The effect of Urtica dioica extract on the number of astrocytes in the dentate gyrus of diabetic rats
|
|
|
- Angelica Lawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 2, pp Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN The effect of Urtica dioica extract on the number of astrocytes in the dentate gyrus of diabetic rats M. Jahanshahi 1, M.J. Golalipour 1, M. Afshar 2 1 Department of Anatomy, Gorgan University of Medical Sciences, Gorgan, Iran 2 Department of Anatomy, Birjand University of Medical Sciences, Birjand, Iran [Received 29 January 2009; Accepted 16 March 2009] Diabetes mellitus is associated with cerebral alterations in both human and animal models of the disease. These alterations include abnormal expression of hypothalamic neuropeptides and hippocampal astrogliosis. Urtica dioica (Nettle) is among several species listed for their use against diabetes in folk medicine. The aim of this study was the evaluation of the astrocyte number in the dentate gyrus of diabetic rats after treatment with nettle. A total of 21 male albino Wistar rats were used in the present study. The animals were divided into three groups: control, nettle-untreated diabetic, and nettle treated diabetic. Hyperglycaemia was induced by streptozotocin (80 mg/kg) in the animals of the diabetic and treatment groups. One week after injection of the streptozotocin, the animals in the treatment group received a hydroalcoholic extract of Urtica dioica (100 mg/kg/day) for 4 weeks intraperitoneally. After a 5-week survival period, all the rats were sacrificed and coronal sections were taken from the dorsal hippocampal formation of the right cerebral hemispheres. The area densities of the astrocytes were measured and compared between the three groups (p < 0.05). The number of astrocytes increased in the diabetic rats (24.06 ± 9.57) compared with the controls (17.52 ± 6.66). The densities in the treated rats (19.50 ± 6.16) were lower than in the diabetic rats. Furthermore, the control and treated rats showed similar densities. We concluded that U. dioica extract helped compensate for astrocytes in the treatment rats dentate gyrus in comparison with diabetic rats. (Folia Morphol 2009; 68, 2: 93 97) Key words: diabetes, astrocyte, dentate gyrus, Urtica dioica INTRODUCTION Diabetes mellitus is a common metabolic disorder in humans, which is associated with cerebral changes. More than 1% of the world population suffer from diabetes and their numbers are gradually increasing [12]. A high occurrence of the disease is noted in Iran, especially in urban populations, and is therefore a major health problem [15]. Diabetes mellitus is associated with cerebral changes in both human and animal models of the disease. These changes include abnormal expression Address for correspondence: Dr. M. Jahanshahi, PhD, Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Gorgan University of Medical Sciences, km 4 Gorgan-Sari road (Shastcola), Gorgan, Iran, P.O. Box: , tel: , mejahanshahi@yahoo.com 93
2 Folia Morphol., 2009, Vol. 68, No. 2 of hypothalamic neuropeptides, astrogliosis in the hippocampus [18], decreased synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus, neurotoxicity, and changes in glutamate neurotransmission [20]. Increasing evidence has shown that diabetes may be associated with learning and memory deficits in humans [4, 5, 14]. Studies examining the effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on memory function in mice and rat models have also shown deficits in memory retention and retrieval, compared to non-diabetic controls [2, 3, 8, 19]. As we showed in our previous studies, astrocytes have the capacity to increase after spatial learning in the hippocampal subfields and dentate gyrus with Morris water maze techniques [10, 11], astrocytes also increased in diabetes [18]. Urtica L., the stinging nettle (Urticacea), is an annual perennial herb that is distinguished by its stinging hairs [13]. Urtica dioica (U. dioica), among the Urtica species, has been known for a long time as a medicinal plant. The decreasing effect on blood sugar of U. dioica as a medicinal herb has been introduced in old writings such as those by Avicenna [6]. In addition, U. dioica is among several species listed for their use against diabetes in folk medicine, in a large pharmacological screen of European species [17]. As the dentate gyrus is an important site for adult neurogenesis in mammals and neuropathological damage occurs in diabetic cases, and also because the number of astrocytes is increased in this disease, and lastly because there is no almost documentation regarding the effects of treatment with nettle on astrocytes in the Dentate gyrus of diabetic rats, the aim of this study was the evaluation of the astrocyte number in the dentate gyrus of diabetic rats treated with nettle. MATERIAL AND METHODS Animals Twenty-one adult male Wistar rats (weighing g) were used. The animals were divided into three groups: control, nettle-untreated diabetic, and nettle treated diabetic. All the animals were treated in agreement with the Helsinki Convention on the use of animals in research, approved by the Institutional Review Board. The animals were kept in an air-conditioned animal room (22 ± 2 o C) under a 12-hour light/dark cycle; food and water were available. Induction of diabetes by streptozotocin The streptozotocin (STZ) used was of analytical grade, obtained from Merck and Sigma. STZ was dissolved in saline for immediate use and injected intraperitoneally. Diabetes was induced with a single IP injection of streptozotocin (STZ) (80 mg/kg) to overnight-fasting rats. Blood samples for glucose measurements were taken from the tail vein. Diabetes was confirmed by measuring the glucose concentration by using the glucometer method. In the experiments, 7 rats were used in each group. Preparation of the Urtica dioica hydroalcoholic extract Leaves of U. dioica were collected from a suburb of Gorgan, northern Iran (Golestan, Iran) in 2005 and taxonomically identified by the Department of Pharmacognosy at Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences. A voucher specimen (5-77-1) was deposited in the herbarium of Mazandaran University. Powder of U. dioica leaves was percolated with hydroalcoholic (60 ) solvent for 48 hours. The extract was filtered and concentrated in a vacuum at 40 C to make a jelly material. Study design This study consisted of three groups: a normal healthy control group that received saline daily for 4 weeks, a diabetic group which received saline daily for 4 weeks after STZ injection, and the treatment group diabetic rats that were administered 100 mg/kg hydroalcoholic extract of U. dioica [9] daily for 4 weeks. Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (GTT) was performed on 16-hour fasted rats using 2 g glucose/kg body weight. In all groups, blood was collected from the animals by tail snipping at 0, 30, 90, and 120 minutes after glucose load. In addition, glucose tests were performed after IP injection STZ at 1 and 5 weeks. Tissue processing After the animals had been sacrificed, the brains were removed and fixed in buffered formaldehyde 10% solution for histological analysis. After processing and embedding, the brains were cut coronally into 7 µm slices. Approximately 10 slices were obtained from each brain. Then they were stained with phosphotungstic acid haematoxylin (PTAH) staining [10, 11]. We used PTAH staining for astrocyte staining because it is one of the special staining methods 94
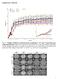
