Examining the Fingernails When Evaluating Presenting Symptoms in Elderly
|
|
|
- Kerrie Russell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page 1 of 30 Examining the Fingernails When Evaluating Presenting Symptoms in Elderly Patients CME/CE Complete author affiliations and disclosures are at the end of this activity. Release Date: March 26, 2008; Valid for credit through March 26, 2009 Target Audience This activity is intended for primary care professionals who treat the elderly patient. Goal The goal of this activity is to appropriate assess the fingernails of the elderly patient Learning Objectives Upon completion of this activity, participants will be able to: 1. Visually examine the fingernails for abnormalities 2. Recognize specific fingernail abnormalities 3. Identify systemic conditions associated with fingernail abnormalities Credits Available Physicians - maximum of 0.5 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s) for physicians; Nurses nursing contact hours (None of these credits is in the area of pharmacology) All other healthcare professionals completing continuing education credit for this activity will be issued a certificate of participation. Physicians should only claim credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity. Accreditation Statements For Physicians Medscape, LLC is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) to provide continuing medical education for physicians. Medscape, LLC designates this educational activity for a maximum of 0.5 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s). Physicians should only claim credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity. For questions regarding the content of this activity, contact the accredited provider for this CME/CE activity: CME@medscape.net. For technical assistance, contact CME@webmd.net.
2 Page 2 of 30 For Nurses This Activity is sponsored by Medscape Continuing Education Provider Unit. Medscape is an approved provider of continuing nursing education by the New York State Nurses Association, an accredited approver by the American Nurses Credentialing Center's Commission on Accreditation. Awarded 0.5 contact hour(s) of continuing nursing education for RNs and APNs; none of these credits is in the area of pharmacology. Provider Number: 6FDKKC-PRV-05 For questions regarding the content of this activity, contact the accredited provider for this CME/CE activity: CME@medscape.net. For technical assistance, contact CME@webmd.net. Instructions for Participation and Credit There are no fees for participating in or receiving credit for this online educational activity. For information on applicability and acceptance of continuing education credit for this activity, please consult your professional licensing board. This activity is designed to be completed within the time designated on the title page; physicians should claim only those credits that reflect the time actually spent in the activity. To successfully earn credit, participants must complete the activity online during the valid credit period that is noted on the title page. Follow these steps to earn CME/CE credit*: 1. Read the target audience, learning objectives, and author disclosures. 2. Study the educational content online or printed out. 3. Online, choose the best answer to each test question. To receive a certificate, you must receive a passing score as designated at the top of the test. Medscape encourages you to complete the Activity Evaluation to provide feedback for future programming. You may now view or print the certificate from your CME/CE Tracker. You may print the certificate but you cannot alter it. Credits will be tallied in your CME/CE Tracker and archived for 6 years; at any point within this time period you can print out the tally as well as the certificates by accessing "Edit Your Profile" at the top of your Medscape homepage. *The credit that you receive is based on your user profile. This activity is supported by funding from WebMD. Legal Disclaimer The material presented here does not necessarily reflect the views of Medscape or companies that support educational programming on These materials may discuss therapeutic products that have not been approved by the US Food and Drug Adm Copyright 2008 Medscape. Contents of This CME/CE Activity Examining the Fingernails When Evaluating Presenting Symptoms in Elderly Patients
3 Page 3 of 30 Mark E. Williams, MD Examining the Fingernails When Evaluating Presenting Symptoms in Elderly Patients Introduction Human fingernails, located on the dorsal aspect of the terminal 40% of the distal phalanx of each finger, are complex structures involving 3 different layers: The nail plate (the nail). This is the keratinized structure, which grows throughout life; The nail bed (ventral matrix, sterile matrix). This is the vascular bed that is responsible for nail growth and support. It lies protected between the lunula (the "half moon" seen through the nail) and the hyponychium (the posterior part of the nail bed epithelium); and The eponychium (cuticle). The epidermal layer between the proximal nail fold and the dorsal aspect of the nail plate. The primary purpose of the nail is protection. Abnormalities of the nail are often caused by skin disease and infection (most often fungal) but may also indicate more general medical conditions. This discussion does not address localized trauma or nail infections but offers examples of nail abnormalities that may occur with systemic disease. Check to see whether the nails are normal by looking at the following (Figure 1): Softness and flexibility of free edge; Shape and color; Quality of paronychial tissue; and Growth rate (about 6 months from cuticle to free edge). Time of events can be estimated from location. Figure 1. The normal nail.
4 Page 4 of 30 Examining the Nails Elderly people carry the last 6 months of their medical record on the approximately 10 square centimeters of keratin comprising the fingernails. Examining the fingernails can help the clinician detect a number of general and specific factors, including the following: Overall vitality; Inner emotional state; Cerebral dominance; Occupations and hobbies; Medical history; Nutritional status; Cardiovascular function; Rheumatic conditions; and Dermatologic problems. The patient's manicure can reveal state of health, nutritional status, past events, personality, occupation, and one's inner state. Systemic illness should show the nail changes in each of the nails on one hand. The thumb may reveal more extensive changes given its increased size. It is useful to follow the following sequence when examining the nails: Check the nail shape; Examine the nail color; Survey processes around the nails; Compare hands; and Note skin conditions. It is critical to examine the nails in adequate light. Gently rotate the nail in the light so that the reflection highlights all aspects of the nail. Notice the lunula, the pale crescent moonlike coloration at the base of the nail. Leukonychia stria and a pointed tent-like lunula suggest an excessive manicure and pushing on the cuticle. Paronychias suggest stress and poor attention to hygiene. This can reflect depression, dementia, or psychiatric illness. Nail Growth Nail growth is continuous. It takes about 6 months for a fingernail in an elderly person to completely grow out. Cold temperature can slow growth rates but not to any clinically significant degree (pun intended). The middle finger nail grows the fastest, followed by the forefinger and ring finger. Aging slows the growth rate from approximately 3 months in childhood to 6 months in 70-year-olds. Nails in elderly people are also thicker than in younger people. Thin nails in a postmenopausal woman raise the possibility of metabolic bone disease. The nails of the dominant hand grow slightly more quickly than the nondominant nails, probably because minor trauma accelerates nail growth. Conversely, immobility slows the growth rate of fingernails. Understanding the growth rate is important because the time interval from a critical event can be estimated from the location of a nail lesion. For example, a white line appearing transversely halfway up the nail suggests an acute illness 3 months earlier. Regular observation will demonstrate its progression to the end of the nail edge. Nail Polish
5 Page 5 of 30 Distance from base and line of polish gives approximate date of application (nails grow 0.1 mm/day). Picking at polish reflects nervousness and agitation. Toenail polish suggests unusual flexibility or a friendly helper. Observing the Nail Shape and Surface Clubbed Fingernails Clubbing involves a softening of the nail bed with the loss of normal Lovibond angle between the nail bed and the fold, an increase in the nail fold convexity, and a thickening of the end of the finger so it resembles a drumstick. To determine whether nails are clubbed, have the patient place both forefinger nails together and look between them. If you can see a small diamond space between them (Schamroth's window) then the nails are not clubbed (Schamroth's sign) (Figure 2). Figure 2. Schamroth's sign. Causes of clubbing (not exhaustive) include the following (Figure 3): Pulmonary and cardiovascular causes (80%) Lung cancer, pulmonic abscess, interstitial pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, beryllium poisoning, pulmonary arteriovenous fistula, subacute bacterial endocarditis, infected arterial grafts, aortic aneurysm Gastrointestinal causes (about 5%) Inflammatory bowel disease, sprue, neoplasms (esophagus, liver, bowel) Hyperthyroidism (about 1%) Note: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease does not cause clubbing.
