1 Recombinant proteins in insect and mammal cells , F E B R U A R Y 2 3 RD
|
|
|
- Wilfrid Mosley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Recombinant proteins in insect and mammal cells , F E B R U A R Y 2 3 RD
2 Bacteria Yeast Insect cells Mammalian Cell growth Medium complexity Rapid (30 min) Rapid (90 min) Slow (18-24h) Slow (24h) No No Yes Yes Cost Low Low High High Expression High Low-high Low-high Mow-medium 2
3 Post-translational modifications (PTMs) N/O-Glycosylation attaches a sugar ; one of the most important modification with significant effects on protein folding, conformation, distribution, stability and activity Phosporylation adds a phosphate to Ser, Thr, Tyr; critical in the regulation of cell cycle, growth, signal transduction Methylation adds a methyl group at Lys or Arg; increases hydrophobicity of proteins N-acetylation adds acetyl group to N-term or at Lys; initially found to be important for the regulation of histone activity in the nucleus, it also occurs on cytosolic proteins. S-nitrosylation: stabilization of proteins γ-carboxylation converts glutamate to γ-carboxyglutamate; facilitates calcium binding, which is important/essential for the function of the protein 3
4 Post-translational modifications Protein folding N-linked glycosylation O-linked glycosylation Bacteria Yeast Insect Mammals Not reliable None Usually reliable High mannose Very reliable Simple, no sialic acid Very reliable Complex N Y Y Y Phosphorylation N Y Y Y Acetylation N Y Y Y Acylation N Y Y Y g-carboxylation N N N Y 4
5 Post-translational modifications Protein folding N-linked glycosylation O-linked glycosylation Bacteria Yeast Insect Mammals Not reliable None Usually reliable High mannose Very reliable Simple, no sialic acid Very reliable Complex N Y Y Y Phosphorylation N Y Y Y Acetylation N Y Y Y Acylation N Y Y Y g-carboxylation N N N Y 5
6 Post-translational modifications Protein folding N-linked glycosylation O-linked glycosylation Bacteria Yeast Insect Mammals Not reliable None Usually reliable High mannose Very reliable Simple, no sialic acid Very reliable Complex N Y Y Y Phosphorylation N Y Y Y Acetylation N Y Y Y Acylation N Y Y Y g-carboxylation N N N Y 6
7 Baculovirus-insect cell expression systems 7
8 Baculovirus 8 16 th century: wilting disease of silk-producing larvae More than 600 species of insects: Lepidoptera (butterflies and moths) Hymenoptera (sawflies and wasps) Diptera (flies) Coleoptera (beetles) Since 1940s: biopesticides in crop fields Non-infected larvae of Mamestra brassicae Larvae of Mamestra brassicae 7 days after infection
9 Baculovirus Since 1990s: production of complex eukaryotic proteins in insect cell cultures 1- research purposes - no need of codon optimization - post-translational modifications: glycosylation, phosporylation, S-nitrosylation, methylation, N-acetylation Brickey et al Expression and characterization of the alpha-subunit of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II using the baculovirus expression system. Biochem Biophys Res Com, 173: Ardisson-Araujo et al A baculovirus-mediated strategy for full-length plant virus coat protein expression and purification. Virol J. 10: human and veterinary purposes - vaccine against foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) of goat, sheep and other cloven-hoof animals (Li et al Expression of foot-and-mouth disease virus capsid proteins in silkworm-baculovirus expression system and its utilization as a subunit vaccine. PlosONe, 3(5): e2283) - vaccine for prevention of H5N1 Avian influenza in chickens (Nwe et al Expression of hemagglutinin protein from the avion influenza virus H5N1 in a baculovirus/insect cell system significantly enhanced by suspension culture. BMC Microbiol, 6:16) - production of the human nerve growth factor, rhngf (Nguyen et al Fed-batch culture of insect cells: a method to increase the yield of recombinant human nerve growth factor (rhngf) in the baculovirus expression system. J Biotech, 31: ) - gene therapy (Kohlbrenner et al Successful production of pseudotyped raav vectors using a modified baculovirus expression system. Mol Terap, 12: )
10 Baculovirus Since 1990s: production of complex eukaryotic proteins in insect cell cultures 1- research purposes - no need of codon optimization - post-translational modifications: glycosylation, phosporylation, S-nitrosylation, methylation, N-acetylation (Brickey et al Expression and characterization of the alpha-subunit of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II using the baculovirus expression system. Biochem Biophys Res Com, 173: ) 2- human and veterinary purposes 10 - vaccine against foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) of goat, sheep and other cloven-hoof animals (Li et al Expression of foot-and-mouth disease virus capsid proteins in silkworm-baculovirus expression system and its utilization as a subunit vaccine. PlosONe, 3(5): e2283) - vaccine for prevention of H5N1 Avian influenza in chickens (Nwe et al Expression of hemagglutinin protein from the avion influenza virus H5N1 in a baculovirus/insect cell system significantly enhanced by suspension culture. BMC Microbiol, 6:16) - production of the human nerve growth factor, rhngf (Nguyen et al Fed-batch culture of insect cells: a method to increase the yield of recombinant human nerve growth factor (rhngf) in the baculovirus expression system. J Biotech, 31: ) - gene therapy (Kohlbrenner et al Successful production of pseudotyped raav vectors using a modified baculovirus expression system. Mol Terap, 12: )
11 Baculovirus Insect pathogen with > 500 baculovirus isolated Double-strand circular supercoiled DNA virus in a rod-shaped capsid kbp size 53 baculovirus isolates completely sequenced (January 2011) High conservation of core genes involved in crucial functions Two baculoviruses widely used in biotechnology: - Autographa california multiple nulceopolyhedrovirus (AcMNPV) - Bombyx mori (BmNPV) Two different virion types: - budded virions (BV) - occlusion derived virus (ODV) 11
12 Baculovirus Autographa californica multicapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus (AcMNPV) 12 Autographa californica (alfalfa looper - Lepidoptera) Polyhedrin: major constituent of the polyhedron matrix viral protein of 29 kda protection solubilized only in highly alkalin conditions
13 Baculovirus 13 Life cycle in 2 phases: 1- budded-virus to spread infection from cell to cell within individual 2- Occlusion-derived virus as dispersal agent between individuals and survival mechanism
14 Baculovirus 14 Schematic representation of the four phases of baculovirus gene expression in vitro
15 Baculovirus Life cycle in vitro recombinant virus by homologous recombination 15 Baculovirus genome is too large to directly insert foreign genes easily Cloning of the foreign gene into a transfer vector which contains flanking sequences which are homologous to baculovirus genome. Co-transfection into insect cells. Homologous recombination takes place inside the insect cells, leading to recombinant baculovirus which will produce the foreign protein Screening by plaque assay : occlusion-negative phenotype.
