Original Article The Effect of MDMA-Induced Anxiety on Neuronal Apoptosis in Adult Male Rats Hippocampus
|
|
|
- Derick Lloyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article The Effect of MDMA-Induced Anxiety on Neuronal Apoptosis in Adult Male Rats Hippocampus (MDMA / anxiety / apoptosis / plus-maze / hippocampus / rats) S. Karimi, M. Jahanshahi, M. J. Golalipour Department of Anatomy, Neuroscience Research Centre, Faculty of Medicine, Golestan University of Medical Sciences, Gorgan, Iran. Abstract. Ecstasy or MDMA as a psychoactive drug and hallucinogen is considered one of the most commonly used drugs in the world. This psychotropic substance is discussed both as sexually stimulating and reducing fear and anxiety. Amphetamines also destroy neurons in some brain areas. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of MDMA on anxiety and apoptosis of hippocampal neurons. Fortytwo male Wistar rats of mean weight g were used and distributed into six groups [control, control-saline, and experimental groups (1.25, 2.5, 5, 10 mg/kg)]. Rats in experimental groups received MDMA at different doses for seven days by intraperitoneal injection and the control-saline group received saline (1 ml/kg); anxiety was then investigated by plus-maze test. Forty-eight hours after behavioural testing brains were taken from animals and fixed, and after tissue processing, slices were stained with TUNEL kit for apoptotic cells. The area densities of apoptotic neurons were measured throughout the hippocampus and compared in all groups (P < 0.05). Physiological studies showed that 1.25 mg/kg and 2.5 mg/kg doses caused anti-anxiety behaviour and 5 and 10 mg/kg doses of MDMA caused anxietylike behaviour. Moreover, our histological study showed that ecstasy increased apoptotic cell numbers and the highest increase was observed with the 10 mg/kg dose of MDMA. We concluded that MDMA can cause different responses of anxiety-like behaviour in different doses. This phenomenon causes a Received October 2, Accepted March 12, The project was financially supported from research affair of Golestan University of Medical Sciences. Corresponding author: Mehrdad Jahanshahi, Department of Anatomy, Neuroscience Research Centre, Faculty of Medicine, Golestan University of Medical Sciences, km 4 Gorgan-Sari road (Shastcola), Gorgan, Iran. Phone: ; Fax: ; mejahanshahi@yahoo.com Abbreviations: MDMA 3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine or ecstasy. Folia Biologica (Praha) 60, (2014) different ratio of apoptosis in hippocampal formation. Reduction of anxiety-like behaviour induced by the 2.5 mg/kg dose of MDMA can control apoptosis. Introduction Anxiety is one of the most common mental disorders affecting many people in different populations. Anxiety is an uncomfortable feeling evoked by an unknown danger (Wang et al., 2007). Different parts of the brain such as amygdala, hypothalamus, hippocampus and septum are involved in mediating anxiety (Cho et al., 2007, 2008; Wang et al., 2007). Hippocampus as a part of the limbic system is involved in the pathophysiology of affective disorders, fear and anxiety behaviour (Kjelstrup et al., 2002; McHugh et al., 2004; Wang et al., 2007; Cho et al., 2008). Hippocampal cholinergic input from the septum and the middle part of Broca diagonal band (Rosene and Van Hoesen, 1987) plays an important role in physiological changes during memory formation and learning (Stephan, 1983) and anxiety-related behaviours (Knowles, 1992). The elevated plus-maze is a widely used behavioural paradigm in the experimental anxiety research (Rodgers and Cole, 1994). During a typical plus-maze test fearmotivated avoidance behaviour is measured (Handley and McBlane, 1993). Naturally, the animals due to their fear of open spaces spend most of the time in the closed arms of the maze (Treit, 1985). Anxiogenic drugs can increase this natural aversion toward the open arms, whereas anxiolytic drugs can decrease it (Pellow et al., 1985). MDMA (3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine or ecstasy) as an amphetamine derivative is a popular drug of abuse (Fantegrossi et al., 2008) and it can increase the levels of free radicals, which are involved in the neurotoxic effects (Green et al., 2003). Anxiolytic and anxiogenic-like behavioural outcomes have been extensively studied in MDMA-treated animals using a variety of anxiety models (Palenicek et al., 2005). The effects of MDMA vary according to the dose and the frequency and duration of use (Kalant, 2001). Although MDMA has been shown to reduce humans anxiety in the labora
2 188 S. Karimi et al. Vol. 60 tory, it may also cause an increase of anxiety (Cole and Sumnall, 2003). There is some evidence for deficits in serotonergic biochemical markers in human ecstasy abusers (Capela et al., 2009; Riezzo et al., 2010). Apoptosis is one of the most characterized types of cell death. The main molecular pathways of apoptosis are: one extrinsic signal involving activation of death receptors in the cell membrane, and another intrinsic stimulus involving mitochondrial membrane permeabilization. These pathways may activate cysteine aspartic proteases, activated by proteolysis, named caspases (Kroemer and Martin, 2005). The main cells in the hippocampus are pyramidal neurons, and in dentate gyrus these are granular neurons (Jahanshahi et al., 2006); therefore, the aim of this study was to determine various effects of MDMA on anxiety and the effects of anxiety on apoptosis of neurons in the rats hippocampus. Material and Methods Animals Forty-two Wistar male rats weighing 200 ± 20 g (Pasteur Institute, Tehran, Iran) were used. Animals were housed in plastic cages, under standardized lighting conditions (12 h light / 12 h dark cycle), a constant temperature (22 24 C), food and tap water available and libitum, except during behavioural tests. For a week, the rats were allowed to adapt to laboratory conditions before starting the experiment, and the tests were performed at a certain time of day. This experiment was carried out in accordance with the guiding principles for care and use of laboratory animals approved by the Golestan University of Medical Sciences. Drug administration Animal were randomly allocated to six groups (N = 7); one control group without injection and behavioural test, a control-saline group receiving normal saline (1 ml/kg) and behavioural test, and four experimental groups (N = 7) receiving MDMA (1.25, 2.5, 5, 10 mg/kg) intraperitoneal injections and behavioural test. MDMA (Sigma Laboratories, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) was diluted in physiological saline to appropriate doses for injections (for seven consecutive days). Apparatus and behavioural test The plus-maze apparatus consists of two open arms and two closed arms, with two pairs of identical platforms which emerge from a central platform (5 5 cm), positioned opposite each other. The apparatus was elevated 50 cm above the floor. Animals were tested in the maze in randomized order. The test was initiated by placing the rat on the central platform of the maze, facing one of the open arms, and letting it move freely. Each session lasted 5 min; all tests were carried out under dim red lighting between the second and seventh hour of the dark phase. After each test, the maze was thoroughly cleaned. Behavioural analysis was performed by a trained experimenter who was unaware of treatment of the groups (Jahanshahi et al., 2013a). A number of classical parameters were collected during the session, including: (1) open arm duration: the total amount of time the rat spent in the open arms; (2) closed arm duration: the total amount of time the rat spent in the closed arms; (3) central platform duration: the total amount of time the rat spent in the central platform; (4) open arm frequency: the frequency of rat entry with all four paws into the open, unprotected arms; and (5) closed arm frequency: the frequency of rat entry with all four paws into the closed, protected arms. Histology Forty-eight hours after the behavioural testing session, rats were anaesthetized with chloroform and after perfusion, their brains were removed from the skull and stored in paraformaldehyde (4%) for two weeks, and then, the brains were placed in tissue processor apparatus for tissue procedures. Following this session, samples of the brain were embedded in paraffin and kept in a refrigerator. Then the brains were sliced coronally into 6-µm sections (from bregma -2.5 mm to -4.5 mm of the hippocampal formation) with a rotary microtome (MK 1110) and for 10 s with 50 µm interval were stained with TUNEL assay in accordance with routine laboratory procedures (Jahanshahi et al., 2013b). Photographs of each section were produced using an Olympus BX 51 microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) and DP 12 digital camera (Olympus) under 400 magnification for the pyramidal layer of CA1, CA3 and granular layer of DG areas (Fig. 1). To measure the apoptotic cells, the images were trans ferred to the computer and the cells were counted with image G software. Data analysis Data were analysed using SPSS software (version 11.0, Chicago, IL). One-way analysis of variance was used to determine the overall significance. Differences between control and experimental groups were assessed Fig. 1. TUNEL assay technique for apoptotic cells in the DG area of hippocampus. Red arrow points to an apoptotic cell and blue arrow to normal neurons.
