Sodium Stibogluconate treatment for cutaneous leishmaniasis: A clinical study of 43 cases from the north of Jordan
|
|
|
- Ralf Cooper
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sodium Stibogluconate treatment for cutaneous leishmaniasis: A clinical study of 43 cases from the north of Jordan Mamoun Mohammad Al-Athamneh Hiathem Qasem Abu Al-haija Ra ed Smadi Ayman S. Qaqaa Heba Ajlouni Correspondence: Dr. Mamoun Al-Athamneh Amman, Jordan Mobile: mamounathamnehh@yahoo.com Abstract Objective: to study the efficacy of Sodium Stibogluconate intramuscular injections in the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis, safety and side effects. Method: A total 43 patients were seen over a period of 12 months, from January 2009 to December All cases were seen at Prince Rashed Military Hospital in the north of Jordan. The diagnosis of localized cutaneous leishmania was made on clinical grounds proved by leishmania smear or skin biopsy. The distribution of patients according to gender, age groups, time of the year, was made. The criteria for sodium stibogluconate injection were: the severity of symptoms, site of lesion on face (ear, nose and cheek), and multiplicity of lesions. The dose of sodium stibogluconate given was 10 mg\kg given as intramuscular injections daily for total two weeks followed by complete blood count, liver function test, electrocardiogram as base line. One patient (2.3%) demonstrated increase in liver enzymes after one week of treatment upon stopping treatment for one week the patient then resumes treatment with no complications and with complete remission. Conclusion: Many cases of cutaneous leishmaniasis are seen in Jordan causing cosmetic problems. Early introduction of systemic anti-leishmania agent is recommended. Sodium stibogluconate is an effective way to decrease scarring and dispigmentation, with minimum side effects. Key words: cutaneous leishmania, sodium stibogluconate, scar Results: 23 patients were males and 20 were females (16 of them were 14 years and below). The age group ranged from 2-72 years. One patient (2.3%) had resistant infection to sodium stibogluconate; and an admission was for one patient (2, 3%) for a few days because of a picture of Hepatotoxicity. 42 patients showed improvement of the lesion (98%); improvement is defined when the lesion flattens and ulceration disappears. MIDDLE MIDDLE EAST EAST JOURNAL JOURNAL OF FAMILY OF MEDICINE FAMILY MEDICINE VOLUME 12 ISSUE VOLUME 7 SEPTEMBER 7, ISSUE
2 Introduction Leishmaniasis is a widely distributed disease with both visceral and cutaneous manifestations. Cutaneous leishmaniasis is the most common form of this disease. It has an annual incidence of 1 to 1.5 million cases. 90% of cases are reported in just six countries, Afghanistan, Brazil, Iran, Peru, Saudi Arabia and Syria (1). Cutaneous leishmaniasis causes three distinct clinical entities: localized cutaneous leishmaniasis (a few lesions), diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis (large number of lesions), mucocutaneous leishmaniasis (involving mucus membrane like nose, mouth, larynx). Other leishmania species may attack viscera causing visceral leishmaniasis or kala-azar (1,2). Cutaneous leishmaniasis is divided into: the Old World and new world leishmaniasis (3). Old world leishmaniasis is due to L. major (zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis which tends to heal within 2-4 months), L. tropica (anthroponotic tends to heal 6-15 months), L. aethiopica and to L. infantum, which is responsible for all the cutaneous disease in the northern Mediterranean region and for some of the disease in North Africa. In the New World, localized cutaneous leishmaniasis is caused mainly by L. peruviana, L. guyanensis, L. braziliensis or L. mexicana species. Diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis is an infection caused by L. aethiopica in Africa, and L. amazonensis in South America. However, diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis is also observed in immunosuppressed patients infected with species isolated commonly in localized forms. Mucosal dissemination is described in South America. It is caused by L. braziliensis, and, less frequently by L. panamensis or L. guyanensis(4). Leishmania is highly contagious with at least ninety percent attack rate among susceptible individuals (5). Affecting children mainly, usually lesions are at site of sandfly bites on exposed areas like face (7). Cutaneous leishmaniasis is a disfiguring disease that normally resolves within 3 to 18 months of initial infection. Treatment aims to cure as well as prevent the development of more complex manifestations like Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis and disseminated cutaneous leishmaniasis (10). This study was conducted to examine cutaneous leishmania cases seen over a 12-month period, taking into consideration patients ages, the time of occurrence during the year, the symptoms and signs at presentation, the treatments given and the complications encountered in affected patients. Methods Forty three patients clinically diagnosed to have cutaneous leishmaniasis were seen at Prince Rashid Hospital over a period of 12 months (between January 2009 to December 2010). The distribution of patients as regards the time of disease occurrence during the year, sex and age group, were documented. The diagnosis of cutaneous leishmania was established on clinical grounds. Noduloulcerative skin lesion, with erythematous, violaceous, edematous edge were the most common presenting features. Laboratory investigations were carried out for all patients and included leishmania smear to demonstrate Donovan bodies, skin biopsy was done only if the lesion was clinically suggestive but smear negative, followed by routine and biochemical blood tests including liver function test, ECG as base line. All patients were given systemic sodium stibogluconate intramuscular injections, 10 mg/kg per dose daily for two weeks. The 1st injection was given in the clinic with the availability of resuscitation facilities to observe and interfere if anaphylactic reaction developed, then patient completed the course of injections at the nearest clinic. Patients received instructions in regard to the nature of disease and treatment options and to apply topical antibiotics. All patients were re-examined at follow up visit after two weeks to ensure complete cure of the lesion. Simple non-parametric statistical analysis was made when necessary. Results Twenty three patients (53.5%) were males and 20 patients were females (46.5%). The age ranged from 2-72 years. The site of involvement in our patients is shown in Table 1. The distribution of patients according to age groups is shown in Table 2. The patients were from four districts, Table 3. The face was commonly involved (49%) : cheeks (39.2%), nose (18%), forehead (14.3%), pinna (14.3%), lip (10.7), eyelid (3.5%). One patient (2.3%) who was hospitalized, was 6 years old with three skin lesions on hand, neck and ear and received 2 ml sodium stibogluconate IM injections for one week and came to hospital with nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain. Liver function test showed raised liver enzyme SGOT 1838, SGPT 1306 Alkaline phosphatase 316, the 2nd day after cessation of therapy SGOT and SGPT dropped to 1314,741 respectively. WBC, PCV, PLATELET were normal. PT, PTT, INR normal, abdominal U/S normal, HBSAG, HC antibodies were negative. After 6 days SGOT and SGPT dropped to 180 and 175 respectively; lesions at these time showed 70% improvement. One patient (2.3%) who had ulcerative nodule at the lower lip, clinically consistent with Cutaneous leishmania. Leishmania smear was negative but biopsy confirmative, and patient received sodium stibogluconate injection for one week and developed a slight rise in liver enzyme, Patient was stopped for one week and returned to normal resumption of injections with no complications with complete healing but with atrophic scar. One patient (2.3%) received sodium stibogluconate injections for two weeks but did not show clinical improvement after completion of the course of injections, and was given alternative treatment. 18 MIDDLE EAST JOURNAL OF FAMILY MEDICINE VOLUME 12 ISSUE 7 SEPTEMBER 2014 MIDDLE EAST JOURNAL OF FAMILY MEDICINE VOLUME 7, ISSUE 10
