2 o Strengthening the Global IB VPD Laboratory Network. 2 o Ensuring Adherence to Case Definitions
|
|
|
- Isaac Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Global Invasive Bacterial Vaccine Preventable Diseases (IB VPD) Information and Surveillance Bulletin Volume 3: April 2011 The World Health Organization (WHO) produces this twice-yearly global IB VPD Information and Surveillance Bulletin to share activities and data with partners at the national, regional and global levels. Comments on this Bulletin? Please Dr. Mary AgÓcs Table of Contents Section Page Spotlight on Efforts to Improve Data Quality Challenges 1 Update on Actions Implemented to Improve Quality 2 o Strengthening the Global IB VPD Laboratory Network 2 o Ensuring Adherence to Case Definitions 3 Summary of January through June 2010 IB VPD Surveillance Data 4 Annex: January through June 2010 IB VPD Surveillance Data 5 The Global IB VPD Surveillance Network 5 Tier 1 Meningitis Surveillance 6 Tier 2 Pneumonia and/or Sepsis Surveillance 9 Tier 3 Population-based Surveillance (Mongolia) 12 Acknowledgements and WHO IB VPD Surveillance Websites 12 Spotlight on Efforts to Improve Data Quality Challenges IB VPD surveillance is needed to provide information related to the introduction and use of vaccines that prevent severe illness and death among children (i.e. Hib and PCV) to Ministries of Health and other decision makers. However, launching a global high quality IB VPD surveillance network is challenging for many reasons, including: Weak health infrastructure: Capacity for IB VPD surveillance is weak in many developing countries. When it exists, it is mainly limited to academic institutions engaged in research, rather than public health facilities and laboratories that provide data to national Ministries of Health. Initiating surveillance in sentinel hospitals and linking them with laboratories often require providing infrastructure (e.g. microscopes, and laboratory reagents), providing training to clinicians and laboratory personnel, and establishing internal and external quality assurance programmes. In countries with the weakest health systems, at least 2 to 3 years may be required to build the required capacity and generate surveillance data of sufficient quality to meet public health needs. In many instances, the data from such surveillance may not by themselves provide a comprehensive picture of disease epidemiology, but may need to be bridged to data from more intensive surveillance in the region to inform local policy. 1
2 Fragile organisms: There are inherent diagnostic difficulties in isolating and identifying the bacteria causing IB VPD, particularly Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae. These organisms are fastidious and fail to grow in media containing human blood, which is often used instead of the recommended sheep or horse blood in many developing country laboratories. In addition, prior antibiotic use, improper specimen handling, and delays in processing samples affect the ability to isolate the bacteria in culture. Forming a new surveillance network: Before WHO assumed full coordination of the IB VPD surveillance network in 2009, countries in the network were conducting surveillance using different protocols and standard operation procedures. In order to align countries under a global network, time will be required to implement standardized surveillance practices (e.g. by developing a WHO global IB VPD standard operating procedure), establish quality assurance systems, monitor compliance with standards using pre-defined indicators and periodic audits, and to clearly define roles and responsibilities within the network. Update on Actions Implemented to Improve Quality To improve the quality of the WHO-coordinated surveillance network for IB VPD, WHO works with Ministries of Health to: 1. Strengthen the IB VPD Laboratory Network By conducting trainings Ongoing training of laboratory professionals ensures adherence to standard procedures. The Global Reference Laboratories (GRL) provide support and training to Regional Reference Laboratories (RRL), who in turn train sentinel site laboratorians (photo). By utilizing RRL Diagnostic Capacity RRL support to sentinel sites can include provision of advanced diagnostic testing methods, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR). For example, the WHO African Region coordinates a process in West Africa whereby cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples tested negative at sentinel hospital laboratories are sent to the Gambia RRL for additional testing. During 2010, 450 of 1509 (30%) CSF samples tested negative by Gram stain and culture at the sentinel hospital laboratories were found to contain a bacterial organism by PCR (table and photo, pg 3). The information not only highlights the importance of RRL support to sentinel sites, but also illustrates the weakness of conducting surveillance that depends only on Gram stain and conventional bacterial culture to detect bacterial pathogens of meningitis. These results are also provided to sentinel sites and used during training (table and photo, pg 3). Photo: WHO-coordinated IB VPD training in the Western Pacific Region in March Here, the U.S. CDC GRL provides training to RRL colleagues from Australia and South Korea, and NL colleagues from Vietnam, Papua New Guinea, Mongolia, Philippines and Laos. 2
3 Vaccine preventable bacterial pathogens detected by polymerase chain reaction at the Gambia Regional Reference Laboratory (RRL) from meningitis cases with culture-negative cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) at the hospital sentinel site laboratory, January to December 2010 Country Hib S. Pneumoniae Neisseria meningitidis Total No. (%) of CSF samples received by RRL No. % No. % No. % No. % Nigeria Senegal Ghana Togo Benin Niger Gambia Total By purchasing laboratory supplies WHO purchased basic laboratory supplies, such as tubes, pipettes, reagents of assured quality, and microscopes, for needy sentinel hospital laboratories. While countries in all WHO Regions were supported, most countries were in the WHO African Region and included: Benin, Burundi, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Cote D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gambia, Ghana, Kenya, Lesotho, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Senegal, Swaziland, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. 2. Ensure adherence to standardized meningitis case definitions at sentinel hospital sites: Photo: Practical training on various laboratory techniques for diagnosis and characterization of bacterial pathogens, MRC The Gambia; 22-27th February Sentinel hospitals participating in the WHO-coordinated IB VPD surveillance network should use the following case definitions: Suspected Meningitis Case: Any child aged 0-59 months admitted to a sentinel hospital conducting surveillance with sudden onset of fever (> 38.5 C rectal or 38.0 C axillary) plus a history of one of the following signs: neck stiffness, altered consciousness with no other alternative CNS diagnosis, or other meningeal sign. Probable Bacterial Meningitis Case: A suspected meningitis case (as defined above) with CSF examination showing at least one of the following: Turbid appearance; Leukocytosis (> 100 cells/mm 3 ); Source: Meningitissymptomsguide.com 3
