Topic 11 - Parietal Association Cortex. 1. Sensory-to-motor transformations. 2. Activity in parietal association cortex and the effects of damage
|
|
|
- Bertram Edwards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Topic 11 - Parietal Association Cortex 1. Sensory-to-motor transformations 2. Activity in parietal association cortex and the effects of damage Sensory to Motor Transformation Sensory information (visual, somatosensation etc.) is integrated and used to generate an appropriate motor output. Posterior Parietal Cortex (PPC) association area Superior parietal lobule (SPL) Intraparietal sulcus (IPS) Inferior parietal lobule (IPL) Anterior Posterior Culham and Kanwisher, (2001) Cur. Opinion in Neurobiol. 11:
2 PPC association area - PPC is neither purely sensory nor purely motor ("association cortex") - important for integration of sensory information - sends information to motor areas (e.g. premotor and M1) - important for "sensory-to-motor" transformation Topic 11 - Parietal Association Cortex 1. Sensory-to-motor transformations 2. Activity in parietal association cortex and the effects of damage Parietal Association Cortex Superior parietal lobule (SPL) - integrates information from several sensory modalities (e.g. V1 and S1) Source: MacKay, Neuro 101, Sefalotek Ltd., 1999
3 Dorsal vs. Ventral Streams Milner & Goodale, 1995 Dorsal vs. Ventral Streams
4 Ventral Stream Dorsal Stream Object identification Relational metrics Long term representation Conscious Visual control of motor output Absolute metrics Moment-to-moment computations Unconscious Goodale, MA & Humphrey, GK. (1998). Cognition Lesions of parietal association cortex produce complicated deficits
5 Advantages Why study lesions? Disadvantages Provides insight into normal functioning of the brain. Lesions are rarely focal Tells you which areas are necessary for which functions Astereognosis - inability to recognize objects by touch alone??? Balint s syndrome Visuomotor and visuospatial disorders Bilateral damage to posterior parietal lobes Simultanagnosia inability to interpret the visual field as a whole Ocular apraxia deficit of visual scanning Optic ataxia inability to reach accurately under visual guidance
6 Simultanagnosia Difficulty copying/drawing/writing because they can t see the end of the pen and what is on the paper at the same time. Spatial disorientation: unable to discern spatial properties of objects e.g. distance and size. Difficulty describing complex scenes (eg. Boston cookie theft) Simultanagnosia Ocular Apraxia Impaired visual scanning (moving the eyes voluntarily) Not an oculomotor deficit Reflexive movements are spared Eye movements toward auditory stimuli are spared Gaze restricted to narrow band, right of midline (similar to neglect)
7 Ocular Apraxia Normal eye movements Apraxic eye movements Optic Ataxia "dorsal" and "ventral" streams Parietal lobe Dorsal stream Optic Ataxia Temporal lobe Ventral stream Primary visual area (V1) Optic Ataxia The inability to accurately reach for visible objects From: Perenin & Vighetto (1988) Brain. 111:
8 Optic Ataxia Visuomotor deficits - errors in visuallyguided movements No other perceptual or motor deficits Two types of optic ataxia patients Unilateral Optic Ataxia Optic Ataxia Bilateral Optic Ataxia Optic Ataxia Unilateral Optic Ataxia
9 Unilateral Optic Ataxia Healthy Hand Ataxic Hand Vighetto, 1980 Healthy Field Ataxic Field Unilateral Optic Ataxia Revol et al., 2003 Optic Ataxia Bilateral Optic Ataxia
10 Bilateral Optic Ataxia Jeannerod, Neuropsychologia. Bilateral Optic Ataxia Control Optic Ataxia Patient Immediate Delayed Milner et al., 1999; 2001; 2003 Ideomotor Apraxia Loss of ability to perform previously learned motor tasks Parietal lobe Dorsal stream? Temporal lobe Ventral stream Primary visual area (V1)
11 Personal neglect syndrome - lack of awareness of a body part? Neglect Mostly found with right lesions in the IPL. May be in the superior temporal cortex site in monkeys that is associated with spatial awareness. Some subcortical damage: basal ganglia and thalamus. Karnath, HO, Ferber, S, & Himmelbach, M. (2001). Nature Neglect Lack of awareness of personal and extra-personal space contralateral to lesioned hemisphere, e.g. patient may believe the left side of body is someone else s. patient eats only the food in the right half of plate. patient may only dress or shave on side.
12 Neglect Attention Deficits Yves Rossetti, INSERM 534, France Neglect Yves Rossetti, INSERM 534, France Neglect Yves Rossetti, INSERM 534, France
13 Neglect Visuo-motor deficits. Yves Rossetti, INSERM 534, France Neglect Anosognosia- The loss of recognition or awareness of a disease. Most people with neglect are also unaware that they have the disorder.