3 M. Jahanshahi et al., Urtica dioica extract and astrocytes Table 1. Mean of astrocytes in dentate gyrus (DG) in control, diabetic, and treatment groups DG Mean Std. error mean Area [mm 2 ] Control Diabetic Treatment Table 2. Mean of astrocytes in dentate gyrus (DG) of all rats in control, diabetic and treatment groups Figure 1. Blood glucose concentration in control, diabetic and treatment groups. DG Control Diabetes Treatment Rat Rat for astrocyte cells and their processes. Using this method the astrocytes appeared blue and the neurons appeared pink [1]. Quantification of the number of astrocytes A photograph of each section was produced using an Olympus BX 51 microscope and a DP 12 digital camera under a magnification of 400X. An area of µm 2 was selected randomly in the dentate gyrus in all sections. To measure the area density of the astrocytes, the images were transferred onto a computer. Using OLYSIA Autobioreport software, Olympus Co., the appropriate grids were superimposed on the pictures and the cells were counted manually. Statistical analysis Experimental results concerning this study were evaluated using SPSS v.11.5 and expressed as mean ± SE. To compare the means of the measured parameters in the three groups by analysis of variance (ANOVA) test, after confirmation of normality, the means were compared by the ANOVA Post Hoc Tukey test; p < 0.05 was considered significant. Rat Rat Rat Rat Rat Mean RESULTS The GTT of the three groups at the beginning and on the 5 th week of the study are shown in Figure 1. As can be seen in Figure 1, the GTT results of all rats were normal at the beginning of the experiment. The GTT results at the end of the study show a marked difference to the previous results in the rats that received STZ, i.e. the rats from the diabetic and treatment groups. The control rats which did not receive STZ showed a normal GTT. In contrast, the diabetic rats which had undergone STZ-induced diabetes on the first day of the study and did not receive the nettle extract showed the most profound impairment in GTT. The means of the astrocyte number (per µm 2 ) in the control, diabetic, and treatment groups are shown in Table 1, and the mean of the astrocytes in each rat is shown in Table 2. Morphometric evaluation showed that the number of astrocytes in the diabetic group (24.06 ± 9.57) was higher than in the control group (17.52 ± 6.66), and also that the number of astrocytes in the treatment group (19.50 ± 6.16) was higher than in the control group, but the treatment group had less astrocytes than the diabetic group. On the other hand, there was a significant difference in astrocyte number between the control and the diabetic groups, but the difference between the treatment group and the other groups was not significant. It seams that nettle can decrease the density of astrocytes that increase in diabetes. The transitions showed that the anterior-posterior distributions of astrocyte densities were not the same in the three groups (Table 3), but some similarities between the control and treatment groups 95
4 Folia Morphol., 2009, Vol. 68, No. 2 Table 3. Mean of astrocytes in dentate gyrus (DG) from anterior to posterior in control, diabetic and treatment groups DG Control Diabetes Treatment were seen. In addition, no significant regression model was compatible with the transitions drawn up (p < 0.05). DISCUSSION The present data showed that the astrocytes in the dentate gyrus of diabetic rats, as we thought, increased in comparison with nondiabetic controls, and this difference was significant (p < 0.05). Additionally, in the treatment group with hydroalcoholic extract of U. dioica, the number of astrocytes was higher than in the nondiabetic controls, but this difference was not significant (p < 0.05). Our data showed that the treatment group had less astrocytes compared with diabetic rats, but this difference was not significant (p < 0.05). On the other hand, the number of astrocytes after treatment with extract of U. dioica decreased in the diabetic rats. An attempt was made to find the anterior-posterior transitions of the astrocyte densities and provide mathematical equations for computational analysis. The transition of the cell density can show the distribution of the density in anterior-posterior transition. The underlying trends of the transitions drawn up were not significantly describable by regression models. This finding is opposite to our previous studies in spatial learning. In our previous studies we found different increases in astrocytes in the anterior and posterior of hippocampal formation [10, 11]. It seems the diabetes, despite of spatial learning examination, does not have a different effect in the anterior-posterior of hippocampal formation. The increase in cell density seen in the diabetic group was compatible with the results of previous studies. For example, Revsin et al. [20] in 2005 reported that one month after STZ treatment, the number of astrocytes was significantly increased in the STZ-treated group as compared to the vehicletreated group (p < 0.001, n = 5); this finding is similar to our results. Saravia et al. [18] in 2002 showed that the number of GFAP astrocytes increased 3-fold in the hippocampal stratum radiatum of STZ-diabetic female mice compared with age-matched, vehicle-treated nondiabetic controls (p < 0.005). Muranyi et al. [16] showed that the number of GFAP-positive astrocytes increased significantly in the hippocampal formation of diabetic rats. The diameters of astrocyte cell bodies were found to be enlarged, and the number and length of astrocyte foot processes were increased. What is more, in our previous study in which we worked on the granule cell in the dentate gyrus, we showed that Urtica dioica extract can help to restore diabetes-induced granule-cell loss in the rat dentate gyrus [7]. However, by comparison of our results with our previous study it seems that nettle extract administration can be a beneficial treatment for the regulation of cell density in the dentate gyrus of diabetic patients and that this can ameliorate cognitive impairment in the diabetic patient. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We are grateful to the research departments of Golestan and Birjand Universities of Medical Sciences and to Mr A.M. Gharavi and Mrs S. Ghaffari for their help with histological processing. REFERENCES 1. Bancroft JB, and Stevens A (2002) Theory and practice of histological techniques. 5 th Ed. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh. 2. Biessels GJ, Gispen WH (2005) The impact of diabetes on cognition: what can be learned from rodent models? Neurobiol Aging, 26 (suppl. 1): Biessels GJ, Kamal A, Ramakers GM, Urban IJ, Spruijt BM, Erkelens DW, Gispen WH (1996) Place learning and hippocampal synaptic plasticity in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Diabetes, 45: Biessels GJ, Kappelle AC, Bravenboer B, Erkelens DW, Gispen WH (1994) Cerebral function in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia, 37: Brands AM, Biessels GJ, de Haan EH, Kappelle LJ, Kessels RP (2005) The effects of type 1 diabetes on cognitive performance: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care, 28:
5 M. Jahanshahi et al., Urtica dioica extract and astrocytes 6. Farzami B, Ahmadvand D, Vardasbi S, Majin FJ, Khaghani Sh (2003) Induction of insulin secretion by a component of Urtica dioica leave extract in perifused islets of langerhans and its in vivo effects in normal and streptozotocin diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol, 89: Fazeli SA, Gharravi AM, Ghafari S, Jahanshahi M, Golalipour MJ (2008) The granule cell density of the dentate gyrus following administration of Urtica dioica extract to young diabetic rats. Folia Morphol, 67: Gispen WH, Biessels GJ (2000) Cognition and synaptic plasticity in diabetes mellitus. Trends Neurosci, 23: Gülçin I, Küfrevioglu ÖI, Oktay M, Büyükokuroglu ME (2004) Antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiulcer and analgesic activities of nettle (Urtica dioica L.). J Ethnopharmacol, 90: Jahanshahi M, Sadeghi Y, Hosseini A, Naghdi N, Marjani A (2008) the effect of spatial learning on the number of astrocytes in CA3 subfield of rat hippocampus. Singaporemed J, 49: Jahanshahi M, Sadeghi Y, Hosseini A, Naghdi N (2007) the effect of spatial learning on the number of astrocytes in rats dentate gyrus. Neuroanatomy, 6: Kar A, Choudhary BK and Bandyopadhyay NG (2003) Comparative evaluation of hypoglycaemic activity of some Indian medicinal plants in alloxan diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol, 84: Kavalali G, Tuncel H, Goksel S, Hatemi HH (2003) Hypoglycemic activity of Urtica pilulifera in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Ethnopharmacol, 84: Liang XC, Guo SS, Hagino N (2006) Current status of clinical and experimental researche on cognitive impairment in diabetes. Chin J Integr Med, 12: Maroo J, Vasu VT, Aalinkeel R, Gupta S (2002) Glucose lowering effect of aqueous of Enicostemma Littorale Blume in diabetes: A possible mechanism of action. J Ethnopharmacol, 81: Muranyi M, Ding Ch, He QP, Lin Y, An Li P (2006) Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Causes Astrocyte Death after Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury. Diabetes, 55: Rahman AU, Zaman K (1989) Medicinal plants with hypoglycemic activity. J Ethnopharmacol, 26: Saravia FE, Revsin Y, Gonzalez Deniselle MC, Gonzalez S, Roig P, Lima A, Homo-Delarche F, De Nicola AF (2002) Increased astrocyte reactivity in the hippocampus of murine models of type I diabetes: the nonobese diabetic (NOD) and streptozotocin treated mice. Brain Res, 957: Trudeau F, Gagnon S, Massicotte G (2004) Hippocampal synaptic plasticity and glutamate receptor regulation: influences of diabetes mellitus. Eur J Pharmacol, 490: Revsin Y, Saravia F, Roig P, Lima A, De Kloet ER, Homo- -Delarche F, De Nicola AF (2005) Neuronal and astroglial alterations in the hippocampus of a mouse model for type 1 diabetes. Brain Res, 1038:
Effect of Urtica dioica Leaf Alcoholic and Aqueous Extracts on the Number and the Diameter of the Islets in Diabetic Rats
