This lecture is sponsored by a grant from the Delta Dental of Iowa Foundation IDA Annual Conference Guest Lecture Series.
|
|
|
- Samuel Hutchinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This lecture is sponsored by a grant from the Delta Dental of Iowa Foundation IDA Annual Conference Guest Lecture Series.
2 Radiology: Back to the Classroom! Juan F. Yepes DDS, MD, MPH, MS, DrPH Associate Professor of Pediatric Dentistry Indiana University School of Dentistry James Whitcomb Hospital for Children Member of the Executive Committee of the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology ( )
3 Radiation Safety
4 Population case-control study: almost 2,800 subjects, aged 20 to 79. Introduction Subjects were asked to recall their frequencies of dental radiographic examinations during four age-periods; younger than 10 years of age, between 10 and 19, 20 and 49, and older than 50. The researchers reported an increased risk of meningioma in individuals who received bitewing radiographs on one or more occasions per year in all age groups. (OR=2) Subjects who received a panoramic film were reported to be an increased risk for meningioma (OR=4.9) if were exposed under 10 years of age. No increased risk of meningioma was noted for subjects who received panoramic film over the age of 10 or a full mouth series of intra-oral radiographs at any age.
5 Introduction Some issues to consider Recall bias!! asking a subject to recall an event 50 years ago or more. Bitewing radiographs (2-4) were reported to place patients at a higher risk for meningioma than a full mouth series (up to 20 exposures). Different radiographic equipment with intrinsic variations in the exposure times. Impossible to calculate dose-response.
6 Radiation.Who cares? Antepartum dental radiography and Infant low birth weight Potential mothers Chronic exposure to radiation (stochastic) Develop subclinical hypothyroidism Got pregnant Delivery babies with LBW Images downloaded from Microsoft Office Clip Art
7 Radiation Biology and Protection
8 Let s review the basic concepts in radiation biology Radiation biology Radiation Protection Dosimetry
9 Radiation Biology It is the study of the effects of ionizing radiation on living systems. Ionizing radiation Tissues Modification of biological molecules Alterations in cells (time?) Injury or death.
10 Radiation Biology x ray An electromagnetic radiation of great penetrating power, produced by the bombardment of a substance (usually a heavy metal) by a stream of high velocity electrons, usually in a vacuum tube. The wavelength is usually less than 2 Å.
11 Radiation Biology
12 Radiation Biology Radiosensitivity and Cell Type Bergonie and Tribondeau 1906 Most radiosensitive cells 1. Cells with a high mitotic rate 2.Those cells who undergo many future mitosis 3. Cells with very primitive differentiation
13 Radiation Biology Deterministic effects The response is proportional with the magnitude of the dose Biologic effects of x-rays Example: effects of radiation therapy in the mouth Stochastic effect The response is proportional with the frequency of the dose
14 Radiation Biology Cancer Type Estimated New Cases Estimated Deaths Bladder 74,690 15,580 Breast (Female Male) 232,670 2,360 40, Colon and Rectal (Combined) 136,830 50,310 Endometrial 52,630 8,590 Kidney (Renal Cell and Renal Pelvis) Cancer 63,920 13,860 Leukemia (All Types) 52,380 24,090 Lung (Including Bronchus) 224, ,260 Melanoma 76,100 9,710 Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma 70,800 18,990 Pancreatic 46,420 39,590 Prostate 233,000 29,480 Thyroid 62,980 1,890 American Cancer Society: Cancer Facts and Figures Atlanta, Ga: American Cancer Society, 2014.
15 Radiation Biology Using statistical models for analysis, rates for new thyroid cancer cases have been rising on average 4.5% each year over the last 10 years. Using statistical models for analysis, rates for new female breast cancer cases have been stable over the last 10 years. Death rates have been falling on average 1.9% each year over
16 Let s review the basic concepts in radiation protection and dosimetry Radiation biology Radiation Protection Dosimetry
17 Radiation Safety and Protection Dosimetry Equivalent dose (Ht): it is used to compare the biological effects of different types of radiation to a tissue or organ. It is the sum of the products of the absorbed dose (Dt) averaged over a tissue or organ and the radiation weighting factor (Wr) depends on the specific tissue Ht = Σ Wr x Dt IS Unit Sievert (Sv) Traditional unit rem 1 Sv = 100 rem
18 Radiation Safety and Protection Dosimetry IS Unit Sievert (Sv) Traditional unit rem 1 Sv = 100 rem
19 Radiation Safety and Protection Sources of Radiation Exposure Natural Radiation Cosmic Sources Subatomic particles and photons from the sun. It is primarily a function of altitude Orlando (82 ft.): 0.24 msv / Year Denver (5,280 ft.): 0.50 msv/year Indianapolis (715 ft.): 0.28 msv/year Exposure resulting from airline travel 5 hours flight: msv
20 Radiation Safety and Protection Natural Radiation Terrestrial Sources External Radiation: Radioactive nuclides in the soil, primarily potassium 40 and the radioactive decay products of uranium 238, and thorium 232 (0.5 msv / year) Radon: Radon is a decay product in the uranium series. It is responsible of 52% of the radiation exposure of the world s population (1.2 msv/year). It is a GAS attached to dust particles LUNGS Other Internal: Ingestion of uranium
21 Radiation Safety and Protection Man-Made Radiation Medical Diagnosis and Treatment Well over one billion medical x-ray examinations are performed annually worldwide. Consumer and Industrial Products Domestic water supply, tobacco products, combustible fuels, dental porcelain, television receivers, pocket watches, smoke alarms, and airport inspection systems.