16 Commercially available from Pharmingen: - BaculoGold baculovirus DNA bears a lethal deletion and does not code for viable virus. The co-transfection with a complementing baculovirus transfer vector rescues the lethal deletion. Recombination frequencies exceed 99%. - Linearized AcRP23.lacZ baculovirus DNA is a modified AcNPV baculovirus DNA in which the polyhedrin was replaced by a lacz gene. The recombination disrupts the lacz gene, allowing a blue/white screening. 30% of virus will be recombinant - Linearized AcUW1.lacZ baculovirus DNA: same as precedent but lacz gene under the control of p10 promoter 16
17 Bac-to-Bac Invitrogen/LifeTech 17 in vitro-recombinant virus by site-specific transposition: use site-specific transposition with Tn7 to insert foreign genes into bacmid (baculovirus shuttle vector) propagated in E.coli
18 Bac-to-Bac BES - ThermoFisher 18 Gene under the control of polyhedrin promoter: high yield pfastbac1: virus which express unfused recombinant proteins pfastbac HT series allows expression of polyhistidine-tagged proteins which can be purified rapidly on metal affinity resins pfastbac DUAL vector contains two promoters (polyhedrin and p10) allowing expression of 2 genes pfastbac HBM TOPO vector enables secreted protein expression because it has the honeybee melittin (HBM) secretion signal
19 FlashBAC Oxford Expression Technologies 19 combines the advantages of bacmid technology with homologous recombination in insect cells
20 FlashBAC Oxford Expression Technologies 20
21 FlashBAC Oxford Expression Technologies 21 flashbac Backbone virus DNA has a chia deletion, which prevents production of virus chitinase. This enzyme blocks the secretory pathway and its absence helps improve membrane and secreted protein production1. flashbac GOLD Backbone virus DNA has gene deletions for chia and v-cath. This avoids production of chitinase and cathepsin, a viral protease that may otherwise degrade susceptible target proteins. flashbac ULTRA Backbone virus DNA has deletions of chia, v-cath and p10/p26/p74. Deletion of p10 results in delayed cell lysis (particularly noticeable) in TnHi5 cells and thus can extend protein production times. It also reduces the metabolic burden on the cell of producing high levels of P10 protein. flashbac PRIME No gene deletions in the virus back bone. Useful if the proteins being expressed form complexes inside the cytoplasm or nucleus that need to be purified. We find that the relatively early cell lysis associated with PRIME makes it easier to purify these complexes e.g. VLPs.
22 Comparison of different systems 22
23 Insect cell lines 23
24 Insect cell lines 24
25 Growing insect cells Monolayer culture Suspension culture 25 Requirements for proper insect cell culture: Temperature- Optimal range is C ph- Optimal range is 6.1 to 6.4 Aeration-Requires passive 02 diffusion for optimal growth & recombinant protein expression Osmolality- Optimum is mosm/kg Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS): source of nutrients and protection from cellular shear forces
26 Insect cell transfection Calcium phosphate coprecipitation: the method involves the formation of a coprecipitate of calcium phosphate and DNA that is taken up by the cells. DEAE-dextran-mediated transfection: DEAE-dextran is a polycation that binds both DNA and the cell surface, promoting thus adsoprtion of the DNA by the cell. Liposome-mediated transfection: this method employs the synthetic lipid DOTMA which was specifically designed to form positively charged liposomes that spontaneously interact with DNA. Upon addition to the cells, the liposome/dna complex binds to the ngatively charged cell surface. The liposome then fused with the cell membrane, efficiently introducing the DNA into the cells. Electroporation Cellfectin/Cellfectin II and more 26
27 Limitations of BV-insect cell expression systems BV infection ultimately results in cell death and lysis in a few days due to the very strong expression driven by Polh or p10 promoter Glycosylation in insect cells differs in many aspect from in mammalian cells: oligosaccharides are shorter in insect cells nature of N- and O-glucoside is different: Mammalian cells N-glucosides Complex (mannose, galactose, N- acetylglucosamine, neuramic acid) with sialylation O-glucosides 27 Galactose, N-acetylglucosamine, N-acetylgalactosamine, neuramic acid Insect cells Simple (mannose) but no sialylation Not identical but very similar to mammalian cells absence of sialylation of N-glycans in insect cells: problem for human therapeutics insect cells are not able to properly process proteins that are initially synthesized as large inactive precursor proteins
28 Protein expression in mammalian cells 28
29 Baculovirus gene transfer into Mammalian cells 29 Baculovirus can enter mammalian cells via endocytosis BUT they are not able to replicate into mammalian cells and require the insertion of a strong mammalian gene regulatory element