 IJMCM Winter 2013, Vol 2, No 1 Original Article Effect of Urtica dioica Leaf Alcoholic and Aqueous Extracts on the Number and the Diameter of the Islets in Diabetic Rats Durdi Qujeq 1,2, Mohsen Tatar 2,
IJMCM Winter 2013, Vol 2, No 1 Original Article Effect of Urtica dioica Leaf Alcoholic and Aqueous Extracts on the Number and the Diameter of the Islets in Diabetic Rats Durdi Qujeq 1,2, Mohsen Tatar 2,
The Effect of Scopolamine on Avoidance Memory and Hippocampal Neurons in Male Wistar Rats
 The Effect of Scopolamine on Avoidance Memory and Hippocampal Neurons in Male Wistar Rats Saba Seifhosseini 1, Mehrdad Jahanshahi 2,*, Ali Moghimi 3, Nasrin-Sadat Aazami 4 1. Department of Biology, Faculty
The Effect of Scopolamine on Avoidance Memory and Hippocampal Neurons in Male Wistar Rats Saba Seifhosseini 1, Mehrdad Jahanshahi 2,*, Ali Moghimi 3, Nasrin-Sadat Aazami 4 1. Department of Biology, Faculty
Effect of Gestational Diabetes on Purkinje and Granule Cells Distribution of the Rat Cerebellum in 21 and 28 days of Postnatal Life
 Effect of Gestational Diabetes on Purkinje and Granule Cells Distribution of the Rat Cerebellum in 21 and 28 days of Postnatal Life Elahe Mirarab Razi 1, Soraya Ghafari 2, Mohammad Jafar Golalipour 3*
Effect of Gestational Diabetes on Purkinje and Granule Cells Distribution of the Rat Cerebellum in 21 and 28 days of Postnatal Life Elahe Mirarab Razi 1, Soraya Ghafari 2, Mohammad Jafar Golalipour 3*
International Journal of Phytomedicine 2 (2010) Hypoglycemic activity of aqueous extract of Urtica parviflora roxb. in normoglycemic rats
 International Journal of Phytomedicine 2 (2010) 47-51 http://www.arjournals.org/ijop.html Research article ISSN: 0975-0185 Hypoglycemic activity of aqueous extract of Urtica parviflora roxb. in normoglycemic
International Journal of Phytomedicine 2 (2010) 47-51 http://www.arjournals.org/ijop.html Research article ISSN: 0975-0185 Hypoglycemic activity of aqueous extract of Urtica parviflora roxb. in normoglycemic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
Effects of Repeated Administration of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) on Avoidance Memory and Cell Density in Rats' Hippocampus
 Effects of Repeated Administration of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) on Avoidance Memory and Cell Density in Rats' Hippocampus Mehrdad Jahanshahi 1*, Kamran Haidari 1, Simin Mahaki-Zadeh 1, EmseGol
Effects of Repeated Administration of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) on Avoidance Memory and Cell Density in Rats' Hippocampus Mehrdad Jahanshahi 1*, Kamran Haidari 1, Simin Mahaki-Zadeh 1, EmseGol
Pharmacologyonline 3: (2009) I VESTIGATIO OF A TIHYPERGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF MORUS IGRA O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I STREPTOZOTOCI DIABETIC RATS
 I VESTIGATIO OF A TIHYPERGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF MORUS IGRA O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I STREPTOZOTOCI DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2, Ahmad R. Gohari 2*, Mojgan Yazdanpanah 2, Abbass
I VESTIGATIO OF A TIHYPERGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF MORUS IGRA O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I STREPTOZOTOCI DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2, Ahmad R. Gohari 2*, Mojgan Yazdanpanah 2, Abbass
ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT
 ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT Sama Venkatesh *1, G.Dayananda Reddy 1, B.Madhava Reddy 1, M.Lakshman 2. 1 Department of Pharmacognosy, G.Pulla Reddy College of Pharmacy, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad
ANTI-DIABETIC ACTIVITY OF HELICTERES ISORA ROOT Sama Venkatesh *1, G.Dayananda Reddy 1, B.Madhava Reddy 1, M.Lakshman 2. 1 Department of Pharmacognosy, G.Pulla Reddy College of Pharmacy, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Fig. S1. Weights of full-dose treatment groups comparing 1 st, 2 nd, and 3 rd generation gene replacement therapy. Mice were treated at p1 with 4x10 11 GC of the three different
Supplementary Materials Fig. S1. Weights of full-dose treatment groups comparing 1 st, 2 nd, and 3 rd generation gene replacement therapy. Mice were treated at p1 with 4x10 11 GC of the three different
28/04/51. Introduction. Insulin signaling effects on memory and mood. Is accelerated brain aging a consequence of diabetes? chronic hyperglycemia
 Introduction Insulin signaling effects on memory and mood (Review) Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Long-term diabetes Lawrence
Introduction Insulin signaling effects on memory and mood (Review) Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Long-term diabetes Lawrence
Radiation-induced lowered neurogenesis associated with shortened latency of inhibitory avoidance memory response
 Original article Radiation-induced lowered neurogenesis associated with shortened latency of inhibitory avoidance memory response Mehrdad Jahanshahi 1, Alireza Khoshbin Khoshnazar 2, Nasrin-Sadat Azami
Original article Radiation-induced lowered neurogenesis associated with shortened latency of inhibitory avoidance memory response Mehrdad Jahanshahi 1, Alireza Khoshbin Khoshnazar 2, Nasrin-Sadat Azami
Pharmacologyonline 3: (2009)
 THE EFFECT OF ASTURTIUM OFFICIALE O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Ahmad R. Gohari 2, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2 *, aghi Shahabi Majd 3, Abbass Hadjiakhoondi 2 1- Department of Pharmacology,
THE EFFECT OF ASTURTIUM OFFICIALE O BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL I DIABETIC RATS Hassan Fallah Hoseini 1, Ahmad R. Gohari 2, Soodabeh Saeidnia 2 *, aghi Shahabi Majd 3, Abbass Hadjiakhoondi 2 1- Department of Pharmacology,
The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females
 The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females Samantha Pavlock (Medical Student) Pradeep Bhide and Deirdre McCarthy (Faculty
The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females Samantha Pavlock (Medical Student) Pradeep Bhide and Deirdre McCarthy (Faculty
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics
 International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278-2648 IJRPP Vol.3 Issue 4 Oct-Dec-2014 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access Anti-diabetic
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278-2648 IJRPP Vol.3 Issue 4 Oct-Dec-2014 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access Anti-diabetic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Time Course of Changes in Passive Avoidance and Y-Maze Performance in Male Diabetic Rats
 Iranian Biomedical Journal 10 (2): 99-104 (April 2006) Time Course of Changes in Passive Avoidance and Y-Maze Performance in Male Rats Mehrdad Roghani 1, Mohammad Taghi Joghataie 2, Mohammad Reza Jalali
Iranian Biomedical Journal 10 (2): 99-104 (April 2006) Time Course of Changes in Passive Avoidance and Y-Maze Performance in Male Rats Mehrdad Roghani 1, Mohammad Taghi Joghataie 2, Mohammad Reza Jalali
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(1):452-456 Evaluation of anti hyperglycaemic activity
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(1):452-456 Evaluation of anti hyperglycaemic activity
HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTION OF THE FLAVONOID FRACTION OF ARTOCARPUS HETEROPHYLLUS LEAF
 42 Research Paper ISSN 0189-6016 2006 Afr. J. Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines www.africanethnomedicines.net HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTION OF THE FLAVONOID FRACTION OF ARTOCARPUS HETEROPHYLLUS
42 Research Paper ISSN 0189-6016 2006 Afr. J. Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines www.africanethnomedicines.net HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTION OF THE FLAVONOID FRACTION OF ARTOCARPUS HETEROPHYLLUS
7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY. 7.1 Introduction
 268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
Abstract. Introduction
 International Journal of PharmTech Research ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1,No.1,pp 43-49, Jan March 2009 Comparative evaluation of antidiabetic activity of some marketed polyherbal formulations in alloxan induced
International Journal of PharmTech Research ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1,No.1,pp 43-49, Jan March 2009 Comparative evaluation of antidiabetic activity of some marketed polyherbal formulations in alloxan induced
Antidiabetic effect of Teucrium polium aqueous extract in multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced model of type 1 diabetes in rat
 Antidiabetic effect of Teucrium polium aqueous extract in multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced model of type 1 diabetes in rat Zari Sabet 1, Mehrdad Roghani 2*, Maryam Najafi 3, Zahra Maghsoudi 3 1.
