DIABETIC EYE DISEASE: STRENGTHENING SERVICES TO PREVENT BLINDNESS LONDON SCHOOL OF HYGIENE & TROPICAL MEDICINE
|
|
|
- Penelope Stokes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DIABETIC EYE DISEASE: STRENGTHENING SERVICES TO PREVENT BLINDNESS LONDON SCHOOL OF HYGIENE & TROPICAL MEDICINE LONDON. SCHOOLef HYGIENE l?l &TROPICAL ~ MEDICINE GLOSSARY A Acute extraocular muscle palsy Airlie House classification Anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy (AION) Anti-hypertensive drugs Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-vegf) Anti-VEGF therapy Artificial tears Asprin Sudden onset paralysis resulting from lesions in the third, fourth or sixth cranial nerves causing failure of one or both eyes to rotate in concert with the other eye. The original diabetic retinopathy classification system, developed in A sudden loss of vision due to an interruption of blood flow to the front (anterior) of the optic nerve, also known as the optic nerve head. A class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Medicines which reduce new blood vessel growth or oedema (swelling). Anti-VEGF treatment blocks the activity of VEGF and slows the progress of macular oedema. Once oedema subsides there is likely to be some vision improvement. Lubricant eye drops used to treat the dryness and irritation associated with deficient tear production in dry eyes. A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain, fever, or inflammation. FutureLearn 1
2 B Bionic pancreas (ilet) Blindness Medical technology that can deliver both insulin and glucagon every 5 minutes. Visual acuity of less than 3/60, or a corresponding visual field loss to less than 10, in the better eye with the best possible correction. FutureLearn 2
3 C Capillaries Cardiologist Cardiovascular Cardiovascular disease Cataract Central retinal artery Central retinal vein Central-involved DME Cholesterol Chronic condition Cohort Fine branching blood vessels that form a network between the arterioles and venules. Doctor dealing with disorders of the heart as well as parts of the circulatory system. Relating to the circulatory system, which comprises the heart and blood vessels. Conditions that involve narrowed or blocked blood vessels that can lead to a heart attack, chest pain (angina) or stroke. Other heart conditions, such as those affecting heart muscle, valves or rhythm, also are considered forms of heart disease. Opacification of the lens in the eye. Part of the retinal circulation, it brings oxygenated blood to the retina. Part of the retinal circulation system, it takes blood away from the retina. Clinical signs: Retinal thickening in the macula that does involve the central sub field zone that is 1 mm in diameter. A fatty substance (lipid) vital for the normal functioning of the body. Mainly made by the liver, but can also be found in some foods. Having an excessively high level of lipids in the blood (hyperlipidemia) can have a negative effect on health. Health condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. Population of individuals who are at risk of developing a specific disease or health outcome. FutureLearn 3
4 Contact lens Corneal disease CPD Cranial nerves A thin, curved lens for vision correction placed on the film of tears that covers the surface of your eye. Infections, tissue breakdown, and other disorders affecting the clear, dome shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. Continuing Professional Development (CPD) is the term used to describe the learning activities professionals engage in to develop and enhance their abilities The nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), in contrast to spinal nerves (which emerge from segments of the spinal cord). FutureLearn 4
5 D Diabetic macular oedema (DME) Diabetic nurse Diabetic retinopathy (DR) Diabetic Retinopathy Barometer Study Diabetic Retinopathy Candesartan Trials (DIRECT) Diabetologist Dilated funduscopy Dioptre Diplopia Direct ophthalmoscopy DME is defined as retinal thickening and requires dilated examination using slit-lamp biomicroscopy and/or stereo fundus photography. Specialised nurses working as part of an integrated diabetes team and assessing patients with diabetes who have complex needs. DR damages blood vessels inside the retina at the back of the eye. It commonly affects both eyes and can lead to vision loss if it is not treated. A study to assess the level of awareness, prevention and treatment of Diabetic Eye Disease (DED) among adults with diabetes and health professionals. Large randomised trials designed (start date 2001) to assess whether reducing blood pressure in diabetic patients who did not have hypertension lowered the incidence/ progression of diabetic retinopathy. The trials showed that there was no effect on either the incidence or progression of the disease. A doctor who specialises in the treatment of diabetes. A diagnostic procedure that employs the use of mydriatic eye drops (such as tropicamide) to dilate or enlarge the pupil in order to obtain a better view of the fundus of the eye. A unit of measurement of the optical power of a lens which is equal to the reciprocal of the focal length measured in meters. Double vision. A test that allows a health professional to see the fundus of the eye and other structures using an ophthalmoscope FutureLearn 5
6 and gives a monocular, upright, image of approximately 15 times magnification. Dyslipidemia An abnormal amount of lipids (e.g. triglycerides, cholesterol and/or fat phospholipids) in the blood. FutureLearn 6
7 E Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy Study EDTRS classification Endocrinology Endolaser Endophthalmitis Epidemiology Epithelial damage Evaluation A multicenter, randomized clinical trial designed to evaluate argon laser photocoagulation and aspirin treatment in the management of patients with nonproliferative or early proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Modified version of the Airlie House classification system, adopted by the Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy Study (EDTRS) in the late 1970s and has remained the gold standard classification for many years. The branch of physiology and medicine concerned with endocrine glands and hormones. A procedure wherein laser is done by a probe put in the eye during vitreous surgery. It is used to treat retinal tears in retinal detachment and to do panretinal photocoagulation in proliferative retinopathies. A severe infection within the eye. The study of how often diseases or health-related conditions occur in different groups of people (populations) and why. Damage to the thin tissue forming the outer layer of a body's surface. An objective assessment of an ongoing or, more commonly, a completed programme. It can be done at the mid-point (mid-term evaluation) or at the end (terminal evaluation) of the programme. FutureLearn 7