3 Table 1: Site of involvements and their percentages In endemic areas like Jordan where transmission is stable, children are especially affected. Un our study children were affected in 37% of the cases, as shown in Table 7, and the cumulative rate of infection as determined by the presence of scars and positive leishmanin tests may approach 100%. The treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis depends on the species of leishmania but identification of the species by culture and isoenzyme is time consuming. Also new techniques of DNA amplification by polymerase chain reaction are not widely available which makes treatment depend on the geographical area and the epidemiology of the disease; the main cause of cutaneous leishmania in our area is leishmania tropica (5). Table 2: The distribution of patients according to age group Table 3. The demographic distribution Discussion Leishmaniasis are a group of chronic infections affecting human and other animal species, belonging to flagellated protozoans of the order kinetoplastidae, and transmitted by the bite of sandflies of the genera phlebotomus and lutzomyia (5). It is an obligate intracellular parasite that presents in two forms: promastigote in the gut of sandflies where it multiplies and migrates to the proboscis and is introduced to the host whether human, rodent, or other animal species and immediately phagocytosed by host phagocytes where it changed into amastigote(7). It is considered to be a self- limiting disease when localized to skin but always heals with retracted scar and dispigmentation but some may become chronic or disseminated(2). Cutaneous leshmaniasis is the primary infection with one of the leishmania species starting as a papule then increasing in size resulting in a nodulo-ulcerative lesion, usually on exposed areas at the site of sandfly bite (5). In our study, there are 21 cases (49%) involving the face, 8 cases (18.6%) involving the hand and forearm, 7 cases (16.2%) involving the foot and leg, 2 cases (4.6%) involving the neck, 5 cases (11.6%) involving multiple sites of those mentioned above with no single case involving a non-exposed area. Ajloun district had the highest number of patients simply because towns of Ajloun are geographically appropriate for sandflies living and reproduction regarding temperature and humidity. Our study shows the highest number of patients in January and December then March (Figure 1, next page), and this may be due to rainy season in winter with the formation of swamps which allow reproduction and growth of sand flies which facilitate vector transmission. Pentavalent antimonials are the mainstay treatment for both visceral and cutaneous leishmaniasis (8). Two forms are currently available: meglumine antimoniate and sodium stibogluconate. The mechanism for their effectiveness is not well understood, but may involve inhibition of adenosine triphosphate synthesis(9). The face is affected in 49% of the cases; it results in scarring and dispigmentation which is disfiguring on the face. It is generally recommended that anyone with cutaneous leishmaniasis is to be treated with systemic sodium stibogluconate (especially children and when face is involved) because scar and dispigmentation will be inevitable and disastrous. Systemic antimonial decrease the size of the lesion, there is no progression to ulceration MIDDLE MIDDLE EAST EAST JOURNAL JOURNAL OF FAMILY OF MEDICINE FAMILY MEDICINE VOLUME 12 ISSUE VOLUME 7 SEPTEMBER 7, ISSUE
4 Figure 1: The distribution of patients according to the time of year and results in less scarring, and rapid healing. Therefore, we started all patients on sodium stibogluconate injection for two weeks; 98% showed complete cure of the lesion upon follow up 2-3 months after completion of the course. One of the most important side effects of sodium stibogluconate is prolongation of QT interval predisposing to arrhythmias, which are uncommon when used in doses less than 20mg/kg and within a period of less than 2 weeks (6). In our study base line ECG was done excluding patients with abnormal Electrocardiogram from the study; follow up Electrocardiogram was done with no change. Hepatotoxicity is another side effect of sodium stibogluconate injection which is reversible withen 6 weeks of cessation of treatment (6). Base line liver function tests were done to exclude any patient with liver disease from the study; two patients developed increases in liver enzyme which returned to normal within two weeks of cessation of treatment. Wide use of sodium stibogluconate in the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis can result in the emergence of a resistant strain(9). In our study one patient did not show improvement clinically after completion of the course of injections (still the lesion was wet and increasing in size). The mechanism for the development of resistance is not well understood. It could be an intrinsic difference in the species sensitivity to these medications; another mechanism is the efflux of a drug or its active derivative(9). Studies showed that the addition of allopurinol to the treatment regimen gave better results regarding decrease of the size of the lesion and clearance (4). In our resistant case just when it showed no healing, a change to rifampicin 300mg daily for 2 weeks allowed healing of the lesion. In addition, there are several alternative treatment options available; local infiltration with sodium stibgluonate of the whole lesion intradermally with 2-3ml every week until 4 weeks (4). Also Oral zinc sulphate (5 mg/kg/day for 4 weeks) showed promising results in a recent Indian trial (8). Cryotherapy using liquid nitrogen is a well known option for treatment in the middle east including Jordan where 2-3 sessions for seconds freezing (one month interval) resulted in healing of most of the lesion but with a different degree of atrophic scar and dispigmentation. But when multiple lesions, large lesions, over the joint, are on the face, the cosmetic unit usually tries to avoid cryotherapy. Conclusion Cutaneous Leishmaniasis is cosmetically disfiguring and slowly growing skin lesions are not fatal but occasionally can result in significant morbidity especially when present on the face. Early treatment with systemic antimonial agent is essential in the adults and children to prevent or decrease the risks of complication like: scarring and dispigmentation. We believe that it is highly recommended to give systemic sodium stibogluconate injection to all patients with Cutaneous leishmaniasis, especially when certain areas like ear, eyelid, lip, cheek, nose, and multiple lesions are present. 20 MIDDLE EAST JOURNAL OF FAMILY MEDICINE VOLUME 12 ISSUE 7 SEPTEMBER 2014 MIDDLE EAST JOURNAL OF FAMILY MEDICINE VOLUME 7, ISSUE 10
5 References 1. World health organization (WHO). Leishmaniasis: background information. A brief history of disease.who available from: 2. Omar Lupi. Protozoa and worms. In: bolongia dermatology 2nd Ed.2008.p Blum J, Desjeux P, Schwartz E, Beck B, Hatz C. Treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis among travellers. J Antimicrob Chemother 2004; 53: Philippe Minodiera, Philippe Parolab. Cutaneous leishmaniasis treatment. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease (2007) 5, (review article free online). 5. Barbara L. Herwaldt. Leishmaniasis. In: Kasper DL (Editor-In-Chief). Harrison s principles of internal medicine. 16th Ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc p Wise ES, Armstrong MS, Watson J, Lockwood DN. Monitoring Toxicity Associated with Parenteral Sodium Stibogluconate in the Day-Case Management of Returned Travellers with New World Cutaneous Leishmaniasis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 6(6): e1688. doi: /journal.pntd2012 (free online). 7. Wolff, Klaus; Goldsmith, Lowell A. Leishmaniasis and other protozoan infections. In: Fitzpatrick s Dermatology in General Medicine, 7th Edition. McGraw-Hill, Inc ch J.A.A. Hunter, J.A. Savin, M.V. Dahl. Leishmaniasis. In: Clinical dermatology. 3rd Ed.2003.p Arun Kumar Haldar, Pradip Sen, and Syamal Roy.Use of Antimony in the treatment of Leishmaniasis: Current Status and Future Directions. Review Article. Molecular Biology International at: Tracy Garnier & Simon L Croft. Topical treatment for cutaneous leishmaniasis. Department of Infectious and Tropical Diseases, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine. simon. croft@lshtm.ac.uk,current Opinion in Investigational Drugs (4): MIDDLE MIDDLE EAST EAST JOURNAL JOURNAL OF FAMILY OF MEDICINE FAMILY MEDICINE VOLUME 12 ISSUE VOLUME 7 SEPTEMBER 7, ISSUE
The Most Common Parasitic Infections In Yemen. Medical Parasitology
 The Most Common Parasitic Infections In Yemen Medical Parasitology ﻓﺎﯾز اﻟﺧوﻻﻧﻲ / د 2 : is a vector-borne disease that transmitted by sandflies and caused by obligate intracellular protozoa of the genus