Antidiabetic effect of Teucrium polium aqueous extract in multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced model of type 1 diabetes in rat Zari Sabet 1, Mehrdad Roghani 2*, Maryam Najafi 3, Zahra Maghsoudi 3 1.
Short-Term Environmental Enrichment Enhances Adult Neurogenesis, Vascular Network and Dendritic Complexity in the Hippocampus of Type 1 Diabetic Mice
 Short-Term Environmental Enrichment Enhances Adult Neurogenesis, Vascular Network and Dendritic Complexity in the Hippocampus of Type 1 Diabetic Mice Juan Beauquis 1, Paulina Roig 1, Alejandro F. De Nicola
Short-Term Environmental Enrichment Enhances Adult Neurogenesis, Vascular Network and Dendritic Complexity in the Hippocampus of Type 1 Diabetic Mice Juan Beauquis 1, Paulina Roig 1, Alejandro F. De Nicola
Neuronal and astroglial alterations in the hippocampus of a mouse model for type 1 diabetes
 CHAPTER 4 Neuronal and astroglial alterations in the hippocampus of a mouse model for type 1 diabetes Yanina Revsin, Flavia Saravia, Paulina Roig, Analia Lima, E. Ronald de Kloet, Francoise Homo-Delarche,
CHAPTER 4 Neuronal and astroglial alterations in the hippocampus of a mouse model for type 1 diabetes Yanina Revsin, Flavia Saravia, Paulina Roig, Analia Lima, E. Ronald de Kloet, Francoise Homo-Delarche,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2275
 Supplementary Figure S1. The presence of MeCP2 in enriched primary glial cultures from rat or mouse brains is not neuronal. Western blot analysis of protein extracts from (a) rat glial and neuronal cultures.
Supplementary Figure S1. The presence of MeCP2 in enriched primary glial cultures from rat or mouse brains is not neuronal. Western blot analysis of protein extracts from (a) rat glial and neuronal cultures.
AviJMB Avicenna Journal of Medical Biochemistry
 Original Article AviJMB Avicenna Journal of Medical Biochemistry journal homepage: http://ajmb.umsha.ac.ir Anti-diabetic effects of aqueous extracts of three Iranian medicinal plants in type 2 diabetic
Original Article AviJMB Avicenna Journal of Medical Biochemistry journal homepage: http://ajmb.umsha.ac.ir Anti-diabetic effects of aqueous extracts of three Iranian medicinal plants in type 2 diabetic
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Antidiabetic Activity of Alcoholic Extract of Neem (Azadirachta Indica) Root Bark
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Antidiabetic Activity of Alcoholic Extract of Neem (Azadirachta Indica) Root Bark Prabhakar Patil 1, Sudha Patil 2, Abhay Mane 3, Sushilkumar Verma 4 1 Department of Pharmacology, Navodaya
RESEARCH ARTICLE Antidiabetic Activity of Alcoholic Extract of Neem (Azadirachta Indica) Root Bark Prabhakar Patil 1, Sudha Patil 2, Abhay Mane 3, Sushilkumar Verma 4 1 Department of Pharmacology, Navodaya
HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF CECROPIA PELTATA L. ON N5-STZ TYPE 2 DIABETIC RATS. México, México DF. México, México DF.
 HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF CECROPIA PELTATA L. ON N5-STZ TYPE 2 DIABETIC RATS Adolfo Andrade-Cetto a * René Cárdenas b and Brenda Ramírez-Reyes a a Lab. Etnofarmacología, Fac. de Ciencias, Universidad Nacional
HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF CECROPIA PELTATA L. ON N5-STZ TYPE 2 DIABETIC RATS Adolfo Andrade-Cetto a * René Cárdenas b and Brenda Ramírez-Reyes a a Lab. Etnofarmacología, Fac. de Ciencias, Universidad Nacional
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70%
 Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
TREATMENT OF PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A RANDOMIZED DOUBLE-BLIND PLACEBO-CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL
 Research Article ISSN: 2277-8713 URTICA DIOICA L. IN TREATMENT OF PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A RANDOMIZED DOUBLE-BLIND PLACEBO-CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL KIANBAKHT S 1, KHALIGHI-SIGAROODI F
Research Article ISSN: 2277-8713 URTICA DIOICA L. IN TREATMENT OF PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A RANDOMIZED DOUBLE-BLIND PLACEBO-CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL KIANBAKHT S 1, KHALIGHI-SIGAROODI F
SCIFED. Publishers. SciFed Journal of Public Health. Comparing Modified and Relationship Study of Gymnema Sylvestre Against Diabetes
 Research Article SCIFED Publishers Rahul Hajare,, 2018, 2:2 SciFed Journal of Public Health Open Access Comparing Modified and Relationship Study of Gymnema Sylvestre Against Diabetes * Rahul Hajare *
Research Article SCIFED Publishers Rahul Hajare,, 2018, 2:2 SciFed Journal of Public Health Open Access Comparing Modified and Relationship Study of Gymnema Sylvestre Against Diabetes * Rahul Hajare *
Pharmacologyonline 1: (2009) HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF PHOEBE LA CEOLATA O ALLOXA -I DUCED DIABETIC MICE
 HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF PHOEBE LA CEOLATA O ALLOXA -I DUCED DIABETIC MICE SEMWAL DK 1 *, RAWAT U 1, SEMWAL R 2, SINGH K 3, SINGH R 3, SAINI B 3, KRISHAN P 3, SINGH M 4 1 Department of Chemistry, University
HYPOGLYCEMIC EFFECT OF PHOEBE LA CEOLATA O ALLOXA -I DUCED DIABETIC MICE SEMWAL DK 1 *, RAWAT U 1, SEMWAL R 2, SINGH K 3, SINGH R 3, SAINI B 3, KRISHAN P 3, SINGH M 4 1 Department of Chemistry, University
Comparative Hypoglycemic Effects of Different Extract of Clitoria Ternatea Leaves on Rats
 IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn: 2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 10, Issue 2 Ver. III (Mar -Apr. 2015), PP 60-65 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Hypoglycemic Effects
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn: 2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 10, Issue 2 Ver. III (Mar -Apr. 2015), PP 60-65 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Hypoglycemic Effects
Antidiabetic and Hypoglycaemic Activity of the Crude Extracts of the Plant Leucas Aspera
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL INNOVATIONS RESEARCH ARTICLE Antidiabetic and Hypoglycaemic Activity of the Crude Extracts of the Plant Leucas Aspera Gupta N *a, Subhramanyam EVS b, Sharma R K
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL INNOVATIONS RESEARCH ARTICLE Antidiabetic and Hypoglycaemic Activity of the Crude Extracts of the Plant Leucas Aspera Gupta N *a, Subhramanyam EVS b, Sharma R K
ANTI-DIABETIC EFFECT OF THUNBERGIA LAURIFOLIA LINN. AQUEOUS EXTRACT
 ANTI-DIABETIC EFFECT OF THUNBERGIA LAURIFOLIA LINN. AQUEOUS EXTRACT S Aritajat, S Wutteerapol and K Saenphet Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Abstract.