30 Baculovirus gene transfer into Mammalian cells 30 Known as BacMam and initiated by Boyce and Bucher Baculoviral transfer plasmid: lacz reporter gene under control of RSV (Rous sarcoma virus) promoter together with mammalian SV40 splice and polyadenylation signals
31 Baculovirus gene transfer into Mammalian cells 31 Transfer plasmid AcMNPV Recombination by co-transfection of Sf21 insect cells Purification of modified-acmnpv Transfection of a variety of mammalian cell lines
32 Mammalian cells 32 Expression cassette: - strong viral promoters from cytomegalovirus (CMV) or SV40 - Kozak sequence (ggrccaugg in higher vertebrate) - signal sequence for secretion - sequence tag - cleavage site - poly-adenylation signal Expression vector: - antibiotic resistance gene for selection of stable mammalian cell line - antibiotic resistance gene for selection in E. coli - puc origin for multiplication in E. coli - multiple cloning site
33 Mammalian cells 33
34 Mammalian cells 34 Transfection of mammalian cells: - calcium phosphate (Chen and Okayama, 1987;Wigler et al., 1977), - lipid-mediated (Felgner et al., 1989; Felgner and Ringold, 1989) - and electroporation (Chu et al., 1987; Shigekawa and Dower, 1988)
35 Mammalian cells 35 Cell line CHO DG44 DUK-B11 NSO HEK293 BHK COS PER.C6 Origin An epithelial cell line derived from the ovaries of Chinese hamsters A CHO cell line (marker: DHFR) A CHO cell line (marker: GS) A myeloma cell line derived from B lymphocytes of mice An epithelial cell line derived from human embryonic kidney cells transformed with adenovirus DNA A cell line derived from the kidney cells of baby Syrian golden hamsters Fibroblast cell lines derived from the kidney cells (SV40 transformed) of African green minkeys A trademarked cell line derived from a human retinal cell (fron Crucell Holland BV)
36 36
37 Baculovirus in plants 37
38 38
39 39
40 baculovirus vector can be used to express recombinant proteins in plants. baculovirus vector- mediated gene delivery and expression system could be used in plant biotechnology for fast and efficient production of recombinant proteins and for molecular virology studies in plants. 40
Oxford Expression Technologies Ltd
 Oxford Expression Technologies Ltd Founded in 2007 as a spin out from Oxford Brookes University and Natural Environment Research Council Technology based on the insect baculovirus expression vectors (BEVs)
Oxford Expression Technologies Ltd Founded in 2007 as a spin out from Oxford Brookes University and Natural Environment Research Council Technology based on the insect baculovirus expression vectors (BEVs)
Enhancing the baculovirus expression system with VANKYRIN technology. Kendra Steele, Ph.D.
 Enhancing the baculovirus expression system with VANKYRIN technology Kendra Steele, Ph.D. Insect cells Can express mammalian proteins Similarities with mammalian cells Eukaryotic systems How protein are
Enhancing the baculovirus expression system with VANKYRIN technology Kendra Steele, Ph.D. Insect cells Can express mammalian proteins Similarities with mammalian cells Eukaryotic systems How protein are
Development of a Novel Recombinant Influenza Vaccine in Insect Cells
 Development of a Novel Recombinant Influenza Vaccine in Insect Cells Clifton McPherson New Cells for New Vaccines II September 18, 2007 cmcpherson@proteinsciences.com New Cell for New Vaccines II Topics:
Development of a Novel Recombinant Influenza Vaccine in Insect Cells Clifton McPherson New Cells for New Vaccines II September 18, 2007 cmcpherson@proteinsciences.com New Cell for New Vaccines II Topics:
Getting the Most Out of Baculovirus. Linda Lua
 Getting the Most Out of Baculovirus Linda Lua Enabling World Class Research Recombinant Protein Production Discovery, Translational, Preclinical Drug discovery, vaccinology, diagnostics, functional materials,
Getting the Most Out of Baculovirus Linda Lua Enabling World Class Research Recombinant Protein Production Discovery, Translational, Preclinical Drug discovery, vaccinology, diagnostics, functional materials,
Baculovirus Reference Material Initiative. Kuopio, Finland, Document for discussion BRMWT
 Baculovirus Reference Material Initiative Kuopio, Finland, 08-27-2010 Document for discussion BRMWT BRM-discussion Molecular design Bulk Production Downstream processing Quantitation & Characterization
Baculovirus Reference Material Initiative Kuopio, Finland, 08-27-2010 Document for discussion BRMWT BRM-discussion Molecular design Bulk Production Downstream processing Quantitation & Characterization
Chapter 5. Viral infections (I)
 Chapter 5. Viral infections (I) 1. Properties of virus - Virus: derived from Latin and means poison or stench (foul odor) - Definition an infectious, potentially pathogenic nucleoprotein entity which reproduces
Chapter 5. Viral infections (I) 1. Properties of virus - Virus: derived from Latin and means poison or stench (foul odor) - Definition an infectious, potentially pathogenic nucleoprotein entity which reproduces
The humoral immune responses to IBV proteins.