14 IT Functions Object perception, recognition, memory Face perception Visual Agnosia Inability to recognize objects from sight Deficient shape perception Famous case D.F. Can t recognize or copy drawings of common objects (such as an apple or a key) but can draw from memory Can t estimate size, distance of objects Visual Agnosia Milner & Goodale, 1995
15 Prosopagnosia Inability to recognize faces by sight, Even themselves Can by recognize by voice Can recognize faces as faces and name parts Can discriminate faces (tell two faces apart) Based on feature comparison not global recognition Summary Dissociation between ventral and dorsal streams Parietal Damage Can recognize objects Can judge relative distance, size Cannot make accurate visual guided actions e.g. saccades, pointing, grasping Lack of attention of space Milner & Goodale, 1995 Inferior Temporal Damage Cannot recognize objects, faces Cannot judge relative distance, size Can make accurate visually guided action (taking shape into account) Aware of space General Take-Home Message! PPC is involved in transforming sensory cues into info regarding - the locations of objects in the environment - the location of our limbs in the environment - relative location of body segments helps provide a "reference frame" for the world around us.
Chapter 3: 2 visual systems
 Chapter 3: 2 visual systems Overview Explain the significance of the turn to the brain in cognitive science Explain Mishkin and Ungerleider s hypothesis that there are two distinct visual systems Outline
Chapter 3: 2 visual systems Overview Explain the significance of the turn to the brain in cognitive science Explain Mishkin and Ungerleider s hypothesis that there are two distinct visual systems Outline
Cortical Organization. Functionally, cortex is classically divided into 3 general types: 1. Primary cortex:. - receptive field:.
 Cortical Organization Functionally, cortex is classically divided into 3 general types: 1. Primary cortex:. - receptive field:. 2. Secondary cortex: located immediately adjacent to primary cortical areas,
Cortical Organization Functionally, cortex is classically divided into 3 general types: 1. Primary cortex:. - receptive field:. 2. Secondary cortex: located immediately adjacent to primary cortical areas,
Cortical Visual Symptoms
 대한안신경의학회지 : 제 6 권 Supplement 2 ISSN: 2234-0971 Jeong-Yoon Choi Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea Jeong-Yoon Choi. MD. PhD. Department of Neurology, Seoul
대한안신경의학회지 : 제 6 권 Supplement 2 ISSN: 2234-0971 Jeong-Yoon Choi Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea Jeong-Yoon Choi. MD. PhD. Department of Neurology, Seoul
Sensorimotor Functioning. Sensory and Motor Systems. Functional Anatomy of Brain- Behavioral Relationships
 Sensorimotor Functioning Sensory and Motor Systems Understanding brain-behavior relationships requires knowledge of sensory and motor systems. Sensory System = Input Neural Processing Motor System = Output
Sensorimotor Functioning Sensory and Motor Systems Understanding brain-behavior relationships requires knowledge of sensory and motor systems. Sensory System = Input Neural Processing Motor System = Output
Disorders of Object and Spatial perception. Dr John Maasch Brain Injury Rehabilitation Service Burwood Hospital.
 Disorders of Object and Spatial perception Dr John Maasch Brain Injury Rehabilitation Service Burwood Hospital. Take Home Message 1 Where there are lesions of the posterior cerebrum and posterior temporal
Disorders of Object and Spatial perception Dr John Maasch Brain Injury Rehabilitation Service Burwood Hospital. Take Home Message 1 Where there are lesions of the posterior cerebrum and posterior temporal
Excellent Network Courses. Department of Neurology Affiliated hospital of Jiangsu University
 Excellent Network Courses Department of Neurology Affiliated hospital of Jiangsu University Agnosia Visual Agnosia Lissauer (1890) described 2 types: a) Apperceptive Cannot see objects b) Associative Does
Excellent Network Courses Department of Neurology Affiliated hospital of Jiangsu University Agnosia Visual Agnosia Lissauer (1890) described 2 types: a) Apperceptive Cannot see objects b) Associative Does
Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg
 Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite
Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite
Human Paleoneurology and the Evolution of the Parietal Cortex
 PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
The origins of localization
 Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions. Michael E. Goldberg, M.D.
 Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
FRONTAL LOBE. Central Sulcus. Ascending ramus of the Cingulate Sulcus. Cingulate Sulcus. Lateral Sulcus
 FRONTAL LOBE Central Ascending ramus of the Cingulate Cingulate Lateral Lateral View Medial View Motor execution and higher cognitive functions (e.g., language production, impulse inhibition, reasoning
FRONTAL LOBE Central Ascending ramus of the Cingulate Cingulate Lateral Lateral View Medial View Motor execution and higher cognitive functions (e.g., language production, impulse inhibition, reasoning
Key questions about attention
 Key questions about attention How does attention affect behavioral performance? Can attention affect the appearance of things? How does spatial and feature-based attention affect neuronal responses in
Key questions about attention How does attention affect behavioral performance? Can attention affect the appearance of things? How does spatial and feature-based attention affect neuronal responses in
Higher Cortical Function
 Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Higher Cortical Function Objectives Describe the association cortical areas processing sensory, motor, executive, language, and emotion/memory information (know general location
Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Higher Cortical Function Objectives Describe the association cortical areas processing sensory, motor, executive, language, and emotion/memory information (know general location
Topics in Spatial Cognition from Barbara Hidalgo-Sotelo
 Topics in Spatial Cognition from Barbara Hidalgo-Sotelo Spatial frames of reference Structure of space Arriving at a unified sense of space is complex Three cases: (1)Hemispatial Neglect (2)Visual form
Topics in Spatial Cognition from Barbara Hidalgo-Sotelo Spatial frames of reference Structure of space Arriving at a unified sense of space is complex Three cases: (1)Hemispatial Neglect (2)Visual form
DISORDERS OF PATTERN RECOGNITION
 DISORDERS OF PATTERN RECOGNITION A. Visual agnosia inability to identify objects by sight Types (1) apperceptive agnosia unable to form stable [presemantic] representations of objects (2) associative agnosia
DISORDERS OF PATTERN RECOGNITION A. Visual agnosia inability to identify objects by sight Types (1) apperceptive agnosia unable to form stable [presemantic] representations of objects (2) associative agnosia
Avoidance of obstacles in the absence of visual awareness
 irstcite e-publishing Received 8 July 23 Accepted 31 July 23 Published online Avoidance of obstacles in the absence of visual awareness R. D. McIntosh 1,2*, K. I. McClements 1, I. Schindler 1, T. P. Cassidy
irstcite e-publishing Received 8 July 23 Accepted 31 July 23 Published online Avoidance of obstacles in the absence of visual awareness R. D. McIntosh 1,2*, K. I. McClements 1, I. Schindler 1, T. P. Cassidy
Learning Objectives.
 Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the types of deficits that occur with lesions in association areas including: prosopagnosia, neglect, aphasias, agnosia, apraxia 2. Discuss
Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the types of deficits that occur with lesions in association areas including: prosopagnosia, neglect, aphasias, agnosia, apraxia 2. Discuss
 Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization
 LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization THE VISUAL SYSTEM Higher Visual Processing Martin Paré Assistant Professor Physiology & Psychology Most of the cortex that covers the cerebral hemispheres is
LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization THE VISUAL SYSTEM Higher Visual Processing Martin Paré Assistant Professor Physiology & Psychology Most of the cortex that covers the cerebral hemispheres is
Identify these objects
 Pattern Recognition The Amazing Flexibility of Human PR. What is PR and What Problems does it Solve? Three Heuristic Distinctions for Understanding PR. Top-down vs. Bottom-up Processing. Semantic Priming.
Pattern Recognition The Amazing Flexibility of Human PR. What is PR and What Problems does it Solve? Three Heuristic Distinctions for Understanding PR. Top-down vs. Bottom-up Processing. Semantic Priming.
The Relation Between Perception and Action: What Should Neuroscience Learn From Psychology?
 ECOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY, 13(2), 117 122 Copyright 2001, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. The Relation Between Perception and Action: What Should Neuroscience Learn From Psychology? Patrick R. Green Department
ECOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY, 13(2), 117 122 Copyright 2001, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. The Relation Between Perception and Action: What Should Neuroscience Learn From Psychology? Patrick R. Green Department
Delayed reaching and grasping in patients with optic ataxia
 C. Prablanc, D. Pélisson and Y. Rossetti (Eds.) Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 142 2003 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved CHAPTER 14 Delayed reaching and grasping in patients with optic ataxia
C. Prablanc, D. Pélisson and Y. Rossetti (Eds.) Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 142 2003 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved CHAPTER 14 Delayed reaching and grasping in patients with optic ataxia
Exam 1 PSYC Fall 1998
 Exam 1 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Briefly describe the difference between a dualistic and a materialistic explanation of brain-mind relationships. (1 point) True or False. George Berkely was a monist.
Exam 1 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Briefly describe the difference between a dualistic and a materialistic explanation of brain-mind relationships. (1 point) True or False. George Berkely was a monist.
Agnosia. Introduction
 Agnosia L A Baugh, L Desanghere, and J J Marotta, The University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada ª 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Glossary Apperceptive agnosia A form of visual agnosia in which
Agnosia L A Baugh, L Desanghere, and J J Marotta, The University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada ª 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Glossary Apperceptive agnosia A form of visual agnosia in which
FAILURES OF OBJECT RECOGNITION. Dr. Walter S. Marcantoni
 FAILURES OF OBJECT RECOGNITION Dr. Walter S. Marcantoni VISUAL AGNOSIA -damage to the extrastriate visual regions (occipital, parietal and temporal lobes) disrupts recognition of complex visual stimuli
FAILURES OF OBJECT RECOGNITION Dr. Walter S. Marcantoni VISUAL AGNOSIA -damage to the extrastriate visual regions (occipital, parietal and temporal lobes) disrupts recognition of complex visual stimuli
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Lingnau et al. 10.1073/pnas.0902262106 Fig. S1. Material presented during motor act observation (A) and execution (B). Each row shows one of the 8 different motor acts. Columns in
Supporting Information Lingnau et al. 10.1073/pnas.0902262106 Fig. S1. Material presented during motor act observation (A) and execution (B). Each row shows one of the 8 different motor acts. Columns in
It Doesn t Take A Lot of Brains to Understand the Brain: Functional Neuroanatomy Made Ridiculously Simple
 It Doesn t Take A Lot of Brains to Understand the Brain: Functional Neuroanatomy Made Ridiculously Simple 6 th Annual Northern Kentucky TBI Conference March 23, 2012 www.bridgesnky.org James F. Phifer,
It Doesn t Take A Lot of Brains to Understand the Brain: Functional Neuroanatomy Made Ridiculously Simple 6 th Annual Northern Kentucky TBI Conference March 23, 2012 www.bridgesnky.org James F. Phifer,
Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology. Lecture 3: Disorders of Perception
 Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology Lecture 3: Disorders of Perception Sensation vs Perception Senses capture physical energy from environment that are converted into neural signals and elaborated/interpreted
Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology Lecture 3: Disorders of Perception Sensation vs Perception Senses capture physical energy from environment that are converted into neural signals and elaborated/interpreted
Fundamentals of Cognitive Psychology, 3e by Ronald T. Kellogg Chapter 2. Multiple Choice
 Multiple Choice 1. Which structure is not part of the visual pathway in the brain? a. occipital lobe b. optic chiasm c. lateral geniculate nucleus *d. frontal lobe Answer location: Visual Pathways 2. Which
Multiple Choice 1. Which structure is not part of the visual pathway in the brain? a. occipital lobe b. optic chiasm c. lateral geniculate nucleus *d. frontal lobe Answer location: Visual Pathways 2. Which
Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal.
