Usher syndrome type 1C: Mechanisms, Animal Models and the hunt for a Cure. Jennifer J. Lentz Usher Coali>on November 2012
|
|
|
- Kathryn Malone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Usher syndrome type 1C: Mechanisms, Animal Models and the hunt for a Cure Jennifer J. Lentz Usher Coali>on November 2012
2 1. Lentz Lab Mission 2. Usher syndrome type 1C 3. Acadian Usher syndrome 4. USH1C and Harmonin 5. Ush1c.216A knock-in mouse 6. Treatment with Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs) 7. Future directions
3 Lentz Lab LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans, La Mission To develop a therapeutic approach to prevent or cure the deafness and blindness associated with Usher syndrome
4 Focus: Usher syndrome type 1C Congenital Deafness born with severe to profound hearing impairment Vestibular Areflexia difficulty with balance Retinitis Pigmentosa begins in early adolescence with night-blindness 6-8% of Usher 1 cases are caused by mutations in the USH1C gene, which encodes the protein harmonin All cases of Usher 1 in Acadian populations (South Louisiana and Canada) are caused by the USH1C.216G>A mutation (216A)
5 216G>A muta>on USH1C and Harmonin Protein Isoforms USH1C gene mrna splice variants Harmonin isoforms Reiners et al 2006
6 Harmonin Cochlear Hair Cell ROD photoreceptor Bundle morphogenesis Mechanotransduction Bundle Cuticular plate Outer Segments? Inner Segments Ribbon synapse??
7 Acadian Usher Syndrome type 1C Gene Expression in USH1C Patients Ush1c216 genotype USH1C Patient USH1C Patient USH1C Patient GG GA AA GA GA AA GG AA - pcr Wild- type Harmonin MDRKVAREFRHKVDFLIENDAEKDYLYDVLRMYHQTMDVAVLVGDLKLVINEPSRLPLFDAIRPLIPL KHQVEYDQLTPRRSRKLKEVRLDRLHPEGLGLSVRGGLEFGCGLFISHLIKGGQADSVGLQVGDEIVR INGYSISSCTHEEVINLIRTKKTVSIKVRHIGLIPVKSSPDEPLTWQYVDQFVSESGGVRGSLGSPGN RENKEKKVFISLVGSRGLGCSISSGPIQKPGIFISHVKPGSLSAEVGLEIGDQIVEVNGVDFSNLDHK EAVNVLKNSRSLTISIVAAAGRELFMTDRERLAEARQRELQRQELLMQKRLAMESNKILQEQQEMERQ RRKEIAQKAAEENERYRKEMEQIVEEEEKFKKQWEEDWGSKEQLLLPKTITAEVHPVPLRKPKYDQGV EPELEPADDLDGGTEEQGEQDFRKYEEGFDPYSMFTPEQIMGKDVRLLRIKKEGSLDLALEGGVDSPI GKVVVSAVYERGAAERHGGIVKGDEIMAINGKIVTDYTLAEADAALQKAWNQGGDWIDLVVAVCPPKE YDDELTFLLKSKRGNQIHALGNSELRPHLVNTKPRTSLERGHMTHTRWHPWDLNLSPRNLKLPLALNQ GQIRNSSGHFFEGQCGGKGAASRLGEDLKDPDSHSFPLAQ Truncated 216A mrna Transla>on MDRKVAREFRHKVDFLIENDAEKDYLYDVLRMYHQTMDVAVLVGDLKLVINEPSRLPLFDAIRPLIPL KHQEAEGGASGPSAPRRPRPECAWWPGVWLWALHLPPHQRRSGRQRRAPGRGRDRPDQWIFHLLLYP Truncated mrna with 35 bp dele>on at the end of exon 3 Predicted to encode a truncated harmonin Lentz et al 2005
8 Put the Human 216A muta>on into the Mouse Ush1c gene (knock- in) Ush1c216A A Ush1c genotype Cochlea GG GG AA AA GA GA GA GA - RT - PCR - 35 bp Ush1c genotype GG GG AA AA GA Re>na GA GA GA - RT - PCR - 35 bp 216AA mice express truncated mrna in cochlea and re>na Lentz et al 2007
9 216AA mice have ves>bular dysfunc>on and are deaf No Auditory- evoked Brainstem Response (ABR) Circling and head tossing behavior No ABR at high, mid or low frequencies Lentz et al 2010
10 216AA mice have abnormal bundles and missing hair cells IHC OHC WT Apex IHC OHC WT Base Mutant Apex Parvalbumin Neurofilament DAPI Mutant Base Abnormal bundles Disorganized OHC rows Mutant Mid turn Missing IHC & OHCs Lentz et al 2010
11 216AA mice have progressive photoreceptor degenera>on Wild Type 216AA Lentz et al 2010
12 216AA mice have reduced visual func>on and re>nal degenera>on Lentz et al 2010
13 216AA mice have slow rod adapta>on Twin flash protocol Minimal Bleach (> 1% rhodopson) Deac>va>on of Rhodopsin Kine>cs Amplitude (uv) Test flash WT 12 months a- wave ISI (sec) Probe flash 1 sec ISI 2 sec ISI 4 sec ISI 8 sec ISI (Panel F) a- wave recovery from minimal bleach takes 2 4 >mes as long Lentz unpublished data
14 Visual Cycle Kine>cs Paired flash protocol Bleach % Rhodopson Test flash 3000 lux 2 min ISI (min) Probe flash Mutant a- wave not recovered a^er 30 min Lentz unpublished data
15 216AA mice express both wt and mutant harmonin Re>na Can we detect both wt and mutant Ush1c mrna? Lentz unpublished data
16 Can we modulate the use of the mutant and wild type splice sites by trea>ng with an>sense oligonucleo>des (ASOs)? ASO Correct Splice Truncated Harmonin X Cryp>c Splice ASO targeted to 216 mutation prevents cryptic splicing and forces correct splicing Hastings Lab
17 An>sense Oligonucleo>des (ASOs) ASOs are small molecules that are - designed to have high affinity for their RNA target through unique sequence base pairing - resistant to degradation, which allows for high potency and specificity, and low toxicity ASO-based therapeutics have been FDA approved for other conditions and toxicity studies have proven the ASO chemistry is not toxicity for humans