ANTI-DIABETIC EFFECT OF THUNBERGIA LAURIFOLIA LINN. AQUEOUS EXTRACT S Aritajat, S Wutteerapol and K Saenphet Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Abstract.
Enhanced ACTH release precedes the onset of diabetes in the NOD mice?
 CHAPTER 2 Enhanced ACTH release precedes the onset of diabetes in the NOD mice? Yanina Revsin, Melly S. Oitzl and E. Ronald de Kloet 33 Abstract Defects in the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
CHAPTER 2 Enhanced ACTH release precedes the onset of diabetes in the NOD mice? Yanina Revsin, Melly S. Oitzl and E. Ronald de Kloet 33 Abstract Defects in the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
The Use of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) and Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) in Alloxan Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Rats
 The Use of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) and Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) in Alloxan Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Rats Florin Muselin*, Diana Brezovan, Jelena Savici, Romeo T. Cristna, Eugenia
The Use of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) and Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) in Alloxan Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Rats Florin Muselin*, Diana Brezovan, Jelena Savici, Romeo T. Cristna, Eugenia
Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences
 Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences ijbms.mums.ac.ir Synergism effects of pioglitazone and Urtica dioica extract in streptozotocin-induced nephropathy via attenuation of oxidative stress Mohammad
Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences ijbms.mums.ac.ir Synergism effects of pioglitazone and Urtica dioica extract in streptozotocin-induced nephropathy via attenuation of oxidative stress Mohammad
Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis of individual mice during maze learning. a,
 Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Prevention of Development of Tolerance and Dependence to Opiate in Mice by BR-16A (Mentat) A Herbal Psychotropic Preparation
 [Indian Journal of Experimental Biology (1992): (30), 885] Prevention of Development of Tolerance and Dependence to Opiate in Mice by BR-16A (Mentat) A Herbal Psychotropic Preparation Kulkarni, S.K. and
[Indian Journal of Experimental Biology (1992): (30), 885] Prevention of Development of Tolerance and Dependence to Opiate in Mice by BR-16A (Mentat) A Herbal Psychotropic Preparation Kulkarni, S.K. and
Clinical abstracts. Diabetes
 Clinical abstracts Diabetes Antidiabetic Activity Of Aloes: Preliminary Clinical & Experimental Observations Ghannam N; Kingston M; Al-Meshaal IA; Tariq M; Parman NS; Woodhouse N Horm Res 24(4):288-94
Clinical abstracts Diabetes Antidiabetic Activity Of Aloes: Preliminary Clinical & Experimental Observations Ghannam N; Kingston M; Al-Meshaal IA; Tariq M; Parman NS; Woodhouse N Horm Res 24(4):288-94
Cognitive Dysfunction in Diabetic Rats. Effect of Minocycline
 Cognitive Dysfunction in Diabetic Rats. Effect of Minocycline *Author for correspondence Falgun Bhuva, Veeranjaneyulu Addepalli* Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy and Technology Management,
Cognitive Dysfunction in Diabetic Rats. Effect of Minocycline *Author for correspondence Falgun Bhuva, Veeranjaneyulu Addepalli* Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy and Technology Management,
Effect of chronic treatment of ketamine on hippocampus cell count of adult rats
 Quarterly of the Horizon of Medical Sciences Vol. 19, No. 1, Spr 2013 Pages: 35-39 Effect of chronic treatment of ketamine on hippocampus cell count of adult rats Downloaded from hms.gmu.ac.ir at 12:09
Quarterly of the Horizon of Medical Sciences Vol. 19, No. 1, Spr 2013 Pages: 35-39 Effect of chronic treatment of ketamine on hippocampus cell count of adult rats Downloaded from hms.gmu.ac.ir at 12:09
Hypoglycemic Activity of Seerankottai Thiravam (Semicarpus Anacardium. Linn) in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats
 Research Article Hypoglycemic Activity of Seerankottai Thiravam (Semicarpus Anacardium. Linn) in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats P. Parthiban 1, K. Kanagavalli 1, P. Sathiya Rajeswaran 2, J. Anbu 3, A. Chinnasamy
Research Article Hypoglycemic Activity of Seerankottai Thiravam (Semicarpus Anacardium. Linn) in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats P. Parthiban 1, K. Kanagavalli 1, P. Sathiya Rajeswaran 2, J. Anbu 3, A. Chinnasamy
1138
 EFFECT OF CLITORIA TERNATEA (LINN) PLANT ROOT EXTRACT ON THE NEURONS OF FRONTAL CORTEX AND DENTATE GYRUS OF YOUNG DIABETIC RATS A PRELIMINARY INVESTIGATION. ABSTRACT Aim and objective To study the effect
EFFECT OF CLITORIA TERNATEA (LINN) PLANT ROOT EXTRACT ON THE NEURONS OF FRONTAL CORTEX AND DENTATE GYRUS OF YOUNG DIABETIC RATS A PRELIMINARY INVESTIGATION. ABSTRACT Aim and objective To study the effect
An experimental study to evaluate the potentiating effect of Selenium and Vitamin-E as supplement to Sulfonylureas on Alloxan induced diabetic rats
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 10 (October-2014) pp. 37-47 www.ijcrar.com An experimental study to evaluate the potentiating effect of Selenium and Vitamin-E as supplement to Sulfonylureas on Alloxan
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 10 (October-2014) pp. 37-47 www.ijcrar.com An experimental study to evaluate the potentiating effect of Selenium and Vitamin-E as supplement to Sulfonylureas on Alloxan
mm Distance (mm)
 b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences
 International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences REVIEW ARTICLE PHARMACOLOGY A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON THE ANTIDIABETIC EFFECT OF NELUMBO NUCIFERA AND GLIMEPIRIDE IN STREPTOZOTOCIN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS POLURU
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences REVIEW ARTICLE PHARMACOLOGY A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON THE ANTIDIABETIC EFFECT OF NELUMBO NUCIFERA AND GLIMEPIRIDE IN STREPTOZOTOCIN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS POLURU
Effect of Diabetes on Median and Dorsal Raphe Nuclei Efferent Fibers to CA3 Hippocampal Area in Rat
 ORIGINAL REPORT Effect of Diabetes on Median and Dorsal Raphe Nuclei Efferent Fibers to CA3 Hippocampal Area in Rat Gholamreza Hassanzadeh *1, Adib Zendedel 1, Mohammad Akbari 1, Seyed Behnam-edin Jemeie
ORIGINAL REPORT Effect of Diabetes on Median and Dorsal Raphe Nuclei Efferent Fibers to CA3 Hippocampal Area in Rat Gholamreza Hassanzadeh *1, Adib Zendedel 1, Mohammad Akbari 1, Seyed Behnam-edin Jemeie
