Radiation-induced lowered neurogenesis associated with shortened latency of inhibitory avoidance memory response
|
|
|
- Angelina Ellis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original article Radiation-induced lowered neurogenesis associated with shortened latency of inhibitory avoidance memory response Mehrdad Jahanshahi 1, Alireza Khoshbin Khoshnazar 2, Nasrin-Sadat Azami 3, Mahmoud Heidari 3 1Department of Anatomy, Neuroscience Research Center, Golestan University of Medical Sciences, Gorgan, Iran, 2Department of Biochemistry and Medical Physics, Golestan University of Medical Sciences, Gorgan, Iran, 3Department of Biology, Gorgan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Gorgan, Iran Folia Neuropathol 2011; 49 (2): Abstract The neural system is less sensitive to radiation than other late-responding organs and tissues such as the kidney and lung. The generation of new neurons in the adult mammalian brain has been documented in several works. Many studies show that adult hippocampal neurogenesis relates to hippocampal function, in several ways. In this study, we assessed the effect of single and fractionated cobalt radiation on neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampal formation. The irradiation time for delivering 2 Gy (for fractionated dose radiation) and 10 Gy (for single dose radiation) at maximum depth were respectively 1.98 min and 9.92 min. To study the association with memory function we examined inhibitory avoidance memory using a step-through device. Brains were withdrawn and fixed, and then sections were stained with cresyl violet for neurons. We found that a 10 Gy dose can induce lower neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus (p < 0.05), in such a way that a fractionated dose (5 fractions of 2 Gy) is more effective than a single dose (one fraction of 10 Gy). Moreover, a fractionated dose could reduce step-through latency corresponding to damaged inhibitory avoidance memory (p < 0.05). Synergic action of an anaesthetic drug may be the cause of more reduction of neurogenesis in fractionated irradiated rats. There was no significant difference in latency of the inhibitory avoidance memory response between the single 10 Gy group and the sham group, while fractionated 10 Gy could reduce latency. Diffe rent mechanisms of action in the two regimens of irradiation may be a reason. Key words: cobalt radiation, neurogenesis, step-through, dentate gyrus, inhibitory avoidance memory. Introduction Radiation therapy is one of the first choices of treatment for intracranial tumours, which is restricted by damage to normal brain tissue [7,12]. Of course, the mechanism of this damage remains unclear; however, the number of studies on this issue is increasing [26]. Certain glial, neural, and endothelial cells in the CNS after irradiation suffer from apoptosis [4,10-12,18,29]. Radiation-induced lowered neurogenesis of hippocam- Communicating author: Dr. Alireza Khoshbin Khoshnazar, Department of Biochemistry and Medical Physics, Faculty of Medicine, Golestan University of Medical Sciences, km 4 Gorgan-Sari Road (Shastcola), Gorgan, Iran, P.O. Box: , phone: , akhoshbin@yahoo.com Folia Neuropathologica 2011; 49/2 103
2 Mehrdad Jahanshahi, Alireza Khoshbin Khoshnazar, Nasrin-Sadat Azam, Mahmoud Heidari pus in rodents has been evidenced by many authors [1,14,15]. A number of studies have shown increased hippo - campal neurogenesis in response to its function [3,6,22]. Trained rats have a higher rate of neurogenesis [28]. Dentate granular neurons derive from precursor cells located in the subgranular zone [5]. Knowing radiation effects on neurogenic cells may provide a tool to understand specific consequences associated with cranial radiation. Months to years following radiotherapy many patients may suffer from damaged short-term memory, spatial relations, visual motor processing, quanti - tative skills and attention [23]. Damage to neural precursor cells may be responsible for some of the above con sequences [14,15,20]. In the mammalian brain two regions have active neurogenesis: the subventricular zone of the anterior lateral ventricles and the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus in the hippocampus [5,25]. Neurogenic cells in dentate subgranular cells are sensitive to ionizing radiation, undergoing apoptosis after doses ranging from 0.4 Gy to 18 Gy [13,16,21,23, 24,27]. Madsen et al. reported that subjecting adult rats to fractionated brain radiation blocked the formation of neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampal formation [10, 14]. Animals with blocked neurogenesis showed poorer performance in a hippocampus-dependent place recognition task. Other reports documented the functional significance of newly generated neurons in the dentate gyrus. In this study, we assessed the effect of single dose radiation (10 Gy) and fractionated dose radiation (five fractions of 2 Gy) on neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of hippocampal formation. Material and methods Animals Forty-two adult male Wistar rats, weighing g, were used in the study. They were given free access to normal laboratory chow and water. Tempe - rature of the animal house was 22 ± 3 C. The rats were kept in groups of six. Irradiation The radiation machine was a cobalt 60 unit routi - nely used for radiotherapy. Its output was cgy/ min at SSD of 80 cm at maximum depth. The field size was 5 5 cm 2 including the shielded area. The ir - radiation time for delivering 2 Gy (for fractionated dose radiation) and 10 Gy (for single dose radiation) at maximum depth was respectively 1.98 min and 9.92 min. Eyes of rats were shielded by lead blocks to avoid any ophthalmic reaction interrupting the memory test. Inhibitory avoidance memory apparatus The apparatus consisted of two chambers of the same size ( cm) separated by a dividing wall, a guillotine door (7.9 cm 2 ) which could be lifted manually. The walls and floor of one chamber were made of white opaque resin, while the other was dark. The floor of the dark chamber was made of stainless steel rods (3 mm in diameter and 1 cm intervals). Intermittent electric shocks (50 Hz, 3 s, 1 ma intensity) were delivered to the grid floor of the dark chamber by an isolated stimulator. Behavioural test All animals were allowed to habituate in the ex - perimental room for at least 30 min prior to the experiments. Then each rat was lightly placed in the bright chamber. After 5 s the guillotine door was opened and the animal was permitted to enter the dark chamber. The latency with which the animal entered the dark chamber was recorded. Animals that delayed more than 100 s to enter the dark chamber were excluded. When the rat crossed with the four paws to the dark chamber, the guillotine door was closed and the rat was quickly removed from the dark chamber. After 30 min when the rat crossed to the dark chamber, the guillotine door was closed and a foot electric shock was delivered to the grid floor of the dark room. After 20 s the rat was removed from the apparatus and placed temporarily in the home cage. After 2 min the animal was tested again by the same method as before. If the rat did not enter the dark chamber within 120 s a successful acquisition of the response was recorded. Otherwise when the rat entered the dark chamber with a delay less than 120 s the door was closed and the second shock was delivered. If the rat passed the second test successfully, it would be accepted for the experiment. Rats with delays less than 120 s were rejected. 104 Folia Neuropathologica 2011; 49/2