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
Optic ataxia and the dorsal visual steam re-visited: Impairment in bimanual haptic matching performed without vision
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Optic ataxia and the dorsal visual steam re-visited: Impairment in bimanual haptic matching performed without vision This item was submitted to Loughborough
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Optic ataxia and the dorsal visual steam re-visited: Impairment in bimanual haptic matching performed without vision This item was submitted to Loughborough
Visually guided reaching: bilateral posterior parietal lesions cause a switch from fast visuomotor to slow cognitive control
 Neuropsychologia 43 (2005) 162 177 Visually guided reaching: bilateral posterior parietal lesions cause a switch from fast visuomotor to slow cognitive control Y. Rossetti a,e,,p.revol a, R. McIntosh b,1,
Neuropsychologia 43 (2005) 162 177 Visually guided reaching: bilateral posterior parietal lesions cause a switch from fast visuomotor to slow cognitive control Y. Rossetti a,e,,p.revol a, R. McIntosh b,1,
Dorsal and Ventral Stream Interaction: Contributions from Optic Ataxia
 Dorsal and Ventral Stream Interaction: Contributions from Optic Ataxia Marc Himmelbach and Hans-Otto Karnath Abstract & In monkeys and humans, two functionally specialized cortical streams of visual processing
Dorsal and Ventral Stream Interaction: Contributions from Optic Ataxia Marc Himmelbach and Hans-Otto Karnath Abstract & In monkeys and humans, two functionally specialized cortical streams of visual processing
shows syntax in his language. has a large neocortex, which explains his language abilities. shows remarkable cognitive abilities. all of the above.
 Section: Chapter 14: Multiple Choice 1. Alex the parrot: pp.529-530 shows syntax in his language. has a large neocortex, which explains his language abilities. shows remarkable cognitive abilities. all
Section: Chapter 14: Multiple Choice 1. Alex the parrot: pp.529-530 shows syntax in his language. has a large neocortex, which explains his language abilities. shows remarkable cognitive abilities. all
Cerebral Cortex: Association Areas and Memory Tutis Vilis
 97 Cerebral Cortex: Association Areas and Memory Tutis Vilis a) Name the 5 main subdivisions of the cerebral cortex. Frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal, and limbic (on the medial side) b) Locate the
97 Cerebral Cortex: Association Areas and Memory Tutis Vilis a) Name the 5 main subdivisions of the cerebral cortex. Frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal, and limbic (on the medial side) b) Locate the
Biological Bases of Behavior. 6: Vision
 Biological Bases of Behavior 6: Vision Sensory Systems The brain detects events in the external environment and directs the contractions of the muscles Afferent neurons carry sensory messages to brain
Biological Bases of Behavior 6: Vision Sensory Systems The brain detects events in the external environment and directs the contractions of the muscles Afferent neurons carry sensory messages to brain
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu www.cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html n Learning and Memory n Human Communication n Emotion 1 What is memory? n Working Memory:
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu www.cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html n Learning and Memory n Human Communication n Emotion 1 What is memory? n Working Memory:
De ning the cortical visual systems: ``What'', ``Where'', and ``How''
 Acta Psychologica 107 2001) 43±68 www.elsevier.com/locate/actpsy De ning the cortical visual systems: ``What'', ``Where'', and ``How'' Sarah H. Creem a,*, Dennis R. Pro tt b a Department of Psychology,
Acta Psychologica 107 2001) 43±68 www.elsevier.com/locate/actpsy De ning the cortical visual systems: ``What'', ``Where'', and ``How'' Sarah H. Creem a,*, Dennis R. Pro tt b a Department of Psychology,
LISC-322 Neuroscience. Visual Field Representation. Visual Field Representation. Visual Field Representation. Visual Field Representation
 LISC-3 Neuroscience THE VISUAL SYSTEM Central Visual Pathways Each eye sees a part of the visual space that defines its visual field. The s of both eyes overlap extensively to create a binocular. eye both
LISC-3 Neuroscience THE VISUAL SYSTEM Central Visual Pathways Each eye sees a part of the visual space that defines its visual field. The s of both eyes overlap extensively to create a binocular. eye both
The Frontal Lobes. Anatomy of the Frontal Lobes. Anatomy of the Frontal Lobes 3/2/2011. Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions. Readings: KW Ch.