3 Vol. 60 MDMA-Induced Anxiety and Hippocampus Apoptosis 189 Table 1. Mean and SD of apoptotic neuron numbers in the CA1 area of hippocampus Groups CA1 Mean Std. deviation P value Control Control-saline mg/kg MDMA * 2.5 mg/kg MDMA mg/kg MDMA * 10 mg/kg MDMA * Table 2. Mean and SD of apoptotic neuron numbers in the CA3 area of hippocampus Groups CA3 Mean Std. deviation P value Control Control-saline mg/kg MDMA mg/kg MDMA mg/kg MDMA * 10 mg/kg MDMA * with post-hoc Tukey test comparison, with significant differences represented as P < Results Behavioural results Our findings showed that the highest increase of open arm entries as an index for decrease of anxiety was observed in the 2.5 mg/kg group compared to the others, and the difference between this group and the controlsaline group was significant (P < 0.05). The highest percentage of remaining in the open arms was also observed in the 2.5 mg/kg group. Also, the least delay on entering the open arm as an index for decrease of anxiety was observed in the 2.5 mg/kg group in comparison with the other groups. Rats treated with high doses of MDMA showed elevated levels of anxiety-like behaviour. The findings suggest that the locomotor activity index in the 1.25 and 2.5 mg/kg experimental groups compared to the control-saline group showed significant differences (P < 0.05). In summary, the effective dose for reduction of anxiety was 2.5 mg/kg. Histological results In the CA1 region of hippocampus the number of apoptotic cells was increased in all groups compared to the control. However, there were no significant differences in the number of apoptotic cells between the control and control-saline groups. Also, there were no significant differences in the number of apoptotic cells between the 2.5 mg/kg experimental group and control group (P < 0.05). Nevertheless, the differences between the other three experimental groups and the control group were significant (Table 1). Table 2 shows the mean and SD of the number of apoptotic cells in the CA3 region of hippocampus in all groups. In the CA3 region of hippocampus the number of apoptotic cells was increased in all groups compared to control. As we show, the least change compared to the control group was in the 2.5 mg/kg group. The number of apoptotic cells in the DG area of hippocampus is shown in Table 3. There were no significant differences in the number of apoptotic cells between the 2.5 mg/kg experimental group and control group (P < Table 3. Mean and SD of apoptotic neuron numbers in the DG area of hippocampus Groups DG Mean Std. deviation P value Control Control-saline mg/kg MDMA * 2.5 mg/kg MDMA mg/kg MDMA * 10 mg/kg MDMA * 0.05). Nevertheless, the differences between the other three experimental groups and the control group were significant (Table 3). Discussion The elevated plus-maze test uses the natural aversion of rodents to heights and open spaces. Therefore, the animals prefer to spend time in the closed arms rather than in the open arms of a maze. The present study showed that taking low doses (1.25 and 2.5 mg/kg) of MDMA in five days had an anxiolytic effect and taking high doses (5 and 10 mg/kg) of MDMA had an anxiogenic effect. Our behavioural finding was similar to others (Bhattacharya et al., 1998; Lin, et al., 1999; Navarro and Maldonado, 2002; Ferraz-de-Paula et al., 2011). Our data also showed that the relationship between MDMA doses and increase of apoptotic cells in all areas of the hippocampus is not linear. On the other hand, when the rats displayed less anxiety (2.5 mg/kg dose of MDMA), the number of apoptotic cells was lower than with the other doses. Gurtman et al. (2002) examined the long-term behavioural and neurotoxic effects of MDMA in rats. They showed that four and six weeks after the drug administration the rats previously treated with MDMA showed elevated levels of anxiety-like behaviour in the emergence and social interaction tests, respectively. The authors compared their results with human studies and they suggested that exposure to high doses of MDMA may predispose to long-term psychological problems such as anxiety and depression (Gurtman et al., 2002).
4 190 S. Karimi et al. Vol. 60 Sometimes MDMA not only has acute and dose-dependent effects in the elevated plus maze, but can also have relatively long lasting effects on the behaviour. It seems that these latter effects depend (A) on the kind of the test paradigm used, and (B) on subject-dependent factors, such as individual levels of anxiety (Ho et al., 2004). Hernandez-Rabaza et al. (2006) showed that the administration of MDMA damages the survival rate of neural precursors in adult hippocampal dentate gyrus cells, but not the proliferation rate of progenitor cells. In another study, cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus was suppressed by chronic administration of MDMA (Cho et al., 2007). In contrast, MDMA did not cause cell death in organotypic hippocampal cultures (Sveen et al., 2004). Hernandez-Rabaza et al. (2006) found that administration of MDMA has deleterious effects on adult neurogenesis by impairing the short-term survival of vulnerable neural precursors. Also, Cho et al. (2007) showed that chronic exposure to MDMA reduces cell proliferation in the adult dentate gyrus in a dose-dependent manner in male and female mice. Wang et al. (2009) studied the neuron apoptosis induced by i.p. MDMA and the expression of apoptosisrelated factors in the rat brain. Neuron apoptosis was measured by the TUNEL assay similarly to our study. These authors showed that MDMA could induce neuron apoptosis and expression of apoptosis-related factors such as caspase 3 and cytochrome c (Cyt c) in the rat brain (Wang et al., 2009). Azami et al. (2009) also showed that MDMA exhibits dual effects on hippocampal neuronal viability and caspase 3 activity. The mechanism of MDMA effect on cell apoptosis was shown by Riezzo et al. in They suggested that injection of a single dose of MDMA in rats caused an increase in oxidative stress and subsequent apoptosis (TUNEL assay) in the striatum, hippocampus, and frontal cortex (Riezzo et al., 2010). Also chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and a significant increase in caspase 3 activity and Cyt c are markers of apoptosis (Jiménez et al., 2004). Conclusion We concluded that MDMA in different doses can cause different responses of anxiety-like behaviour. This phenomenon causes different ratios of apoptosis in the hippocampal formation. Reduction of anxiety-like behaviour induced by the 2.5 mg/kg dose of MDMA can control apoptosis in all areas of the hippocampus. On the other hand, if we can control the anxiety, we can probably also inhibit neuron apoptosis. Acknowledgment The authors would like to thank the Neuroscience Research Centre for behavioural and histological experiments. References Azami, A., Pasbakhsh, P., Akbari, M., Barbarestani, M., Ghahremani, M., Shokrgozar, M., et al. (2009) Dual effects of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (ecstasy) on survival and apoptosis of primary hippocampal neurons. Neural Regen. Res. 4, Bhattacharya, S. K., Bhattacharya, A., Ghosal, S. (1998) Anxiogenic activity of methylenedioxymethamphetamine (Ecstasy): an experimental study. Biogenic Amines 14, Capela, J. P., Carmo, H., Remião, F., Bastos, M. L., Meisel, A., Carvalho, F. (2009) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of ecstasy-induced neurotoxicity: an overview. Mol. Neurobiol. 