The Most Common Parasitic Infections In Yemen Medical Parasitology ﻓﺎﯾز اﻟﺧوﻻﻧﻲ / د 2 : is a vector-borne disease that transmitted by sandflies and caused by obligate intracellular protozoa of the genus
HAEMOFLAGELLATES. Dr. Anuluck Junkum Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine
 HAEMOFLAGELLATES Dr. Anuluck Junkum Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of Leishmania spp. and Trypanosoma
HAEMOFLAGELLATES Dr. Anuluck Junkum Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of Leishmania spp. and Trypanosoma
Welcome to the Jungle! Dr Aileen Oon, 2017 Microbiology Registrar
 Welcome to the Jungle! Dr Aileen Oon, 2017 Microbiology Registrar AA 55M presented with sores on left olecranon and umbilical area Umbilical sores present for 3 weeks Left olecranon lesions for 1 week
Welcome to the Jungle! Dr Aileen Oon, 2017 Microbiology Registrar AA 55M presented with sores on left olecranon and umbilical area Umbilical sores present for 3 weeks Left olecranon lesions for 1 week
~Trichinella Spiralis:
 Musculoskeletal System **Today we are going to talk about the parasites that affect the musculoskeletal system ~Trichinella Spiralis: It s a small nematode that measures to about 2-3mm in length. In general
Musculoskeletal System **Today we are going to talk about the parasites that affect the musculoskeletal system ~Trichinella Spiralis: It s a small nematode that measures to about 2-3mm in length. In general
Leishmaniasis. CDR R.L. Gutierrez Oct 2014
 Leishmaniasis CDR R.L. Gutierrez Oct 2014 Overview Protozoan parasite(s) of tissue and WBCs Many species / Many Syndromes (Cutaneous / Visceral) Pathogen: Location - Old World vs. New World Host: Immune
Leishmaniasis CDR R.L. Gutierrez Oct 2014 Overview Protozoan parasite(s) of tissue and WBCs Many species / Many Syndromes (Cutaneous / Visceral) Pathogen: Location - Old World vs. New World Host: Immune
Acta Dermatovenerol Croat 2008;16(2):60-64 CLINICAL ARTICLE
 2008;16(2):60-64 CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical Efficacy of Intramuscular Meglumine Antimoniate Alone and in Combination with Intralesional Meglumine Antimoniate in the Treatment of Old World Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
2008;16(2):60-64 CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical Efficacy of Intramuscular Meglumine Antimoniate Alone and in Combination with Intralesional Meglumine Antimoniate in the Treatment of Old World Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
World Health Organization Department of Communicable Disease Surveillance and Response
 WHO Report on Global Surveillance of Epidemic-prone Infectious Diseases World Health Organization Department of Communicable Disease Surveillance and Response This document has been downloaded from the
WHO Report on Global Surveillance of Epidemic-prone Infectious Diseases World Health Organization Department of Communicable Disease Surveillance and Response This document has been downloaded from the
Leishmaniasis. MAJ Kris Paolino September 2014
 Leishmaniasis MAJ Kris Paolino September 2014 Thanks to COL (Ret) Kent Kester MAJ Leyi Lin http://www.niaid.nih.gov/topics/leishmaniasis History Sir William Boog Leishman (1865-1926) Matriculated at the
Leishmaniasis MAJ Kris Paolino September 2014 Thanks to COL (Ret) Kent Kester MAJ Leyi Lin http://www.niaid.nih.gov/topics/leishmaniasis History Sir William Boog Leishman (1865-1926) Matriculated at the
BIO Parasitology Spring 2009
 BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 5 Discovery of the Disease In 1924 the Kala-Azar Commission noted that the distribution
BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 5 Discovery of the Disease In 1924 the Kala-Azar Commission noted that the distribution
SUMMARY. Cutaneous leishmaniasis with only skin involvement: single to multiple skin ulcers, satellite lesions and nodular lymphangitis.
 SUMMARY Leishmaniasis is a disease affecting predominantly people in the developing countries; 350 million people worldwide are at risk and yearly more than 2 million new cases occur. Leishmaniasis is
SUMMARY Leishmaniasis is a disease affecting predominantly people in the developing countries; 350 million people worldwide are at risk and yearly more than 2 million new cases occur. Leishmaniasis is
Laboratory diagnosis of Blood and tissue flagellates
 Laboratory diagnosis of Blood and tissue flagellates (Leishmania and trypanosma) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University Leishmania and trypanosma:
Laboratory diagnosis of Blood and tissue flagellates (Leishmania and trypanosma) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University Leishmania and trypanosma:
Leishmaniasis, Kala Azar(The Black Fever)
 Leishmaniasis, Kala Azar(The Black Fever) By Lawrence Hall Etiologic agent Protist obligate intracellular parasite, Transmission Vectors Phylum: Euglenozoa (genus Leishmania) Over 21 species that infect
Leishmaniasis, Kala Azar(The Black Fever) By Lawrence Hall Etiologic agent Protist obligate intracellular parasite, Transmission Vectors Phylum: Euglenozoa (genus Leishmania) Over 21 species that infect
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis : Global overview
 Cutaneous Leishmaniasis : Global overview Meeting of stakeholders for selected Health R&D Demostration Projects, 7-10 May 2014, WHO, Geneva Dr. Daniel Argaw Dagne, NTD/WHO CSR - DDC AFRO Leishmaniasis
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis : Global overview Meeting of stakeholders for selected Health R&D Demostration Projects, 7-10 May 2014, WHO, Geneva Dr. Daniel Argaw Dagne, NTD/WHO CSR - DDC AFRO Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis. By Joseph Knight, PA-C. 2. Explain the differences in the reasons leishmaniasis is spreading in Afghanistan and India.
 Leishmaniasis By Joseph Knight, PA-C Objectives 1. Identify the two types of leishmaniasis. 2. Explain the differences in the reasons leishmaniasis is spreading in Afghanistan and India. 3. Discuss how
Leishmaniasis By Joseph Knight, PA-C Objectives 1. Identify the two types of leishmaniasis. 2. Explain the differences in the reasons leishmaniasis is spreading in Afghanistan and India. 3. Discuss how
Leishmaniasis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course
 Leishmaniasis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course UNCLASSIFIED Acknowledgments LTC James E. Moon, MD Chief, Sleep Trials Branch Walter Reed Army Institute of Research CDR Ramiro
Leishmaniasis WRAIR- GEIS 'Operational Clinical Infectious Disease' Course UNCLASSIFIED Acknowledgments LTC James E. Moon, MD Chief, Sleep Trials Branch Walter Reed Army Institute of Research CDR Ramiro
Departments of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprosy and *Microbiology, Indira Gandhi Medical College, Shimla, India.
 Net Study Comparative efþ cacy of intralesional sodium stibogluconate (SSG) alone and its combination with intramuscular SSG to treat localized cutaneous leishmaniasis: Results of a pilot study Ajeet K.
Net Study Comparative efþ cacy of intralesional sodium stibogluconate (SSG) alone and its combination with intramuscular SSG to treat localized cutaneous leishmaniasis: Results of a pilot study Ajeet K.
Treatment of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis with Allopurinol and Stibogluconate
 165 Treatment of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis with Allopurinol and S. Martinez, M. Gonzalez, and M. E. Vernaza From the Department of Internal Medicine, University of Cauca, Popayan, and the University Hospital
165 Treatment of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis with Allopurinol and S. Martinez, M. Gonzalez, and M. E. Vernaza From the Department of Internal Medicine, University of Cauca, Popayan, and the University Hospital
Cutaneous leishmaniasis in an overseas Filipino worker who responded favorably to oral itraconazole
 CSE REPORT Cutaneous leishmaniasis in an overseas Filipino worker who responded favorably to oral itraconazole udi, MD 1, ilza ellamy R. Limcangco, MD, FPDS 2, Johannes F, Dayrit, MD, FPDS 2,3 Introduction:
CSE REPORT Cutaneous leishmaniasis in an overseas Filipino worker who responded favorably to oral itraconazole udi, MD 1, ilza ellamy R. Limcangco, MD, FPDS 2, Johannes F, Dayrit, MD, FPDS 2,3 Introduction:
VISERAL LEISHMANIASI S (KALA-AZAR)
 VISERAL LEISHMANIASI S (KALA-AZAR) :OUTLINES DEFINITION. EPIDEMIOLOGY. PARASITE & VECTOR. PATHOLOGY CLINICAL & LIFE CYCLE. PICTURE. COMPLICATIONS. DIAGNOSIS. INVESTIGATIONS. MANAGEMENT TREATMENT S CONTROL.