3 Cobalt radiation and DG neurons To examine inhibitory memory each rat was placed in the bright chamber, the guillotine door was opened after 5 s and latency of entering the dark room was taken as the evaluation score. The longest latency to enter the dark room (place of receiving the shock) was considered as full memory, which normally is 300 s. Histology Tissue processing: After behavioural testing rats were decapitated under diethyl ether anaesthesia. Brains were withdrawn and then fixed for two weeks in 10% formaldehyde. Different degrees of alcohol were used for dehydration followed by clarification with xylol. After histological processing, tissue was impregnated and then embedded in paraffin wax. The 7 μm coronal sections were serially collected from Bregma 3.30 mm to 6.04 mm of the hippo - campal formation. An interval of 20 μm was placed between each two consecutive sections. The sections were stained with cresyl violet in accordance with routine laboratory procedures [2]. A photograph of each section was produced us - ing an Olympus BX 51 microscope and a DP 12 digi - tal camera under a magnification of An area of 3600 μm 2 was selected in the lower horn of the dentate gyrus in all sections. To measure the area density of the granule cells, the images were transferred to the computer. Using OLYSIA Autobioreport software, Olympus Co, the appropriate grids were superimposed on the pictures and the cells were counted manually. To perform an unbiased measurement, the individual was double-blinded and only the cells with significant granule cell characteristics were counted [8,9]. Statistical analysis All the data were entered into and analysed by SPSS 11.5 software. The data were expressed as mean ± SEM. The statistical analysis was performed using one and two way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Post-hoc comparison of means was carried out with the Tukey test for multiple comparisons, when appropriate. The level of statistical significance was set at P < Calculations were performed using the SPSS statistical package. Results Avoidance inhibitory memory test In experimental groups the rats were trained and one month later at the same time were tested. Table I shows the results of the memory test. As the table shows, latency of response in the sham group given anaesthesia on 5 consecutive days without radiation was ± s while for the 2 5 Gy group and 10 Gy group it was respectively ± s and 203 ± s, showing a significant difference between sham and fractionated (2 5 Gy) groups (p < 0.05). We found no significant difference between sham and single fraction (10 Gy) groups. Moreover, there was no significant difference between control and sham groups. Fig. 1 shows the results as statistical bars. Step through latency (sec) *** control sham 2 10 pre-test treatment (gray/rat) Fig. 1. Significance difference between sham and fractionated radiation. Table I. Latency of entrance (in seconds) to dark chamber in different groups of rats Rat 1 Rat 2 Rat 3 Rat 4 Rat 5 Rat 6 Control Sham Gy Gy Folia Neuropathologica 2011; 49/2 105
4 Mehrdad Jahanshahi, Alireza Khoshbin Khoshnazar, Nasrin-Sadat Azam, Mahmoud Heidari Table II. Mean number of neurons in all groups DG Mean Std. deviation Area μm 2 1 Control Sham anaesthesia Sham avoidance Rad 10 avoidance Rad 2 5 avoidance Rad 10 + avoidance Rad avoidance Cell counts (neurogenesis) Table II shows the results of cell counts in diffe - rent groups. Granular cells in the lower horn in the dentate gyrus were counted. The number of neurons in all study groups was lower than in the control group and the differences were significant (P < 0.05). The analysis shows a significant difference bet - ween the sham anaesthesia group and the fractionated radiation group (p = 0.002). We found no significant difference between the single fraction ra diation and sham anaesthesia group (p = 0.999), which is consistent with the memory test. Also we found that not only the avoidance test can reduce the neuron density, but also the radiation can do it (Table II). Discussion This study was performed to assess whether radiation can decrease the number of granular neurons proliferating in the dentate gyrus of the hippo - campal formation, and if this can affect its function as inhibitory memory latency. We observed good consistency between neurogenesis reduction and shortness of inhibitory memory latency. Five fractions of 2 Gy was more effective than single 10 Gy to reduce neurogenesis, while the same result was obtained during the inhibitory memory test. Our results showed that fractionated radiation is more effective than single radiation to shorten latency of the memory response. Based on our results there was no significance difference between the number of granular neurons in the hippocampal formation after a single fraction of 10 Gy and the anaesthesia sham group (P = 0.999), a result which verified inhibitory memory test data. Our results resemble those of another study that showed a decrease of cell density after the avoidance memory test [17]. It seems that three factors play roles in reduction of neurons in the dentate gyrus: anaesthesia, avoidance test and radiation. Meanwhile there is a significant difference bet - ween the fractionated group and the anaesthesia group, suggesting that the anaesthetic drug behaves as an interfering parameter or additive agent to ra - diation. For early responding tissues (with high α/β ratio) there is little sensitization to fractionation [7], as we also observed. But more effectiveness of the fractionated regimen may be related to five administrations of the anaesthetic drug. Synergic action of the drug and radiation to kill neural cells in the hippocampal formation is a hypothesis which should be assessed and proved. Madsen et al. observed blocked neurogenesis after 3 Gy irradiation. Animals with blocked neurogenesis performed poorer than controls in hippo - campus-dependent function [14]. Our data showed the same effect on inhibitory avoidance memory, another hippocampus-dependent function. Many researchers have addressed the potential effectiveness of neurogenesis as a cause of hippo - campal functions of learning and memory [5,22,28]. According to our results there is a relationship bet - ween radiation-induced lowered neurogenesis and shortness of memory latency, giving a clue for management of radiotherapy consequences. 106 Folia Neuropathologica 2011; 49/2
5 Cobalt radiation and DG neurons This was consistent with the results of Santarelli et al. and Raber et al., who reported an association between decreased neurogenesis and cognitive deterioration [7,19,21]. Conclusions We summarize our conclusions in five main topics: 1. There is good consistency between reduction of neurogenesis and shortness of the inhibitory memory response as a hippocampus-dependent function. 2. As we are dealing with an early responding tissue it is reasonable that there is low sensitization to fractionation. 3. Greater efficacy of the fractionated regimen to reduce neurogenesis may be due to synergic action of the anaesthetic drug. 4. No effect of single 10 Gy on reduction of latency of the inhibitory avoidance response, in comparison with a fractionated dose, may be due to different mechanisms of action in the two regimens. 5. Three factors play roles in reduction of neurons in the dentate gyrus: anaesthesia, avoidance test and radiation. Acknowledgments The authors wish to thank the Research and Technology Center of Golestan University of Medical Sciences. We are also grateful to staff of the Radiotherapy section of 5 Azar hospital of Gorgan. Moreover, we extend our appreciation to the Neuroscience Center of the university. References 1. Andres-Mach M, Rola R, Fike J. Radiation effects on neural precursor cells in the dentate gyrus. Cell Tissue Res 2008; 331: Bancroft J, Gamble M. Theory and practice of histological techniques. Elsevier Health Sciences, Philadelphia Barnea A, Nottebohm F. Seasonal recruitment of hippocampal neurons in adult free-ranging black-capped chickadees. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: Chow B, Li Y, Wong C. Radiation-induced apoptosis in the adult central nervous system is p53-dependent. Cell Death Differ 2000; 7: Gage F, Kempermann G, Palmer T, Peterson D, Ray J. Multipotent progenitor cells in the adult dentate gyrus. J Neurobiol 1998; 36: Gould E, Beylin A, Tanapat P, Reeves A, Shors T. Learning en - hances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation. Nat Neurosci 1999; 2: Halperin E, Perez C, Brady L. Perez and Brady's principles and practice of radiation oncology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia Jahanshahi M, Golalipour M, Afshar M. The effect of Urtica dioica extract on the number of astrocytes in the dentate gyrus of diabetic rats. Folia Morphol 2009; 68: Jahanshahi M, Sadeghi Y, Hosseini A, Naghdi N, Marjani A. The effect of spatial learning on the number of astrocytes in the CA3 subfield of the rat hippocampus. Singapore Med J 2008; 49: Li Y, Chen P, Haimovitz-Friedman A, Reilly R, Wong C. Endothelial apoptosis initiates acute blood-brain barrier disruption after ionizing radiation. Cancer Res 2003; 63: Li Y, Guo Y, Jay V, Stewart P, Wong C. Time course of radiationinduced apoptosis in the adult rat spinal cord. Radiother Oncol 1996; 39: Li Y, Jay V, Wong C. Oligodendrocytes in the adult rat spinal cord undergo radiation-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 1996; 56: Lonergan P, Martin D, Horrobin D, Lynch M. Neuroprotective effect of eicosapentaenoic acid in hippocampus of rats ex - posed to gamma-irradiation. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: Madsen T, Kristjansen P, Bolwig T, Wörtwein G. Arrested neuronal proliferation and impaired hippocampal function following fractionated brain irradiation in the adult rat. Neurosci 2003; 119: Mizumatsu S, Monje M, Morhardt D, Rola R, Palmer T, Fike J. Extreme sensitivity of adult neurogenesis to low doses of X- irradiation. Cancer Res 2003; 63: Nagai R, Tsunoda S, Hori Y, Asada H. Selective vulnerability to radiation in the hippocampal dentate granule cells. Surg Neurol 2000; 53: Nikolakopoulou A, Dermon C, Panagis L, Pavlidis M, Stewart M. Passive avoidance training is correlated with decreased cell proliferation in the chick hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 2006; 24: Pen ~ a L, Fuks Z, Kolesnick R. Radiation-induced apoptosis of endothelial cells in the murine central nervous system: protection by fibroblast growth factor and sphingomyelinase deficiency. Cancer Res 2000; 60: Raber J, Rola R, LeFevour A, Morhardt D, Curley J, Mizumatsu S, VandenBerg SR, Fike JR19. Radiation-induced cognitive im - pairments are associated with changes in indicators of hippocampal neurogenesis. Radiat Res 2004; 162: Rola R, Sarkissian V, Obenaus A, Nelson GA, Otsuka S, Limoli CL, Fike JR20. High-LET radiation induces inflammation and persistent changes in markers of hippocampal neurogenesis. Radiat Res 2005; 164: Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, Surget A, Battaglia F, Dulawa S, Weisstaub N, Lee J, Duman R21. Arancio O, Belzung C, Hen R. Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science 2003; 301: Shors T, Miesegaes G, Beylin A, Zhao M, Rydel T, Gould E. Neurogenesis in the adult is involved in the formation of trace memories. Nature 2001; 410: Folia Neuropathologica 2011; 49/2 107
6 Mehrdad Jahanshahi, Alireza Khoshbin Khoshnazar, Nasrin-Sadat Azam, Mahmoud Heidari 23. Strother D, Pollack I, Fisher P, Hunter J, Woo S, Pomeroy S. Tumors of the central nervous system. In: Pizzo PA, Poplack DG (eds.). Principles and Practice of Pediatric Oncology. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia Tada E, Yang C, Gobbel G, Lamborn K, Fike J. Long-term impairment of subependymal repopulation following damage by ionizing irradiation. Exp Neurol 1999; 160: Temple S, Alvarez-Buylla A. Stem cells in the adult mammalian central nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 1999; 9: Tofilon P, Fike J. The radioresponse of the central nervous system: a dynamic process. Radiat Res 2000; 153: Uberti D, Piccioni L, Cadei M, Grigolato P, Rotter V, Memo M. p53 is dispensable for apoptosis but controls neurogenesis of mouse dentate gyrus cells following [gamma]-irradiation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2001; 93: van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage F. Running increases cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci 1999; 2: Wong C, Van der Kogel A. Mechanisms of radiation injury to the central nervous system: implications for neuroprotection. Mol Interv 2004; 4: Folia Neuropathologica 2011; 49/2
The Effect of Scopolamine on Avoidance Memory and Hippocampal Neurons in Male Wistar Rats
 The Effect of Scopolamine on Avoidance Memory and Hippocampal Neurons in Male Wistar Rats Saba Seifhosseini 1, Mehrdad Jahanshahi 2,*, Ali Moghimi 3, Nasrin-Sadat Aazami 4 1. Department of Biology, Faculty
The Effect of Scopolamine on Avoidance Memory and Hippocampal Neurons in Male Wistar Rats Saba Seifhosseini 1, Mehrdad Jahanshahi 2,*, Ali Moghimi 3, Nasrin-Sadat Aazami 4 1. Department of Biology, Faculty
Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing. Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2
 ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
The effect of Urtica dioica extract on the number of astrocytes in the dentate gyrus of diabetic rats
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 2, pp. 93 97 Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The effect of Urtica dioica extract on the number of astrocytes in the
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 2, pp. 93 97 Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The effect of Urtica dioica extract on the number of astrocytes in the
Neurogenesis in Adult Central Nervous System: Death of a Dogma
 Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece, Nov. 2007 Neurogenesis in Adult Central Nervous System: Death of a Dogma Anton B. Tonchev Division of Cell Biology, Varna University of Medicine, Bulgaria
Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece, Nov. 2007 Neurogenesis in Adult Central Nervous System: Death of a Dogma Anton B. Tonchev Division of Cell Biology, Varna University of Medicine, Bulgaria
The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females
 The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females Samantha Pavlock (Medical Student) Pradeep Bhide and Deirdre McCarthy (Faculty
The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females Samantha Pavlock (Medical Student) Pradeep Bhide and Deirdre McCarthy (Faculty
Effects of Repeated Administration of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) on Avoidance Memory and Cell Density in Rats' Hippocampus
 Effects of Repeated Administration of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) on Avoidance Memory and Cell Density in Rats' Hippocampus Mehrdad Jahanshahi 1*, Kamran Haidari 1, Simin Mahaki-Zadeh 1, EmseGol
Effects of Repeated Administration of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) on Avoidance Memory and Cell Density in Rats' Hippocampus Mehrdad Jahanshahi 1*, Kamran Haidari 1, Simin Mahaki-Zadeh 1, EmseGol
Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Bromodeoxyuridine
 Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
Ablation of hippocampal neurogenesis impairs contextual fear conditioning and synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus
 Ablation of hippocampal neurogenesis impairs contextual fear conditioning and synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus Michael D. Saxe*, Fortunato Battaglia*, Jing-Wen Wang*, Gael Malleret*, Denis J. David*,
Ablation of hippocampal neurogenesis impairs contextual fear conditioning and synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus Michael D. Saxe*, Fortunato Battaglia*, Jing-Wen Wang*, Gael Malleret*, Denis J. David*,
Functional significance of adult neurogenesis Gerd Kempermann 1, Laurenz Wiskott 2 and Fred H Gage,3
 Functional significance of adult neurogenesis Gerd Kempermann 1, Laurenz Wiskott 2 and Fred H Gage,3 Function is the key criterion for determining whether adult neurogenesis be it endogenous, induced,
Functional significance of adult neurogenesis Gerd Kempermann 1, Laurenz Wiskott 2 and Fred H Gage,3 Function is the key criterion for determining whether adult neurogenesis be it endogenous, induced,
Adult Neurogenesis and Hippocampal Memory Function: New Cells, More Plasticity, New Memories?
 Neurosurg Clin N Am 18 (2007) 105 113 Adult Neurogenesis and Hippocampal Memory Function: New Cells, More Plasticity, New Memories? Yasuji Kitabatake, MD, PhD, Kurt A. Sailor, BS, Guo-li Ming, MD, PhD,
Neurosurg Clin N Am 18 (2007) 105 113 Adult Neurogenesis and Hippocampal Memory Function: New Cells, More Plasticity, New Memories? Yasuji Kitabatake, MD, PhD, Kurt A. Sailor, BS, Guo-li Ming, MD, PhD,
Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2+ cells in different brain regions.
 Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS
 TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Differential Recovery of Neural Stem Cells in the Subventricular Zone and Dentate Gyrus After Ionizing Radiation NINA A.K. HELLSTRÖM, a THOMAS BJÖRK-ERIKSSON, b,c KLAS BLOMGREN,
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Differential Recovery of Neural Stem Cells in the Subventricular Zone and Dentate Gyrus After Ionizing Radiation NINA A.K. HELLSTRÖM, a THOMAS BJÖRK-ERIKSSON, b,c KLAS BLOMGREN,
Learning Enhances the Survival of New Neurons beyond the Time when the Hippocampus Is Required for Memory
 The Journal of Neuroscience, August 25, 2004 24(34):7477 7481 7477 Brief Communication Learning Enhances the Survival of New Neurons beyond the Time when the Hippocampus Is Required for Memory Bendetta
The Journal of Neuroscience, August 25, 2004 24(34):7477 7481 7477 Brief Communication Learning Enhances the Survival of New Neurons beyond the Time when the Hippocampus Is Required for Memory Bendetta
A ROLE FOR ADULT NEUROGENESIS IN SPATIAL LONG-TERM MEMORY
 Neuroscience 130 (2005) 843 852 A ROLE FOR ADULT NEUROGENESIS IN SPATIAL LONG-TERM MEMORY J. S. SNYDER, a N. S. HONG, b R. J. MCDONALD b AND J. M. WOJTOWICZ a * a Department of Physiology, University of
Neuroscience 130 (2005) 843 852 A ROLE FOR ADULT NEUROGENESIS IN SPATIAL LONG-TERM MEMORY J. S. SNYDER, a N. S. HONG, b R. J. MCDONALD b AND J. M. WOJTOWICZ a * a Department of Physiology, University of
Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex?
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 107 (2006) No. 1, p. 71 80 71) Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex? Šimonová Z., Dutt J. Department of Neuroscience of the Institute
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 107 (2006) No. 1, p. 71 80 71) Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex? Šimonová Z., Dutt J. Department of Neuroscience of the Institute
Supplementary Methods
 1 Supplementary Methods Social Preference Test Subjects Seventy-four Long-Evans, male rats served as subjects (S-rats) in the foodpreference test, with 40 assigned to the CXT-Same (CXT-S) Condition and
1 Supplementary Methods Social Preference Test Subjects Seventy-four Long-Evans, male rats served as subjects (S-rats) in the foodpreference test, with 40 assigned to the CXT-Same (CXT-S) Condition and
Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis of individual mice during maze learning. a,
 Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Radiation-induced changes in brain function after cranial irradiation: Radiobiology and clinical review
 Radiation-induced changes in brain function after cranial irradiation: Radiobiology and clinical review Brian Marples PhD Beaumont Health System Royal Oak, Michigan Disclosures Radiobiologist Department
Radiation-induced changes in brain function after cranial irradiation: Radiobiology and clinical review Brian Marples PhD Beaumont Health System Royal Oak, Michigan Disclosures Radiobiologist Department
INJURY FOLLOWING WHOLE-BRAIN IRRADIATION KELLY R. CONNER WAKE FOREST UNIVERSITY GRADUATE SCHOOL OF ARTS AND SCIENCES
 EFFECTS OF AT 1 R ANTAGONIST L-158,809 ON NORMAL BRAIN TISSUE INJURY FOLLOWING WHOLE-BRAIN IRRADIATION BY KELLY R. CONNER A Dissertation Submitted to the Graduate School Faculty of WAKE FOREST UNIVERSITY
EFFECTS OF AT 1 R ANTAGONIST L-158,809 ON NORMAL BRAIN TISSUE INJURY FOLLOWING WHOLE-BRAIN IRRADIATION BY KELLY R. CONNER A Dissertation Submitted to the Graduate School Faculty of WAKE FOREST UNIVERSITY
Advances on Learning-modulated Adult Neurogenesis
 Advances on Learning-modulated Adult Neurogenesis Nieto-Escámez F.A. 1, *, Ruiz-Muñoz A. 1, Sánchez-Santed F. 1 1 Dept. Neuroscience and Health Sciences. Universidad de Almeria. CP04120 La Cañada de San
Advances on Learning-modulated Adult Neurogenesis Nieto-Escámez F.A. 1, *, Ruiz-Muñoz A. 1, Sánchez-Santed F. 1 1 Dept. Neuroscience and Health Sciences. Universidad de Almeria. CP04120 La Cañada de San
Yasuhiko Matsumori, Jialing Liu, Philip R. Weinstein, Takamasa Kayama ABSTRACT
 Yamagata Med J 2003 21 2) 171-175 Yasuhiko Matsumori, Jialing Liu, Philip R. Weinstein, Takamasa Kayama Department of Neurosurgery, Yamagata University School of Medicine, Yamagata, Japan Department of
Yamagata Med J 2003 21 2) 171-175 Yasuhiko Matsumori, Jialing Liu, Philip R. Weinstein, Takamasa Kayama Department of Neurosurgery, Yamagata University School of Medicine, Yamagata, Japan Department of
Environmental influences on brain and behaviour
 Environmental influences on brain and behaviour Abdul H. Mohammed Dept. of Neurotec Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden IBRO African Neuroscience School, Nairobi, 2005 Environmental interventions affecting
Environmental influences on brain and behaviour Abdul H. Mohammed Dept. of Neurotec Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden IBRO African Neuroscience School, Nairobi, 2005 Environmental interventions affecting
Adaptive Responses Induced by Low Dose Radiation in Dentate Gyrus of Rats
 J Korean Med Sci 26; 21: 113-7 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Adaptive Responses Induced by Low Dose Radiation in Dentate Gyrus of Rats The purpose of this study is to investigate
J Korean Med Sci 26; 21: 113-7 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Adaptive Responses Induced by Low Dose Radiation in Dentate Gyrus of Rats The purpose of this study is to investigate
Molecular Brain. Open Access. Abstract
 Molecular Brain BioMed Central Research Effect of ablated hippocampal neurogenesis on the formation and extinction of contextual fear memory Hyoung-Gon Ko 1, Deok-Jin Jang 1, Junehee Son 1, Chuljung Kwak
Molecular Brain BioMed Central Research Effect of ablated hippocampal neurogenesis on the formation and extinction of contextual fear memory Hyoung-Gon Ko 1, Deok-Jin Jang 1, Junehee Son 1, Chuljung Kwak
Diode calibration for dose determination in total body irradiation
 Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2008; 6 (1): 43-50 Diode calibration for dose determination in total body irradiation M.Allahverdi 1*, Gh. Geraily 1, M. Esfehani 3,A. Sharafi 2,A. Shirazi 1 1 Department of Medical
Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2008; 6 (1): 43-50 Diode calibration for dose determination in total body irradiation M.Allahverdi 1*, Gh. Geraily 1, M. Esfehani 3,A. Sharafi 2,A. Shirazi 1 1 Department of Medical
NeuroReport 2009, 20: a Department of Neurology, Children s Hospital of Chongqing Medical University
 Regeneration and transplantation 295 In-vitro effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on neural progenitor/stem cells from rat hippocampus Tingsong Li a,b, Li Jiang a, Xiaoping Zhang b and Hengsheng
Regeneration and transplantation 295 In-vitro effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on neural progenitor/stem cells from rat hippocampus Tingsong Li a,b, Li Jiang a, Xiaoping Zhang b and Hengsheng
The regulation of adult rodent hippocampal neurogenesis by deep brain stimulation
 J Neurosurg 108:132 138, 2008 The regulation of adult rodent hippocampal neurogenesis by deep brain stimulation Laboratory investigation HIROKI TODA, M.D., PH.D., 1,2 CLEMENT HAMANI, M.D., PH.D., 1 ADRIAN
J Neurosurg 108:132 138, 2008 The regulation of adult rodent hippocampal neurogenesis by deep brain stimulation Laboratory investigation HIROKI TODA, M.D., PH.D., 1,2 CLEMENT HAMANI, M.D., PH.D., 1 ADRIAN
Why Are Some Neurons Replaced in Adult Brain?