39, Cho, K. O., Kim, S. K., Rhee, G. S., Kwack, S. J., Cho, D. H., Sung, K. W., Kim, S. Y. (2007) Chronic 3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine treatment suppresses cell proliferation in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 566, Cho, K. O., Rhee, G., Kwack, S., Chung, S., Kim, S. (2008) Developmental exposure to 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine results in downregulation of neurogenesis in the adult mouse hippocampus. Neuroscience 154, Cole, J. C., Sumnall, H. R. (2003) Altered states: the clinical effects of Ecstasy. Pharmacol. Ther. 98, Fantegrossi, W. E., Ciullo, J. R., Wakabayashi, K. T., Garza, R. (2008) A comparison of the physiological, behavioral, neurochemical and microglial effects of methamphetamine and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine in the mouse. Neuroscience 151, Ferraz-de-Paula, V., Stankevicius, D., Ribeiro, A., Pinheiro, M., Rodrigues-Costa, E., Florio, J., Lapachinske, S. F., Moreau, R. L. M., Palermo-Neto, J. (2011) Differential behavioral outcomes of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA-ecstasy) in anxiety-like responses in mice. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 44, Green, A. R., Mechan, A. O., Elliott, J. M., O Shea, E., Colado, M. I. (2003) The pharmacology and clinical pharmacology of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, ecstasy ). Pharmacol. Rev. 55, Gurtman, C. G., Morley, K. C., Li, K. M., Hunt, G. E., McGregor, I. S. (2002) Increased anxiety in rats after 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine: association with serotonin depletion. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 446, Handley, S. L., McBlane, J. W. (1993) An assessment of the elevated X-maze for studying anxiety and anxiety-modulating drugs. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 29, Hernandez-Rabaza, V., Domínguez-Escrib, L., Barcia, J. A., Rosel, J. F., Romero, F. J., Garcia-Verdugo, J. M., Canales, J. J. (2006) Binge administration of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine ( ecstasy ) impairs the survival of neural precursors in adult rat dentate gyrus. Neuropharmacology 51, Ho, Y. J., Pawlak, C. R., Guo, L., Schwarting, R. K. W. (2004) Acute and long-term consequences of single MDMA administration in relation to individual anxiety levels in the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 149, Jahanshahi, M., Sadeghi, Y., Hosseini, A. (2006) Estimation of astrocyte number in different subfield of rat hippocampus. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 9,
5 Vol. 60 MDMA-Induced Anxiety and Hippocampus Apoptosis 191 Jahanshahi, M., Nickmahzar, E., Babakordi, F. (2013a) The effect of Ginkgo biloba extract on scopolamine-induced apoptosis in the hippocampus of rats. Anat. Sci. Int. 17, 1-6. Jahanshahi, M., Nikmahzar, E. G., Babakordi, F., Khosravi, M., Seid-Hosseini, F. (2013b) Ecstasy, anxiety and rat hippocampal astrocytes. Eur. J. Anat. 17, Jiménez, A., Jordà, E. G., Verdaguer, E., Pubill, D., Sureda, F. X., Canudas, A. M., Escubedoa, E., Camarasaa, J., Caminsa, A., Pallàs, M. (2004) Neurotoxicity of amphetamine derivatives is mediated by caspase pathway activation in rat cerebellar granule cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 196, Kalant, H. (2001) The pharmacology and toxicology of ecstasy (MDMA) and related drugs. CMAJ 165, Kjelstrup, K. G., Tuvnes, F. A., Steffenach, H. A., Murison, R., Moser, E. I., Moser, M. B. (2002) Reduced fear expression after lesions of the ventral hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, Knowles, W. D. (1992) Normal anatomy and neurophysiology of the hippocampal formation. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 9, Kroemer, G., Martin, S. J. (2005) Caspase-independent cell death. Nat. Med. 11, Lin, H. Q., Burden, P. M., Christie, M. J., Johnston, G. A. R. (1999) The anxiogenic-like and anxiolytic-like effects of MDMA on mice in the elevated plus-maze: a comparison with amphetamine. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 62, McHugh, S. B., Deacon, R. M. J., Rawlins, J. N. P., Bannerman, D. M. (2004) Amygdala and ventral hippocampus contribute differentially to mechanisms of fear and anxiety. Behav. Neurosci. 118, Navarro, J. F., Maldonado, E. (2002) Acute and subchronic effects of MDMA. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 26, Palenicek, T., Votava, M., Bubenikova, V., Horacek, J. (2005) Increased sensitivity to the acute effects of MDMA. Physiol. Behav. 86, Pellow, S., Chopin, P., File, S. E., Briley, M. (1985) Validation of open:closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 14, Riezzo, I., Cerretani, D., Fiore, C., Bello, S., Centini, F., D Errico, S., Fiaschi, A. I., Giorgi, G., Neri, M., Pomara, C., Turillazzi, E., Fineschi, V. (2010) Enzymatic-nonenzymatic cellular antioxidant defense systems response and immunohistochemical detection of MDMA, VMAT2, HSP70, and apoptosis as biomarkers for MDMA (ecstasy) neurotoxicity. J. Neurosci. Res. 88, Rodgers, R., Cole, J. (1994) The elevated plus-maze: pharmacology, methodology and ethology. In: Ethology and Psychopharmacology, eds. Coopper S. J., Hendrie C. A., pp. 9-43, John Wiley and Sons Ltd., New York Rosene, D. L., Van Hoesen, G. W. (1987) The hippocampal formation of the primate brain. A review of some comparative aspects of cytoarchitecture and connections. Cereb. Cortex 6, Stephan, H. (1983) Evolutionary trends in limbic structures. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 7, Sveen, M. L., Knudsen, G. M., Aznar, S. (2004) No effect of MDMA (ecstasy) on cell death and 5-HT2A receptor density in organotypic rat hippocampal cultures. Neurosci. Lett. 362, 6-9. Treit, D. (1985). Animal models for the study of anti-anxiety agents: a review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 9, Wang, X., Li, J., Zhu, S. P. (2007) Neuron apoptosis induced by 3,4-methylenedioxy methamphetamine and the expression of caspase-3. West China Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 22, 511. Wang, X., Zhu, S. P., Kuang, W. H., Li, J., Sun, X., Huang, M. S., Sun, X. (2009). Neuron apoptosis induced by 3,4-methylenedioxy methamphetamine and expression of apoptosis-related factors in rat brain. Journal of Sichuan University. Medical science edition 40, , 1037.
Effects of Repeated Administration of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) on Avoidance Memory and Cell Density in Rats' Hippocampus
 Effects of Repeated Administration of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) on Avoidance Memory and Cell Density in Rats' Hippocampus Mehrdad Jahanshahi 1*, Kamran Haidari 1, Simin Mahaki-Zadeh 1, EmseGol
Effects of Repeated Administration of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) on Avoidance Memory and Cell Density in Rats' Hippocampus Mehrdad Jahanshahi 1*, Kamran Haidari 1, Simin Mahaki-Zadeh 1, EmseGol
The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females
