Index A Acetazolamide, hypokpp, 190 Acid maltase deficiency, ACTA1 (alpha-actin gene), 141, 142 ADOA. See Autosomal dominant optic atrophy (AD
|
|
|
- Franklin Barrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Acetazolamide, hypokpp, 190 Acid maltase deficiency, ACTA1 (alpha-actin gene), 141, 142 ADOA. See Autosomal dominant optic atrophy (ADOA) Adynamia episodica hereditaria, 185 Alpha-actinin. See ACTA1 (alpha-actin gene) Alpha-sarcoglycan complex and loss of, 57 genetic data, 57, 58 protein, 57, 58 ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) frontotemporal dementia, 372 genetic data, 371 noninvasive ventilation, 372 SOD1 gene mutation, 372 TDP-43, 371 type 1 (ALS1) genetic data, 367 genetic heterogeneity, 368, 369 motor neuron disease, 368 progressive muscle paralysis, 367 SOD1 gene mutation, 368 spasticity, 367 Androgen receptor, 307 Arachnodactyly, 35, 36 AT. See Ataxia-telangiectasia (AT) Ataxia, 244, 245, 247, 255, 260, 289, 290. See also Ataxia-telangiectasia (AT); Friedreich ataxia (FA) Ataxia-telangiectasia (AT) alpha-fetoprotein, 352 choreoathetosis, 351 genetic data, 351 ocular telangiectasia, 352 Ataxic gait, 240, 241 ATGL protein, 273 ATP2A1 gene, 199, 201 Autosomal dominant optic atrophy (ADOA), 363, 364 Axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease (CMT), 320 B Babinski sign, 347, 348, 356 BAG3 gene mutations, 153, 154 Barth syndrome or tafazzin deficiency, 147 Becker disease, 181, 182 Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) central rod domain, 15 cramps and myalgia, 15 dystrophin immunoblot, 16 genetic data, 13, 14 heart involvement, 16 hyperckemia, 13 late-onset myopathy, 15 muscle weakness, 15 myoglobinuria, 15 Beta-sarcoglycanopathy, Bethlem myopathy early childhood, 101, 103 Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, 101 finger contractures, genetic data and heterogeneity, 101, 102 LGMDs, 103 mildforms of muscular dystrophy, 101 muscle biopsy, 102 mutations, 101, 102 BMD. See Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) Bone marrow examination, 290 Brachial plexopathy, 339 C. Angelini, Genetic Neuromuscular Disorders: A Case-Based Approach, DOI / , Springer International Publishing Switzerland
2 374 Brody disease ATP2A1 gene, 199, 201 genetic heterogeneity, 199, 200 muscle biopsy, muscle relaxation, 199, 200 pseudo-myotonia or silent myotonia, 199 sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), SERCA1, symptoms, 199 C CACNA1S. See Calcium channel gene mutations (CACNA1S) Calcium ATPase, 202 Calcium channel gene mutations (CACNA1S), 189, 190 Calpain-3 (CAPN3), 20, 24, 39, 41, 43, 44 Calpainopathy, Cardiac rhythm abnormalities, 19, 23, 227 Cardiac transplantation, 222 Cardiomyopathy atrioventricular block, 28 cardiac transplantation, 221 congenital fiber-type disproportion, 145, 147 Danon disease, 221 echocardiogram, 154 LGMD2E, LGMD2F, 67, 68 LGMD2I, 71, 73 myofibrillar myopathies, 150 myosin light chain, 147 respiratory failure, 3 respiratory insufficiency, 40 Carnitine deficiency. See Systemic primary carnitine deficiency (SCD) Carnitine palmitoyl transferase II (CPT-II) deficiency clinical phenotypes, 285 CPT2 gene mutation, 285, 286 fever (morbillus), 286, 287 life-threatening events, 285 muscle biopsy, myalgia, 286 myoglobinuria, 287 rhabdomyolytic episodes, 285 Carpal tunnel syndrome, 340 Caveolin-3 immunolabeling, 32, 33 Caveolinopathy, CCD. See Central core disease (CCD) Central core disease (CCD) CCD, genetic data, 121, 122 hypotonia and delayed motor development, 121, malignant hyperthermia, 123 malignant hyperthermia syndrome, muscle biopsy, 122 Centronuclear myopathy type 1 DNM2 gene, 125, 126 genetic data, 125, 126 muscle biopsy, 126 ptosis and ophthalmoplegia, 125 CFTD. See Congenital fiber-type disproportion (CFTD) CGI-58 gene mutation, Chanarin-Dorfman syndrome. See NLSD-I Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease neuronal type (CMT2B1), neuropathy (CMT4A), type 1A (CMT1A), type 4A (CMT4A), type 1B (CMT1B), type X1 (CMTX1), Charlevoix-Saguenay type. See Spastic ataxia, Charlevoix-Saguenay type Chloride channel gene mutation (CLCN1), 181, 182 Chronic myopathy, 37, 73, 186 Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia bilateral ptosis, genetic heterogeneity, 229, 230 lactic acidosis, 230 mtdna deletion, 229 ophthalmoplegia, 231 CLCN1. See Chloride channel gene mutation (CLCN1) Club foot, 63, 85, 173, 311 CMAPs. See Compound muscle action potentials (cmaps) CMS. See Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) CMT. See Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease CMT1A genetic data, 311, 312 genetic heterogeneity, 311, 313 peroneal nerve biopsy, 312 PMP22, 311 polyneuropathy, 311 progressive muscular atrophy, 312, 314 CMT4A distal hypotrophy, 328 distal leg muscles, 324, 325 distal muscle atrophy and pes cavus, 328, 329
3 375 fibers isolation, 329 GDAP1 gene, 324 genetic data, 323, 324, 327 HSP, 327 NCV, 323 paraparesis, 329 peroneal nerve biopsy, 329 restless legs syndrome, 328 spastic paraparesis, 329 vocal cord paralysis, 323 CMT1B Dejerine-Sottas syndrome, 316 MPZ gene, 316 myelin protein zero, 315, 316 NCV, 315 polyneuropathy, 316 progressive muscular atrophy, 317 CMT2B1 axonal peripheral sensorimotor polyneuropathy, 319 buffalo hump, 320 cmap, 319 lamin A/C, 319, 320 laminopathy, 322 SAPs, 320 sural nerve biopsy, 320, 321 CMTX1 connexin-32, 331 gait disturbances, 333 genetic data, 331 GJB1 gene, 331 sural nerve biopsy, 333 X-linked dominant form, 332 Coenzyme Q10 deficiency muscle biopsy, 248 nephrotic syndrome, 248 optic atrophy, 248 oxidative stress, 247 phenotypes, 247 radioisotope assays, 249 respiratory chain enzyme activity (complex II-III), 249 Compound muscle action potentials (cmaps), 319, 320 Congenital fiber-type disproportion (CFTD) genetic heterogeneity, 145, 146 muscle biopsy, MYL2 gene mutations, 145, 146 type 1 (CFTD1) ACTA1, 141, 142 diagnosis and management, 142 genetic heterogeneity, 141, 142 hypotonia and muscle weakness, 141 joint contractures, 141 muscle biopsy, 141, 142 Congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD) integrin-alpha-7 deficiency, rigid spine, type1a (MCD1A), type1c (MDC1C), Ullrich disease, Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) diagnostic strategy, 195 DOK7 gene mutation, 195, 196 muscle biopsy, 196 symptoms, 195 Connexin-32, 331, 332 Cori-Forbes disease AGL gene encoding, 213, 215 biopsy, 215 characteristics, 213 childhood, 213 high-protein diet, 215 hypotonia and fasting hypoglycemia, polysaccharide deposition, 213 splenectomy, 214 symptoms, 213 treatment, 213 Corticosteroids, 4 6 COX deficiency Leigh syndrome, 239 mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, 243 CPT2 gene mutation, 285, 286 CPT-II. See Carnitine palmitoyltransferase II (CPT-II) deficiency Cramps calf muscles, 54 denervation, 308 dorsal and pectoral, 200 lower limbs, 178 myalgia, 14, 15 myoglobinuric episodes, 15 nocturnal muscle, 312 paresthesias, 252 rippling muscle disease, 31 CTG triplet expansion, 167 D Danon disease dystrophin, 221 genetic heterogeneity, 221, 222 LAMP-2 protein analysis, 221 muscle biopsies, 221, 222, 224 WPW syndrome, 222 X-linked dominant inheritance pattern, 223
