Mycoplasma pneumoniae 23S rrna Gene Mutations and Mechanisms of Macrolide Resistance
|
|
|
- Heather Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mycoplasma pneumoniae 23S rrna Gene Mutations and Mechanisms of Macrolide Resistance Yun Ye, MS,* Suliang Li, MS, Yajun Li, PhD, Tianshun Ren, MS, and Kaige Liu, PhD ABSTRACT Objective: Resistant strains of Mycoplasma pneumoniae lead to antibiotic inefficacy. The relationship between M pneumoniae 23S rrna (GenBank: X ) gene mutations and macrolide resistance phenotype has not been fully established, to our knowledge. In this study, we isolated and cultured macrolide-resistant strains of M pneumoniae and tested them for 23S rrna gene mutations. Methods: Throat swab samples from patients (n = 800) with community-acquired respiratory tract infections were isolated by nested PCR for the molecular identification of clinical isolates. An in vitro drug sensitivity test was performed on clinical isolates for macrolide antibiotic efficacy. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was used to select resistant strains. Resistant strains of 23S rrna were sequenced and compared with the sequences of standard macrolidesensitive M129 strains by comparative sequence analysis, focusing the analysis on mutations linked to the drug-resistance phenotype. M pneumoniae is responsible for respiratory-tract infections in children and adolescents, and is one of the main pathogens that causes pneumonia and pulmonary complications. 1,2,3 M pneumoniae lack a peptidoglycan cell wall; thus, beta-lactam antibiotics, such as penicillin and cephalosporins, are ineffective. Instead, antibiotics that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis, such as macrolides and fluoroquinolones, are effective. 4 Since children are in a growth and development phase, 14-ring DOI: /LMYEY7P26RHWRRUL Abbreviations PCR, polymerase chain reaction, PPLO, pleuropneumonialike organism; MIC, minimal inhibitory concentration; EDTA, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid; bp, base pairs Clinical Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Xi an Medical University, Xi an China *To whom correspondence should be addressed. yeyun236@163.com Results: One hundred M pneumoniae strains were isolated, of which 82 strains were macrolide sensitive and 18 strains were resistant. Mutations were identified in 16 of the 18 macrolide-resistant strains. The following mutations were detected: A2063G, A2064G, C2617G, and A2067G. Of these mutations, A2063G exhibited 14-ring macrolide resistance, A2064G exhibited 14- and 16-ring macrolide resistance, C2617G demonstrated 14- and 15-ring macrolide resistance, and A2067G demonstrated josamycin resistance. Conclusion: M pneumoniae resistance to macrolide antibiotics is a serious clinical issue: our results indicate that 23S rrna mutations are associated with drug resistance. By analysis of the 23S rrna mutation and resistance phenotype, our understanding of the clinical drug resistance of M pneumoniae can aid in the rational selection and application of antibiotics for optimal therapeutic treatments. Keywords: Mycoplasma pneumoniae, gene mutation, macrolide, microbial sensitivity tests erythromycin and 15-ring azithromycin are the preferred antibiotics because they have minimal effects on human development. In recent years many countries, including China, have reported the emergence of resistant strains of M pneumoniae, 5,6 resulting in the failure of antibiotic therapy. Isolated cultures of M pneumoniae are difficult to analyze, in part because the doubling time is quite long. Few studies have investigated the mechanisms by which resistant M pneumoniae strains develop. Therefore, a better understanding of M pneumoniae resistance may greatly improve disease-treatment options. 23S rrna mutations cause ribosome conformational changes that alter the macrolide antibiotic binding site, which may result in antibiotic resistance. Mutations in 23S rrna have been previously reported 7 to confer resistance to strains of M pneumoniae. The relationship between M pneumoniae 23S rrna gene mutations and the macrolide resistance phenotype, however, is not well understood. In this study, we isolated and cultured M pneumoniae resistant strains and detected 23S rrna mutations using nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and DNA Winter 2013 Volume 44, Number 1 Lab Medicine 63
2 sequencing, focusing the analysis on mutations that could confer the drug-resistance phenotype. Materials and Methods Isolation of M pneumoniae Specimens Clinical specimens were obtained from patients with symptoms of community-acquired respiratory tract infections who had been admitted to the Affiliated Hospital of Xi an Medical University in China between June 2008 and February A total of 800 throat swab specimens (from 500 boys and 300 girls) were collected from children ranging from age 1 to 12 years. Sterilized swabs were used to collect posterior-wall secretions from the children. The swabs were inoculated in the M pneumoniae medium and incubated at 37ºC. The positive control was an antibioticfree growth control and the negative control was an M pneumoniae free control. Indicators of M pneumoniae growth included glucose fermentation and acid production (indicated by a drop in ph). The positive control was used for comparison. M pneumoniae Medium The medium was composed of 70 ml pleuropneumonialike organism (PPLO) broth supplemented with 20 ml of newborn calf serum (20% final; Econazole Biological Co, Zhengzhou, China), 5 ml of 50% yeast extract (2.5% final; Guangdong Jiangmen Center For Biotechnology Development Co, Ltd, Jiangmen, China), 2.5 ml of 20% glucose (0.5% final; Guangdong Jiangmen Center For Biotechnology Development Co, Ltd, Jiangmen, China), 500 μl of 1% phenol red (0.005% final; SINOPHARM Group, Ltd, Beijing, China), 1 ml of 2.5% thallium acetate (0.025% final), 0.5 ml of 200,000 units per ml potassium penicillin (100,000 units final), and 0.5 ml of 20,000 μg per ml cefotaxime (10,000 μg final; Shenzhen Zhijun Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd, Shenzhen, China), in a total volume of 100 ml. M pneumonia was identified by a change in the color of the broth from red to yellow. The M pneumoniae strain M129 (ATCC 29342D) was used as a control and was purchased from the Pediatric Research Institute of Capital Medical University, Beijing, China. Application of In Vitro Drug Sensitivity Test The MIC of macrolide antibiotics was determined by a broth microdilution method using PPLO broth, based on the method established by the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. 8,10 M pneumoniae liquid media with dilutions of drug standards from 256 to mg per L (pharmaceutical and biological products) were added combined with an equal volume of M pneumoniae bacilli (concentration, color change unit (CCU)/L) and placed in a CO 2 incubator at 37ºC for 5-14 days until the color changed in the antibiotic-free growth control. The MIC was defined as the lowest concentration of each antibiotic that failed to elicit a color change when the antimicrobial-free control plate demonstrated growth of the organism. If the MIC value was at least 4-fold higher than the MIC values of the standard strains, the strain was classified as being resistant. 23S rrna Gene Analysis DNA Extraction From Clinical Isolates We transferred 20 μl of inoculated broth into a 1.5-mL centrifugal tube and centrifuged it at 12,000 rpm for 10 minutes. After removal of the supernatant, the sediment was suspended in 200 μl of Tris(hydroxymethyl) aminomethane-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (Tris-EDTA) 10mM Tris-HCl, 1 mm EDTA (ph, 8.0), and 1% (V/V) Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich Co, Ltd, St. Louis, MO). The tube was placed in a boiling-water bath at 100ºC for 10 minutes to extract the DNA. 23S rrna Nested PCR and DNA Sequencing The 23S rrna sequence in resistant strains was identified by nested PCR and DNA sequencing. The M pneumoniae 23S rrna nucleic acid sequence (GenBank: X ) from the GenBank database was entered into the free Primer software, version 5.0, to design the primers for nested PCR amplification. The fragment was amplified using the primers shown in Table 1. The forward primer Mp-1 F and reverse primer Mp-1 R (15 pmol of each) and TaqDNA polymerase (1 U) were added to a total reaction volume of 20 μl, in which the template solution (5 μl) was added. Thermal cycling parameters were 94ºC at 2 minutes for denaturation, 94ºC for 45 seconds, 55ºC for 1 minute, and 72ºC for 80 seconds, for a total of 30 cycles, with a final 1-cycle extension of 72ºC for 5 minutes. The 290-bp amplicand (2 μl) was used as the template for a second amplification. Mp-2 F and Mp-2 R were used as the primers; the second amplification was completed under the same conditions described. The final amplicand was 244 base pairs (bp). The amplified products were examined by gel electrophoresis (Figure 1). For the specimens that tested positive by electrophoresis, 10 μl of the specimen was sequencedusing the DYEnamic ET Terminator Cycle 64 Lab Medicine Winter 2013 Volume 44, Number 1