VISERAL LEISHMANIASI S (KALA-AZAR) :OUTLINES DEFINITION. EPIDEMIOLOGY. PARASITE & VECTOR. PATHOLOGY CLINICAL & LIFE CYCLE. PICTURE. COMPLICATIONS. DIAGNOSIS. INVESTIGATIONS. MANAGEMENT TREATMENT S CONTROL.
Laboratory investigation of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Karachi
 Laboratory investigation of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Karachi Pages with reference to book, From 248 To 250 G.M. Rajpar, M.A. Khan, A. Hafiz ( Department of Microbiology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
Laboratory investigation of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Karachi Pages with reference to book, From 248 To 250 G.M. Rajpar, M.A. Khan, A. Hafiz ( Department of Microbiology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in a Chinese man returning from the Amazon forest in Brazil
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2013) 21, 79-83 Case Report Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in a Chinese man returning from the Amazon forest in Brazil JTHT Yu and SY Wong A 60-year-old man presented with ulcerated
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2013) 21, 79-83 Case Report Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in a Chinese man returning from the Amazon forest in Brazil JTHT Yu and SY Wong A 60-year-old man presented with ulcerated
CUTANEOUS LEISHMANIASIS
 CUTANEOUS LEISHMANIASIS Why are you neglecting me? A WHO initiative to control Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in selected Old World areas This document has been produced as the result of a WHO Informal Consultative
CUTANEOUS LEISHMANIASIS Why are you neglecting me? A WHO initiative to control Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in selected Old World areas This document has been produced as the result of a WHO Informal Consultative
Control of leishmaniasis
 SIXTIETH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A60/10 Provisional agenda item 12.3 22 March 2007 Control of leishmaniasis Report by the Secretariat BACKGROUND 1. Leishmaniasis is endemic in 88 countries in the world and
SIXTIETH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A60/10 Provisional agenda item 12.3 22 March 2007 Control of leishmaniasis Report by the Secretariat BACKGROUND 1. Leishmaniasis is endemic in 88 countries in the world and
Blood Smears Only 6 October Sample Preparation and Quality Control 15B-K
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 6 October 5 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 6 October 5 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
Oral miltefosine for Indian post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis: a randomised trial
 Tropical Medicine and International Health doi:10.1111/tmi.12015 volume 18 no 1 pp 96 100 january 2013 Oral miltefosine for Indian post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis: a randomised trial Shyam Sundar 1,
Tropical Medicine and International Health doi:10.1111/tmi.12015 volume 18 no 1 pp 96 100 january 2013 Oral miltefosine for Indian post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis: a randomised trial Shyam Sundar 1,
Epidemiological Study of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Tuz
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 1 (2017) pp. 477-483 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.601.056
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 1 (2017) pp. 477-483 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.601.056
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Pentostam Injection. 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Sodium Stibogluconate equivalent to 100 mg pentavalent antimony in each
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Pentostam Injection. 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Sodium Stibogluconate equivalent to 100 mg pentavalent antimony in each
Original Article Chloroquine in cutaneous leishmaniasis
 Original Article Chloroquine in cutaneous leishmaniasis Ikramullah Khan, Rifat Yasmin, Iqbal Sidiqui Department of Dermatology, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad Abstract Background Chloroquine
Original Article Chloroquine in cutaneous leishmaniasis Ikramullah Khan, Rifat Yasmin, Iqbal Sidiqui Department of Dermatology, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad Abstract Background Chloroquine
Flagellates. Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA
 Flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317242 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellates Classification of Protozoa Based on locomotive
Flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317242 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellates Classification of Protozoa Based on locomotive
WMLN Case Study. Necrotizing Palate Biopsy Specimen. Youngmi Kim Sr. Microbiologist TB Lab & Parasitology Lab MS, M(ASCP)
 WMLN Case Study Necrotizing Palate Biopsy Specimen Youngmi Kim Sr. Microbiologist TB Lab & Parasitology Lab MS, M(ASCP) 44 year old male from Honduras Immigrated to US 12 years ago to WI 4 years ago Seen
WMLN Case Study Necrotizing Palate Biopsy Specimen Youngmi Kim Sr. Microbiologist TB Lab & Parasitology Lab MS, M(ASCP) 44 year old male from Honduras Immigrated to US 12 years ago to WI 4 years ago Seen
What is Kala-azar? What are Signs & Symptoms of Kala-Azar?
 What is Kala-azar? Kala-azar is a slow progressing indigenous disease caused by a protozoan parasite of genus Leishmania In India Leishmania donovani is the only parasite causing this disease The parasite
What is Kala-azar? Kala-azar is a slow progressing indigenous disease caused by a protozoan parasite of genus Leishmania In India Leishmania donovani is the only parasite causing this disease The parasite
Cutaneous Leishmania
 DISCLOSURE OF RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Cutaneous Leishmania Ibrahim Khalifeh, MD I do not have any relevant relationships with industry. Cutaneous Leishmania: Is it a Legend? Ibrahim Khalifeh,
DISCLOSURE OF RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Cutaneous Leishmania Ibrahim Khalifeh, MD I do not have any relevant relationships with industry. Cutaneous Leishmania: Is it a Legend? Ibrahim Khalifeh,
Leishmaniasis: A forgotten disease among neglected people
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 11 Number 2 Leishmaniasis: A forgotten disease among neglected people Y Homsi, G Makdisi Citation Y Homsi, G Makdisi. Leishmaniasis: A forgotten disease
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 11 Number 2 Leishmaniasis: A forgotten disease among neglected people Y Homsi, G Makdisi Citation Y Homsi, G Makdisi. Leishmaniasis: A forgotten disease
Original Article Comparison of fine needle aspiration with biopsy in the diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis Ikramullah Khan, Rifat Yasmin
 Original Article Comparison of fine needle aspiration with biopsy in the diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis Ikramullah Khan, Rifat Yasmin Department of Dermatology, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences,
Original Article Comparison of fine needle aspiration with biopsy in the diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis Ikramullah Khan, Rifat Yasmin Department of Dermatology, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences,
Cutaneous leishmaniasis: advances in disease pathogenesis, diagnostics and therapeutics
 Clinical dermatology Review article CED Clinical and Experimental Dermatology Cutaneous leishmaniasis: advances in disease pathogenesis, diagnostics and therapeutics M. Ameen Royal Free Hospital, Royal
Clinical dermatology Review article CED Clinical and Experimental Dermatology Cutaneous leishmaniasis: advances in disease pathogenesis, diagnostics and therapeutics M. Ameen Royal Free Hospital, Royal
Therapeutic Options for Visceral Leishmaniasis
 Drugs (2013) 73:1863 1888 DOI 10.1007/s40265-013-0133-0 REVIEW ARTICLE Therapeutic Options for Visceral Leishmaniasis Begoña Monge-Maillo Rogelio López-Vélez Published online: 30 October 2013 Ó The Author(s)
