUF University Police Information given for this lecture is not meant to replace any official training by the American Red Cross, or any other
Basic First Aid Sue Fisher Emergency Management Coordinator CSUF University Police Information given for this lecture is not meant to replace any official training by the American Red Cross, or any other
Burns. There is also technically a fourth-degree burn. In this type, the damage of third-degree burns extends beyond the skin into tendons and bones.
 Burns can be caused by a variety of household items, including electrical equipment and chemicals. Very light burns can be treated at home and only cause superficial damage, while more severe burns need
Burns can be caused by a variety of household items, including electrical equipment and chemicals. Very light burns can be treated at home and only cause superficial damage, while more severe burns need
Management of severe burns
 Management of severe burns Who gets admitted to the ICU? Large % surface area burns >25% adults >15% children/elderly Inhalational or airway burns Multi-trauma Co-morbidities Burns centres Regional referral
Management of severe burns Who gets admitted to the ICU? Large % surface area burns >25% adults >15% children/elderly Inhalational or airway burns Multi-trauma Co-morbidities Burns centres Regional referral
Urgent Care Burn Management. Neil Uspal Division of Emergency Medicine Seattle Children s Hospital October 6 th, 2017
 Urgent Care Burn Management Neil Uspal Division of Emergency Medicine Seattle Children s Hospital October 6 th, 2017 Objectives Epidemiology of Burn Injuries Classification of Burns Initial Burn Management
Urgent Care Burn Management Neil Uspal Division of Emergency Medicine Seattle Children s Hospital October 6 th, 2017 Objectives Epidemiology of Burn Injuries Classification of Burns Initial Burn Management
TRAUMATIC EMERGENCIES
 TRAUMATIC EMERGENCIES I. General. A. Follow General Principles/Routine Care protocol unless otherwise indicated. B. Limit scene time for trauma patients, with goal of 15 minutes. C. See Appendix B for
TRAUMATIC EMERGENCIES I. General. A. Follow General Principles/Routine Care protocol unless otherwise indicated. B. Limit scene time for trauma patients, with goal of 15 minutes. C. See Appendix B for
Northwest Community EMS System Continuing Education Class Credit Questions for April 2014 Summer Emergencies
 Northwest Community EMS System Continuing Education Class Credit Questions for April 2014 Summer Emergencies Name (PRINT): Date submitted: Affiliation: Rating: [ ] Complete [ ] Incomplete The answers are
Northwest Community EMS System Continuing Education Class Credit Questions for April 2014 Summer Emergencies Name (PRINT): Date submitted: Affiliation: Rating: [ ] Complete [ ] Incomplete The answers are
Modern management of paediatric burns
 Modern management of paediatric burns Burn injuries pose a major threat to children in South Africa and remain a devastating injury, because of the resulting severe emotional and physical scarring and
Modern management of paediatric burns Burn injuries pose a major threat to children in South Africa and remain a devastating injury, because of the resulting severe emotional and physical scarring and
Essex and Herts Air Ambulance Trust (EHAAT) Essex and Herts Air Ambulance: a focused case series for pre-hospital practice
 Essex and Herts Air Ambulance: a focused case series for pre-hospital practice Case 1: management of a paediatric burn Erica Ley, critical care paramedic, Essex and Herts Air Ambulance; Adam Chesters,
Essex and Herts Air Ambulance: a focused case series for pre-hospital practice Case 1: management of a paediatric burn Erica Ley, critical care paramedic, Essex and Herts Air Ambulance; Adam Chesters,
Initial assessment. ATLS/ABLS protocol and assess for other injuries/fractures based on mechanism. Inhalational injury. Vascular compromise:
 Complex Hand Burns Brent Egeland, MD Assistant Professor Dell Medical School Department of Surgery and Perioperative Care Institute of Reconstructive Plastic Surgery Plastic, Hand, and Reconstructive Microsurgery
Complex Hand Burns Brent Egeland, MD Assistant Professor Dell Medical School Department of Surgery and Perioperative Care Institute of Reconstructive Plastic Surgery Plastic, Hand, and Reconstructive Microsurgery
Critical Care of the Post-Surgical Patient
 Critical Care of the Post-Surgical Patient, Dr med vet, DEA, DECVIM-CA Many critically ill patients require surgical treatments. These patients often have multisystem abnormalities during the immediate
Critical Care of the Post-Surgical Patient, Dr med vet, DEA, DECVIM-CA Many critically ill patients require surgical treatments. These patients often have multisystem abnormalities during the immediate
Burns & its Homoeopathic Management - Pawan Satyanarayan Chandak
 Page 1 of 7 Burns & its Homoeopathic Management Pawan Satyanarayan Chandak A burn is a tissue injury from thermal heat or cold application or from the absorption of physical energy or chemical contact.
Page 1 of 7 Burns & its Homoeopathic Management Pawan Satyanarayan Chandak A burn is a tissue injury from thermal heat or cold application or from the absorption of physical energy or chemical contact.
TITLE OF CASE: Burn Injuries and Management
 TITLE OF CASE: Burn Injuries and Management AUTHOR OF CASE: Magdalena Malinowska SUMMARY: Patient is a 23 year old female who was brought in by EMS to the Emergency Room post a motor vehicle accident in
TITLE OF CASE: Burn Injuries and Management AUTHOR OF CASE: Magdalena Malinowska SUMMARY: Patient is a 23 year old female who was brought in by EMS to the Emergency Room post a motor vehicle accident in
INTRODUCTION. Objectives. When the student has finished this module, he/she will be able to:
 Hydrofluoric Acid Burns WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
Hydrofluoric Acid Burns WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017 RN.ORG, S.A., RN.ORG,
Patient Assessment From Brady s First Responder (8th Edition) 83 Questions
 Patient Assessment From Brady s First Responder (8th Edition) 83 Questions 1. Which question is important if your patient may be a candidate for surgery? p. 183 *A.) When did you last eat? B.) What is
Patient Assessment From Brady s First Responder (8th Edition) 83 Questions 1. Which question is important if your patient may be a candidate for surgery? p. 183 *A.) When did you last eat? B.) What is
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: ASSESSMENT Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: ASSESSMENT Revised: 11/2013 DEFINITIONS General Impression - EMT develops a plan of action from the
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: ASSESSMENT Revised: 11/2013 DEFINITIONS General Impression - EMT develops a plan of action from the
CARE OF PATIENTS WITH BURNS. NUR 240 Donna Ricketts, MSN, RN, OCN
 CARE OF PATIENTS WITH BURNS NUR 240 Donna Ricketts, MSN, RN, OCN INCIDENCE/PREVALENCE OF BURN INJURY 5 th most common unintentional injury deaths 3 rd leading cause of fatal home injuries 4,000 burn deaths
CARE OF PATIENTS WITH BURNS NUR 240 Donna Ricketts, MSN, RN, OCN INCIDENCE/PREVALENCE OF BURN INJURY 5 th most common unintentional injury deaths 3 rd leading cause of fatal home injuries 4,000 burn deaths
-Cardiogenic: shock state resulting from impairment or failure of myocardium
 Shock chapter Shock -Condition in which tissue perfusion is inadequate to deliver oxygen, nutrients to support vital organs, cellular function -Affects all body systems -Classic signs of early shock: Tachycardia,tachypnea,restlessness,anxiety,
Shock chapter Shock -Condition in which tissue perfusion is inadequate to deliver oxygen, nutrients to support vital organs, cellular function -Affects all body systems -Classic signs of early shock: Tachycardia,tachypnea,restlessness,anxiety,