18 ASO design & op>miza>on 1. Tested 50 different ASOs in cell lines transfected with 216A minigenes Selected an ASO that showed the largest increase in correct splicing and the largest decrease in cryp>c splicing 2. Tested that ASO in pa>ent cell lines and cells from 216AA mice Ush- ASO corrected cryp>c splicing and increased correct splicing 3. Tested the Ush- ASO in Adult mice Ush- ASO corrected cryp>c splicing and increased correct splicing in a dose dependent manor Has>ngs Lab
19 Treatment Model with ASOs ASO-Ush Usher pup Injection Time (Postnatal Day) P3-5, P10 or P16-18 Behavior Vestibular function (Open-field chamber) Physiology Hearing function (ABRs, preyer reflex) Histology Hair cell morphology (Immunohistochemistry) ASO-C Usher pup Molecular Ush1c and Harmonin Expression Lentz & Has>ngs
20 Treatment of 216AA mice with Ush-ASO Ves>bular Func>on- Single treatment between postnatal day 5 (P5) P13 rescues ves>bular func>on Hearing func>on- Single treatment at P5 restores hearing at low mid frequencies similar to wild type levels Histology- Single treatment at P5 rescues harmonin expression in the hair cell bundle and at the synapse; par>ally restores hair bundle structure; and rescues hair cells at the apex and middle turn Molecular- Single treatment at P5 decreases cryp>c splicing and increases wt expression of Ush1c and harmonin in the ear
21 Conclusions ASOs targeted to the 216A mutation rescue gene and protein expression in patient and mouse cell lines A single systemic injection in 216AA mice- Cures vestibular dysfunction Rescues hearing at low and mid frequencies Partially restores hair bundle morphology and decreases hair cell loss Partially rescues Ush1c and harmonin expression in the ear
22 Future Direc>ons Further develop an ASO treatment regiment in our mouse model to prevent deafness and vestibular defects with the goal of providing pre-clinical data that would lay the framework for clinical trials in patients Test the ASO for the treatment of blindness in our mouse model Continue studies in the ear and eye to understand how the 216A mutation causes deafness and blindness
23 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Neuroscience Center, LSU Nicolas G. Bazan Hamilton E. Farris William C. Gordon Cornelius Regan Mathew J. Spila_a Me_e Flaat Chicago Medical School, RFU Michelle L. Has>ngs Francine M. Joelka Anthony J. Hinrich Kate E. McCaffery Dominik M. Duelli Isis Pharmaceu>cals, Inc. (Carlsbad, CA) Frank Rigo
Advances in Drug Therapy for Usher Syndrome. Jennifer J. Lentz Usher Syndrome Family Conference July 11, 2015
 Advances in Drug Therapy for Usher Syndrome Jennifer J. Lentz Usher Syndrome Family Conference July 11, 2015 Ø Overall goal Ø Usher syndrome update and current hypotheses Ø New therapeuec approaches Ø
Advances in Drug Therapy for Usher Syndrome Jennifer J. Lentz Usher Syndrome Family Conference July 11, 2015 Ø Overall goal Ø Usher syndrome update and current hypotheses Ø New therapeuec approaches Ø
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
JARO. Research Article. Rescue of Outer Hair Cells with Antisense Oligonucleotides in Usher Mice Is Dependent on Age of Treatment
 JARO (217) DOI:.7/s162-17-64-x D 217 The Author(s). This article is an open access publication Research Article JARO Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology Rescue of Outer Hair Cells
JARO (217) DOI:.7/s162-17-64-x D 217 The Author(s). This article is an open access publication Research Article JARO Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology Rescue of Outer Hair Cells
Therapies to preserve vision in Usher syndrome
 USH Talks Therapies to preserve vision in Usher syndrome Monte Westerfield Institute of Neuroscience University of Oregon Usher syndrome is caused by gene mutations Mutations in any one of 11 different
USH Talks Therapies to preserve vision in Usher syndrome Monte Westerfield Institute of Neuroscience University of Oregon Usher syndrome is caused by gene mutations Mutations in any one of 11 different
Supplemental Information. Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate. Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation. through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway
 Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Kumar N. Alagramam, PhD Associate Professor Director of Research UH Ear, Nose & Throat Institute Anthony J. Maniglia Chair for Research and Education
 Kumar N. Alagramam, PhD Associate Professor Director of Research UH Ear, Nose & Throat Institute Anthony J. Maniglia Chair for Research and Education University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center Case
Kumar N. Alagramam, PhD Associate Professor Director of Research UH Ear, Nose & Throat Institute Anthony J. Maniglia Chair for Research and Education University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center Case
2. stereocilia make contact with membrane, feel vibration. Tiplink is deflected, allows ions to go inside cell body and chemical signal is generated.