22 Radiation Safety and Protection Cosmic Natural 83% (3mSv / year) Terrestrial Sources of Radiation Exposure 3.6 msv / year Internal radon Ingestion of food Artificial 17% (0.6mSv / year) 2.4 msv
23 Radiation Safety and Protection Risk Estimates The primary risk from dental radiography is radiation-induced cancer (stochastic ) The risk for cancer being induced in human as a result of exposure to low doses of radiation is difficult to estimate for different reasons: - The data for the cancer risk from radiation exposure involve exposures many times larger than dental radiology - Cancer is a common disease. It is difficult to detected the effect of dental radiography - The time between the radiation exposure and the development of cancer may be years to decades.
24 Radiation Safety and Protection Key Principles of Radiological Protection The Principle of Justification: Any decision that alters the radiation exposure situation should do more good than harm. The Principle of Optimization of Protection: The likelihood of incurring exposure, the number of people exposed, and the magnitude of their individual doses should all be kept as low as reasonably achievable, taking into account economic and societal factors. The Principle of Application of Dose Limits: The total dose to any individual from regulated sources in planned exposure situations other than medical exposure of patients should not exceed the appropriate limits specified by the Commission.
25 Effective Dose from Diagnostic Radiology and equivalent background Examination Intraoral Posterior BW (F-speed) (rectangular collimation) FMX (rectangular c.) FMX (round collimation) Panoramic Cephalometric Extraoral CBCT I-CAT (extended view: 16 x 13 cm) 10 y.o. CBCT Accuitomo 170 (small view: <40 cm²) 10 y.o. CBCT Kodak D (small view: <40cm²) 10 y.o. CBCT I-CAT Next generation (medium view) 10. y.o Effective Dose (msv) Equivalent background radiation (days) CT Head Background radiation: 3.6 msv / year
26 NCRP Report 145 Radiation Protection in Dentistry December, 2003 Pg. 21: Rectangular collimation of the x-ray beam shall be routinely used for periapical radiography
27 Collimation Collimation limits the amount of radiation, primary and scattered, to which the patient is exposed Rectangular collimator decreases the radiation dose by up to fivefold as compared with a circular one. (1) Use of long source-to skin distances of 40 cm, rather than short distance of 20 cm.(2) (1) Gibbs SJ. Effective dose equivalence and effective dose. OOOO 2000; 90(4): (2) National Council of Radiation Protection 2003
28 Intraoral Radiographic Imaging: A Study Comparing Collimation and Thyroid Shielding Methods on a Pediatric Phantom Patient Zachary D. Bozic 1 Juan F Yepes, DDS, MD, MPH, MS, DrPH Indiana University School of Dentistry, Indianapolis Indiana Units: (μsv) Rectangl e w/tc Round w/ TC Bone Marrow thyroid esophagus skin bone surface Salivary glands lens of eyes Pituitary Effective Dose
29 Radiation Safety and Protection Leaded aprons and thyroid shields that contain lead or other materials are patient protective equipment. If all the NCRP recommendations are followed rigorously, the use of lead apron on patients is not required. (1) Thyroid shielding with a leaded thyroid shield or collar is strongly recommended for children and pregnant women. (2) Thyroid collars are also recommended for adults when it will not interfere with the exposure. (1) To prevent cracks in the leaded shield, practitioners should enforce that leaded aprons and collars are hung and not folded (1) National Council for Radiation Protection & Measurements; 2003 (2) US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, FDA and American Dental Association Council of Scientific Affairs, 2004
30 We learned about radiation biology, radiation protection, dosimetry.now, let s review how often and when we prescribe radiographs.
31 Radiation Safety and Protection Patient Selection Criteria Little evidence to support radiographic exposure of all edentulous areas of the oral cavity. Clinical evaluation + Combined selected periapical radiographs can result in a 43% reduction in the number of films without a clinical consequential increase in the rate of undiagnosed disease. ADA and FDA developed guidelines for the selection of patients for dental radiographic examination. Revised 2012
32 Radiation Safety and Protection Patient Selection Criteria Radiographs must be limited to the areas required for adequate diagnosis and treatment based on professional judgment Dentist should not prescribe routine radiographs at preset intervals for all patients For new or referred patients, clinicians should obtain recent dental radiographs from the patient s previous dental health care provider Dental radiographs my be prescribed for pregnant patients with careful adherence to the radiation safety protocols Dentist should prescribe dental radiographs ONLY after clinical evaluation Revised 2012
33 Dosimetry of two direct digital imaging devices using a pediatric phantom J.R. Schulten 1, J.F. Yepes 1, J. Ludlow 2, A. Page 1 1 Department of Dentistry, Division of Pediatric Dentistry, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 2 Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC
34 Dosimetry of two direct digital imaging devices using a pediatric phantom J.R. Schulten 1, J.F. Yepes 1, J. Ludlow 2, A. Page 1 1 Department of Dentistry, Division of Pediatric Dentistry, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 2 Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC West to East Flight: 25µSv Equivalent doses in µsv PBW avg Pan avg Bone Marrow 3 3 thyroid esophagus 1 2 skin 8 16 bone surface Salivary glands brain* 4 6 remainder average lymphatic nodes* 6 7 extrathoracic airway* muscle* 6 7 oral mucosa* lens of eyes 11 6 Pituitary 8 9
35 Radiation Safety and Protection Digital Imaging DOSE REDUCTION Practitioners and manufacturers frequently use the reduction of the radiation dose that the patient receives as a reason to implement digital radiography. There are several reasons why the dose reduction is not as large as often suggested: The dose reduction compared with F-speed film is somewhere between 0 to 50% (** phosphorous plate carry the risk of higher exposure than conventional films) Increase in the number of radiographs made: Several studies indicate that the decision to make a radiograph is reached more easily with a digital system Increase in the number and ease or remakes
36 ALARA Principle Only perform imaging when there is a clear medical or dental benefit to the child. Use the lowest amount of radiation for adequate imaging based on the size of the child. Only take images on the indicated area and always using the thyroid collar Avoid multiple unnecessary images (Role of digital Imaging). Use alternative diagnostic studies, if possible.