4 376 Dejerine-Sottas syndrome, 316 Delta-sarcoglycanopathy, 67, 68 Desmin arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia, 149 cardioskeletal myopathy, 149 gene mutations, 149, 150 Diabetes bipolar syndrome, 178 endocrine disturbances, 232 MELAS syndrome, 237 NLSD-M, Diffuse hypotonia, Dilated cardiomyopathy cardiac anomalies, 19 cardiac transplantation, 15 childhood-onset muscular dystrophy, 68 DMD carriers, 9 mitral regurgitation, 63 muscular dystrophy, 61 primary systemic carnitine deficiency, 261 restrictive respiratory insufficiency, 71 Distal atrophy, 168, 222, 333, 340 Distal myopathy, 31, 32, 49, 161, 192, 213 Distal spinal muscular atrophy axonal neuronopathy manifests, 336 BSCL2-related neurological disorders, 336 characteristic features, 335 distal hereditary motor neuropathy type V, 335 genetic data, 335 heterozygous mutation, 336 slow shuffling gait, 336 DM. See Myotonic dystrophy (DM) DM1 distal muscular atrophy, 169 DMPK gene (DM-protein kinase), 137, 168 genetic heterogeneity, 167, 168 heart block, 168 management, peculiar facies, masseter atrophy, 169, 170 shuffling gait, 169, 170 DM2 bipolar syndrome, 178 genetic heterogeneity, 177, 178 management and follow-up, 179 mild myopathy, 178 muscle biopsy, myotonia and diabetes, 178 PROMM and DM1, 179, 180 proximal myopathy, quadruplet CCTG repeat, 177 symptoms, 177 ZNF9 gene, 177, 178 DMD. See Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) DMPK gene analysis, 137, 168, DOK7 gene mutation, 195, 196 Dominant limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD), 28, 37, 103 Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) corticosteroids, 4, 5 6 dystrophin gene, 4 dystrophin immunofluorescence analysis, 4, 11 electrocardiography and echocardiography, 10 genetic data, 3, 4, 9, 10 orthotopic heart transplantation, 10 skeletal and cardiac muscles, 3, 9 upper and lower girdle muscles, 10 waddling gait, 4 Dynamin-2 (DNM2) gene, 125, 126 Dysferlin, Dysmetria, 235 Dysphonia, 195, 307, 309, 324 Dystroglycanopathy LGMD2K, LGMD2N, Dystrophin antibody, 4 DMD, 3 Duchenne dystrophy, 4 immunoblot, 16 immunofluorescence, 11 muscle biopsy, 9 protein expression, 20 X-chromosome inactivation pattern, 12 E EDMD. See Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD) EDMD1 clinical triad, 19 emerin, 20, 21 genetic data, 19, 20 heterogeneity, 19, 20 immunohistochemical studies, 20 muscular dystrophy, 19 EDMD2 Achilles tendon, 23, 25 LMNA gene, 23, 24 muscle biopsy, 24 spine syndrome, tachyarrhythmias and atrioventricular block, 24 Emerin deficiency (EMD), Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD)
5 377 type I (EDMD1), type 2 (EDMD2), Encephalopathy, 233 Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), 205 Epilepsy, , Epileptic West syndrome, 257 Episodic muscle weakness, 157 Epsilon and alpha subunits of acetylcholine receptor, 194 Erb muscular dystrophy, 39, 44 ERT. See Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) Eye controversion, 352 F FA. See Friedreich ataxia (FA) Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) calpainopathy, 44 dominant inherited disorder, 111 muscle weakness, 111 myopathy, 105 type 1A (FSHD1A), type 2 (FSHD2), Fiber-type disproportion. See Congenital fiber-type disproportion (CFTD) Finger contractures, 36, , 103 Floppy infants baby position, 296, 297 cardiomyopathy, 145, 147 Foamy cells, 290 Friedreich ataxia (FA) coenzyme Q, 343 dorsal root ganglia damage, 343 dysarthria, 344, 345 GAA triplet expansion, 344 genetic data, 343 mitral prolapse, 344 muscle fibers and secondary mitochondrial change, 344 neurodegenerative disorder, 343 Frontotemporal dementia, 372 FSHD. See Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) FSHD1A EMG and muscle biopsy, 106, 108 facial weakness, 109 genetic data, 105, 106 hyperlorosis and thin muscles, pectus excavatus, 106, 108 impacts, genetic counselling, 109 intrafamilial clinical variability, 108 molecular diagnosis, 105 muscle weakness, 105 orbicularis oculi and ori, 106, 107 palpebral fissures, 106, 107 prevalence, 105 scapulae winging, 106, 107 scapular fixator, 106, 107 FSHD2 abnormality, movement of limbs, 111, 113 biopsy, 112 cervical dystonia, 112 characteristics, 111 genetic heterogeneity, 111, 112 genotype-phenotype correlations, 112 patter, muscle weakness, 111 SMCHD1gene mutations, 111 symptoms, 111 Fukutin-related protein (FKRP) gene mutation, G Glutaric acidemia. See Multiple acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency (MADD) Glutaric aciduria type II. See Multiple acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency (MADD) Glycogenosis type 2 (see Pompe disease) type 3 (see Cori-Forbes disease) type 5 (see McArdle disease) Glycogen storage disease (GSD) type II (GSDII), type III (GSDIII) ( see Cori-Forbes disease) Glycogen storage disease type 5 (GSDV). See McArdle disease GNE inclusions, 161 GNEopathies, 162 Gynecomastia, 307 Gypsy mutation, 53, 54 H Hearing loss, 234, 244, 247, 253, 255, 259, 260, 273, 274, 315, 363 Heart block, 80, 168 Hereditary motor neuropathy type V (HMN5A). See Distal spinal muscular atrophy Hereditary neuropathy with pressure palsies (HNPP) brachial plexopathy, 339 Carpal tunnel syndrome, 340 genetic data, 339, 340 peripheral mononeuropathy, 339 PMP22 gene, 340 tomaculous peripheral neuropathy, 340 Hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP), 327
6 378 Hip luxation, 117 HNPP. See Hereditary neuropathy with pressure palsies (HNPP) HSP. See Hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) Hyaline body myopathy autosomal dominant scapuloperoneal myopathy, hyaline bodies, 129, 131 muscle biopsies, 131 muscle weakness, 131 MYH7 gene, slow heavy chain myosin (MyHC 1), 129 HyperCKemia, 13, 14, 31 33, 209 Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis (HyperPP) episodic attacks of muscle weakness or paralysis, 185 genetic heterogeneity, 185, 186 management, 186 muscle biopsy, 186 SCN4A gene, 185, 186 sodium channel gene mutation, 185, 186 Hypertrophic muscles, 181 Hypertrophic proximal myopathy, 71, 72 Hypogonadism, 307 Hypokalemic periodic paralysis (hypokpp) type 1 acetazolamide treatment, 190 CACNA1S gene, 189, 190 genetic heterogeneity, 189, 190 hypokpp probands, muscle weakness, 189 Hypomethylation, 112 Hypopallesthesia, 348 Hypotonia, 121, 141, 299 I Ichthyosis, Inclusion body myopathy type 2 (IBM2) genetic heterogeneity, 161, 162 GNE gene mutations, 161, 162 muscle biopsy, 161, 162 Infantile fiber-type disproportion, 145 Infantile hypotonia, 121 Inflammatorymyopathy, 48, 49 Integrin-alpha-7 deficiency characteristics, 95 dystrophic changes, 95 gene encoding, 96 mental retardation, 95 miscarriage, 96 muscle biopsy, 95 mutations, ITGA7 gene, 95 white matter signal abnormalities and cortical atrophy, 96 Intermittent muscle weakness, 189 J Joint contractures Bethlem myopathy, 103 EDMD, 19 hypotonia, 84 limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 1B, 27 neonatal form, 296 Jordan s phenomenon, 267, 270, 273, 276 K Kearns-Sayre Syndrome (KSS) genetic heterogeneity, 225 mtdna deletions, 225 muscle biopsy, 227 ptosis and ophthalmoplegia, 226 ragged-red fibers, 226 Kennedy disease. See Spinal bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA) Kugelberg-Welander disease. See SMA3 L Lactic acidosis, 230, 233 Lamin A/C, 19, 23, 27, 319, 320 Laminopathy, 27, 29, 322 LAMP-2 protein analysis, 221, 224 Leiden-Möbius phenotype, 39 Leigh syndrome COX deficiency, 239 diffuse asthenia, 240 SURF1 gene mutations, 239, 241 LGMD1B genetic data and heterogeneity, 27, 28 lamins, 27 LMNA mutation carriers, 28 mild calves hypertrophy and quadriceps wasting, 28, 29 muscle biopsy, 28 LGMD1C caveolin-3 immunolabeling, 32, 33 caveolinopathy, 31, 32 distal myopathy, 32 fatigability and hyperckemia, 32 genetic data, 31, 32
7 379 muscle weakness and exercise-induced cramps, 33 rippling muscle disease, 31 LGMD1F chronic myopathic changes, 37 genetic data, 35, 36 mild proximal weakness, 37 pelvic girdle muscle, 35 proximal lower limb muscles, 35, 36 LGMD2A calpain-3 immunoblot analysis, 41 calpainopathy, 41, fatigability, 41 FSHD, 44 genetic data and heterogeneity, 39, 40 muscle biopsy, muscle involvement, 39 tiptoes and mild calf hypertrophy, 41 LGMD2B atrophy of calves, 49, 50 clinical features, 47 distalmyopathy, 49 dysferlin, 47 genetic data, 48 inflammatory reaction, 47, 49 and MM, 47 myalgias and high CK, 48 proximal, waddling gait, 47, 48 treatment, 49 upper girdle muscle, 49, 51 LGMD2C CK values, 53, 55 consanguineous Gypsy, gamma-sarcoglycan, muscle biopsy, 54 psychomotor development, LGMD2D alpha-sarcoglycan, biopsy, 58 child and adolescence, 58, 59 CK levels, 57 CT scan, 58 loss of ambulation, 58, 59 MRC index, 58 pathology, 59 thoracic scoliosis, 57 LGMD2E beta-sarcoglycanopathy, biopsy, cardiomyopathy, genetic data, 61, 62 high CPK values, 61 homozygous mutation, 65 psychomotor development, 63 scapular winging and Gowers sign, 61, 63 severe, 61 smooth muscle and coronary vessels, 61 LGMD2F biopsy, 68 characteristics, 67 Duchenne-like phenotype, dystrophin, 68 encoding, delta-sarcoglycan protein, 67, 68 identification, mutations, 68 LGMD2I alpha-dystroglycan glycosylation, 71 biopsy, 73 cardiomyopathy, 71, 73 congenital, 71 disease progression, Duchenne, FKRP mutations, 71 genetic data, 72 hypertrophic proximal myopathy, 73 mild dystrophinopathy, 72 weakness, limbs, 71 LGMD2K congenital, 76 diffuse LV wall hypokinesia, dystroglycanopathy, 75 mild myopathic alterations and perimysial fibrosis, 76 O-mannosyl-transferase-1 protein, 75 psychomotor development, 75 WWS/MEB, 75 LGMD2N calf hypertrophy, mild mental retardation, 80 muscle biopsy, 80 mutation, POMT2 gene, 79, 80 physical examination, 79, 80 Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD) type 1B (LGMD1B), type 1C (LGMD1C), type 1F (LGMD1F), type 2A (LGMD2A), type 2B (LGMD2B), type 2C (LGMD2C), type 2D (LGMD2D), type 2E (LGMD2E), type 2F (LGMD2F), type 2I (LGMD2I), type 2K (LGMD2K), type 2N (LGMD2N), 79 80