4 Leukocytosis ( cells/ mm 3 ) AND either an elevated protein (>100 mg/dl) or decreased glucose (< 40 mg/dl) Note: if protein and glucose results are not available, diagnose using the first two conditions (i.e. turbid appearance or leukocytosis > 100 cells/mm 3 ) Confirmed IB VPD Meningitis Case: A suspected meningitis case that is laboratoryconfirmed by growing (i.e. culturing) or identifying (i.e. by Gram stain 1, antigen detection, PCR or other methods) a bacterial pathogen (Hib, pneumococcus or meningococcus) in the CSF or from the blood in a child with a clinical syndrome consistent with bacterial meningitis Summary of January through June 2010 IB VPD Surveillance Data The global IB VPD surveillance network collects data related to the detection of 3 vaccine-preventable organisms: Haemophilus influenzae (Hi), Streptococcus pneumoniae (Spn) and Neisseria meningitidis (Nm). Furthermore, the global IB VPD sentinel surveillance utilizes a 3-tiered approach: Tier 1 surveillance targets children under-five with suspected meningitis; Tier 2 surveillance also targets children under-five with pneumonia and/or sepsis; Tier 3 surveillance seeks to determine incidence rates of IB VPD The current network, consisting mainly of tier 1 sentinel sites, provides information that will be useful to monitor trends in disease occurrence and to estimate vaccine effectiveness using a case-control approach, once high-quality data are obtained. However, information from tier 1 sites should be bridged with data from tier 2 and tier 3 surveillance sites as well as from special studies in order to provide a comprehensive understanding of disease epidemiology. This Bulletin presents IB VPD surveillance data for January through June Summarized below are the main findings: 44 Member States reported IB VPD surveillance data to WHO o 34 of 44 (77%) reporting countries were GAVI Phase II eligible countries Among children with probable bacterial meningitis: Spn, Hi and Nm were not detected in 14 of 43 (32%) reporting countries (11 were from the African Region), pointing to the need to strengthen surveillance practices in these countries o Deaths were reported in 23 of 42 (55%) participating countries As previously discussed, data in this bulletin come from a nascent IB VPD surveillance network where quality assurance systems are only now being established. Thus, care needs to be taken in interpreting the data and drawing conclusions. The wide variation in data from different countries reported in this bulletin may represent variation in surveillance quality, rather than true epidemiological differences. 1 The use of Gram stain in culture negative specimens as an indicator of confirmed meningitis will be further validated using newer diagnostic tests such as PCR 4
5 Annex: January through June 2010 IB VPD Surveillance Data The Global IB VPD Surveillance Network In the first semester of 2010, 44 WHO Member States participated in the global surveillance network for IB VPD and reported data to WHO (Figure 1). Twenty-one (48%) of these countries were based in the African Region. Overall, 34 of 44 (77%) participating countries were eligible for GAVI funding (Table 1). Figure 1: WHO Member States reporting to the global surveillance network for IB VPD Jan-June Member States reporting to the network The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on this map do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the World Health Organization concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Dotted lines on maps represent approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement. WHO All rights reserved Source: Data collected from WHO Regions and partners. Date of slide: 29 March
6 Out of 44 countries that reported Tier 1 meningitis surveillance data, 15 countries also reported Tier 2 pneumonia and/or sepsis surveillance data from January through June Furthermore, 1 country in the Western Pacific Region reported Tier 3 surveillance data (Table 2). Tier 1 - Meningitis Surveillance From January through June 2010, 10,350 children <5 years of age with suspected meningitis were reported to the global IB VPD surveillance network; 51% were from the African Region (Table 3). Among children with suspected meningitis, the percent with probable bacterial meningitis varied greatly between countries (range: 4-100%). All countries in the Region of the Americas, the European Region and the Western Pacific Region met or exceeded the network target of 20%. In the African Region, 16 of 21 (76%) countries reported less than 20% of suspected meningitis cases as probable bacterial meningitis. (Figure 2). Low detection may be due to problems with case ascertainment, adherence to case definitions, specimen collection, transportation and laboratory practices; issues with data management procedures may also contribute. WHO Regional Offices are working with countries and sites to improve data management practices and to provide technical support to identify and rectify problems. 6
7 Figure 2: Percent of suspected meningitis cases with probable bacterial meningitis, by country and WHO region - Jan- June The number of suspected meningitis cases (n= ) stated next to the country. PNG n=158 Viet Nam n=141 Mongolia n=20 Bangl. n=1652 Nepal n=289 India n=141 Sri Lanka n=78 Georgia n=45 Azerbaijan n=30 Ukraine n=48 Sudan n=734 Iraq n=157 Yemen n=499 Pakistan n=394 Syria n=97 Afghanistan n=23 Ecuador n=254 Honduras n=6 Panama n=112 Paraguay n=61 Venezuela n=30 El Salvador n=17 Rwanda n=25 Togo n=236 Burundi n=21 Nigeria n=300 Burkina Faso n=89 Gambia n=26 DR Congo n=34 Malawi n=846 Uganda n=742 Niger n=349 Ethiopia n=847 Ghana n=340 Côte d'ivoire n=146 Kenya n=235 Swaziland n=24 Senegal n=88 Zimbabwe n=601 Tanzania n=21 Zambia n=85 Namibia n=227 Cameroon n=30 WPR SEAR EUR EMR AMR AFR Note: missing data from the Philippines % of suspected meningitis with probable bacterial meningitis From January through June 2010, Spn was detected in 23 of 43 (53%) reporting countries, Hi in 20 of 43 (46%) countries, and Nm in 9 of 37 (24%) countries (Figure 3). Furthermore, the percent of probable bacterial meningitis due to Spn, Hi and Nm varied greatly between countries, which likely reflects differences in specimen handling processes, laboratory capacity and choice of detection methods. Among children with probable bacterial meningitis, 14 of 43 (32%) reporting countries (11 from the African Region) did not detect any of the 3 organisms (Figure 3). The IB VPD surveillance network is working to include information on the number of samples with bacterial contaminants, but there is currently no information on the percent of probable bacterial meningitis due to other pathogens. Inability to identify the 3 organisms of interest may be attributable to several factors including prior use of antibiotics, poor specimen storage and transportation conditions, weak laboratory capacity, and low sensitivity of detection methods used. In most countries in the African Region, only conventional culture techniques are used to detect bacteria pathogens, the sensitivity of which is affected by the above factors. WHO is working to improve access to antigen detection and PCR diagnostics either at the sentinel site or at the supporting RRL. Furthermore, the global EQA programme 7
8 launched in the first quarter of 2011 will provide valuable information to help better target WHO's support. Figure 3: Percent of probable bacterial meningitis due to Streptococcus pneumoniae (Spn), Haemophilus influenzae (Hi) and Neisseria meningitidis (Nm), by country and WHO region Jan-June No. of probable bacterial meningitis stated next to country. WPR SEAR EUR EMR AMR AFR Viet Nam n=50 PNG n=42 Mongolia n=8 *India n=41 Sri Lanka n=39 Nepal n=65 Bangladesh n=180 *Azerbaijan n=15 Georgia n=9 Ukraine n=39 Syria n=19 Afghanistan n=21 Pakistan n=54 Yemen n=61 *Sudan n=29 *Iraq n=18 Ecuador n=67 Honduras n=2 Venezuela n=30 Paraguay n=43 El Salvador n=17 Panama n=45 Rwanda n=1 Burundi n=1 *Nigeria n=17 DR Congo n=3 Niger n=39 Ghana n=44 Côte d'ivoire n=22 Kenya n=38 Zimbabwe n=128 Tanzania n=5 Zambia n=22 Uganda n=78 Malawi n=83 Cameroon n=18 Namibia n=77 Ethiopia n=107 Togo n=11 Swaziland n=4 Burkina Faso n=6 Senegal n=17 Gambia n=2 Spn Hi Nm % of probable bacte rial meningitis due to Hi, Spn and Nm *Countries that have not introduced Hib vaccine into national immunization programmes Note: No data about % due to Nm for all countries in the Region of the Am ericas (AMR). Missing data from the Philippines. Mortality From January through June 2010, deaths among children with probable bacterial meningitis were reported from 23 of 42 countries (55%) that provided data to the global IB VPD surveillance network. The percent of children with probable bacterial meningitis who died varied between countries; however, it is important to note that some countries reported very few cases of probable bacterial meningitis (Figure 4). 8