6 Page 6 of 30 Koilonychia Figure 3. Example of clubbed fingernails. Koilonychia are spoon-shaped concave nails (Figures 4A, 4B). This occurs normally in children and usually resolves with aging. To determine whether a nail is spooned, perform the water drop test. Place a drop of water on the nail. If the drop does not slide off, then the nail is flattened from early spooning. An experienced clinician can look at the nail and perform a "mental" water drop test. Causes include the following: Iron deficiency; Diabetes mellitus; Protein deficiency, especially in sulfur-containing amino acids (cysteine or methionine); Exposure to petroleum-based solvents; Systemic lupus erythematosus; and Raynaud's disease.
7 Page 7 of 30 Figure 4A. Spooned nail. Figure 4B. Spooned nail. In 1846, Joseph Honoré Simon Beau described transverse lines in the substance of the nail as signs of previous acute illness. The lines look as if a little furrow had been plowed across the nail. Illnesses producing Beau's lines include the following: Severe infection; Myocardial infarction; Hypotension, shock; Hypocalcemia; and Surgery. Intermittent doses of immunosuppressive therapy or chemotherapy can also produce Beau's lines. Severe zinc deficiency has also been proposed as a cause of Beau's lines. By noting its location on the nail, the approximate date of the illness associated with it can be determined (Figures 5A, 5B). Moreover, the depth of the line provides a clue to the severity of the illness.
8 Page 8 of 30 Figure 5A. The location of Beau's lines half way up the nail suggests illness 3 months ago. Figure 5B. Two Beau's lines suggest illnesses about 2 months apart. Thin Brittle Nails Thin, brittle nails can indicate the following (Figure 6): Metabolic bone disease (nail thinness is correlated with osteopenia); Thyroid disorder; Systemic amyloidosis (indicated by yellow waxy flaking); and Severe malnutrition.
9 Page 9 of 30 Figure 6. Note the thin nails in this woman with severe osteopenia. Onychorrhexis is the presence of longitudinal striations or ridges (Figure 7). It can simply be a sign of advanced age but it can also occur with the following: Rheumatoid arthritis; Peripheral vascular disease; Lichen planus; and Darier's disease (striations are red/white). Central ridges can be caused by: Iron deficiency; Folic acid deficiency; and Protein deficiency.
10 Page 10 of 30 Figure 7. Example of a central nail ridge. Central Nail Canal (Median Nail Dystrophy) When a central nail canal is present, the cuticle is usually normal (Figure 8A). Central nail canal is associated with: Severe arterial disease ("Heller's fir tree deformity" -- a central canal with a fir tree appearance -- may occur with peripheral artery disease (Figure 8B); Severe malnutrition; and Repetitive trauma. Figure 8A. Example of central nail canal. Nail Pitting Figure 8B. Central nail canal with Heller's fir tree deformity.
11 Page 11 of 30 Nail pitting -- small punctate depressions -- are caused by nail matrix inflammation, which can be the result of: Psoriasis (random appearance of pits) (Figure 9); Alopecia areata (geometric rippled grid) (Figure 10); Eczema; and Lichen planus. Figure 9. Indication of psoriasis.
12 Page 12 of 30 Figure 10. Indication of alopecia areata. Nail Beading With nail beading, the beads seem to drip down the nail like wax (Figure 11). It is associated with endocrine conditions, including the following: Diabetes mellitus; Thyroid disorders; Addison's disease; and Vitamin B deficiency. Figure 11. Nail beading. Rough Nail Surface When nails look sandpapered and dull, consider (Figure 12):
13 Page 13 of 30 Autoimmune disease; Psoriasis; Chemical exposure; and Lichen planus. Figure 12. Example of a rough nail surface. Nail Thickening Slow nail growth produces thickness (Figure 13). In such cases, the following should be considered: Onychomycosis; Chronic eczema; Peripheral vascular disease; Yellow nail syndrome; and Psoriasis.
14 Page 14 of 30 Figure 13. Example of a nail thickening. Onycholysis Onycholysis is distal separation of the nail plate from the underlying nail bed (Figure 14). It is associated with the following: Thyrotoxicosis; Psoriasis; Trauma; Contact dermatitis; Tetracycline; Eczema; Toxic exposures (solvents); Blistering from autoimmune disease; and Porphyria cutanea tarda (onycholysis and skin blistering from sun exposure).
15 Page 15 of 30 Figure 14. Traumatic onycholysis (involving only 1 nail). Severe Nail Curvature (Beaked Nails) Curved or beaked nails are caused by resorption of distal digit (Figure 15). Consider the following: Hyperparathyroidism Renal failure Psoriasis Systemic sclerosis Figure 15. Example of severe nail curvature. Complete Nail Destruction Complete local nail destruction can be caused by local mechanisms, including trauma and paronychia. Generalized
16 Page 16 of 30 conditions that might cause complete nail destruction include the following: Toxic epidermal necrolysis; Chemotherapy; Bullous diseases; and Vasculitis. Observing Nail Color Abnormalities of the Lunula If the lunula is absent, consider anemia or malnutrition (Figure 16). A pyramidal lunula might indicate excessive manicure or trauma (Figure 17). A pale blue lunula suggests diabetes mellitus. If the lunula has red discoloration, consider the following causes among others (Figure 18): Cardiovascular disease; Collagen vascular disease; and Hematologic malignancy. Figure 16. Absent lunula.
17 Page 17 of 30 Figure 17. Pyramidal lunula. Figure 18. Lunula with red discoloration. Transverse White Lines (Mee's lines) Any acute illness can produce transverse milky white lines. In addition, they might be caused by heavy metal toxicity (classically arsenic) or chemotherapy. The time of event may be determined from the location of the lines on nail (Figure 19).
18 Page 18 of 30 Figure 19. Note the Mee's line approximately one third of the way up the nail, suggesting a significant illness 2 months previously. Leukonychia Striae Leukonychia striae are white splotches caused by minor trauma to the nail matrix (Figure 20). The timing can be determined by the location of the splotches on the nail. Figure 20. Example of leukonychia striae. Note location of white splotches, which can indicate timing of the traumatic event. Longitudinal Brown Lines Longitudinal brown lines form because of increased melanin produced by nail matrix melanocytes (Figure 21). They are associated with: Addison's disease; Nevus at the nail base; Breast cancer;
19 Page 19 of 30 Melanoma (check for periungal pigmentation); and Trauma. Figure 21. Longitudinal brown lines. Splinter Hemorrhages Splinter hemorrhages are caused by hemorrhage of the distal capillary loop (Figure 22). Note the thickness of these areas. They are associated with the following: Subacute bacterial endocarditis; Systemic lupus erythematosus; Trichinosis; Pityriasis rubra pilaris; Psoriasis; and Renal failure.
20 Page 20 of 30 Figure 22. Splinter hemorrhages tend to be fat. Terry's Half and Half Nails With Terry's half and half nails, the proximal portion is white (edema and anemia) and the distal portion is dark. These nails imply either renal or liver disease (Figures 23A, 23B). Figure 23A. This example of Terry's half and half nails suggests liver disease (no brown lines).