 The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females Samantha Pavlock (Medical Student) Pradeep Bhide and Deirdre McCarthy (Faculty
The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females Samantha Pavlock (Medical Student) Pradeep Bhide and Deirdre McCarthy (Faculty
Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing. Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2
 ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
ATTENUATION OF STRESS-INDUCED BEHAVIORAL DEFICITS BY AZADIRACHTA INDICA (NEEM): ROLE OF SEROTONIN
 Pak. J. Bot., 38(1): 131-138, 26. ATTENUATION OF STRESS-INDUCED BEHAVIORAL DEFICITS BY AZADIRACHTA INDICA (NEEM): ROLE OF SEROTONIN NOREEN SAMAD, TAHIRA PARVEEN, SAIDA HAIDER AND DARAKHSHAN JABEEN HALEEM
Pak. J. Bot., 38(1): 131-138, 26. ATTENUATION OF STRESS-INDUCED BEHAVIORAL DEFICITS BY AZADIRACHTA INDICA (NEEM): ROLE OF SEROTONIN NOREEN SAMAD, TAHIRA PARVEEN, SAIDA HAIDER AND DARAKHSHAN JABEEN HALEEM
The Effect of Scopolamine on Avoidance Memory and Hippocampal Neurons in Male Wistar Rats
 The Effect of Scopolamine on Avoidance Memory and Hippocampal Neurons in Male Wistar Rats Saba Seifhosseini 1, Mehrdad Jahanshahi 2,*, Ali Moghimi 3, Nasrin-Sadat Aazami 4 1. Department of Biology, Faculty
The Effect of Scopolamine on Avoidance Memory and Hippocampal Neurons in Male Wistar Rats Saba Seifhosseini 1, Mehrdad Jahanshahi 2,*, Ali Moghimi 3, Nasrin-Sadat Aazami 4 1. Department of Biology, Faculty
Subconvulsive Dose of Kainic Acid Transiently Increases the Locomotor Activity of Adult Wistar Rats
 Physiol. Res. 64: 263-267, 2015 SHORT COMMUNICATION Subconvulsive Dose of Kainic Acid Transiently Increases the Locomotor Activity of Adult Wistar Rats V. RILJAK 1, D. MAREŠOVÁ 1, J. POKORNÝ 1, K. JANDOVÁ
Physiol. Res. 64: 263-267, 2015 SHORT COMMUNICATION Subconvulsive Dose of Kainic Acid Transiently Increases the Locomotor Activity of Adult Wistar Rats V. RILJAK 1, D. MAREŠOVÁ 1, J. POKORNÝ 1, K. JANDOVÁ
Physiology & Behavior 85 (2005) Effect of different illumination levels on rat behavior in the elevated plus-maze
 Physiology & Behavior 85 (25) 265 27 Abstract Effect of different illumination levels on rat behavior in the elevated plus-maze Andrea Milena Becerra Garcia, Fernando Parra Cardenas, Silvio Morato Faculdade
Physiology & Behavior 85 (25) 265 27 Abstract Effect of different illumination levels on rat behavior in the elevated plus-maze Andrea Milena Becerra Garcia, Fernando Parra Cardenas, Silvio Morato Faculdade
Emotion I: General concepts, fear and anxiety
 C82NAB Neuroscience and Behaviour Emotion I: General concepts, fear and anxiety Tobias Bast, School of Psychology, University of Nottingham 1 Outline Emotion I (first part) Studying brain substrates of
C82NAB Neuroscience and Behaviour Emotion I: General concepts, fear and anxiety Tobias Bast, School of Psychology, University of Nottingham 1 Outline Emotion I (first part) Studying brain substrates of
Effect of chronic treatment of ketamine on hippocampus cell count of adult rats
 Quarterly of the Horizon of Medical Sciences Vol. 19, No. 1, Spr 2013 Pages: 35-39 Effect of chronic treatment of ketamine on hippocampus cell count of adult rats Downloaded from hms.gmu.ac.ir at 12:09
Quarterly of the Horizon of Medical Sciences Vol. 19, No. 1, Spr 2013 Pages: 35-39 Effect of chronic treatment of ketamine on hippocampus cell count of adult rats Downloaded from hms.gmu.ac.ir at 12:09
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
The effect of Urtica dioica extract on the number of astrocytes in the dentate gyrus of diabetic rats
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 2, pp. 93 97 Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The effect of Urtica dioica extract on the number of astrocytes in the
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 2, pp. 93 97 Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The effect of Urtica dioica extract on the number of astrocytes in the
AN EXPERIMENTAL MODEL OF ALCOHOL-INDUCED ANXIETY AND DEPRESSIVE BEHAVIOUR IN RATS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES AN EXPERIMENTAL MODEL OF ALCOHOL-INDUCED ANXIETY AND DEPRESSIVE BEHAVIOUR IN RATS Stefka Valcheva-Kuzmanova 1, Miroslav Eftimov 1, Krasimir Kuzmanov 2 ABSTRACT 1 Department of Preclinical
ORIGINAL ARTICLES AN EXPERIMENTAL MODEL OF ALCOHOL-INDUCED ANXIETY AND DEPRESSIVE BEHAVIOUR IN RATS Stefka Valcheva-Kuzmanova 1, Miroslav Eftimov 1, Krasimir Kuzmanov 2 ABSTRACT 1 Department of Preclinical
Adolescent Prozac Exposure Enhances Sensitivity to Cocaine in Adulthood INTRODUCTION
 INTRODUCTION Epidemiologic reports indicate that mood disorders in children and adolescents are quite common, with up to 70% of depressed children and adolescents experiencing a recurrence within 5 years
INTRODUCTION Epidemiologic reports indicate that mood disorders in children and adolescents are quite common, with up to 70% of depressed children and adolescents experiencing a recurrence within 5 years
"One-trial tolerance" to the anxiolytic actions of benzodiazepines in the elevated plus-maze, or the development of a phobic state?
 Psychopharmacology (1993) 11:24-244 Psychopharmacology Springer-Verlag 1993 "One-trial tolerance" to the anxiolytic actions of benzodiazepines in the elevated plus-maze, or the development of a phobic
Psychopharmacology (1993) 11:24-244 Psychopharmacology Springer-Verlag 1993 "One-trial tolerance" to the anxiolytic actions of benzodiazepines in the elevated plus-maze, or the development of a phobic
Protective Effect of Mentat (BR-16A) A Herbal Preparation, on Alcohol Abstinence-Induced Anxiety and Convulsions
 [Indian Journal of Experimental Biology (1993): (31), 435] Protective Effect of Mentat (BR-16A) A Herbal Preparation, on Alcohol Abstinence-Induced Anxiety and Convulsions Kulkarni, S.K. and Anita Verma,
[Indian Journal of Experimental Biology (1993): (31), 435] Protective Effect of Mentat (BR-16A) A Herbal Preparation, on Alcohol Abstinence-Induced Anxiety and Convulsions Kulkarni, S.K. and Anita Verma,
Acute Effects of Ecstasy on Memory Are more Extensive than Chronic Effects
 Basic and Clinical Summer 2014, Volume 5, Number 3 Acute Effects of Ecstasy on Memory Are more Extensive than Chronic Effects Mohamad Bakhtiar Hesam Shariati 1, Maryam Sohrabi 2, Siamak Shahidi 3, Ali
Basic and Clinical Summer 2014, Volume 5, Number 3 Acute Effects of Ecstasy on Memory Are more Extensive than Chronic Effects Mohamad Bakhtiar Hesam Shariati 1, Maryam Sohrabi 2, Siamak Shahidi 3, Ali
Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Bromodeoxyuridine
 Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
Anxiolytic-Like Effects of Ginsenosides on the Elevated Plus-Maze Model in Mice
 September 2005 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28(9) 1621 1625 (2005) 1621 Anxiolytic-Like Effects of Ginsenosides on the Elevated Plus-Maze Model in Mice Hwa-Young CHA, a Jeong-Hill PARK, b Jin-Tae HONG, a Hwan-Soo
September 2005 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28(9) 1621 1625 (2005) 1621 Anxiolytic-Like Effects of Ginsenosides on the Elevated Plus-Maze Model in Mice Hwa-Young CHA, a Jeong-Hill PARK, b Jin-Tae HONG, a Hwan-Soo
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2+ cells in different brain regions.
 Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
SHORT COMMUNICATION EFFECT OF SILDENAFIL ON ANXIETY IN THE PLUS-MAZE TEST IN MICE
 Copyright 2004 by Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences Polish Journal of Pharmacology Pol. J. Pharmacol., 2004, 56, 353 357 ISSN 1230-6002 SHORT COMMUNICATION EFFECT OF SILDENAFIL ON ANXIETY
Copyright 2004 by Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences Polish Journal of Pharmacology Pol. J. Pharmacol., 2004, 56, 353 357 ISSN 1230-6002 SHORT COMMUNICATION EFFECT OF SILDENAFIL ON ANXIETY
Thigmotactic responses in an open-field
 Brazilian Thigmotaxis Journal in the of open-field Medical and Biological Research (2008) 41: 135-140 ISSN 0100-879X 135 Thigmotactic responses in an open-field M.R. Lamprea 1, F.P. Cardenas 2, J. Setem
Brazilian Thigmotaxis Journal in the of open-field Medical and Biological Research (2008) 41: 135-140 ISSN 0100-879X 135 Thigmotactic responses in an open-field M.R. Lamprea 1, F.P. Cardenas 2, J. Setem
AM281, Cannabinoid Antagonist/Inverse agonist, Ameliorates Scopolamine- Induced Cognitive Deficit
 Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences Vol. 15, No. 5, Sep-Oct 2012, 1106-1110 Received: May 28, 2011; Accepted: Dec 24, 2011 www.mums.ac.ir Short Communication AM281, Cannabinoid Antagonist/Inverse
Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences Vol. 15, No. 5, Sep-Oct 2012, 1106-1110 Received: May 28, 2011; Accepted: Dec 24, 2011 www.mums.ac.ir Short Communication AM281, Cannabinoid Antagonist/Inverse
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY. 7.1 Introduction
 268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
Amphetamine-induced anxiety-related behavior in animal models
 Pharmacological Reports 2007, 59, 636 644 ISSN 1734-1140 Copyright 2007 by Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences Amphetamine-induced anxiety-related behavior in animal models Gra yna Bia³a,
Pharmacological Reports 2007, 59, 636 644 ISSN 1734-1140 Copyright 2007 by Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences Amphetamine-induced anxiety-related behavior in animal models Gra yna Bia³a,
Ketamine also decreases serum BDNF levels and spatial learning while causes apoptosis in neonatal rats
 Ketamine also decreases serum BDNF levels and spatial learning while causes apoptosis in neonatal rats A. B. Ozer 1, S. Ceribasi 2, A. O. Ceribasi 2, I. Demirel 1, M. K. Bayar 3, B. Ustundag 4, A. Yildiz
Ketamine also decreases serum BDNF levels and spatial learning while causes apoptosis in neonatal rats A. B. Ozer 1, S. Ceribasi 2, A. O. Ceribasi 2, I. Demirel 1, M. K. Bayar 3, B. Ustundag 4, A. Yildiz
LONG TERM EFFECTS OF MDMA ADMINISTRATION IN RATS DURING EARLY AND LATE ADOLESCENCE
 LONG TERM EFFECTS OF MDMA ADMINISTRATION IN RATS DURING EARLY AND LATE ADOLESCENCE A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the Degree of Master of Science in Psychology by Olga
LONG TERM EFFECTS OF MDMA ADMINISTRATION IN RATS DURING EARLY AND LATE ADOLESCENCE A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the Degree of Master of Science in Psychology by Olga
Study of Agomelatine for the Reduction of Marble Buying Behavior in Brain Disorder
 Research Article Study of Agomelatine for the Reduction of Marble Buying Behavior in Brain Disorder Shaily Chaudhary* 1,2 Akash Yadav 3 Nikunjana Patel 4 Indrajeet Singhvi 1 1Faculty of Pharmacy, Pacific
Research Article Study of Agomelatine for the Reduction of Marble Buying Behavior in Brain Disorder Shaily Chaudhary* 1,2 Akash Yadav 3 Nikunjana Patel 4 Indrajeet Singhvi 1 1Faculty of Pharmacy, Pacific
NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update
 NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update 1 Overview The natural growth factor IGF-1 is broken down in the body to IGF-1[1-3] NNZ-2566 is an analogue of IGF-1[1-3] developed
NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update 1 Overview The natural growth factor IGF-1 is broken down in the body to IGF-1[1-3] NNZ-2566 is an analogue of IGF-1[1-3] developed
Deficits in amygdaloid camp-responsive element binding protein signaling play a role in genetic predisposition to anxiety and alcoholism
 Research article Related Commentary, page 2697 Deficits in amygdaloid camp-responsive element binding protein signaling play a role in genetic predisposition to anxiety and alcoholism Subhash C. Pandey,
Research article Related Commentary, page 2697 Deficits in amygdaloid camp-responsive element binding protein signaling play a role in genetic predisposition to anxiety and alcoholism Subhash C. Pandey,
Contrasting effects of acute and chronic treatments with ketamine on inhibitory avoidance and escape latency in the elevated-t-maze
 Available online at http://ajol.info/index.php/ijbcs Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 8(6): 2387-2394, December 2014 ISSN 1997-342X (Online), ISSN 1991-8631 (Print) Original Paper http://indexmedicus.afro.who.int
Available online at http://ajol.info/index.php/ijbcs Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 8(6): 2387-2394, December 2014 ISSN 1997-342X (Online), ISSN 1991-8631 (Print) Original Paper http://indexmedicus.afro.who.int
EFFECTS OF CHLOROGENIC ACID ON LEARNING AND MEMORY IN RATS
 Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 12, Suppl. 1, pp 132-136, 2014 Copyright 2014 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) EFFECTS OF CHLOROGENIC
Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 12, Suppl. 1, pp 132-136, 2014 Copyright 2014 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) EFFECTS OF CHLOROGENIC
Science & Technologies COMPARISON THE EFFECTS OF TACRINE AND GALANTAMINE ON ACTIVE AVOIDANCE TEST IN RATS WITH DIAZEPAM-AMNESIA MODEL
 COMPARISON THE EFFECTS OF TACRINE AND GALANTAMINE ON ACTIVE AVOIDANCE TEST IN RATS WITH DIAZEPAM-AMNESIA MODEL Darinka Dimitrova, Damianka Getova Medical University Plovdiv, Medical Faculty, 4002 Plovdiv,
COMPARISON THE EFFECTS OF TACRINE AND GALANTAMINE ON ACTIVE AVOIDANCE TEST IN RATS WITH DIAZEPAM-AMNESIA MODEL Darinka Dimitrova, Damianka Getova Medical University Plovdiv, Medical Faculty, 4002 Plovdiv,
EFFECTS OF NITRIC OXIDE SYNTHASE INHIBITOR N G -NITRO-L-ARGININE METHYL ESTER ON SPATIAL AND CUED LEANING
 Pergamon Neuroscience Vol. 83, No. 3, pp. 837 841, 1998 Copyright 1998 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved PII: S0306-4522(97)00457-0 0306 4522/98 $19.00+0.00
Pergamon Neuroscience Vol. 83, No. 3, pp. 837 841, 1998 Copyright 1998 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved PII: S0306-4522(97)00457-0 0306 4522/98 $19.00+0.00
Effects of Acute, Subchronic and Intermittent MDMA ( ECSTASY ) Administration on Agonistic Interactions Between Male Mice
 AGGRESSIVE BEHAVIOR Volume 30, pages 84 91 (2004) Effects of Acute, Subchronic and Intermittent MDMA ( ECSTASY ) Administration on Agonistic Interactions Between Male Mice José Francisco Navarro and Enrique
AGGRESSIVE BEHAVIOR Volume 30, pages 84 91 (2004) Effects of Acute, Subchronic and Intermittent MDMA ( ECSTASY ) Administration on Agonistic Interactions Between Male Mice José Francisco Navarro and Enrique
Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference In Adolescent Male and Female Mice of Two Strains
 City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works School of Arts & Sciences Theses Hunter College Summer 8-10-2017 Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference In Adolescent Male and Female
City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works School of Arts & Sciences Theses Hunter College Summer 8-10-2017 Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference In Adolescent Male and Female
C81ADD Psychology of Addiction. Alcohol. Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) School of Psychology. Tobias Bast.