9 Figure 4: Percent of children with probable bacterial meningitis who died, by country and WHO region - Jan- June The number of probable bacterial meningitis cases (n= ) stated next to the country. Mongolia n=8 Viet Nam n=50 Sri Lanka n=39 India n=41 Nepal n=65 Bangl. n=180 Ukraine n=39 Azerbaijan n=15 Georgia n=9 Sudan n=29 Pakistan n=54 Yemen n=61 Iraq n=18 Syria n=19 Afghanistan n=21 Venezuela n=30 Ecuador n=67 Paraguay n=43 Panama n=45 El Salvador n=17 Honduras n=2 Rwanda n=1 Togo n=11 Burundi n=1 Nigeria n=17 Burkina Faso n=6 Gambia n=2 Malawi n=83 Ethiopia n=107 Côte d'ivoire n=22 Kenya n=38 Swaziland n=4 Tanzania n=5 Namibia n=77 Uganda n=78 Niger n=39 Zambia n=22 Zimbabwe n=128 Ghana n=44 Senegal n=17 Cameroon n=18 DR Congo n=3 WPR SEAR EUR EMR AMR AFR Note: m issing data from the Philippines and PNG. % of childre n with probable bacterial meningitis who died Tier 2 - Pneumonia and/or Sepsis Surveillance From January through June 2010, 4 of 6 WHO Regions reported Tier 2 surveillance data 2. A total of 14,933 children <5 years of age with pneumonia were captured in the IB VPD surveillance network; 84% of these children came from the Region of the Americas and the South-East Asia Region. The Eastern Mediterranean Region and Western- Pacific Region reported a total of 118 children <5 years of age with sepsis (Table 4). 2 Tier 2 surveillance data from the African Region are not reported in this Bulletin. However, pneumonia surveillance is currently under-way in the Region and data is expected to be presented in future issues of the Bulletin. 9
10 In 11 countries reporting from January through June 2010, Hi was isolated from the blood of less than 2% of children with pneumonia who had blood cultures performed, and the isolation of Spn ranged from 0-6.7% (Figure 5). Difficulties in detecting the etiological agents of pneumonia may be partly due to limitations with current diagnostic tools and the low predictive value of the clinical case definitions used for pneumonia. The clinical case definitions for pneumonia were formulated for case management, where specificity was sacrificed to get optimal sensitivity. Hence, the positive predictive value of the case definitions of pneumonia for identifying radiologically confirmed pneumonia among children with cough would range from 7 to 26%. 3 Among children with radiologically confirmed pneumonia, clinical trials have shown that the proportion of radiological pneumonia prevented by Hib and pneumococcal vaccines far exceeds the proportion with a positive blood culture In addition, studies looking at the occurrence of pneumococcal bacteraemic pneumonia by blood culture have reported results as low as %. 7,8 Although our surveillance data is in keeping with expected numbers, such low isolations rates may suggest a need to review the Tier 2 surveillance strategy. In 5 countries reporting from January through June 2010, Hi was not detected in the blood of any children with sepsis who had blood cultures performed, and Spn was detected in <2.5% of these children (Figure 6). These data should be interpreted cautiously as information on the vaccination status of these children is unavailable. Thus, it is not possible to determine whether the low detection of Hi is due to Hib vaccine receipt. 3 Cherian T, John TJ, Simoes E, Steinhoff MC, John M. Evaluation of simple clinical signs for the diagnosis of acute lower respiratory tract infection. Lancet 1988;2(8603): Klugman K.P., Madhi S.A., Huebner R.E., Kohberger R., Mbelle N., Pierce N. et al. A trial of a 9-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in children with and those without HIV infection. New England Journal of Medicine. 2003;349(14): Mulholland K, Hilton S, Adegbola R. Randomised trial of Haemophilus influenzae type b-tetanus protein conjugate for prevention of pneumonia and meningitis in Gambian infants. Lancet 1997;349: Cutts FT, Zaman SMA, Enwere G, Jaffar S, Levine OS, Okoko JB et al. Efficacy of nine-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine against pneumonia and invasive pneumococcal disease in The Gambia: randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2005;365: Resti M, Moriondo M, Cortimiglia M, Indolfi G, Canessa C, Becciolini L, et al. Community-acquired bacteremic pneumococcal pneumonia in children: diagnosis and serotyping by real-time polymerase chain reaction using blood samples. Clin Infect Dis 2010 Nov 1;51(9): Shah SS, Alpern ER, Zwerling L, McGowan KL, Bell LM. Risk of bacteremia in young children with pneumonia treated as outpatients. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2003 Apr;157(4):
11 Figure 5: Percent of pneumonia cases due to Streptococcus pneumoniae (Spn) and Haemophilus influenzae (Hi),* by country and WHO region - Jan-June Number of pneumonia cases with blood culture performed (n= ) stated next to country. WPR Mongolia n=1579 Yem en n=5 EMR Afghanistan n=2 Pakistan n=704 Syria n=84 Venezuela n=2 Ecuador n=2133 Spn Hi AMR Panam a n=1365 Honduras n=106 Paraguay n=546 El Salvador n= % due to Hi and Spn *Among pneumonia cases w ith blood culture performed Note: Countries in the South-East Asia Region not show n because data not differentiated betw een pneumonia and sepsis cases. Figure 6: Percent of sepsis cases due to Streptococcus pneumoniae (Spn) and Haemophilus influenzae (Hi),* by country and WHO region - Jan-June Number of sepsis cases with blood culture performed (n= ) stated next to country. WPR Mongolia n=42 Yemen n=1 EMR Syria n=10 Spn Hi Afghanistan n=3 Pakistan n= % due to Hi and Spn *Among sepsis cases w ith blood culture performed Note: Countries in the South-East Asia Region not show n because data not differentiated betw een pneumonia and sepsis cases. Countries in the Region of the Americas do not conduct Tier 2 surveillance for sepsis. 11
12 Tier 3 - Population-based Surveillance (Mongolia) From January through June 2010, Mongolia reported population-based surveillance data for IB VPD. This is the first time the global surveillance network for IB VPD has received population-based surveillance data, and more countries (particularly in the African Region) are expected to report similar data in the future. A total of 99,264 children under 5 years of age were enumerated in the catchment area of the sentinel hospital sites; in order to accommodate surveillance data collected from January through June 2010, 49,632 child-years of observation were used to calculate incidence rates for meningitis, pneumonia and sepsis, as well as Hi, Spn and Nm (Table 5). Rates generated from sentinel site surveillance may be large under-estimates as they only reflect children under-five with access to the sentinel hospitals, and among those, children who are hospitalized with a syndrome under surveillance and tested for the pathogens of interest. Furthermore, pneumonia is the most common syndrome captured at sentinel sites in Mongolia, but the incidence rates reflected here only include cases of bacteraemic Hi and Spn pneumonia cases. Challenges in isolating these organisms (as previously discussed) must also be taken into consideration when interpreting these incidence rates. Hib vaccine was introduced into the country during , which may account for the absence of Hi detected. Acknowledgements WHO gratefully acknowledges the dedicated efforts of the numerous individuals and organizations involved with compiling this surveillance information, including Ministries of Health, sentinel hospitals, as well as the network of global, regional and national reference laboratories. WHO IB VPD Surveillance Websites
Comments on this bulletin are welcome. Please to Dr. Mary Agócs
 Global Invasive Bacterial Vaccine Preventable Diseases (IB-VPD) Information and Surveillance Bulletin Reporting Period: January through December 2010 Volume 4: October 2011 The World Health Organization
Global Invasive Bacterial Vaccine Preventable Diseases (IB-VPD) Information and Surveillance Bulletin Reporting Period: January through December 2010 Volume 4: October 2011 The World Health Organization
Table of Contents. 1 3 Update on Activities from Global and Regional Reference Laboratories. 3 The 2012 IB-VPD Laboratory External Quality Assessment
 Global Invasive Bacterial Vaccine Preventable Diseases (IB-VPD) Information and Surveillance Bulletin Reporting Period: January through December 2011 Volume 6: October 2012 The World Health Organization
Global Invasive Bacterial Vaccine Preventable Diseases (IB-VPD) Information and Surveillance Bulletin Reporting Period: January through December 2011 Volume 6: October 2012 The World Health Organization
Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa
 Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa 355 million people at risk for malaria in 215 297 million at high risk A. Parasite prevalence, 215 Funding for malaria increased from US$ 233 million to US$ 262
Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa 355 million people at risk for malaria in 215 297 million at high risk A. Parasite prevalence, 215 Funding for malaria increased from US$ 233 million to US$ 262
What is this document and who is it for?