Drugs (2013) 73:1863 1888 DOI 10.1007/s40265-013-0133-0 REVIEW ARTICLE Therapeutic Options for Visceral Leishmaniasis Begoña Monge-Maillo Rogelio López-Vélez Published online: 30 October 2013 Ó The Author(s)
Leishmaniaand Leishmaniasis
 Leishmaniaand Leishmaniasis Methodenseminar SS2014 IRMA SCHABUSSOVA, PhD Institute of Specific Prophylaxis and Tropical Medicine; Medical University Vienna Kinderspitalgasse 15, A-1090 Vienna, Austria
Leishmaniaand Leishmaniasis Methodenseminar SS2014 IRMA SCHABUSSOVA, PhD Institute of Specific Prophylaxis and Tropical Medicine; Medical University Vienna Kinderspitalgasse 15, A-1090 Vienna, Austria
Morphological forms of hemoflagellates
 Parasitology Lecture: 1 Hemoflagellates (blood and tissue flagellates) *Classification: - Sub-kingdom: Protozoa -Phylum: Sarcomastigophora -Sub-phylum: Mastigiphora -Class: Zoomastigophora د. رائد *Flagellates
Parasitology Lecture: 1 Hemoflagellates (blood and tissue flagellates) *Classification: - Sub-kingdom: Protozoa -Phylum: Sarcomastigophora -Sub-phylum: Mastigiphora -Class: Zoomastigophora د. رائد *Flagellates
Leishmaniasis. caused by Leishmania spp. 利什曼原蟲 transmitted by Phlebotomine flies (Sandflies 白蛉 )
 Leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania spp. 利什曼原蟲 transmitted by Phlebotomine flies (Sandflies 白蛉 ) Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis Visceral Leishmaniasis About 12 million people are currently
Leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania spp. 利什曼原蟲 transmitted by Phlebotomine flies (Sandflies 白蛉 ) Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis Visceral Leishmaniasis About 12 million people are currently
WRAIR- GEIS 'OPERATIONAL CLINICAL INFECTIOUS DISEASE' COURSE
 Leishmaniasis WRAIR- GEIS 'OPERATIONAL CLINICAL INFECTIOUS DISEASE' COURSE The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the author, and are not to be construed as official, or as
Leishmaniasis WRAIR- GEIS 'OPERATIONAL CLINICAL INFECTIOUS DISEASE' COURSE The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the author, and are not to be construed as official, or as
Leishmaniasis. caused by Leishmania spp. 利什曼原蟲 transmitted by Phlebotomine flies (Sandflies 白蛉 ) 皮膚型黏膜型內臟型. Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
 Leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania spp. 利什曼原蟲 transmitted by Phlebotomine flies (Sandflies 白蛉 ) 皮膚型黏膜型內臟型 Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis Visceral Leishmaniasis About 12 million people
Leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania spp. 利什曼原蟲 transmitted by Phlebotomine flies (Sandflies 白蛉 ) 皮膚型黏膜型內臟型 Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis Visceral Leishmaniasis About 12 million people
Visceral leishmaniasis: an endemic disease with global impact
 Visceral leishmaniasis: an endemic disease with global impact Professor Olivier Lortholary, MD, PhD Department of Infectious and Tropical diseases Hôpital Necker-Enfants Malades Université Paris Descartes
Visceral leishmaniasis: an endemic disease with global impact Professor Olivier Lortholary, MD, PhD Department of Infectious and Tropical diseases Hôpital Necker-Enfants Malades Université Paris Descartes
2.Trichomonas vaginalis
 2.Trichomonas vaginalis 1. Pathogenic to human &causes vaginitis (trichomoniasis). 2. troph. Is round or pear like in shape, contains 4-6 flagella, all originating from anterior end & only one extend posteriorly.
2.Trichomonas vaginalis 1. Pathogenic to human &causes vaginitis (trichomoniasis). 2. troph. Is round or pear like in shape, contains 4-6 flagella, all originating from anterior end & only one extend posteriorly.
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in an Immigrant Saudi Worker: A Case Report
 J HEALTH POPUL NUTR 2014 Jun;32(2):372-376 ISSN 1606-0997 $ 5.00+0.20 INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR DIARRHOEAL DISEASE RESEARCH, BANGLADESH CASE STUDY Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in an Immigrant Saudi Worker: A
J HEALTH POPUL NUTR 2014 Jun;32(2):372-376 ISSN 1606-0997 $ 5.00+0.20 INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR DIARRHOEAL DISEASE RESEARCH, BANGLADESH CASE STUDY Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in an Immigrant Saudi Worker: A
New insights on leishmaniasis in immunosuppressive conditions
 New insights on leishmaniasis in immunosuppressive conditions Javier Moreno Immunoparasitology Unit WHO Collaborative Center for Leishmaniasis Centro Nacional de Microbiología INSTITUTO DE SALUD CARLOS
New insights on leishmaniasis in immunosuppressive conditions Javier Moreno Immunoparasitology Unit WHO Collaborative Center for Leishmaniasis Centro Nacional de Microbiología INSTITUTO DE SALUD CARLOS
Evaluation of Thermotherapy for the Treatment of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Kabul, Afghanistan: A Randomized Controlled Trial
 MILITARY MEDICINE, 177, 3:345, 2012 Evaluation of Thermotherapy for the Treatment of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Kabul, Afghanistan: A Randomized Controlled Trial Najibullah Safi, MD*; COL Gary D. Davis,
MILITARY MEDICINE, 177, 3:345, 2012 Evaluation of Thermotherapy for the Treatment of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Kabul, Afghanistan: A Randomized Controlled Trial Najibullah Safi, MD*; COL Gary D. Davis,
ISPUB.COM. Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Iran. C Yazdi, M Narmani, B Sadri INTRODUCTION CASE 1 CASE 2
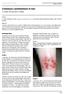 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Infectious Diseases Volume 3 Number 1 Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Iran C Yazdi, M Narmani, B Sadri Citation C Yazdi, M Narmani, B Sadri. Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Iran.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Infectious Diseases Volume 3 Number 1 Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Iran C Yazdi, M Narmani, B Sadri Citation C Yazdi, M Narmani, B Sadri. Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Iran.
Control of leishmaniasis
 EXECUTIVE BOARD EB118/4 118th Session 11 May 2006 Provisional agenda item 5.1 Control of leishmaniasis Report by the Secretariat BACKGROUND 1. Leishmaniasis is endemic in 88 countries in the world and
EXECUTIVE BOARD EB118/4 118th Session 11 May 2006 Provisional agenda item 5.1 Control of leishmaniasis Report by the Secretariat BACKGROUND 1. Leishmaniasis is endemic in 88 countries in the world and
Leishmaniasis in the WhO european region
 Leishmaniasis in the WhO european region This information leaflet contains six sections and is intended for a generic and public health audience: 1.Leishmaniasis is present in europe. What are the risks
Leishmaniasis in the WhO european region This information leaflet contains six sections and is intended for a generic and public health audience: 1.Leishmaniasis is present in europe. What are the risks
Research Article Efficacy and Safety of Paromomycin in Treatment of Post-Kala-Azar Dermal Leishmaniasis
 ISRN Parasitology, Article ID 548010, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/548010 Research Article Efficacy and Safety of Paromomycin in Treatment of Post-Kala-Azar Dermal Leishmaniasis Shyam Sundar,
ISRN Parasitology, Article ID 548010, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/548010 Research Article Efficacy and Safety of Paromomycin in Treatment of Post-Kala-Azar Dermal Leishmaniasis Shyam Sundar,
Summary of Cases & Epidemiology Aspects of Leishmaniasis in Thailand
 Summary of Cases & Epidemiology Aspects of Leishmaniasis in Thailand Sukmee T. 1, Mungthin M. 2, Apiwathanasorn C. 3, Leelayoova S. 2 1 Department of Microbiology, Phramongkutklao College of Medicine 2
Summary of Cases & Epidemiology Aspects of Leishmaniasis in Thailand Sukmee T. 1, Mungthin M. 2, Apiwathanasorn C. 3, Leelayoova S. 2 1 Department of Microbiology, Phramongkutklao College of Medicine 2
Prevalence of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis among HIV and Non-HIV Patients attending some Selected Hospitals in Jos Plateau State
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.307