3 Table 1. Primers Used in Testing Primer Name Sequence (5'-3') Position Product Size (bp) M pneumonia-1 F GGTCCTAAGGTAGCGAAATT M pneumonia-1 R CAGTTACCAATTAGAACAGC NA M pneumonia-2 F CCTAGTCGGGTAAATTCCGT M pneumonia-2 R CCAAGGGTAGTATTCCACCT NA Abbreviations: F, forward; R, right. sequencing kit (Shanghai Sangon Biological Engineering Technology and Service Co, Ltd). The nucleotide were determined with an Applied Biosystems Inc 3730 XL sequencer (Life Technologies Corporation, Carlsbad, CA), and the results were compared to the National Center for Biotechnology Information logged standard strain M129 M pneumoniae (ATCC 29342D). 11,12 Results Of a total of 800 throat-swab specimens that were isolated and cultured, M pneumoniae was identified in 100 isolates, for a positive rate of 12.5%. Samples were confirmed to be M pneumoniae by nested PCR. The 100 M pneumoniae strains and M129 controls were subject to drug sensitivity tests. The MICs in this study were determined for erythromycin, clarithromycin, telithromycin, roxithromycin (14-ring macrolide), josamycin, Table 2. Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations of the 82 Sensitive Strains Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC; μg/ml) a Antibiotic Range MIC 50 MIC 90 M129 Erythromycin Clarithromycin Azithromycin Josamycin Midecamycin Telithromycin Spiramycin Roxithromycin a MIC 50 and MIC 90 indicate the minimum concentrations at which 50% and 90%, respectively, are inhibited. midecamycin, midecamycin (16-ring macrolide), and azithromycin (15- ring macrolide). We found that 82 strains were sensitive and 18 were resistant (18% resistance; Table 2). As shown in Figure 1, the target band appeared by nested PCR amplification in all cases. As shown in Figure 2, of the 18 resistant strains, A2063G, A2064G, C2617G, and A2067G mutations were observed in 16 of them. Of note, no mutations were identified in 2 of the resistant strains. We randomly selected 10 sensitive strains for sequencing and did not find mutations in any of these strains. The A2063G and C2617G mutations showed 14- ring macrolide resistance, the A2064G mutation showed 14- and 16-ring macrolide resistance, and the A2067G mutation demonstrated josamycin resistance (Table 3). Discussion Macrolide-resistant M pneumoniae present therapeutic challenges, and the mechanisms of the resistance are unclear Our study focused on the role of target mutations in resistant strains. 17 The most significant findings of this study were the identification of 18 mutations in M pneumoniae strains that associated with macrolide resistance that may be used for antibiotic development to increase treatment efficacy against these resistant strains. Mycoplasma can produce clinical manifestations that vary from mild to severe upper respiratory tract infections to fatal pneumonia. Also, M pneumoniae infections are capable of causing extrapulmonary complications, such as meningoencephalitis, myocarditis, pericarditis, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, and nephritis. 18,19 M pneumoniae is not endemic in children, but still accounts for approximately 10% to 20% of pneumonia cases, with a prevalence as high as 30% each year. M pneumoniae is the common pathogen in children aged 5 years and older; Winter 2013 Volume 44, Number 1 Lab Medicine 65
4 Figure M Corresponding target band (244 base pairs) by nested polymerase chain reaction amplification. Lanes 1 through 3 show partially resistant strains; M indicates the molecular weight marker. Figure 2 Multiple alignment of the 23S rrna genes of Mycoplasma pneumonia M129 and the 18 macrolide-resistant M pneumonia strains. Partial sequences from position 2051 through 2071 and 2610 through 2630 are shown. The positions 2063, 2064, 2067, and 2617 are underlined. Strains 5 and 14 showed no mutations. 244bp M GCAACGGGACGGAAAGACCCC GTTGGTCCCTATCTATTGTGC G G... 3 G G G G. 8 G G G.. 11 G G G G G.. 17 G G also, the occurrence in infants and young children is not uncommon. Mycoplasma can account for incidence rates of 50% or more in older children. M pneumoniae infection has become a significant clinical issue in pediatric patients in recent years due to the increased prevalence of antibiotic-resistant strains. 20,21 Macrolide antibiotics are the treatment of choice in children with M pneumoniae infection due to the structural characteristics of the drug that limit the adverse effects on growth and development observed with the use of other antibiotics. In recent years, however, an increasing number 66 Lab Medicine Winter 2013 Volume 44, Number 1
5 Table 3. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of 8 Agents Against Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma Pneumonia Strains MIC (μg/ml) Strain Age, y ERY CLA AZM JOS MID TEL SPI ROX Mutation A2063G A2063G A2064G C2617G None A2063G C2617G A2063G A2067G A2063G A2064G A2063G A2063G None A2063G A2064G A2063G A2063G Abbreviations: ERY, erythromycin; CLA, clarithromycin; AZM, azithromycin; JOS, josamycin; MID, midecamycin; TEL, telithromycin; SPI, spiramycin; ROX, roxithromycin. a n = 18. of drug-resistant strains have been isolated. Okazaki et al 22 reported that increasing numbers of the mycoplasma infections have been caused by macrolide-resistance strains. Pereyre and colleagues 5 first reported antibioticresistant strains of M pneumonia-resistant Morozumi et al 23 identified several strains of macrolide resistant M pneumoniae and found that resistant strains of this infectious agent were appearing faster when observed with other bacterial species, concluding that M pneumoniae resistance to macrolide antibiotics was rapidly becoming a very serious clinical concern. Macrolide antibiotics function by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, targeting the large bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit that binds peptides GGT in the output channels, and mechanically obstructing nascent chain extension, thereby preventing protein synthesis. 24 The binding sites have been localized to the center of the 23S rrna V ring, namely, the A2063 and A2064 sites. 4,5 Of interest, 16 resistant strains identified in our study showed point mutations at amino acid positions 2063, 2064, 2617, and 2067 but not in any other region. Of these mutations, A2063G exhibited 14-ring macrolide resistance, A2064G exhibited 14- and 16-ring macrolide resistance, and A2067G demonstrated josamycin resistance. The relationship of 3 mutations and the drugresistance phenotype is consistent with the findings of previous studies. 8,12 The mutation C2617G, however, has not been previously reported, to our knowledge. The C2617G mutation demonstrated 14- and 15-ring macrolide resistance. In the 2 resistant strains that showed no mutations, other mechanisms are likely to confer macrolide resistance, including the possible decrease in antibiotic intracellular concentration by active efflux and antibiotic inactivation (enzymatic modification of antibiotics). 25 All resistant strains were sensitive to telithromycin, which widens the antibacterial range and provides an additional drug to select when antibiotic resistance is encountered. M pneumoniae infection is usually a self-limited disease in that bacterial growth can stop automatically without producing severe sequelae. 26 This may explain why the samples taken from the children showed a low positive culture rate. Our results, therefore, may not reflect the actual occurrence of macrolide resistance. In summary, we isolated and identified 18 pairs of macrolide-resistant strains of M pneumoniae and identified the mutations of the 23S rrna in these isolates. The identification of 23S rrna mutation associated with a resistance phenotype increases our previous Winter 2013 Volume 44, Number 1 Lab Medicine 67
6 understanding of the clinical drug resistance of M pneumoniae and also provides potential insights into antibiotic resistance in other bacterial species. LM Acknowledgments This study was supported by funds from the Affiliated Hospital of Xi an Medical College, China (XYFY-09-20). We express our gratitude to the study participants and research personnel for their involvement in this study and thank the following individuals for their valuable assistance: Ming Xie, PhD; Kai Wen, MS; and Yang Ji, MS. We thank Medjaden Bioscience Limited, Hong Kong, for assisting in the preparation of this manuscript. References To read this article online, scan the QR code, ascpjournals.org/content/44/1/63. full.pdf+html 1. Schmidt-Ioanas M, Bender M, Roth A, et al. Serologic early diagnosis of pneumonia caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae [in German]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2006;131(12): Harris JA, Kolokathis A, Campbell M, Cassell GH, Hammerschlag MR. Safety and efficacy of azithromycin in the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998;17(10): Matsuoka M, Narita M, Okazaki N, et al. Characterization and molecular analysis of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae clinical isolates obtained in Japan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48(12): Bébéar CM, Pereyre S. Mechanisms of drug resistance in Mycoplasma pneumonia. Curr Drug Targets Infect Discord. 2005;5(3): Pereyre S, Charron A, Renaudin H, Bébéar C, Bébéar CM. First report of macrolide-resistant strains and description of a novel nucleotide sequence variation in the P1 adhesin gene in Mycoplasma pneumoniae clinical strains isolated in France over 12 years. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45(11): Matsuoka M, Narita M, Okazaki N, et al. Characterization and molecular analysis of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae clinical isolates obtained in Japan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48(12): Morozumi M, Hasegawa K, Kobayashi R, et al. Emergence of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae with a 23S rrna gene mutation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49(6): Pereyre S, Guyot C, Renaudin H, Charron A, Bébéar C, Bébéar CM. In vitro selection and characterization of resistance to macrolides and related antibiotics in Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48(2): Takahata M, Shimakura M, Hori R, et al. In vitro and in vivo efficacies of T-3811ME (BMS ) against Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001;45(1): Li RK, Elie CM, Clayton GE, Ciblak MA. Comparison of a new colorimetric assay with the NCCLS broth microdilution method (M-27A) for antifungal drug MIC determination. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38(6): Matsuoka M, Narita M, Okazaki N, et al. Characterization and molecular analysis of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae clinical isolates obtained in Japan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48(12): Okazaki N, Narita M, Yamada S, et al. Characteristics of macrolideresistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae strains isolated from patients and induced with erythromycin in vitro. Microbiol Immunol. 2001;45: Niitu Y, Hasegawa S, Suetake T, Kubota H, Kobatsu S, Horikawa M. Resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to erythromycin and other antibiotics. J Pediatr. 1970;76(3): Poehlsgaard J, Douthwaite S. Macrolide antibiotic interaction and resistance on the bacterial ribosome. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2003;4(2): Rosato A, Vicarini H, Bonnefoy A, Chantot J-F, Leclercq R. A new ketolide, HMR 3004, active against streptococci inducibly resistant to erythromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42(6): Stopler T, Branski D. Resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to macrolides, lincomycin and streptogramin B. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986;18(3): Lucier TS, Heitzman K, Liu S-K, Hu P-C. Transition mutations in the 23S rrna of erythromycin-resistant isolates of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995;39(12): Harwick HJ, Kalmanson GM, Guze LB. Human diseases associated with Mycoplasms With an appendix on simple culture techniques. Calif Med. 1972;116(5): Denny FW, Clyde WA Jr, Glezen WP. Mycoplasma pneumoniae disease: clinical spectrum, pathophysiology, epidemiology, and control. J Infect Dis. 1971;123(1): Adam D. Clinical use of the new macrolides, azalides, and streptogramins in pediatrics. J Chemother. 1992;4(6): Matsubara K, Morozumi M, Okada T, et al. A comparative clinical study of macrolide-sensitive and macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in pediatric patients. J Infect Chemother. 2009;15(6): Okazaki N, Ohya H, Sasaki T. Mycoplasma pneumoniae isolated from patients with respiratory infection in Kanagawa Prefecture in : emergence of macrolide-resistant strains. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2007;60(5): Morozumi M, Iwata S, Hasegawa K, et al. Increased macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in pediatric patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52(1): Wilson DN, Harms JM, Nierhaus KH, et al. Species-specific antibiotic-ribosome interactions: implications for drug development. Biol Chem. 2005;386(12): Ungureanu V. Macrolides, lincosamides, streptogramines (MLS): mechanisms of action and resistance [in Romanian]. Bacteriol Virusol Parazitol Epidemiol. 2010;55(2): Wang RS, Wang SY, Hsieh KS, et al. Necrotizing pneumonitis caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae in pediatric patients: report of five cases and review of literature. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004;23(6): Lab Medicine Winter 2013 Volume 44, Number 1
S. Pereyre,* A. Charron, H. Renaudin, C. Bébéar, and C. M. Bébéar
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2007, p. 3534 3539 Vol. 45, No. 11 0095-1137/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jcm.01345-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. First Report
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2007, p. 3534 3539 Vol. 45, No. 11 0095-1137/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jcm.01345-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. First Report
Multi-clonal origin of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae isolates. determined by multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00678-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Multi-clonal origin
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00678-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Multi-clonal origin
Emergence of Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae with a 23S rrna Gene Mutation
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, June 2005, p. 2302 2306 Vol. 49, No. 6 0066-4804/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aac.49.6.2302 2306.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, June 2005, p. 2302 2306 Vol. 49, No. 6 0066-4804/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/aac.49.6.2302 2306.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Causative Pathogens in Community-acquired Pneumonia by Real-time PCR (1167)
 From the Japanese Association of Medical Sciences The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Causative Pathogens in Community-acquired Pneumonia by Real-time PCR
From the Japanese Association of Medical Sciences The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Causative Pathogens in Community-acquired Pneumonia by Real-time PCR
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP): important respiratory pathogen in children that cause many upper and lower respiratory tract diseases, including
 KHOA DICH VU HO HAP - Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP): important respiratory pathogen in children that cause many upper and lower respiratory tract diseases, including wheezing, coryza, bronchopneumonia. -
KHOA DICH VU HO HAP - Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP): important respiratory pathogen in children that cause many upper and lower respiratory tract diseases, including wheezing, coryza, bronchopneumonia. -
Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae: its role in respiratory infection
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published November 20, 2012 J Antimicrob Chemother doi:10.1093/jac/dks457 Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae: its role in respiratory infection
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy Advance Access published November 20, 2012 J Antimicrob Chemother doi:10.1093/jac/dks457 Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae: its role in respiratory infection
Characterization and Molecular Analysis of Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae Clinical Isolates Obtained in Japan
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Dec. 2004, p. 4624 4630 Vol. 48, No. 12 0066-4804/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.12.4624 4630.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Dec. 2004, p. 4624 4630 Vol. 48, No. 12 0066-4804/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.12.4624 4630.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
telithromycin oral streptococci 140 telithromycin TEL azithromycin AZM clarithromycin CAM roxithromycin RXM levofloxacin LVFX ampicillin ABPC
 telithromycin 3 0 3 0 oral streptococci 0 telithromycintelazithromycin AZMclarithromycinCAMroxithromycinRXMlevofloxacinLVFXampicillinABPC erythromycinem TEL EM erm mef 5 Streptococcus mitis MIC90 ml TEL
telithromycin 3 0 3 0 oral streptococci 0 telithromycintelazithromycin AZMclarithromycinCAMroxithromycinRXMlevofloxacinLVFXampicillinABPC erythromycinem TEL EM erm mef 5 Streptococcus mitis MIC90 ml TEL
ISOLATION AND POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION DETECTION OF MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE IN MALAYSIAN PATIENTS WITH RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS
 ISOLATION AND POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION DETECTION OF MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE IN MALAYSIAN PATIENTS WITH RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS Tay ST, Habsah MY, Tan SC and Rohani MY Bacteriology Division, Institute
ISOLATION AND POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION DETECTION OF MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE IN MALAYSIAN PATIENTS WITH RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS Tay ST, Habsah MY, Tan SC and Rohani MY Bacteriology Division, Institute
Macrolides & Ketolides. Objectives. Protein Synthesis
 Macrolides & Ketolides Elizabeth D. Hermsen, Pharm.D. Infectious Diseases Research Fellow University of Minnesota College of Pharmacy bjectives Participant should be able to explain macrolide/ketolide
Macrolides & Ketolides Elizabeth D. Hermsen, Pharm.D. Infectious Diseases Research Fellow University of Minnesota College of Pharmacy bjectives Participant should be able to explain macrolide/ketolide
Macrolides, Clindamycin & Ketolides Polymyxins
 Macrolides, Clindamycin & Ketolides Polymyxins Kwan Soo Ko Macrolides - Erythromycin - Azithromycin - Clarithromycin Lincosamides - Lincomycin - Clindamycin Unrelated chemically But, many similar biological
Macrolides, Clindamycin & Ketolides Polymyxins Kwan Soo Ko Macrolides - Erythromycin - Azithromycin - Clarithromycin Lincosamides - Lincomycin - Clindamycin Unrelated chemically But, many similar biological
/01/$ DOI: /AAC Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Sept. 2001, p. 2604 2608 Vol. 45, No. 9 0066-4804/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.9.2604 2608.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Sept. 2001, p. 2604 2608 Vol. 45, No. 9 0066-4804/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.9.2604 2608.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
L élargissement des indica1ons des macrolides au long cours doit- il faire craindre l émergence de Mycoplasma pneumoniae résistant aux macrolides?