 Hearing Loss 1. Most common sensory deficit in human 2. 3 in ten people over age 60 have hearing loss 3. At least 1.4 million children have hearing problems 4. Estimated that 3 in 1,000 infants are born
Hearing Loss 1. Most common sensory deficit in human 2. 3 in ten people over age 60 have hearing loss 3. At least 1.4 million children have hearing problems 4. Estimated that 3 in 1,000 infants are born
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Experimental strategy to generate sensory hair cells in the mammalian cochlea and evaluate their morphological, molecular, and biophysical properties. A) Expression plasmid encoding
Supplementary Figure 1. Experimental strategy to generate sensory hair cells in the mammalian cochlea and evaluate their morphological, molecular, and biophysical properties. A) Expression plasmid encoding
The BEACH protein LRBA is Required for Hair Bundle Maintenance in Cochlear Hair
 The BEACH protein LRBA is Required for Hair Bundle Maintenance in Cochlear Hair Cells and for Hearing Short title: LRBA is Required for Hair Bundle Maintenance in Cochlear Hair Cells Christian Vogl 1,*,
The BEACH protein LRBA is Required for Hair Bundle Maintenance in Cochlear Hair Cells and for Hearing Short title: LRBA is Required for Hair Bundle Maintenance in Cochlear Hair Cells Christian Vogl 1,*,
Lauer et al Olivocochlear efferents. Amanda M. Lauer, Ph.D. Dept. of Otolaryngology-HNS
 Lauer et al. 2012 Olivocochlear efferents Amanda M. Lauer, Ph.D. Dept. of Otolaryngology-HNS May 30, 2016 Overview Structural organization Responses Hypothesized roles in hearing Olivocochlear efferent
Lauer et al. 2012 Olivocochlear efferents Amanda M. Lauer, Ph.D. Dept. of Otolaryngology-HNS May 30, 2016 Overview Structural organization Responses Hypothesized roles in hearing Olivocochlear efferent
Clinical and Research Interest
 Clinical and Research Interest Daniel W. Nuss, MD FACS Professor & Chairman, Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Skull Base Surgery/Head and Neck Oncology Dr. Nuss chief clinical interests
Clinical and Research Interest Daniel W. Nuss, MD FACS Professor & Chairman, Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Skull Base Surgery/Head and Neck Oncology Dr. Nuss chief clinical interests
(Thomas Lenarz) Ok, thank you, thank you very much for inviting me to be here and speak to you, on cochlear implant technology.
 (Thomas Lenarz) Ok, thank you, thank you very much for inviting me to be here and speak to you, on cochlear implant technology. I want to briefly mention what hearing loss is. And what a cochlear implant
(Thomas Lenarz) Ok, thank you, thank you very much for inviting me to be here and speak to you, on cochlear implant technology. I want to briefly mention what hearing loss is. And what a cochlear implant
Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder. Yvonne S. Sininger PhD Professor of Head & Neck Surgery University of California Los Angeles
 Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder Yvonne S. Sininger PhD Professor of Head & Neck Surgery University of California Los Angeles 1 Financial Disclosure Information I have no relevant financial relationship
Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder Yvonne S. Sininger PhD Professor of Head & Neck Surgery University of California Los Angeles 1 Financial Disclosure Information I have no relevant financial relationship
Cochlear Synaptopathy and Neurodegeneration in Hidden and Overt Hearing Loss
 Cochlear Synaptopathy and Neurodegeneration in Hidden and Overt Hearing Loss Sharon G. Kujawa Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary Harvard Medical School National Hearing Conservation Association San Antonio,
Cochlear Synaptopathy and Neurodegeneration in Hidden and Overt Hearing Loss Sharon G. Kujawa Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary Harvard Medical School National Hearing Conservation Association San Antonio,
Required Slide. Session Objectives
 Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Sense system. Introduction The visual system Hearing. Introduction to sensory mechanisms
 Sense system Introduction The visual system Hearing Introduction to sensory mechanisms Sensory receptors & sense organs Sensory neurons & Receptor cells Adequate stimulus threshold Transduction Receptor
Sense system Introduction The visual system Hearing Introduction to sensory mechanisms Sensory receptors & sense organs Sensory neurons & Receptor cells Adequate stimulus threshold Transduction Receptor
Progressive Hearing Loss and Increased Susceptibility to Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in Mice Carrying a Cdh23 but not a Myo7a Mutation
 JARO 5: 66 79 (2004) DOI: 10.1007/s10162-003-4021-2 JARO Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology Progressive Hearing Loss and Increased Susceptibility to Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in
JARO 5: 66 79 (2004) DOI: 10.1007/s10162-003-4021-2 JARO Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology Progressive Hearing Loss and Increased Susceptibility to Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in
EGFR shrna A: CCGGCGCAAGTGTAAGAAGTGCGAACTCGAGTTCGCACTTCTTACACTTGCG TTTTTG. EGFR shrna B: CCGGAGAATGTGGAATACCTAAGGCTCGAGCCTTAGGTATTCCACATTCTCTT TTTG
 Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
4. Which letter in figure 9.1 points to the fovea centralis? Ans: b
 Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
Deafness and hearing impairment
 Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Vision and Audition. This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems.
 Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
Synaptopathy Research Uwe Andreas Hermann
 Potential diagnose and basic understanding of hidden hearing loss Synaptopathy Research Uwe Andreas Hermann Motivation Synaptopathy is a current hot topic in the research field because it focuses on a
Potential diagnose and basic understanding of hidden hearing loss Synaptopathy Research Uwe Andreas Hermann Motivation Synaptopathy is a current hot topic in the research field because it focuses on a
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Introduction. IAPA: June 04 1
 Introduction Conflicting views on the prevalence and nature of otoacoustic emission [OAE] abnormalities in ARNSHL families (Morell et al, 1998; Cohn & Kelley, 1999). Detailed study of OAEs in greater number
Introduction Conflicting views on the prevalence and nature of otoacoustic emission [OAE] abnormalities in ARNSHL families (Morell et al, 1998; Cohn & Kelley, 1999). Detailed study of OAEs in greater number
Hope and Building an Usher Syndrome Community. Mark Dunning Chairman, Coalition for Usher Syndrome Research
 Hope and Building an Usher Syndrome Community Mark Dunning Chairman, Coalition for Usher Syndrome Research 14 years old Born deaf Diagnosed with Usher at age 8 Loves horses Grudgingly loves her little
Hope and Building an Usher Syndrome Community Mark Dunning Chairman, Coalition for Usher Syndrome Research 14 years old Born deaf Diagnosed with Usher at age 8 Loves horses Grudgingly loves her little
Auditory nerve. Amanda M. Lauer, Ph.D. Dept. of Otolaryngology-HNS
 Auditory nerve Amanda M. Lauer, Ph.D. Dept. of Otolaryngology-HNS May 30, 2016 Overview Pathways (structural organization) Responses Damage Basic structure of the auditory nerve Auditory nerve in the cochlea
Auditory nerve Amanda M. Lauer, Ph.D. Dept. of Otolaryngology-HNS May 30, 2016 Overview Pathways (structural organization) Responses Damage Basic structure of the auditory nerve Auditory nerve in the cochlea
Defining Protein Interactions: Ankle Link Proteins of Stereocilia in Hair Cells
 Portland State University PDXScholar University Honors Theses University Honors College 2016 Defining Protein Interactions: Ankle Link Proteins of Stereocilia in Hair Cells Ladan Yazdidoust Portland State
Portland State University PDXScholar University Honors Theses University Honors College 2016 Defining Protein Interactions: Ankle Link Proteins of Stereocilia in Hair Cells Ladan Yazdidoust Portland State
Modeling and Preventing Progressive Hearing Loss in Usher Syndrome III
 www.nature.com/scientificreports Received: 21 April 2017 Accepted: 29 September 2017 Published: xx xx xxxx OPEN Modeling and Preventing Progressive Hearing Loss in Usher Syndrome III Ruishuang Geng 1,
www.nature.com/scientificreports Received: 21 April 2017 Accepted: 29 September 2017 Published: xx xx xxxx OPEN Modeling and Preventing Progressive Hearing Loss in Usher Syndrome III Ruishuang Geng 1,
MECHANISM OF HEARING
 MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology I. Professor Dave Furness Keele University
 Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology I Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of these lectures Introduction to gross anatomy of the cochlea Focus (1) on
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology I Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of these lectures Introduction to gross anatomy of the cochlea Focus (1) on
RNA-Seq guided gene therapy for vision loss. Michael H. Farkas
 RNA-Seq guided gene therapy for vision loss Michael H. Farkas The retina is a complex tissue Many cell types Neural retina vs. RPE Each highly dependent on the other Graw, Nature Reviews Genetics, 2003
RNA-Seq guided gene therapy for vision loss Michael H. Farkas The retina is a complex tissue Many cell types Neural retina vs. RPE Each highly dependent on the other Graw, Nature Reviews Genetics, 2003
Over-expression of myosin7a in cochlear hair cells of circling mice
 ISSN 1738-6055 (Print) ISSN 2233-7660 (Online) Lab Anim Res 2017: 33(1), 1-7 https://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2017.33.1.1 Over-expression of myosin7a in cochlear hair cells of circling mice Yoo Yeon Kim, Hajin
ISSN 1738-6055 (Print) ISSN 2233-7660 (Online) Lab Anim Res 2017: 33(1), 1-7 https://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2017.33.1.1 Over-expression of myosin7a in cochlear hair cells of circling mice Yoo Yeon Kim, Hajin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Auditory System Feedback
 Feedback Auditory System Feedback Using all or a portion of the information from the output of a system to regulate or control the processes or inputs in order to modify the output. Central control of
Feedback Auditory System Feedback Using all or a portion of the information from the output of a system to regulate or control the processes or inputs in order to modify the output. Central control of
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 29. Hearing
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
C ritical Review: Can individuals with hearing impairment associated with Usher Syndrome benefit from a cochlear implant?