8 F Failsafe officer Failsafe processes Far sightedness Fenofibrate Fibrosis Fibrovascular membranes Fibrovascular proliferation Field-testing Financing Floaters Fluctuating refractive errors Focal laser Fundoscopy Responsible for ensuring that patients are following the correct pathways and have appointments in the recommended time frame. Minimise risks of anything going wrong in the screening pathways. Farsightedness (hyperopia) is a common vision condition in which you can see distant objects clearly, but objects nearby may be blurry. Drug used to reduce cholesterol levels. The thickening and scarring of connective tissue. The product of inflammation and new blood vessel growth at the interface of the retina and vitreous secondary to ischemia; can lead to tractional retinal detachment when contraction of the membrane occurs. The growth of new blood vessels and fibrous tissues on the surface of the retina and optic nerve in diabetic retinopathy. Testing a product or device in the environment in which it is to be used. Providing funding for a person or enterprise. Opacities in the vitreous (the gel-like substance that fills about 80 percent of the eye) that cast tiny shadows on the retina. Usually caused by age-related shrinkage of the vitreous. Changes in degree of myopia or hyperopia associated with variable control of diabetes. Localised to the affected area. Examination of the fundus (interior surface of the eye). FutureLearn 8
9 Fundus photography Capturing a photograph of the back of the eye (fundus) using specialised flash-enabled cameras. FutureLearn 9
10 G Genetically engineered insulin Gestational diabetes Glaucoma Gliclazide Glycaemic control Glycated haemoglobin Glycogen metabolism Glycosuria Graders Grading Guidelines Plasmid genetically modified with human insulin gene is introduced into a new bacteria or yeast cell. This cell then divides rapidly and starts making insulin. This is in contrast to insulin taken from pigs or cattle. High blood glucose that develops during pregnancy if your body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the extra needs in pregnancy. It usually disappears after giving birth. A group of eye conditions in which the optic nerve is damaged and involves irreversible loss of visual field. A medicine used to treat type 2 diabetes. Regulation and maintenance blood glucose levels within normal ranges, which is the aim of the treatment of diabetes mellitus. A form of haemoglobin (HbA1c) formed by exposure to plasma glucose that is measured primarily to identify the three-month average plasma glucose concentration. The reversible storage of glucose in the form of glycogen mainly in the liver and skeletal muscle. The presence of sugar urine in the urine. People employed to undertake grading. Determines the level of disease present in the retina using a nationally agreed classification system and management protocols. Grading the changes seen in diabetic retinopathy screening describes the clinical severity of the condition and can be used to predict the risk of vision loss and provide appropriate management guidelines. Statement by which to determine a course of action. FutureLearn 10
11 H haemoglobin A1c Health information management system (HMIS) Health systems High coverage High resource setting High sensitivity High specificity High-income countries Human leukocyte antigens (HLA ) Human resources Humulin A form of haemoglobin (HbA1c) formed by exposure to plasma glucose that is measured primarily to identify the three-month average plasma glucose concentration. An HMIS enables the collection, storage, reporting, processing, analysis and dissemination of health-related data, based on a programme s monitoring needs. All the organisations, people and actions concerned with promoting, restoring and maintaining health. A high proportion of a target population receiving or taking up a service planned for them. Have the necessary health care structures and resources (funding, trained workforce, medical and surgical facilities). The test must correctly identify all cases of retinopathy (known as true positives). The test must minimise falsely identifying cases as having retinopathy (false positives). A developed economy and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialised nations. Gene complex involved in the immune system. Can be an associated risk in autoimmnune conditions. The personnel of an organization, regarded as an asset in terms of skills and abilities. Human resources for health are identified as one of the core building blocks of a health system. The first biosynthetic Human insulin s. It was identical to the structure of human insulin and with the advantage of being less likely to lead to allergic reactions than animal insulin. FutureLearn 11
12 Hyperglycaemia Hyperlipidaemia Hypertension High blood sugar Hyperglycaemia is the main feature of diabetes. Excessive levels of fat (or lipids) in the blood High blood pressure. Hypocholesterolaemia A low blood cholesterol Hypoxia Loss of oxygen FutureLearn 12
13 I Incidence Indirect ophthalmoscope Insulin Insulin pumps International Agency for the Prevention of Blindness International Council of Ophthalmology s classification of diabetic retinopathy International nongovernmental Incidence is a measure of how many people get a disease or health condition, in a given population during a specified period of time. It estimates the possibility, or risk, that an individual will develop a disease during that time. To calculate incidence, we divide the number of new cases identified (the numerator) by the at risk population (denominator) that was followed up over the specified period of time. Headset mounted on the head of the viewer and a condensing lens is held close to the eye. The viewer is about arms-length away from the patient. It provides the viewer a much wider field of vision of the back of the eye than a direct ophthalmoscope and the view shows elevation and depth. A hormone produced by the pancreas. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein by promoting the absorption of carbohydrates, especially glucose from the blood into liver, fat and skeletal muscle cells. An insulin pump delivers tiny amounts of insulin into the blood throughout the day and night. This reduces hypoglycaemia and can improve blood glucose levels. An alliance of civil society organisations, corporates and professional bodies promoting eye health and leading international efforts in blindness prevention activities. The ICO system combines evidence on disease progression as found by the EDTRS with severity of disease based on the observation of various kinds lesions in the retina. Organizations, usually non-profit, independent of governments and international governmental organizations that are active in humanitarian, educational, health care, FutureLearn 13