37
38 Principles of Radiographic Interpretation
39 Principles of Radiographic Interpretation Condensing osteitis There is a radiopacity, not too big, not too small, looks actually funny..located at the apex of tooth # 28.
40 Principles of Radiographic Interpretation Radiographic Description Differential Interpretation
41 Some Definitions
42 Well localized Well defined The item being reported is limited to a specific area, and does not extend beyond that locality. The edges of the item being reported are reasonably sharp and clearly define the extent of the lesion.
43 Poorly localized Poorly defined The item being reported is not limited to a specific area, and extends into surrounding anatomical sites. The edges of the item being reported are not sharp. The actual borders and thus the exact extent of the lesion are not clearly defined.
44 Corticated The entity being reported is not only well defined, but has a cortex, i.e. an osseous border, seen as a thin white line.
45 Multilocular The entity being reported is usually well defined and has a cortex, i.e. an osseous border, seen as a thin white line, but is partially or totally subdivided into several loculi.
46 Summary of Interpretation Steps 1. Radiopaque / Radiolucent / mix 2. Well defined / ill defined / mix 3. Corticated / non-corticated / mix 4. Location, size and shape 5. What happen in the neighborhood 6. Differential interpretation
47 Time for practice
48 Summary of Interpretation Steps 1. Radiopaque / Radiolucent / mix 2. Well defined / ill defined / mix 3. Corticated / non-corticated / mix 4. Location, size and shape 5. What happen in the neighborhood 6. Differential interpretation
49 Most Common Jaw Lesions
50 Bone Disorders
51 Bone Disorders 1. Idiopathic Bone Sclerosis 2. Fibrous Dysplasia 3. Ossifying Fibroma 4. Simple Bone Cyst 5. Cemento-osseous dysplasia
52 Idiopathic Bone Sclerosis (not condensing osteitis!)
53 Idiopathic Bone Sclerosis IBS is a focal solitary sclerotic lesion that arises in the late 1st or early 2nd decade of life. Its cause is unknown. It is asymptomatic, is not associated with inflammation, and may remain static or demonstrate slow growth that usually stops when the patient reaches skeletal maturity.
54 Idiopathic Bone Sclerosis In 90% of patients it occurs in the mandible, usually near the first molar or second molar or premolar. At imaging, IBS is radiopaque, well defined, well localized, non-corticated, located at the apex of vital teeth. No root resorption and no teeth displacement. Some patients may have multiple lesions.
55 Simple Bone Cyst
56 -Traumatic bone cyst, hemorrhagic bone cyst, solitary bone cyst -Simple bone cyst: It is a cavity within bone that is lined with connective tissue. It may be empty or it may contain fluid -It is not a true cyst -Etiology unknown, however Localized aberration in normal bone remodeling or metabolism -First two decades of life (mean 17 years) -Females 2:1 -Expansion is possible but unusual, discovery by chance Simple Bone Cyst
57 Mandible Posterior mandible Associated with cemento-osseous dysplasia and fibrous dysplasia Margin: Well defined to ill-defined border Internal structure: Radiolucent, it may appear multilocular, although the lesion does not contain true septa No effect on the surrounding teeth Lamina dura intact and vitality positive
58 Fibrous Dysplasia
59 Localized change in normal bone metabolism Replacement of all components of normal bone by fibrous tissue containing varying amounts of abnormal appearing bone Solitary or multiple (monostotic 70% of all cases) McCune-Albright syndrome Asymptomatic, rare associated with pain The lesion may become active Pregnant, etc.. The skull is involved in 10 to 25% of cases Patients between 10 and 30 years old
60
61 Focal Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia
62 Focal cemento-osseous dysplasia -Localized change in normal bone metabolism Replacement of the components of normal bone with fibrous tissue and cementum-like material, abnormal bone or a mixture of the two -Near the apex of a tooth -Middle age, females 9:1, Afro-American -Incidental finding -The involved teeth are vital -Sometimes quite larger Source: Oral Radiology, Principles and Interpretation. White et al,2000
63 Focal cemento-osseous dysplasia -Epicenter usually at the apex of a tooth -Well defined, Irregularly shaped -Internal structure: Varies Radiolucent area Mixed stage: Radiopaque and Radiolucent areas Mature stage: Radiopaque -Lamina dura of the teeth involved with the lesion is lost -Rare: resorption of the roots
64 Odontogenic Cysts
65 Radiographic Features: Location Cyst may occur centrally in any location in the maxilla or mandible Cyst are rare in the condyle and the coronoid process A few cyst arise in the soft tissues of the orofacial region Cyst Periphery Radiolucent Well defined and corticated However a secondary infection can change this
66 Radiographic Features: Shape Cyst are usually round or oval, resembling a fluid filled balloon Some cyst may have a scalloped borders Internal Structure Cyst Cyst are often totally radiolucent Long standing cyst may have some calcifications inside Some cyst have septa
67 Cyst Radiographic Features: Effects on Surrounding Structures Cyst grow slowly Sometimes displacement and resorption of the teeth Cyst can expand the mandible
68 Odontogenic Cyst Radicular Cyst Residual Cyst Dentigerous Cyst Buccal bifurcation cyst Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor Basal cell nevus syndrome Lateral Periodontal Cyst Calcifying odontogenic Cyst Non-Odontogenic Cyst Naso-palatine canal cyst Images downloaded from Microsoft Galleries