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.307
CASE OF CUTANEOUS LEISHMANIASIS OF THE LID*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 542 CASE OF CUTANEOUS LEISHMANIASIS OF THE LID* BY GWYN MORGAN Department ofpathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London THE lid is involved only in about 2
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 542 CASE OF CUTANEOUS LEISHMANIASIS OF THE LID* BY GWYN MORGAN Department ofpathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London THE lid is involved only in about 2
Cutaneous leishmaniasis: an epidemiological survey in Iran during
 Nikouee Journal of F, Nursing et al. and Midwifery Sciences 2017: 4(1): 58-62. http://jnms.mazums.ac.ir Short Communication Cutaneous leishmaniasis: an epidemiological survey in Iran during 2013-2015 Farhood
Nikouee Journal of F, Nursing et al. and Midwifery Sciences 2017: 4(1): 58-62. http://jnms.mazums.ac.ir Short Communication Cutaneous leishmaniasis: an epidemiological survey in Iran during 2013-2015 Farhood
Blood Smears Only 07 February Sample Preparation and Quality Control 12B A
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 07 February 2012 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology Blood Smears Only
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 07 February 2012 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology Blood Smears Only
by author Drug Therapy in African Visceral Leishmaniasis 28th ECCMID Conference, Madrid, Spain 21 April 2018
 Drug Therapy in African Visceral Leishmaniasis 28th ECCMID Conference, Madrid, Spain 21 April 2018 Dr. Monique Wasunna, Director, DNDi Africa Regional Office Presentation Outline 1 2 4 5 Introduction leishmaniasis
Drug Therapy in African Visceral Leishmaniasis 28th ECCMID Conference, Madrid, Spain 21 April 2018 Dr. Monique Wasunna, Director, DNDi Africa Regional Office Presentation Outline 1 2 4 5 Introduction leishmaniasis
Lupoid Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: a Case Report
 Dermatol Ther (2011) 1(2):36-41. DOI 10.1007/s13555-011-0008-9 CASE REPORT Lupoid Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: a Case Report Aida Khaled Samia Goucha Sonia Trabelsi Rachida Zermani Bécima Fazaa To view enhanced
Dermatol Ther (2011) 1(2):36-41. DOI 10.1007/s13555-011-0008-9 CASE REPORT Lupoid Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: a Case Report Aida Khaled Samia Goucha Sonia Trabelsi Rachida Zermani Bécima Fazaa To view enhanced
ORIGINAL ARTICLE AFRICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY MAY 2012 ISBN X VOL 13(2)
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE AFRICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY MAY 2012 ISBN 1595-689X VOL 13(2) AJCEM/201179/21203 -http://www.ajol.info/journals/ajcem COPYRIGHT 2012 AFR. J. CLN. EXPER. MICROBIOL
ORIGINAL ARTICLE AFRICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY MAY 2012 ISBN 1595-689X VOL 13(2) AJCEM/201179/21203 -http://www.ajol.info/journals/ajcem COPYRIGHT 2012 AFR. J. CLN. EXPER. MICROBIOL
GENUS: LEISHMANIA. Under the genus Leishmania, there are 2 subgenus: SPECIES PARASITIC IN MEN. Under subgenus Leishmania, there are following species:
 GENUS: LEISHMANIA Species parasitic in man: Under the genus Leishmania, there are 2 subgenus: 1. Leishmania 2. Viannia SPECIES PARASITIC IN MEN Under subgenus Leishmania, there are following species: LEISHMANIA
GENUS: LEISHMANIA Species parasitic in man: Under the genus Leishmania, there are 2 subgenus: 1. Leishmania 2. Viannia SPECIES PARASITIC IN MEN Under subgenus Leishmania, there are following species: LEISHMANIA
Human Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Three Districts of Sindh in Pakistan
 Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences, 2017, 13, 611-615 611 Human Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Three Districts of Sindh in Pakistan Farah Sharif 1,*, Imtiaz Ahmad 2 and Rafia Rehana Ghazi 3 1 Department of
Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences, 2017, 13, 611-615 611 Human Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Three Districts of Sindh in Pakistan Farah Sharif 1,*, Imtiaz Ahmad 2 and Rafia Rehana Ghazi 3 1 Department of
Frequently Asked Questions on Visceral Leishmaniasis (Kala-azar)
 SEA-CD-274 Frequently Asked Questions on Visceral Leishmaniasis (Kala-azar) World Health Organization 2013 All rights reserved. Requests for publications, or for permission to reproduce or translate WHO
SEA-CD-274 Frequently Asked Questions on Visceral Leishmaniasis (Kala-azar) World Health Organization 2013 All rights reserved. Requests for publications, or for permission to reproduce or translate WHO
Short-Course Paromomycin Treatment of Visceral Leishmaniasis in India: 14-Day vs 21-Day Treatment
 MAJOR ARTICLE Short-Course Paromomycin Treatment of Visceral Leishmaniasis in India: 14-Day vs 21-Day Treatment Shyam Sundar, Neha Agrawal, Rakesh Arora, Dipti Agarwal, Madhukar Rai, and Jaya Chakravarty
MAJOR ARTICLE Short-Course Paromomycin Treatment of Visceral Leishmaniasis in India: 14-Day vs 21-Day Treatment Shyam Sundar, Neha Agrawal, Rakesh Arora, Dipti Agarwal, Madhukar Rai, and Jaya Chakravarty
History of Leishmaniasis (from Wikipedia)
 History of Leishmaniasis (from Wikipedia) Descriptions of conspicuous lesions similar to cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) has been discovered on tablets from King Ashurbanipal from the 7th century BC, some
History of Leishmaniasis (from Wikipedia) Descriptions of conspicuous lesions similar to cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) has been discovered on tablets from King Ashurbanipal from the 7th century BC, some
Animal Models of Leishmaniasis Relevant to Vaccine Development. David Sacks Laboratory of Parasitic Diseases NIAID, NIH
 Animal Models of Leishmaniasis Relevant to Vaccine Development David Sacks Laboratory of Parasitic Diseases NIAID, NIH Leishmaniasis: A spectrum of diseases associated with a diversity of parasite species,
Animal Models of Leishmaniasis Relevant to Vaccine Development David Sacks Laboratory of Parasitic Diseases NIAID, NIH Leishmaniasis: A spectrum of diseases associated with a diversity of parasite species,
CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE
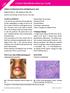 CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE Solitary erythematous firm noduloplaque on nose Hassab El-Naby H., MD, Mosbeh Al Sadat, MD Department of Dermatology, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. CLINICAL FINDINGS A 36-year-old
CLINCOPATHOLOGICAL CASE Solitary erythematous firm noduloplaque on nose Hassab El-Naby H., MD, Mosbeh Al Sadat, MD Department of Dermatology, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. CLINICAL FINDINGS A 36-year-old
Efficacy of pentavalent antimoniate intralesional infiltration therapy for cutaneous leishmaniasis: A systematic review
 COLLECTION REVIEW Efficacy of pentavalent antimoniate intralesional infiltration therapy for cutaneous leishmaniasis: A systematic review Nayara Castelano Brito, Ana Rabello, Gláucia Fernandes Cota* Pesquisas
COLLECTION REVIEW Efficacy of pentavalent antimoniate intralesional infiltration therapy for cutaneous leishmaniasis: A systematic review Nayara Castelano Brito, Ana Rabello, Gláucia Fernandes Cota* Pesquisas
Review Cutaneous Manifestations of Human and Murine Leishmaniasis
 Review Cutaneous Manifestations of Human and Murine Leishmaniasis Breanna M. Scorza 1, Edgar M. Carvalho 2,3 and Mary E. Wilson 1,4,5,6, * 1 Interdisciplinary Graduate Program in Immunology, University
Review Cutaneous Manifestations of Human and Murine Leishmaniasis Breanna M. Scorza 1, Edgar M. Carvalho 2,3 and Mary E. Wilson 1,4,5,6, * 1 Interdisciplinary Graduate Program in Immunology, University
Leishmaniasis impact and treatment access
 REVIEW 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03635.x Leishmaniasis impact and treatment access M. den Boer, D. Argaw, J. Jannin and J. Alvar Leishmaniasis Control Programme, WHO/IDM. Av. Appia, Geneva, Switzerland