14 organisations (INGOs) Intraocular pressure Intraretinal Microvascular Abnormality Ischaemia public policy, social, human rights, environmental, and other areas to affect changes according to their objectives. Pressure inside the eye measured in millimeters of mercury (mmhg). Abnormal branching or dilation of existing blood vessels (capillaries) within the retina that act to supply areas of non-perfusion in diabetic retinopathy. A restriction in blood supply to tissues, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). FutureLearn 14
15 L Laser treatment Lipidil Lipids Longitudinal data Low resource setting Low-income countries To treat new blood vessels at the back of the eyes in the advanced stages of diabetic retinopathy. This is done because the new blood vessels tend to be very weak and often cause bleeding into the eye. Medication used to help regulate cholesterol. Fatty substances in the blood. Collecting and following patient data over time. Settings where health care structures and resources (funding, trained workforce, medical and surgical facilities) may be in short or variable supply A country with a less developed industrial base and fewer resources for health and other services FutureLearn 15
16 M Macular oedema Maculopathy Mellitus Metformin Microvascular damage Mild non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy Mobile service Moderate nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy Monitoring Multi-disciplinary team Mydriatic camera (and non-mydriatic camera) Swelling at the macular caused by leakage and build of fluid into the retina, affecting vision. The risk of damage to the central area of the fovea. Mellitus means honeyed in Latin, a reference to the sweet urine. A medicine used to treat type 2 diabetes. disease of the finer blood vessels in the body, including the capillaries. Clinical signs: Microaneurysms only. A public health strategy to provide targeted screening and other services to people with diabetes who live in different locations. Clinical signs: Microaneurysms and other signs (e.g. dot and blot haemorrhages, hard exudates, cotton wool spots). but less than severe nonproliferative DR. Monitoring is concerned with the ongoing oversight of a programme as it is implemented. It helps you to verify whether the programme is running as planned and reaching the people it is meant for. A group of health care workers who independently treat various issues a patient may have, focusing on the issues in which they specialize. Retinal camera that requires a dilated pupil, through the use of topical eye drop such as tropcamide ( non mydriatic is when the pupil does not need to be dilated). FutureLearn 16
17 N Natural history Near sightedness Neovascular glaucoma Neovascularisation Nephrologist Nerve fiber layer Neuropathy Non-central-involved DME Non-mydriatic camera (and mydriatic camera) Non-sight threatening disease The course a disease takes from its pathological onset until its eventual resolution through complete recovery or death. Also known as short-sightedness and myopia, is a condition of the eye where light focuses in front of, instead of on, the retina. This causes distant objects to be blurry while close objects appear normal. Inadequate blood supply leads to neovascularisation of the iris or neovascularisation of the lens for drainage in the eye and this ultimately leads to increased pressure. Abnormal and fragile new blood vessel growth on the retinal surface, which can bleed easily, affecting vision. A doctor specialising in the diagnosis and management of kidney disease. Innermost layer of the retina formed by the expansion of the fibers of the optic nerve. Disease or dysfunction of one or more peripheral nerves, typically causing numbness or weakness. Clinical signs: Retinal thickening in the macula that does not involve the central subfield zone that is 1mm in diameter. Retinal camera that requires a dilated pupil, through the use of topical eye drop such as tropcamide ( non mydriatic is when the pupil does not need to be dilated). Clinical signs: No abnormalities. NovoPen The first insulin pen delivery system FutureLearn 17
18 O Ocular comorbidities Ocular conditions Ocular surface diseases Oedema Ophthalmic lead Ophthalmic nurse Ophthalmologist Ophthalmoscopy Opportunistic screening Optical coherence tomography (OCT Osmotic changes Outreach service All other eye diseases an individual patient might have other than the primary eye disease of interest. Diseases affecting the structure and function of the eye. A range of conditions affecting the front surface of the eye and the tear film. A build-up of fluid when small blood vessels leak fluid into nearby tissue causing it to become swollen. Key individual with a remit to lead and help manage and improve eye care service. Nursing professional that specialises in assessing and treating patients with eye diseases. A doctor specialising in the diagnosis and management of eye disease. A test that allows a health professional to see inside of the eye and other structures using an ophthalmoscope. Involves examining eyes of people with diabetes when the opportunity arises e.g. when they attend a diabetes clinic for treatment or an optometrist for a general check-up. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an imaging technique that captures high resolution, two- and threedimensional images of biological tissue. Swelling and shrinking due to changes in water content within cells. Provision of medical / surgical or screening services outside the hospital but using the resources from the hospital e.g the doctors and nurses would travel out to another location to provide services. FutureLearn 18
19 FutureLearn 19
20 P Pancreas Pan-retinal Pan-retinal photocoagulation (PRP) Pathophysiology Phaco equipment Phacoemulsification Pharmacological agent An organ of the digestive system and endocrine system that secretes into the blood several important hormones, including insulin. All around the retina. Also known as a scatter laser, is the main form of treatment for proliferative diabetic retinopathy. The aim of the laser is to induce regression of new blood vessels (that is, to make them stop growing and shrink) through the use of tiny burns. The study of the changes of normal mechanical, physical, and biochemical functions caused by a disease. Equipment for phacoemulsification in cataract surgery. Modern cataract surgery in which the eye's internal lens is emulsified with an ultrasonic handpiece and aspirated from the eye. Biologically active substance applied pharmacologically to the body for therapeutic effect. Photoreceptors Specialised retinal cells that respond to light. There are 2 types of photoreceptors in the retina: rods and cones. Platelets Polydypsia posterior segment Posterior subcapsular cataract Small colourless disc-shaped cells found in blood and involved in clotting. Increased thirst. All the parts behind the lens. Choroid, Retina, Vitreous humor, Fovea, Optic nerve, Central retinal vein, Central retinal artery. Opacity located on the back surface of the lens directly under the lens capsule. FutureLearn 20