Available online through ISSN
 Research Article Available online through www.ijrap.net ISSN 2229-3566 A COMPARATIVE ANTIDIABETIC AND HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ALCOHOLIC EXTRACTS OF THE PLANT LEUCAS ASPERA AND SEEDS OF PITHECELLOBIUM
Research Article Available online through www.ijrap.net ISSN 2229-3566 A COMPARATIVE ANTIDIABETIC AND HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ALCOHOLIC EXTRACTS OF THE PLANT LEUCAS ASPERA AND SEEDS OF PITHECELLOBIUM
Original Article The Effect of MDMA-Induced Anxiety on Neuronal Apoptosis in Adult Male Rats Hippocampus
 Original Article The Effect of MDMA-Induced Anxiety on Neuronal Apoptosis in Adult Male Rats Hippocampus (MDMA / anxiety / apoptosis / plus-maze / hippocampus / rats) S. Karimi, M. Jahanshahi, M. J. Golalipour
Original Article The Effect of MDMA-Induced Anxiety on Neuronal Apoptosis in Adult Male Rats Hippocampus (MDMA / anxiety / apoptosis / plus-maze / hippocampus / rats) S. Karimi, M. Jahanshahi, M. J. Golalipour
ANTIHYPERGLYCEMIC ACTIVITY OF METHANOLIC EXTRACT OF MADHUCA LONGIFOLIA BARK
 1 Departments of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, 2 Pharmacology, 3 Pharmacognosy B. Pharmacy College, Rampura, Kakanpur, Godhara, Dist. Panchmahal, Gujarat, India Original Research Article Received: July 9,
1 Departments of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, 2 Pharmacology, 3 Pharmacognosy B. Pharmacy College, Rampura, Kakanpur, Godhara, Dist. Panchmahal, Gujarat, India Original Research Article Received: July 9,
Dr Francis A. Olaolorun Report on ISN/CAEN category 1A August 2016 research grant Home institution: Host institution:
 Dr Francis. Olaolorun Report on ISN/CEN category 1 ugust 2016 research grant Home institution: Neuroscience Unit, Department of Veterinary natomy, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria. Host institution:
Dr Francis. Olaolorun Report on ISN/CEN category 1 ugust 2016 research grant Home institution: Neuroscience Unit, Department of Veterinary natomy, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria. Host institution:
Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Bromodeoxyuridine
 Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
Cognitive Function Test. NOR & spatial NOR task. Introduction. Novel Object Recognition (NOR) Estrogen Receptor (ER) in Brain
 Cognitive Function Test Human Rodent Sutcliffe JS, Marshall KM, Neill JC. Behavioral Brain Research 177(2007) 117-125. Radial Arm maze Morris Water maze Siriporn Vongsaiyat 16 th Feb 2007 Novel Object
Cognitive Function Test Human Rodent Sutcliffe JS, Marshall KM, Neill JC. Behavioral Brain Research 177(2007) 117-125. Radial Arm maze Morris Water maze Siriporn Vongsaiyat 16 th Feb 2007 Novel Object
Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties of Nettle Leaf Oil
 Journal of Food Biosciences and Technology, Islamic Azad University, Science and Research Branch, Vol. 5, No. 1, 77-86, 2015 Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties of Nettle Leaf Oil S. Kamyab a, A.
Journal of Food Biosciences and Technology, Islamic Azad University, Science and Research Branch, Vol. 5, No. 1, 77-86, 2015 Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties of Nettle Leaf Oil S. Kamyab a, A.
The effect of gabapentin and phenytoin on sperm morphology in Wistar rats
 Vol. 7, No. 3 247 short communication The effect of gabapentin and phenytoin on sperm morphology in Wistar rats Akhila J. Shetty 1 Department of Pharmacology, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal University,
Vol. 7, No. 3 247 short communication The effect of gabapentin and phenytoin on sperm morphology in Wistar rats Akhila J. Shetty 1 Department of Pharmacology, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal University,
CHAPTER V ANTIDIABETIC ACTMTY OF AQUEOUS EXTRACT OF AGG~MARMZZLOS
 CHAPTER V ANTIDIABETIC ACTMTY OF AQUEOUS EXTRACT OF AGG~MARMZZLOS CHAPTER V Antidiabetic effect of the aqueous extract of Aegle marmelos leaves 5.1. Introduction Plant extracts are used in the treatment
CHAPTER V ANTIDIABETIC ACTMTY OF AQUEOUS EXTRACT OF AGG~MARMZZLOS CHAPTER V Antidiabetic effect of the aqueous extract of Aegle marmelos leaves 5.1. Introduction Plant extracts are used in the treatment
Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing. Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2
 ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
Chapter 7. Discussion and impact
 Chapter 7 Discussion and impact 225 Affective pathology is a complex construct which encompasses a pathological disturbance in primary emotions, rapidly shifting from neutral to intense perception, associated
Chapter 7 Discussion and impact 225 Affective pathology is a complex construct which encompasses a pathological disturbance in primary emotions, rapidly shifting from neutral to intense perception, associated
EVALUATION OF ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF TRIUMFETTA PILOSA ROTH IN STREPTOZOTOCIN- INDUCED DIABETIC RATS
 EVALUATION OF ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF TRIUMFETTA PILOSA ROTH IN STREPTOZOTOCIN- INDUCED DIABETIC RATS * D Ramakrishna 1, G Vidyasagar 2, K Pavan Kumar 1, I Madhusudhana Reddy 3, VSS S Gupta Atyam 4 1
EVALUATION OF ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF TRIUMFETTA PILOSA ROTH IN STREPTOZOTOCIN- INDUCED DIABETIC RATS * D Ramakrishna 1, G Vidyasagar 2, K Pavan Kumar 1, I Madhusudhana Reddy 3, VSS S Gupta Atyam 4 1
Toxicological Assessments of Piper nigrum on Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats
 American-Eurasian Journal of Toxicological Sciences 6 (2): 30-34, 2014 ISSN 2079-2050 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.aejts.2014.6.2.8490 Toxicological Assessments of Piper nigrum on Alloxan
American-Eurasian Journal of Toxicological Sciences 6 (2): 30-34, 2014 ISSN 2079-2050 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.aejts.2014.6.2.8490 Toxicological Assessments of Piper nigrum on Alloxan
Ketamine also decreases serum BDNF levels and spatial learning while causes apoptosis in neonatal rats
 Ketamine also decreases serum BDNF levels and spatial learning while causes apoptosis in neonatal rats A. B. Ozer 1, S. Ceribasi 2, A. O. Ceribasi 2, I. Demirel 1, M. K. Bayar 3, B. Ustundag 4, A. Yildiz
Ketamine also decreases serum BDNF levels and spatial learning while causes apoptosis in neonatal rats A. B. Ozer 1, S. Ceribasi 2, A. O. Ceribasi 2, I. Demirel 1, M. K. Bayar 3, B. Ustundag 4, A. Yildiz
PHARMACODYNAMIC EFFECTS OF CIMETIDINE AND METRONIDAZOLE ON THE BLOOD GLUCOSE LOWERING EFFECT OF GLYBURIDE IN RATS.