 L élargissement des indica1ons des macrolides au long cours doit- il faire craindre l émergence de Mycoplasma pneumoniae résistant aux macrolides? écile Bébéar H de Bordeaux, France niversité de Bordeaux,
L élargissement des indica1ons des macrolides au long cours doit- il faire craindre l émergence de Mycoplasma pneumoniae résistant aux macrolides? écile Bébéar H de Bordeaux, France niversité de Bordeaux,
Mycoplasma Total Solution. Mycoplasma Detection Mycoplasma Elimination Mycoplasma Prevention Cell Freezing Medium (Mycoplasma Free)
 Mycoplasma Total Solution Mycoplasma Detection Mycoplasma Elimination Mycoplasma Prevention Cell Freezing Medium (Mycoplasma Free) Mycoplasma Detection Mycoplasma Detection CellSafe s Mycoplasma Detection
Mycoplasma Total Solution Mycoplasma Detection Mycoplasma Elimination Mycoplasma Prevention Cell Freezing Medium (Mycoplasma Free) Mycoplasma Detection Mycoplasma Detection CellSafe s Mycoplasma Detection
Comparison of Two Laboratory Techniques for Detecting Mycoplasmas in Genital Specimens. Osama Mohammed Saed Abdul-Wahab, BSc, MSc, PhD*
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 32, No. 4, December 200 Comparison of Two Laboratory Techniques for Detecting Mycoplasmas in Genital Specimens Osama Mohammed Saed Abdul-Wahab, BSc, MSc, PhD* Objective:
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 32, No. 4, December 200 Comparison of Two Laboratory Techniques for Detecting Mycoplasmas in Genital Specimens Osama Mohammed Saed Abdul-Wahab, BSc, MSc, PhD* Objective:
Guiding principles* for treating Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
 1 Guiding principles* for treating Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia The Committee of Japanese Society of Mycoplasmology Shigeru Kohno (Chair, Nagasaki University) Tadashi Ishida (Kurashiki Central Hospital)
1 Guiding principles* for treating Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia The Committee of Japanese Society of Mycoplasmology Shigeru Kohno (Chair, Nagasaki University) Tadashi Ishida (Kurashiki Central Hospital)
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors. Ass Prof. Dr. Naza M. Ali 15 Nov 2018 Lec 8
 Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Ass Prof. Dr. Naza M. Ali 15 Nov 2018 Lec 8 These drugs selectively inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. The selectivity is due to the differences between bacterial and human
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Ass Prof. Dr. Naza M. Ali 15 Nov 2018 Lec 8 These drugs selectively inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. The selectivity is due to the differences between bacterial and human
Pharmacokinetics of the New Ketolide Telithromycin (HMR 3647) Administered in Ascending Single and Multiple Doses
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Jan. 2001, p. 170 175 Vol. 45, No. 1 0066-4804/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.1.170 175.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Jan. 2001, p. 170 175 Vol. 45, No. 1 0066-4804/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.1.170 175.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Effect of efflux pump inhibitors on antimicrobial resistance and in vivo colonization of Campylobacter jejuni
 Effect of efflux pump inhibitors on antimicrobial resistance and in vivo colonization of Campylobacter jejuni J. Lin & M. Ensminger Department of Animal Science, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville,
Effect of efflux pump inhibitors on antimicrobial resistance and in vivo colonization of Campylobacter jejuni J. Lin & M. Ensminger Department of Animal Science, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville,
Isolation and identification of Mycoplasma gallisepticum in chickensbn from industrial farms in Kerman province
 Available online at http://www.ijabbr.com International journal of Advanced Biological and Biomedical Research Volume 2, Issue 1, 2014: 100-104 Isolation and identification of Mycoplasma gallisepticum
Available online at http://www.ijabbr.com International journal of Advanced Biological and Biomedical Research Volume 2, Issue 1, 2014: 100-104 Isolation and identification of Mycoplasma gallisepticum
ENG MYCO WELL D- ONE REV. 1.UN 29/09/2016 REF. MS01283 REF. MS01321 (COMPLETE KIT)
 ENG MYCO WELL D- ONE MYCO WELL D-ONE System for the presumptive identification and antimicrobial susceptibility test of urogenital mycoplasmas, Gardnerella vaginalis, Trichomonas vaginalis, Candida albicans
ENG MYCO WELL D- ONE MYCO WELL D-ONE System for the presumptive identification and antimicrobial susceptibility test of urogenital mycoplasmas, Gardnerella vaginalis, Trichomonas vaginalis, Candida albicans
Radiologic findings as a determinant and no effect of macrolide resistance on clinical course of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
 Yoon et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2017) 17:402 DOI 10.1186/s12879-017-2500-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Radiologic findings as a determinant and no effect of macrolide resistance on clinical course of Mycoplasma
Yoon et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2017) 17:402 DOI 10.1186/s12879-017-2500-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Radiologic findings as a determinant and no effect of macrolide resistance on clinical course of Mycoplasma
Value of serum Mycoplasma pneumoniae immunoglobulin in the diagnosis of mycoplasma-related pneumonia in newborns
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 14: 1445-1449, 2017 Value of serum Mycoplasma pneumoniae immunoglobulin in the diagnosis of mycoplasma-related pneumonia in newborns YAN DONG, WEI LV and ZHEN LIN
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 14: 1445-1449, 2017 Value of serum Mycoplasma pneumoniae immunoglobulin in the diagnosis of mycoplasma-related pneumonia in newborns YAN DONG, WEI LV and ZHEN LIN
The macrolide family...