 C ritical Review: Can individuals with hearing impairment associated with Usher Syndrome benefit from a cochlear implant? Chantal Arsenault M.Cl.Sc. (AUD) Candidate University of Western Ontario: School
C ritical Review: Can individuals with hearing impairment associated with Usher Syndrome benefit from a cochlear implant? Chantal Arsenault M.Cl.Sc. (AUD) Candidate University of Western Ontario: School
Differentiation of the lateral compartment of the cochlea requires a temporally restricted FGF20 signal
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2012 Differentiation of the lateral compartment of the cochlea requires a temporally restricted FGF20 signal Sung-Ho
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2012 Differentiation of the lateral compartment of the cochlea requires a temporally restricted FGF20 signal Sung-Ho
Mechanical Properties of the Cochlea. Reading: Yost Ch. 7
 Mechanical Properties of the Cochlea CF Reading: Yost Ch. 7 The Cochlea Inner ear contains auditory and vestibular sensory organs. Cochlea is a coiled tri-partite tube about 35 mm long. Basilar membrane,
Mechanical Properties of the Cochlea CF Reading: Yost Ch. 7 The Cochlea Inner ear contains auditory and vestibular sensory organs. Cochlea is a coiled tri-partite tube about 35 mm long. Basilar membrane,
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-414 TITLE: Prevention and Treatment of Noise-Induced Tinnitus PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Richard A. Altschuler CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Michigan Ann Arbor,
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-414 TITLE: Prevention and Treatment of Noise-Induced Tinnitus PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Richard A. Altschuler CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Michigan Ann Arbor,
Usher syndrome Close to a cure? The Path to Clinical Trials
 Usher syndrome Close to a cure? The Path to Clinical Trials William J. Kimberling, PhD Boys Town Hospital, Omaha NE and and Institute for Vision Research Collaborative Center for Deaf-Blind Studies University
Usher syndrome Close to a cure? The Path to Clinical Trials William J. Kimberling, PhD Boys Town Hospital, Omaha NE and and Institute for Vision Research Collaborative Center for Deaf-Blind Studies University
Sensation and Perception. 8.2 The Senses
 Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Acoustics, signals & systems for audiology. Psychoacoustics of hearing impairment
 Acoustics, signals & systems for audiology Psychoacoustics of hearing impairment Three main types of hearing impairment Conductive Sound is not properly transmitted from the outer to the inner ear Sensorineural
Acoustics, signals & systems for audiology Psychoacoustics of hearing impairment Three main types of hearing impairment Conductive Sound is not properly transmitted from the outer to the inner ear Sensorineural
TMIE Is an Essential Component of the Mechanotransduction Machinery of Cochlear Hair Cells
 Article TMIE Is an Essential Component of the Mechanotransduction Machinery of Cochlear Hair Cells Bo Zhao, 1 Zizhen Wu, 1 Nicolas Grillet, 1,2 Linxuan Yan, 1 Wei Xiong, 1 Sarah Harkins-Perry, 1 and Ulrich
Article TMIE Is an Essential Component of the Mechanotransduction Machinery of Cochlear Hair Cells Bo Zhao, 1 Zizhen Wu, 1 Nicolas Grillet, 1,2 Linxuan Yan, 1 Wei Xiong, 1 Sarah Harkins-Perry, 1 and Ulrich
OtoAcoustic Emissions (OAE s)
 OtoAcoustic Emissions (OAE s) Phenomenon and applications in audiological diagnostics Measurement procedures TEOAE and DPOAE Physiological backgound, functional models Acknowledgment: several illustrations
OtoAcoustic Emissions (OAE s) Phenomenon and applications in audiological diagnostics Measurement procedures TEOAE and DPOAE Physiological backgound, functional models Acknowledgment: several illustrations
Usher Syndrome: When to Suspect it and How to Find It
 Usher Syndrome: When to Suspect it and How to Find It Margaret Kenna, MD, MPH Katherine Lafferty, MS, CGC Heidi Rehm, PhD Anne Fulton, MD Harvard Medical School Harvard Medical School Center for Hereditary
Usher Syndrome: When to Suspect it and How to Find It Margaret Kenna, MD, MPH Katherine Lafferty, MS, CGC Heidi Rehm, PhD Anne Fulton, MD Harvard Medical School Harvard Medical School Center for Hereditary
Hearing Screening, Diagnostics and Intervention
 JCIH Newborn Hearing Screening Guidelines 1-3-6 Model By 1 month Screenhearing Hearing Screening, Diagnostics and Intervention By 3 months: Evaluate hearing and complete diagnosticaudiology and otolaryngology
JCIH Newborn Hearing Screening Guidelines 1-3-6 Model By 1 month Screenhearing Hearing Screening, Diagnostics and Intervention By 3 months: Evaluate hearing and complete diagnosticaudiology and otolaryngology
Hearing. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 14. Hearing. Hearing
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
Usher syndrome Close to a cure? The Path to Clinical Trials
 Usher syndrome Close to a cure? The Path to Clinical Trials William J. Kimberling, PhD Boys Town Hospital, Omaha NE and and Institute for Vision Research Collaborative Center for Deaf-Blind Studies University
Usher syndrome Close to a cure? The Path to Clinical Trials William J. Kimberling, PhD Boys Town Hospital, Omaha NE and and Institute for Vision Research Collaborative Center for Deaf-Blind Studies University
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Genetics of Hearing Loss
 Genetics of Hearing Loss Daryl A. Scott MD/PhD Molecular & Human Genetics 1/20/2015 Why do we care? 1 100% 75% Hearing Loss 500:1000 50% 314:1000 25% 1:1000 17:1000 Newborn 18 yrs 65 yrs 75 yrs 60% Members
Genetics of Hearing Loss Daryl A. Scott MD/PhD Molecular & Human Genetics 1/20/2015 Why do we care? 1 100% 75% Hearing Loss 500:1000 50% 314:1000 25% 1:1000 17:1000 Newborn 18 yrs 65 yrs 75 yrs 60% Members
INDEX. Genetics. French poodle progressive rod-cone degeneration,
 INDEX Acuity in Stargardt's macular dystrophy, 25-34 ADRP (Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa), see Retinitis pigmentosa and Genetics afgf, 294, 296 Age-related maculopathy, see Macular degeneration
INDEX Acuity in Stargardt's macular dystrophy, 25-34 ADRP (Autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa), see Retinitis pigmentosa and Genetics afgf, 294, 296 Age-related maculopathy, see Macular degeneration
Tacoma, WA U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-15-2-0024 TITLE: Assessment and Treatment of blast-induced Auditory and Vestibular Injuries PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Joseph B. Long CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: The Geneva Foundation
AD Award Number: W81XWH-15-2-0024 TITLE: Assessment and Treatment of blast-induced Auditory and Vestibular Injuries PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Joseph B. Long CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: The Geneva Foundation
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Biological Bases of Age- Related Hearing Loss
 Biological Bases of Age- Related Hearing Loss Robert D. Frisina,, PhD Professor and Assoc. Chair Otolaryngology Department University of Rochester Medical School, International Center for Hearing & Speech
Biological Bases of Age- Related Hearing Loss Robert D. Frisina,, PhD Professor and Assoc. Chair Otolaryngology Department University of Rochester Medical School, International Center for Hearing & Speech
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH).