 The Journal of Neuroscience, February 1, 2002, 22(3):624 628 Why Are Some Neurons Replaced in Adult Brain? Fernando Nottebohm The Rockefeller University, Field Research Center, Millbrook, New York 12545
The Journal of Neuroscience, February 1, 2002, 22(3):624 628 Why Are Some Neurons Replaced in Adult Brain? Fernando Nottebohm The Rockefeller University, Field Research Center, Millbrook, New York 12545
Effect of chronic treatment of ketamine on hippocampus cell count of adult rats
 Quarterly of the Horizon of Medical Sciences Vol. 19, No. 1, Spr 2013 Pages: 35-39 Effect of chronic treatment of ketamine on hippocampus cell count of adult rats Downloaded from hms.gmu.ac.ir at 12:09
Quarterly of the Horizon of Medical Sciences Vol. 19, No. 1, Spr 2013 Pages: 35-39 Effect of chronic treatment of ketamine on hippocampus cell count of adult rats Downloaded from hms.gmu.ac.ir at 12:09
Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell
 2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
Minocycline ameliorates cognitive impairment induced by whole-brain irradiation: an animal study
 Zhang et al. Radiation Oncology 2014, 9:281 RESEARCH Open Access Minocycline ameliorates cognitive impairment induced by whole-brain irradiation: an animal study Liyuan Zhang 1,2,3, Kun Li 1,2,4, Rui Sun
Zhang et al. Radiation Oncology 2014, 9:281 RESEARCH Open Access Minocycline ameliorates cognitive impairment induced by whole-brain irradiation: an animal study Liyuan Zhang 1,2,3, Kun Li 1,2,4, Rui Sun
Divisional Director of International Clinical Research Mood & Anxiety Disorders. Year Education Education institution
 Curriculum Vitae Torsten Meldgaard Madsen MD H. Lundbeck A/S Divisional Director of International Clinical Research Mood & Anxiety Disorders Education Year Education Education institution 1993 Diploma
Curriculum Vitae Torsten Meldgaard Madsen MD H. Lundbeck A/S Divisional Director of International Clinical Research Mood & Anxiety Disorders Education Year Education Education institution 1993 Diploma
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70%
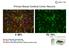 Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
THE EFFECTS OF bfgf TREATMENT IN THE AGED BRAIN FOLLOWING TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY
 Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2010 THE EFFECTS OF bfgf TREATMENT IN THE AGED BRAIN FOLLOWING TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Michael Zeigler Virginia
Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2010 THE EFFECTS OF bfgf TREATMENT IN THE AGED BRAIN FOLLOWING TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY Michael Zeigler Virginia
Long-term administration of ginsenoside Rh 1 enhances learning and memory by promoting cell survival in the mouse hippocampus
 234 Long-term administration of ginsenoside Rh 1 enhances learning and memory by promoting cell survival in the mouse hippocampus JINGANG HOU, JIANJIE XUE, MIRA LEE, JIAOJIAO YU and CHANGKEUN SUNG Department
234 Long-term administration of ginsenoside Rh 1 enhances learning and memory by promoting cell survival in the mouse hippocampus JINGANG HOU, JIANJIE XUE, MIRA LEE, JIAOJIAO YU and CHANGKEUN SUNG Department
EFFECTS OF CHLOROGENIC ACID ON LEARNING AND MEMORY IN RATS
 Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 12, Suppl. 1, pp 132-136, 2014 Copyright 2014 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) EFFECTS OF CHLOROGENIC
Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 12, Suppl. 1, pp 132-136, 2014 Copyright 2014 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) EFFECTS OF CHLOROGENIC
Original Article The Effect of MDMA-Induced Anxiety on Neuronal Apoptosis in Adult Male Rats Hippocampus
 Original Article The Effect of MDMA-Induced Anxiety on Neuronal Apoptosis in Adult Male Rats Hippocampus (MDMA / anxiety / apoptosis / plus-maze / hippocampus / rats) S. Karimi, M. Jahanshahi, M. J. Golalipour
Original Article The Effect of MDMA-Induced Anxiety on Neuronal Apoptosis in Adult Male Rats Hippocampus (MDMA / anxiety / apoptosis / plus-maze / hippocampus / rats) S. Karimi, M. Jahanshahi, M. J. Golalipour
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Neurosurg Clin N Am 18 (2007) 191 198 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A AC133 antigen, in brain tumor cancer cells, 32 35 Activity-based restoration therapy, for spinal
Neurosurg Clin N Am 18 (2007) 191 198 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A AC133 antigen, in brain tumor cancer cells, 32 35 Activity-based restoration therapy, for spinal
Pathophysiological Responses in Rat and Mouse Models of Radiation-Induced Brain Injury
 Mol Neurobiol (2017) 54:1022 1032 DOI 10.1007/s12035-015-9628-x Pathophysiological Responses in Rat and Mouse Models of Radiation-Induced Brain Injury Lianhong Yang 1,2 & Jianhua Yang 1,2 & Guoqian Li
Mol Neurobiol (2017) 54:1022 1032 DOI 10.1007/s12035-015-9628-x Pathophysiological Responses in Rat and Mouse Models of Radiation-Induced Brain Injury Lianhong Yang 1,2 & Jianhua Yang 1,2 & Guoqian Li
Exploring the potential for clinical introduction of hippocampal-sparing IMPT of pediatric medulloblastoma - Past present and future
 Exploring the potential for clinical introduction of hippocampal-sparing IMPT of pediatric medulloblastoma - Past present and future Daniel Gasic Disclosure Nothing to disclose Introduction Background
Exploring the potential for clinical introduction of hippocampal-sparing IMPT of pediatric medulloblastoma - Past present and future Daniel Gasic Disclosure Nothing to disclose Introduction Background
Short-Term But Not Long-Term Exercise Ameliorates Depressive Behavior in Mice
 Short-Term But Not Long-Term Exercise Ameliorates Depressive Behavior in Mice Hiroki Yashima, Aya Matsushita, Ken-ichi Kinoshita, Yoshikage Muroi, and Toshiaki Ishii ABSTRACT Objective Voluntary exercise
Short-Term But Not Long-Term Exercise Ameliorates Depressive Behavior in Mice Hiroki Yashima, Aya Matsushita, Ken-ichi Kinoshita, Yoshikage Muroi, and Toshiaki Ishii ABSTRACT Objective Voluntary exercise
Astroglia induce neurogenesis from adult neural stem cells
 Astroglia induce neurogenesis from adult neural stem cells Hongjun Song*, Charles F. Stevens* & Fred H. Gage * Molecular Neurobiology Laboratory, Howard Hughes Medical Institute at the Salk Institute,
Astroglia induce neurogenesis from adult neural stem cells Hongjun Song*, Charles F. Stevens* & Fred H. Gage * Molecular Neurobiology Laboratory, Howard Hughes Medical Institute at the Salk Institute,
Dr Francis A. Olaolorun Report on ISN/CAEN category 1A August 2016 research grant Home institution: Host institution:
 Dr Francis. Olaolorun Report on ISN/CEN category 1 ugust 2016 research grant Home institution: Neuroscience Unit, Department of Veterinary natomy, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria. Host institution:
Dr Francis. Olaolorun Report on ISN/CEN category 1 ugust 2016 research grant Home institution: Neuroscience Unit, Department of Veterinary natomy, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria. Host institution:
The technique of craniospinal irradiation of paediatric patients in supine position
 The technique of craniospinal irradiation of paediatric patients in supine position Pavel Šlampa 1, Zuzana Seneklova 1, Jiri Simicek 1, Renata Soumarova 1, Petr Burkon 2, Ludmila Burianova 2 1 Masaryk
The technique of craniospinal irradiation of paediatric patients in supine position Pavel Šlampa 1, Zuzana Seneklova 1, Jiri Simicek 1, Renata Soumarova 1, Petr Burkon 2, Ludmila Burianova 2 1 Masaryk
Learning enhances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation
 Learning enhances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation Elizabeth Gould 1, Anna Beylin 1, Patima Tanapat 1, Alison Reeves 1 and Tracey J. Shors 2 1 Department of Psychology, Princeton University,
Learning enhances adult neurogenesis in the hippocampal formation Elizabeth Gould 1, Anna Beylin 1, Patima Tanapat 1, Alison Reeves 1 and Tracey J. Shors 2 1 Department of Psychology, Princeton University,
An examination of avian hippocampal neurogenesis in relationship to photoperiod
 MOLECULAR NEUROSCIENCE An examination of avian hippocampal neurogenesis in relationship to photoperiod Jennifer S. Hoshooley, CA Leslie S. Phillmore and Scott A. MacDougall-Shackleton Program in Neuroscience
MOLECULAR NEUROSCIENCE An examination of avian hippocampal neurogenesis in relationship to photoperiod Jennifer S. Hoshooley, CA Leslie S. Phillmore and Scott A. MacDougall-Shackleton Program in Neuroscience
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function
 Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (21): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (21): ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Inhibition of convulsive status epilepticus-induced abnormal neurogenesis by sodium valproate. Peng Wu 1, Yue Hu 1, Xiujuan Li 1, Min
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (21): ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Inhibition of convulsive status epilepticus-induced abnormal neurogenesis by sodium valproate. Peng Wu 1, Yue Hu 1, Xiujuan Li 1, Min
Recently, it has been proposed that neurogenesis in the
 Neurogenesis and Helplessness Are Mediated by Controllability in Males But Not in Females Tracey J. Shors, Jason Mathew, Helene M. Sisti, Carol Edgecomb, Steven Beckoff, and Christina Dalla Background:
Neurogenesis and Helplessness Are Mediated by Controllability in Males But Not in Females Tracey J. Shors, Jason Mathew, Helene M. Sisti, Carol Edgecomb, Steven Beckoff, and Christina Dalla Background:
Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus
 Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus Gerd Kempermann 1,2, Sebastian Jessberger 2, Barbara Steiner 2 and Golo Kronenberg 1,3 1 Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch,
Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus Gerd Kempermann 1,2, Sebastian Jessberger 2, Barbara Steiner 2 and Golo Kronenberg 1,3 1 Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch,
Young and excitable: the function of new neurons in the adult mammalian brain Fiona Doetsch 1 and Rene Hen 2
 Young and excitable: the function of new neurons in the adult mammalian brain Fiona Doetsch 1 and Rene Hen 2 Adult neurogenesis occurs in most species and is regulated by a wide variety of environmental
Young and excitable: the function of new neurons in the adult mammalian brain Fiona Doetsch 1 and Rene Hen 2 Adult neurogenesis occurs in most species and is regulated by a wide variety of environmental
20: c 2009 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. NeuroReport 2009, 20:
 Developmental neuroscience 371 Intracerebroventricular infusion of cytosine-arabinoside causes prepulse inhibition disruption Benson W.M. Lau a,b,d, Suk-Yu Yau a,b,d, Tatia M.C. Lee b,c, Yick-Pang Ching
Developmental neuroscience 371 Intracerebroventricular infusion of cytosine-arabinoside causes prepulse inhibition disruption Benson W.M. Lau a,b,d, Suk-Yu Yau a,b,d, Tatia M.C. Lee b,c, Yick-Pang Ching
Ophthalmology, Radiation Oncology,
 Supporting Online Material Journal: Nature Neuroscience Article Title: Corresponding Author: All Authors: Affiliations: Tanycytes of the Hypothalamic Median Eminence Form a Diet- Responsive Neurogenic
Supporting Online Material Journal: Nature Neuroscience Article Title: Corresponding Author: All Authors: Affiliations: Tanycytes of the Hypothalamic Median Eminence Form a Diet- Responsive Neurogenic
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
From Stem Cells to Grandmother Cells: How Neurogenesis Relates to Learning and Memory
 From Stem Cells to Grandmother Cells: How Neurogenesis Relates to Learning and Memory Tracey J. Shors 1,2, * 1 Department of Psychology 2 Center for Collaborative Neuroscience Rutgers University, 152 Frelinghuysen
From Stem Cells to Grandmother Cells: How Neurogenesis Relates to Learning and Memory Tracey J. Shors 1,2, * 1 Department of Psychology 2 Center for Collaborative Neuroscience Rutgers University, 152 Frelinghuysen
Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, Jeremy Miller Scientist I
 Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, 2013 Jeremy Miller Scientist I jeremym@alleninstitute.org Outline 1. Brief introduction to previous WGCNA studies in brain 2.
Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, 2013 Jeremy Miller Scientist I jeremym@alleninstitute.org Outline 1. Brief introduction to previous WGCNA studies in brain 2.
Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals
 Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals Nissl stained coronal or horizontal sections were made from kainate injected (right) and saline injected (left) animals at different
Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals Nissl stained coronal or horizontal sections were made from kainate injected (right) and saline injected (left) animals at different
Exercising Our Minds: Effects of Exercise on Brain Structure & Function
 Public Lecture Exercising Our Minds: Effects of Exercise on Brain Structure & Function Dr. Brian R. Christie Division of Medical Sciences, University of Victoria Cellular and Physiological Sciences, UBC
Public Lecture Exercising Our Minds: Effects of Exercise on Brain Structure & Function Dr. Brian R. Christie Division of Medical Sciences, University of Victoria Cellular and Physiological Sciences, UBC
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation. Reading: BCP Chapter 23
 Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Regulation of Adult Neurogenesis by Antidepressant Treatment Ronald S. Duman, Ph.D., Shin Nakagawa, M.D., and Jessica Malberg, Ph.D.