 Measles and Rubella Initiative s Standard Operating Procedures for Accessing Support for Measles and Rubella Supplementary Immunization Activities During 2016 In the context of measles and rubella elimination
Measles and Rubella Initiative s Standard Operating Procedures for Accessing Support for Measles and Rubella Supplementary Immunization Activities During 2016 In the context of measles and rubella elimination
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook. UNICEF Supply Division
 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook UNICEF Supply Division Update: October 2013 0 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Supply & Demand Outlook October 2013 Update Key updates
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook UNICEF Supply Division Update: October 2013 0 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Supply & Demand Outlook October 2013 Update Key updates
EXPLANATION OF INDICATORS CHOSEN FOR THE 2017 ANNUAL SUN MOVEMENT PROGRESS REPORT
 UNICEF / Zar Mon Annexes EXPLANATION OF INDICATORS CHOSEN FOR THE 2017 ANNUAL SUN MOVEMENT PROGRESS REPORT This report includes nine nutrition statistics, as per the 2017 Global Nutrition Report. These
UNICEF / Zar Mon Annexes EXPLANATION OF INDICATORS CHOSEN FOR THE 2017 ANNUAL SUN MOVEMENT PROGRESS REPORT This report includes nine nutrition statistics, as per the 2017 Global Nutrition Report. These
Eligibility List 2018
 The Global Fund s 2017-2022 strategy and allocation-based approach enables strategic investment to accelerate the end of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria and build resilient and sustainable systems for
The Global Fund s 2017-2022 strategy and allocation-based approach enables strategic investment to accelerate the end of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria and build resilient and sustainable systems for
The Promise of Introducing Rubella Containing Vaccines on the Impact of Rubella and Measles Control
 The Promise of Introducing Rubella Containing Vaccines on the Impact of Rubella and Measles Control GAVI Partners Forum 4 6 December 2012, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania Maya van den Ent, MPH, UNICEF Peter Strebel,
The Promise of Introducing Rubella Containing Vaccines on the Impact of Rubella and Measles Control GAVI Partners Forum 4 6 December 2012, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania Maya van den Ent, MPH, UNICEF Peter Strebel,
Global Measles and Rubella Update. April 2018
 Global Measles and Rubella Update April 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct
Global Measles and Rubella Update April 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct
Global Fund ARV Fact Sheet 1 st June, 2009
 Global Fund ARV Fact Sheet 1 st June, 2009 This fact sheet outlines the principles and approach in determining the number of people on antiretroviral drugs (ARVs) for HIV/AIDS treatment, with a breakdown
Global Fund ARV Fact Sheet 1 st June, 2009 This fact sheet outlines the principles and approach in determining the number of people on antiretroviral drugs (ARVs) for HIV/AIDS treatment, with a breakdown
Global Measles and Rubella Update November 2018
 Global Measles and Rubella Update November 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep
Global Measles and Rubella Update November 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep
Comparative Analyses of Adolescent Nutrition Indicators
 Comparative Analyses of Adolescent Nutrition Indicators Rukundo K. Benedict, PhD The DHS Program Stakeholders Consultation on Adolescent Girls Nutrition: Evidence, Guidance, and Gaps October 30 31, 2017
Comparative Analyses of Adolescent Nutrition Indicators Rukundo K. Benedict, PhD The DHS Program Stakeholders Consultation on Adolescent Girls Nutrition: Evidence, Guidance, and Gaps October 30 31, 2017
Impact Dashboard - October 2014
 Impact Dashboard - 2014 By 2014, PSI and its network members averted an estimated 44.2 million DALYs globally. PSI has met 60.6% of the strategic plan (SP) target to avert 198.7 million DALYs, and 56.4%
Impact Dashboard - 2014 By 2014, PSI and its network members averted an estimated 44.2 million DALYs globally. PSI has met 60.6% of the strategic plan (SP) target to avert 198.7 million DALYs, and 56.4%
Impact Dashboard - August 2014
 Impact Dashboard - By, PSI and its network members averted an estimated 29.7 million DALYs globally. PSI has met 53.3% of the strategic plan (SP) target to avert 198.7 million DALYs, and 53.0% of the SP
Impact Dashboard - By, PSI and its network members averted an estimated 29.7 million DALYs globally. PSI has met 53.3% of the strategic plan (SP) target to avert 198.7 million DALYs, and 53.0% of the SP
THE CARE WE PROMISE FACTS AND FIGURES 2017
 THE CARE WE PROMISE FACTS AND FIGURES 2017 2 SOS CHILDREN S VILLAGES INTERNATIONAL WHERE WE WORK Facts and Figures 2017 205 58 79 families and transit 31 Foster homes 162 8 3 173 214 2 115 159 136 148
THE CARE WE PROMISE FACTS AND FIGURES 2017 2 SOS CHILDREN S VILLAGES INTERNATIONAL WHERE WE WORK Facts and Figures 2017 205 58 79 families and transit 31 Foster homes 162 8 3 173 214 2 115 159 136 148
Rotavirus: WHO Global Recommendations, Policy, and Surveillance
 Rotavirus: WHO Global Recommendations, Policy, and Surveillance 9 th International Rotavirus Symposium 2 August 2010 Mary Agócs, MD, MSc Department of Immunization, Vaccines & Biologicals From 1999 2009:
Rotavirus: WHO Global Recommendations, Policy, and Surveillance 9 th International Rotavirus Symposium 2 August 2010 Mary Agócs, MD, MSc Department of Immunization, Vaccines & Biologicals From 1999 2009:
Update from GAVI Aurelia Nguyen
 Update from GAVI Aurelia Nguyen (Copenhagen, Denmark, 27 June 2012) GAVI vaccine support Currently supported vaccines: pentavalent, pneumococcal, rotavirus, meningitis A, human papillomavirus (HPV), rubella,
Update from GAVI Aurelia Nguyen (Copenhagen, Denmark, 27 June 2012) GAVI vaccine support Currently supported vaccines: pentavalent, pneumococcal, rotavirus, meningitis A, human papillomavirus (HPV), rubella,
宮村参考人提出資料 資料 2-2
 宮村参考人提出資料 資料 - Highlights of New Wild Poliovirus and cvdpv Positives Reported Globally this Week WPV cvdpv AFP other AFP other Afghanistan 5 Pakistan 3 Nigeria Location: state/province/governorate Kunar
宮村参考人提出資料 資料 - Highlights of New Wild Poliovirus and cvdpv Positives Reported Globally this Week WPV cvdpv AFP other AFP other Afghanistan 5 Pakistan 3 Nigeria Location: state/province/governorate Kunar
Current State of Global HIV Care Continua. Reuben Granich 1, Somya Gupta 1, Irene Hall 2, John Aberle-Grasse 2, Shannon Hader 2, Jonathan Mermin 2
 Current State of Global HIV Care Continua Reuben Granich 1, Somya Gupta 1, Irene Hall 2, John Aberle-Grasse 2, Shannon Hader 2, Jonathan Mermin 2 1) International Association of Providers of AIDS Care
Current State of Global HIV Care Continua Reuben Granich 1, Somya Gupta 1, Irene Hall 2, John Aberle-Grasse 2, Shannon Hader 2, Jonathan Mermin 2 1) International Association of Providers of AIDS Care
GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION. (indicator G2.2) Highlights
 GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION (indicator G2.2) Highlights As of December 2014, 140 Member States had introduced rubella vaccines; coverage, however, varies from 12% to 94% depending on region.
GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION (indicator G2.2) Highlights As of December 2014, 140 Member States had introduced rubella vaccines; coverage, however, varies from 12% to 94% depending on region.
Financing malaria control
 Chapter 6. Financing malaria control The three major sources of funds for malaria control pro - grammes are national government spending, external assistance from donors and household or private out-of-pocket
Chapter 6. Financing malaria control The three major sources of funds for malaria control pro - grammes are national government spending, external assistance from donors and household or private out-of-pocket
Rotavirus Vaccine: Supply & Demand Update. UNICEF Supply Division
 Rotavirus Vaccine: & Demand Update UNICEF Division July 0 Rotavirus Vaccine (RV): & Demand Update July This update provides new information on countries and their scheduled RV introductions, forecasted
Rotavirus Vaccine: & Demand Update UNICEF Division July 0 Rotavirus Vaccine (RV): & Demand Update July This update provides new information on countries and their scheduled RV introductions, forecasted
Global Measles and Rubella Update October 2018
 Global Measles and Rubella Update October 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles Cases by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug
Global Measles and Rubella Update October 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles Cases by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug
Global Rotavirus Surveillance Network
 Global Rotavirus Surveillance Network Dr. Adam L. Cohen World Health Organization 7 September 2016 1 TITLE from VIEW and SLIDE MASTER 22 September 2016 Vaccine-preventable disease surveillance Active vs.
Global Rotavirus Surveillance Network Dr. Adam L. Cohen World Health Organization 7 September 2016 1 TITLE from VIEW and SLIDE MASTER 22 September 2016 Vaccine-preventable disease surveillance Active vs.