21 Page 21 of 30 Figure 23B. Half and half nails imply renal disease when there is a brown band at the junction of the erythema and the free edge. Image courtesy of Used with permission. Generalized Discolorations of the Nail Plate Nail discoloration is a useful method for identifying potential problems. White Nails White nails can be caused by anemia, edema, or vascular conditions (Figure 24). Consider the following: Anemia; Renal failure; Cirrhosis; Diabetes mellitus; Chemotherapy; and Hereditary (rare).
22 Page 22 of 30 Figure 24. Example of white nails. Pink or Red Nails With pink or red nail discoloration, the following should be considered (Figure 25): Polycythemia (dark); Systemic lupus erythematosus; Carbon monoxide (cherry red); Angioma; and Malnutrition. Figure 25. Example of pink and red nails. Brown-Gray Nails Brown-gray nails may suggest the following (Figure 26): Cardiovascular disease; Diabetes mellitus; Vitamin B12 deficiency; Breast cancer; Malignant melanoma; Lichen planus; Syphilis; and Topical agents, including hair dyes, solvents for false nails, varnish, and formaldehyde (among many others)
23 Page 23 of 30 Figure 26. Example of brown-gray nails. Yellow Nails Yellow nails suggest the following (Figure 27): Diabetes mellitus; Amyloidosis; Median/ulnar nerve injury; Thermal injury; and Jaundice. Consider yellow nail syndrome if a patient has lymphedema and bronchiectasis. Figure 27. Example of yellow nails. Image courtesy of Used with permission. Green or Black Nails
24 Page 24 of 30 Green or black nails indicate the following (Figure 28): Topical preparations, including chlorophyll derivations, methyl green, and silver nitrate (among others); Chronic Pseudomonas spp infection; and Trauma. Figure 28. Example of black nails. Processes Around the Nail Paronychial Inflammation Paronychia is associated with separation of the seal between the proximal nail fold and the nail plate that provides entry for bacteria and leads to a localized infection of the paronychial tissues of the hands (Figure 29). Symptoms may include inflammation, swelling, and/or scaling.
25 Page 25 of 30 Figure 29. Example chronic paronychial inflammation. Periungal Telangeictasia Periungal telangeictasia is caused by dilated capillary loops and results in atrophy of the cuticle (Figure 30). It is strongly associated with collagen vascular disease, including the following: Systemic lupus erythematosus; Dermatomyositis (especially with Gotton's papules over knuckles); and Scleroderma. Mucus Cyst Figure 30. Example of periungal telangeictasia. Image courtesy of Used with permission. A mucous or myxoid cyst is a collection of degenerative collagen that can cause swelling and ridging of the nail above the cyst, forming a "gutter" (Figure 31).
26 Page 26 of 30 Figure 31. Example of a mucus cyst. Cases The following are examples of patients in whom examining the fingernails may help identify their conditions.
27 Page 27 of 30 Slide year-old with multiple conditions. Slide year-old man with a painful ankle.
28 Page 28 of 30 Slide year-old man with esophageal cancer. Slide year-old woman with dermatomyositis. Acknowledgments The author would like to thank the University of Virginia GME Office for funding support; Jim Thomas, MD, of for permission to use images from their extensive dermatologic atlas; and the internal medicine residents at the University of Virginia for pre-testing and their helpful feedback.
29 Page 29 of 30 References [ CLOSE WINDOW ] References 1. Baran R, Dawber RPR, De Berker D, Haneke E, Tosti A, eds. Baran & Dawber's Diseases of the Nails and Their Management. 3rd ed. London, UK: Blackwell Publishing; Fawcett RS, Lindford S, Stulberg DL. Nail abnormalities: clues to systemic disease. Am Fam Physician. 2004;69: Abstract 3. Koler RA, Montemarano A. Dermatomyositis. Am Fam Physician. 2001;64: Abstract 4. Longshore TS, Tomecky KJ. Nail disease: signs for the internist. Cleveland Clinic Web site. Available at: dermatology/naildisease/naildisease.htm Accessed March 2, Fleckman P, Lee J, Astion ML. Nail-Tutor: an image-based personal computer program that teaches the anatomy, patterns of pathology, and disorders of the nails. Dermatology Online Journal. 1997;3 (2):2. Available at: Accessed March 2, Rich P, Scher RK. An Atlas of Diseases of the Nail. Boca Raton, Fla: CRC Press; Encyclopedia of Visual Medicine Series; vol Rockwell PG. Acute and chronic paronychia. Am Fam Physician. 2001;63: Abstract 8. Williams ME. Assessing the hands and wrists in elderly people Medscape. Available at: Accessed March 2, Williams ME. Geriatric Physical Diagnosis: A Guide to Observation and Assessment. Jefferson, NC: McFarland and Company, Inc. Publishers; Authors and Disclosures As an organization accredited by the ACCME, Medscape, LLC requires everyone who is in a position to control the content of an education activity to disclose all relevant financial relationships with any commercial interest. The ACCME defines "relevant financial relationships" as financial relationships in any amount, occurring within the past 12 months, including financial relationships of a spouse or life partner, that could create a conflict of interest. Medscape, LLC encourages Authors to identify investigational products or off-label uses of products regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration, at first mention and where appropriate in the content. Author Mark E. Williams, MD Ward K. Ensminger Distinguished Professor of Geriatric Medicine, University of Virginia, University of Virginia Healthsystem, Charlottesville, Virginia; Attending Physician, University of Virginia Healthsystem, Charlottesville, Virginia Disclosure: Mark E. Williams, MD, has disclosed that he is a Co-Founder and Chief Scientist of BioMotion Analytics, LLC. Dr. Williams has also disclosed that he owns stock, stock options, or bonds for BioMotion Analytics, LLC. Editor Carol Peckham
30 Page 30 of 30 Director, Editorial Development, Medscape, LLC Disclosure: Carol Peckham has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Registration for CME credit, the post test and the evaluation must be completed online. To access the activity Post Test and Evaluation link, please go to:
Nail Biology: The Nail Apparatus. Nail plate Proximal nail fold Nail matrix Nail bed Hyponychium
 Nail Biology: The Nail Apparatus Nail plate Proximal nail fold Nail matrix Nail bed Hyponychium Nail Biology: The Nail Apparatus Lies immediately above the periosteum of the distal phalanx The shape
Nail Biology: The Nail Apparatus Nail plate Proximal nail fold Nail matrix Nail bed Hyponychium Nail Biology: The Nail Apparatus Lies immediately above the periosteum of the distal phalanx The shape
Nail diseases This page outlines the terms used by dermatologists to describe diseases of the fingernails and toenails.