69 Radicular Cyst
70 Radicular Cyst Periapical cyst, Dental cyst Radicular cyst is a cyst most likely originated when rest of epithelial cells (Malassez) in the periodontal ligament are stimulated to proliferate and undergo cyst degeneration by inflammatory products from a non-vital tooth. Most common cyst in the jaws They arise from non-vital teeth Asymptomatic, unless secondary infection occurs
71 Radicular Cyst Periapical cyst, Dental cyst In most cases the epicenter of the RC is located at the apex 60% are found in the maxilla, especially around incisors and canines Well defined cortical border, if secondary infected, the inflammatory reaction may result in loss of the cortical bone Internal structure Radiolucent
72 Buccal Bifurcation Cyst
73 Buccal Bifurcation Cyst Buccal bifurcation cyst (BBC) is an inflammatory odontogenic cyst that usually occurs at the buccal region of the first or second primary mandibular molars. Several names are used to describe this condition including the term juvenile paradental cyst. According to the World Health Organization the BBC is listed under the category of paradental cyst and named mandibular infected buccal cyst. BBC occurs in children between 5 and 13 years of age. Usually affects the second primary molar. Delayed tooth eruption and swelling at the affected area is commonly observed. In some cases, partial tooth eruption with crown buccal tilting and deep periodontal pockets is observed. Radiographically, the BBC is characterized by a well-defined radiolucent area, often corticated around the roots of the involved teeth. Usually the lamina dura is not affected. Surgical excision of the lesion is the treatment of choice.
74 Dentigerous Cyst
75 Dentigerous Cyst A dentigerous cyst is a cyst that forms around the crown of an unerupted tooth. It begins from accumulation in the layers of reduced enamel epithelium or between the epithelium and the crown of the unerupted tooth. Second most common cyst in the jaws They develop around the crown of an unerupted or supernumerary tooth
76 Dentigerous Cyst Radiology Features The epicenter is just above the crown of the involved tooth The cyst is attaches at the CEJ Very often are quite big before diagnosis Well defined cortex Completely radiolucent
77 Dentigerous Cyst Radiology Features -DG often displace and resorb adjacent teeth -Displaces the associated tooth in a apical direction Differential Diagnosis - Hyperplastic follicle - KOT: Less likely resorb teeth Attach more apical - Cystic ameloblastoma
78 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor (former OKC)
79 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor Non-inflammatory odontogenic cyst that arises from the dental lamina. Unlike other cyst, the epithelium of the OKC appears to have innate growth potential. The epithelium lining is keratinized and thin. Inside the cyst viscous white material cheese
80 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor -OKCs account for above 1/10 of all cyst in the jaws -Second and third decades with slightly male predilection -No symptoms until mid size swelling -High recurrence -Aspiration Keratin
81 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor Radiographic The Features: Radiology of Oral and Perioral Cysts -90% Posterior body of the mandible -Epicenter superior to the inferior alveolar canal -Looks very similar to dentigerous cyst -Well corticated and radiolucent -MINIMAL EXPANSION -Resorb teeth bust less than DC
82 Non-Odontogenic Cysts
83 Naso-palatine Canal Cyst -Remnants of the naso-palatine duct -10% of jaw cyst -Most cases between years old -Asymptomatic or mild symptoms
84 Naso-palatine Canal Cyst RADIOGRAPHIC FEATURES: -Well defined, corticated and is circular or oval in shape. The shadow of the ANS sometimes is superimposed heart shape -Internal structure: complete radiolucent -Most common this cyst causes the roots of the central incisors to diverge and occasionally root resorption occurs.
85 Inflammatory Lesions
86 Osteomyelitis
87 Osteomyelitis Osteomyelitis affects children with a strong male predilection Typical signs and symptoms (acute): rapid onset pain, swelling, fever, and lymphadenopathy. The associated teeth may be mobile and sensitive to percussion. Paresthesia is NOT uncommon Very early in the disease no radiographic changes
88 Osteomyelitis The most common location is the posterior body of the mandible (rare in the maxilla) Ill-defined periphery with gradual transition to normal bone trabeculae. Initially decrease in the density of the bone Later regions of sclerotic bone : sequestra Acute osteomyelitis can stimulate either bone resorption or bone formation Differential diagnosis in children: fibrous dysplasia
89 Benign Tumors
90 Benign Tumors 1. Ameloblastoma 2. Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor (Pindborg tumor) 3. Odontoma 4. Ameloblastic Fibroma 5. Adenoid Odontogenic Tumor (AOT) 6. Myxoma 7. Benign Cementoblastoma 8. Osteoma 9. Hemangioma
91 Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor (AOT)
92 Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Most frequently found in child or adolescent. Frequently but not invariably envelopes crown of unerupted tooth especially maxillary canine. Most frequently unilocular but can be loculated. Well defined margin. Homogeneous radiolucent area initially but later develops calcified floccules as content. Cortical expansion may occur. Tends to displace rather than cause resorption of adjacent teeth.