21 Prevalence Primary healthcare facilities Primary prevention Procurement Programme manager Proliferative diabetic retinopathy Protocol Public health Pupil dilation (mydriasis) Prevalence is a measure of how many people have a disease, or a health condition (cases), in a given population at a specific time. To calculate the prevalence of a disease or condition we divide the number of people with the disease (the cases) at the specified time by the total number of people in the population we are studying. We then multiply by 100 to get a percentage. Health posts or centres that offer primary healthcare to communities. Interventions BEFORE any diabetes occurs. Utilising Health promotion to raise awareness and lifestyle changes - good nutrition, exercise, quit smoking, avoidance of obesity. Finding, agreeing terms and acquiring goods, services or works from an external source. A person responsible for planning and governance and for overseeing the successful delivery of a programme's output. Clinical signs: Severe non-proliferative DR and 1 or more of the following signs - neovascularisation, vitreous/preretinal haemorrhage. A predefined written procedural method. WHO definition -"the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting human health through organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals" Widening of the pupil with mydriatic eye drops to facilitate internal eye examination. FutureLearn 21
22 FutureLearn 22
23 Q Qualitative data Quality Assurance Quantitative data Non-numeric data typically collected through interview and observation and concerned with understanding behaviour or attitudes Maintenance of a desired level of quality in a service especially by means of attention to every stage of the process of delivery Data in a numerical form, such as height or weight FutureLearn 23
24 R Ramipril Recombinant DNA techniques Refractive error Retinal artery occlusion (RAO) Retinal image Retinal photography Retinal vein occlusion (RVO) Retinopathy Rhegmatogenous Risk factors Anti-hypertensive medication. Combining DNA molecules from two different sources to produce new genetic combinations. Condition where the shape of the eye does not focus light on the retina but rather in front or behind it, resulting in a blurred image. Sudden obstruction of the arterial blood flow in the retinal circulation causing damage to the retina and painless vision loss. Image of the retina captured in a fundus photograph. Capturing a photograph of the back of the eye (retina or fundus) using specialised flash-enabled cameras. An interruption of the normal venous drainage from the retinal tissue causing damage to the retina and painless vision loss. Disease of the retina which results in impairment or loss of vision. Type of retinal detachment following a tear or break in the retina. Risk factors are the features/attributes, characteristics or exposures that increase someones likelihood of developing a disease. FutureLearn 24
25 S Scatter laser Screener Screening Screening test Secretions Self-care Self-care educator Service delivery Seven standard fields (30 ) Severe nonproliferative DR Pan-retinal photocoagulation (PRP) is the main form of treatment for proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Cadre of eye care worker employed in the screening programme to measure vision, take retinal photographs and potentially grade the images A specific intervention to detect people with disease early and refer them for treatment. Screening is a case finding activity, which as a public health service is offered to people in defined populations, who may or may not perceive they are at risk of a disease or its complications. A test designed to catch people who are at risk of a disease (it must be very sensitive) and allow those not at risk to pass through (it must be very specific). Substances produced and discharged from a cell, gland, or organ. Self-management to support healthy living through improved understanding of diabetes. Person delivering diabetes education to patients. The process of providing a service to patients. The gold standard imaging used in the ETDRS protocol to assess the posterior pole for diabetic retinopathy severity. 7 images of the fundus are overlapped to create a montage 75-degree field of view. Clinical signs: Any of the following signs - intraretinal haemorrhages ( 20 in each quadrant), definite venous beading in 2 quadrants or intraretinal microvascular abnormalities in 1 quadrant - and no signs of proliferative retinopathy. FutureLearn 25
26 Sight threatening disease Situational analysis Slit-lamp biomicroscopy Stakeholders Standard List for DR Static service Stereoscopic color fundus photography Steroid triamcinolone acetonide (IVTA) Synthetic human insulin Systematic screening Vision-threatening consequences of diabetes include proliferative retinopathy and maculopathy. An assessment of the current health situation fundamental to designing and updating policies, strategies and plans. Procedure using a microscope and light source to examine the anterior eye. Individuals, groups, or organizations, who may affect, be affected by, or perceive itself to be affected by a decision, activity, or outcome of a project. IAPB standard equipment and consumables list for management of diabetic retinopathy. A public health strategy to provide screening and other services to people with diabetes from a fixed location at a health facility. Production of an image from two separate photographs giving perception of depth. May help distinguish subtle retinopathy signs. Special equipment is needed to review the image. Intrvitreal injection of triamcinolone acetonide (a steroid). Insulin produced by recombinant DNA techniques. Inviting the eligible population top undertake a regular screening test to identify the presence or absence of a disease. e.g for type 1 diabetes all eligible persons with diabetes over the age of 12 years or 5 years after diagnosis, and all persons with type 2 diabetes in the defined location are invited to a screening examination. FutureLearn 26