 1 The macrolide family... erythromycin roxithromycin clarithromycin dirithromycin telithromycin azithromycin the last one!! josamycin spiramycin miocamycin 2 Erythromycin: activity Erythromycin A : mostly
1 The macrolide family... erythromycin roxithromycin clarithromycin dirithromycin telithromycin azithromycin the last one!! josamycin spiramycin miocamycin 2 Erythromycin: activity Erythromycin A : mostly
Upper Respiratory Infections. Mehreen Arshad, MD Assistant Professor Pediatric Infectious Diseases Duke University
 Upper Respiratory Infections Mehreen Arshad, MD Assistant Professor Pediatric Infectious Diseases Duke University Disclosures None Objectives Know the common age- and season-specific causes of pharyngitis
Upper Respiratory Infections Mehreen Arshad, MD Assistant Professor Pediatric Infectious Diseases Duke University Disclosures None Objectives Know the common age- and season-specific causes of pharyngitis
Do You Suspect Mycoplasma Contamination? Prevention, Detection and Treatment of Mycoplasma Contamination
 Biological Industries Ltd. Kibbutz Beit Haemek 25115 Tel (972) 4 996 0595 Fax (972) 4 996 8896 E-mail info@bioind.com www.bioind.com Do You Suspect Mycoplasma Contamination? Prevention, Detection and Treatment
Biological Industries Ltd. Kibbutz Beit Haemek 25115 Tel (972) 4 996 0595 Fax (972) 4 996 8896 E-mail info@bioind.com www.bioind.com Do You Suspect Mycoplasma Contamination? Prevention, Detection and Treatment
VOL. 36 NO. 6. Key words: Methylglyoxal bis-thiosemicarbazones,
 VOL. 36 NO. 6 Key words: Methylglyoxal bis-thiosemicarbazones, CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1988 Table1. Effect of methylglyoxal bis (4-methyl-thiosemicarbazone) and methylglyoxal bis (4-ethyl-thiosemicarbazone)
VOL. 36 NO. 6 Key words: Methylglyoxal bis-thiosemicarbazones, CHEMOTHERAPY JUNE 1988 Table1. Effect of methylglyoxal bis (4-methyl-thiosemicarbazone) and methylglyoxal bis (4-ethyl-thiosemicarbazone)
GAS surveillance. emm12 emm28 emm89 GAS GAS. A GAS Streptococcus pyogenes GAS GAS PSAGN GAS GAS. emm. Vol. 26 No GAS surveillance study group
 014 Vol. 6No. 11 A 1 1 GAS surveillance study group A GAS GAS surveillance study group01 GAS 44 PCR 60 GAS emm emm8emm8 GAS emm GAS A GASStreptococcus pyogenes GAS 1 6 1 GAS 1, GAS GAS GAS PSAGN GAS Key
014 Vol. 6No. 11 A 1 1 GAS surveillance study group A GAS GAS surveillance study group01 GAS 44 PCR 60 GAS emm emm8emm8 GAS emm GAS A GASStreptococcus pyogenes GAS 1 6 1 GAS 1, GAS GAS GAS PSAGN GAS Key
Effect of Azithromycin plus Rifampin versus That of Azithromycin Alone on the Eradication of Chlamydia pneumoniae
 Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, June 1999, p. 1491-1493, Vol. 43, No. 6 0066-4804/99/$04.00+0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All rights reserved. Effect of Azithromycin plus
Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, June 1999, p. 1491-1493, Vol. 43, No. 6 0066-4804/99/$04.00+0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All rights reserved. Effect of Azithromycin plus
Antibiotics.. Tetracyclines. Aminoglycoside. Macrolides. Chloramphenicol
 Antibiotics. Tetracyclines. Aminoglycoside. Macrolides. Chloramphenicol Antibiotics as disturber with the biosynthesis of protein These antibiotics all target the bacterial ribosome and interfere in the
Antibiotics. Tetracyclines. Aminoglycoside. Macrolides. Chloramphenicol Antibiotics as disturber with the biosynthesis of protein These antibiotics all target the bacterial ribosome and interfere in the
Abstract. Introduction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY In-Vitro activities of tetracyclines, macrolides, fluoroquinolones and clindamycin against Mycoplasma hominis and Ureaplasma ssp. isolated in Germany over 20 years R. Krausse
ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY In-Vitro activities of tetracyclines, macrolides, fluoroquinolones and clindamycin against Mycoplasma hominis and Ureaplasma ssp. isolated in Germany over 20 years R. Krausse
Bordeaux, France, from 1999 to 2002 and Description of Two tet(m)-positive Isolates of ACCEPTED
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 November 2007 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00960-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 November 2007 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00960-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
The macrolide family...
 1 The macrolide family... erythromycin roxithromycin clarithromycin dirithromycin telithromycin azithromycin josamycin spiramycin miocamycin 2 1 Erythromycin: activity Erythromycin A : mostly Gram (+)
1 The macrolide family... erythromycin roxithromycin clarithromycin dirithromycin telithromycin azithromycin josamycin spiramycin miocamycin 2 1 Erythromycin: activity Erythromycin A : mostly Gram (+)
Macrolide Resistance and Its Impacts on M. Pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children: Comparison of Two Recent Epidemics in Korea
 Original Article Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017 July;9(4):340-346. https://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2017.9.4.340 pissn 2092-7355 eissn 2092-7363 Macrolide Resistance and Its Impacts on M. Pneumoniae Pneumonia
Original Article Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017 July;9(4):340-346. https://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2017.9.4.340 pissn 2092-7355 eissn 2092-7363 Macrolide Resistance and Its Impacts on M. Pneumoniae Pneumonia
Characterization of the DNA-mediated Oxidation of Dps, a Bacterial Ferritin
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Characterization of the DNA-mediated Oxidation of Dps, a Bacterial Ferritin Anna R. Arnold, Andy Zhou, and Jacqueline K. Barton Division of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, California
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Characterization of the DNA-mediated Oxidation of Dps, a Bacterial Ferritin Anna R. Arnold, Andy Zhou, and Jacqueline K. Barton Division of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, California
In vitro assessment of dual drug combinations to inhibit growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 26 January 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.04127-14 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 In vitro assessment
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 26 January 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.04127-14 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 In vitro assessment
TREATMENT OF JAPANESE PATIENTS WITH ENTERIC FEVER USING AZITHROMYCIN AND MIC LEVELS FOR CAUSATIVE ORGANISMS
 TREATMENT OF JAPANESE PATIENTS WITH ENTERIC FEVER USING AZITHROMYCIN AND MIC LEVELS FOR CAUSATIVE ORGANISMS Kenji Ohnishi, Ken-ichiro Kobayashi, Sentaro Iwabuchi and Fukumi Nakamura-Uchiyama Department
TREATMENT OF JAPANESE PATIENTS WITH ENTERIC FEVER USING AZITHROMYCIN AND MIC LEVELS FOR CAUSATIVE ORGANISMS Kenji Ohnishi, Ken-ichiro Kobayashi, Sentaro Iwabuchi and Fukumi Nakamura-Uchiyama Department
ANALYSIS OF MYCOPLASMA GENITALIUM STRAINS ISOLATED FROM PREGNANT WOMEN AT AN ACADEMIC HOSPITAL IN PRETORIA, SOUTH AFRICA
 ANALYSIS OF MYCOPLASMA GENITALIUM STRAINS ISOLATED FROM PREGNANT WOMEN AT AN ACADEMIC HOSPITAL IN PRETORIA, SOUTH AFRICA Mafunise M 1, Le Roux MC 1, de Villiers BE 1, Ditsele RMM 1,2 1 Department of Microbiological
ANALYSIS OF MYCOPLASMA GENITALIUM STRAINS ISOLATED FROM PREGNANT WOMEN AT AN ACADEMIC HOSPITAL IN PRETORIA, SOUTH AFRICA Mafunise M 1, Le Roux MC 1, de Villiers BE 1, Ditsele RMM 1,2 1 Department of Microbiological
Cases in employees. Cases. Day of onset (July)
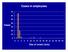 Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
Plasmonic blood glucose monitor based on enzymatic. etching of gold nanorods
 Plasmonic blood glucose monitor based on enzymatic etching of gold nanorods Xin Liu, Shuya Zhang, Penglong Tan, Jiang Zhou, Yan Huang, Zhou Nie* and Shouzhuo Yao State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing
Plasmonic blood glucose monitor based on enzymatic etching of gold nanorods Xin Liu, Shuya Zhang, Penglong Tan, Jiang Zhou, Yan Huang, Zhou Nie* and Shouzhuo Yao State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing
OUTLINE Laboratory Detection and Reporting of Streptococcus agalactiae
 OUTLINE Laboratory Detection and Reporting of Streptococcus agalactiae I. Importance of prenatal screening strategies II. Past approaches Erik Munson Clinical Microbiology Wheaton Franciscan Laboratory
OUTLINE Laboratory Detection and Reporting of Streptococcus agalactiae I. Importance of prenatal screening strategies II. Past approaches Erik Munson Clinical Microbiology Wheaton Franciscan Laboratory
Laboratory Detection and Reporting of Streptococcus agalactiae
 Laboratory Detection and Reporting of Streptococcus agalactiae Erik Munson Clinical Microbiology Wheaton Franciscan Laboratory Milwaukee, Wisconsin The presenter states no conflict of interest and has
Laboratory Detection and Reporting of Streptococcus agalactiae Erik Munson Clinical Microbiology Wheaton Franciscan Laboratory Milwaukee, Wisconsin The presenter states no conflict of interest and has
Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics. Question No. 1 of 10. Question. Feedback. Question
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics No. 1 of 10 1. An effective chemotherapeutic drug should have. (A) Low therapeutic index (B) More toxicity (C) Selective toxicity (D) Mutation inducing properties
Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics No. 1 of 10 1. An effective chemotherapeutic drug should have. (A) Low therapeutic index (B) More toxicity (C) Selective toxicity (D) Mutation inducing properties
Mohammed Nooraldeen Al-Qattan (PhD)
 Mohammed Nooraldeen Al-Qattan (PhD) Macrolides are macro lactone rings made up of 12 or more atoms, and usually contain one or more sugars. They are bacteriostatic agents that inhibit protein synthesis
Mohammed Nooraldeen Al-Qattan (PhD) Macrolides are macro lactone rings made up of 12 or more atoms, and usually contain one or more sugars. They are bacteriostatic agents that inhibit protein synthesis
Dissemination of Macrolide-Resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae Isolates Containing Both erm(b) and mef(a) in South Korea
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 2003, p. 5787 5791 Vol. 41, No. 12 0095-1137/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.12.5787 5791.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 2003, p. 5787 5791 Vol. 41, No. 12 0095-1137/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.12.5787 5791.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs ) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis
 EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
Objectives: Prof.Dr. H.D.El-Yassin
 Protein Synthesis and drugs that inhibit protein synthesis Objectives: 1. To understand the steps involved in the translation process that leads to protein synthesis 2. To understand and know about all
Protein Synthesis and drugs that inhibit protein synthesis Objectives: 1. To understand the steps involved in the translation process that leads to protein synthesis 2. To understand and know about all
The macrolide family...