NO CHILD SHOULD DIE OF DIABETES
 NO CHILD SHOULD DIE OF DIABETES THE PROBLEM There is an estimated 1 million youth under the age of 25 with diabetes in the world. In high income countries, children with diabetes have full access to the
NO CHILD SHOULD DIE OF DIABETES THE PROBLEM There is an estimated 1 million youth under the age of 25 with diabetes in the world. In high income countries, children with diabetes have full access to the
Global Fund Results Fact Sheet Mid-2011
 Global Fund Results Fact Sheet Mid-2011 This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach
Global Fund Results Fact Sheet Mid-2011 This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach
511,000 (57% new cases) ~50,000 ~30,000
 Latest global TB estimates - 2007 (Updated Mar 2009) All forms of TB Greatest number of cases in Asia; greatest rates per capita in Africa Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) Estimated number of cases 9.27
Latest global TB estimates - 2007 (Updated Mar 2009) All forms of TB Greatest number of cases in Asia; greatest rates per capita in Africa Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) Estimated number of cases 9.27
Global reductions in measles mortality and the risk of measles resurgence
 Global reductions in measles mortality 2000 2008 and the risk of measles resurgence Measles is one of the most contagious human diseases. In 1980 before the use of measles vaccine was widespread, there
Global reductions in measles mortality 2000 2008 and the risk of measles resurgence Measles is one of the most contagious human diseases. In 1980 before the use of measles vaccine was widespread, there
Vaccines against Rotavirus & Norovirus. Umesh D. Parashar CDC, Atlanta, GA
 TM Vaccines against Rotavirus & Norovirus Umesh D. Parashar CDC, Atlanta, GA 1 Rotavirus is the Leading Cause Of Severe Diarrhea in Children
TM Vaccines against Rotavirus & Norovirus Umesh D. Parashar CDC, Atlanta, GA 1 Rotavirus is the Leading Cause Of Severe Diarrhea in Children
Global Invasive Bacterial Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Surveillance
 Global Invasive Bacterial Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Surveillance-2008-2014 Jillian Murray, World Health Organization (WHO) Mary Agocs, World Health Organization (WHO) Fatima Serhan, World Health Organization
Global Invasive Bacterial Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Surveillance-2008-2014 Jillian Murray, World Health Organization (WHO) Mary Agocs, World Health Organization (WHO) Fatima Serhan, World Health Organization
BCG. and your baby. Immunisation. Protecting babies against TB. the safest way to protect your child
 BCG and your baby Protecting babies against TB Immunisation the safest way to protect your child This leaflet is about the BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin) vaccination that is being offered to protect your
BCG and your baby Protecting babies against TB Immunisation the safest way to protect your child This leaflet is about the BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin) vaccination that is being offered to protect your
Vaccine Preventable Disease Surveillance: Overview. Thomas Cherian, WHO
 Vaccine Preventable Disease Surveillance: Overview Thomas Cherian, WHO Global Framework on Immunization Monitoring and Surveillance (GFIMS) l An extension of the GIVS, published on December 07 - http://www.who.int/immunization/en/
Vaccine Preventable Disease Surveillance: Overview Thomas Cherian, WHO Global Framework on Immunization Monitoring and Surveillance (GFIMS) l An extension of the GIVS, published on December 07 - http://www.who.int/immunization/en/
World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts
 World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts (charts in colour) (These charts will be updated in 2014) 2 1. Introduction 2. Instructions on how to use
World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts (charts in colour) (These charts will be updated in 2014) 2 1. Introduction 2. Instructions on how to use
Analysis of Immunization Financing Indicators from the WHO-UNICEF Joint Reporting Form (JRF),
 Analysis of Immunization Financing Indicators from the WHO-UNICEF Joint Reporting Form (JRF), 2008-2010 Claudio Politi and Oumar Sagna Department of Immunization Vaccines and Biologicals, World Health
Analysis of Immunization Financing Indicators from the WHO-UNICEF Joint Reporting Form (JRF), 2008-2010 Claudio Politi and Oumar Sagna Department of Immunization Vaccines and Biologicals, World Health
Impact and cost-effectiveness of rotavirus vaccination in 73 Gavi countries
 August 29, 2018 Impact and cost-effectiveness of rotavirus vaccination in 73 Gavi countries Thirteenth International Rotavirus Symposium 29 31 August 2018 Minsk, Belarus Frédéric Debellut Health Economist,
August 29, 2018 Impact and cost-effectiveness of rotavirus vaccination in 73 Gavi countries Thirteenth International Rotavirus Symposium 29 31 August 2018 Minsk, Belarus Frédéric Debellut Health Economist,
ONLINE APPENDIX. The Lives Saved Tool (LiST) (Version 4.2 Beta 7) was used to. project the number of child deaths that would be averted between
 Stack ML, Ozawa S, Bishai DM, Mirelman A, Tam Y, Niessen, et al. Estimated economic benefits during the Decade of Vaccines include treatment savings, gains in labor productivity. Health Aff (Millwood).
Stack ML, Ozawa S, Bishai DM, Mirelman A, Tam Y, Niessen, et al. Estimated economic benefits during the Decade of Vaccines include treatment savings, gains in labor productivity. Health Aff (Millwood).
APPENDIX II - TABLE 2.3 ANTI-TOBACCO MASS MEDIA CAMPAIGNS
 WHO REPORT ON THE GLOBAL TOBACCO EPIDEMIC, 2011 APPENDIX II - TABLE 2.3 ANTI-TOBACCO MASS MEDIA CAMPAIGNS (SEE TABLE 4.9) Africa The Americas South-East Asia Europe Eastern Mediterranean Western Pacific
WHO REPORT ON THE GLOBAL TOBACCO EPIDEMIC, 2011 APPENDIX II - TABLE 2.3 ANTI-TOBACCO MASS MEDIA CAMPAIGNS (SEE TABLE 4.9) Africa The Americas South-East Asia Europe Eastern Mediterranean Western Pacific
Rotavirus Vaccines. Gagandeep Kang Christian Medical College Vellore
 Rotavirus Vaccines Gagandeep Kang Christian Medical College Vellore Rotavirus disease burden Rotavirus vaccines and candidates Performance of vaccines in developed and developing countries Longitudinal
Rotavirus Vaccines Gagandeep Kang Christian Medical College Vellore Rotavirus disease burden Rotavirus vaccines and candidates Performance of vaccines in developed and developing countries Longitudinal
COLD CHAIN EQUIPMENT OPTIMISATION PLATFORM (CCEOP)
 COLD CHAIN EQUIPMENT OPTIMISATION PLATFORM (CCEOP) Sushila Maharjan Senior Manager, Innovative Finance International Conference on Sustainable Cooling World Bank Washington DC - 29 November 2018 Reach
COLD CHAIN EQUIPMENT OPTIMISATION PLATFORM (CCEOP) Sushila Maharjan Senior Manager, Innovative Finance International Conference on Sustainable Cooling World Bank Washington DC - 29 November 2018 Reach
impact dashboard - august 2018
 impact dashboard - august 2018 PSI 2015 As of August, PSI averted an estimated 15.2 M DALYs, provided 10.9 M CYPs, and reached 16.7 M users globally. Globally PSI has reached at least 16.7 million users
impact dashboard - august 2018 PSI 2015 As of August, PSI averted an estimated 15.2 M DALYs, provided 10.9 M CYPs, and reached 16.7 M users globally. Globally PSI has reached at least 16.7 million users
Sexual and reproductive health care: A comparison of providers and delivery points between the African Region and other regions
 Core competencies in primary care: Supplement 2 Sexual and reproductive health care: A comparison of providers and delivery points between the African Region and other regions The Core competencies in
Core competencies in primary care: Supplement 2 Sexual and reproductive health care: A comparison of providers and delivery points between the African Region and other regions The Core competencies in
Update on Progress and Challenges in Achieving Measles and Rubella Targets
 Update on Progress and Challenges in Achieving Measles and Rubella Targets SAGE Meeting 6 November 2013 P. Strebel, WHO/IVB/EPI Overview Global progress Regional updates Summary 2 Measles and Rubella Targets
Update on Progress and Challenges in Achieving Measles and Rubella Targets SAGE Meeting 6 November 2013 P. Strebel, WHO/IVB/EPI Overview Global progress Regional updates Summary 2 Measles and Rubella Targets
impact dashboard year-end with 2017 coefficients
 impact dashboard - 2017 year-end with 2017 coefficients In 2017, PSI averted an estimated 30.5 million DALYs and provided 20 million CYPs globally. PSI met global 2017 program targets for DALYs averted
impact dashboard - 2017 year-end with 2017 coefficients In 2017, PSI averted an estimated 30.5 million DALYs and provided 20 million CYPs globally. PSI met global 2017 program targets for DALYs averted
Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005