 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Allied Sciences 3 (1) (2006) 283-288 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Allied Sciences PHARMACODYNAMIC EFFECTS OF CIMETIDINE AND METRONIDAZOLE ON THE BLOOD GLUCOSE LOWERING EFFECT
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Allied Sciences 3 (1) (2006) 283-288 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Allied Sciences PHARMACODYNAMIC EFFECTS OF CIMETIDINE AND METRONIDAZOLE ON THE BLOOD GLUCOSE LOWERING EFFECT
HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTIVITY OF ETHANOLIC EXTRACT OF ACTINIOPTERIS DICHOTOMA BEDD IN NORMAL AND STREPTOZOTOCIN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS
 e - ISSN - 2348-2206 Print ISSN - 2348-2192 European Journal of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ejmbb HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTIVITY OF ETHANOLIC EXTRACT OF ACTINIOPTERIS
e - ISSN - 2348-2206 Print ISSN - 2348-2192 European Journal of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ejmbb HYPOGLYCAEMIC ACTIVITY OF ETHANOLIC EXTRACT OF ACTINIOPTERIS
GFP/Iba1/GFAP. Brain. Liver. Kidney. Lung. Hoechst/Iba1/TLR9!
 Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Subconvulsive Dose of Kainic Acid Transiently Increases the Locomotor Activity of Adult Wistar Rats
 Physiol. Res. 64: 263-267, 2015 SHORT COMMUNICATION Subconvulsive Dose of Kainic Acid Transiently Increases the Locomotor Activity of Adult Wistar Rats V. RILJAK 1, D. MAREŠOVÁ 1, J. POKORNÝ 1, K. JANDOVÁ
Physiol. Res. 64: 263-267, 2015 SHORT COMMUNICATION Subconvulsive Dose of Kainic Acid Transiently Increases the Locomotor Activity of Adult Wistar Rats V. RILJAK 1, D. MAREŠOVÁ 1, J. POKORNÝ 1, K. JANDOVÁ
RESEARCH ARTICLE. *Corresponding
 Available online at www.aexpbio.com RESEARCH ARTICLE Annals of Experimental Biology 2014, 2 (3):58-62 ISSN : 2348-1935 Hypoglycaemic effects of melatonin and ethanol extract of Azadirachta indica administration
Available online at www.aexpbio.com RESEARCH ARTICLE Annals of Experimental Biology 2014, 2 (3):58-62 ISSN : 2348-1935 Hypoglycaemic effects of melatonin and ethanol extract of Azadirachta indica administration
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Received on: 08/02/2017 Published on:27/03/2017
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Received on: 08/02/2017 Published on:27/03/2017 Corresponding Author Anuradha VivekanandPhatak, Department of Pharmacology, Dr.BhanubenNanavati College of Pharmacy, Vile Parle (West),
RESEARCH ARTICLE Received on: 08/02/2017 Published on:27/03/2017 Corresponding Author Anuradha VivekanandPhatak, Department of Pharmacology, Dr.BhanubenNanavati College of Pharmacy, Vile Parle (West),
Effect of D-400, a Herbal Formulation, on Blood Sugar of Normal and Alloxan-induced Diabetic Rats
 [Indian Journal Physiol. Pharmacol. (1995): (39), 2, 95-100] Effect of D-400, a Herbal Formulation, on Blood Sugar of Normal and Alloxan-induced Diabetic Rats Anturlikar, S.D., Gopumadhavan, S., Chauhan,
[Indian Journal Physiol. Pharmacol. (1995): (39), 2, 95-100] Effect of D-400, a Herbal Formulation, on Blood Sugar of Normal and Alloxan-induced Diabetic Rats Anturlikar, S.D., Gopumadhavan, S., Chauhan,
Available online at
 Original Article Available online at http://pbr.mazums.ac.ir PBR Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Research Evaluation of anti-diabetic effects of hydroalcoholic extract of green tea and cinnamon on streptozotocin-induced
Original Article Available online at http://pbr.mazums.ac.ir PBR Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Research Evaluation of anti-diabetic effects of hydroalcoholic extract of green tea and cinnamon on streptozotocin-induced
Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma
 Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma Paper: Abraham, Wickliffe C., and Anthony Robins. "Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma." Trends in neurosciences
Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma Paper: Abraham, Wickliffe C., and Anthony Robins. "Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma." Trends in neurosciences
Systems Neuroscience CISC 3250
 Systems Neuroscience CISC 325 Memory Types of Memory Declarative Non-declarative Episodic Semantic Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 328A Hippocampus (MTL) Cerebral cortex Basal ganglia Motor
Systems Neuroscience CISC 325 Memory Types of Memory Declarative Non-declarative Episodic Semantic Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 328A Hippocampus (MTL) Cerebral cortex Basal ganglia Motor
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
African Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Development Vol. 4 No.1 pp (2012)
 African Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Development Vol. 4 No.1 pp.16-19 (2012) Effects of Antimalarial Herbal Mixture (Abc 123) on the Liver of Rats *Iliya HA, Wannang NN, Andrew MM, Ibrahim H Department
African Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Development Vol. 4 No.1 pp.16-19 (2012) Effects of Antimalarial Herbal Mixture (Abc 123) on the Liver of Rats *Iliya HA, Wannang NN, Andrew MM, Ibrahim H Department
Effect of Acute Administration of loganin on Spatial Memory in Diabetic Male Rats
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5681/apb.2013.015 http://apb.tbzmed.ac.ir/ Effect of Acute Administration of loganin on Spatial Memory in Diabetic Male Rats Shirin Babri 1, Saeideh Hasani Azami 1, Gisou Mohaddes
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5681/apb.2013.015 http://apb.tbzmed.ac.ir/ Effect of Acute Administration of loganin on Spatial Memory in Diabetic Male Rats Shirin Babri 1, Saeideh Hasani Azami 1, Gisou Mohaddes
Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 )
 770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
(Streptozotocin) ( ) (Regeneration) (Micro vascular) (Retinopathy) (Neuropathy) (Nephropathy) (Dementia) (Macrovascular)
 1 Micro vascular Retinopathy Neuropathy Nephropathy Macrovascular 2 Regeneration 3 Dementia 4 kiasalari@yahoocom * * najafabady@yahoocom khalili@shahedacir Streptozotocin Crocus sativus 30 Shuttle box
1 Micro vascular Retinopathy Neuropathy Nephropathy Macrovascular 2 Regeneration 3 Dementia 4 kiasalari@yahoocom * * najafabady@yahoocom khalili@shahedacir Streptozotocin Crocus sativus 30 Shuttle box
Memory: Computation, Genetics, Physiology, and Behavior. James L. McClelland Stanford University
 Memory: Computation, Genetics, Physiology, and Behavior James L. McClelland Stanford University A Playwright s Take on Memory What interests me a great deal is the mistiness of the past Harold Pinter,
Memory: Computation, Genetics, Physiology, and Behavior James L. McClelland Stanford University A Playwright s Take on Memory What interests me a great deal is the mistiness of the past Harold Pinter,
Treatment of Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats with Metformin or Glitazones is Associated with Amelioration of Hyperglycaemia and Neuroprotection
 8 The Open Diabetes Journal, 2012, 5, 8-12 Open Access Treatment of Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats with Metformin or Glitazones is Associated with Amelioration of Hyperglycaemia and Neuroprotection Oluwole
8 The Open Diabetes Journal, 2012, 5, 8-12 Open Access Treatment of Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats with Metformin or Glitazones is Associated with Amelioration of Hyperglycaemia and Neuroprotection Oluwole
Modeling of Hippocampal Behavior
 Modeling of Hippocampal Behavior Diana Ponce-Morado, Venmathi Gunasekaran and Varsha Vijayan Abstract The hippocampus is identified as an important structure in the cerebral cortex of mammals for forming