REVIEW 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03635.x Leishmaniasis impact and treatment access M. den Boer, D. Argaw, J. Jannin and J. Alvar Leishmaniasis Control Programme, WHO/IDM. Av. Appia, Geneva, Switzerland
Framework for action on cutaneous leishmaniasis in the Eastern Mediterranean Region
 Framework for action on cutaneous leishmaniasis in the Eastern Mediterranean Region 2014 2018 Framework for action on cutaneous leishmaniasis in the Eastern Mediterranean Region 2014 2018 WHO Library Cataloguing
Framework for action on cutaneous leishmaniasis in the Eastern Mediterranean Region 2014 2018 Framework for action on cutaneous leishmaniasis in the Eastern Mediterranean Region 2014 2018 WHO Library Cataloguing
Buruli ulcer disease. Epidemiology and transmission l Clinical manifestations and diagnosis l Treatment. Chapter 2
 Epidemiology and transmission l Clinical manifestations and diagnosis l Treatment Chapter 2 KEY POINTS Buruli ulcer is an infection caused by an organism called Mycobacterium ulcerans that lives in the
Epidemiology and transmission l Clinical manifestations and diagnosis l Treatment Chapter 2 KEY POINTS Buruli ulcer is an infection caused by an organism called Mycobacterium ulcerans that lives in the
1 INTRODUCTION. 1.1 Historical background
 1 Parasites are living organisms that use other living creatures like our body for food and a place to live. We can get them from contaminated food or water, a bug bite, or sexual contact. Parasitic diseases
1 Parasites are living organisms that use other living creatures like our body for food and a place to live. We can get them from contaminated food or water, a bug bite, or sexual contact. Parasitic diseases
Table of Contents GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT AND PREVENTION OF CUTANEOUS LEISHMANIASIS IN PAKISTAN
 GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT AND PREVENTION OF CUTANEOUS LEISHMANIASIS IN PAKISTAN Table of Contents Acknowledgements 2 Introduction 3 1. Leishmaniasis 4 1.1. Disease incidence 5 1.2. Leishmaniasis in
GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT AND PREVENTION OF CUTANEOUS LEISHMANIASIS IN PAKISTAN Table of Contents Acknowledgements 2 Introduction 3 1. Leishmaniasis 4 1.1. Disease incidence 5 1.2. Leishmaniasis in
ESCMID Online Lecture Library ESCMID PGTW PARASITIC INFECTIONS OF THE ARABIAN PENINSULA AL AIN, UAE MARCH by author
 ESCMID PGTW PARASITIC INFECTIONS OF THE ARABIAN PENINSULA AL AIN, UAE 17-19 MARCH 2016 Leishmania Míriam J. Álvarez-Martínez M.D., Ph.D. Microbiology Department Hospital Clinic, Barcelona (Spain) ISGlobal
ESCMID PGTW PARASITIC INFECTIONS OF THE ARABIAN PENINSULA AL AIN, UAE 17-19 MARCH 2016 Leishmania Míriam J. Álvarez-Martínez M.D., Ph.D. Microbiology Department Hospital Clinic, Barcelona (Spain) ISGlobal
DENDRITIC CELLS ACTIVATED BY CpG MOTIFS ARE POTENT INDUCERS OF A TH1 IMMUNE RESPONSE THAT PROTECTS MICE AGAINST LEISHMANIASIS
 DENDRITIC CELLS ACTIVATED BY CpG MOTIFS ARE POTENT INDUCERS OF A TH1 IMMUNE RESPONSE THAT PROTECTS MICE AGAINST LEISHMANIASIS Dissertation zur Erlangung des naturwissenschaftlichen Doktorgrades der Bayerischen
DENDRITIC CELLS ACTIVATED BY CpG MOTIFS ARE POTENT INDUCERS OF A TH1 IMMUNE RESPONSE THAT PROTECTS MICE AGAINST LEISHMANIASIS Dissertation zur Erlangung des naturwissenschaftlichen Doktorgrades der Bayerischen
Impavido. (miltefosine) New Product Slideshow
 Impavido (miltefosine) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Impavido Generic name: Miltefosine Pharmacological class: Antileishmanial agent Strength and Formulation: 50mg; hard gel capsules Manufacturer:
Impavido (miltefosine) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Impavido Generic name: Miltefosine Pharmacological class: Antileishmanial agent Strength and Formulation: 50mg; hard gel capsules Manufacturer:
Visceral childhood leishmaniasis in southern Turkey: experience of twenty years
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2009; 51: 1-5 Original Visceral childhood leishmaniasis in southern Turkey: experience of twenty years Oğuz Dursun 1, Seyhan Erişir 2, Akif Yeşilipek 3 Divisions of 1
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2009; 51: 1-5 Original Visceral childhood leishmaniasis in southern Turkey: experience of twenty years Oğuz Dursun 1, Seyhan Erişir 2, Akif Yeşilipek 3 Divisions of 1
Nanomedicine & Drug Delivery Systems Group Research Institute for Medicines and Pharmaceutical Sciences (imed.ul)
 Faculty of Pharmacy of the University of Lisbon Nanomedicine & Drug Delivery Systems Group Research Institute for Medicines and Pharmaceutical Sciences (imed.ul) Leishmania in southern Europe. (Duiardin,
Faculty of Pharmacy of the University of Lisbon Nanomedicine & Drug Delivery Systems Group Research Institute for Medicines and Pharmaceutical Sciences (imed.ul) Leishmania in southern Europe. (Duiardin,
Elimination of VL in the Indian subcontinent is it achievable?
 Elimination of VL in the Indian subcontinent is it achievable? P Das Rajendra Memorial Research Institute, Patna Jorge Alvar DNDi, Geneva Bhawna Sharma DNDi, India Leishmaniasis 350 million at risk worldwide
Elimination of VL in the Indian subcontinent is it achievable? P Das Rajendra Memorial Research Institute, Patna Jorge Alvar DNDi, Geneva Bhawna Sharma DNDi, India Leishmaniasis 350 million at risk worldwide
LeishMan Recommendations for Treatment of Cutaneous and Mucosal Leishmaniasis in Travelers, 2014
 I S T M 116 REVIEW LeishMan Recommendations for Treatment of Cutaneous and Mucosal Leishmaniasis in Travelers, 2014 Johannes Blum, MD, Pierre Buffet, MD, Leo Visser, MD, # Gundel Harms, MD, Mark S. Bailey,
I S T M 116 REVIEW LeishMan Recommendations for Treatment of Cutaneous and Mucosal Leishmaniasis in Travelers, 2014 Johannes Blum, MD, Pierre Buffet, MD, Leo Visser, MD, # Gundel Harms, MD, Mark S. Bailey,
Mechanistic Studies of Pentamidine Analogs on Leishmania donovani Promastigotes
 Mechanistic Studies of Pentamidine Analogs on Leishmania donovani Promastigotes Undergraduate Honors Thesis The Ohio State University, College of Pharmacy Division of Medicinal Chemistry and Pharmacognosy
Mechanistic Studies of Pentamidine Analogs on Leishmania donovani Promastigotes Undergraduate Honors Thesis The Ohio State University, College of Pharmacy Division of Medicinal Chemistry and Pharmacognosy
DTA3/COFUND Programme Research Project Proforma
 Page 1 General Information Project Code Partner University Faculty/School/Department/Research Centres First supervisor Please provide name and weblink Second supervisor Please provide name and weblink
Page 1 General Information Project Code Partner University Faculty/School/Department/Research Centres First supervisor Please provide name and weblink Second supervisor Please provide name and weblink
Necrotizing and suppurative lymphadenitis in Leishmania
 Tropical Medicine and International Health VOLUME I NO. 2 PP 243-250 APRIL 1996 Necrotizing and suppurative lymphadenitis in Leishmania major infections A. Gaafar r, A. Ismai13, A. Y. El Kadaro4, Elsir
Tropical Medicine and International Health VOLUME I NO. 2 PP 243-250 APRIL 1996 Necrotizing and suppurative lymphadenitis in Leishmania major infections A. Gaafar r, A. Ismai13, A. Y. El Kadaro4, Elsir
EVALUATION OF MILTEFOSINE AGAINST LEISHMANIA MAJOR (MRHO/IR/75/ER): IN VITRO AND IN VIVO STUDIES
 ORIGINAL REPORT EVALUATION OF MILTEFOSINE AGAINST LEISHMANIA MAJOR (MRHO/IR/75/ER): IN VITRO AND IN VIVO STUDIES J. Esmaeili 1, M. Mohebali 1*, G. H. Edrissian 1, S. M. Rezayat 2, M. Ghazi-Khansari 2 and
ORIGINAL REPORT EVALUATION OF MILTEFOSINE AGAINST LEISHMANIA MAJOR (MRHO/IR/75/ER): IN VITRO AND IN VIVO STUDIES J. Esmaeili 1, M. Mohebali 1*, G. H. Edrissian 1, S. M. Rezayat 2, M. Ghazi-Khansari 2 and
Case Report Development of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis after Leishmania Skin Test
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 631079, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/631079 Case Report Development of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis after Leishmania Skin Test Paulo R. Machado, 1, 2 Augusto M.