 1 The macrolide family... erythromycin roxithromycin clarithromycin dirithromycin telithromycin azithromycin Coming soon!! josamycin spiramycin miocamycin 2 Erythromycin: mode of action 3 Erythromycin:
1 The macrolide family... erythromycin roxithromycin clarithromycin dirithromycin telithromycin azithromycin Coming soon!! josamycin spiramycin miocamycin 2 Erythromycin: mode of action 3 Erythromycin:
Mycoplasma genitalium: epidemiology, diagnostics and antimicrobial resistance
 Mycoplasma genitalium: epidemiology, diagnostics and antimicrobial resistance Cécile Bébéar USC EA 3671 Mycoplasmal and chlamydial infections in humans INRA - University of Bordeaux Bordeaux University
Mycoplasma genitalium: epidemiology, diagnostics and antimicrobial resistance Cécile Bébéar USC EA 3671 Mycoplasmal and chlamydial infections in humans INRA - University of Bordeaux Bordeaux University
Mohammed Nooraldeen Al-Qattan (PhD)
 Mohammed Nooraldeen Al-Qattan (PhD) Macrolides are macro lactone rings made up of 12 or more atoms, and usually contain one or more sugars. They are bacteriostatic agents that inhibit protein synthesis
Mohammed Nooraldeen Al-Qattan (PhD) Macrolides are macro lactone rings made up of 12 or more atoms, and usually contain one or more sugars. They are bacteriostatic agents that inhibit protein synthesis
Human leukocyte antigen-b27 alleles in Xinjiang Uygur patients with ankylosing spondylitis
 Human leukocyte antigen-b27 alleles in Xinjiang Uygur patients with ankylosing spondylitis H.-Y. Zou, W.-Z. Yu, Z. Wang, J. He and M. Jiao Institute of Clinical Medicine, Urumqi General Hospital, Lanzhou
Human leukocyte antigen-b27 alleles in Xinjiang Uygur patients with ankylosing spondylitis H.-Y. Zou, W.-Z. Yu, Z. Wang, J. He and M. Jiao Institute of Clinical Medicine, Urumqi General Hospital, Lanzhou
Affinity of Doripenem and Comparators to Penicillin-Binding Proteins in Escherichia coli and ACCEPTED
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on February 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.01-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on February 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.01-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Update on resistance and epidemiology of CAP pathogens in Asia. Cao Bin, MD
 Update on resistance and epidemiology of CAP pathogens in Asia Cao Bin, MD Dept Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Capital Medical University Outlines Resistance trends
Update on resistance and epidemiology of CAP pathogens in Asia Cao Bin, MD Dept Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Capital Medical University Outlines Resistance trends
EPIDEMIOLOGY OF MORAXELLA CATARRHALIS INFECTIONS AMONG THAI PATIENTS TREATED AT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL, THAILAND DURING
 EPIDEMIOLOGY OF MORAXELLA CATARRHALIS INFECTIONS AMONG THAI PATIENTS TREATED AT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL, THAILAND DURING 2012-2015 Chanwit Tribuddharat and Somporn Srifuengfung Department of Microbiology, Faculty
EPIDEMIOLOGY OF MORAXELLA CATARRHALIS INFECTIONS AMONG THAI PATIENTS TREATED AT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL, THAILAND DURING 2012-2015 Chanwit Tribuddharat and Somporn Srifuengfung Department of Microbiology, Faculty
Application of real-time PCR for the detection of macrolide resistance in Belgian M. pneumoniae strains
 Application of real-time PCR for the detection of macrolide resistance in Belgian M. pneumoniae strains K. Loens, S. C. Masha,, K. Lagrou, H. Goossens and M. Ieven Introduction (1) One of the smallest
Application of real-time PCR for the detection of macrolide resistance in Belgian M. pneumoniae strains K. Loens, S. C. Masha,, K. Lagrou, H. Goossens and M. Ieven Introduction (1) One of the smallest
International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety, 2012, 1(2): International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety
 International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety, 2012, 1(2): 54-59 International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety Journal homepage: www.modernscientificpress.com/journals/ijfns.aspx ISSN: 2165-896X
International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety, 2012, 1(2): 54-59 International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety Journal homepage: www.modernscientificpress.com/journals/ijfns.aspx ISSN: 2165-896X
Drug Class Review on Macrolides
 Drug Class Review on Macrolides Preliminary Scan Report 5 July 2014 Last Report: Original August 2006 The purpose of reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness
Drug Class Review on Macrolides Preliminary Scan Report 5 July 2014 Last Report: Original August 2006 The purpose of reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness
in the Gastrointestinal and Reproductive Tracts of Quarter Horse Mares
 Influence of Probiotics on Microflora in the Gastrointestinal and Reproductive Tracts of Quarter Horse Mares Katie Barnhart Research Advisors: Dr. Kimberly Cole and Dr. John Mark Reddish Department of
Influence of Probiotics on Microflora in the Gastrointestinal and Reproductive Tracts of Quarter Horse Mares Katie Barnhart Research Advisors: Dr. Kimberly Cole and Dr. John Mark Reddish Department of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Clin Microbiol Infect 2002; 8:
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE In vitro activity of levofloxacin against contemporary clinical isolates of Legionella pneumophila, Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydia pneumoniae from North America and Europe I. A. Critchley
ORIGINAL ARTICLE In vitro activity of levofloxacin against contemporary clinical isolates of Legionella pneumophila, Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydia pneumoniae from North America and Europe I. A. Critchley
life-threatening infections
 Vancomycin Vancomycin has become increasingly important in the treatment of life-threatening infections. MRSA infections. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) infections Enterococcal
Vancomycin Vancomycin has become increasingly important in the treatment of life-threatening infections. MRSA infections. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) infections Enterococcal
ISOLATION OF SPOTTED FEVER GROUP RICKETTSIA FROM APODEMUS SPECIOSUS IN AN ENDEMIC AREA IN JAPAN
 Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol., 45, 81-86, 1992. Short Communication ISOLATION OF SPOTTED FEVER GROUP RICKETTSIA FROM APODEMUS SPECIOSUS IN AN ENDEMIC AREA IN JAPAN Seigo YAMAMOTO, Chiharu MORITA1 and Kimiyuki
Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol., 45, 81-86, 1992. Short Communication ISOLATION OF SPOTTED FEVER GROUP RICKETTSIA FROM APODEMUS SPECIOSUS IN AN ENDEMIC AREA IN JAPAN Seigo YAMAMOTO, Chiharu MORITA1 and Kimiyuki
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A. Real-Time RT-PCR Detection.