 The humoral immune responses to IBV proteins. E. Dan Heller and Rosa Meir The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel COST FA1207 meeting WG2 + WG3, Budapest, Jan. 2015 1 IBV encodes four major structural
The humoral immune responses to IBV proteins. E. Dan Heller and Rosa Meir The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel COST FA1207 meeting WG2 + WG3, Budapest, Jan. 2015 1 IBV encodes four major structural
Auxin-Inducible Degron (AID) System Total Set
 Catalog No. BRS-APC011A Auxin-Inducible Degron (AID) System Total Set This AID System Charactoristics Principle of Auxin-Inducible Degron (AID ) System AID plasmid protein 1. Transfection of AID plasmid
Catalog No. BRS-APC011A Auxin-Inducible Degron (AID) System Total Set This AID System Charactoristics Principle of Auxin-Inducible Degron (AID ) System AID plasmid protein 1. Transfection of AID plasmid
Name Section Problem Set 6
 Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 6 Question 1 The viral family Orthomyxoviridae contains the influenza A, B and C viruses. These viruses have a (-)ss RNA genome surrounded by a capsid composed of lipids
Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 6 Question 1 The viral family Orthomyxoviridae contains the influenza A, B and C viruses. These viruses have a (-)ss RNA genome surrounded by a capsid composed of lipids
Size nm m m
 1 Viral size and organization Size 20-250nm 0.000000002m-0.000000025m Virion structure Capsid Core Acellular obligate intracellular parasites Lack organelles, metabolic activities, and reproduction Replicated
1 Viral size and organization Size 20-250nm 0.000000002m-0.000000025m Virion structure Capsid Core Acellular obligate intracellular parasites Lack organelles, metabolic activities, and reproduction Replicated
7.012 Problem Set 6 Solutions
 Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 6 Solutions Question 1 The viral family Orthomyxoviridae contains the influenza A, B and C viruses. These viruses have a (-)ss RNA genome surrounded by a capsid composed
Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 6 Solutions Question 1 The viral family Orthomyxoviridae contains the influenza A, B and C viruses. These viruses have a (-)ss RNA genome surrounded by a capsid composed
Significance and Functions of Carbohydrates. Bacterial Cell Walls
 Biochemistry 462a - Carbohydrate Function Reading - Chapter 9 Practice problems - Chapter 9: 2, 4a, 4b, 6, 9, 10, 13, 14, 15, 16a, 17; Carbohydrate extra problems Significance and Functions of Carbohydrates
Biochemistry 462a - Carbohydrate Function Reading - Chapter 9 Practice problems - Chapter 9: 2, 4a, 4b, 6, 9, 10, 13, 14, 15, 16a, 17; Carbohydrate extra problems Significance and Functions of Carbohydrates
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways
 Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Viruses. Rotavirus (causes stomach flu) HIV virus
 Viruses Rotavirus (causes stomach flu) HIV virus What is a virus? A virus is a microscopic, infectious agent that may infect any type of living cell. Viruses must infect living cells in order to make more
Viruses Rotavirus (causes stomach flu) HIV virus What is a virus? A virus is a microscopic, infectious agent that may infect any type of living cell. Viruses must infect living cells in order to make more
Introduction retroposon
 17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
Lecture 2: Virology. I. Background
 Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
5/6/17. Diseases. Disease. Pathogens. Domain Bacteria Characteristics. Bacteria Viruses (including HIV) Pathogens are disease-causing organisms
 5/6/17 Disease Diseases I. II. Bacteria Viruses (including HIV) Biol 105 Chapter 13a Pathogens Pathogens are disease-causing organisms Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic.
5/6/17 Disease Diseases I. II. Bacteria Viruses (including HIV) Biol 105 Chapter 13a Pathogens Pathogens are disease-causing organisms Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic.
Construction and Bioassay of Recombinant AcNPV Containing SpltNPV gp37 Fusion gene
 Construction and Bioassay of Recombinant AcNPV Containing SpltNPV gp37 Fusion gene Chongbi Li 1, *, Zhaofei Li 2, Guanghong Li 2, Yi Pang 2 1 Biopharmaceutical Engineering Center of Zhaoqing University,
Construction and Bioassay of Recombinant AcNPV Containing SpltNPV gp37 Fusion gene Chongbi Li 1, *, Zhaofei Li 2, Guanghong Li 2, Yi Pang 2 1 Biopharmaceutical Engineering Center of Zhaoqing University,
Polyomaviridae. Spring
 Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Summary of Endomembrane-system
 Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
Page 32 AP Biology: 2013 Exam Review CONCEPT 6 REGULATION
 Page 32 AP Biology: 2013 Exam Review CONCEPT 6 REGULATION 1. Feedback a. Negative feedback mechanisms maintain dynamic homeostasis for a particular condition (variable) by regulating physiological processes,
Page 32 AP Biology: 2013 Exam Review CONCEPT 6 REGULATION 1. Feedback a. Negative feedback mechanisms maintain dynamic homeostasis for a particular condition (variable) by regulating physiological processes,
1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled
 Protein Targeting Objectives 1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled As a protein is being synthesized, decisions
Protein Targeting Objectives 1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled As a protein is being synthesized, decisions
8/13/2009. Diseases. Disease. Pathogens. Domain Bacteria Characteristics. Bacteria Shapes. Domain Bacteria Characteristics
 Disease Diseases I. Bacteria II. Viruses including Biol 105 Lecture 17 Chapter 13a are disease-causing organisms Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic 2. Lack a membrane-bound
Disease Diseases I. Bacteria II. Viruses including Biol 105 Lecture 17 Chapter 13a are disease-causing organisms Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic 2. Lack a membrane-bound
III. What are the requirements for taking and passing this course?
 1 Molecular Virology Lecture # 1: Course Introduction I. Instructor and Background Dr. Richard Kuhn rjkuhn@bragg.bio.purdue.edu B-129 Lilly Hall 494-1164 Office Hours - Wednesday 10:30-11:30 II. Objective:
1 Molecular Virology Lecture # 1: Course Introduction I. Instructor and Background Dr. Richard Kuhn rjkuhn@bragg.bio.purdue.edu B-129 Lilly Hall 494-1164 Office Hours - Wednesday 10:30-11:30 II. Objective:
19/06/2013. Viruses are not organisms (do not belong to any kingdom). Viruses are not made of cells, have no cytoplasm, and no membranes.