8 380 Limb-girdle myasthenia, 196 Lipid storage myopathy, 263, 269, 270, 275, Lipoma, Louis-Bar syndrome. See Ataxia-telangiectasia (AT) M MADD. See Multiple acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency (MADD) Madelung s collar, 251 Malignant hyperthermia. See Central core disease (CCD) Malignant hyperthermia susceptibility (MHS), McArdle disease atrophy and muscle weakness, 218 genetic heterogeneity, 217 muscle biopsy, 219 PYGM gene, 217 MCD1A birth/infancy, 83 diagnosis, 83 distal compartment, 84 epileptic attacks, 83 genetic data and heterogeneity, 83, 84 LAMA2 gene coding, 83 laminin-alpha-2-deficient, 84, 85 low birth weight, 84 merosin deficiency, 83 muscle biopsy, 85 prognosis, 86 respiratory and feeding disorders, 83 severe hypotonia and joint contractures, MDC1C characteristics, 89 dystocic delivery with fetal distress, dystroglycanopathies, 89 FKRP-related muscular dystrophy, 89, 90 genetic data, 89, 90 laminin-alpha-2chain (LAMA2), 89 mental retardation, 89 muscle biopsies, 89, 90 WWS, 90 MELAS (Myopathy, Encephalopathy, Lactic Acidosis, Stroke-like Episodes) biochemical abnormalities, genetic heterogeneity, heteroplasmy, lactic acidosis, 233 mitochondrial DNA (mtdna) mutations, muscle biopsy, 233, 236 stroke-like episodes, 233 symptoms, 233 Mental retardation, 173, 223 Merosin deficiency, 83 MFM1 desmin-related myopathy, 149, 150 muscle biopsy, 150 pathologic finding, 149 restrictive cardiomyopathy, 149, 150 MFM6 BAG3, 153 genetic heterogeneity, 153, 154 respiratory insufficiency, skeletal muscle biopsy, 154 Z disc and myofibrils, 153 MHS. See Malignant hyperthermia susceptibility (MHS) Miglustat, Mild proximal weakness, 28, 37, 112 Minicore. See Multiminicore disease (MmD) Mini-polymyoclonus, 304 Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy with COX deficiency, 243 genetic heterogeneity, mitochondrial complex IV deficiency, myoclonic epilepsy and ataxia, 244, 245 Motor neuron disease, 213, 307, 368, 372 MRI changes, 248 MtDNA deletion, 229 MTM1 gene (myotubularin protein), 133, 134 MTMX. See X-linked myopathy Multiminicore disease (MmD) central core disease, 117 genetic heterogeneity, 117 hip luxation, 117 muscle biopsy, RYR1 gene, 117, 119 SEPN1 mutations, 117, 119 skeletal deformities, Multiple acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency (MADD) carnitine deficiency, ETFDH gene mutation, 279, 280 genetic heterogeneity, 279, 280 lipid storage myopathy, mitochondrial secondary complex II III, 283 muscle atrophy, 283 polymyositis, symptoms and age at onset, 279
9 381 Multiple symmetric lipomatosis (MSL) deletions in mtdna, 251, 252 genetic heterogeneity, 251, 252 lipomatosis, muscle biopsy, 253 Muscle relaxation, 199, 200 Muscle rigidity, 199 Myalgia Brody disease, 199 congenital myopathy, 157 cramps, 14, 15 denervation, 308 febrile illness, 286 inflammatory myopathy, 49 myotonic dystrophy type 2, 177 tubular aggregation, 159 MYH7 gene mutations, MYL2 gene, 145, 146 Myoclonic epilepsy with ragged-red fibers (MERRF) syndrome, 251, 253 Myoclonus, 244, 245 Myofibrillar myopathies (MFM) type 1 (MFM1), type 6 (MFM6), Myogenic hyperuricemia, 218 Myoglobinuria, 287 Becker dystrophy, 15 cerebellar ataxia, 247 coronary heart disease, 218 febrile illness, 286 metabolic disorders, 287 rhabdomyolysis, 217 X-linked-positive family history, 14, 15 Myosin heavy chain (MyHC 1), 129 Myotonia CLCN1 gene product, 181, 182 genetic heterogeneity, 181, 182 hypertrophic muscles, 181 muscle biopsy, 182 muscle bulk, 182, 183 myotonia, 181, 182 treatment, 182 Myotonic dystrophy (DM) central nervous system involvement, 167, 173 DMPK gene analysis, genetic heterogeneity, 173, 174 large CTG triplet expansion, 173 marked hypotonia, 173 mental retardation, 173 muscle biopsy, 175 type 1 (DM1), type 2 (DM2), Myotubular myopathy diffuse hypotonia, , 135 genetic data, 133, 134 MTM1 gene mutations, 133 MTMX, 133 myotubes, 133 respiratory insufficiency, 134 N NAIP gene, deletions, 299 NARP (Neuropathy, Ataxia, Retinitis Pigmentosa) syndrome ataxia, 255 genetic heterogeneity, muscle biopsy, 256 peripheral neuropathy, 255 NCV. See Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) Nebulin (NEB gene), 137, 138 Nemaline bodies, 137 Nemaline myopathy type 2 genetic data and heterogeneity, 137, 138 muscle biopsy, 140 NEB gene, 137 nemaline bodies, 137 rods, 137 Neonatal hypotonia, 133 Nephrotic syndrome, 248 Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) electrophysiological studies, 331 hypertrophic demyelinating form, 312 polyneuropathy, 316 papillary abnormalities, 315 ulnar nerve, 332 Neurogenic atrophy, 215, 329 Neurogenic EMG, 215, 244, 274, 308, 329, 368 Neuropathy axonal, 29 Carpal tunnel syndrome, 340 cerebellar dysfunction, 293 hereditary motor sensory, 317 peripheral, 194 progressive disorder, 335 Neutral lipid storage disease (NLSD) with ichthyosis (NLSD-I), with myopathy (NLSD-M), Niemann-Pick disease type C1 (NPC1) ataxia, 289, 290 deficiency of sphingomyelinase, 289 genetic heterogeneity, 289, 290 Miglustat, NPC1 gene (type C1) mutation, 289, 290 symptoms, 289
10 382 NLSD. See Neutral lipid storage disease (NLSD) NLSD-I CGI-58 gene mutation, genetic heterogeneity, ichthyosis, Jordan s anomaly, 267, 270 myopathy, NLSD-M ATGL protein, 273 clinical features, 273 Jordan s anomaly, 273, 276 PNPLA2 gene mutation, 273, 274, 276 Nonaka distal myopathy. See Inclusion body myopathy type 2 (IBM2) Noninvasive ventilation, 300, 368, 372 NPC1 gene (type C1) mutation, 289, 290 Nystagmus, 243, 248, 267, 289, 344, 349 O Ocular telangiectasia, 352 Ophthalmoparesis, 126 Ophthalmoplegia Kearns-Sayre syndrome, 225 myopathic face, 83 neonatal hypotonia, 133 OPA1, 364 RYR1, 117 strabismus, 236 Optic atrophy plus syndrome ADOA, 363 genetic data, 363 muscle electron microscopy, 364 neuromuscular involvement, 365 OPA1 gene, 364 PEO, 363 PNPLA2 gene mutation, 273, 274, 276 POLG1 gene, 259, 260 Polyneuropathy, 311, 315, 316, 319, 323, 339, 340 Pompe disease adult, 205 biopsy, characteristics, 205 climbing rope, climbing stairs and walking, 206, 208 ERT, 205, 210 GAA gene encoding, 205, 206 guidelines, hypercapnia, 207, 209 hyperckemia, 209 juvenile-onset, 206, 207, 210 late-onset, 206, 208 limb-girdle dystrophy/polymyositis, 205 monoclonal M paraproteinemia, 206 muscle weakness, 205 neurological examination, 209 respiratory failure, 210 upper extremities, 206 Progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO), 229, 260, 363 Progressive muscular atrophy, 53, 55, 101, 312, 314, 317, 324 Proximal lower limb muscles, 35, 36 Proximal myopathy, 79, 80, Proximal myotonic myopathy (PROMM). See DM2 Proximal weakness, 304, 305 Psychomotor regression, 256 Ptosis, 135, 229 PYGM gene mutation, 217, 218 Pyramidal syndrome, 347 P Paraparesis, 327, 329, 331 Paraplegin, 359 Pelvic girdle muscle, 35, 90, 316 PEO. See Progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO) Peripheral myelin protein 22 (PMP22), , 339, 340 Peroneal muscular atrophy. See Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease Peroneal nerve biopsy, 312, 329 Pes cavus, 312, 328, 329, 335 PMP22. See Peripheral myelin protein 22 (PMP22) Q Quadriceps-sparing inclusion body myopathy type 2. See Inclusion body myopathy type 2 (IBM2) Quadruplet expansion mutation, 177 R Ragged-red fibers, 226 Respiratory insufficiency myofibrillar myopathies, 153 myotubular myopathy, Restless legs syndrome, 328 Reye s syndrome, 261 Rhinolalia, 308