 Nail diseases This page outlines the terms used by dermatologists to describe diseases of the fingernails and toenails. Abnormalities of the nail plate surface Nail discolouration Abnormalities of the
Nail diseases This page outlines the terms used by dermatologists to describe diseases of the fingernails and toenails. Abnormalities of the nail plate surface Nail discolouration Abnormalities of the
Nails Examination and Disorders. Overview. Case 1 15/09/2016. Samantha Eisman. 25 year old woman Noticed at pedicure Single toe
 Nails Examination and Disorders Samantha Eisman Dermatologist MBChB/ MRCP/ FCDerm(SA)/ FACD Demystify nails Overview QUIZ Talk Examination nails and and site specific disease QUIZ answers and cover common
Nails Examination and Disorders Samantha Eisman Dermatologist MBChB/ MRCP/ FCDerm(SA)/ FACD Demystify nails Overview QUIZ Talk Examination nails and and site specific disease QUIZ answers and cover common
PERDUE NFPE: Tongue
 NFPE: Tongue NFPE: Nail Reference Guide Techniques: Inspection: Inspect the shape of the nails for - spooning - abnormal color or color patterns - splinter hemorrhages - white spots - presence of the lunula
NFPE: Tongue NFPE: Nail Reference Guide Techniques: Inspection: Inspect the shape of the nails for - spooning - abnormal color or color patterns - splinter hemorrhages - white spots - presence of the lunula
Chapter 10 Nail Disorders & Diseases
 Chapter 10 Nail Disorders & Diseases MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The surface of a healthy natural nail should be. a. smooth and spotted b. flexible and spotted c. smooth and unspotted d. pitted and rough ANS: C
Chapter 10 Nail Disorders & Diseases MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The surface of a healthy natural nail should be. a. smooth and spotted b. flexible and spotted c. smooth and unspotted d. pitted and rough ANS: C
Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious, Inflammatory and Neoplastic Nail Conditions
 OFFICE DERMATOLOGY, PART I 0025-7125/98 $8.00 +.OO NAIL DISORDERS Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious, Inflammatory and Neoplastic Nail Conditions Phoebe Rich, MD Nail problems (Table 1) are common complaints
OFFICE DERMATOLOGY, PART I 0025-7125/98 $8.00 +.OO NAIL DISORDERS Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious, Inflammatory and Neoplastic Nail Conditions Phoebe Rich, MD Nail problems (Table 1) are common complaints
Reduced Carbohydrate Intake May Lower Cardiovascular Risk CME
 To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/516977 This activity is supported by funding from WebMD. Reduced
To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/516977 This activity is supported by funding from WebMD. Reduced
Nail Matrix Disorders Nail Fold Disorders Nail Bed Disorders Nail Plate Disorders
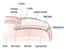 The most commonly reported nail conditions, seen by podiatrists, are: Onychocryptosis, 26% Onychauxis & onychogryphosis 22.8% Onychophosis 18.8% Onychomycosis 8.3% Nail Matrix Disorders Nail Fold Disorders
The most commonly reported nail conditions, seen by podiatrists, are: Onychocryptosis, 26% Onychauxis & onychogryphosis 22.8% Onychophosis 18.8% Onychomycosis 8.3% Nail Matrix Disorders Nail Fold Disorders
The Integumentary System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
Internal medicine and medical investigation (ISSN: ) May 2017, Volume:2, Issue:2, Page: 57-62
 Internal medicine and medical investigation (ISSN: 2474-7750) www.imminv.com May 2017, Volume:2, Issue:2, Page: 57-62 Determining the Prevalence and Types of Nail Involvement in Patients with Severe Acne
Internal medicine and medical investigation (ISSN: 2474-7750) www.imminv.com May 2017, Volume:2, Issue:2, Page: 57-62 Determining the Prevalence and Types of Nail Involvement in Patients with Severe Acne
This article is a CME certified activity. To earn credit for this activity visit: /viewarticle/758676
 This article is a CME certified activity. To earn credit for this activity visit: /viewarticle/758676 CME Information CME Released: 02/15/2012; Valid for credit through 02/15/2013 Target Audience www.medscape.org
This article is a CME certified activity. To earn credit for this activity visit: /viewarticle/758676 CME Information CME Released: 02/15/2012; Valid for credit through 02/15/2013 Target Audience www.medscape.org
Poonkiat Suchonwanit, MD Hair and Scalp Disorders Unit Division of Dermatology Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital
 Poonkiat Suchonwanit, MD Hair and Scalp Disorders Unit Division of Dermatology Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital Hair loss Excessive hair growth Hair haft abnormalities Hair color Anagen Catagen
Poonkiat Suchonwanit, MD Hair and Scalp Disorders Unit Division of Dermatology Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital Hair loss Excessive hair growth Hair haft abnormalities Hair color Anagen Catagen
2 Anonychia/Micronychia
 2 Anonychia/Micronychia Total or partial absence of the nail May be congenital or acquired Table 2.1. Causes of anonychia/micronychia Congenital Acquired Trauma Amniotic bands Bullous Teratogens (drugs,
2 Anonychia/Micronychia Total or partial absence of the nail May be congenital or acquired Table 2.1. Causes of anonychia/micronychia Congenital Acquired Trauma Amniotic bands Bullous Teratogens (drugs,
Phoebe Rich MD Adjunct Professor OHSU Portland, Oregon
 Nail Tips for Diagnosis and Management of Nail Disorders Winter Clinical Dermatology Conference 2017 Hawaii Phoebe Rich MD Adjunct Professor OHSU Portland, Oregon Objectives diagnostic clues for benign
Nail Tips for Diagnosis and Management of Nail Disorders Winter Clinical Dermatology Conference 2017 Hawaii Phoebe Rich MD Adjunct Professor OHSU Portland, Oregon Objectives diagnostic clues for benign
Classification. Distal & Lateral Subungual OM. White Superficial OM. Proximal Subungual OM. Candidal OM. Total dystrophic OM
 Onychomycosis Commonest dermatological condition Definition: Infection of the nail caused by fungi that include dermatophytes, non-dermatophyte moulds and yeasts (mainly Candida). 80% of all OM affects
Onychomycosis Commonest dermatological condition Definition: Infection of the nail caused by fungi that include dermatophytes, non-dermatophyte moulds and yeasts (mainly Candida). 80% of all OM affects
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Foley P, Gordon K, Griffiths, CEM, et al. Efficacy of guselkumab compared with adalimumab and placebo for psoriasis in specific body regions: a secondary analysis of 2 randomized
Supplementary Online Content Foley P, Gordon K, Griffiths, CEM, et al. Efficacy of guselkumab compared with adalimumab and placebo for psoriasis in specific body regions: a secondary analysis of 2 randomized
HMCL312. Session 8 Nail signs.