 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH). (a), (b), PRPH immunolabelling of cryosections from post-natal day
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH). (a), (b), PRPH immunolabelling of cryosections from post-natal day
au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg
 Biology of the ear http://www.nal.gov. au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg Agenda Pre-test Lecture Group Gesture Types of hearing losses Audiograms Views Post-test Pretest!! See how much you know Answer
Biology of the ear http://www.nal.gov. au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg Agenda Pre-test Lecture Group Gesture Types of hearing losses Audiograms Views Post-test Pretest!! See how much you know Answer
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Emissions are low-intensity sounds that may be detected in the external ear canal by a microphone
 OAEs Emissions are low-intensity sounds that may be detected in the external ear canal by a microphone OAE is a pre-neural phenomenon They can be measured even when the 8 th cranial nerve is severely damaged
OAEs Emissions are low-intensity sounds that may be detected in the external ear canal by a microphone OAE is a pre-neural phenomenon They can be measured even when the 8 th cranial nerve is severely damaged
Music and Hearing in the Older Population: an Audiologist's Perspective
 Music and Hearing in the Older Population: an Audiologist's Perspective Dwight Ough, M.A., CCC-A Audiologist Charlotte County Hearing Health Care Centre Inc. St. Stephen, New Brunswick Anatomy and Physiology
Music and Hearing in the Older Population: an Audiologist's Perspective Dwight Ough, M.A., CCC-A Audiologist Charlotte County Hearing Health Care Centre Inc. St. Stephen, New Brunswick Anatomy and Physiology
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
A mouse model for human hearing loss DFNB30 due to loss of function of myosin IIIA
 Mamm Genome (2011) 22:170 177 DOI 10.1007/s00335-010-9310-6 A mouse model for human hearing loss DFNB30 due to loss of function of myosin IIIA Vanessa L. Walsh Dorith Raviv Amiel A. Dror Hashem Shahin
Mamm Genome (2011) 22:170 177 DOI 10.1007/s00335-010-9310-6 A mouse model for human hearing loss DFNB30 due to loss of function of myosin IIIA Vanessa L. Walsh Dorith Raviv Amiel A. Dror Hashem Shahin
The Research Progress of Stem Cell Based Therapies for Regenerating Inner Ear Hair Cells
 The Research Progress of Stem Cell Based Therapies for Regenerating Inner Ear Hair Cells Professor Wang Jinfu College of Life Sciences, Zhejiang University Institute of Cell and Developmental Biology The
The Research Progress of Stem Cell Based Therapies for Regenerating Inner Ear Hair Cells Professor Wang Jinfu College of Life Sciences, Zhejiang University Institute of Cell and Developmental Biology The
Taste buds Gustatory cells extend taste hairs through a narrow taste pore
 The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Sensory System Sensory information Conscious sensations Unconscious sensations Sensory processing Transferring stimulus energy into a graded potential
Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Sensory System Sensory information Conscious sensations Unconscious sensations Sensory processing Transferring stimulus energy into a graded potential
The Sense Organs 10/13/2016. The Human Eye. 1. Sclera 2. Choroid 3. Retina. The eye is made up of three layers:
 The human body gathers information from the outside world by using the five senses of: The Sense Organs 12.3 Sight Hearing Taste Smell Touch This information is essential in helping the body maintain homeostasis.
The human body gathers information from the outside world by using the five senses of: The Sense Organs 12.3 Sight Hearing Taste Smell Touch This information is essential in helping the body maintain homeostasis.
Cell and Tissue-based Therapies for Hearing Loss
 Cell and Tissue-based Therapies for Hearing Loss Anne L. van de Ven 19 Nov 2003 BioE 492/592 Sensory Neuroengineering Lecture 16 Causes of Hearing Loss Age (34%) Loud noise (40 %) Disease/trauma (21%)
Cell and Tissue-based Therapies for Hearing Loss Anne L. van de Ven 19 Nov 2003 BioE 492/592 Sensory Neuroengineering Lecture 16 Causes of Hearing Loss Age (34%) Loud noise (40 %) Disease/trauma (21%)
HEARING & BALANCE RESEARCH GRANT RECIPIENTS
 2007-2008 HEARING & BALANCE RESEARCH GRANT RECIPIENTS Each year since its inception, the Deafness Research Foundation (DRF) has funded promising research in the field of hearing and balance science. This
2007-2008 HEARING & BALANCE RESEARCH GRANT RECIPIENTS Each year since its inception, the Deafness Research Foundation (DRF) has funded promising research in the field of hearing and balance science. This
Sound Waves. Sound and Sensa3on. Chapter 9. Sound waves are composed of compression and rarefac3on of air molecules. Domain
 Chapter 9 Majority of illustra3ons in this presenta3on are from Biological Psychology 4 th edi3on ( Sinuer Publica3ons) Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of compression and rarefac3on of air molecules.