93 Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor (AOT) (14 years of age) Anterior maxilla or mandible Radiolucent with radiopaque foci May mimic dentigerous cyst In the canine area most frequent location
94 Ameloblastic Fibroma
95 Ameloblastic fibroma Most frequently found in children and adolescents. Quite uncommon. Can be unilocular, crenulated or multilocular. Outline well-delineated and corticated. Homogeneous radiolucency. Cortical expansion a late finding. May cause displacement of teeth. Less aggressive locally than non-unicystic ameloblastomas.
96 Odontoma
97 Summary of Interpretation Steps 1. Radiopaque / Radiolucent / mix 2. Well defined / ill defined / mix 3. Corticated / non-corticated / mix 4. Location, size and shape 5. What happen in the neighborhood 6. Differential interpretation
98 Compound Odontoma
99 Compound Odontoma A malformation in which all the dental tissues are represented in a more orderly pattern than in the complex odontoma, so that the lesion consists of many toothlike structures.
100 Compound Odontoma Most of these structures do not represent, morphologically, the teeth of the normal dentition, but in each one, enamel, dentin, cementum and pulp are arranged as in a normal tooth.
101 Benign Cementoblastoma
102 Benign Cementoblastoma Second or third decade, usually before 18 Slow growing mesenchymal neoplasms Composed principally of cementum-like tissue and attached to the apex of a tooth root. More common in males than females. Continuous with root, which is resorbed Pulp vitality unrelated but the involved tooth is OFTEN painful
103 Benign Cementoblastoma Cementoblastomas occur more often in the mandible (premolar or first molar) The lesion is well defined and radiopaque with cortical border and then a well defined radiolucent band inside the cortical border. Differential diagnosis FCOD
104 Ossifying Fibroma
105 Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma
106 Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma (trabecular pattern) Radiographic Features: The lesion is often well defined and unilocular. The borders are well defined. Tumor-like behavior growth of the lesion, displacement of teeth and the inferior alveolar canal. Usually the cortical borders remain intact Depending on the amount of calcified material produced in the tumor, it may appears completely radiolucent; more often, different degrees of radiopaques areas are noted inside.
107 Malignant Tumors
108 Again 1. Radiolucent / radiopaque 2. Well defined or poor defined 3. Corticated or non corticated 4. What happen around: resorption? 5. Differential Interpretation
109 Malignant Tumors 1. Sarcoma 2.Chondrosarcoma 3. Ewing s Sarcoma 4.Multiple Myeloma 5. Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
110 Ewing s Sarcoma
111 Ewing s Sarcoma Ewing s sarcoma is a tumor of long bones that is relatively rare in the jaws. Lesions arise in the medullary portion of the bone and spread to the endosteal and later to the periosteal surface. It is most common in the middle of the second decade of life (~ 15 y.o.) Most patients are between the ages of 5 and 30 years old. Males are twice as likely to manifest the disease as females Swelling, pain, loose teeth, paresthesia and trismus are clinical features associated with this tumor.
112 Ewing s Sarcoma Radiographic Features: - The majority of cases are located in the mandible (posterior area) - Radiolucent, ill-defined and NEVER corticated - Destruction of bone in an UNEVEN fashion - The lesions are usually solitary - Periosteal reactions (sunray appearance) Differential Diagnosis - Osteomyelitis (sequestra)
113 Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
114 Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Leukemia is a malignant tumor of the hematopoietic stem cells. The most common leukemia in children is ALL. Radiographic features: - Mandible and maxilla in areas of developing teeth - Often around the periapical region of a tooth (periapical lesion) - ill defined radiolucent-radiopaque areas - NO expansion of the bone but displacement of the unerupted teeth - Premature loss of teeth
115 Thank you so MUCH!!!!!!!!! Juan F. Yepes DDS, MD, MPH, DrPH
Disclosure. Educational Objectives. Terminology. Odontogenic Cysts. Terminology
 Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例
 高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis
 RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
Common/Important Radiolucencies. B. Most Common Location Apex of permanent first molar, rare in primary teeth.
 Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors
 Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT
 Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws. Cyst. Effects on adjacent structures. Types. Odontogenic Cysts. Non-Odontogenic cysts
 Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall Steven R. Singer,
Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall Steven R. Singer,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours
 Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
Vascular. Extravasated blood. Melanocytic. Tattoo. Epidermolysis bullosa. Lichen planus. Pemphigoid Pemphigus Lupus. Candidosis. Surface Epithelial
 Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Radiology. & supporting structures. Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej
 Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies
 Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman
 IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
4/2/17. Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology. Composite of in-focused and blurred images. It s a type of Tomogram.
 Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
Pre-reading - radiolucencies
 Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
Index. oralmaxsurgery.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Patient Management Image Selection Radiation Biology, Dosimetry & Protection
 Patient Management Image Selection Radiation Biology, Dosimetry & Protection Objectives: Following this course, the participants will have the information necessary to: 1. Identify the techniques used
Patient Management Image Selection Radiation Biology, Dosimetry & Protection Objectives: Following this course, the participants will have the information necessary to: 1. Identify the techniques used
Only 40% of the Story
 X-RAY, X-RAY, READ ALL ABOUT IT! The Use and Utility of Dental Radiographs in Practice Lisa Fink, DVM, DAVDC Dentistry & Oral Surgery Service October 4, 2015 Only 40% of the Story Radiographs of teeth
X-RAY, X-RAY, READ ALL ABOUT IT! The Use and Utility of Dental Radiographs in Practice Lisa Fink, DVM, DAVDC Dentistry & Oral Surgery Service October 4, 2015 Only 40% of the Story Radiographs of teeth
10/23/2014. features to image interpretation what to look for and what it means. interpretation vs. diagnosis. science or art? image investigation
 features to image interpretation what to look for and what it means interpretation vs. diagnosis ERNEST LAM, DMD, MSc, PhD, FRCD(C) PROFESSOR AND THE DR. LLOYD & MRS. KAY CHAPMAN CHAIR IN CLINICAL SCIENCES
features to image interpretation what to look for and what it means interpretation vs. diagnosis ERNEST LAM, DMD, MSc, PhD, FRCD(C) PROFESSOR AND THE DR. LLOYD & MRS. KAY CHAPMAN CHAIR IN CLINICAL SCIENCES
[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018
![[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018 [ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018](/thumbs/87/95905171.jpg) Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts. SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST
 The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
Radiation Safety & Determining Need for Radiographs
 Radiation Safety & Determining Need for Radiographs Guidelines for Radiographic Examination All radiation is harmful! These guidelines have been established to protect the patient and operator from unnecessary
Radiation Safety & Determining Need for Radiographs Guidelines for Radiographic Examination All radiation is harmful! These guidelines have been established to protect the patient and operator from unnecessary
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
Malignant Lesions Steven R. Singer, DDS
 Definitions Malignant Lesions Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Malignancies are uncontrolled growths of tissue Primary tumors represent de novo tumors in their initial site Metastatic
Definitions Malignant Lesions Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Malignancies are uncontrolled growths of tissue Primary tumors represent de novo tumors in their initial site Metastatic
INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Jaws: Cysts and Odontogenic Neoplasms
 Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
 Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2018, Article ID 6987050, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6987050 Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2018, Article ID 6987050, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6987050 Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
Pictorial Essay. CT of Calcifying Jaw Bone Diseases
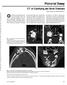 Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions
 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Development of teeth. 5.DM - Pedo
 Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Kodak Dental Radiography Series. Radiation Safety in Dental Radiography. Dental
 Kodak Dental Radiography Series Radiation Safety in Dental Radiography Dental Radiation Safety in Dental Radiography The goal of dental radiography is to obtain diagnostic information while keeping the
Kodak Dental Radiography Series Radiation Safety in Dental Radiography Dental Radiation Safety in Dental Radiography The goal of dental radiography is to obtain diagnostic information while keeping the
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dental Radiography Series
 Dental Radiography Series Guidelines for prescribing dental radiographs. Background Radiological s are used to discover and define the type and extent of disease in many clinical situations. However, public
Dental Radiography Series Guidelines for prescribing dental radiographs. Background Radiological s are used to discover and define the type and extent of disease in many clinical situations. However, public
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
 DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
Dental Hygiene Spring 2018 Summer 2014 Fall COURSE OUTLINE DHT 1032 Dental Radiography 2 Credit Hours
 COURSE OUTLINE DHT 1032 Dental Radiography 2 Credit Hours Course Description This course prepares the dental hygiene student to expose, process and critique intra and extraoral radiographs for clinical
COURSE OUTLINE DHT 1032 Dental Radiography 2 Credit Hours Course Description This course prepares the dental hygiene student to expose, process and critique intra and extraoral radiographs for clinical
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
Radiation Safety for Dental Auxiliaries. Susan W. Grammer, RDH, M.Ed. Course Content. A. Radiation History and the Use of Radiographs
 Radiation Safety for Dental Auxiliaries Susan W. Grammer, RDH, M.Ed. Course Content A. Radiation History and the Use of Radiographs B. Introduction to Physics C. X-ray Machine and Production of X-Rays
Radiation Safety for Dental Auxiliaries Susan W. Grammer, RDH, M.Ed. Course Content A. Radiation History and the Use of Radiographs B. Introduction to Physics C. X-ray Machine and Production of X-Rays
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases
 (2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
(2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report
 Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinomycosis, 200 201 Adenoid cystic carcinoma, 148 150 Adenomatoid odontogenic tumors, 134, 135 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, 134 Ameloblastoma,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinomycosis, 200 201 Adenoid cystic carcinoma, 148 150 Adenomatoid odontogenic tumors, 134, 135 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, 134 Ameloblastoma,
Unusually large erupted complex odontoma: A rare case report
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2015; 45: 49-54 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.1.49 Unusually large erupted complex odontoma: A rare case report Shivanand B. Bagewadi 1, *, Rahul Kukreja 1, Gundareddy