 For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Kylt Rotavirus A Real-Time RT-PCR Detection A. General Kylt Rotavirus A products are
M. Khanna and S. Visuri
 The ProPneumo1 Assay: Detection of Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and an Internal Control Using Multiplex PCR on Multiple Real Time PCR Systems S. Dollhopf,, W. Majewski,, P. Douglass,
The ProPneumo1 Assay: Detection of Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and an Internal Control Using Multiplex PCR on Multiple Real Time PCR Systems S. Dollhopf,, W. Majewski,, P. Douglass,
Global challenge of antibiotic-resistant Mycoplasma genitalium. by author. Sabine Pereyre
 Global challenge of antibiotic-resistant Mycoplasma genitalium Sabine Pereyre USC EA 3671 Mycoplasmal and chlamydial infections in humans INRA - University of Bordeaux -Bordeaux University Hospital National
Global challenge of antibiotic-resistant Mycoplasma genitalium Sabine Pereyre USC EA 3671 Mycoplasmal and chlamydial infections in humans INRA - University of Bordeaux -Bordeaux University Hospital National
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. showed that all three replicates had similar growth trends (Figure 4.1) (p<0.05; p=0.0000)
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
Anti-Microbial Drugs
 Name: Date: Monday March 7 th 2011 Class: I "Pharmacology Anti-Microbial Drugs Lecture 5 د. حيدر الشكرجي Macrolides: Anti-Microbial Drugs Erythromycin was the 1 st of macrolides to find clinical application,
Name: Date: Monday March 7 th 2011 Class: I "Pharmacology Anti-Microbial Drugs Lecture 5 د. حيدر الشكرجي Macrolides: Anti-Microbial Drugs Erythromycin was the 1 st of macrolides to find clinical application,
Product # Kit Components
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Pneumocystis jirovecii PCR Kit Product # 42820 Product Insert Background Information
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Pneumocystis jirovecii PCR Kit Product # 42820 Product Insert Background Information
Table S1. Primers and PCR protocols for mutation screening of MN1, NF2, KREMEN1 and ZNRF3.
 Table S1. Primers and PCR protocols for mutation screening of MN1, NF2, KREMEN1 and ZNRF3. MN1 (Accession No. NM_002430) MN1-1514F 5 -GGCTGTCATGCCCTATTGAT Exon 1 MN1-1882R 5 -CTGGTGGGGATGATGACTTC Exon
Table S1. Primers and PCR protocols for mutation screening of MN1, NF2, KREMEN1 and ZNRF3. MN1 (Accession No. NM_002430) MN1-1514F 5 -GGCTGTCATGCCCTATTGAT Exon 1 MN1-1882R 5 -CTGGTGGGGATGATGACTTC Exon
Clarithromycin-resistant Mycobacterium Shinjukuense Lung Disease: Case Report and Literature Review
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 28 4, 373 377, December 2016 Case Report Clarithromycin-resistant Mycobacterium Shinjukuense Lung Disease: Case Report and Literature Review Makoto HAYASHI 1, Satoshi MATSUKURA 1,
Showa Univ J Med Sci 28 4, 373 377, December 2016 Case Report Clarithromycin-resistant Mycobacterium Shinjukuense Lung Disease: Case Report and Literature Review Makoto HAYASHI 1, Satoshi MATSUKURA 1,
A Platform for the Discovery of New Macrolide Antibiotics
 A Platform for the Discovery of New Macrolide Antibiotics Ian B. Seiple, Ziyang Zhang, Pavol Jakubec, Audrey Langlois-Mercier, Peter M. Wright, Daniel T. Hog, Kazuo Yabu, Senkara Rao Allu, Takehiro Fukuzaki,
A Platform for the Discovery of New Macrolide Antibiotics Ian B. Seiple, Ziyang Zhang, Pavol Jakubec, Audrey Langlois-Mercier, Peter M. Wright, Daniel T. Hog, Kazuo Yabu, Senkara Rao Allu, Takehiro Fukuzaki,
Hepatitis B Virus Genemer
 Product Manual Hepatitis B Virus Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HBV Viral Specific Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2007-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Product Manual Hepatitis B Virus Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HBV Viral Specific Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2007-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Resistance to linezolid in enterococci and staphylococci referred to the national reference laboratory
 Resistance to linezolid in enterococci and staphylococci referred to the national reference laboratory Dr Danièle Meunier, AMRHAI BSAC - Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing User Days Oxazolidinone Linezolid
Resistance to linezolid in enterococci and staphylococci referred to the national reference laboratory Dr Danièle Meunier, AMRHAI BSAC - Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing User Days Oxazolidinone Linezolid
Résistance bactérienne au cours des Infections Sexuellement Transmissibles Cécile Bébéar
 Résistance bactérienne au cours des Infections Sexuellement Transmissibles Cécile Bébéar French Na*onal Center for bacterial STIs Bordeaux University hospital, Bordeaux, France University of Bordeaux,
Résistance bactérienne au cours des Infections Sexuellement Transmissibles Cécile Bébéar French Na*onal Center for bacterial STIs Bordeaux University hospital, Bordeaux, France University of Bordeaux,
Kit Components Product # EP42720 (24 preps) MDx 2X PCR Master Mix 350 µl Cryptococcus neoformans Primer Mix 70 µl Cryptococcus neoformans Positive
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cryptococcus neoformans End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42720 Product
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cryptococcus neoformans End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42720 Product
Rates of clarithromycin resistance in Helicobacter pylori sampled from healthy subjects in Cheonan, Korea
 Rates of clarithromycin resistance in Helicobacter pylori sampled from healthy subjects in Cheonan, Korea Young Sam Yuk 1, Ga-Yeon Kim 2 1. Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Dankook University
Rates of clarithromycin resistance in Helicobacter pylori sampled from healthy subjects in Cheonan, Korea Young Sam Yuk 1, Ga-Yeon Kim 2 1. Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Dankook University
In vitro and Intracellular Activities of Peptide Deformylase. Inhibitor GSK against Legionella pneumophila Isolates
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 27 October 2014 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.04006-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 In vitro
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 27 October 2014 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.04006-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 In vitro
Surveillance of antimicrobial susceptibility of Enterobacteriaceae pathogens isolated from intensive care units and surgical units in Russia
 Feb. 2016 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 69 1 41 41 Surveillance of antimicrobial susceptibility of Enterobacteriaceae pathogens isolated from intensive care units and surgical units in Russia IRINA
Feb. 2016 THE JAPANESE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS 69 1 41 41 Surveillance of antimicrobial susceptibility of Enterobacteriaceae pathogens isolated from intensive care units and surgical units in Russia IRINA
Vancomycin. A bactericidal drug which acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Active only against gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci.