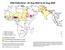 Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005 Wild virus type 1 Wild virus type 3 Wild virus type 1 & 3 Endemic countries Re-established transmission countries Case or outbreak following importation *Excludes
Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005 Wild virus type 1 Wild virus type 3 Wild virus type 1 & 3 Endemic countries Re-established transmission countries Case or outbreak following importation *Excludes
impact dashboard - september 2018
 impact dashboard - september 2018 PSI 2015 As of, PSI averted an estimated 17.1 M DALYs, provided 12.5 M CYPs, and reached 18.4 M users globally. Globally PSI has reached at least 18.4 million users across
impact dashboard - september 2018 PSI 2015 As of, PSI averted an estimated 17.1 M DALYs, provided 12.5 M CYPs, and reached 18.4 M users globally. Globally PSI has reached at least 18.4 million users across
JOINT TB AND HIV PROGRAMMING
 JOINT TB AND HIV PROGRAMMING Haileyesus Getahun, WHO. On behalf of the Global Fund Interagency TB and HIV Working Group (Global Fund, PEPFAR, Stop TB Partnership, UNAIDS, WHO) I was admitted in a hospital
JOINT TB AND HIV PROGRAMMING Haileyesus Getahun, WHO. On behalf of the Global Fund Interagency TB and HIV Working Group (Global Fund, PEPFAR, Stop TB Partnership, UNAIDS, WHO) I was admitted in a hospital
impact dashboard - june 2018
 impact dashboard - june 2018 As of June, PSI averted an estimated 11.3 M DALYs, provided 8.1 M CYPs, and reached 12.5 M users globally. Ethiopia, Zambia, and Cameroon have made considerable progress on
impact dashboard - june 2018 As of June, PSI averted an estimated 11.3 M DALYs, provided 8.1 M CYPs, and reached 12.5 M users globally. Ethiopia, Zambia, and Cameroon have made considerable progress on
O c t o b e r 1 0,
 STUDENT VOICES FROM THE FIELD: WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION GENEVA, SWITZERLAND O c t o b e r 1 0, 2 0 1 6 M o l l y P e z z u l o University at Albany School of Public Health MPH Epidemiology Candidate 17
STUDENT VOICES FROM THE FIELD: WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION GENEVA, SWITZERLAND O c t o b e r 1 0, 2 0 1 6 M o l l y P e z z u l o University at Albany School of Public Health MPH Epidemiology Candidate 17
impact dashboard - may 2018
 impact dashboard - may 2018 As of May, PSI averted an estimated 8.0 M DALYs, provided 6.2 M CYPs, and reached 8.1 M users globally. In May alone, PSI added 2.6 M users toward the goal of 90 M reached by
impact dashboard - may 2018 As of May, PSI averted an estimated 8.0 M DALYs, provided 6.2 M CYPs, and reached 8.1 M users globally. In May alone, PSI added 2.6 M users toward the goal of 90 M reached by
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report
 Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report October 2013 I N F O R M A T I O N S O U R C E S U S E D: Databases: OIE WAHID World Animal Health
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report October 2013 I N F O R M A T I O N S O U R C E S U S E D: Databases: OIE WAHID World Animal Health
Seizures of ATS (excluding ecstasy ), 2010
 Seizures of ATS (excluding ecstasy ), 2010 (countries and territories reporting seizures* of more than 10 kg) 9 5.1 8.7 12.9 Ghana Armenia 0.7 9.9 1 2.1 Syrian Arab Republic Korea (Republic of) Iraq Islamic
Seizures of ATS (excluding ecstasy ), 2010 (countries and territories reporting seizures* of more than 10 kg) 9 5.1 8.7 12.9 Ghana Armenia 0.7 9.9 1 2.1 Syrian Arab Republic Korea (Republic of) Iraq Islamic
Funding for AIDS: The World Bank s Role. Yolanda Tayler, WB Bi-regional Workshop for the Procurement of ARVs Phnom Penh, Cambodia
 Funding for AIDS: The World Bank s Role Yolanda Tayler, WB Bi-regional Workshop for the Procurement of ARVs Phnom Penh, Cambodia Outline New resources needs estimates Bridging the gap Global overview of
Funding for AIDS: The World Bank s Role Yolanda Tayler, WB Bi-regional Workshop for the Procurement of ARVs Phnom Penh, Cambodia Outline New resources needs estimates Bridging the gap Global overview of
Rotavirus vaccines: Issues not fully addressed in efficacy trials
 Rotavirus vaccines: Issues not fully addressed in efficacy trials TM Umesh D. Parashar Lead, Viral Gastroenteritis Team CDC, Atlanta, USA uparashar@cdc.gov 1 Two New Rotavirus Vaccines Licensed in 2006
Rotavirus vaccines: Issues not fully addressed in efficacy trials TM Umesh D. Parashar Lead, Viral Gastroenteritis Team CDC, Atlanta, USA uparashar@cdc.gov 1 Two New Rotavirus Vaccines Licensed in 2006
CEO Board report Seth Berkley MD CEO
 CEO Board report Seth Berkley MD CEO Dhaka, Bangladesh, 16 17 November 2011 Bangladesh, November 2011 Meningitis Incidence Children < 12 months Dhaka Shishu / Shishu Shahsta Catchment Area 2008 2011 1800
CEO Board report Seth Berkley MD CEO Dhaka, Bangladesh, 16 17 November 2011 Bangladesh, November 2011 Meningitis Incidence Children < 12 months Dhaka Shishu / Shishu Shahsta Catchment Area 2008 2011 1800
Sourcing of ARVs & HIV diagnostics. Procurement for Impact P4i
 Sourcing of ARVs & HIV diagnostics Procurement for Impact P4i AMDS ANNUAL STAKEHOLDERS AND PARTNERS MEETING 29 September 2014 Global Fund: Procurement for Impact: P4i Our objective was straightforward:
Sourcing of ARVs & HIV diagnostics Procurement for Impact P4i AMDS ANNUAL STAKEHOLDERS AND PARTNERS MEETING 29 September 2014 Global Fund: Procurement for Impact: P4i Our objective was straightforward:
AIDS in Africa. An Update. Basil Reekie
 AIDS in Africa An Update Basil Reekie Contents General Statistics The trend of HIV in Africa Ugandan experience UNAIDS 2006 Latest African Statistics by Country HIV Intervention Light at the end of the
AIDS in Africa An Update Basil Reekie Contents General Statistics The trend of HIV in Africa Ugandan experience UNAIDS 2006 Latest African Statistics by Country HIV Intervention Light at the end of the
PROGRESS REPORT ON CHILD SURVIVAL: A STRATEGY FOR THE AFRICAN REGION. Information Document CONTENTS
 29 June 2009 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, 31 August 4 September 2009 Provisional agenda item 9.2 PROGRESS REPORT ON CHILD SURVIVAL: A
29 June 2009 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, 31 August 4 September 2009 Provisional agenda item 9.2 PROGRESS REPORT ON CHILD SURVIVAL: A
#1 #2 OR Immunity verified by immune titer (please attach report) * No titer needed if proof of two doses of Varicella provided
 Student Information: Date of Birth: There are two ways to provide us with your immunization information. 1) Students can have their healthcare provider fill out and sign the form below. A healthcare provider
Student Information: Date of Birth: There are two ways to provide us with your immunization information. 1) Students can have their healthcare provider fill out and sign the form below. A healthcare provider
TT Procured by UNICEF
 TT TT Procured by UNICEF 2001-08 250,000,000 200,000,000 150,000,000 100,000,000 50,000,000 0 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 Routine SIA TT historical demand and forecast overview Upcoming Tender
TT TT Procured by UNICEF 2001-08 250,000,000 200,000,000 150,000,000 100,000,000 50,000,000 0 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 Routine SIA TT historical demand and forecast overview Upcoming Tender
Content. Introduction. Overview of reported outbreaks in WHO African Region. Disease Surveillance and Response. Vol. 2 Issue 3, April 30, 2012
 Vol. 2 Issue 3, April 30, 2012 Content Introduction Overview of reported outbreaks in the WHO African Region Cholera Meningitis Ongoing outbreaks Lassa Fever in Nigeria Typhoid in Zimbabwe Meningitis in
Vol. 2 Issue 3, April 30, 2012 Content Introduction Overview of reported outbreaks in the WHO African Region Cholera Meningitis Ongoing outbreaks Lassa Fever in Nigeria Typhoid in Zimbabwe Meningitis in
IMMUNIZATION VACCINES & EMERGENCIES
 No report No data No data IMMUNIZATION VACCINES & EMERGENCIES ROUTINE IMMUNIZATION PERFORMANCE IN THE AFRICAN REGION October 2013 issue Number of children vaccinated with the 3 rd dose of DTPcontaining
No report No data No data IMMUNIZATION VACCINES & EMERGENCIES ROUTINE IMMUNIZATION PERFORMANCE IN THE AFRICAN REGION October 2013 issue Number of children vaccinated with the 3 rd dose of DTPcontaining
מדינת ישראל. Tourist Visa Table
 Updated 23/05/2017 מדינת ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. Exe = exempted Req = required Press the first
Updated 23/05/2017 מדינת ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. Exe = exempted Req = required Press the first
Diagnostic Procurement The Clinton Foundation HIV/AIDS Initiative
 Diagnostic Procurement The Clinton Foundation HIV/AIDS Initiative 28 October 2008 Geneva 1 CHAI Work in Diagnostics - Context Diagnostic Test Agreements - In 2002 when CHAI was formed, the price of many
Diagnostic Procurement The Clinton Foundation HIV/AIDS Initiative 28 October 2008 Geneva 1 CHAI Work in Diagnostics - Context Diagnostic Test Agreements - In 2002 when CHAI was formed, the price of many