 HMCL312 Session 8 Nail signs www.endeavour.edu.au SN08 Overview Nutrient deficiency and disease associated Nail Diagnosis Pre-Assessment Considerations: o Working hypothesis of the pattern of disturbance
HMCL312 Session 8 Nail signs www.endeavour.edu.au SN08 Overview Nutrient deficiency and disease associated Nail Diagnosis Pre-Assessment Considerations: o Working hypothesis of the pattern of disturbance
Nail Disorders. Disclosure Statement: Objectives. Normal Nail Anatomy. Normal Nail Anatomy
 Nail Disorders Disclosure Statement: Co-Author, Dermatologic and Cosmetic Procedures in Office Practice. Elsevier, Inc., Philadelphia. 2012. Cutaneous Cryosurgery Fourth EditionCRC press 2014 Daniel Stulberg,
Nail Disorders Disclosure Statement: Co-Author, Dermatologic and Cosmetic Procedures in Office Practice. Elsevier, Inc., Philadelphia. 2012. Cutaneous Cryosurgery Fourth EditionCRC press 2014 Daniel Stulberg,
Chapter 05. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Study of the Nail. Copyright 2013 SAP
 Study of the Nail Copyright 2013 SAP THE NAIL An appendage of the skin, this horny, translucent plate protects the tips of fingers and toes. Onyx is the technical term for the nail. The nail is composed
Study of the Nail Copyright 2013 SAP THE NAIL An appendage of the skin, this horny, translucent plate protects the tips of fingers and toes. Onyx is the technical term for the nail. The nail is composed
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 4
 *We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
*We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
B. Incorrect! The ectoderm does not produce the dermis. C. Incorrect! The dermis is derived from the mesoderm.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
This article is a CME certified activity. To earn credit for this activity visit:
 This article is a CME certified activity. To earn credit for this activity visit: http://cme.medscape.com/viewarticle/716379 cme.medscape.com From MedscapeCME Clinical Briefs Exercise May Improve Cognitive
This article is a CME certified activity. To earn credit for this activity visit: http://cme.medscape.com/viewarticle/716379 cme.medscape.com From MedscapeCME Clinical Briefs Exercise May Improve Cognitive
Presentation Notes Be Visually Aware Nail Diseases and Disorders. Be Visually Aware. Nail Diseases and Disorders
 Slide 1 Be Visually Aware Nail Diseases and Disorders Page1 Slide 2 Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2013. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education
Slide 1 Be Visually Aware Nail Diseases and Disorders Page1 Slide 2 Copyright Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2013. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education
The Nail Common terms & Anatomy Onychomycosis Causes and Background Onychomycosis Classification Treatment Basics
 FOX Podiatry Applications The Nail Common terms & Anatomy Onychomycosis Causes and Background Onychomycosis Classification Treatment Basics The Nail - Areas definitions Proximal nail fold Nail plate area
FOX Podiatry Applications The Nail Common terms & Anatomy Onychomycosis Causes and Background Onychomycosis Classification Treatment Basics The Nail - Areas definitions Proximal nail fold Nail plate area
3 section of the Foot
 TERMINOLOGY 101 How many Bones 3 section of the Foot Bilateral Relating to both Plantar Relating to the bottom or sole Lateral Relating to the outside or farther from the median Medial Relating to the
TERMINOLOGY 101 How many Bones 3 section of the Foot Bilateral Relating to both Plantar Relating to the bottom or sole Lateral Relating to the outside or farther from the median Medial Relating to the
Chapter 4 Opener Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
1 Assessment Techniques General Survey Skin, Hair, and Nails. 2 Cultivating Your Senses
 1 Assessment Techniques General Survey Skin, Hair, and Nails 2 Cultivating Your Senses Inspection Always performed first Palpation Purpose Use different parts of the hands Light vs. deep palpation 3 Cultivating
1 Assessment Techniques General Survey Skin, Hair, and Nails 2 Cultivating Your Senses Inspection Always performed first Palpation Purpose Use different parts of the hands Light vs. deep palpation 3 Cultivating
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
Integumentary System
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Internal Medicine Certification Examination Blueprint
 Internal Medicine Certification Examination Blueprint What Does the Examination Cover? The exam is designed to evaluate the extent of the candidate s knowledge and clinical judgment in the areas in which
Internal Medicine Certification Examination Blueprint What Does the Examination Cover? The exam is designed to evaluate the extent of the candidate s knowledge and clinical judgment in the areas in which
PEDIATRIC & ADOLESCENT MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: GASTROENTEROLOGY/GYNECOLOGY/PSYCHIATRY/ RHEUMATOLOGY
 PEDIATRIC & ADOLESCENT MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: GASTROENTEROLOGY/GYNECOLOGY/PSYCHIATRY/ RHEUMATOLOGY San Juan, Puerto Rico The Ritz-Carlton, San Juan March 15 18, 2018 Thursday, March 15th: 7:30 am 8:00
PEDIATRIC & ADOLESCENT MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: GASTROENTEROLOGY/GYNECOLOGY/PSYCHIATRY/ RHEUMATOLOGY San Juan, Puerto Rico The Ritz-Carlton, San Juan March 15 18, 2018 Thursday, March 15th: 7:30 am 8:00
NAIL SURGERY TECHNIQUES
 NAIL SURGERY TECHNIQUES TRACEY C. VLAHOVIC, DPM FFPM RCPS (GLASG) ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, J STANLEY AND PEARL LANDAU FACULTY FELLOW TEMPLE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF PODIATRIC MEDICINE, PHILA, PA THE AGENDA Pincer
NAIL SURGERY TECHNIQUES TRACEY C. VLAHOVIC, DPM FFPM RCPS (GLASG) ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, J STANLEY AND PEARL LANDAU FACULTY FELLOW TEMPLE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF PODIATRIC MEDICINE, PHILA, PA THE AGENDA Pincer
Nail Surface Topography and Onychochronobiology
 Nail Surface Topography and Onychochronobiology 40 Gérald E. Piérard and Claudine Piérard-Franchimont 40.1 Introduction Some chronic skin disorders are responsible for concurrent nail changes. Typical
Nail Surface Topography and Onychochronobiology 40 Gérald E. Piérard and Claudine Piérard-Franchimont 40.1 Introduction Some chronic skin disorders are responsible for concurrent nail changes. Typical
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition)
 Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Sialendoscopy and Minimally-Invasive Salivary Gland Surgery
 05.22.2016 Sialendoscopy and Minimally-Invasive Salivary Gland Surgery Hosted by: NorthShore Grainger Center for Simulation and Innovation (NCSI) NorthShore University Health System Evanston Hospital 2650
05.22.2016 Sialendoscopy and Minimally-Invasive Salivary Gland Surgery Hosted by: NorthShore Grainger Center for Simulation and Innovation (NCSI) NorthShore University Health System Evanston Hospital 2650
The Integumentary System: An Overview
 The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
GERIATRIC MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: NEUROLOGY/PALLIATIVE CARE/RHEUMATOLOGY. San Diego, California Hotel del Coronado October 26 28, 2018
 GERIATRIC MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: NEUROLOGY/PALLIATIVE CARE/RHEUMATOLOGY San Diego, California Hotel del Coronado October 26 28, 2018 Friday, October 26th: 7:00 am 7:30 am Registration and Hot Breakfast