Chapter 9 Majority of illustra3ons in this presenta3on are from Biological Psychology 4 th edi3on ( Sinuer Publica3ons) Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of compression and rarefac3on of air molecules.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
Psychology Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception. Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed!
 Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
2/16/2012. Pediatric Auditory Assessment: Using Science to Guide Clinical Practice
 Pediatric Auditory Assessment: Using Science to Guide Clinical Practice Doug Sladen, Ph.D. Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota sladen.douglas@mayo.edu Evidence Based Practice The conscientious, explicit,
Pediatric Auditory Assessment: Using Science to Guide Clinical Practice Doug Sladen, Ph.D. Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota sladen.douglas@mayo.edu Evidence Based Practice The conscientious, explicit,
Supplemental Figure S1. PLAG1 kidneys contain fewer glomeruli (A) Quantitative PCR for Igf2 and PLAG1 in whole kidneys taken from mice at E15.
 Supplemental Figure S1. PLAG1 kidneys contain fewer glomeruli (A) Quantitative PCR for Igf2 and PLAG1 in whole kidneys taken from mice at E15.5, E18.5, P4, and P8. Values shown are means from four technical
Supplemental Figure S1. PLAG1 kidneys contain fewer glomeruli (A) Quantitative PCR for Igf2 and PLAG1 in whole kidneys taken from mice at E15.5, E18.5, P4, and P8. Values shown are means from four technical
Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism
 Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism Objectives (1) Anatomy of the inner ear Functions of the cochlear and vestibular systems Three compartments within the cochlea and membranes
Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism Objectives (1) Anatomy of the inner ear Functions of the cochlear and vestibular systems Three compartments within the cochlea and membranes
Sensation and Perception. A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations
 I. Overview Sensation and Perception A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations C. Top-Down vs Bottom-up Processing D. Psychophysics -- thresholds 1.
I. Overview Sensation and Perception A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations C. Top-Down vs Bottom-up Processing D. Psychophysics -- thresholds 1.
HST 721 Lecture 4: Mechanics, electromotility and the cochlear amplifier
 HST 721 Lecture 4: Mechanics, electromotility and the cochlear amplifier 1 Cochlear Mechanics: Measures of Basilar Membrane Motion 2 Cochlear Mechanics: Measures of Basilar Membrane Motion Bekesy s experiments
HST 721 Lecture 4: Mechanics, electromotility and the cochlear amplifier 1 Cochlear Mechanics: Measures of Basilar Membrane Motion 2 Cochlear Mechanics: Measures of Basilar Membrane Motion Bekesy s experiments
Year 4 Results For a Phase 1 Trial of Voretigene Neparvovec in Biallelic RPE65- Mediated Inherited Retinal Disease
 8:00 AM Year 4 Results For a Phase 1 Trial of Voretigene Neparvovec in Biallelic RPE65- Mediated Inherited Retinal Disease Albert M. Maguire, MD OBJECTIVE Assess maintenance of functional vision/visual
8:00 AM Year 4 Results For a Phase 1 Trial of Voretigene Neparvovec in Biallelic RPE65- Mediated Inherited Retinal Disease Albert M. Maguire, MD OBJECTIVE Assess maintenance of functional vision/visual
ILDR1 null mice, a model of human deafness DFNB42, show structural aberrations of tricellular tight junctions and degeneration of auditory hair cells
 Human Molecular Genetics, 2015, Vol. 24, No. 3 609 624 doi:10.1093/hmg/ddu474 Advance Access published on September 12, 2014 ILDR1 null mice, a model of human deafness DFNB42, show structural aberrations
Human Molecular Genetics, 2015, Vol. 24, No. 3 609 624 doi:10.1093/hmg/ddu474 Advance Access published on September 12, 2014 ILDR1 null mice, a model of human deafness DFNB42, show structural aberrations
The Outer and Middle Ear PERIPHERAL AUDITORY SYSTEM HOW WE HEAR. The Ear in Action AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK. The 3 parts of the ear
 AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8
 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Psychological and Physiological Acoustics Session 3aPP: Auditory Physiology
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Psychological and Physiological Acoustics Session 3aPP: Auditory Physiology
HST 721 Efferent Control Lecture October 2004
 HST 721 Efferent Control Lecture October 2004 1 Stapedius Muscle Central Circuitry 2 Hypotheses for MEM Function A. Stapedius 1. Extend Dynamic Range - a gain control system 2. Protect the Inner Ear from
HST 721 Efferent Control Lecture October 2004 1 Stapedius Muscle Central Circuitry 2 Hypotheses for MEM Function A. Stapedius 1. Extend Dynamic Range - a gain control system 2. Protect the Inner Ear from
Presentation On SENSATION. Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur
 Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
A PROPOSAL FOR THE HEAR SEE HOPE FOUNDATION VISUALIZING A CURE
 A PROPOSAL FOR THE HEAR SEE HOPE FOUNDATION VISUALIZING A CURE SEPTEMBER 2017 VISUALIZING A CURE: UNDERSTANDING CONE DEGENERATION IN USHER SYNDROME AND RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA Within the retina, photoreceptors
A PROPOSAL FOR THE HEAR SEE HOPE FOUNDATION VISUALIZING A CURE SEPTEMBER 2017 VISUALIZING A CURE: UNDERSTANDING CONE DEGENERATION IN USHER SYNDROME AND RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA Within the retina, photoreceptors