 VIRUSES Many diseases of plants and animals are caused by bacteria or viruses that invade the body. Bacteria and viruses are NOT similar kinds of micro-organisms. Bacteria are classified as living organisms,
VIRUSES Many diseases of plants and animals are caused by bacteria or viruses that invade the body. Bacteria and viruses are NOT similar kinds of micro-organisms. Bacteria are classified as living organisms,
I. Bacteria II. Viruses including HIV. Domain Bacteria Characteristics. 5. Cell wall present in many species. 6. Reproduction by binary fission
 Disease Diseases I. Bacteria II. Viruses including are disease-causing organisms Biol 105 Lecture 17 Chapter 13a Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic 2. Lack a membrane-bound
Disease Diseases I. Bacteria II. Viruses including are disease-causing organisms Biol 105 Lecture 17 Chapter 13a Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic 2. Lack a membrane-bound
Steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled. Cell 7.5
 Steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled Cell 7.5 Protein Variability and Protein Activity Control Aminoacid sequence Three-dimensional shape (conformation) Function Protein processing
Steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled Cell 7.5 Protein Variability and Protein Activity Control Aminoacid sequence Three-dimensional shape (conformation) Function Protein processing
Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells
 Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria
 Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
7.013 Spring 2005 Problem Set 7
 MI Department of Biology 7.013: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor yler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel 7.013 Spring 2005 Problem Set 7 FRIDAY May 6th, 2005 Question
MI Department of Biology 7.013: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor yler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel 7.013 Spring 2005 Problem Set 7 FRIDAY May 6th, 2005 Question
This training module is required for all personnel listed on an IBC protocol that describes work utilizing viral vectors (both replication competent
 This training module is required for all personnel listed on an IBC protocol that describes work utilizing viral vectors (both replication competent and incompetent) regardless of the biosafety level used
This training module is required for all personnel listed on an IBC protocol that describes work utilizing viral vectors (both replication competent and incompetent) regardless of the biosafety level used
LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK. How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
7.012 Quiz 3 Answers
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
Large DNA viruses: Herpesviruses, Poxviruses, Baculoviruses and Giant viruses
 Large DNA viruses: Herpesviruses, Poxviruses, Baculoviruses and Giant viruses Viruses are the only obstacles to the domination of the Earth by mankind. -Joshua Lederberg Recommended reading: Field s Virology
Large DNA viruses: Herpesviruses, Poxviruses, Baculoviruses and Giant viruses Viruses are the only obstacles to the domination of the Earth by mankind. -Joshua Lederberg Recommended reading: Field s Virology
Chapter13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
 Chapter13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions 11/20/2017 MDufilho 1 Characteristics of Viruses Viruses Minuscule, acellular, infectious agent having either DNA or RNA Cause infections
Chapter13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions 11/20/2017 MDufilho 1 Characteristics of Viruses Viruses Minuscule, acellular, infectious agent having either DNA or RNA Cause infections
General Virology I. Dr Esam Ibraheem Azhar (BSc, MSc, Ph.D Molecular Medical Virology) Asst. Prof. Medical Laboratory Technology Department
 General Virology I Dr Esam Ibraheem Azhar (BSc, MSc, Ph.D Molecular Medical Virology) Asst. Prof. Medical Laboratory Technology Department ١ General Virology I Lecture Outline Introduction istory Definition
General Virology I Dr Esam Ibraheem Azhar (BSc, MSc, Ph.D Molecular Medical Virology) Asst. Prof. Medical Laboratory Technology Department ١ General Virology I Lecture Outline Introduction istory Definition
 http://nmhm.washingtondc.museum/collections/archives/agalleries/1918flu/ncp1603.jpg 1 https://assets-production-webvanta-com.s3-us-west- 2 2.amazonaws.com/000000/47/62/original/images/img_109_influenza/Spanish_flu_death_chart.jpg
http://nmhm.washingtondc.museum/collections/archives/agalleries/1918flu/ncp1603.jpg 1 https://assets-production-webvanta-com.s3-us-west- 2 2.amazonaws.com/000000/47/62/original/images/img_109_influenza/Spanish_flu_death_chart.jpg
Cell Quality Control. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses*
 Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
Role of the ubiquitin proteasome system in Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus infection
 Journal of General Virology (2011), 92, 699 705 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.027573-0 Role of the ubiquitin proteasome system in Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus infection Susumu Katsuma, 1 Ayumi Tsuchida, 1 Noriko
Journal of General Virology (2011), 92, 699 705 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.027573-0 Role of the ubiquitin proteasome system in Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus infection Susumu Katsuma, 1 Ayumi Tsuchida, 1 Noriko
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression. Chromatin Array of nuc
 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Challenges in Vaccine Production and Rapid Scale up to Meet Emerging Pandemic Threats
 Challenges in Vaccine Production and Rapid Scale up to Meet Emerging Pandemic Threats Susan Dana Jones, Ph.D. BioProcess Technology Consultants, Inc. BIO 2009 Process Zone Theater Atlanta, GE May 20, 2009
Challenges in Vaccine Production and Rapid Scale up to Meet Emerging Pandemic Threats Susan Dana Jones, Ph.D. BioProcess Technology Consultants, Inc. BIO 2009 Process Zone Theater Atlanta, GE May 20, 2009
B19, see Parvovirus B19 Bone marrow, gene transfer with parvovirus. Erythrovirus, see Parvovirus B19, Simian parvovirus
 ... Subject Index Adeno-associated virus Cap and genome encapsidation 87 DNA integration homologous recombination 90, 91 latency vs replication 77, 78 mechanism 79 requirements 78, 79 site in human genome
... Subject Index Adeno-associated virus Cap and genome encapsidation 87 DNA integration homologous recombination 90, 91 latency vs replication 77, 78 mechanism 79 requirements 78, 79 site in human genome
Display of Heterologous Proteins on gp64null Baculovirus Virions and Enhanced Budding Mediated by a Vesicular Stomatitis Virus G-Stem Construct
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2008, p. 1368 1377 Vol. 82, No. 3 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.02007-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Display of Heterologous
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2008, p. 1368 1377 Vol. 82, No. 3 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.02007-07 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Display of Heterologous
VACCINE ENGINEERING Dr.T.V.Rao MD
 VACCINE ENGINEERING Dr.T.V.Rao MD DR.T.V.RAO MD 1 HISTORICAL PICTURE OF VACCINATION DR.T.V.RAO MD 2 WHAT IS A VACCINE A vaccine is any preparation intended to produce immunity to a disease by stimulating
VACCINE ENGINEERING Dr.T.V.Rao MD DR.T.V.RAO MD 1 HISTORICAL PICTURE OF VACCINATION DR.T.V.RAO MD 2 WHAT IS A VACCINE A vaccine is any preparation intended to produce immunity to a disease by stimulating
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions. Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003
 Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
LESSON 1.4 WORKBOOK. Viral sizes and structures. Workbook Lesson 1.4
 Eukaryotes organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. Prokaryotes organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Viruses small, non-cellular (lacking a cell), infectious
Eukaryotes organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. Prokaryotes organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Viruses small, non-cellular (lacking a cell), infectious
Viral Genetics. BIT 220 Chapter 16
 Viral Genetics BIT 220 Chapter 16 Details of the Virus Classified According to a. DNA or RNA b. Enveloped or Non-Enveloped c. Single-stranded or double-stranded Viruses contain only a few genes Reverse
Viral Genetics BIT 220 Chapter 16 Details of the Virus Classified According to a. DNA or RNA b. Enveloped or Non-Enveloped c. Single-stranded or double-stranded Viruses contain only a few genes Reverse
Protein Modification Overview DEFINITION The modification of selected residues in a protein and not as a component of synthesis
 Lecture Four: Protein Modification & Cleavage [Based on Chapters 2, 9, 10 & 11 Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer] (Figures in red are for the 7th Edition) (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) Protein Modification
Lecture Four: Protein Modification & Cleavage [Based on Chapters 2, 9, 10 & 11 Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer] (Figures in red are for the 7th Edition) (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) Protein Modification
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5
 Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل
 Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل Viruses must reproduce (replicate) within cells, because they cannot generate energy or synthesize proteins. Because they can reproduce only within cells, viruses are obligate
Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل Viruses must reproduce (replicate) within cells, because they cannot generate energy or synthesize proteins. Because they can reproduce only within cells, viruses are obligate
Virus Entry/Uncoating
 Virus Entry/Uncoating Delivery of genome to inside of a cell Genome must be available for first step of replication The Problem--barriers to infection Virion Barriers: Non-enveloped viruses capsid Enveloped
Virus Entry/Uncoating Delivery of genome to inside of a cell Genome must be available for first step of replication The Problem--barriers to infection Virion Barriers: Non-enveloped viruses capsid Enveloped
Why chaperone vectors?