 The Frontal Lobes Readings: KW Ch. 16 Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions E.L. Highly organized college professor Became disorganized, showed little emotion, and began to miss deadlines Scores on intelligence
The Frontal Lobes Readings: KW Ch. 16 Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions E.L. Highly organized college professor Became disorganized, showed little emotion, and began to miss deadlines Scores on intelligence
Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To describe the functional divisions of thalamus. II: To state the functions of thalamus and the thalamic syndrome. III: To define the somatic sensory
Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To describe the functional divisions of thalamus. II: To state the functions of thalamus and the thalamic syndrome. III: To define the somatic sensory
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Selective Attention. Modes of Control. Domains of Selection
 The New Yorker (2/7/5) Selective Attention Perception and awareness are necessarily selective (cell phone while driving): attention gates access to awareness Selective attention is deployed via two modes
The New Yorker (2/7/5) Selective Attention Perception and awareness are necessarily selective (cell phone while driving): attention gates access to awareness Selective attention is deployed via two modes
The objects of action and perception
 COGNITION Cognition 67 (1998) 181 207 The objects of action and perception Melvyn A. Goodale*, G. Keith Humphrey Department of Psychology, University of Western Ontario, London, ON N6A 5C2, Canada Abstract
COGNITION Cognition 67 (1998) 181 207 The objects of action and perception Melvyn A. Goodale*, G. Keith Humphrey Department of Psychology, University of Western Ontario, London, ON N6A 5C2, Canada Abstract
Geography of the Forehead
 5. Brain Areas Geography of the Forehead Everyone thinks the brain is so complicated, but let s look at the facts. The frontal lobe, for example, is located in the front! And the temporal lobe is where
5. Brain Areas Geography of the Forehead Everyone thinks the brain is so complicated, but let s look at the facts. The frontal lobe, for example, is located in the front! And the temporal lobe is where
Visual Selection and Attention
 Visual Selection and Attention Retrieve Information Select what to observe No time to focus on every object Overt Selections Performed by eye movements Covert Selections Performed by visual attention 2
Visual Selection and Attention Retrieve Information Select what to observe No time to focus on every object Overt Selections Performed by eye movements Covert Selections Performed by visual attention 2
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer The automatic pilot of the hand is unbalanced by visual neglect Citation for published version: McIntosh, RD, Rossit, S, Malhotra, P, Harvey, M & Butler, SH 2010, 'The automatic
Edinburgh Research Explorer The automatic pilot of the hand is unbalanced by visual neglect Citation for published version: McIntosh, RD, Rossit, S, Malhotra, P, Harvey, M & Butler, SH 2010, 'The automatic
Layered organization of cortex: Paleocortex 3 layers hippocampal formation / ventral & medial cortex closest to brainstem
 Layered organization of cortex: Paleocortex 3 layers hippocampal formation / ventral & medial cortex closest to brainstem Archicortex 3-4 layers hippocampal formation / amygdala Neocortex 6 layers more
Layered organization of cortex: Paleocortex 3 layers hippocampal formation / ventral & medial cortex closest to brainstem Archicortex 3-4 layers hippocampal formation / amygdala Neocortex 6 layers more
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
A UNIFIED PERSPECTIVE OF UNILATERAL SPATIAL NEGLECT
 Running head: A UNIFIED PERSPECTIVE OF UNILATERAL SPATIAL NEGLECT 1 A UNIFIED PERSPECTIVE OF UNILATERAL SPATIAL NEGLECT Master Degree Project in Cognitive Neuroscience One year 30 ECTS Spring term 2012
Running head: A UNIFIED PERSPECTIVE OF UNILATERAL SPATIAL NEGLECT 1 A UNIFIED PERSPECTIVE OF UNILATERAL SPATIAL NEGLECT Master Degree Project in Cognitive Neuroscience One year 30 ECTS Spring term 2012
Maintaining internal representations: the role of the human superior parietal lobe
 Maintaining internal representations: the role of the human superior parietal lobe Daniel M. Wolpert 1, Susan J. Goodbody 1 and Masud Husain 2 1 Sobell Department of Neurophysiology, Institute of Neurology,
Maintaining internal representations: the role of the human superior parietal lobe Daniel M. Wolpert 1, Susan J. Goodbody 1 and Masud Husain 2 1 Sobell Department of Neurophysiology, Institute of Neurology,
How do individuals with congenital blindness form a conscious representation of a world they have never seen? brain. deprived of sight?
 How do individuals with congenital blindness form a conscious representation of a world they have never seen? What happens to visual-devoted brain structure in individuals who are born deprived of sight?
How do individuals with congenital blindness form a conscious representation of a world they have never seen? What happens to visual-devoted brain structure in individuals who are born deprived of sight?
Blindsight in action: what can the different sub-types of blindsight tell us about the control of visually guided actions?
 Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews 29 (2005) 1035 1046 www.elsevier.com/locate/neubiorev Review Blindsight in action: what can the different sub-types of blindsight tell us about the control of visually
Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews 29 (2005) 1035 1046 www.elsevier.com/locate/neubiorev Review Blindsight in action: what can the different sub-types of blindsight tell us about the control of visually
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis Neurophysiology We are working under the following hypothesis What we see is determined by the pattern of neural activity in the brain This leads to several interesting
Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis Neurophysiology We are working under the following hypothesis What we see is determined by the pattern of neural activity in the brain This leads to several interesting
Motor Systems I Cortex. Reading: BCP Chapter 14
 Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
The Neuroscience of Vision II
 Striate Cortex (V1) is not Sufficient for Seeing The Neuroscience of Vision II Hubel and Wiesel conclude their 1968 paper by Where else is Visual Processing Performed? Beyond V1 An important step in identifying
Striate Cortex (V1) is not Sufficient for Seeing The Neuroscience of Vision II Hubel and Wiesel conclude their 1968 paper by Where else is Visual Processing Performed? Beyond V1 An important step in identifying
Vision II. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Vision II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Ganglion Cells The axons of the retinal ganglion cells form the optic nerve and carry visual information into the brain. 2 Optic
Vision II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Ganglion Cells The axons of the retinal ganglion cells form the optic nerve and carry visual information into the brain. 2 Optic
correlates with social context behavioral adaptation.
 REVIEW OF FRONTAL LOBE STRUCTURES Main organization of frontal cortex: 1. Motor area (precentral gyrus). 2. Premotor & supplementary motor areas (immediately anterior to motor area). Includes premotor,
REVIEW OF FRONTAL LOBE STRUCTURES Main organization of frontal cortex: 1. Motor area (precentral gyrus). 2. Premotor & supplementary motor areas (immediately anterior to motor area). Includes premotor,
Rules of apparent motion: The shortest-path constraint: objects will take the shortest path between flashed positions.
 Rules of apparent motion: The shortest-path constraint: objects will take the shortest path between flashed positions. The box interrupts the apparent motion. The box interrupts the apparent motion.
Rules of apparent motion: The shortest-path constraint: objects will take the shortest path between flashed positions. The box interrupts the apparent motion. The box interrupts the apparent motion.
Attention: Neural Mechanisms and Attentional Control Networks Attention 2
 Attention: Neural Mechanisms and Attentional Control Networks Attention 2 Hillyard(1973) Dichotic Listening Task N1 component enhanced for attended stimuli Supports early selection Effects of Voluntary
Attention: Neural Mechanisms and Attentional Control Networks Attention 2 Hillyard(1973) Dichotic Listening Task N1 component enhanced for attended stimuli Supports early selection Effects of Voluntary
Control of visuo-spatial attention. Emiliano Macaluso
 Control of visuo-spatial attention Emiliano Macaluso CB demo Attention Limited processing resources Overwhelming sensory input cannot be fully processed => SELECTIVE PROCESSING Selection via spatial orienting
Control of visuo-spatial attention Emiliano Macaluso CB demo Attention Limited processing resources Overwhelming sensory input cannot be fully processed => SELECTIVE PROCESSING Selection via spatial orienting
Introduction to sensory pathways. Gatsby / SWC induction week 25 September 2017
 Introduction to sensory pathways Gatsby / SWC induction week 25 September 2017 Studying sensory systems: inputs and needs Stimulus Modality Robots Sensors Biological Sensors Outputs Light Vision Photodiodes
Introduction to sensory pathways Gatsby / SWC induction week 25 September 2017 Studying sensory systems: inputs and needs Stimulus Modality Robots Sensors Biological Sensors Outputs Light Vision Photodiodes
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory II
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory II ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html Memory Working Memory Long-term Memory Declarative Memory Procedural Memory
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory II ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html Memory Working Memory Long-term Memory Declarative Memory Procedural Memory
Separate neural pathways for the visual analysis of object shape in perception and prehension
 Separate neural pathways for the visual analysis of object shape in perception and prehension Melvyn A. Goodale*, John Paul Meenan*, Heinrich H. Bulthofft, David A. Nicolle*, Kelly 1. Murphy* and Carolynn.
Separate neural pathways for the visual analysis of object shape in perception and prehension Melvyn A. Goodale*, John Paul Meenan*, Heinrich H. Bulthofft, David A. Nicolle*, Kelly 1. Murphy* and Carolynn.