 Vancomycin A bactericidal drug which acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Active only against gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci. Used IV in treating endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant
Vancomycin A bactericidal drug which acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Active only against gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci. Used IV in treating endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate
 Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Determination of MIC & MBC
 1 Determination of MIC & MBC Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) are defined as the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial that will inhibit the visible growth of a microorganism after overnight
1 Determination of MIC & MBC Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) are defined as the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial that will inhibit the visible growth of a microorganism after overnight
ACCEPTED. Comparison of disk diffusion and agar dilution methods for erythromycin and
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on January 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.000-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on January 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.000-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
ACCEPTED ANTIPNEUMOCOCCAL ACTIVITY OF LBM415 COMPARED TO OTHER AGENTS. KLAUDIA KOSOWSKA-SHICK KIM L. CREDITO GLENN A. PANKUCH BONIFACIO DEWASSE
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 20 November 2006 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01150-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 20 November 2006 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01150-06 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
Recommended laboratory tests to identify influenza A/H5 virus in specimens from patients with an influenza-like illness
 World Health Organization Recommended laboratory tests to identify influenza A/H5 virus in specimens from patients with an influenza-like illness General information Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI)
World Health Organization Recommended laboratory tests to identify influenza A/H5 virus in specimens from patients with an influenza-like illness General information Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI)
Emergence et impact clinique de la résistance aux antibiotiques chez Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, les mycoplasmes
 Emergence et impact clinique de la résistance aux antibiotiques chez Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, les mycoplasmes Cécile Bébéar French National Center for bacterial STIs Bordeaux University
Emergence et impact clinique de la résistance aux antibiotiques chez Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, les mycoplasmes Cécile Bébéar French National Center for bacterial STIs Bordeaux University
High dose amoxicillin for sinusitis
 High dose amoxicillin for sinusitis Amoxil ( amoxicillin ) is a commonly used penicillin antibiotic. It is produced in tablets (500 mg 875 mg), capsules, chewable tablets and oral suspensions. 6-3-2018
High dose amoxicillin for sinusitis Amoxil ( amoxicillin ) is a commonly used penicillin antibiotic. It is produced in tablets (500 mg 875 mg), capsules, chewable tablets and oral suspensions. 6-3-2018
Pneumocystis Carinii Real Time PCR Kit. For In Vitro Diagnostic Use Only User Manual
 Revision No.: ZJ0003 Issue Date: Aug 7 th, 2008 Pneumocystis Carinii Real Time PCR Kit Cat. No.: QD-0082-02 For use with ABI Prism 7000/7300/7500/7900; Smart CyclerII; icycler iq 4/iQ 5; Rotor Gene 2000/3000;
Revision No.: ZJ0003 Issue Date: Aug 7 th, 2008 Pneumocystis Carinii Real Time PCR Kit Cat. No.: QD-0082-02 For use with ABI Prism 7000/7300/7500/7900; Smart CyclerII; icycler iq 4/iQ 5; Rotor Gene 2000/3000;
Standard Operating Procedure
 Standard Operating Procedure 1. Definitions Section: Laboratory Version No. 1.2 Initials: AD Title: 2.0 Testing Algorithm Revision Date: 01 Sep 2011 1.1 SOP: Standard Operating Procedure 1.2 CRF: Case
Standard Operating Procedure 1. Definitions Section: Laboratory Version No. 1.2 Initials: AD Title: 2.0 Testing Algorithm Revision Date: 01 Sep 2011 1.1 SOP: Standard Operating Procedure 1.2 CRF: Case
Best Practice of in vitro Methods on Measuring Anti Microbial of Chemical Substance on Root Canal Treatment: Literature Review
 Best Practice of in vitro Methods on Measuring Anti Microbial of Chemical Substance on Root Canal Treatment: Literature Review Dani Rizali Firman 1, Indra Primathena 2 1 Oral Biology Department, Faculty
Best Practice of in vitro Methods on Measuring Anti Microbial of Chemical Substance on Root Canal Treatment: Literature Review Dani Rizali Firman 1, Indra Primathena 2 1 Oral Biology Department, Faculty
Neonatal Pneumonia-2 assay
 Neonatal Pneumonia-2 assay For the detection of Ureaplasma species (Ureaplasma parvum and Ureaplasma urealyticum), Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma hominis using the BD MAX TM system. Instructions
Neonatal Pneumonia-2 assay For the detection of Ureaplasma species (Ureaplasma parvum and Ureaplasma urealyticum), Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma hominis using the BD MAX TM system. Instructions
Streptococcus pneumoniae 356 moxifloxacin (MFLX), garenoxacin (GRNX) sitafloxacin
 2009 21 1) 1, 2) 1, 2) 1) 1) 2) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1, 2) 1) 2) 20 2 29 21 1 14 Streptococcus pneumoniae 356 moxifloxacin (MFLX), garenoxacin (GRNX) sitafloxacin (STFX), DX619 S. pneumoniae S. pneumoniae 60
2009 21 1) 1, 2) 1, 2) 1) 1) 2) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1) 1, 2) 1) 2) 20 2 29 21 1 14 Streptococcus pneumoniae 356 moxifloxacin (MFLX), garenoxacin (GRNX) sitafloxacin (STFX), DX619 S. pneumoniae S. pneumoniae 60
The study of phospholipids in single cells using an integrated microfluidic device
 Supporting Information: The study of phospholipids in single cells using an integrated microfluidic device combined with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry Weiyi Xie,, Dan Gao,
Supporting Information: The study of phospholipids in single cells using an integrated microfluidic device combined with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry Weiyi Xie,, Dan Gao,
Rapid-VIDITEST. Strep A Card. One step Strep A Card for the detection of Group A Streptococcal antigen from throat swabs or culture.
 Rapid-VIDITEST Strep A Card One step Strep A Card for the detection of Group A Streptococcal antigen from throat swabs or culture. Instruction manual Producer: VIDIA spol. s r.o., Nad Safinou II 365, Vestec,
Rapid-VIDITEST Strep A Card One step Strep A Card for the detection of Group A Streptococcal antigen from throat swabs or culture. Instruction manual Producer: VIDIA spol. s r.o., Nad Safinou II 365, Vestec,
Antibacterials and Antivirals
 Structure of a Bacterium: Antibacterials and Antivirals Capsule: protective layer made up of proteins, sugars and lipids Cell wall: provides the bacteria with its shape and structure Cell membrane: permeable
Structure of a Bacterium: Antibacterials and Antivirals Capsule: protective layer made up of proteins, sugars and lipids Cell wall: provides the bacteria with its shape and structure Cell membrane: permeable
Key words: Chlamydia pneumoniae, acute upper resiratory infections, culture, micro-if method
 Key words: Chlamydia pneumoniae, acute upper resiratory infections, culture, micro-if method Table 1 Prevalence of antibodies to C. pneumoniae in patients and control group There was no statistically significant
Key words: Chlamydia pneumoniae, acute upper resiratory infections, culture, micro-if method Table 1 Prevalence of antibodies to C. pneumoniae in patients and control group There was no statistically significant
Adenium Biotech. Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes
 Adenium Biotech Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes Board of Directors: - Stephan Christgau, PhD, chairman,
Adenium Biotech Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes Board of Directors: - Stephan Christgau, PhD, chairman,
Retapamulin Inhibition of Translation and ACCEPTED. 50S Ribosomal Subunit Formation in. Staphylococcus aureus Cells
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 11 June 2007 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00475-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 11 June 2007 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00475-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
Human Hemoglobin Colorimetric Detection Kit
 Human Hemoglobin Colorimetric Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2522 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hemoglobin detection kit is designed to quantitatively measure all forms of hemoglobin present in blood
Human Hemoglobin Colorimetric Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2522 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hemoglobin detection kit is designed to quantitatively measure all forms of hemoglobin present in blood
Received 30 March 2005; returned 16 June 2005; revised 8 September 2005; accepted 12 September 2005
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2005) 56, 1047 1052 doi:10.1093/jac/dki362 Advance Access publication 20 October 2005 Evaluation of PPI-0903M (T91825), a novel cephalosporin: bactericidal activity,
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2005) 56, 1047 1052 doi:10.1093/jac/dki362 Advance Access publication 20 October 2005 Evaluation of PPI-0903M (T91825), a novel cephalosporin: bactericidal activity,
Isolation of High Level Macrolide Resistant Bordetella pertussis Without Transition Mutation at Domain V in Iran
 Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2015 July; 8(7): e18190. Published online 2015 July 25. DOI: 10.5812/jjm.8(5)2015.18190 Research Article Isolation of High Level Macrolide Resistant Bordetella pertussis Without
Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2015 July; 8(7): e18190. Published online 2015 July 25. DOI: 10.5812/jjm.8(5)2015.18190 Research Article Isolation of High Level Macrolide Resistant Bordetella pertussis Without