Modeling of Hippocampal Behavior Diana Ponce-Morado, Venmathi Gunasekaran and Varsha Vijayan Abstract The hippocampus is identified as an important structure in the cerebral cortex of mammals for forming
Anti diabetic activity of Zizipus mauritiana Lam. In streptozotocin induced Diabetic Rats and its comparison with some standard flavonoids
 Research Paper Anti diabetic activity of Lam. In streptozotocin induced Diabetic Rats and its comparison with some standard flavonoids Bhargava Amit * and Rana A.C. 1 *B. N. College of Pharmacy, Udaipur
Research Paper Anti diabetic activity of Lam. In streptozotocin induced Diabetic Rats and its comparison with some standard flavonoids Bhargava Amit * and Rana A.C. 1 *B. N. College of Pharmacy, Udaipur
ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF KOVAI KIZHANGU CHOORANAM IN ALLOXAN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS ABSTRACT
 ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF KOVAI KIZHANGU CHOORANAM IN ALLOXAN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS P. PARTHIBAN 1, RAVIKUMAR 1, J. ANBU *2 AND ASHWINI ANJANA 2 1 Department of Medicine, Govt. Siddha College, Arumbakkam,
ANTIDIABETIC ACTIVITY OF KOVAI KIZHANGU CHOORANAM IN ALLOXAN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS P. PARTHIBAN 1, RAVIKUMAR 1, J. ANBU *2 AND ASHWINI ANJANA 2 1 Department of Medicine, Govt. Siddha College, Arumbakkam,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE
 APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
Mohammad et al., Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. (2015) 12(5):84-88
 LAMIUM ALBUM OR URTICA DIOICA? WHICH IS MORE EFFECTIVE IN DECREASING SERUM GLUCOSE, LIPID AND HEPATIC ENZYMES IN STREPTOZOTOCIN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY Mohammad Mohseni Mehran a, Mohammad
LAMIUM ALBUM OR URTICA DIOICA? WHICH IS MORE EFFECTIVE IN DECREASING SERUM GLUCOSE, LIPID AND HEPATIC ENZYMES IN STREPTOZOTOCIN INDUCED DIABETIC RATS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY Mohammad Mohseni Mehran a, Mohammad
Pharmacological evaluation of the central nervous system activity of Aframomum melegueta seed extract in mice
 Vol. 5/2 (2005) 141-146 141 JOURNAL OF NATURAL REMEDIES Pharmacological evaluation of the central nervous system activity of Aframomum melegueta seed extract in mice Umukoro S*, Ashorobi R. B. Department
Vol. 5/2 (2005) 141-146 141 JOURNAL OF NATURAL REMEDIES Pharmacological evaluation of the central nervous system activity of Aframomum melegueta seed extract in mice Umukoro S*, Ashorobi R. B. Department
Prof. Patrick E. Ebong
 A PAPER PRESENTED AT INTERNATIONAL NEEM CONFERENCE IN KUNMING, CHINA, NOVEMBER 2006 BY Prof. Patrick E. Ebong Department of Biochemistry, College of Medical Sciences, University of Calabar P.M.B 1115,
A PAPER PRESENTED AT INTERNATIONAL NEEM CONFERENCE IN KUNMING, CHINA, NOVEMBER 2006 BY Prof. Patrick E. Ebong Department of Biochemistry, College of Medical Sciences, University of Calabar P.M.B 1115,
effect on the upregulation of these cell surface markers. The mean peak fluorescence intensity
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 Supplementary Figure 1 ASIC1 disruption or blockade does not effect in vitro and in vivo antigen-presenting cell activation. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface molecules
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 Supplementary Figure 1 ASIC1 disruption or blockade does not effect in vitro and in vivo antigen-presenting cell activation. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface molecules
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Long-term protection studies. 45 minutes of ischemia was induced in wild type (S1pr2 +/+ ) and S1pr2 -/- by MCAO. A) 5 days later brains were harvested
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Long-term protection studies. 45 minutes of ischemia was induced in wild type (S1pr2 +/+ ) and S1pr2 -/- by MCAO. A) 5 days later brains were harvested
EFFECTS OF NITRIC OXIDE SYNTHASE INHIBITOR N G -NITRO-L-ARGININE METHYL ESTER ON SPATIAL AND CUED LEANING
 Pergamon Neuroscience Vol. 83, No. 3, pp. 837 841, 1998 Copyright 1998 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved PII: S0306-4522(97)00457-0 0306 4522/98 $19.00+0.00
Pergamon Neuroscience Vol. 83, No. 3, pp. 837 841, 1998 Copyright 1998 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved PII: S0306-4522(97)00457-0 0306 4522/98 $19.00+0.00
PRESENTER: DR. DEEPA JJM MEDICAL COLLEGE DAVANGERE
 PRESENTER: DR. DEEPA JJM MEDICAL COLLEGE DAVANGERE Depression is a most common mood disorders characterised by a feeling of worthlessness, sadness and suicidal thoughts. Affects more than 10-15% of the
PRESENTER: DR. DEEPA JJM MEDICAL COLLEGE DAVANGERE Depression is a most common mood disorders characterised by a feeling of worthlessness, sadness and suicidal thoughts. Affects more than 10-15% of the
Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals
 Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals Nissl stained coronal or horizontal sections were made from kainate injected (right) and saline injected (left) animals at different
Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals Nissl stained coronal or horizontal sections were made from kainate injected (right) and saline injected (left) animals at different
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by
 Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
<student name> Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal
 Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
BIOCHEMISTRY ondmolecular BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Poges
 Vol. 40, No. 3, October 1996 BIOCHEMISTRY ondmolecular BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Poges 515-520 ATTENUATION BY NICOTINAMIDE OF THE STREPTOZOCIN INDUCED EARLY HYPERGLYCAEMIA IN FASTING RATS Kai K. Wong Department
Vol. 40, No. 3, October 1996 BIOCHEMISTRY ondmolecular BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Poges 515-520 ATTENUATION BY NICOTINAMIDE OF THE STREPTOZOCIN INDUCED EARLY HYPERGLYCAEMIA IN FASTING RATS Kai K. Wong Department
Gestational Diabetes Induces Pancreatic Beta-Cells Apoptosis in Adult Rat Offspring
 Int. J. Morphol., 35(1):16-20, 2017. Gestational Diabetes Induces Pancreatic Beta-Cells Apoptosis in Adult Rat Offspring Diabetes Gestacional Induce Apoptosis de Células Beta del Páncreas en Crías de Ratas
Int. J. Morphol., 35(1):16-20, 2017. Gestational Diabetes Induces Pancreatic Beta-Cells Apoptosis in Adult Rat Offspring Diabetes Gestacional Induce Apoptosis de Células Beta del Páncreas en Crías de Ratas
Neuroprotective properties of GLP-1 - a brief overview. Michael Gejl Jensen, MD Dept. Of Pharmacology, AU
 Neuroprotective properties of GLP-1 - a brief overview Michael Gejl Jensen, MD Dept. Of Pharmacology, AU mg@farm.au.dk Agenda Glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) GLP-1 and neuronal activity GLP-1 in disease-specific
Neuroprotective properties of GLP-1 - a brief overview Michael Gejl Jensen, MD Dept. Of Pharmacology, AU mg@farm.au.dk Agenda Glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) GLP-1 and neuronal activity GLP-1 in disease-specific
Supplementary Fig. 1
 PDK1-dependent quenching of TACE shedding activity in prion and Alzheimer s diseases Mathéa Pietri, Caroline Dakowski, Samia Hannaoui, Aurélie Alleaume-Butaux, Julia Hernandez-Rapp, Audrey Ragagnin, Sophie
PDK1-dependent quenching of TACE shedding activity in prion and Alzheimer s diseases Mathéa Pietri, Caroline Dakowski, Samia Hannaoui, Aurélie Alleaume-Butaux, Julia Hernandez-Rapp, Audrey Ragagnin, Sophie