 Regulation of Adult Neurogenesis by Antidepressant Treatment Ronald S. Duman, Ph.D., Shin Nakagawa, M.D., and Jessica Malberg, Ph.D. Demonstration of neurogenesis in adult brain represents a major advance
Regulation of Adult Neurogenesis by Antidepressant Treatment Ronald S. Duman, Ph.D., Shin Nakagawa, M.D., and Jessica Malberg, Ph.D. Demonstration of neurogenesis in adult brain represents a major advance
Modeling origin and natural evolution of low-grade gliomas
 Modeling origin and natural evolution of low-grade gliomas Mathilde Badoual Paris Diderot University, IMNC lab 2nd HTE workshop: Mathematical & Computer Modeling to study tumors heterogeneity in its ecosystem,
Modeling origin and natural evolution of low-grade gliomas Mathilde Badoual Paris Diderot University, IMNC lab 2nd HTE workshop: Mathematical & Computer Modeling to study tumors heterogeneity in its ecosystem,
Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS
 12 Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 1 12-21 2002 Research Report HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS YM Shivarajashankara, a AR Shivashankara, a P Gopalakrishna Bhat, b S Muddanna
12 Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 1 12-21 2002 Research Report HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS YM Shivarajashankara, a AR Shivashankara, a P Gopalakrishna Bhat, b S Muddanna
Environment-dependent fate of implanted neural stem cells in the brain
 Environment-dependent fate of implanted neural stem cells in the brain PhD theses Anita Zádori MD Semmelweis University János Szentágothai Doctoral School of Neurosciences Supervisor: Dr. Emília Madarász
Environment-dependent fate of implanted neural stem cells in the brain PhD theses Anita Zádori MD Semmelweis University János Szentágothai Doctoral School of Neurosciences Supervisor: Dr. Emília Madarász
Supplemental Information. A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit. for Place Navigation
 Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Spinal Cord Doses in Palliative Lung Radiotherapy Schedules
 Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 8, No., June: -, 00 Spinal Cord Doses in Palliative Lung Radiotherapy Schedules HODA AL-BOOZ, FRCR FFRRCSI M.D.* and CAROL PARTON, Ph.D.** The Departments
Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 8, No., June: -, 00 Spinal Cord Doses in Palliative Lung Radiotherapy Schedules HODA AL-BOOZ, FRCR FFRRCSI M.D.* and CAROL PARTON, Ph.D.** The Departments
EFFECTS OF NITRIC OXIDE SYNTHASE INHIBITOR N G -NITRO-L-ARGININE METHYL ESTER ON SPATIAL AND CUED LEANING
 Pergamon Neuroscience Vol. 83, No. 3, pp. 837 841, 1998 Copyright 1998 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved PII: S0306-4522(97)00457-0 0306 4522/98 $19.00+0.00
Pergamon Neuroscience Vol. 83, No. 3, pp. 837 841, 1998 Copyright 1998 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved PII: S0306-4522(97)00457-0 0306 4522/98 $19.00+0.00
<student name> Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal
 Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
Department of Psychology, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48104
 BEHAVIORAL BIOLOGY, 8, 749-754 (1973), Abstract No. I228R Effects of Prior Exposure to Animate Objects on Approach Tendency in Chicks SUSAN SAEGERT and D. W. RAJECKI 1 Department of Psychology, The University
BEHAVIORAL BIOLOGY, 8, 749-754 (1973), Abstract No. I228R Effects of Prior Exposure to Animate Objects on Approach Tendency in Chicks SUSAN SAEGERT and D. W. RAJECKI 1 Department of Psychology, The University
Decreased Neurogenesis Increases Spatial Reversal Errors in Chickadees (Poecile atricapillus)
 Decreased Neurogenesis Increases Spatial Reversal Errors in Chickadees (Poecile atricapillus) Nicole A. Guitar, 1,2,3 David F. Sherry 1,2 1 Advanced Facility for Avian Research, Western University, London,
Decreased Neurogenesis Increases Spatial Reversal Errors in Chickadees (Poecile atricapillus) Nicole A. Guitar, 1,2,3 David F. Sherry 1,2 1 Advanced Facility for Avian Research, Western University, London,
Neurogenesis and brain injury: managing a renewable resource for repair
 SPOTLIGHT Neurogenesis and brain injury: managing a renewable resource for repair Anna F. Hallbergson, Carmen Gnatenco, and Daniel A. Peterson Neural Repair and Neurogenesis Laboratory, Department of Neuroscience,
SPOTLIGHT Neurogenesis and brain injury: managing a renewable resource for repair Anna F. Hallbergson, Carmen Gnatenco, and Daniel A. Peterson Neural Repair and Neurogenesis Laboratory, Department of Neuroscience,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/328/5983/1288/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Induction of Fear Extinction with Hippocampal-Infralimbic BDNF Jamie Peters, Laura M. Dieppa-Perea, Loyda M. Melendez,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/328/5983/1288/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Induction of Fear Extinction with Hippocampal-Infralimbic BDNF Jamie Peters, Laura M. Dieppa-Perea, Loyda M. Melendez,
Activity-dependent Extrinsic Regulation of Adult Olfactory Bulb and Hippocampal Neurogenesis
 INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON OLFACTION AND TASTE Activity-dependent Extrinsic Regulation of Adult Olfactory Bulb and Hippocampal Neurogenesis Dengke K. Ma, a,b Woon Ryoung Kim, b,c Guo-li Ming, a,b,c and
INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON OLFACTION AND TASTE Activity-dependent Extrinsic Regulation of Adult Olfactory Bulb and Hippocampal Neurogenesis Dengke K. Ma, a,b Woon Ryoung Kim, b,c Guo-li Ming, a,b,c and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
Spatially Fractionated Radiation Therapy: GRID Sponsored by.decimal Friday, August 22, Pamela Myers, Ph.D.
 Spatially Fractionated Radiation Therapy: GRID Sponsored by.decimal Friday, August 22, 2014 Pamela Myers, Ph.D. Introduction o o o o o Outline GRID compensator Purpose of SFRT/GRID therapy Fractionation
Spatially Fractionated Radiation Therapy: GRID Sponsored by.decimal Friday, August 22, 2014 Pamela Myers, Ph.D. Introduction o o o o o Outline GRID compensator Purpose of SFRT/GRID therapy Fractionation
Ali Alawieh 1, Andrew Elvington 1, Hong Zhu 2, Jin Yu 2, Mark S. Kindy 2,3, Carl Atkinson 1 and Stephen Tomlinson 1,3*
 Alawieh et al. Journal of Neuroinflammation (2015) 12:247 DOI 10.1186/s12974-015-0464-8 RESEARCH Open Access Modulation of post-stroke degenerative and regenerative processes and subacute protection by
Alawieh et al. Journal of Neuroinflammation (2015) 12:247 DOI 10.1186/s12974-015-0464-8 RESEARCH Open Access Modulation of post-stroke degenerative and regenerative processes and subacute protection by
The Four R s. Repair Reoxygenation Repopulation Redistribution. The Radiobiology of Small Fraction Numbers. The Radiobiology of Small Fraction Numbers
 The Radiobiology of Small Fraction Numbers David J. Brenner, PhD, DSc Center for Radiological Research Columbia University Medical Center djb3@columbia.edu The Radiobiology of Small Fraction Numbers 1.
The Radiobiology of Small Fraction Numbers David J. Brenner, PhD, DSc Center for Radiological Research Columbia University Medical Center djb3@columbia.edu The Radiobiology of Small Fraction Numbers 1.
Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury
 Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury Bridgette Semple Ph.D. Postdoctoral Fellow, Noble Laboratory Department of Neurological Surgery, UCSF Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury
Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury Bridgette Semple Ph.D. Postdoctoral Fellow, Noble Laboratory Department of Neurological Surgery, UCSF Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury
Quality assurance program for prototype stereotactic system developed for Neptun 10 PC linac
 Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2005; 3 (2): 73-78 Quality assurance program for prototype stereotactic system developed for Neptun 10 PC linac A.R. Khoshbin Khoshnazar 1*, M.T. Bahreyni Toossi 2, A.R. Hashemiyan
Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2005; 3 (2): 73-78 Quality assurance program for prototype stereotactic system developed for Neptun 10 PC linac A.R. Khoshbin Khoshnazar 1*, M.T. Bahreyni Toossi 2, A.R. Hashemiyan
Brain, Cranial Nerves, and Spinal Cord
 Bio101 Laboratory 13 Neuron/Spinal Cord Histology Brain Anatomy Ear & Eye Anatomy 1 Brain, Cranial Nerves, and Spinal Cord Objectives for today s lab Become familiar with the gross anatomy of the brain
Bio101 Laboratory 13 Neuron/Spinal Cord Histology Brain Anatomy Ear & Eye Anatomy 1 Brain, Cranial Nerves, and Spinal Cord Objectives for today s lab Become familiar with the gross anatomy of the brain
Acetylcholine again! - thought to be involved in learning and memory - thought to be involved dementia (Alzheimer's disease)
 Free recall and recognition in a network model of the hippocampus: simulating effects of scopolamine on human memory function Michael E. Hasselmo * and Bradley P. Wyble Acetylcholine again! - thought to
Free recall and recognition in a network model of the hippocampus: simulating effects of scopolamine on human memory function Michael E. Hasselmo * and Bradley P. Wyble Acetylcholine again! - thought to
CNS Developmental. Anke van Eekelen, PhD. Telethon Institute for Child Health Research
 CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
( neural progeni2 tor cell), ,,,, , (neural crest) (radial glial cell) mrna [2 ]
![( neural progeni2 tor cell), ,,,, , (neural crest) (radial glial cell) mrna [2 ] ( neural progeni2 tor cell), ,,,, , (neural crest) (radial glial cell) mrna [2 ]](/thumbs/92/110608454.jpg) 246, 1999 6, 51 (3), 246 252 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 P19 3 3 (, 200031 ;, 200031) (nestin),, RA P19,, (neural precursor cell) BMP4, (NF160), ( neural progeni2 tor cell),, : ; P19 ; BMP4 ; : Q71,,,,
246, 1999 6, 51 (3), 246 252 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 P19 3 3 (, 200031 ;, 200031) (nestin),, RA P19,, (neural precursor cell) BMP4, (NF160), ( neural progeni2 tor cell),, : ; P19 ; BMP4 ; : Q71,,,,
Brain ischemia, neurogenesis, and neurotrophic receptor expression in primates
 Archives Italiennes de Biologie, 149: 225-231, 2011. Brain ischemia, neurogenesis, and neurotrophic receptor expression in primates A.B. Tonchev Laboratory of Cell Biology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Medical
Archives Italiennes de Biologie, 149: 225-231, 2011. Brain ischemia, neurogenesis, and neurotrophic receptor expression in primates A.B. Tonchev Laboratory of Cell Biology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Medical
Therapeutic ratio - An Overview. Past Present Future Prof Ramesh S Bilimaga
 Therapeutic ratio - An Overview Past Present Future Prof Ramesh S Bilimaga Radiation Oncology Discipline of human medicine concerned with the generation, conservation and dissemination of knowledge concerning
Therapeutic ratio - An Overview Past Present Future Prof Ramesh S Bilimaga Radiation Oncology Discipline of human medicine concerned with the generation, conservation and dissemination of knowledge concerning
Chemokine Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord. Bob Avino Saint Louis University Senior Honors Thesis April 19, 2011
 Chemokine Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord Bob Avino Saint Louis University Senior Honors Thesis April 19, 2011 Richard J. Miller, PhD Northwestern University Feinberg School
Chemokine Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord Bob Avino Saint Louis University Senior Honors Thesis April 19, 2011 Richard J. Miller, PhD Northwestern University Feinberg School
Radiotherapy in feline and canine head and neck cancer
 Bettina Kandel Like surgery radiotherapy is usually a localized type of treatment. Today it is more readily available for the treatment of cancer in companion animals and many clients are well informed
Bettina Kandel Like surgery radiotherapy is usually a localized type of treatment. Today it is more readily available for the treatment of cancer in companion animals and many clients are well informed
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
4- to 6-Week-Old Adult-Born Hippocampal Neurons Influence Novelty-Evoked Exploration and Contextual Fear Conditioning
 HIPPOCAMPUS 22:1188 1201 (2012) 4- to 6-Week-Old Adult-Born Hippocampal Neurons Influence Novelty-Evoked Exploration and Contextual Fear Conditioning Christine A. Denny, 1,2 Nesha S. Burghardt, 2,4 Daniel
HIPPOCAMPUS 22:1188 1201 (2012) 4- to 6-Week-Old Adult-Born Hippocampal Neurons Influence Novelty-Evoked Exploration and Contextual Fear Conditioning Christine A. Denny, 1,2 Nesha S. Burghardt, 2,4 Daniel
Mini-Review Adult Neurogenesis and Neural Stem Cells of the Central Nervous System in Mammals
 Journal of Neuroscience Research 69:745 749 (2002) Mini-Review Adult Neurogenesis and Neural Stem Cells of the Central Nervous System in Mammals Philippe Taupin * and Fred H. Gage * Laboratory of Genetics,
Journal of Neuroscience Research 69:745 749 (2002) Mini-Review Adult Neurogenesis and Neural Stem Cells of the Central Nervous System in Mammals Philippe Taupin * and Fred H. Gage * Laboratory of Genetics,
effect on the upregulation of these cell surface markers. The mean peak fluorescence intensity
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 Supplementary Figure 1 ASIC1 disruption or blockade does not effect in vitro and in vivo antigen-presenting cell activation. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface molecules
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 Supplementary Figure 1 ASIC1 disruption or blockade does not effect in vitro and in vivo antigen-presenting cell activation. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface molecules
Serum Proteins in Rats Exposed to Ionizing Radiation and Thermal Injury
 Physiol. Res. 42: 403-407, 1993 Serum Proteins in Rats Exposed to Ionizing Radiation and Thermal Injury K. CHLEBOVSKÂ, O. CHLEBOVSKŸ, B. SMAJDA1 Department of Anthropology and Zoology, and department of
Physiol. Res. 42: 403-407, 1993 Serum Proteins in Rats Exposed to Ionizing Radiation and Thermal Injury K. CHLEBOVSKÂ, O. CHLEBOVSKŸ, B. SMAJDA1 Department of Anthropology and Zoology, and department of
Contact: Course outline: Contact for other times.
 Contact: kdelaney@uvic.ca Course outline: http://web.uvic.ca/~kdelaney/b367 Scheduled office hours: 1:00-3:00, M&Th Cunn. 259A Contact kdelaney@uvic.ca for other times. Quiz (0.5 hrs) midterm (1.4 hrs)
Contact: kdelaney@uvic.ca Course outline: http://web.uvic.ca/~kdelaney/b367 Scheduled office hours: 1:00-3:00, M&Th Cunn. 259A Contact kdelaney@uvic.ca for other times. Quiz (0.5 hrs) midterm (1.4 hrs)
Increased Neurogenesis in a Model of Electroconvulsive Therapy
 Increased Neurogenesis in a Model of Electroconvulsive Therapy Torsten M. Madsen, Alexandra Treschow, Johan Bengzon, Tom G. Bolwig, Olle Lindvall, and Anders Tingström Background: Electroconvulsive therapy
Increased Neurogenesis in a Model of Electroconvulsive Therapy Torsten M. Madsen, Alexandra Treschow, Johan Bengzon, Tom G. Bolwig, Olle Lindvall, and Anders Tingström Background: Electroconvulsive therapy
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Evaluation of Chromatin Clumping and Myelination of the Spinal Cord of Pigs with Congenital Tremor
 Vet. Pathol. 12: 1-5 (1975) Evaluation of Chromatin Clumping and Myelination of the Spinal Cord of Pigs with Congenital Tremor C.H. LAMAR and D.C. VAN SICKLE School of Veterinary Medicine, Purdue University,
Vet. Pathol. 12: 1-5 (1975) Evaluation of Chromatin Clumping and Myelination of the Spinal Cord of Pigs with Congenital Tremor C.H. LAMAR and D.C. VAN SICKLE School of Veterinary Medicine, Purdue University,
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Sendai, Japan, 2
 Low-energy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Promotes VEGF Expression and Angiogenesis and Improve Locomotor and Sensory Functions after spinal cord injury Kenichiro Yahata 1, Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D.
Low-energy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Promotes VEGF Expression and Angiogenesis and Improve Locomotor and Sensory Functions after spinal cord injury Kenichiro Yahata 1, Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D.
Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse
 Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Experimental Neurology
 Experimental Neurology 216 (2009) 56 65 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Experimental Neurology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yexnr Basic fibroblast growth factor-enhanced neurogenesis
Experimental Neurology 216 (2009) 56 65 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Experimental Neurology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yexnr Basic fibroblast growth factor-enhanced neurogenesis
X-ray therapy promotes structural regeneration after spinal cord injury in a rat model
 Liu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:6 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0327-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE X-ray therapy promotes structural regeneration after spinal cord injury in a rat model
Liu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:6 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0327-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE X-ray therapy promotes structural regeneration after spinal cord injury in a rat model