 Why chaperone vectors? A protein folding initiative An open discussion with structural biologists Protein Structure Initiative: Pilot Phase Whether the pilot phase achieved its goal depends on how we measure
Why chaperone vectors? A protein folding initiative An open discussion with structural biologists Protein Structure Initiative: Pilot Phase Whether the pilot phase achieved its goal depends on how we measure
Viral reproductive cycle
 Lecture 29: Viruses Lecture outline 11/11/05 Types of viruses Bacteriophage Lytic and lysogenic life cycles viruses viruses Influenza Prions Mad cow disease 0.5 µm Figure 18.4 Viral structure of capsid
Lecture 29: Viruses Lecture outline 11/11/05 Types of viruses Bacteriophage Lytic and lysogenic life cycles viruses viruses Influenza Prions Mad cow disease 0.5 µm Figure 18.4 Viral structure of capsid
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
18.2 Viruses and Prions
 KEY CONCEPT Infections can be caused in several ways. Viruses, bacteria, viroids, and prions can all cause infection. Any disease-causing agent is called a pathogen. 1 nanometer (nm) = one billionth of
KEY CONCEPT Infections can be caused in several ways. Viruses, bacteria, viroids, and prions can all cause infection. Any disease-causing agent is called a pathogen. 1 nanometer (nm) = one billionth of
Amino acids. Side chain. -Carbon atom. Carboxyl group. Amino group
 PROTEINS Amino acids Side chain -Carbon atom Amino group Carboxyl group Amino acids Primary structure Amino acid monomers Peptide bond Peptide bond Amino group Carboxyl group Peptide bond N-terminal (
PROTEINS Amino acids Side chain -Carbon atom Amino group Carboxyl group Amino acids Primary structure Amino acid monomers Peptide bond Peptide bond Amino group Carboxyl group Peptide bond N-terminal (
Overview of virus life cycle
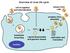 Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
NOTES. Received 27 December 2005/Accepted 25 January 2006
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2006, p. 4168 4173 Vol. 80, No. 8 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.80.8.4168 4173.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. NOTES Expression
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2006, p. 4168 4173 Vol. 80, No. 8 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.80.8.4168 4173.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. NOTES Expression
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life
 Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Viral vaccines. Lec. 3 أ.د.فائزة عبد هللا مخلص
 Lec. 3 أ.د.فائزة عبد هللا مخلص Viral vaccines 0bjectives 1-Define active immunity. 2-Describe the methods used for the preparation of attenuated live & killed virus vaccines. 3- Comparison of Characteristics
Lec. 3 أ.د.فائزة عبد هللا مخلص Viral vaccines 0bjectives 1-Define active immunity. 2-Describe the methods used for the preparation of attenuated live & killed virus vaccines. 3- Comparison of Characteristics
Introductory Virology. Ibrahim Jamfaru School of Medicine UHAS
 Introductory Virology Ibrahim Jamfaru School of Medicine UHAS Lecture outline Definition of viruses and general characteristics Structure of virus (virion) Chemical composition of viruses Virus morphology
Introductory Virology Ibrahim Jamfaru School of Medicine UHAS Lecture outline Definition of viruses and general characteristics Structure of virus (virion) Chemical composition of viruses Virus morphology
Glycosaminoglycans: Anionic polysaccharide chains made of repeating disaccharide units
 Glycosaminoglycans: Anionic polysaccharide chains made of repeating disaccharide units Glycosaminoglycans present on the animal cell surface and in the extracellular matrix. Glycoseaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides)
Glycosaminoglycans: Anionic polysaccharide chains made of repeating disaccharide units Glycosaminoglycans present on the animal cell surface and in the extracellular matrix. Glycoseaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides)
Virology Introduction. Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment.