1. Consent for Treatment This form must be completed in order to receive healthcare services in the campus clinic.
 HEALTH & WELLNESS SERVICES INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING THE REQUIRED MEDICAL FORMS FOR: U.S. CITIZENS 18 YEARS OF AGE OR OLDER AT THE TIME THE FORMS ARE COMPLETED. THIS REQUIREMENT MUST BE COMPLETED WHETHER:
HEALTH & WELLNESS SERVICES INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING THE REQUIRED MEDICAL FORMS FOR: U.S. CITIZENS 18 YEARS OF AGE OR OLDER AT THE TIME THE FORMS ARE COMPLETED. THIS REQUIREMENT MUST BE COMPLETED WHETHER:
The epidemiology of tuberculosis
 The epidemiology of tuberculosis Tuberculosis Workshop Shanghai, 12-22 May 28 Philippe Glaziou World Health Organization Outline Epidemiology refresher Estimates of tuberculosis disease burden Notifications
The epidemiology of tuberculosis Tuberculosis Workshop Shanghai, 12-22 May 28 Philippe Glaziou World Health Organization Outline Epidemiology refresher Estimates of tuberculosis disease burden Notifications
Global summary of the AIDS epidemic, December 2007
 Global summary of the AIDS epidemic, December 27 Number of people living with HIV in 27 Total Adults Women Children under 15 years 33.2 million [3.6 36.1 million] 3.8 million [28.2 33.6 million] 15.4 million
Global summary of the AIDS epidemic, December 27 Number of people living with HIV in 27 Total Adults Women Children under 15 years 33.2 million [3.6 36.1 million] 3.8 million [28.2 33.6 million] 15.4 million
Prioritizing Emergency Polio Eradication Activities
 Prioritizing Emergency Polio Eradication Activities Managing the Financing Gap the other half of the Emergency Hamid Jafari GPEI Financing 2012-13: Budget = $2.23 b - Confirmed contributions = $1.14 b
Prioritizing Emergency Polio Eradication Activities Managing the Financing Gap the other half of the Emergency Hamid Jafari GPEI Financing 2012-13: Budget = $2.23 b - Confirmed contributions = $1.14 b
מדינת ישראל. Tourist Visa Table. Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents.
 Updated 25/05/2015 ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. (C) Bearers of official passports requiring tourist
Updated 25/05/2015 ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. (C) Bearers of official passports requiring tourist
Procedure for Expedited Review of imported pre-qualified vaccines for use in national immunization programmes
 Procedure for Expedited Review of imported pre-qualified vaccines for use in national immunization programmes Dr Nora Dellepiane/Dr Anil Kumar Chawla WHO/HQ-Geneva, Switzerland 1 Expedited review procedure
Procedure for Expedited Review of imported pre-qualified vaccines for use in national immunization programmes Dr Nora Dellepiane/Dr Anil Kumar Chawla WHO/HQ-Geneva, Switzerland 1 Expedited review procedure
VIEW-hub Report: Global Vaccine Introduction and Implementation
 A report on current global access to new childhood vaccines VIEW-hub Report: Global Vaccine Introduction and Implementation December 2016 INTERNAL VERSION Developed from data in VIEW-hub www.view-hub.org
A report on current global access to new childhood vaccines VIEW-hub Report: Global Vaccine Introduction and Implementation December 2016 INTERNAL VERSION Developed from data in VIEW-hub www.view-hub.org
Certificate of Immunization
 Certificate of Immunization Required of all students (Page 1 of 5) QUESTIONS? 440-775-8180 or student.health@oberlin.edu (e-mail preferred) RETURN TO: Oberlin College Student Health Services 247 W. Lorain
Certificate of Immunization Required of all students (Page 1 of 5) QUESTIONS? 440-775-8180 or student.health@oberlin.edu (e-mail preferred) RETURN TO: Oberlin College Student Health Services 247 W. Lorain
Review of decisions Debbie Adams
 Review of decisions Debbie Adams Geneva, Switzerland, Decision 1: Board/Committee member appointments (1/3) The GAVI Alliance Board: (a) Appointed the following Board members: Joan Awunyo-Akaba as Board
Review of decisions Debbie Adams Geneva, Switzerland, Decision 1: Board/Committee member appointments (1/3) The GAVI Alliance Board: (a) Appointed the following Board members: Joan Awunyo-Akaba as Board
Various interventions for controlling sexually transmitted infections have proven effective, including the syndromic
 levels, as understaffing is a chronic issue in all the countries that are scaling up male circumcision. Current achievements notwithstanding, it is necessary to reinforce and strengthen national political
levels, as understaffing is a chronic issue in all the countries that are scaling up male circumcision. Current achievements notwithstanding, it is necessary to reinforce and strengthen national political
Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved
 UNAIDS DATA TABLES 2011 Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved UNAIDS / JC2225E The designations employed and the presentation of the material in this publication
UNAIDS DATA TABLES 2011 Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved UNAIDS / JC2225E The designations employed and the presentation of the material in this publication
Global Fund Mid-2013 Results
 Global Fund Mid-2013 Results This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach in determining
Global Fund Mid-2013 Results This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach in determining
Maternal Deaths Disproportionately High in Developing Countries
 EMBARGOED until Monday, 20 October, 6am GMT HQ/2003/24 20 October 2003 CF/DOC/PR/2003-82 Maternal Deaths Disproportionately High in Developing Countries African women are 175 times more likely to die in
EMBARGOED until Monday, 20 October, 6am GMT HQ/2003/24 20 October 2003 CF/DOC/PR/2003-82 Maternal Deaths Disproportionately High in Developing Countries African women are 175 times more likely to die in
ANNEX 3: Country progress indicators
 : progress indicators 541 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS 2006 REPORT ON THE GLOBAL AIDS EPIDEMIC Annex 3 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS As of March 2006, 115 countries had reported indicators on progress
: progress indicators 541 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS 2006 REPORT ON THE GLOBAL AIDS EPIDEMIC Annex 3 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS As of March 2006, 115 countries had reported indicators on progress
IMMUNIZATION VACCINE DEVELOPMENT
 IMMUNIZATION VACCINE DEVELOPMENT MONTHLY IMMUNIZATION UPDATE IN THE AFRICAN REGION July-August 2016 (Vol 4, issue N 5) Special issue on 2015 WHO/UNICEF Estimates of National Immunization Coverage (WUENIC)
IMMUNIZATION VACCINE DEVELOPMENT MONTHLY IMMUNIZATION UPDATE IN THE AFRICAN REGION July-August 2016 (Vol 4, issue N 5) Special issue on 2015 WHO/UNICEF Estimates of National Immunization Coverage (WUENIC)
ICM: Trade-offs in the fight against HIV/AIDS
 ICM: Trade-offs in the fight against HIV/AIDS 1 As the HIV/AIDS pandemic enters its 25 th year, both the number of infections and number of deaths due to the disease continue to rise. Despite an enormous
ICM: Trade-offs in the fight against HIV/AIDS 1 As the HIV/AIDS pandemic enters its 25 th year, both the number of infections and number of deaths due to the disease continue to rise. Despite an enormous
CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS
 2016 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS August 2017 CONNECT WITH US Courtesy of DKT International 1701 K Street, NW Suite 900 Washington DC 20006 SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS 2016 Highlights 2016
2016 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS August 2017 CONNECT WITH US Courtesy of DKT International 1701 K Street, NW Suite 900 Washington DC 20006 SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS 2016 Highlights 2016
VPD in Mediterranean Basin and Black Sea: the Polio case
 Screening practices for infectious diseases among newly arrived migrants and Vaccine Preventable Disease (VPD): strategies and coverage ISS 29 MAY 2015 VPD in Mediterranean Basin and Black Sea: the Polio
Screening practices for infectious diseases among newly arrived migrants and Vaccine Preventable Disease (VPD): strategies and coverage ISS 29 MAY 2015 VPD in Mediterranean Basin and Black Sea: the Polio
Landscape Analysis on Countries' Readiness to Accelerate Action to Reduce Maternal and Child Undernutrition
 35 th Session of the UN Standing Committee on Nutrition (SCN) Hanoi, 3 6 March 2008 Landscape Analysis on Countries' Readiness to Accelerate Action to Reduce Maternal and Child Undernutrition Jorgen Schlundt