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 631079, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/631079 Case Report Development of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis after Leishmania Skin Test Paulo R. Machado, 1, 2 Augusto M.
Treatment of Disseminated Leishmaniasis With Liposomal Amphotericin B
 MAJOR ARTICLE Treatment of Disseminated Leishmaniasis With Liposomal Amphotericin B Paulo R. L. Machado, 1,2 Maria Elisa A. Rosa, 1 Luís H. Guimarães, 1,2 Fernanda V. O. Prates, 1 Adriano Queiroz, 1,2
MAJOR ARTICLE Treatment of Disseminated Leishmaniasis With Liposomal Amphotericin B Paulo R. L. Machado, 1,2 Maria Elisa A. Rosa, 1 Luís H. Guimarães, 1,2 Fernanda V. O. Prates, 1 Adriano Queiroz, 1,2
DOI /j x
 THERAPEUTICS DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.07872.x Diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis responds to miltefosine but then relapses O. Zerpa, M. Ulrich, B. Blanco, M. Polegre, A. Avila, N. Matos,* I. Mendoza,
THERAPEUTICS DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.07872.x Diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis responds to miltefosine but then relapses O. Zerpa, M. Ulrich, B. Blanco, M. Polegre, A. Avila, N. Matos,* I. Mendoza,
Adverse Effects of Amphotericin B in Patients of Visceral Leishmaniasis: A Short Survey at Research Hospital Patna
 American Journal of Virology 2 (1): 20-24, 2013 ISSN: 1949-0097 2013 Science Publication doi:10.3844/ajvsp.2013.20.24 Published Online 2 (1) 2013 (http://www.thescipub.com/ajv.toc) Adverse Effects of Amphotericin
American Journal of Virology 2 (1): 20-24, 2013 ISSN: 1949-0097 2013 Science Publication doi:10.3844/ajvsp.2013.20.24 Published Online 2 (1) 2013 (http://www.thescipub.com/ajv.toc) Adverse Effects of Amphotericin
Neglected Diseases (NDs) Landscape in Brazil and South America
 Frontiers in Science on Neglected Diseases 13 th November 2014 Neglected Diseases (NDs) Landscape in Brazil and South America Jeffrey Shaw São Paulo University Biomedical Sciences Institute jeffreyj@usp.br
Frontiers in Science on Neglected Diseases 13 th November 2014 Neglected Diseases (NDs) Landscape in Brazil and South America Jeffrey Shaw São Paulo University Biomedical Sciences Institute jeffreyj@usp.br
Studying the Dynamics of Visceral Leishmaniasis Epidemic in India - A System Dynamic Approach for Policy Development
 Studying the Dynamics of Visceral Leishmaniasis Epidemic in India - A System Dynamic Approach for Policy Development Hiba Ahmed Supervised by: Pål Davidsen Submitted in Partial Fulfillment Of the Requirement
Studying the Dynamics of Visceral Leishmaniasis Epidemic in India - A System Dynamic Approach for Policy Development Hiba Ahmed Supervised by: Pål Davidsen Submitted in Partial Fulfillment Of the Requirement
Authors Chappuis, François; Alirol, Emilie; Worku, Dagemlidet T; Mueller, Yolanda; Ritmeijer, Koert
 MSF Field Research High mortality among older patients treated with pentavalent antimonials for visceral leishmaniasis in East Africa and rationale for switch to liposomal amphotericin B Item type Article
MSF Field Research High mortality among older patients treated with pentavalent antimonials for visceral leishmaniasis in East Africa and rationale for switch to liposomal amphotericin B Item type Article
CONTROLE DAS LEISHMANIOSES O QUE FALTA FAZER? Centro de Convenções de Reboças Red Room 17: 00h
 CONTROLE DAS LEISHMANIOSES O QUE FALTA FAZER? Centro de Convenções de Reboças 08.04.2014 Red Room 17: 00h Leishmaniasis - a Global Problem Visceral 2012 300 000 cases 20,000 deaths (6.7%) 310 million at
CONTROLE DAS LEISHMANIOSES O QUE FALTA FAZER? Centro de Convenções de Reboças 08.04.2014 Red Room 17: 00h Leishmaniasis - a Global Problem Visceral 2012 300 000 cases 20,000 deaths (6.7%) 310 million at
Anthroponotic Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Nonendemic Quarters of a Centeral City in Iran
 Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 6, No., 7, pp.7- Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 6, No., 7, pp.7- Original Articles Anthroponotic Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Nonendemic Quarters of a Centeral City in Iran *AR Zahraei-Ramazani,
Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 6, No., 7, pp.7- Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 6, No., 7, pp.7- Original Articles Anthroponotic Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Nonendemic Quarters of a Centeral City in Iran *AR Zahraei-Ramazani,
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Series Editors Samuel J. Black, University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA, US.A. J. Richard Seed, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC, US.A.
 LEISHMANIA World Class Parasites VOLUME 4 Volumes in the World Class Parasites book series are written for researchers, students and scholars who enjoy reading about excellent research on problems of global
LEISHMANIA World Class Parasites VOLUME 4 Volumes in the World Class Parasites book series are written for researchers, students and scholars who enjoy reading about excellent research on problems of global
Protozoa from tissues. Leishmania spp. Naegleria fowleri Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma spp.
 Protozoa from tissues Leishmania spp. Naegleria fowleri Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma spp. Leishmaniasis Leishmania infantum, Leishmania donovani, in macrophages of man. Female sandflies:
Protozoa from tissues Leishmania spp. Naegleria fowleri Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma spp. Leishmaniasis Leishmania infantum, Leishmania donovani, in macrophages of man. Female sandflies:
Clinical pharmacology in leishmaniasis: treatment optimization of a neglected disease Dorlo, T.P.C.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Clinical pharmacology in leishmaniasis: treatment optimization of a neglected disease Dorlo, T.P.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Dorlo,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Clinical pharmacology in leishmaniasis: treatment optimization of a neglected disease Dorlo, T.P.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Dorlo,
Downloaded from:
 Wise, ES; Armstrong, MS; Watson, J; Lockwood, DN (2012) Monitoring toxicity associated with parenteral sodium stibogluconate in the day-case management of returned travellers with New World cutaneous leishmaniasis
Wise, ES; Armstrong, MS; Watson, J; Lockwood, DN (2012) Monitoring toxicity associated with parenteral sodium stibogluconate in the day-case management of returned travellers with New World cutaneous leishmaniasis
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 08 Page August 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i8.12 Original Research Article Lip
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i8.12 Original Research Article Lip
Current therapeutics for visceral leischmaniasis. F.Amri
 Current therapeutics for visceral leischmaniasis F.Amri Department of pediatrics Kairouan Intoduction The visceral leischmaniasis is an anthropozoonose caused by a protozoar, the Leishmania infantum The
Current therapeutics for visceral leischmaniasis F.Amri Department of pediatrics Kairouan Intoduction The visceral leischmaniasis is an anthropozoonose caused by a protozoar, the Leishmania infantum The