GERIATRIC MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: NEUROLOGY/PALLIATIVE CARE/RHEUMATOLOGY San Diego, California Hotel del Coronado October 26 28, 2018 Friday, October 26th: 7:00 am 7:30 am Registration and Hot Breakfast
PEDIATRIC & ADOLESCENT MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: GASTROENTEROLOGY/NEUROLOGY/RHEUMATOLOGY
 PEDIATRIC & ADOLESCENT MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: GASTROENTEROLOGY/NEUROLOGY/RHEUMATOLOGY Quebec City, Quebec, Canada Fairmont Le Chateau Frontenac June 22 24, 2018 Friday, June 22nd: 7:30 am 8:00 am Registration
PEDIATRIC & ADOLESCENT MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: GASTROENTEROLOGY/NEUROLOGY/RHEUMATOLOGY Quebec City, Quebec, Canada Fairmont Le Chateau Frontenac June 22 24, 2018 Friday, June 22nd: 7:30 am 8:00 am Registration
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY
 CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
11/8/2012. Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane. The Structure of Skin. Epidermis
 Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
PEDIATRIC & ADOLESCENT MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: DERMATOLOGY/EMERGENCY MEDICINE/RHEUMATOLOGY
 PEDIATRIC & ADOLESCENT MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: DERMATOLOGY/EMERGENCY MEDICINE/RHEUMATOLOGY Napa Valley/Sonoma, California The Fairmont Sonoma Mission Inn & Spa October 5 7, 2018 Friday, October 5th:
PEDIATRIC & ADOLESCENT MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: DERMATOLOGY/EMERGENCY MEDICINE/RHEUMATOLOGY Napa Valley/Sonoma, California The Fairmont Sonoma Mission Inn & Spa October 5 7, 2018 Friday, October 5th:
Skin and Body Membranes
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
Chapter 12 - Vital_Signs_and_Monitoring_Devices
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 12.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 13 15, 17, 21 22, 26, 28, 30, 32 33, 35, 44, 47 48, 50, 55, 60 12.2 Identify the vital signs
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 12.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 13 15, 17, 21 22, 26, 28, 30, 32 33, 35, 44, 47 48, 50, 55, 60 12.2 Identify the vital signs
CUMULATIVE ILLNESS RATING SCALE (CIRS)
 CUMULATIVE ILLNESS RATING SCALE (CIRS) The CIRS used in this protocol is designed to provide an assessment of recurrent or ongoing chronic comorbid conditions, classified by 14 organ systems. Using the
CUMULATIVE ILLNESS RATING SCALE (CIRS) The CIRS used in this protocol is designed to provide an assessment of recurrent or ongoing chronic comorbid conditions, classified by 14 organ systems. Using the
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
B. Connective tissue membranes lubricate & cushion 1. made of areolar tissue 2. synovial line fibrous joint capsules & secrete fluid
 I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
Let's Nail It! Nail Workshop Hospital Kuala Lumpur & Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Center
 10 CPD points awarded Theme Organized by Let's Nail It! Dermatological Society of Malaysia Department of Dermatology, Hospital Kuala Lumpur Dermatology Unit, National University of Malaysia The speaker:
10 CPD points awarded Theme Organized by Let's Nail It! Dermatological Society of Malaysia Department of Dermatology, Hospital Kuala Lumpur Dermatology Unit, National University of Malaysia The speaker:
INTERNAL MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: ORTHOPEDICS/RHEUMATOLOGY/DERMATOLOGY
 INTERNAL MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: ORTHOPEDICS/RHEUMATOLOGY/DERMATOLOGY Las Vegas, Nevada The Bellagio December 28 30, 2014 Participating Faculty Tanya Doan, MDCM Rheumatologist PMG Physician Associates,
INTERNAL MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: ORTHOPEDICS/RHEUMATOLOGY/DERMATOLOGY Las Vegas, Nevada The Bellagio December 28 30, 2014 Participating Faculty Tanya Doan, MDCM Rheumatologist PMG Physician Associates,
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System. Skin Cells. Layers of Skin. Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer beneath dermis not part of skin
 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
THE TONGUE. In Clinical Diagnosis
 THE TONGUE In Clinical Diagnosis A Colour Atlas of The Tongue in Clinical Diagnosis D.W. BEAVEN S.E. BROOKS BATES Guide to Physical Examination Lynn s. Bickley רויטל רחימי, תום כספי פנימית ב', תל-השומר
THE TONGUE In Clinical Diagnosis A Colour Atlas of The Tongue in Clinical Diagnosis D.W. BEAVEN S.E. BROOKS BATES Guide to Physical Examination Lynn s. Bickley רויטל רחימי, תום כספי פנימית ב', תל-השומר
Hair and Nail Disorders
 Hair and Nail Disorders E.J. Mayeaux, Jr., M.D., FAAFP Professor of Family Medicine Professor of Obstetrics/Gynecology Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Shreveport, LA Hair Classification
Hair and Nail Disorders E.J. Mayeaux, Jr., M.D., FAAFP Professor of Family Medicine Professor of Obstetrics/Gynecology Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Shreveport, LA Hair Classification
Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function.
 Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Nail Rounds for the PCP
 Nail Rounds for the PCP Learning Objectives 1. Identify pathognomonic physical features from nails 2. Develop a differential diagnosis from such findings Faculty Salvatore Mangione, MD Associate Professor
Nail Rounds for the PCP Learning Objectives 1. Identify pathognomonic physical features from nails 2. Develop a differential diagnosis from such findings Faculty Salvatore Mangione, MD Associate Professor
2018 Surgical Pathology Update: Diagnostic Pearls for the Practicing Pathologist - Volume II
 Release Date: January 1, 15.25 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s) TM About This CME Teaching Activity This CME Activity is designed to provide a comprehensive review of soft tissue, gastrointestinal, genitourinary,
Release Date: January 1, 15.25 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s) TM About This CME Teaching Activity This CME Activity is designed to provide a comprehensive review of soft tissue, gastrointestinal, genitourinary,
Skin Basics. About skin. Reviewed By: Kimberly Bazar, M.D., AAD Mary Ellen Luchetti, M.D., AAD
 Page 1 of 5 Skin Basics Reviewed By: Kimberly Bazar, M.D., AAD Mary Ellen Luchetti, M.D., AAD Summary The skin is the largest organ in the body. It consists of three layers the epidermis, the dermis and
Page 1 of 5 Skin Basics Reviewed By: Kimberly Bazar, M.D., AAD Mary Ellen Luchetti, M.D., AAD Summary The skin is the largest organ in the body. It consists of three layers the epidermis, the dermis and
Pain Management Overview Information
 Pain Management Overview Information Format Clinical Review Time to Complete 12.00 hours Released August 15, 2014 Expires August 15, 2017 MAXIMUM CREDITS 12.00 / AMA PRA Category 1 Credits TM 12.00 / CE
Pain Management Overview Information Format Clinical Review Time to Complete 12.00 hours Released August 15, 2014 Expires August 15, 2017 MAXIMUM CREDITS 12.00 / AMA PRA Category 1 Credits TM 12.00 / CE
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
DERMOSCOPY. October 23-24, 2015 INTERMEDIATE COURSE. 11th Annual. New York. is pleased to announce:
 is pleased to announce: October 23-24, 2015 11th Annual INTERMEDIATE COURSE COURSE LOCATION Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center ZUCKERMAN RESEARCH CENTER 417 East 68th Street between First and York
is pleased to announce: October 23-24, 2015 11th Annual INTERMEDIATE COURSE COURSE LOCATION Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center ZUCKERMAN RESEARCH CENTER 417 East 68th Street between First and York