 DEVH Virology Introduction Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment. Definitions Virology: The science which study the
DEVH Virology Introduction Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment. Definitions Virology: The science which study the
The Zombies of the Scientific Community Viruses and Other Acellular Infectious Agents. Acellular Agents
 viruses protein and nucleic acid viroids RNA virusoids RNA prions proteins The Zombies of the Scientific Community Viruses and Other Acellular Infectious Agents Acellular Agents Viruses major cause of
viruses protein and nucleic acid viroids RNA virusoids RNA prions proteins The Zombies of the Scientific Community Viruses and Other Acellular Infectious Agents Acellular Agents Viruses major cause of
Viral Vectors In The Research Laboratory: Just How Safe Are They? Dawn P. Wooley, Ph.D., SM(NRM), RBP, CBSP
 Viral Vectors In The Research Laboratory: Just How Safe Are They? Dawn P. Wooley, Ph.D., SM(NRM), RBP, CBSP 1 Learning Objectives Recognize hazards associated with viral vectors in research and animal
Viral Vectors In The Research Laboratory: Just How Safe Are They? Dawn P. Wooley, Ph.D., SM(NRM), RBP, CBSP 1 Learning Objectives Recognize hazards associated with viral vectors in research and animal
Part I. Content: History of Viruses. General properties of viruses. Viral structure. Viral classifications. Virus-like agents.
 Viruses Part I Content: History of Viruses. General properties of viruses. Viral structure. Viral classifications. Virus-like agents. History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something
Viruses Part I Content: History of Viruses. General properties of viruses. Viral structure. Viral classifications. Virus-like agents. History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something
VIROIDS, PRIONS. Infectious Stage When virus infects a cell, nucleic acid must be uncoated and gain access to metabolic machinery of cell.
 VIROIDS, PRIONS A virus is a small infectious agent that can replicate only inside the living cells of organisms. Most viruses are too small to be seen directly with a light microscope. Viruses infect
VIROIDS, PRIONS A virus is a small infectious agent that can replicate only inside the living cells of organisms. Most viruses are too small to be seen directly with a light microscope. Viruses infect
AP Biology. Viral diseases Polio. Chapter 18. Smallpox. Influenza: 1918 epidemic. Emerging viruses. A sense of size
 Hepatitis Viral diseases Polio Chapter 18. Measles Viral Genetics Influenza: 1918 epidemic 30-40 million deaths world-wide Chicken pox Smallpox Eradicated in 1976 vaccinations ceased in 1980 at risk population?
Hepatitis Viral diseases Polio Chapter 18. Measles Viral Genetics Influenza: 1918 epidemic 30-40 million deaths world-wide Chicken pox Smallpox Eradicated in 1976 vaccinations ceased in 1980 at risk population?
Virus and Prokaryotic Gene Regulation - 1
 Virus and Prokaryotic Gene Regulation - 1 We have discussed the molecular structure of DNA and its function in DNA duplication and in transcription and protein synthesis. We now turn to how cells regulate
Virus and Prokaryotic Gene Regulation - 1 We have discussed the molecular structure of DNA and its function in DNA duplication and in transcription and protein synthesis. We now turn to how cells regulate
Posttranslational Modification and Targeting of Proteins
 Posttranslational Modification and Targeting of Proteins Graduate Biochemistry Term 2/2016 Assist. Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla School of Chemistry, Institute of Science Suranaree University of Technology
Posttranslational Modification and Targeting of Proteins Graduate Biochemistry Term 2/2016 Assist. Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla School of Chemistry, Institute of Science Suranaree University of Technology
What do we (need to) know about low-susceptibility of codling moth against Cydia pomonella granulovirus (CpGV)!
 What do we (need to) know about low-susceptibility of codling moth against Cydia pomonella granulovirus (CpGV)! Was wir über die Minderempfindlichkeit des Apfelwicklers gegenüber dem Cydia pomonella Granulovirus
What do we (need to) know about low-susceptibility of codling moth against Cydia pomonella granulovirus (CpGV)! Was wir über die Minderempfindlichkeit des Apfelwicklers gegenüber dem Cydia pomonella Granulovirus
Fayth K. Yoshimura, Ph.D. September 7, of 7 RETROVIRUSES. 2. HTLV-II causes hairy T-cell leukemia
 1 of 7 I. Diseases Caused by Retroviruses RETROVIRUSES A. Human retroviruses that cause cancers 1. HTLV-I causes adult T-cell leukemia and tropical spastic paraparesis 2. HTLV-II causes hairy T-cell leukemia
1 of 7 I. Diseases Caused by Retroviruses RETROVIRUSES A. Human retroviruses that cause cancers 1. HTLV-I causes adult T-cell leukemia and tropical spastic paraparesis 2. HTLV-II causes hairy T-cell leukemia
Influenza viruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Influenza viruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped particles, quasi-spherical or filamentous Diameter 80-120 nm Envelope is derived
Influenza viruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped particles, quasi-spherical or filamentous Diameter 80-120 nm Envelope is derived
Chapter 2 Transport Systems
 Chapter 2 Transport Systems The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier between the cell and the extracellular environment. It permeability properties ensure that essential molecules such as
Chapter 2 Transport Systems The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier between the cell and the extracellular environment. It permeability properties ensure that essential molecules such as
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology
 علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology What is a virus? Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), and which obligatory
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology What is a virus? Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), and which obligatory
VIROLOGY. Engineering Viral Genomes: Retrovirus Vectors
 VIROLOGY Engineering Viral Genomes: Retrovirus Vectors Viral vectors Retrovirus replicative cycle Most mammalian retroviruses use trna PRO, trna Lys3, trna Lys1,2 The partially unfolded trna is annealed
VIROLOGY Engineering Viral Genomes: Retrovirus Vectors Viral vectors Retrovirus replicative cycle Most mammalian retroviruses use trna PRO, trna Lys3, trna Lys1,2 The partially unfolded trna is annealed
Warts are a skin virus!
 Viruses Warts are a skin virus! Herpes mouth virus: Other Viral Diseases Measles Polio Smallpox Influenza Hepatitis B Virus Viruses & Cancer Human Papilloma Virus HPV Tree Man - HPV Is a Virus a Living
Viruses Warts are a skin virus! Herpes mouth virus: Other Viral Diseases Measles Polio Smallpox Influenza Hepatitis B Virus Viruses & Cancer Human Papilloma Virus HPV Tree Man - HPV Is a Virus a Living
Fayth K. Yoshimura, Ph.D. September 7, of 7 HIV - BASIC PROPERTIES
 1 of 7 I. Viral Origin. A. Retrovirus - animal lentiviruses. HIV - BASIC PROPERTIES 1. HIV is a member of the Retrovirus family and more specifically it is a member of the Lentivirus genus of this family.