11 383 Riboflavin-responsive MADD (RR-MADD) patients, 283 Rigid spine syndrome characteristics, 93 genetic data, 93, 94 lower girdle muscle weakness, 93, 94 Mallory body myopathy, 93 muscle biopsy, 93, 94 muscular dystrophy, 93 mutations, SEPN1gene, 93, 94 waddling gait with hyperlordosis, 93 Rimmed vacuoles, 161 Rippling muscle disease, 31, 33 Rods, 137, 140 Ryanodine receptor (RYR1) gene mutations, 121, 122 related MmD, 117, 119 RYR1. See Ryanodine receptor (RYR1) gene S SANDO (Sensory Ataxic Neuropathy, Dysarthria, Ophthalmoparesis) genetic heterogeneity, 259, 260 mtdna depletion, 259 POLG1 gene, 259, 260 symptoms, 259 SAPs. See Sensory nerve action potentials (SAPs) Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), SBMA. See Spinal bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA) Scapuloperoneal dystrophin, 129, 130 SCARMD. See Severe childhood-onset autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy (SCARMD) SCD. See Systemic primary carnitine deficiency (SCD) SCN4A gene, 185, 186 Scoliosis cardiac abnormalities, 345 congenital muscular dystrophy, 95 corset/back brace, 300 distal muscle weakness, 35 joint contractures, 63 respiratory failure, 93 Second wind phenomenon, 217 Selenoprotein-1 (SEPN1) mutations, 93, 94 related MmD, 117, 119 Sensory nerve action potentials (SAPs), 319, 320 SERCA1 gene mutation, Severe childhood-onset autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy (SCARMD) CK values, 53, 55 consanguineous Gypsy, gamma-sarcoglycan, muscle biopsy, 54 psychomotor development, Sialic acid biosynthetic pathway, 161 Skeletal deformities, SLC22A5 gene mutations, 261, 264 Slow-channel congenital myasthenic syndrome CHRNE gene mutations, 191 distal myopathy, 192 fluoxetin, 193 genetic heterogeneity, 191, 192 partial ophthalmoparesis, postsynaptic congenital myasthenic syndrome, 191 ptosis and ophthalmoplegia, 192 SMA. See Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) SMA1 floppy baby position, 296, 297 genetic heterogeneity, 295, 296 SMN1 gene mutation, 295, 296 symptoms, 295 SMA2 delayed motor milestones and muscle weakness, 299 deletions of NAIP gene, 299 hypotonia, 299 management, 300 SMN1 gene mutation, 299, 300 SMA3 deletions in SMN1 gene, 303, 304 genetic heterogeneity, 303, 304 proximal weakness, 304, 305 SMN1 gene mutation, 295, 296, 299, 300 SOD1 gene mutation, 367, 368, 371 Sodium channel gene mutation, 185, 186 Spastic ataxia, Charlevoix-Saguenay Type genetic heterogeneity, 347, 348 hyperreactive fibers, 349 hypotrophic fiber, 348 neurodegenerative disorders, 347 pes cavus, 348 pyramidal syndrome, 347 Spastic paraparesis (SPG) type 4 (SPG4), type 7 (SPG7), Spastin, 355 SPG. See Spastic paraparesis (SPG)
12 384 SPG4 autosomal dominant, 355, 356 heterogeneous disorders, 355 hypertonic and hypotrophic legs, 356 musclebiopsy, 356 sensory changes, 357 SPAST gene, 355 SPG7 clinical features, 359 dying back, 359 genetic heterogeneity, 359, 360 lower limbs, nystagmus and mental retardation, 360, 361 m-aaa protease, 360 muscle tightness, 361 Spinal bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA) androgen receptor, 307, 308 calf hypertrophy, 308 genetic data, 307, 308 gynecomastia and hypogonadism, 307 limb-girdle symptoms, 309 muscle biopsy, 309 proximal and bulbar muscle weakness, 307 skeletal muscle strength, 309 Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) type 1 (SMA1), type 2 (SMA2), type 3 (SMA3), Steinert disease. See DM1 Stepping gait, 169, 170 Steroid-resistant polymyositis, 49 STIM1 gene mutations, 157, 158 Stroke-like episodes, 233 Sural nerve biopsy, 320, 321, 333 Systemic primary carnitine deficiency (SCD) cardiomyopathy, 261 hepatomegaly and cardiomegaly, 262 muscle biopsy, 264 muscle hypotonia, 263 SLC22A5 gene mutations, 261, 264 T TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43), 367, 371 TDP-43. See TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) Tegretol therapy, 263 Telangiectasia. See Ataxia-telangiectasia (AT) Thomsen disease (THD). See Myotonia Tomaculous neuropathy, 340 Tongue weakness and fasciculations, 304, 308, 372 Tremor, 112, 145, 235, 240, 248, 259, 283, 307, 309, 332, 344 Tubular aggregate myopathy (TAM) episodic muscle weakness, 157 genetic heterogeneity, 157, 158 STIM1 gene mutations, 157, 158 U Ubiquinone (CoQ), 247 Ullrich disease (UCMD) characteristics, 99 differential diagnoses, 100 genetic data and heterogeneity, 99, 100 muscle weakness and contractures, 99 scleroatonic muscular dystrophy, 99 spinal rigidity and scoliosis, 99 V Vocal cord paralysis, 323 W Walker-Warburg syndrome (WWS), 90 Werdnig-Hoffmann disease type 1 (see SMA1) type 2 (see SMA2) White matter brain abnormalities MCD1A, MDC1C, Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome, 221 X X-linked dominant inheritance pattern, 223 X-linked myopathy, Z Z-line, 153 ZNF9 gene mutation, 177, 178
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report
 Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Muscular Dystrophies. Pinki Munot Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Great Ormond Street Hospital Practical Neurology Study days April 2018
 Muscular Dystrophies Pinki Munot Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Great Ormond Street Hospital Practical Neurology Study days April 2018 Definition and classification Clinical guide to recognize muscular
Muscular Dystrophies Pinki Munot Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Great Ormond Street Hospital Practical Neurology Study days April 2018 Definition and classification Clinical guide to recognize muscular
A rare case of muscular dystrophy with POMT2 and FKRP gene mutation. Present by : Ghasem Khazaei Supervisor :Dr Mina Mohammadi Sarband
 A rare case of muscular dystrophy with POMT2 and FKRP gene mutation Present by : Ghasem Khazaei Supervisor :Dr Mina Mohammadi Sarband Index : Congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD) Dystroglycanopathies Walker-Warburg
A rare case of muscular dystrophy with POMT2 and FKRP gene mutation Present by : Ghasem Khazaei Supervisor :Dr Mina Mohammadi Sarband Index : Congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD) Dystroglycanopathies Walker-Warburg
CONTENT ANATOMIC LOCI OF NM DISEASE ASSOCIATED FEATURES FUNCTIONAL DIFFICULTIES. CLINICAL HISTORY IN NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASES Weakness 06/11/60
 CONTENT HOW TO APPROACH LIMB GIRDLE AND NON-LIMB GIRDLE WEAKNESS Kongkiat Kulkantrakorn, M.D. Professor Thammasat University Clinical approach in NM disease and phenotype Common and uncommon LGMDs Common
CONTENT HOW TO APPROACH LIMB GIRDLE AND NON-LIMB GIRDLE WEAKNESS Kongkiat Kulkantrakorn, M.D. Professor Thammasat University Clinical approach in NM disease and phenotype Common and uncommon LGMDs Common
Neonatal Hypotonia. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy. Neurology Chapter of IAP
 The floppy infant assumes a frog legged position. On ventral suspension, the baby can not maintain limb posture against gravity and assumes the position of a rag doll. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy
The floppy infant assumes a frog legged position. On ventral suspension, the baby can not maintain limb posture against gravity and assumes the position of a rag doll. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy
The Floppy Baby. Clare Betteridge
 The Floppy Baby Clare Betteridge The floppy baby Identification Evaluation Investigation Diagnosis Examples What is a floppy baby? Elbows and knees loosely extended. Head control is usually poor or absent.
The Floppy Baby Clare Betteridge The floppy baby Identification Evaluation Investigation Diagnosis Examples What is a floppy baby? Elbows and knees loosely extended. Head control is usually poor or absent.
Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy
 Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy Reza Shervin Badv MD, Pediatric Neurologist Children s Medical Center Pediatrics Center of Excellence Tehran University of Medical Sciences Limb-girdle muscular dystrophies(lgmd)
Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy Reza Shervin Badv MD, Pediatric Neurologist Children s Medical Center Pediatrics Center of Excellence Tehran University of Medical Sciences Limb-girdle muscular dystrophies(lgmd)
AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer
 AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer ( )1. Choose one best answer for the following pathologic pictures. A. choroid cyst B. choroid papilloma C. pontine glioma D. ependymoma E. metastatic tumor
AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer ( )1. Choose one best answer for the following pathologic pictures. A. choroid cyst B. choroid papilloma C. pontine glioma D. ependymoma E. metastatic tumor
Index. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) 445 453 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid maltase deficiencies, electrodiagnosis of, 420, 422 Acquired peripheral neuropathy,
Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) 445 453 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid maltase deficiencies, electrodiagnosis of, 420, 422 Acquired peripheral neuropathy,
Disorders of Muscle. Disorders of Muscle. Muscle Groups Involved in Myopathy. Needle Examination of EMG. History. Muscle Biopsy
 Disorders of Muscle Disorders of Muscle Zakia Bell, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology and Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Virginia Commonwealth University Cardinal symptom of diseases of the muscle
Disorders of Muscle Disorders of Muscle Zakia Bell, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology and Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Virginia Commonwealth University Cardinal symptom of diseases of the muscle
Evaluation of the Hypotonic Infant and Child
 Evaluation of the Hypotonic Infant and Child Basil T. Darras, M.D. Neuromuscular Program Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Classification and General Clinical Evaluation
Evaluation of the Hypotonic Infant and Child Basil T. Darras, M.D. Neuromuscular Program Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Classification and General Clinical Evaluation
muscle biopsy How to do it
 How to do it muscle biopsy Gillian Hall Department of Clinical Neurosciences, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh EH4 2XU. Email: ghall@skull.dcn.ed.ac.uk INTRODUCTION Good clinical evaluation remains
How to do it muscle biopsy Gillian Hall Department of Clinical Neurosciences, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh EH4 2XU. Email: ghall@skull.dcn.ed.ac.uk INTRODUCTION Good clinical evaluation remains
Lumbosacral plexus lesion Lumbosacral plexus disorders G54.1 Neuralgic amyotrophy Neuralgic amyotrophy G
 ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM NEUROMUSCULAR DIAGNOSIS CODES Focal Neuropathy ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM Mononeuropathy G56.00 Carpal tunnel syndrome 354.00 Other median nerve lesion 354.10 Lesion of ulnar nerve 354.20
ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM NEUROMUSCULAR DIAGNOSIS CODES Focal Neuropathy ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM Mononeuropathy G56.00 Carpal tunnel syndrome 354.00 Other median nerve lesion 354.10 Lesion of ulnar nerve 354.20
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders
 Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
Recent Advances in Neurology 2014: Neuromuscular Case Presentations
 Recent Advances in Neurology 2014: Neuromuscular Case Presentations Jeffrey W. Ralph, MD Associate Clinical Professor Patient #1: Young woman with severe polyneuropathy 25 year-old woman Normal motor and
Recent Advances in Neurology 2014: Neuromuscular Case Presentations Jeffrey W. Ralph, MD Associate Clinical Professor Patient #1: Young woman with severe polyneuropathy 25 year-old woman Normal motor and
Iowa Wellstone Center Muscle Tissue and Cell Culture Repository
 Iowa Wellstone Center Muscle Tissue and Cell Culture Repository Steven A. Moore, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Iowa Department of Pathology and Iowa Wellstone Muscular Dystrophy Cooperative Research Center
Iowa Wellstone Center Muscle Tissue and Cell Culture Repository Steven A. Moore, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Iowa Department of Pathology and Iowa Wellstone Muscular Dystrophy Cooperative Research Center
Dysferlinopathies. LGMD2B, Miyoshi & Others. 2B Empowered Conference
 Dysferlinopathies LGMD2B, Miyoshi & Others 2B Empowered Conference Matthew P. Wicklund, MD, FAAN Professor of Neurology and Pediatrics Penn State Health May 24, 2015 Outline A. Empower you with knowledge
Dysferlinopathies LGMD2B, Miyoshi & Others 2B Empowered Conference Matthew P. Wicklund, MD, FAAN Professor of Neurology and Pediatrics Penn State Health May 24, 2015 Outline A. Empower you with knowledge
Muscular Dystrophies in Adulthood Matthew P. Wicklund, MD, FAAN Professor of Neurology University of Colorado School of Medicine
 Disclosure Information Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Muscular Dystrophies in Adulthood Matthew P. Wicklund, MD, FAAN Professor of Neurology University of Colorado School of Medicine I
Disclosure Information Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Muscular Dystrophies in Adulthood Matthew P. Wicklund, MD, FAAN Professor of Neurology University of Colorado School of Medicine I
The limb girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMDs)
 The limb gird muscular dystrophies (LGMDs) This factsheet is for all peop for whom a diagnosis of limb gird muscular dystrophy (LGMD) has been suggested. This is a complicated subject since there are many
The limb gird muscular dystrophies (LGMDs) This factsheet is for all peop for whom a diagnosis of limb gird muscular dystrophy (LGMD) has been suggested. This is a complicated subject since there are many
Facts About Limb-Girdle. Muscular Dystrophies
 Facts About Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophies Updated December 2009 Mandy Van Benthuysen Dear Friends: When I was 4 years old, my parents took me to a specialist to find out why I walked with an unusual
Facts About Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophies Updated December 2009 Mandy Van Benthuysen Dear Friends: When I was 4 years old, my parents took me to a specialist to find out why I walked with an unusual
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012
 Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
TREAT-NMD Care and Trial Sites Registry Information Chart
 TREAT-NMD Care and Trial Sites Registry Information Chart Below you find a list of the information that is asked in the CTSR of all registered neuromuscular disease sites. For more information please visit
TREAT-NMD Care and Trial Sites Registry Information Chart Below you find a list of the information that is asked in the CTSR of all registered neuromuscular disease sites. For more information please visit
Myopathies. Team Members: Aroob Alhuthail, Moayed Ahmad, Rema Albarrak, Ghadah Almazrou, Noura AlShabib
 Myopathies Objectives: Understanding normal muscle histology and physiology. Understanding Myopathy definition. Understanding Approach to myopathy. Knowing the most common hereditary myopathies. Knowing
Myopathies Objectives: Understanding normal muscle histology and physiology. Understanding Myopathy definition. Understanding Approach to myopathy. Knowing the most common hereditary myopathies. Knowing
Publications List. 1. General factsheets. 2. Medical conditions factsheets
 Publications List We produce a wide range of publications, from factsheets about specific medical conditions to comprehensive guides on adapting your home. To order a free publication: Call the Information
Publications List We produce a wide range of publications, from factsheets about specific medical conditions to comprehensive guides on adapting your home. To order a free publication: Call the Information
Immunohistochemical Study of Dystrophin Associated Glycoproteins in Limb-girdle Muscular Dystrophies
 Dystrophin Immunohistochemical Study of Dystrophin Associated Glycoproteins in Limb-girdle Muscular Dystrophies NSC 89-2314-B-002-111 88 8 1 89 7 31 ( Peroxidase -AntiPeroxidase Immnofluorescence) Abstract
Dystrophin Immunohistochemical Study of Dystrophin Associated Glycoproteins in Limb-girdle Muscular Dystrophies NSC 89-2314-B-002-111 88 8 1 89 7 31 ( Peroxidase -AntiPeroxidase Immnofluorescence) Abstract
1/28/2019. OSF HealthCare INI Care Center Team. Neuromuscular Disease: Muscular Dystrophy. OSF HealthCare INI Care Center Team: Who are we?
 Neuromuscular Disease: Muscular Dystrophy Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) and OSF HealthCare Illinois Neurological Institute (INI) Care Center Team The Neuromuscular clinic is a designated MDA Care
Neuromuscular Disease: Muscular Dystrophy Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) and OSF HealthCare Illinois Neurological Institute (INI) Care Center Team The Neuromuscular clinic is a designated MDA Care
Neuromuscular in the Pediatric Clinic: Recognition and Referral
 Neuromuscular in the Pediatric Clinic: Recognition and Referral Matthew Harmelink, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurology Medical College of Wisconsin Objectives: 1. Understand common presentations
Neuromuscular in the Pediatric Clinic: Recognition and Referral Matthew Harmelink, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurology Medical College of Wisconsin Objectives: 1. Understand common presentations
Strand Neuromuscular Disorders Test: Genes & Test Selection
 1 Strand Neuromuscular Disorders Test: Genes & Test Selection 2 Can the Strand Neuromuscular Disorders Test Be Offered for Prenatal Diagnosis? 3 Strand Neuromuscular Disorders Test: Genes & Test Selection
1 Strand Neuromuscular Disorders Test: Genes & Test Selection 2 Can the Strand Neuromuscular Disorders Test Be Offered for Prenatal Diagnosis? 3 Strand Neuromuscular Disorders Test: Genes & Test Selection
Muscle Dystrophy. Freih Odeh Abu Hassan, F.R.C.S. (Eng.), F.R.C.S. (Tr. & Orth.) Professor of Orthopedics University of Jordan - Amman
 Muscle Dystrophy Freih Odeh Abu Hassan, F.R.C.S. (Eng.), F.R.C.S. (Tr. & Orth.) Professor of Orthopedics University of Jordan - Amman Disorders of Neuromuscular system AHC : SMA, Polio. Nerve fiber : Neuropathies.
Muscle Dystrophy Freih Odeh Abu Hassan, F.R.C.S. (Eng.), F.R.C.S. (Tr. & Orth.) Professor of Orthopedics University of Jordan - Amman Disorders of Neuromuscular system AHC : SMA, Polio. Nerve fiber : Neuropathies.
Statutory Approvals Committee minutes
 Statutory Approvals Committee minutes Centre 0102 (Guys Hospital) Pre-implantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) application for Muscular Dystrophy, Congenital, LMNA-related, (MDCL) OMIM #613205 Thursday, 25
Statutory Approvals Committee minutes Centre 0102 (Guys Hospital) Pre-implantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) application for Muscular Dystrophy, Congenital, LMNA-related, (MDCL) OMIM #613205 Thursday, 25
Sung-Soo Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea
 Other Neuromuscular Disease Sung-Soo Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea I. Muscle & Nerve Disease Muscular dystrophy Myotonic dystrophy Myasthenia Gravis
Other Neuromuscular Disease Sung-Soo Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea I. Muscle & Nerve Disease Muscular dystrophy Myotonic dystrophy Myasthenia Gravis
MP Genetic Testing for Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophies
 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.132 Last Review: 04/30/2018 Effective Date: 04/30/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.04.86 Genetic Testing for Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy 2.04.105 Genetic Testing
BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.132 Last Review: 04/30/2018 Effective Date: 04/30/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.04.86 Genetic Testing for Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy 2.04.105 Genetic Testing
CNEMG. Myopathy, Stålberg. At rest denervation and spec spontaneous activity (myotonia, CRD, neuromyotonia) MUP number of fibres in recorded area
 clincial heredity biochem MYOPATHY biopsy Erik Stålberg Uppsala, Sweden imaging genetics Electrodes A B C MU D E Conc EMG signals from 2-15 muscle fibres CNEMG At rest denervation and spec spontaneous
clincial heredity biochem MYOPATHY biopsy Erik Stålberg Uppsala, Sweden imaging genetics Electrodes A B C MU D E Conc EMG signals from 2-15 muscle fibres CNEMG At rest denervation and spec spontaneous
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Glossary of terms used in the Neuromuscular Disorders Service
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Glossary of terms used in the Neuromuscular Disorders Service This glossary has been put together to help you during
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Glossary of terms used in the Neuromuscular Disorders Service This glossary has been put together to help you during
III./10.4. Diagnosis. Introduction. A.) Laboratory tests. Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques
 III./10.4. Diagnosis Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques After studying this chapter, you will become familiar with the most commonly used diagnostic
III./10.4. Diagnosis Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques After studying this chapter, you will become familiar with the most commonly used diagnostic
Muscle Pathology Surgical Pathology Unknown Conference. November, 2008 Philip Boyer, M.D., Ph.D.