PEDIATRIC & ADOLESCENT MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: ENDOCRINOLOGY/GYNECOLOGY/INFECTIOUS DISEASE. Scottsdale, Arizona The Phoenician February 8 10, 2019
 PEDIATRIC & ADOLESCENT MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: ENDOCRINOLOGY/GYNECOLOGY/INFECTIOUS DISEASE Scottsdale, Arizona The Phoenician February 8 10, 2019 Friday, February 8th: 7:00 am 7:30 am Registration and
PEDIATRIC & ADOLESCENT MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE: ENDOCRINOLOGY/GYNECOLOGY/INFECTIOUS DISEASE Scottsdale, Arizona The Phoenician February 8 10, 2019 Friday, February 8th: 7:00 am 7:30 am Registration and
RELEVANT MEDICAL TERMS AND CONDITIONS
 Acrokeratosis Paraneoplastica Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, Bazex syndrome (also known as acrokeratosis paraneoplastica of Bazex and acrokeratosis neoplastica) is a cutaneous condition characterized by
Acrokeratosis Paraneoplastica Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, Bazex syndrome (also known as acrokeratosis paraneoplastica of Bazex and acrokeratosis neoplastica) is a cutaneous condition characterized by
Geriatrics For Primary Care Providers
 Excellence. Compassion. Longevity Geriatrics For Primary Care Providers SATURDAY, JUNE 23, 2018, 8 a.m. 4 p.m. MD Anderson Mitchell Basic Science Research Building Onstead Auditorium, 3rd Floor 6767 Bertner
Excellence. Compassion. Longevity Geriatrics For Primary Care Providers SATURDAY, JUNE 23, 2018, 8 a.m. 4 p.m. MD Anderson Mitchell Basic Science Research Building Onstead Auditorium, 3rd Floor 6767 Bertner
Color Atlas of Nails
 Color Atlas of Nails Bearbeitet von Antonella Tosti, C Ralph Daniel III, Bianca Maria Piraccini, Matilde Iorizzo 1. Auflage 2009. Buch. viii, 114 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 540 79049 5 Format (B x L): 19,3
Color Atlas of Nails Bearbeitet von Antonella Tosti, C Ralph Daniel III, Bianca Maria Piraccini, Matilde Iorizzo 1. Auflage 2009. Buch. viii, 114 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 540 79049 5 Format (B x L): 19,3
Surgical Correction of Severe Bilateral Thumb Pincer-Nail Deformity
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery September 2006 Surgical Correction of Severe Bilateral Thumb Pincer-Nail
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery September 2006 Surgical Correction of Severe Bilateral Thumb Pincer-Nail
Premium Specialty: Pediatrics
 Premium Specialty: Pediatrics Credentialed Specialties include: Adolescent Medicine, Pediatric Adolescent, and Pediatrics This document is designed to be used in conjunction with the UnitedHealth Premium
Premium Specialty: Pediatrics Credentialed Specialties include: Adolescent Medicine, Pediatric Adolescent, and Pediatrics This document is designed to be used in conjunction with the UnitedHealth Premium
Consists of dead cells Contains hard kera=n; more than soj kera=n of skin Hair pigments: (yellow, rust brown, black) Hair shaft
 10/1/14 Hair Aler=ng the body to presence of insects on the skin Guarding the scalp against physical trauma, heat loss, and sunlight 5 B Notes The Integumentary En=re surface except palms, soles, lips,
10/1/14 Hair Aler=ng the body to presence of insects on the skin Guarding the scalp against physical trauma, heat loss, and sunlight 5 B Notes The Integumentary En=re surface except palms, soles, lips,
The Integumentary System. Chapter 6
 The Integumentary System Chapter 6 What is the integumentary system? skin hair nails glands blood vessels sensory receptors What is your skin made of? 3 layers epidermis (outside) dermis (middle) subcutaneous
The Integumentary System Chapter 6 What is the integumentary system? skin hair nails glands blood vessels sensory receptors What is your skin made of? 3 layers epidermis (outside) dermis (middle) subcutaneous
The Integumentary System: ANATOMY Includes: - Skin (integument) MEMBRANES. PHYSIOLOGY (functions) Protection. EPITHELIAL (cont.
 Did you know. Membranes & The Integumentary System The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It has a surface area of about 25 square-feet! You shed about 1.5 pounds of skin particles each year.
Did you know. Membranes & The Integumentary System The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It has a surface area of about 25 square-feet! You shed about 1.5 pounds of skin particles each year.
This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur.
 Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
A Prospective Study of Nail Changes in Dermatological and Systemic Illnesses.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.2.DT2 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 A Prospective Study of Nail Changes in Dermatological and Systemic Illnesses. Sushil Rathi 1, Dharmendra Mishra
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.2.DT2 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 A Prospective Study of Nail Changes in Dermatological and Systemic Illnesses. Sushil Rathi 1, Dharmendra Mishra
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
Treatment of Chronic Idiopathic Onychodystrophy with Intake of Carotene-rich Food
 6 Treatment of Chronic Idiopathic Onychodystrophy with Intake of Carotene-rich Food Jin Young Jung, M.D., Mi Ryung Roh, M.D., Kee Yang Chung, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Dermatology and Cutaneous Biology
6 Treatment of Chronic Idiopathic Onychodystrophy with Intake of Carotene-rich Food Jin Young Jung, M.D., Mi Ryung Roh, M.D., Kee Yang Chung, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Dermatology and Cutaneous Biology
The nail, a fast-growing organ, is sensitive to
 Anatomical Changes in Retronychia and Onychomadesis Detected Using Ultrasound XIMENA WORTSMAN, MD, JACOBO WORTSMAN, MD, y ROBINSON GUERRERO, MD, z ROSAMARY SOTO, MD, y AND ROBERT BARAN, MD z The authors
Anatomical Changes in Retronychia and Onychomadesis Detected Using Ultrasound XIMENA WORTSMAN, MD, JACOBO WORTSMAN, MD, y ROBINSON GUERRERO, MD, z ROSAMARY SOTO, MD, y AND ROBERT BARAN, MD z The authors
CME/CE POSTTEST CME/CE QUESTIONS
 CME/CE POSTTEST CME/CE QUESTIONS Controlling Asthma Severity: Identifying Unmet Needs and Optimizing Therapeutic Options There are no fees for participating in and receiving continuing medical education
CME/CE POSTTEST CME/CE QUESTIONS Controlling Asthma Severity: Identifying Unmet Needs and Optimizing Therapeutic Options There are no fees for participating in and receiving continuing medical education
78 The Power of Peripheral Blood Smears-Apparent Diagnostic Clues (Part 1) Gene Gulati PhD, SH(ASCP)
 78 The Power of Peripheral Blood Smears-Apparent Diagnostic Clues (Part 1) Gene Gulati PhD, SH(ASCP) 2011 Annual Meeting Las Vegas, NV AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR CLINICAL PATHOLOGY 33 W. Monroe, Ste. 1600 Chicago,
78 The Power of Peripheral Blood Smears-Apparent Diagnostic Clues (Part 1) Gene Gulati PhD, SH(ASCP) 2011 Annual Meeting Las Vegas, NV AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR CLINICAL PATHOLOGY 33 W. Monroe, Ste. 1600 Chicago,
Allergy, Atopy and Skin Cancer
 M. Shane Cahpman, MD, MBA: Dartmouth School of Medicine Boni E. Elewski, MD: University of Alabama Kenneth J. Tomecki, MD: Cleveland Clinic Ted Rosen, MD: Baylor College of Medicine Clinical and Therapeutic
M. Shane Cahpman, MD, MBA: Dartmouth School of Medicine Boni E. Elewski, MD: University of Alabama Kenneth J. Tomecki, MD: Cleveland Clinic Ted Rosen, MD: Baylor College of Medicine Clinical and Therapeutic
PERSONALIZED PSYCHO-ONCOLOGY
 Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center is pleased to present: PERSONALIZED PSYCHO-ONCOLOGY A CASE-BASED APPROACH Saturday, October 12, 2019 Rockefeller Research Laboratories 430 East 67th Street New York,
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center is pleased to present: PERSONALIZED PSYCHO-ONCOLOGY A CASE-BASED APPROACH Saturday, October 12, 2019 Rockefeller Research Laboratories 430 East 67th Street New York,
Subungual blue naevus presenting with elkonyxis
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2016) 24, 87-91 Case Report Subungual blue naevus presenting with elkonyxis S Do an, N Atakan, H Khurami, O Gökoz, O Bitik Common blue naevi usually occur on the skin
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2016) 24, 87-91 Case Report Subungual blue naevus presenting with elkonyxis S Do an, N Atakan, H Khurami, O Gökoz, O Bitik Common blue naevi usually occur on the skin
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
HIV/AIDS in Practice. An Expert Commentary with Myron Cohen, MD. A Clinical Context Report
 HIV/AIDS in Practice An Expert Commentary with Myron Cohen, MD A Clinical Context Report Clinical Context: HIV/AIDS in Practice Expert Commentary Jointly Sponsored by: and Clinical Context: HIV/AIDS in
HIV/AIDS in Practice An Expert Commentary with Myron Cohen, MD A Clinical Context Report Clinical Context: HIV/AIDS in Practice Expert Commentary Jointly Sponsored by: and Clinical Context: HIV/AIDS in
Treatment of Chronic Paronychia: A Double Blind Comparative Clinical Trial Using Singly Vaseline, Nystatin and Fucidic Acid Ointment *
 Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications, 2013, 3, 250-255 Published Online December 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jcdsa) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jcdsa.2013.34038 Treatment
Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications, 2013, 3, 250-255 Published Online December 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jcdsa) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jcdsa.2013.34038 Treatment
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Body Membranes & Skin
 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
Introduction to feet and ageing. Dr Debbie Turner Arthritis Research UK Senior Lecturer in Podiatry Glasgow Caledonian University
 Introduction to feet and ageing Dr Debbie Turner Arthritis Research UK Senior Lecturer in Podiatry Glasgow Caledonian University Looking after your feet to reduce your risk of falling - Webinar 25 th June
Introduction to feet and ageing Dr Debbie Turner Arthritis Research UK Senior Lecturer in Podiatry Glasgow Caledonian University Looking after your feet to reduce your risk of falling - Webinar 25 th June
MKSAP 15. Performance Interpretation Guidelines with Norm Tables. Medical Knowledge Self-Assessment Program
 Medical Knowledge Self-Assessment Program Performance Interpretation Guidelines with Norm Tables MKSAP 15 Copyright 2010 American College of Physicians MKSAP 15 Performance Interpretation Guidelines with
Medical Knowledge Self-Assessment Program Performance Interpretation Guidelines with Norm Tables MKSAP 15 Copyright 2010 American College of Physicians MKSAP 15 Performance Interpretation Guidelines with
GERIATRIC MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE. Chicago, Illinois The Gwen, A Luxury Collection Hotel, Chicago June 22 24, 2018
 GERIATRIC MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE Chicago, Illinois The Gwen, A Luxury Collection Hotel, Chicago June 22 24, 2018 Friday, June 22nd: 7:30 am 8:00 am Registration and Hot Breakfast 8:00 am 9:00 am Faculty
GERIATRIC MEDICINE FOR PRIMARY CARE Chicago, Illinois The Gwen, A Luxury Collection Hotel, Chicago June 22 24, 2018 Friday, June 22nd: 7:30 am 8:00 am Registration and Hot Breakfast 8:00 am 9:00 am Faculty
Skin. the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight
 Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
InterQual Level of Care 2018 Index
 InterQual Level of Care 2018 Index Rehabilitation Criteria Index Words by Subset The Index is an alphabetical listing of conditions and/or diagnoses designed to guide the user to the criteria subset where
InterQual Level of Care 2018 Index Rehabilitation Criteria Index Words by Subset The Index is an alphabetical listing of conditions and/or diagnoses designed to guide the user to the criteria subset where
Goals and objectives 6/23/2018. Nail anatomy and nomenclature. David L. Kaplan, M.D.
 David L. Kaplan, M.D. Goals and objectives Become familiar with basic nail anatomy and nail physical examination Learn a systematic approach to identify source of nail changes Have a working differential
David L. Kaplan, M.D. Goals and objectives Become familiar with basic nail anatomy and nail physical examination Learn a systematic approach to identify source of nail changes Have a working differential
GLOSSARY. Leukonychia: Real or apparent whitening of the nail. plate. Lichen planus: An inflammatory, pruritic cutaneous
 82 DIAGNOSIS OF ONYCHOMYCOSIS AND OTHER NAIL DISORDERS GLOSSARY Acuminate papule: Tapered collection of pus or scale within or beneath the skin, often in a hair follicle or sweat pore. Alopecia areata:
82 DIAGNOSIS OF ONYCHOMYCOSIS AND OTHER NAIL DISORDERS GLOSSARY Acuminate papule: Tapered collection of pus or scale within or beneath the skin, often in a hair follicle or sweat pore. Alopecia areata:
RECOGNIZING & ASSESSING COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT SYMPOSIUM
 RECOGNIZING & ASSESSING COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT SYMPOSIUM PRESENTING EFFICIENT WAYS TO DIAGNOSE COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT IN ORDER TO PROVIDE OPTIMAL CARE FOR PATIENTS AND THEIR FAMILIES JUNE 7, 2019 x 7:30 11:00am
RECOGNIZING & ASSESSING COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT SYMPOSIUM PRESENTING EFFICIENT WAYS TO DIAGNOSE COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT IN ORDER TO PROVIDE OPTIMAL CARE FOR PATIENTS AND THEIR FAMILIES JUNE 7, 2019 x 7:30 11:00am
Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
SENIOR PDHPE WORKSHEET Health Priorities in Australia
 SENIOR PDHPE WORKSHEET Health Priorities in Australia NAME ORGANISATION DATE INSTRUCTIONS 1. Make sure you read the bold text in boxes throughout the worksheet as they contain important information These
SENIOR PDHPE WORKSHEET Health Priorities in Australia NAME ORGANISATION DATE INSTRUCTIONS 1. Make sure you read the bold text in boxes throughout the worksheet as they contain important information These
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
HIV/AIDS in Practice. An Expert Commentary with Nelson Michael, MD, PhD. A Clinical Context Report
 HIV/AIDS in Practice An Expert Commentary with Nelson Michael, MD, PhD A Clinical Context Report Clinical Context: HIV/AIDS in Practice Expert Commentary Jointly Sponsored by: and Clinical Context: HIV/AIDS
HIV/AIDS in Practice An Expert Commentary with Nelson Michael, MD, PhD A Clinical Context Report Clinical Context: HIV/AIDS in Practice Expert Commentary Jointly Sponsored by: and Clinical Context: HIV/AIDS
Moving Beyond Opioids for Chronic Pain
 Back to the Future: Moving Beyond Opioids for Chronic Pain September 15-16, 2018 Hilton Richmond Hotel & Spa / Short Pump 12042 West Broad Street Presented by Departments of Anesthesiology and Physical
Back to the Future: Moving Beyond Opioids for Chronic Pain September 15-16, 2018 Hilton Richmond Hotel & Spa / Short Pump 12042 West Broad Street Presented by Departments of Anesthesiology and Physical