35 th Session of the UN Standing Committee on Nutrition (SCN) Hanoi, 3 6 March 2008 Landscape Analysis on Countries' Readiness to Accelerate Action to Reduce Maternal and Child Undernutrition Jorgen Schlundt
EBOLA SITUATION REPORT
 EBOLA SITUATION REPORT 11 FEBRUARY 2015 CASES/ DEATHS (data up to 8 February 2015) Guinea Liberia Sierra Leone Mali Nigeria Senegal Spain United Kingdom United States of America Total 8 6 20 8 1 0 1 0
EBOLA SITUATION REPORT 11 FEBRUARY 2015 CASES/ DEATHS (data up to 8 February 2015) Guinea Liberia Sierra Leone Mali Nigeria Senegal Spain United Kingdom United States of America Total 8 6 20 8 1 0 1 0
Outcomes of the Global Consultation Interim diagnostic algorithms and Operational considerations
 Outcomes of the Global Consultation Interim diagnostic algorithms and Operational considerations Briefing on Xpert MTB/RIF. Geneva, 21 February, 2011 Fuad Mirzayev TB Laboratory Strengthening and Diagnostics
Outcomes of the Global Consultation Interim diagnostic algorithms and Operational considerations Briefing on Xpert MTB/RIF. Geneva, 21 February, 2011 Fuad Mirzayev TB Laboratory Strengthening and Diagnostics
2015 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS
 2015 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS November 2016 CONNECT WITH US Courtesy of DKT International 1701 K Street, NW Suite 900 Washington, DC 20006 1 SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS 2015 Highlights
2015 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS November 2016 CONNECT WITH US Courtesy of DKT International 1701 K Street, NW Suite 900 Washington, DC 20006 1 SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS 2015 Highlights
Getting to Zero: On the Verge of Polio Eradication. Ellyn Ogden, MPH USAID Worldwide Polio Eradication Coordinator May 17, 2017
 Getting to Zero: On the Verge of Polio Eradication Ellyn Ogden, MPH USAID Worldwide Polio Eradication Coordinator May 17, 2017 Polio Eradication and Endgame Strategy 1. Poliovirus detection & interruption
Getting to Zero: On the Verge of Polio Eradication Ellyn Ogden, MPH USAID Worldwide Polio Eradication Coordinator May 17, 2017 Polio Eradication and Endgame Strategy 1. Poliovirus detection & interruption
Update on progress of MPP sublicensees
 Update on progress of MPP sublicensees Medicines Patent Pool SEPTEMBER 2018 SUMMARY This presentation showcases the progress made by MPP licensees (generic pharmaceutical companies) To date, MPP has signed
Update on progress of MPP sublicensees Medicines Patent Pool SEPTEMBER 2018 SUMMARY This presentation showcases the progress made by MPP licensees (generic pharmaceutical companies) To date, MPP has signed
POLIOMYELITIS ERADICATION: PROGRESS REPORT. Information Document CONTENTS BACKGROUND PROGRESS MADE NEXT STEPS... 12
 5 August 9 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, August 4 September 9 POLIOMYELITIS ERADICATION: PROGRESS REPORT Information Document CONTENTS
5 August 9 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, August 4 September 9 POLIOMYELITIS ERADICATION: PROGRESS REPORT Information Document CONTENTS
Main global and regional trends
 I N T R O D U C T I O N Main global and regional trends Promising developments have been seen in recent years in global efforts to address the AS epidemic, including increased access to effective treatment
I N T R O D U C T I O N Main global and regional trends Promising developments have been seen in recent years in global efforts to address the AS epidemic, including increased access to effective treatment
Shabir A. Madhi. Progress and Challenges of Immunization Contributing Toward Attaining the MDG Goal to Reduce under-5 Childhood Mortality.
 Shabir A. Madhi Progress and Challenges of Immunization Contributing Toward Attaining the MDG Goal to Reduce under-5 Childhood Mortality. National Institute for Communicable Diseases & University of Witwatersrand,
Shabir A. Madhi Progress and Challenges of Immunization Contributing Toward Attaining the MDG Goal to Reduce under-5 Childhood Mortality. National Institute for Communicable Diseases & University of Witwatersrand,
14/10/16. Background. Streptococcus pneumoniae (Sp) is an important cause for these diseases
 Estimates of the potential public health impact and cost-effectiveness of adopting pneumococcal vaccination in the routine immunization programme in African GAVI countries: a modelling study C. Sauboin
Estimates of the potential public health impact and cost-effectiveness of adopting pneumococcal vaccination in the routine immunization programme in African GAVI countries: a modelling study C. Sauboin
PROGRESS REPORT ON THE ROAD MAP FOR ACCELERATING THE ATTAINMENT OF THE MILLENNIUM DEVELOPMENT GOALS RELATED TO MATERNAL AND NEWBORN HEALTH IN AFRICA
 5 July 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 17.1 PROGRESS REPORT ON THE ROAD MAP FOR
5 July 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 17.1 PROGRESS REPORT ON THE ROAD MAP FOR
FORMS MUST BE COMPLETED PRIOR TO THE START OF YOUR FIRST SEMESTER
 HEALTH & WELLNESS SERVICES INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING THE REQUIRED MEDICAL FORMS FOR: U.S. CITIZENS WHO ARE NOT 18 YEARS OF AGE AT THE TIME THE FORMS ARE COMPLETED. THIS REQUIREMENT MUST BE COMPLETED
HEALTH & WELLNESS SERVICES INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING THE REQUIRED MEDICAL FORMS FOR: U.S. CITIZENS WHO ARE NOT 18 YEARS OF AGE AT THE TIME THE FORMS ARE COMPLETED. THIS REQUIREMENT MUST BE COMPLETED
UNDERGRADUATE STUDENT HEALTH PACKET
 UNDERGRADUATE STUDENT HEALTH PACKET Deadlines: Fall: July 15 th Spring: December 1st Enclosed Forms/Documents: Type of Students Required For: Comments: Undergraduate Vaccine Form Physical Examination Form
UNDERGRADUATE STUDENT HEALTH PACKET Deadlines: Fall: July 15 th Spring: December 1st Enclosed Forms/Documents: Type of Students Required For: Comments: Undergraduate Vaccine Form Physical Examination Form
HIBA ABDALRAHIM Capsca Focal Point Public Health Authority
 HIBA ABDALRAHIM Capsca Focal Point Public Health Authority Introduction Definition Symptom Transmission Global situation Local situation Control Content Introduction Yellow fever (YF) is a mosquito-borne
HIBA ABDALRAHIM Capsca Focal Point Public Health Authority Introduction Definition Symptom Transmission Global situation Local situation Control Content Introduction Yellow fever (YF) is a mosquito-borne
1) SO1: We would like to suggest that the indicator used to measure vaccine hesitancy be DTP 1 to measles first dose dropout.
 To SAGE Secretariat, WHO Dear Professor Helen Rees, Dear Dr. Jean Marie Okwo-Bele, On behalf of the Civil Society Constituency of the GAVI Alliance, we would like to thank SAGE and its members for the
To SAGE Secretariat, WHO Dear Professor Helen Rees, Dear Dr. Jean Marie Okwo-Bele, On behalf of the Civil Society Constituency of the GAVI Alliance, we would like to thank SAGE and its members for the
Methodological issues in the use of anthropometry for evaluation of nutritional status
 Methodological issues in the use of anthropometry for evaluation of nutritional status Mercedes de Onis WHO Department of Nutrition Time schedule child anthropometry Measurement Time frame Frequency
Methodological issues in the use of anthropometry for evaluation of nutritional status Mercedes de Onis WHO Department of Nutrition Time schedule child anthropometry Measurement Time frame Frequency
National Institute for Communicable Diseases -- Weekly Surveillance Report --
 Weekly Surveillance Report Week 43, 216 National Institute for Communicable Diseases -- Weekly Surveillance Report -- Page 2 Laboratory-Based Respiratory & Meningeal Disease Surveillance 3 Neisseria meningitidis
Weekly Surveillance Report Week 43, 216 National Institute for Communicable Diseases -- Weekly Surveillance Report -- Page 2 Laboratory-Based Respiratory & Meningeal Disease Surveillance 3 Neisseria meningitidis
2006 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS
 2006 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS August 2007 Courtesy of DKT International 1701 K Street, NW Suite 900 Washington, DC 20006 www.dktinternational.org 1 SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS 2006 Highlights
2006 CONTRACEPTIVE SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS August 2007 Courtesy of DKT International 1701 K Street, NW Suite 900 Washington, DC 20006 www.dktinternational.org 1 SOCIAL MARKETING STATISTICS 2006 Highlights