 Muscle Pathology Surgical Pathology Unknown Conference November, 2008 Philip Boyer, M.D., Ph.D. Etiologic Approach to Differential Diagnosis Symptoms / Signs / Imaging / Biopsy / CSF Analysis Normal Abnormal
Muscle Pathology Surgical Pathology Unknown Conference November, 2008 Philip Boyer, M.D., Ph.D. Etiologic Approach to Differential Diagnosis Symptoms / Signs / Imaging / Biopsy / CSF Analysis Normal Abnormal
Genetic Testing for Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophies
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Genetic Testing for Muscular Dystrophies
 MEDICAL POLICY 12.04.86 Genetic Testing for Muscular Dystrophies BCBSA Ref. Policies: 2.04.86*, 2.04.105*, 2.04.132* Effective Date: June 1, 2018 RELATED MEDICAL POLICIES: Last Revised: May 3, 2018 None
MEDICAL POLICY 12.04.86 Genetic Testing for Muscular Dystrophies BCBSA Ref. Policies: 2.04.86*, 2.04.105*, 2.04.132* Effective Date: June 1, 2018 RELATED MEDICAL POLICIES: Last Revised: May 3, 2018 None
LIMP BABIES - WHAT MAY THAT MEAN?
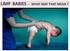 LIMP BABIES - WHAT MAY THAT MEAN? ARE WE LOOKING WHERE WE SHOULD? FLOPPY = LIMP = FLACCID = WEAK Poor head control when pulled C-posture sitting, or in ventral susp. Frog-leg lying Dropping arms Casey
LIMP BABIES - WHAT MAY THAT MEAN? ARE WE LOOKING WHERE WE SHOULD? FLOPPY = LIMP = FLACCID = WEAK Poor head control when pulled C-posture sitting, or in ventral susp. Frog-leg lying Dropping arms Casey
Genetics of Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Dr. Arianna Tucci
 Genetics of Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia 1 Clinical Research Fellow Institute of Neurology University College London Hereditary spastic paraplegia: definition Clinical designation for neurologic syndromes
Genetics of Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia 1 Clinical Research Fellow Institute of Neurology University College London Hereditary spastic paraplegia: definition Clinical designation for neurologic syndromes
REQUISITION FORM NOTE: ALL FORMS MUST BE FILLED OUT COMPLETELY FOR SAMPLE TO BE PROCESSED. Last First Last First
 #: DEPARTMENT OF NEUROLOGY COLUMBIA COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS & SURGEONS Room 4-420 630 West 168th Street, New York, NY 10032 Telephone #: 212-305-3947 Fax#: 212-305-3986 REQUISITION FORM NOTE: ALL FORMS MUST
#: DEPARTMENT OF NEUROLOGY COLUMBIA COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS & SURGEONS Room 4-420 630 West 168th Street, New York, NY 10032 Telephone #: 212-305-3947 Fax#: 212-305-3986 REQUISITION FORM NOTE: ALL FORMS MUST
DSS-1. No financial disclosures
 DSS-1 No financial disclosures Clinical History 9 year old boy with past medical history significant for cerebral palsy, in-turning right foot, left clubfoot that was surgically corrected at 3 years of
DSS-1 No financial disclosures Clinical History 9 year old boy with past medical history significant for cerebral palsy, in-turning right foot, left clubfoot that was surgically corrected at 3 years of
Distal hereditary motor neuropathy with vocal cord paresis: from difficulty in choral singing to a molecular genetic diagnosis
 Distal hereditary motor neuropathy with vocal cord paresis: from difficulty in choral singing to a molecular genetic diagnosis Gillian Ingram 1, Katy ES Barwick 2, Louise Hartley 3, Meriel McEntagart 2,
Distal hereditary motor neuropathy with vocal cord paresis: from difficulty in choral singing to a molecular genetic diagnosis Gillian Ingram 1, Katy ES Barwick 2, Louise Hartley 3, Meriel McEntagart 2,
Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction
 Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Neuromuscular Junction Muscle Myastenia Gravis Eaton-Lambert Syndrome Toxic Infllammatory Denervation Atrophy
Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Neuromuscular Junction Muscle Myastenia Gravis Eaton-Lambert Syndrome Toxic Infllammatory Denervation Atrophy
Charungthai Dejthevaporn 1
 Cramp Neuromuscular disease with abnormal Charungthai Dejthevaporn, MD, PhD, FRCP(T), FRSM Consultant Neurologist, Department of Medicine Head of Clinical Neurophysiology Unit, EMG Laboratory and Neuromuscular
Cramp Neuromuscular disease with abnormal Charungthai Dejthevaporn, MD, PhD, FRCP(T), FRSM Consultant Neurologist, Department of Medicine Head of Clinical Neurophysiology Unit, EMG Laboratory and Neuromuscular
Genetic Testing for Neurologic Disorders
 Genetic Testing for Neurologic Disorders MP9497 Covered Service: Prior Authorization Required: Additional Information: Yes when meets criteria below Yes as shown below Pre- and post-test genetic counseling
Genetic Testing for Neurologic Disorders MP9497 Covered Service: Prior Authorization Required: Additional Information: Yes when meets criteria below Yes as shown below Pre- and post-test genetic counseling
Pathology of Neuromuscular Disease Part 1: muscle
 Pathology of Neuromuscular Disease Part 1: muscle Zarife Sahenk, MD. PhD. Research Institute at Nationwide Children s Hospital Center for gene therapy, Neuromuscular Program Experimental & Clinical Neuromuscular
Pathology of Neuromuscular Disease Part 1: muscle Zarife Sahenk, MD. PhD. Research Institute at Nationwide Children s Hospital Center for gene therapy, Neuromuscular Program Experimental & Clinical Neuromuscular
Aid to the MRCP PACES Volume 1 - Stations 1, 3 and 5,
 Aid to the MRCP PACES Volume 1 - Stations 1, 3 and 5, Ryder ISBN-13: 9780470655092 Table of Contents Preface Preface to the third edition Preface to the second edition Preface to the first edition Introduction
Aid to the MRCP PACES Volume 1 - Stations 1, 3 and 5, Ryder ISBN-13: 9780470655092 Table of Contents Preface Preface to the third edition Preface to the second edition Preface to the first edition Introduction
Muscle Metabolism. Dr. Nabil Bashir
 Muscle Metabolism Dr. Nabil Bashir Learning objectives Understand how skeletal muscles derive energy at rest, moderate exercise, and strong exercise. Recognize the difference between aerobic and anaerobic
Muscle Metabolism Dr. Nabil Bashir Learning objectives Understand how skeletal muscles derive energy at rest, moderate exercise, and strong exercise. Recognize the difference between aerobic and anaerobic
BTS Guideline for Respiratory Management of Children with Neuromuscular Weakness
 BTS Guideline for Respiratory Management of Children with Neuromuscular Weakness Online Appendix 2 Search strategy: Run March 2010 and May 2011 Databases searched: MEDLINE (Ovid) MEDLINE In-Process & Other
BTS Guideline for Respiratory Management of Children with Neuromuscular Weakness Online Appendix 2 Search strategy: Run March 2010 and May 2011 Databases searched: MEDLINE (Ovid) MEDLINE In-Process & Other
panel tests assessing multiple genes at the same time for the diagnosis of one or more related disorders
 NGS tests panel tests assessing multiple genes at the same time for the diagnosis of one or more related disorders UKGTN website lists 13 laboratories offering a total of 56 panel test UKGTN listed panel
NGS tests panel tests assessing multiple genes at the same time for the diagnosis of one or more related disorders UKGTN website lists 13 laboratories offering a total of 56 panel test UKGTN listed panel
CLASSIFICATION OF PERIPHERAL NERVE DISEASES
 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF NEUROGENIC DISORDERS & MYOPATHIES NEUROPATHY MYOPATHY Weakness distal proximal Sensory loss + 0 Loss of reflexes early late CSF protein elevated normal Electromyography neurogenic
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF NEUROGENIC DISORDERS & MYOPATHIES NEUROPATHY MYOPATHY Weakness distal proximal Sensory loss + 0 Loss of reflexes early late CSF protein elevated normal Electromyography neurogenic
EDX in Myopathies Limitations. EDX in Myopathies Utility Causes of Myopathy. Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers
 Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM. Andrzej Sladkowski
 Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM Andrzej Sladkowski Potential causes of weakness in the ICU-1 Muscle disease Critical illness myopathy Inflammatory myopathy Hypokalemic
Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM Andrzej Sladkowski Potential causes of weakness in the ICU-1 Muscle disease Critical illness myopathy Inflammatory myopathy Hypokalemic
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid a-glucosidase deficiency (Pompe disease), 208, 237, 241, 293 Actin defects, in myopathies, 280 Acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid a-glucosidase deficiency (Pompe disease), 208, 237, 241, 293 Actin defects, in myopathies, 280 Acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency,
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF NEUROGENIC DISORDERS & MYOPATHIES
 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF NEUROGENIC DISORDERS & MYOPATHIES NEUROPATHY MYOPATHY Weakness distal proximal Sensory dysfunction + 0 Loss of reflexes early late Serum enzymes +/- +++ CSF protein may be elevated
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF NEUROGENIC DISORDERS & MYOPATHIES NEUROPATHY MYOPATHY Weakness distal proximal Sensory dysfunction + 0 Loss of reflexes early late Serum enzymes +/- +++ CSF protein may be elevated
Project Initiation Document Including Criteria for a Regional Approach
 Meeting: IPG Date: 6 th March 2013 Item: 20/13 (ii) NORTH OF SCOTLAND PLANNING GROUP Project Initiation Document Including Criteria for a Regional Approach Clinical Facilitator - Neuromuscular Author:
Meeting: IPG Date: 6 th March 2013 Item: 20/13 (ii) NORTH OF SCOTLAND PLANNING GROUP Project Initiation Document Including Criteria for a Regional Approach Clinical Facilitator - Neuromuscular Author:
Clinical and pathologic aspects of congenital myopathies
 Neurol J Southeast Asia 2001; 6 : 99 106 88 Clinical and pathologic aspects of congenital myopathies Ikuya NONAKA MD National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry, Kodaira, Tokyo, Japan Abstract The term
Neurol J Southeast Asia 2001; 6 : 99 106 88 Clinical and pathologic aspects of congenital myopathies Ikuya NONAKA MD National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry, Kodaira, Tokyo, Japan Abstract The term
Neuromuscular Diseases: Approach to Clinical Diagnosis
 Neuromuscular Diseases: Approach to Clinical Diagnosis 1 Shannon Venance 1 and Rabi Tawil 2 1 Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada 2 University
Neuromuscular Diseases: Approach to Clinical Diagnosis 1 Shannon Venance 1 and Rabi Tawil 2 1 Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada 2 University
Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease. Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine
 Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Nerves 1. Anterior Horn Cell 2. Dorsal root ganglion cell 3.
Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Nerves 1. Anterior Horn Cell 2. Dorsal root ganglion cell 3.
The Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophies and the Dystrophinopathies Stanley Jones P. Iyadurai, MSc, PhD, MD; John T. Kissel, MD, FAAN
 Review Article Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/continuum by maxwo3znzwrcfjddvmduzvysskax4mzb8eymgwvspgpjoz9l+mqfwgfuplwvy+jmyqlpqmifewtrhxj7jpeo+505hdqh14pdzv4lwky42mcrzqckilw0d1o4yvrwmuvvhuyo4rrbviuuwr5dqytbtk/icsrdbt0hfryk7+zagvaltkgnudxdohhaxffu/7kno26hifzu/+bcy16w7w1bdw==
Review Article Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/continuum by maxwo3znzwrcfjddvmduzvysskax4mzb8eymgwvspgpjoz9l+mqfwgfuplwvy+jmyqlpqmifewtrhxj7jpeo+505hdqh14pdzv4lwky42mcrzqckilw0d1o4yvrwmuvvhuyo4rrbviuuwr5dqytbtk/icsrdbt0hfryk7+zagvaltkgnudxdohhaxffu/7kno26hifzu/+bcy16w7w1bdw==
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for the Diagnosis of Inherited Peripheral Neuropathy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_the_diagnosis_of_inherited_peripheral_neuropathy
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for the Diagnosis of Inherited Peripheral Neuropathy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_the_diagnosis_of_inherited_peripheral_neuropathy
1GENERAL INFORMATION
 1 GENERAL INFORMATION General information 11 1.1 Diagnosis Some children will have a diagnosis of their muscle-wasting condition when they begin their school life. Others will still be having investigations
1 GENERAL INFORMATION General information 11 1.1 Diagnosis Some children will have a diagnosis of their muscle-wasting condition when they begin their school life. Others will still be having investigations
When to think about metabolic disorders in adulthood? Wouter Meersseman
 When to think about metabolic disorders in adulthood? Wouter Meersseman General Internal Medicine Adult Metabolic Clinic Wouter Meersseman, Leuven, Belgium Man, 25 year-old Normal development From 15 months
When to think about metabolic disorders in adulthood? Wouter Meersseman General Internal Medicine Adult Metabolic Clinic Wouter Meersseman, Leuven, Belgium Man, 25 year-old Normal development From 15 months
Congenital myopathies: clinical phenotypes and new diagnostic tools
 Cassandrini et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2017) 43:101 DOI 10.1186/s13052-017-0419-z REVIEW Congenital myopathies: clinical phenotypes and new diagnostic tools Open Access Denise Cassandrini 1,
Cassandrini et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2017) 43:101 DOI 10.1186/s13052-017-0419-z REVIEW Congenital myopathies: clinical phenotypes and new diagnostic tools Open Access Denise Cassandrini 1,
Mark Tarnopolsky, MD, PhD. Dept of Pediatrics (Neuromuscular and Neurometabolic Diseases), McMaster University, Hamilton, ON.
 Late Onset Pompe Disease - General Overview. Mark Tarnopolsky, MD, PhD. Dept of Pediatrics (Neuromuscular and Neurometabolic Diseases), McMaster University, Hamilton, ON. Learning Objectives. To review
Late Onset Pompe Disease - General Overview. Mark Tarnopolsky, MD, PhD. Dept of Pediatrics (Neuromuscular and Neurometabolic Diseases), McMaster University, Hamilton, ON. Learning Objectives. To review
An Introduction to mitochondrial disease.
 9 th September 2017 An Introduction to mitochondrial disease. Dr Andy Schaefer Consultant Neurologist and Clinical Lead NHS Highly Specialised Rare Mitochondrial Disease Service and Wellcome Trust Centre
9 th September 2017 An Introduction to mitochondrial disease. Dr Andy Schaefer Consultant Neurologist and Clinical Lead NHS Highly Specialised Rare Mitochondrial Disease Service and Wellcome Trust Centre
R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology
 Rom J Morphol Embryol 2011, 52(1):111 115 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Value of immunohistochemical investigation in the diagnosis of neuromuscular
Rom J Morphol Embryol 2011, 52(1):111 115 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Value of immunohistochemical investigation in the diagnosis of neuromuscular
Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease (CMT) Sometimes known as Hereditary Motor and Sensory neuropathy (HMSN) or Peroneal Muscular Atrophy (PMA)
 Version: 2 Published: January 2004 Updated: December 2009 Date of review: November 2011 Author: Dr.Hilton-Jones MD, FRCP, FRCPE Clinical Director, Oxford MDC Muscle and Nerve Centre, and revised by Dr.
Version: 2 Published: January 2004 Updated: December 2009 Date of review: November 2011 Author: Dr.Hilton-Jones MD, FRCP, FRCPE Clinical Director, Oxford MDC Muscle and Nerve Centre, and revised by Dr.
Cardiac Involvement in Skeletal Myopathies and Neuromuscular Disorders
 1 1 2 Cardiac Involvement in Skeletal Myopathies and Neuromuscular Disorders Ali J. Marian and James T. Willerson Muscular Dystrophies........................... 2387 Trinucleotide Repeat Syndromes..................
1 1 2 Cardiac Involvement in Skeletal Myopathies and Neuromuscular Disorders Ali J. Marian and James T. Willerson Muscular Dystrophies........................... 2387 Trinucleotide Repeat Syndromes..................
Electron microscopy in the investigation and diagnosis of muscle disease
 Electron microscopy in the investigation and diagnosis of muscle disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Muscle Normal Muscle The Sarcomere The names
Electron microscopy in the investigation and diagnosis of muscle disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Muscle Normal Muscle The Sarcomere The names
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_duchenne_and_becker_muscular_dystrophy
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_duchenne_and_becker_muscular_dystrophy
MITOCHONDRIAL DISEASE. Amel Karaa, MD Mitochondrial Disease Program Massachusetts General Hospital
 MITOCHONDRIAL DISEASE Amel Karaa, MD Mitochondrial Disease Program Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures & Disclaimers United Mitochondrial Disease Foundation Research Grant North American Mitochondrial
MITOCHONDRIAL DISEASE Amel Karaa, MD Mitochondrial Disease Program Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures & Disclaimers United Mitochondrial Disease Foundation Research Grant North American Mitochondrial
SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA)
 DEFICIENCY OF METABOLITE -HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA -HYPOVITAMINOSIS SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA) -SPECIFIC CELL TYPE NEURONS>OLIGODENDROCYTES>ASTROCYTES -SPECIFIC BRAIN REGION PYRAMIDAL
DEFICIENCY OF METABOLITE -HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA -HYPOVITAMINOSIS SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA) -SPECIFIC CELL TYPE NEURONS>OLIGODENDROCYTES>ASTROCYTES -SPECIFIC BRAIN REGION PYRAMIDAL
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess(es) epidural anesthesia-related, 825 826 ACE inhibitors. See Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors Acetaminophen for
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess(es) epidural anesthesia-related, 825 826 ACE inhibitors. See Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors Acetaminophen for
Pompe. Lysosomal Disorders. Introduction
 Introduction disease is an inherited, genetic disorder which results in the lack of an enzyme 'acid alpha-glucosidase. disease is also known as acid maltase deficiency or glycogen storage disease type
Introduction disease is an inherited, genetic disorder which results in the lack of an enzyme 'acid alpha-glucosidase. disease is also known as acid maltase deficiency or glycogen storage disease type
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease.
 Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Listen Observe Evaluate Test Refer Guide for primary care providers includes: Surveillance Aid: Assessing Weakness
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Listen Observe Evaluate Test Refer Guide for primary care providers includes: Surveillance Aid: Assessing Weakness
Gaucher disease 3/22/2009. Mendelian pedigree patterns. Autosomal-dominant inheritance
 Mendelian pedigree patterns Autosomal-dominant inheritance Autosomal dominant Autosomal recessive X-linked dominant X-linked recessive Y-linked Examples of AD inheritance Autosomal-recessive inheritance
Mendelian pedigree patterns Autosomal-dominant inheritance Autosomal dominant Autosomal recessive X-linked dominant X-linked recessive Y-linked Examples of AD inheritance Autosomal-recessive inheritance
Peripheral Neuropathies
 Peripheral Neuropathies ELBA Y. GERENA MALDONADO, MD ACTING ASSISTANT PROFESSOR UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON MEDICAL CENTER Objectives Definition Neurophysiology Evaluation of polyneuropathies Cases Summary
Peripheral Neuropathies ELBA Y. GERENA MALDONADO, MD ACTING ASSISTANT PROFESSOR UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON MEDICAL CENTER Objectives Definition Neurophysiology Evaluation of polyneuropathies Cases Summary
Adult Onset Myopathies
 Adult Onset Myopathies 2010 Course AANEM 57 th Annual Meeting Québec City, Québec, Canada 2010 Courses AANEM 57 th Annual Meeting Québec City, Québec, Canada American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic
Adult Onset Myopathies 2010 Course AANEM 57 th Annual Meeting Québec City, Québec, Canada 2010 Courses AANEM 57 th Annual Meeting Québec City, Québec, Canada American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic
2- and 6-minute walk tests equally well assess walking capability in neuromuscular diseases
 2- and 6-minute walk tests equally well assess walking capability in neuromuscular diseases Linda Kahr Andersen, PT, MSc Copenhagen Neuromuscular Center Background The 6MWT widely used to measure treatment
2- and 6-minute walk tests equally well assess walking capability in neuromuscular diseases Linda Kahr Andersen, PT, MSc Copenhagen Neuromuscular Center Background The 6MWT widely used to measure treatment
Presentation and investigation of mitochondrial disease in children
 Presentation and investigation of mitochondrial disease in children Andrew Morris Willink Unit, Manchester Mitochondrial function Carbohydrate Fat Respiratory chain Energy Mitochondria are the product
Presentation and investigation of mitochondrial disease in children Andrew Morris Willink Unit, Manchester Mitochondrial function Carbohydrate Fat Respiratory chain Energy Mitochondria are the product
AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS AND OTHER MOTOR NEURON DISEASES Eva L. Feldman
 1 Faculdade de Medicina de São José do Rio Preto Departamento de Ciências Neurológicas Laboratório de Investigação Neuromuscular AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS AND OTHER MOTOR NEURON DISEASES Eva L. Feldman
1 Faculdade de Medicina de São José do Rio Preto Departamento de Ciências Neurológicas Laboratório de Investigação Neuromuscular AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS AND OTHER MOTOR NEURON DISEASES Eva L. Feldman
An Overview of Congenital Myopathies Jean K. Mah, MD, MSc, FRCPC; Jeffrey T. Joseph, MD, PhD
 Review Article Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/continuum by maxwo3znzwrcfjddvmduzvysskax4mzb8eymgwvspgpjoz9l+mqfwgfuplwvy+jmyqlpqmifewtrhxj7jpeo+505hdqh14pdzv4lwky42mcrzqckilw0d1o4yvrwmuvvhuyo4rrbviuuwr5dqytbtk/icsrdbt0hfryk7+zagvaltkgnudxdohhaxffu/7kno26hifzu/+bcy16w7w1bdw==
Review Article Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/continuum by maxwo3znzwrcfjddvmduzvysskax4mzb8eymgwvspgpjoz9l+mqfwgfuplwvy+jmyqlpqmifewtrhxj7jpeo+505hdqh14pdzv4lwky42mcrzqckilw0d1o4yvrwmuvvhuyo4rrbviuuwr5dqytbtk/icsrdbt0hfryk7+zagvaltkgnudxdohhaxffu/7kno26hifzu/+bcy16w7w1bdw==
Epidemiology and classification of neuromuscular diseases in Sub-Saharan Africa B Jean KABORE, MD OUAGADOUGOU
 Epidemiology and classification of neuromuscular diseases in Sub-Saharan Africa B Jean KABORE, MD OUAGADOUGOU Definitions Neuromuscular diseases encompass cellular disorders of the motor-unit, wich include
Epidemiology and classification of neuromuscular diseases in Sub-Saharan Africa B Jean KABORE, MD OUAGADOUGOU Definitions Neuromuscular diseases encompass cellular disorders of the motor-unit, wich include
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Next-generation sequencing-based molecular diagnosis of neonatal hypotonia in Chinese
 Title page Next-generation sequencing-based molecular diagnosis of neonatal hypotonia in Chinese Population Yan Wang 1, #,Wei peng 1,#, Hong-Yan Guo 3,4, Hui Li 3,4, Jie Tian 3,4, Yu-Jing Shi 3,4, Xiao
Title page Next-generation sequencing-based molecular diagnosis of neonatal hypotonia in Chinese Population Yan Wang 1, #,Wei peng 1,#, Hong-Yan Guo 3,4, Hui Li 3,4, Jie Tian 3,4, Yu-Jing Shi 3,4, Xiao
MUSCLE DISEASE ANTIBODIES NOVOCASTRA ADVANCING MUSCLE DISEASE DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT AND RESEARCH RESULTS YOU CAN RELY ON
 MUSCLE DISEASE ANTIBODIES ADVANCING MUSCLE DISEASE DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT AND RESEARCH NOVOCASTRA RESULTS YOU CAN RELY ON Novocastra Muscle Disease Antibodies The Novocastra muscle disease portfolio comprises
MUSCLE DISEASE ANTIBODIES ADVANCING MUSCLE DISEASE DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT AND RESEARCH NOVOCASTRA RESULTS YOU CAN RELY ON Novocastra Muscle Disease Antibodies The Novocastra muscle disease portfolio comprises
A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies
 Objectives A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies Tahseen Mozaffar, MD FAAN Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, UC Irvine-MDA ALS and Neuromuscular Center Director, Neurology Residency Training
Objectives A Tale of Five Demyelinating Neuropathies Tahseen Mozaffar, MD FAAN Professor and Vice Chair of Neurology Director, UC Irvine-MDA ALS and Neuromuscular Center Director, Neurology Residency Training
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Breathing problems: and how to get on top of them
 Breathing problems: and how to get on top of them ANITA K SIMONDS PROF OF RESPIRATORY & SLEEP MEDICINE, ROYAL BROMPTON HOSPITAL MYOTUBULAR FAMILY DAY JULY 12 2014 GET THE BREATHING BASICS RIGHT Identify
Breathing problems: and how to get on top of them ANITA K SIMONDS PROF OF RESPIRATORY & SLEEP MEDICINE, ROYAL BROMPTON HOSPITAL MYOTUBULAR FAMILY DAY JULY 12 2014 GET THE BREATHING BASICS RIGHT Identify
Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG
 Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG Drs R Arunachalam Consultant Clinical Neurophysiologist Wessex Neurological Centre Southampton University Hospital EMG/NCS EMG machine For the assessment of patients
Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG Drs R Arunachalam Consultant Clinical Neurophysiologist Wessex Neurological Centre Southampton University Hospital EMG/NCS EMG machine For the assessment of patients
Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Case Study. Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a fairly common genetic disorder, affecting
 Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Case Study Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a fairly common genetic disorder, affecting approximately one in 6,000 babies. It is estimated that one in every 40 Americans carries
Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Case Study Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a fairly common genetic disorder, affecting approximately one in 6,000 babies. It is estimated that one in every 40 Americans carries
Copyright and use of this thesis
 Copyright and use of this thesis This thesis must be used in accordance with the provisions of the Copyright Act 1968. Reproduction of material protected by copyright may be an infringement of copyright
Copyright and use of this thesis This thesis must be used in accordance with the provisions of the Copyright Act 1968. Reproduction of material protected by copyright may be an infringement of copyright
TREAT-NMD Conference 2013
 TREAT-NMD Conference 2013 Utility of patient registries for clinical care and post-marketing surveillance Jan Verschuuren Leiden University Medical Centre Newcastle 30 October 1 November 2013 2 Improving
TREAT-NMD Conference 2013 Utility of patient registries for clinical care and post-marketing surveillance Jan Verschuuren Leiden University Medical Centre Newcastle 30 October 1 November 2013 2 Improving
GENETICS IN HEREDITARY NEUROPATHY
 GENETICS IN HEREDITARY NEUROPATHY ERNESTO ALONSO, SWETHA JASTI,MAZEN M.DIMACHKIE, RICHARD J. BAROHN, MELANIE GLENN, OMAR JAWDAT, JEFFREY STATLAND, LAURA HERBELIN, CONSTANTINE FARMAKIDIS,DUAA JABARI, MAMATHA
GENETICS IN HEREDITARY NEUROPATHY ERNESTO ALONSO, SWETHA JASTI,MAZEN M.DIMACHKIE, RICHARD J. BAROHN, MELANIE GLENN, OMAR JAWDAT, JEFFREY STATLAND, LAURA HERBELIN, CONSTANTINE FARMAKIDIS,DUAA JABARI, MAMATHA
Patient L.L. KRISTEN ARREDONDO, MD CHILD NEUROLOGY PGY5, UT SOUTHWESTERN
 Patient L.L. KRISTEN ARREDONDO, MD CHILD NEUROLOGY PGY5, UT SOUTHWESTERN Birth History LL was born to a healthy first time mother with an uncomplicated pregnancy Delivered at 38 weeks via C-section due
Patient L.L. KRISTEN ARREDONDO, MD CHILD NEUROLOGY PGY5, UT SOUTHWESTERN Birth History LL was born to a healthy first time mother with an uncomplicated pregnancy Delivered at 38 weeks via C-section due
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MYOPATHIES AND MUSCLE DISEASES HANDBOOK OF CLINICAL NEUROLOGY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : MYOPATHIES AND MUSCLE DISEASES HANDBOOK OF CLINICAL NEUROLOGY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 myopathies and muscle diseases handbook of clinical neurology myopathies and muscle diseases
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MYOPATHIES AND MUSCLE DISEASES HANDBOOK OF CLINICAL NEUROLOGY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 myopathies and muscle diseases handbook of clinical neurology myopathies and muscle diseases
Referring Physician Information Name: (Last, First, Middle):
 Page 1 of 5 Patient Information Clinical Indication: Patient Name: (Last, First, Middle): DOB (M/D/Y): Sex: M F Guardian Name (for minor patients only): Address: City: State: ZIP: Phone: Ethnic Background
Page 1 of 5 Patient Information Clinical Indication: Patient Name: (Last, First, Middle): DOB (M/D/Y): Sex: M F Guardian Name (for minor patients only): Address: City: State: ZIP: Phone: Ethnic Background