27 T Telemedicine programmes Tertiary level Thrifty phenotype Topical lubricants Tractional detachment Triamcinolone Type 1 Diabetes Type 2 Diabetes Programmes for remote diagnosis and treatment of patients by means of telecommunications technology. Healthcare requiring highly specialized equipment and expertise. Obesity related health problems that occur later in life amongst people who have experienced poor nutrition during foetal and early life. Eye drops/ointments are used to treat dry and irritated eyes and sometimes to help the eye to heal. Retinal detachment following scar tissue formation which pulls the retina away from the layer underneath. Drug which targets the inflammation that exacerbates oedema. Type 1 diabetes is due to a decrease in insulin secretion from the pancreas. Type 1 diabetes is due to an underproduction of insulin Type 1 has been associated with diabetes mellitus in early childhood. Type 2 with later onset in adulthood. Type 2 diabetes is more common in people who are overweight. 90% of people with diabetes have type 2 diabetes. FutureLearn 27
28 U Ungradeable image Universal Health Coverage Fundus photograph not able to be assessed for diabetic retinopathy e.g. unclear or misaligned. Ensuring that all people have access to needed health services (including prevention, promotion, treatment, rehabilitation and palliation) of sufficient quality to be effective while also ensuring that the use of these services does not expose the user the financial hardship. FutureLearn 28
29 V Vacular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) Vascular Vascular occlusions Venous beading Visual acuity Visual impairment Vitrectomy Vitrector Vitreo-retinal surgery Protein produced by cells that stimulates the growth of new blood vessels which in turn cause new (but abnormal) vessels to grow (neovascularisation). Relating to blood vessels. Blockage of a blood vessel. Venous caliber changes consisting of alternating areas of venous dilation and constriction. How clearly someone is able to see. A decreased ability to see that cannont be corrected with e.g. spectacles. Surgery to remove some or all of the vitreous from the eye. A tool used to cut the vitreous for subsequent removal during a vitrectomy. Any operation to treat eye problems involving the retina, macula, and vitreous fluid. Vitreous haemorrhage Leakage of blood into the areas in and around the vitreous. Vitreous humor A clear gel filling the space between the lens and retina and which makes up four fifths of the volume of the eyeball. FutureLearn 29
30 2018 London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine CC BY-NC-SA FutureLearn 30
FRANZCO, MD, MBBS. Royal Darwin Hospital
 Diabetes and Eye By Dr. Nishantha Wijesinghe FRANZCO, MD, MBBS Consultant Ophthalmologist Royal Darwin Hospital 98% of Diabetics do not need to suffer from severe visual loss Yet Diabetic eye disease is
Diabetes and Eye By Dr. Nishantha Wijesinghe FRANZCO, MD, MBBS Consultant Ophthalmologist Royal Darwin Hospital 98% of Diabetics do not need to suffer from severe visual loss Yet Diabetic eye disease is
The Human Eye. Cornea Iris. Pupil. Lens. Retina
 The Retina Thin layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (the film of the camera). Light rays are focused on the retina then transmitted to the brain. The macula is the very small area in
The Retina Thin layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (the film of the camera). Light rays are focused on the retina then transmitted to the brain. The macula is the very small area in
Diabetes & Your Eyes
 Diabetes & Your Eyes Diabetes is a disease that occurs when the pancreas does not secrete enough insulin or the body is unable to process it properly. Insulin is the hormone that regulates the level of
Diabetes & Your Eyes Diabetes is a disease that occurs when the pancreas does not secrete enough insulin or the body is unable to process it properly. Insulin is the hormone that regulates the level of
PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY
 PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY General Anatomy At Ora Serrata At Optic Nerve Head Fundoscopic View Of Normal Retina What Is So Special About Diabetic Retinopathy? The WHO definition of blindness is
PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY General Anatomy At Ora Serrata At Optic Nerve Head Fundoscopic View Of Normal Retina What Is So Special About Diabetic Retinopathy? The WHO definition of blindness is
Brampton Hurontario Street Brampton, ON L6Y 0P6
 Diabetic Retinopathy What is Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness world-wide. Diabetes damages blood vessels in many organs of the body including the eyes.
Diabetic Retinopathy What is Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness world-wide. Diabetes damages blood vessels in many organs of the body including the eyes.
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes mellitus is one of the leading causes of irreversible blindness worldwide. In the United States, it is the most common cause of blindness in people younger than 65 years.
Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes mellitus is one of the leading causes of irreversible blindness worldwide. In the United States, it is the most common cause of blindness in people younger than 65 years.
Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public
 Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public Ray M. Balyeat, MD The Eye Institute Tulsa, Oklahoma The Healthy Eye Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, pupil and lens. These light rays are
Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public Ray M. Balyeat, MD The Eye Institute Tulsa, Oklahoma The Healthy Eye Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, pupil and lens. These light rays are
A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy 840 Walnut Street, Philadelphia PA 19107 www.willseye.org Diabetic Retinopathy 1. Definition Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes
Diabetic Retinopathy A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy 840 Walnut Street, Philadelphia PA 19107 www.willseye.org Diabetic Retinopathy 1. Definition Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes
Facts About Diabetic Eye Disease
 Facts About Diabetic Eye Disease Points to Remember 1. Diabetic eye disease comprises a group of eye conditions that affect people with diabetes. These conditions include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic
Facts About Diabetic Eye Disease Points to Remember 1. Diabetic eye disease comprises a group of eye conditions that affect people with diabetes. These conditions include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic
Diabetic Retinopathy WHAT IS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? WHAT CAUSES DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? WHAT ARE THE STAGES OF DIABETIC RETINOPATHY?