 C81ADD Psychology of Addiction Alcohol Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) Tobias Bast School of Psychology tobias.bast@nottingham.ac.uk 1 Selected aspects of the psychopharmacology of alcohol (ethanol) Primary neuropharmacological
C81ADD Psychology of Addiction Alcohol Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) Tobias Bast School of Psychology tobias.bast@nottingham.ac.uk 1 Selected aspects of the psychopharmacology of alcohol (ethanol) Primary neuropharmacological
Radiation-induced lowered neurogenesis associated with shortened latency of inhibitory avoidance memory response
 Original article Radiation-induced lowered neurogenesis associated with shortened latency of inhibitory avoidance memory response Mehrdad Jahanshahi 1, Alireza Khoshbin Khoshnazar 2, Nasrin-Sadat Azami
Original article Radiation-induced lowered neurogenesis associated with shortened latency of inhibitory avoidance memory response Mehrdad Jahanshahi 1, Alireza Khoshbin Khoshnazar 2, Nasrin-Sadat Azami
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70%
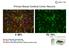 Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Previous maze experience required to increase open arms avoidance in rats submitted to the elevated plus-maze model of anxiety
 Behavioural Brain Research 108 (2000) 197 203 www.elsevier.com/locate/bbr Research report Previous maze experience required to increase open arms avoidance in rats submitted to the elevated plus-maze model
Behavioural Brain Research 108 (2000) 197 203 www.elsevier.com/locate/bbr Research report Previous maze experience required to increase open arms avoidance in rats submitted to the elevated plus-maze model
Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models. From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron of Mice and Rats Figure 1 Open Field Apparatus Open Field Behavior
Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron of Mice and Rats Figure 1 Open Field Apparatus Open Field Behavior
Comparing the effects of hop s hydro alcoholic extract and diazepam on reducing the anxiety in mice
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 216, 8 (15):184-188 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 975-571 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 216, 8 (15):184-188 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 975-571 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Histopathological and Stereological Study of the Effects of Gallic Acid Administration on Hippocampal Neuronal Density after Trimethyltin Toxication
 Report of Health Care Volume 4, Issue 2, 2018, p. 22-27 http://jrhc.miau.ac.ir Original Article Histopathological and Stereological Study of the Effects of Gallic Acid Administration on Hippocampal Neuronal
Report of Health Care Volume 4, Issue 2, 2018, p. 22-27 http://jrhc.miau.ac.ir Original Article Histopathological and Stereological Study of the Effects of Gallic Acid Administration on Hippocampal Neuronal
A brain microdialysis study on 5-HT release in freely moving rat lines selectively bred for differential 5-HT 1A receptor function
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (3) 36: 63-67 Serotonin and 5-HT 1A rat lines ISSN 1-879X 63 A brain microdialysis study on 5-HT release in freely moving rat lines selectively bred
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (3) 36: 63-67 Serotonin and 5-HT 1A rat lines ISSN 1-879X 63 A brain microdialysis study on 5-HT release in freely moving rat lines selectively bred
Rhodiola rosea L- Standardized Extract on Passive
 Research Article ISSN: 0976-5700 Rhodiola rosea L- Standardized Extract on Passive Avoidance in Rats Liliya Vl Vasileva 1,2,3*, Damyanka P Getova 3 1Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology,
Research Article ISSN: 0976-5700 Rhodiola rosea L- Standardized Extract on Passive Avoidance in Rats Liliya Vl Vasileva 1,2,3*, Damyanka P Getova 3 1Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Nat Neurosci. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2006 September 5.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Neurosci. 2006 August ; 9(8): 1004 1006. Maternal presence serves as a switch between learning fear and attraction in infancy
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Neurosci. 2006 August ; 9(8): 1004 1006. Maternal presence serves as a switch between learning fear and attraction in infancy
Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis of individual mice during maze learning. a,
 Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Cognitive Function Test. NOR & spatial NOR task. Introduction. Novel Object Recognition (NOR) Estrogen Receptor (ER) in Brain
 Cognitive Function Test Human Rodent Sutcliffe JS, Marshall KM, Neill JC. Behavioral Brain Research 177(2007) 117-125. Radial Arm maze Morris Water maze Siriporn Vongsaiyat 16 th Feb 2007 Novel Object
Cognitive Function Test Human Rodent Sutcliffe JS, Marshall KM, Neill JC. Behavioral Brain Research 177(2007) 117-125. Radial Arm maze Morris Water maze Siriporn Vongsaiyat 16 th Feb 2007 Novel Object
Recent Advances in Energy, Environment, Biology and Ecology
 Acute and long-term effects elicited by psychoactive drugs on 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations in rats: development of a new experimental tool for the study of drug-mediated reward NICOLA SIMOLA Department
Acute and long-term effects elicited by psychoactive drugs on 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations in rats: development of a new experimental tool for the study of drug-mediated reward NICOLA SIMOLA Department
Ph D THESIS ABSTRACT
 ALEXANDRU IOAN CUZA UNIVERSITY IAŞI FACULTY OF BIOLOGY THE STUDY OF CHANGES FOR SEVERAL BIOCHEMICAL PARAMETERS OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN ANIMAL MODELS FOR NEUROPSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Ph D THESIS ABSTRACT Scientific
ALEXANDRU IOAN CUZA UNIVERSITY IAŞI FACULTY OF BIOLOGY THE STUDY OF CHANGES FOR SEVERAL BIOCHEMICAL PARAMETERS OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN ANIMAL MODELS FOR NEUROPSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Ph D THESIS ABSTRACT Scientific
Abstract. Introduction. R.N. Takahashi 1, O. Berton 2,3, P. Mormède 2 and F. Chaouloff 2
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (21) 34: 675-682 Effects of diazepam and SB 26553 in SHR and Lewis rats ISSN 1-879X 675 Strain-dependent effects of diazepam and the 5-HT 2B/2C receptor
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (21) 34: 675-682 Effects of diazepam and SB 26553 in SHR and Lewis rats ISSN 1-879X 675 Strain-dependent effects of diazepam and the 5-HT 2B/2C receptor
Development of a Touch-Screen-Based Paradigm for Assessing Working Memory in the Mouse
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5607/en.2015.24.1.84 Exp Neurobiol. 2015 Mar;24(1):84-89. pissn 1226-2560 eissn 2093-8144 Original Article Development of a Touch-Screen-Based Paradigm for Assessing Working Memory
http://dx.doi.org/10.5607/en.2015.24.1.84 Exp Neurobiol. 2015 Mar;24(1):84-89. pissn 1226-2560 eissn 2093-8144 Original Article Development of a Touch-Screen-Based Paradigm for Assessing Working Memory
MeCP2 and psychostimulantinduced behavioral adaptations. Anne E. West, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurobiology Duke University Medical Center
 MeCP2 and psychostimulantinduced behavioral adaptations Anne E. West, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurobiology Duke University Medical Center Psychostimulants and antidepressants slowly change behavior Psychostimulants
MeCP2 and psychostimulantinduced behavioral adaptations Anne E. West, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurobiology Duke University Medical Center Psychostimulants and antidepressants slowly change behavior Psychostimulants
Short-Term But Not Long-Term Exercise Ameliorates Depressive Behavior in Mice
 Short-Term But Not Long-Term Exercise Ameliorates Depressive Behavior in Mice Hiroki Yashima, Aya Matsushita, Ken-ichi Kinoshita, Yoshikage Muroi, and Toshiaki Ishii ABSTRACT Objective Voluntary exercise
Short-Term But Not Long-Term Exercise Ameliorates Depressive Behavior in Mice Hiroki Yashima, Aya Matsushita, Ken-ichi Kinoshita, Yoshikage Muroi, and Toshiaki Ishii ABSTRACT Objective Voluntary exercise
Dr Francis A. Olaolorun Report on ISN/CAEN category 1A August 2016 research grant Home institution: Host institution:
 Dr Francis. Olaolorun Report on ISN/CEN category 1 ugust 2016 research grant Home institution: Neuroscience Unit, Department of Veterinary natomy, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria. Host institution:
Dr Francis. Olaolorun Report on ISN/CEN category 1 ugust 2016 research grant Home institution: Neuroscience Unit, Department of Veterinary natomy, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria. Host institution:
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
ZNZ Advanced Course in Neuroscience Mon Limbic System II. David P. Wolfer MD
 ZNZ Advanced Course in Neuroscience Mon 05.05.2014 Limbic System II David P. Wolfer MD Institute of Anatomy, University of Zurich Institute for Human Movement Sciences and Sport, ETH Zurich http://www.dpwolfer.ch
ZNZ Advanced Course in Neuroscience Mon 05.05.2014 Limbic System II David P. Wolfer MD Institute of Anatomy, University of Zurich Institute for Human Movement Sciences and Sport, ETH Zurich http://www.dpwolfer.ch
Acetylcholine again! - thought to be involved in learning and memory - thought to be involved dementia (Alzheimer's disease)
 Free recall and recognition in a network model of the hippocampus: simulating effects of scopolamine on human memory function Michael E. Hasselmo * and Bradley P. Wyble Acetylcholine again! - thought to
Free recall and recognition in a network model of the hippocampus: simulating effects of scopolamine on human memory function Michael E. Hasselmo * and Bradley P. Wyble Acetylcholine again! - thought to
Running head: EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON OBJECT RECOGNITION. Impairing Effects of Alcohol on Object Recognition. A Senior Honors Thesis
 Running head: EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON OBJECT RECOGNITION Alcohol on Object Recognition 1 Impairing Effects of Alcohol on Object Recognition A Senior Honors Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the
Running head: EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON OBJECT RECOGNITION Alcohol on Object Recognition 1 Impairing Effects of Alcohol on Object Recognition A Senior Honors Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the
Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury
 Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D., Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Kenichiro Yahata, M.D.,
Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D., Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Kenichiro Yahata, M.D.,
Limbic system outline
 Limbic system outline 1 Introduction 4 The amygdala and emotion -history - theories of emotion - definition - fear and fear conditioning 2 Review of anatomy 5 The hippocampus - amygdaloid complex - septal
Limbic system outline 1 Introduction 4 The amygdala and emotion -history - theories of emotion - definition - fear and fear conditioning 2 Review of anatomy 5 The hippocampus - amygdaloid complex - septal
Alcohol Abuse in Mothers during Gravidity and Breastfeeding Brings Changes of Hippocampal Neurons in their Offspring
 103) Alcohol Abuse in Mothers during Gravidity and Breastfeeding Brings Changes of Hippocampal Neurons in their Offspring Milotová M., Riljak V., Jandová K., Langmeier M., Marešová D., Pokorný J., Trojan
103) Alcohol Abuse in Mothers during Gravidity and Breastfeeding Brings Changes of Hippocampal Neurons in their Offspring Milotová M., Riljak V., Jandová K., Langmeier M., Marešová D., Pokorný J., Trojan
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/328/5983/1288/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Induction of Fear Extinction with Hippocampal-Infralimbic BDNF Jamie Peters, Laura M. Dieppa-Perea, Loyda M. Melendez,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/328/5983/1288/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Induction of Fear Extinction with Hippocampal-Infralimbic BDNF Jamie Peters, Laura M. Dieppa-Perea, Loyda M. Melendez,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Anxiolytic effects of Elaeocarpus sphaericus fruits on the elevated plus-maze model of anxiety in mice
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.2, No.3, pp 1781-1786, July-Sept 2010 Anxiolytic effects of Elaeocarpus sphaericus fruits on the elevated plus-maze
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.2, No.3, pp 1781-1786, July-Sept 2010 Anxiolytic effects of Elaeocarpus sphaericus fruits on the elevated plus-maze
22 JWA :00-15:
 22 JWA 2018 2018 7 7 13:00-15:00 1 2 1702004 2018 7 7 Saturday, 7 th July, 2018 12:30-2F 1 13:00-14:00 1 (SL-1) Special Lecture 1 Monoaminergic drugs vs. fast-acting antidepressants: effects on glutamate
22 JWA 2018 2018 7 7 13:00-15:00 1 2 1702004 2018 7 7 Saturday, 7 th July, 2018 12:30-2F 1 13:00-14:00 1 (SL-1) Special Lecture 1 Monoaminergic drugs vs. fast-acting antidepressants: effects on glutamate
VASILE HEFCO 1*, LUCIAN HRITCU 1, ADRIAN TIRON 1, ANDREEA-IOANA HEFCO 1
 THE EFFECTS OF NICOTINIC TREATMENT ON MEMORY AND LEARNING IMPAIRMENT INDUCED BY BLOCKADE OF MUSCARINIC ACETYLCHOLINE RECEPTORS ON PERFORMANCE IN RADIAL ARM-MAZE TASK IN RATS VASILE HEFCO, LUCIAN HRITCU,
THE EFFECTS OF NICOTINIC TREATMENT ON MEMORY AND LEARNING IMPAIRMENT INDUCED BY BLOCKADE OF MUSCARINIC ACETYLCHOLINE RECEPTORS ON PERFORMANCE IN RADIAL ARM-MAZE TASK IN RATS VASILE HEFCO, LUCIAN HRITCU,
PROPOSAL: Translational Safety Biomarker Assessment of Neurotoxicity
 PROPOSAL: Translational Safety Biomarker Assessment of Neurotoxicity Andreas Jeromin, PhD Chief Scientific Officer NextGen Sciences DX Boston, MA Emerging Issues Session HESI Annual Meeting 12 June 2012
PROPOSAL: Translational Safety Biomarker Assessment of Neurotoxicity Andreas Jeromin, PhD Chief Scientific Officer NextGen Sciences DX Boston, MA Emerging Issues Session HESI Annual Meeting 12 June 2012
Neurotransmitter Functioning In Major Depressive Disorder
 Neurotransmitter Functioning In Major Depressive Disorder Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. 2017 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc., Rockville, MD January
Neurotransmitter Functioning In Major Depressive Disorder Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. 2017 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc., Rockville, MD January
Supplementary Fig. 1
 PDK1-dependent quenching of TACE shedding activity in prion and Alzheimer s diseases Mathéa Pietri, Caroline Dakowski, Samia Hannaoui, Aurélie Alleaume-Butaux, Julia Hernandez-Rapp, Audrey Ragagnin, Sophie
PDK1-dependent quenching of TACE shedding activity in prion and Alzheimer s diseases Mathéa Pietri, Caroline Dakowski, Samia Hannaoui, Aurélie Alleaume-Butaux, Julia Hernandez-Rapp, Audrey Ragagnin, Sophie
Exercising Our Minds: Effects of Exercise on Brain Structure & Function
 Public Lecture Exercising Our Minds: Effects of Exercise on Brain Structure & Function Dr. Brian R. Christie Division of Medical Sciences, University of Victoria Cellular and Physiological Sciences, UBC
Public Lecture Exercising Our Minds: Effects of Exercise on Brain Structure & Function Dr. Brian R. Christie Division of Medical Sciences, University of Victoria Cellular and Physiological Sciences, UBC
Chapter 6: Hippocampal Function In Cognition. From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Chapter 6: Hippocampal Function In Cognition From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Grid Cell The Hippocampus Serves a Role in Multimodal Information Processing and Memory
Chapter 6: Hippocampal Function In Cognition From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Grid Cell The Hippocampus Serves a Role in Multimodal Information Processing and Memory
Vol 6, Iss 9, May 5, 2016
 Olfactory Recognition Memory Test in Mice Stephanie A. Jacobs 1*, Fengying Huang 1, Joe Z. Tsien 1 and Wei Wei 2* 1 Department of Neurology, Brain and Behavior Discovery Institute, Medical College of Georgia,
Olfactory Recognition Memory Test in Mice Stephanie A. Jacobs 1*, Fengying Huang 1, Joe Z. Tsien 1 and Wei Wei 2* 1 Department of Neurology, Brain and Behavior Discovery Institute, Medical College of Georgia,
Fear conditioning induces associative long-term potentiation in the amygdala
 11 December 1997 Nature 390, 604-607 (1997) Macmillan Publishers Ltd. Fear conditioning induces associative long-term potentiation in the amygdala MICHAEL T. ROGAN, URSULA V. STÄUBLI & JOSEPH E. LEDOUX
11 December 1997 Nature 390, 604-607 (1997) Macmillan Publishers Ltd. Fear conditioning induces associative long-term potentiation in the amygdala MICHAEL T. ROGAN, URSULA V. STÄUBLI & JOSEPH E. LEDOUX
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1.
 Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Neurotoxicol Teratol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2008 January 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2007 ; 29(1): 37 46. Effect of MDMA (ecstasy) on activity and cocaine conditioned place preference in adult
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2007 ; 29(1): 37 46. Effect of MDMA (ecstasy) on activity and cocaine conditioned place preference in adult
The Neurobiology of Ecstasy (MDMA)
 National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) The Neurobiology of Ecstasy (MDMA) Last Updated January 2007 https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents The Neurobiology of Ecstasy (MDMA) Section I Section II
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) The Neurobiology of Ecstasy (MDMA) Last Updated January 2007 https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents The Neurobiology of Ecstasy (MDMA) Section I Section II
Acute and long-term consequences of single MDMA administration in relation to individual anxiety levels in the rat
 Behavioural Brain Research 149 (2004) 135 144 Research report Acute and long-term consequences of single MDMA administration in relation to individual anxiety levels in the rat Ying-Jui Ho a, Cornelius
Behavioural Brain Research 149 (2004) 135 144 Research report Acute and long-term consequences of single MDMA administration in relation to individual anxiety levels in the rat Ying-Jui Ho a, Cornelius
Subject Index. Band of Giacomini 22 Benton Visual Retention Test 66 68
 Subject Index Adams, R.D. 4 Addenbrooke s Cognitive Examination 101 Alzheimer s disease clinical assessment histological imaging 104 neuroimaging 101 104 neuropsychological assessment 101 clinical presentation
Subject Index Adams, R.D. 4 Addenbrooke s Cognitive Examination 101 Alzheimer s disease clinical assessment histological imaging 104 neuroimaging 101 104 neuropsychological assessment 101 clinical presentation
Influence of State and/or Trait Anxieties of Wistar Rats in an Anxiety Paradigm
 Research Article Received: August 8, 2015 Accepted: November 24, 2015 Published online: March 11, 2016 Rashmi Madhava Rao Monika Sadananda Brain Research Laboratory, Biotechnology Division, Department
Research Article Received: August 8, 2015 Accepted: November 24, 2015 Published online: March 11, 2016 Rashmi Madhava Rao Monika Sadananda Brain Research Laboratory, Biotechnology Division, Department
THE SUBCHRONIC EFFECTS OF 3,4-METHYLENDIOXYMETHAMPHETAMINE ON OXIDATIVE STRESS IN RAT BRAIN
 Arch. Biol. Sci., Belgrade, 66 (3), 1075-1081, 2014 DOI:10.2298/ABS1403075S THE SUBCHRONIC EFFECTS OF 3,4-METHYLENDIOXYMETHAMPHETAMINE ON OXIDATIVE STRESS IN RAT BRAIN IVAN SIMIĆ *, VIOLETA IRIĆ-ĆUPIĆ,
Arch. Biol. Sci., Belgrade, 66 (3), 1075-1081, 2014 DOI:10.2298/ABS1403075S THE SUBCHRONIC EFFECTS OF 3,4-METHYLENDIOXYMETHAMPHETAMINE ON OXIDATIVE STRESS IN RAT BRAIN IVAN SIMIĆ *, VIOLETA IRIĆ-ĆUPIĆ,
<student name> Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal
 Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
Stress and the aging brain
 Stress and the aging brain Stress and the aging brain: What are the issues? Aging makes us less able to adjust to change Reactions of elderly to change generate stress Stress response involves acute reactions
Stress and the aging brain Stress and the aging brain: What are the issues? Aging makes us less able to adjust to change Reactions of elderly to change generate stress Stress response involves acute reactions
CASE 49. What type of memory is available for conscious retrieval? Which part of the brain stores semantic (factual) memories?
 CASE 49 A 43-year-old woman is brought to her primary care physician by her family because of concerns about her forgetfulness. The patient has a history of Down syndrome but no other medical problems.
CASE 49 A 43-year-old woman is brought to her primary care physician by her family because of concerns about her forgetfulness. The patient has a history of Down syndrome but no other medical problems.
Psychotropic Drugs Critical Thinking - KEY
 Open Your Class with This Tomorrow Chasing the Scream: The First and Last Days of the War on s Psychotropic s Critical Thinking - KEY Background: The blood-brain barrier is a network of tightly packed
Open Your Class with This Tomorrow Chasing the Scream: The First and Last Days of the War on s Psychotropic s Critical Thinking - KEY Background: The blood-brain barrier is a network of tightly packed
1.0. FSL NMDAR-fEPSP 0.8. amplitude (mv) Intensity (µa) 2.0 SD FSL Time (ms)
 a 2.5 1. AMPAR-fEPSP slope (mv/ms) 2. 1. NMDAR-fEPSP amplitude (mv).8.6.4.5.2. 2 4 6 8. 1 2 3 4 5 Intensity (µa) Intensity (µa) b 2. PPF Ratio (fepsp2/fepsp1) 1..5. 5 1 2 5 Time (ms) Supplementary Figure
a 2.5 1. AMPAR-fEPSP slope (mv/ms) 2. 1. NMDAR-fEPSP amplitude (mv).8.6.4.5.2. 2 4 6 8. 1 2 3 4 5 Intensity (µa) Intensity (µa) b 2. PPF Ratio (fepsp2/fepsp1) 1..5. 5 1 2 5 Time (ms) Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Methods
 1 Supplementary Methods Social Preference Test Subjects Seventy-four Long-Evans, male rats served as subjects (S-rats) in the foodpreference test, with 40 assigned to the CXT-Same (CXT-S) Condition and
1 Supplementary Methods Social Preference Test Subjects Seventy-four Long-Evans, male rats served as subjects (S-rats) in the foodpreference test, with 40 assigned to the CXT-Same (CXT-S) Condition and
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Application Note # MT-91. High Quality MALDI Imaging of Proteins and Peptides in Small Rodent Organ Tissues. Bruker Daltonics.
 Bruker Daltonics Application Note # MT-91 18385 Da 6230 Da 7843 Da High Quality MALDI Imaging of Proteins and Peptides in Small Rodent Organ Tissues New developments in MALDI instrumentation, laser technology
Bruker Daltonics Application Note # MT-91 18385 Da 6230 Da 7843 Da High Quality MALDI Imaging of Proteins and Peptides in Small Rodent Organ Tissues New developments in MALDI instrumentation, laser technology
HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS
 12 Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 1 12-21 2002 Research Report HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS YM Shivarajashankara, a AR Shivashankara, a P Gopalakrishna Bhat, b S Muddanna
12 Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 1 12-21 2002 Research Report HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS YM Shivarajashankara, a AR Shivashankara, a P Gopalakrishna Bhat, b S Muddanna
How to measure rodent behavior and perform a neurological screen.
 An Organ Systems Approach to Experimental Targeting of the Metabolic Syndrome How to measure rodent behavior and perform a neurological screen. Fiona Harrison, PhD Department of Medicine Vanderbilt University
An Organ Systems Approach to Experimental Targeting of the Metabolic Syndrome How to measure rodent behavior and perform a neurological screen. Fiona Harrison, PhD Department of Medicine Vanderbilt University
Entrainment of the mouse circadian clock by sub-acute physical and psychological
 Supplementary Information Entrainment of the mouse circadian clock by sub-acute physical and psychological Yu Tahara 1, Takuya Shiraishi 1, Yosuke Kikuchi 1, Atsushi Haraguchi 1, Daisuke Kuriki 1, Hiroyuki
Supplementary Information Entrainment of the mouse circadian clock by sub-acute physical and psychological Yu Tahara 1, Takuya Shiraishi 1, Yosuke Kikuchi 1, Atsushi Haraguchi 1, Daisuke Kuriki 1, Hiroyuki
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/330/6009/1408/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Paradoxical False Memory for Objects After Brain Damage Stephanie M. McTighe, Rosemary A. Cowell, Boyer D. Winters,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/330/6009/1408/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Paradoxical False Memory for Objects After Brain Damage Stephanie M. McTighe, Rosemary A. Cowell, Boyer D. Winters,
Effects of baseline anxiety on response to kindling of the right medial amygdala
 Physiology & Behavior 70 (2000) 67 80 Effects of baseline anxiety on response to kindling of the right medial amygdala Robert Adamec, Tanya Shallow Dept. of Psychology, Memorial University, St. John s,
Physiology & Behavior 70 (2000) 67 80 Effects of baseline anxiety on response to kindling of the right medial amygdala Robert Adamec, Tanya Shallow Dept. of Psychology, Memorial University, St. John s,
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (21): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (21): ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Inhibition of convulsive status epilepticus-induced abnormal neurogenesis by sodium valproate. Peng Wu 1, Yue Hu 1, Xiujuan Li 1, Min
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (21): ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Inhibition of convulsive status epilepticus-induced abnormal neurogenesis by sodium valproate. Peng Wu 1, Yue Hu 1, Xiujuan Li 1, Min
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Declarative memory includes semantic, episodic, and spatial memory, and
 Gallo Taste Learning and Memory in Aging Milagros Gallo, PhD Declarative memory includes semantic, episodic, and spatial memory, and in humans involves conscious recall. 1 Visual recognition memory is
Gallo Taste Learning and Memory in Aging Milagros Gallo, PhD Declarative memory includes semantic, episodic, and spatial memory, and in humans involves conscious recall. 1 Visual recognition memory is
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
and functional consequences
 Morphological effects of chronic drug use in the brain and functional consequences Christian P. Müller SGDP Center, Institute of Psychiatry King s College London normal behavioural repertoire: driven by
Morphological effects of chronic drug use in the brain and functional consequences Christian P. Müller SGDP Center, Institute of Psychiatry King s College London normal behavioural repertoire: driven by