1 of 7 I. Viral Origin. A. Retrovirus - animal lentiviruses. HIV - BASIC PROPERTIES 1. HIV is a member of the Retrovirus family and more specifically it is a member of the Lentivirus genus of this family.
Nucleic acid: singled stranded, double stranded, RNA, or DNA, linear or circular. Capsid: protein coat that is most of the mass of the virus.
 Viruses General Characteristics of Viruses 1. Depending on view may be regarded as exceptionally complex aggregates of nonliving chemicals or as exceptionally simple living microbes. 2. Contain a single
Viruses General Characteristics of Viruses 1. Depending on view may be regarded as exceptionally complex aggregates of nonliving chemicals or as exceptionally simple living microbes. 2. Contain a single
11/15/2011. Outline. Structural Features and Characteristics. The Good the Bad and the Ugly. Viral Genomes. Structural Features and Characteristics
 Chapter 19 - Viruses Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV II. Prions The Good the Bad and the Ugly Viruses fit into the bad category
Chapter 19 - Viruses Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV II. Prions The Good the Bad and the Ugly Viruses fit into the bad category
Protein Modeling Event
 Protein Modeling Event School Name: School Number: Team Member 1: Team Member 2: : Pre-Build Score: On-Site Build Score: Test Score: Tie Breaker: Total: Final Rank: Part I: Pre-Build (40% of total score)
Protein Modeling Event School Name: School Number: Team Member 1: Team Member 2: : Pre-Build Score: On-Site Build Score: Test Score: Tie Breaker: Total: Final Rank: Part I: Pre-Build (40% of total score)
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001
 BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
Plasmid-Driven Formation of Influenza Virus-Like Particles
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Jan. 2000, p. 547 551 Vol. 74, No. 1 0022-538X/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Plasmid-Driven Formation of Influenza Virus-Like
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Jan. 2000, p. 547 551 Vol. 74, No. 1 0022-538X/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Plasmid-Driven Formation of Influenza Virus-Like
1/29/2013. Viruses and Bacteria. Infectious Disease. Pathogens cause disease by: Chapters 16 and 17
 Viruses and Bacteria Chapters 16 and 17 Infectious Disease Caused by the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host s tissues Can be transmitted to others Pathogen microorganisms that
Viruses and Bacteria Chapters 16 and 17 Infectious Disease Caused by the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host s tissues Can be transmitted to others Pathogen microorganisms that
Viruses. Properties. Some viruses contain other ingredients (e.g., lipids, carbohydrates), but these are derived from their host cells.
 Viruses Properties They are obligate intracellular parasites. Probably there are no cells in nature that escape infection by one or more kinds of viruses. (Viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages.)
Viruses Properties They are obligate intracellular parasites. Probably there are no cells in nature that escape infection by one or more kinds of viruses. (Viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages.)
Herpesviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Antiviral Drugs Lecture 5
 Antiviral Drugs Lecture 5 Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (MLAB 366) 1 Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 2 Introduction Viruses are microscopic organisms that can infect all living cells. They are parasitic and multiply
Antiviral Drugs Lecture 5 Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (MLAB 366) 1 Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 2 Introduction Viruses are microscopic organisms that can infect all living cells. They are parasitic and multiply
Role of Cell Culture Technology in new Vaccine Development
 Role of Cell Culture Technology in new Vaccine Development Asst. Prof. Dr.Kanokwan Poomputsa School of Bioresources and Technology King Mongkut s University of Technology Thonburi Outline Introduction
Role of Cell Culture Technology in new Vaccine Development Asst. Prof. Dr.Kanokwan Poomputsa School of Bioresources and Technology King Mongkut s University of Technology Thonburi Outline Introduction
Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage:
 Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Some living things are made of ONE cell, and are called. Other organisms are composed of many cells, and are called. (SEE PAGE 6)
 Section: 1.1 Question of the Day: Name: Review of Old Information: N/A New Information: We tend to only think of animals as living. However, there is a great diversity of organisms that we consider living
Section: 1.1 Question of the Day: Name: Review of Old Information: N/A New Information: We tend to only think of animals as living. However, there is a great diversity of organisms that we consider living
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Unit 13.2: Viruses. Vocabulary capsid latency vaccine virion
 Unit 13.2: Viruses Lesson Objectives Describe the structure of viruses. Outline the discovery and origins of viruses. Explain how viruses replicate. Explain how viruses cause human disease. Describe how
Unit 13.2: Viruses Lesson Objectives Describe the structure of viruses. Outline the discovery and origins of viruses. Explain how viruses replicate. Explain how viruses cause human disease. Describe how
October 26, Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Current Strategies in HIV-1 Vaccine Development Using Replication-Defective Adenovirus as a Case Study
 Note: I have added some clarifying comments to the slides -- please click on Comments under View to see them. Current Strategies in HIV-1 Vaccine Development Using Replication-Defective Adenovirus as a
Note: I have added some clarifying comments to the slides -- please click on Comments under View to see them. Current Strategies in HIV-1 Vaccine Development Using Replication-Defective Adenovirus as a
numbe r Done by Corrected by Doctor
 numbe r 5 Done by Mustafa Khader Corrected by Mahdi Sharawi Doctor Ashraf Khasawneh Viral Replication Mechanisms: (Protein Synthesis) 1. Monocistronic Method: All human cells practice the monocistronic
numbe r 5 Done by Mustafa Khader Corrected by Mahdi Sharawi Doctor Ashraf Khasawneh Viral Replication Mechanisms: (Protein Synthesis) 1. Monocistronic Method: All human cells practice the monocistronic
Biochemistry: A Short Course
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 10 Carbohydrates 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 10 Outline Monosaccharides are aldehydes or ketones that contain two or
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 10 Carbohydrates 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 10 Outline Monosaccharides are aldehydes or ketones that contain two or