 Diabetic Retinopathy WHAT IS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? Diabetic retinopathy affects 8 million Americans with diabetes. A leading cause of blindness in American adults, it is caused by damage to the small blood
Diabetic Retinopathy WHAT IS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY? Diabetic retinopathy affects 8 million Americans with diabetes. A leading cause of blindness in American adults, it is caused by damage to the small blood
 measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
Diabetic Eye Disease
 Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Medical Retinal Services Information for Patients Diabetic Eye Disease This leaflet sets out to answer some of your questions about diabetic eye disease. You may wish to discuss
Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Medical Retinal Services Information for Patients Diabetic Eye Disease This leaflet sets out to answer some of your questions about diabetic eye disease. You may wish to discuss
Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City
 Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City Disclosures Consulted for Novo Nordisk 2017,2018. Will be discussing
Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City Disclosures Consulted for Novo Nordisk 2017,2018. Will be discussing
Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient
 Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient Rova Virgana FK Unpad Pusat Mata Nasional RS Mata Cicendo Bandung Eye Center (Hospital and Clinic) PIT IDI Jabar 2018 Keys Facts from WHO
Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient Rova Virgana FK Unpad Pusat Mata Nasional RS Mata Cicendo Bandung Eye Center (Hospital and Clinic) PIT IDI Jabar 2018 Keys Facts from WHO
Diabetic Retinopathy. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012
 Diabetic Retinopathy Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Outline Statistics Anatomy Categories Assessment Management Risk factors What do you need to do? Objectives Summarize the
Diabetic Retinopathy Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Outline Statistics Anatomy Categories Assessment Management Risk factors What do you need to do? Objectives Summarize the
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Introduction People with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina that is caused by diabetes.
Diabetic Retinopathy Introduction People with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina that is caused by diabetes.
X-Plain Diabetic Retinopathy Reference Summary
 X-Plain Diabetic Retinopathy Reference Summary Introduction Patients with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina
X-Plain Diabetic Retinopathy Reference Summary Introduction Patients with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems that can lead to blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the eye s retina
GENERAL INFORMATION DIABETIC EYE DISEASE
 GENERAL INFORMATION DIABETIC EYE DISEASE WHAT IS DIABETIC EYE DISEASE? Diabetic eye disease is a term used to describe the common eye complications seen in people with diabetes. It includes: Diabetic retinopathy
GENERAL INFORMATION DIABETIC EYE DISEASE WHAT IS DIABETIC EYE DISEASE? Diabetic eye disease is a term used to describe the common eye complications seen in people with diabetes. It includes: Diabetic retinopathy
RETINAL CONDITIONS RETINAL CONDITIONS
 GENERAL INFORMATION RETINAL CONDITIONS RETINAL CONDITIONS WHAT ARE RETINAL CONDITIONS? Retinal conditions affect the light-sensitive tissue at the back of eye known as the retina. They include diseases
GENERAL INFORMATION RETINAL CONDITIONS RETINAL CONDITIONS WHAT ARE RETINAL CONDITIONS? Retinal conditions affect the light-sensitive tissue at the back of eye known as the retina. They include diseases
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Overview This presentation covers the following topics: Definitions Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy Evidence for public health approaches Screening for diabetic retinopathy Health
Diabetic Retinopathy Overview This presentation covers the following topics: Definitions Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy Evidence for public health approaches Screening for diabetic retinopathy Health
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy
 Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy What Is Diabetic Retinopathy? Diabetes damages blood vessels in the rear of the eye. This condition is called diabetic retinopathy. It can lead to vision loss or blindness.
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy What Is Diabetic Retinopathy? Diabetes damages blood vessels in the rear of the eye. This condition is called diabetic retinopathy. It can lead to vision loss or blindness.
Diabetic retinopathy damage to the blood vessels in the retina. Cataract clouding of the eye s lens. Cataracts develop at an earlier age in people
 Diabetic Retinopathy What is diabetic eye disease? Diabetic eye disease refers to a group of eye problems that people with diabetes may face as a complication of diabetes. All can cause severe vision loss
Diabetic Retinopathy What is diabetic eye disease? Diabetic eye disease refers to a group of eye problems that people with diabetes may face as a complication of diabetes. All can cause severe vision loss
Scrub In. What is the function of vitreous humor? What does the pupil do when exposed to bright light? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision
 Scrub In What is the function of vitreous humor? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision b. Maintain eye shape and refract light rays c. Provide night vision and color vision d. Provide night vision
Scrub In What is the function of vitreous humor? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision b. Maintain eye shape and refract light rays c. Provide night vision and color vision d. Provide night vision
Diabetic Management beyond traditional risk factors and LDL-C control: Can we improve macro and microvascular risks?
 Retinopathy Diabetes has a negative effect on eyes in many ways, increasing the risk of cataracts for example, but the most common and serious ocular complication of diabetes is retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy
Retinopathy Diabetes has a negative effect on eyes in many ways, increasing the risk of cataracts for example, but the most common and serious ocular complication of diabetes is retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes can be classified into type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus, formerly known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and non-insulin diabetes mellitus, respectively.
Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes can be classified into type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus, formerly known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and non-insulin diabetes mellitus, respectively.
Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction
 Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction Lawrence Iu FRCSEd (Ophth), FCOphthHK, FHKAM (Ophthalmology) Department of Ophthalmology, Grantham Hospital & Queen Mary Hospital Background Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction Lawrence Iu FRCSEd (Ophth), FCOphthHK, FHKAM (Ophthalmology) Department of Ophthalmology, Grantham Hospital & Queen Mary Hospital Background Diabetes mellitus (DM)
MANAGING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY. <Your Hospital Name> <Your Logo>
 MANAGING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY It s difficult living with Diabetes Mellitus. Ask any diabetic... Their lives are centered around meal plans, glucose levels, and insulin
MANAGING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY It s difficult living with Diabetes Mellitus. Ask any diabetic... Their lives are centered around meal plans, glucose levels, and insulin
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME)
 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Treatment of Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO)
 Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Medical Retina Services Information for Patients Treatment of Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO) What is a Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO)? The retina is the light sensitive layer
Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Medical Retina Services Information for Patients Treatment of Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO) What is a Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO)? The retina is the light sensitive layer
OAKLEIGH EYE CENTRE. THE EYE Before looking at diabetic retinopathy it is important to understand what the healthy eye looks like and how it works.
 ABN: 80 836 359 971 Dr Mark Steiner 345 799X 135 Warrigal Road Dr Helen Steiner 292 419A OAKLEIGH VIC 3166 Tel: 03 9568 7706 Fax: 03 9568 4498 E-Mail: oakeye13@bigpond.com DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DIABETES
ABN: 80 836 359 971 Dr Mark Steiner 345 799X 135 Warrigal Road Dr Helen Steiner 292 419A OAKLEIGH VIC 3166 Tel: 03 9568 7706 Fax: 03 9568 4498 E-Mail: oakeye13@bigpond.com DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DIABETES
Diabetes and Eye Health more than meets the eye Vision Initiative - in association with PSA
 Diabetes and Eye Health more than meets the eye Vision Initiative - in association with PSA Vision 2020 Australia Vision Initiative RANZCO & OAA (Vic) Proud members of Vision 2020 Australia Outline Vision
Diabetes and Eye Health more than meets the eye Vision Initiative - in association with PSA Vision 2020 Australia Vision Initiative RANZCO & OAA (Vic) Proud members of Vision 2020 Australia Outline Vision
Introduction How the eye works
 1 Introduction Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that can cause permanent loss of eyesight and even blindness. It is a major cause of loss of vision. But if a person with diabetes receives proper eye
1 Introduction Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that can cause permanent loss of eyesight and even blindness. It is a major cause of loss of vision. But if a person with diabetes receives proper eye
INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS Introduction of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a potentially blinding complication of diabetes. It is defined as presence of one or more definite
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS Introduction of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a potentially blinding complication of diabetes. It is defined as presence of one or more definite
Mild NPDR. Moderate NPDR. Severe NPDR
 Diabetic retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of blindness in adults aged 35-65 years-old. Hyperglycaemia is thought to cause increased retinal blood flow and abnormal metabolism in
Diabetic retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of blindness in adults aged 35-65 years-old. Hyperglycaemia is thought to cause increased retinal blood flow and abnormal metabolism in
The College of Optometrists - Learning outcomes for the Professional Certificate in Medical Retina
 Learning outcomes for the Professional Certificate in Medical Retina, incorporating diabetic retinopathy screening and age related macular degeneration The professional certificate is a prerequisite to
Learning outcomes for the Professional Certificate in Medical Retina, incorporating diabetic retinopathy screening and age related macular degeneration The professional certificate is a prerequisite to
Outline. Preventing & Treating Diabetes Related Blindness. Eye Care Center Doctors. Justin Kanoff, MD. Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado
 Outline Preventing & Treating Diabetes Related Blindness Justin Kanoff, MD Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado 303 974 4302 Introduction to Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado How the eye works Eye problems
Outline Preventing & Treating Diabetes Related Blindness Justin Kanoff, MD Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado 303 974 4302 Introduction to Eye Care Center of Northern Colorado How the eye works Eye problems
RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy #
 RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy # Patient Presents a. Screen for Diabetic Retinopathy every 2 years b. Begin screening at diagnosis of Diabetes * Clinical Modifi ers Yearly
RANZCO Screening and Referral Pathway for Diabetic Retinopathy # Patient Presents a. Screen for Diabetic Retinopathy every 2 years b. Begin screening at diagnosis of Diabetes * Clinical Modifi ers Yearly
Diabetic Retinopathy Information
 http://www.midwestretina.com Phone: (614)-339-8500 Toll Free: (866)-373-8462 Sugat S. Patel, M.D. Louis J. Chorich III, M.D. Dino D. Klisovic, M.D. Lisa M. Borkowski, M.D. Dominic M. Buzzacco, M.D. Johnstone
http://www.midwestretina.com Phone: (614)-339-8500 Toll Free: (866)-373-8462 Sugat S. Patel, M.D. Louis J. Chorich III, M.D. Dino D. Klisovic, M.D. Lisa M. Borkowski, M.D. Dominic M. Buzzacco, M.D. Johnstone