SPECIAL INTEREST GROUP MEETING
 SPECIAL INTEREST GROUP MEETING Cognitive Neurorehabilitation S. Clarke & G. Rode Service de Médecine Physique et Réadaptation, Hôpital Henry Gabrielle. Hospices Civils de Lyon, gilles.rode@chu-lyon.fr
SPECIAL INTEREST GROUP MEETING Cognitive Neurorehabilitation S. Clarke & G. Rode Service de Médecine Physique et Réadaptation, Hôpital Henry Gabrielle. Hospices Civils de Lyon, gilles.rode@chu-lyon.fr
How we interact with objects: learning from brain lesions
 How we interact with objects: learning from brain lesions Elena Daprati 1 and Angela Sirigu 2 1 Department of Neuromotor Physiology, IRCCS Santa Lucia Foundation, via Ardeatina 306, 00179 Roma, Italy 2
How we interact with objects: learning from brain lesions Elena Daprati 1 and Angela Sirigu 2 1 Department of Neuromotor Physiology, IRCCS Santa Lucia Foundation, via Ardeatina 306, 00179 Roma, Italy 2
Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 2
 Name: ID # ID: A Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 2 Multiple Choice (38 questions, 1 point each) Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Name: ID # ID: A Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 2 Multiple Choice (38 questions, 1 point each) Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs
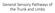 General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
Perceptual Disorders. Agnosias
 Perceptual Disorders Agnosias Disorders of Object Recognition AGNOSIA : a general term for a loss of ability to recognize objects, people, sounds, shapes, or smells. Agnosias result from damage to cortical
Perceptual Disorders Agnosias Disorders of Object Recognition AGNOSIA : a general term for a loss of ability to recognize objects, people, sounds, shapes, or smells. Agnosias result from damage to cortical
SPATIAL DEFICITS IN VISUOMOTOR CONTROL FOLLOWING RIGHT PARIETAL INJURY. Carol Elizabeth Broderick
 SPATIAL DEFICITS IN VISUOMOTOR CONTROL FOLLOWING RIGHT PARIETAL INJURY by Carol Elizabeth Broderick A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the degree
SPATIAL DEFICITS IN VISUOMOTOR CONTROL FOLLOWING RIGHT PARIETAL INJURY by Carol Elizabeth Broderick A thesis presented to the University of Waterloo in fulfillment of the thesis requirement for the degree
Does Wernicke's Aphasia necessitate pure word deafness? Or the other way around? Or can they be independent? Or is that completely uncertain yet?
 Does Wernicke's Aphasia necessitate pure word deafness? Or the other way around? Or can they be independent? Or is that completely uncertain yet? Two types of AVA: 1. Deficit at the prephonemic level and
Does Wernicke's Aphasia necessitate pure word deafness? Or the other way around? Or can they be independent? Or is that completely uncertain yet? Two types of AVA: 1. Deficit at the prephonemic level and
The Role of the Dorsal Visual Processing Stream in Tool Identification
 The Role of the Dorsal Visual Processing Stream in Tool Identification The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
The Role of the Dorsal Visual Processing Stream in Tool Identification The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Cortical Control of Movement
 Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Do we have distinct systems for immediate and delayed actions? A selective review on the role of visual memory in action
 Do we have distinct systems for immediate and delayed actions? A selective review on the role of visual memory in action Thomas Schenk a * & Constanze Hesse b a Department of Psychology, Ludwig-Maximilians-University
Do we have distinct systems for immediate and delayed actions? A selective review on the role of visual memory in action Thomas Schenk a * & Constanze Hesse b a Department of Psychology, Ludwig-Maximilians-University
Cognitive Modelling Themes in Neural Computation. Tom Hartley
 Cognitive Modelling Themes in Neural Computation Tom Hartley t.hartley@psychology.york.ac.uk Typical Model Neuron x i w ij x j =f(σw ij x j ) w jk x k McCulloch & Pitts (1943), Rosenblatt (1957) Net input:
Cognitive Modelling Themes in Neural Computation Tom Hartley t.hartley@psychology.york.ac.uk Typical Model Neuron x i w ij x j =f(σw ij x j ) w jk x k McCulloch & Pitts (1943), Rosenblatt (1957) Net input:
Implicit Perception in Action
 CHAPTER 6 Implicit Perception in Action Short-lived motor representations of space Yves Rossetti Vision et Motricité, I.N.S.E.R.M. Perception is often conscious, which allows one to report about the object
CHAPTER 6 Implicit Perception in Action Short-lived motor representations of space Yves Rossetti Vision et Motricité, I.N.S.E.R.M. Perception is often conscious, which allows one to report about the object
Livingstone M (1988) Scientific American, 258,
 1 General Reading List Farah, MJ (1991). Visual Agnosia. MIT Press (Main Library, Short Loan). Harvey, M and Milner, AD (1995). Balint's patient. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 12, 261-281 (Lynda Young). Milner,
1 General Reading List Farah, MJ (1991). Visual Agnosia. MIT Press (Main Library, Short Loan). Harvey, M and Milner, AD (1995). Balint's patient. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 12, 261-281 (Lynda Young). Milner,
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Neuropsychologia xxx (2009) xxx xxx. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Neuropsychologia
 Neuropsychologia xxx (2009) xxx xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Neuropsychologia journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/neuropsychologia Choosing between alternative wrist postures: Action
Neuropsychologia xxx (2009) xxx xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Neuropsychologia journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/neuropsychologia Choosing between alternative wrist postures: Action
Cognitive Neuroscience Attention
 Cognitive Neuroscience Attention There are many aspects to attention. It can be controlled. It can be focused on a particular sensory modality or item. It can be divided. It can set a perceptual system.
Cognitive Neuroscience Attention There are many aspects to attention. It can be controlled. It can be focused on a particular sensory modality or item. It can be divided. It can set a perceptual system.