Apoptosis Progression in the Hair Cells in the Organ of Corti of GJB2 Conditional Knockout Mice
 Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 5, No. 3: 132-138, September 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2012.5.3.132 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Apoptosis Progression in
Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 5, No. 3: 132-138, September 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2012.5.3.132 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Apoptosis Progression in
Dario Balestra University of Ferrara
 ABERRANT mrna SPLICING IN COAGULATION FACTOR DEFICIENCIES: FROM MOLECULAR MECHANISMS TO RNA-BASED THERAPEUTIC APPROACHES Dario Balestra University of Ferrara mrna SPLICING Several sequence elements, both
ABERRANT mrna SPLICING IN COAGULATION FACTOR DEFICIENCIES: FROM MOLECULAR MECHANISMS TO RNA-BASED THERAPEUTIC APPROACHES Dario Balestra University of Ferrara mrna SPLICING Several sequence elements, both
The Structure and Function of the Auditory Nerve
 The Structure and Function of the Auditory Nerve Brad May Structure and Function of the Auditory and Vestibular Systems (BME 580.626) September 21, 2010 1 Objectives Anatomy Basic response patterns Frequency
The Structure and Function of the Auditory Nerve Brad May Structure and Function of the Auditory and Vestibular Systems (BME 580.626) September 21, 2010 1 Objectives Anatomy Basic response patterns Frequency
N acetyl cysteine prevents age related hearing loss and the progressive loss of inner hair cells in γ glutamyl transferase 1 deficient mice
 www.impactaging.com AGING, April 2016, Vol 8 No 4 Research Paper N acetyl cysteine prevents age related hearing loss and the progressive loss of inner hair cells in γ glutamyl transferase 1 deficient mice
www.impactaging.com AGING, April 2016, Vol 8 No 4 Research Paper N acetyl cysteine prevents age related hearing loss and the progressive loss of inner hair cells in γ glutamyl transferase 1 deficient mice
Converting Sound Waves into Neural Signals, Part 1. What happens to initiate neural signals for sound?
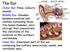 The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
Vision. Vision. Vision. Chem Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 6. Rod cells. E = hν = hc λ
 Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 6 Question of the Day: Who has better color vision, a human or a mantis shrimp? involves the transduction of light energy to an nerve signal.
Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 6 Question of the Day: Who has better color vision, a human or a mantis shrimp? involves the transduction of light energy to an nerve signal.
Intro to Audition & Hearing
 Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
Hearing Evaluation: Diagnostic Approach
 Hearing Evaluation: Diagnostic Approach Hearing Assessment Purpose - to quantify and qualify in terms of the degree of hearing loss, the type of hearing loss and configuration of the hearing loss - carried
Hearing Evaluation: Diagnostic Approach Hearing Assessment Purpose - to quantify and qualify in terms of the degree of hearing loss, the type of hearing loss and configuration of the hearing loss - carried
Biology. Slide 1 of 49. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Chapter 38 Active Reading Guide Nervous and Sensory Systems
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 38 Active Reading Guide Nervous and Sensory Systems Section 1 1. This concept begins with a look at the evolution of nervous systems. You will want to study this to tie
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 38 Active Reading Guide Nervous and Sensory Systems Section 1 1. This concept begins with a look at the evolution of nervous systems. You will want to study this to tie
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221
 BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
DIAGNOSIS Causes/Etiology of Hearing Loss
 DIAGNOSIS Causes/Etiology of Hearing Loss DIAGNOSIS Causes/Etiology of Hearing Loss VI. How Do We Hear? Sound waves enter our ears and are amplified by the ear drum and middle ear bones (ossicles), allowing
DIAGNOSIS Causes/Etiology of Hearing Loss DIAGNOSIS Causes/Etiology of Hearing Loss VI. How Do We Hear? Sound waves enter our ears and are amplified by the ear drum and middle ear bones (ossicles), allowing
2) What is the most robust distortion product evoked with DPOAEs? A. F1 B. F2 C. 2F1-F2 D. 2F2 F1
 Instructions: Look at the following questions below in their respective categories, and check your answers against the Answer Key on the last page. Contact the SAA Programs Subcommittee Chair with any
Instructions: Look at the following questions below in their respective categories, and check your answers against the Answer Key on the last page. Contact the SAA Programs Subcommittee Chair with any
Chapter 13 Physics of the Ear and Hearing
 Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Support. Overview. Auditory Dys-synchrony. Auditory Brainstem Response. Potential Causes
 Potential Role of Genetic Testing in Auditory Neuropathy/Dys-synchrony Christina Runge-Samuelson, Ph.D., CCC-A Associate Professor Co-Director, Koss Cochlear Implant Program Department of tolaryngology
Potential Role of Genetic Testing in Auditory Neuropathy/Dys-synchrony Christina Runge-Samuelson, Ph.D., CCC-A Associate Professor Co-Director, Koss Cochlear Implant Program Department of tolaryngology