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2015; 45: 49-54 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.1.49 Unusually large erupted complex odontoma: A rare case report Shivanand B. Bagewadi 1, *, Rahul Kukreja 1, Gundareddy
Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
Clinical details: Details of scan: CONE BEAM CT REPORT: Name: H. B. Gender: Reason for referral: Referred by:
 Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Course File 243 DDS Physics of Diagnostic Radiology and Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course File 243 DDS Physics of Diagnostic Radiology and Oral and Maxillofacial
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course File 243 DDS Physics of Diagnostic Radiology and Oral and Maxillofacial
JOURNAL TAOMFR Mandiblular Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma
 Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma of the Mandible with Emphasis on Evaluation Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Jing-Yi Chen 1, Frank Lei 2, Yu-Fong Chen 3,4 * Divisions of 1 Oral Pathology, 2 Periodotology,
Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma of the Mandible with Emphasis on Evaluation Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Jing-Yi Chen 1, Frank Lei 2, Yu-Fong Chen 3,4 * Divisions of 1 Oral Pathology, 2 Periodotology,
Epithelial Sources. Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa
 ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Epithelial Sources Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa Epithelial Sources Surface Epithelium Rests of Serres Reduced Enamel Epithelium Rests of
ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Epithelial Sources Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa Epithelial Sources Surface Epithelium Rests of Serres Reduced Enamel Epithelium Rests of
Radiation Safety for New Medical Physics Graduate Students
 Radiation Safety for New Medical Physics Graduate Students John Vetter, PhD Medical Physics Department UW School of Medicine & Public Health Background and Purpose of This Training This is intended as
Radiation Safety for New Medical Physics Graduate Students John Vetter, PhD Medical Physics Department UW School of Medicine & Public Health Background and Purpose of This Training This is intended as
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report
 Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
The College of Dental Surgeons of Saskatchewan Radiation and Imaging Standard
 The College of Dental Surgeons of Saskatchewan Radiation and Imaging Standard Legislation Radiation safety has long been a priority in Saskatchewan. This province, the first in Canada to have radiation
The College of Dental Surgeons of Saskatchewan Radiation and Imaging Standard Legislation Radiation safety has long been a priority in Saskatchewan. This province, the first in Canada to have radiation
Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report
 Case Report Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report Pulivarthi Sushma 1, Sowbhagya M.B 2, Balaji P 3, Mahesh Kumar T.S 4 1 Postgraduate, 2 Reader, 3 Professor and Head of department, 4 Senior
Case Report Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report Pulivarthi Sushma 1, Sowbhagya M.B 2, Balaji P 3, Mahesh Kumar T.S 4 1 Postgraduate, 2 Reader, 3 Professor and Head of department, 4 Senior
An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report.
 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
Case Report Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case Report
 International Dentistry Volume 2009, Article ID 597483, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/597483 Case eport Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case eport Farhan Durrani 1 and oyana Singh 2
International Dentistry Volume 2009, Article ID 597483, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/597483 Case eport Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case eport Farhan Durrani 1 and oyana Singh 2
Inherited & developmental disorders:
 Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report
 457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve involvement
 Yadegari A,et al J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve
Yadegari A,et al J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve
SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare case report
 Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Study of maxillary and mandibular cystic lesions
 Study of maxillary and mandibular cystic lesions Poster No.: C-1428 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. L. Rozas Rodríguez, M. E. Banegas Illescas, M. Y. Torres Sousa, R. M. Fernández
Study of maxillary and mandibular cystic lesions Poster No.: C-1428 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. L. Rozas Rodríguez, M. E. Banegas Illescas, M. Y. Torres Sousa, R. M. Fernández
Diagnosis. overt Examination. Definitive Examination. History. atient interview. Personal History. Clinical Examination.
 Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
Intraosseous Transmigration of Impacted Canines: Report of Five Cases Sulabha AN, Sachin Deshpande, Sameer C
 International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. 2012;3(3):56-60 ISSN 2231 2250 Available online at http://www.journalgateway.com or www.ijomp.org Case Report Intraosseous Transmigration of Impacted
International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. 2012;3(3):56-60 ISSN 2231 2250 Available online at http://www.journalgateway.com or www.ijomp.org Case Report Intraosseous Transmigration of Impacted
Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case Report
 Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown
 Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
CHAPTER 3 - DEFINITION, SCOPE, AND INDICATIONS FOR ENDODONTIC THERAPY ARNALDO CASTELLUCCI
 Contents Volume I CHAPTER 1 - A BRIEF HISTORY OF ENDODONTICS CHAPTER 2 - EMBRYOLOGY Crown formation Root formation Single- and multiple-root formation The formation of lateral canals Exposed dentin and
Contents Volume I CHAPTER 1 - A BRIEF HISTORY OF ENDODONTICS CHAPTER 2 - EMBRYOLOGY Crown formation Root formation Single- and multiple-root formation The formation of lateral canals Exposed dentin and
Extraoral Imaging. Chapter 42. Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1
 Extraoral Imaging Chapter 42 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 42.1: Panoramic Imaging 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Discuss panoramic
Extraoral Imaging Chapter 42 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 42.1: Panoramic Imaging 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Discuss panoramic
The resident will be assigned to be on call with the Oral and Maxillofacial service. Call will be set according to PARO guidelines.
 Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Resident on the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (OMFS) Rotation St. Catharines General Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) During the second year
Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Resident on the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (OMFS) Rotation St. Catharines General Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) During the second year
Radiographic Interpretations
 Continuing Education Brought to you by Radiographic Interpretations Course Author(s): Connie M. Kracher, PhD, MSD CE Credits: 2 hours Intended Audience: Dentists, Dental Hygienists, Dental Assistants,
Continuing Education Brought to you by Radiographic Interpretations Course Author(s): Connie M. Kracher, PhD, MSD CE Credits: 2 hours Intended Audience: Dentists, Dental Hygienists, Dental Assistants,
Arun V Subramaniam et al. / International Journal of Biopharmaceutics. 2014; 5(3): International Journal of Biopharmaceutics
 225 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYSTS: VARIOUS RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCES Arun Subramaniam*
225 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYSTS: VARIOUS RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCES Arun Subramaniam*
Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
FOCAL CEMENTO-OSSEOUS DYSPLASIA OF LOWER JAW IN AN ELDERLY WOMAN: CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL FEATURES AND MANAGEMENT IN A CASE REPORT
 www.djas.co.in ISSN No-31-148 DJAS 4(III), 08-1, 016 All rights are reserved CASE REPORT Dental JOURNAL of Advance Studies FOCAL CEMENTO-OSSEOUS DYSPLASIA OF LOWER JAW IN AN ELDERLY WOMAN: CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL
www.djas.co.in ISSN No-31-148 DJAS 4(III), 08-1, 016 All rights are reserved CASE REPORT Dental JOURNAL of Advance Studies FOCAL CEMENTO-OSSEOUS DYSPLASIA OF LOWER JAW IN AN ELDERLY WOMAN: CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL
Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 255-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.255 Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases Neha Khambete, Rahul Kumar*, Mukund
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 255-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.255 Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases Neha Khambete, Rahul Kumar*, Mukund
WHO Histological typing of odontogenic tumors, A. Epithelial Odontogenic Tumors
 Cheng-Chung Lin, Prof. in Oral Pathology College of Dental Medicine, KMU 2007 Classification: The following classification is based upon the inductive effect of one dental tissue upon another. In normal
Cheng-Chung Lin, Prof. in Oral Pathology College of Dental Medicine, KMU 2007 Classification: The following classification is based upon the inductive effect of one dental tissue upon another. In normal
Impeded Eruption of Mandibular Canine
 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1434 Case Report Gauri S Lele, Darshan Modi Abstract Odontome, tumor of odontogenic origin, is associated with disturbances in the eruption of teeth such as impaction, delayed
10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1434 Case Report Gauri S Lele, Darshan Modi Abstract Odontome, tumor of odontogenic origin, is associated with disturbances in the eruption of teeth such as impaction, delayed
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know?
 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Key words: Third molar, Impacted tooth, Tooth Eruption, Molar, Mandible, Unerupted Tooth.
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
Panoramic Radiology. Seminars on Maxillofacial Imaging and Interpretation. Bearbeitet von Allan G Farman
 Panoramic Radiology Seminars on Maxillofacial Imaging and Interpretation Bearbeitet von Allan G Farman 1. Auflage 2007. Buch. xiv, 232 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 540 46229 3 Format (B x L): 19,3 x 27 cm Gewicht:
Panoramic Radiology Seminars on Maxillofacial Imaging and Interpretation Bearbeitet von Allan G Farman 1. Auflage 2007. Buch. xiv, 232 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 540 46229 3 Format (B x L): 19,3 x 27 cm Gewicht:
Advanced radiographic techniques for the detection of lesions in bone
 Endodontic Topics 2004, 7, 52 72 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard ENDODONTIC TOPICS 2004 Advanced radiographic techniques for the detection of lesions in bone ELISABETTA
Endodontic Topics 2004, 7, 52 72 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard ENDODONTIC TOPICS 2004 Advanced radiographic techniques for the detection of lesions in bone ELISABETTA
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS
 MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report
 SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
Radiology Safety Certification Course
 Radiology Safety Certification Course Laurie Carter, D.D.S., Ph.D. Virginia Commonwealth University School of Dentistry I. Historical Overview A. X-Rays discovered by Wilhelm Roentgen on Nov. 8, 1895 by
Radiology Safety Certification Course Laurie Carter, D.D.S., Ph.D. Virginia Commonwealth University School of Dentistry I. Historical Overview A. X-Rays discovered by Wilhelm Roentgen on Nov. 8, 1895 by
Developmental Mandibular Salivary Gland Defect
 Developmental Mandibular Salivary Gland Defect The Importance of Clinical Evaluation Authored by Sako Ohanesian, DDS Upon successful completion of this CE activity 1 CE credit hour may be awarded A Peer-Reviewed
Developmental Mandibular Salivary Gland Defect The Importance of Clinical Evaluation Authored by Sako Ohanesian, DDS Upon successful completion of this CE activity 1 CE credit hour may be awarded A Peer-Reviewed
Full Mouth Survey. Delta Dental of Massachusetts DeltaDentalMA.com
 X-Rays Having X-rays taken is a painless procedure that uses small amounts of radiation to capture images of your teeth and bones. Because your dentist takes precautions and the amount of radiation used
X-Rays Having X-rays taken is a painless procedure that uses small amounts of radiation to capture images of your teeth and bones. Because your dentist takes precautions and the amount of radiation used
Odontogenic Cysts - An Overview
 Namita V Nayyer Michaelina Macluskey and William Keys Odontogenic Cysts - An Overview Abstract: This article aims to discuss the clinical features, radiological assessment, histopathology and management
Namita V Nayyer Michaelina Macluskey and William Keys Odontogenic Cysts - An Overview Abstract: This article aims to discuss the clinical features, radiological assessment, histopathology and management
INDEX. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. DENTISTRY
 DENTISTRY INDEX Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. Acquired brachygnathia, 302-303 Acquired dental diseases, 291-307. See also Dental diseases, acquired. Adamantinoma(s), 303-305
DENTISTRY INDEX Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. Acquired brachygnathia, 302-303 Acquired dental diseases, 291-307. See also Dental diseases, acquired. Adamantinoma(s), 303-305