3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana
 3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana Introduction Ataxia is derived from Greek word a -not, taxis -orderly, (not orderly/ not in order) Ataxia is the inability to make smooth, accurate and coordinated movements
3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana Introduction Ataxia is derived from Greek word a -not, taxis -orderly, (not orderly/ not in order) Ataxia is the inability to make smooth, accurate and coordinated movements
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception
 COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 6: Beyond V1 - Extrastriate cortex Chapter 4 Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 6: Beyond V1 - Extrastriate cortex Chapter 4 Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17. By: Joseline
 PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
Psy /16 Human Communication. By Joseline
 Psy-302 11/16 Human Communication By Joseline Lateralization Left Hemisphere dominance in speech production in 95% of right handed and 70% of left handed people Left -> Timing, Sequence of events Right
Psy-302 11/16 Human Communication By Joseline Lateralization Left Hemisphere dominance in speech production in 95% of right handed and 70% of left handed people Left -> Timing, Sequence of events Right
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
1. Which part of the brain is responsible for planning and initiating movements?
 Section: Chapter 10: Multiple Choice 1. Which part of the brain is responsible for planning and initiating movements? p.358 frontal lobe hippocampus basal ganglia cerebellum 2. The prefrontal cortex is
Section: Chapter 10: Multiple Choice 1. Which part of the brain is responsible for planning and initiating movements? p.358 frontal lobe hippocampus basal ganglia cerebellum 2. The prefrontal cortex is
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology
 Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
Cerebellum: little brain. Cerebellum. gross divisions
 Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
The space of senses: impaired crossmodal interactions in a patient with Balint syndrome after bilateral parietal damage
 Neuropsychologia 42 (2004) 1737 1748 The space of senses: impaired crossmodal interactions in a patient with Balint syndrome after bilateral parietal damage Nathalie Valenza a, Micah M. Murray b,c, Radek
Neuropsychologia 42 (2004) 1737 1748 The space of senses: impaired crossmodal interactions in a patient with Balint syndrome after bilateral parietal damage Nathalie Valenza a, Micah M. Murray b,c, Radek
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Neuroscience Tutorial
 Neuroscience Tutorial Brain Organization : cortex, basal ganglia, limbic lobe : thalamus, hypothal., pituitary gland : medulla oblongata, midbrain, pons, cerebellum Cortical Organization Cortical Organization
Neuroscience Tutorial Brain Organization : cortex, basal ganglia, limbic lobe : thalamus, hypothal., pituitary gland : medulla oblongata, midbrain, pons, cerebellum Cortical Organization Cortical Organization
Supplementary Material S3 Further Seed Regions
 Supplementary Material S3 Further Seed Regions Figure I. Changes in connectivity with the right anterior insular cortex. (A) wake > mild sedation, showing a reduction in connectivity between the anterior
Supplementary Material S3 Further Seed Regions Figure I. Changes in connectivity with the right anterior insular cortex. (A) wake > mild sedation, showing a reduction in connectivity between the anterior
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS
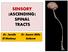 SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
Neurophysiology of systems
 Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
COGS 172 VISION CONTINUED More on Face Processing Dorsal System, Vision for AcCon. Cogs 172 A.P. Saygin
 COGS 172 VISION CONTINUED More on Face Processing Dorsal System, Vision for AcCon Cogs 172 A.P. Saygin Agnosia Videos AppercepCve Are faces special? How to test? Are faces special? How to test? How seleccve
COGS 172 VISION CONTINUED More on Face Processing Dorsal System, Vision for AcCon Cogs 172 A.P. Saygin Agnosia Videos AppercepCve Are faces special? How to test? Are faces special? How to test? How seleccve
Arnold Trehub and Related Researchers 3D/4D Theatre in the Parietal Lobe (excerpt from Culture of Quaternions Presentation: Work in Progress)
 Arnold Trehub and Related Researchers 3D/4D Theatre in the Parietal Lobe (excerpt from Culture of Quaternions Presentation: Work in Progress) 3D General Cognition Models 3D Virtual Retinoid Space with
Arnold Trehub and Related Researchers 3D/4D Theatre in the Parietal Lobe (excerpt from Culture of Quaternions Presentation: Work in Progress) 3D General Cognition Models 3D Virtual Retinoid Space with
UNILATERAL-SPATIAL INATTENTION
 UNILATERAL-SPATIAL INATTENTION \ ICBO CONGRESS POMONA. CA APRIL 8, 2010 ROBERT B. SANET, O.D., F.C.O.V.D. San Diego Center for Vision Care 7898 Broadway Lemon Grove CA 91945 rsanet@cs.com UNILATERAL SPATIAL
UNILATERAL-SPATIAL INATTENTION \ ICBO CONGRESS POMONA. CA APRIL 8, 2010 ROBERT B. SANET, O.D., F.C.O.V.D. San Diego Center for Vision Care 7898 Broadway Lemon Grove CA 91945 rsanet@cs.com UNILATERAL SPATIAL
and Parkinson s disease
 Attention and novelty processing in stroke and Parkinson s disease Victoria Singh-Curry UCL PhD: Neuroscience/Neurology 1 Declaration I, Victoria Singh-Curry, confirm that the work presented in this thesis
Attention and novelty processing in stroke and Parkinson s disease Victoria Singh-Curry UCL PhD: Neuroscience/Neurology 1 Declaration I, Victoria Singh-Curry, confirm that the work presented in this thesis
Clinical Learning Exercise #1
 Clinical Learning Exercise #1 Exercise: We are going to assume nothing is wrong with the peripheral nervous system and attempt to identify the central nervous system anatomical location for the following
Clinical Learning Exercise #1 Exercise: We are going to assume nothing is wrong with the peripheral nervous system and attempt to identify the central nervous system anatomical location for the following
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be?
 Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