Sponsored by. Shared care and referral pathways. Part 2: diabetes screening leading from the front
 CET CONTINUING Sponsored by 1 CET POINT Shared care and referral pathways Part 2: diabetes screening leading from the front Chris Steele, BSc (Hons), FCOptom, DCLP, DipOC, DipTp(IP), FBCLA The alarming
CET CONTINUING Sponsored by 1 CET POINT Shared care and referral pathways Part 2: diabetes screening leading from the front Chris Steele, BSc (Hons), FCOptom, DCLP, DipOC, DipTp(IP), FBCLA The alarming
Ophthamology Directorate. Eye Injection for Macular Disorders Information for Patients
 Ophthamology Directorate Eye Injection for Macular Disorders Information for Patients As discussed at your appointment today, please call the Medical Retinal Services Coordinator as soon as possible (within
Ophthamology Directorate Eye Injection for Macular Disorders Information for Patients As discussed at your appointment today, please call the Medical Retinal Services Coordinator as soon as possible (within
DIABETES AND YOUR EYES. Presented by Dr. Andrea Hagler
 DIABETES AND YOUR EYES Presented by Dr. Andrea Hagler Tahlequah, OK Forest Grove, OR Brief Review of Diabetes The body s endocrine system is responsible for regulating growth, reproduction, and tissue
DIABETES AND YOUR EYES Presented by Dr. Andrea Hagler Tahlequah, OK Forest Grove, OR Brief Review of Diabetes The body s endocrine system is responsible for regulating growth, reproduction, and tissue
Speaker Disclosure Statement. " Dr. Tim Maillet and Dr. Vladimir Kozousek have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
 Speaker Disclosure Statement Dr. Tim Maillet and Dr. Vladimir Kozousek have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Diabetes Morbidity Diabetes doubles the risk of stroke. Diabetes quadruples the risk of
Speaker Disclosure Statement Dr. Tim Maillet and Dr. Vladimir Kozousek have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Diabetes Morbidity Diabetes doubles the risk of stroke. Diabetes quadruples the risk of
Diabetes Eye Q Quiz. 1) Diabetes is the leading cause of new blindness among adults in the US under the age of 74.
 Diabetes Eye Q Quiz From 1997 to 2011, the number of adults with diagnosed diabetes who reported visual impairment, that is, trouble seeing even with their glasses or contact lenses, increased from 2.7
Diabetes Eye Q Quiz From 1997 to 2011, the number of adults with diagnosed diabetes who reported visual impairment, that is, trouble seeing even with their glasses or contact lenses, increased from 2.7
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Ophthalmoscopy. Reviewed & ratified by: Mr M Batterbury Consultant Ophthalmologist
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Ophthalmoscopy Reviewed & ratified by: o Mr M Batterbury Consultant Ophthalmologist Learning objectives o To understand the anatomy and physiology of the external and
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Ophthalmoscopy Reviewed & ratified by: o Mr M Batterbury Consultant Ophthalmologist Learning objectives o To understand the anatomy and physiology of the external and
Frequently Asked Questions about General Ophthalmology:
 1. Normal Eye Structure The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The parts of the eye include: Cornea (a clear dome over the iris), Iris (the pigmented part); Pupil (the black
1. Normal Eye Structure The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The parts of the eye include: Cornea (a clear dome over the iris), Iris (the pigmented part); Pupil (the black
Diabetic Retinopathy in Primary Care
 Diabetic Retinopathy in Primary Care Epidemiology Diabetes is one of the most serious challenges to health care world rld-wide. According to recent projections it will affect 239 million people e by 2010-
Diabetic Retinopathy in Primary Care Epidemiology Diabetes is one of the most serious challenges to health care world rld-wide. According to recent projections it will affect 239 million people e by 2010-
Central Mersey Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme. Referring patients for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
 Central Mersey Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme Referring patients for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Information for GPs in Halton & St Helens, Knowsley and Warrington PCT Version: June 2008 Review
Central Mersey Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Programme Referring patients for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Information for GPs in Halton & St Helens, Knowsley and Warrington PCT Version: June 2008 Review
Retinal Tears and Detachments
 Retinal Tears and Detachments Understanding Retinal Problems When your eyes are working well, it s easy to take them for granted. But a tear or detachment of your eye s retina (the light-sensing lining
Retinal Tears and Detachments Understanding Retinal Problems When your eyes are working well, it s easy to take them for granted. But a tear or detachment of your eye s retina (the light-sensing lining
RVO RETINAL VEIN OCCLUSION
 RVO RETINAL VEIN OCCLUSION A guide to understanding RVO Take some time to learn about RVO - it may help you hold on to your vision Retinal vein occlusion is a common disorder of the retina and a leading
RVO RETINAL VEIN OCCLUSION A guide to understanding RVO Take some time to learn about RVO - it may help you hold on to your vision Retinal vein occlusion is a common disorder of the retina and a leading
MAGNITUDE OF DIABETIC EYE DISEASE IN INDIA
 Dear Doctor This booklet contains information about your role as a physician in preventing blindness in your diabetic patients. You are the first point of contact for your diabetic patients. You see them
Dear Doctor This booklet contains information about your role as a physician in preventing blindness in your diabetic patients. You are the first point of contact for your diabetic patients. You see them
Perspectives on Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy. Dr. Dan Samaha, Optometrist, MSc Clinical Lecturer School of Optometry, Université de Montréal
 Perspectives on Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy 1 Dr. Dan Samaha, Optometrist, MSc Clinical Lecturer School of Optometry, Université de Montréal Current standards 2 According to the Canadian Diabetes
Perspectives on Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy 1 Dr. Dan Samaha, Optometrist, MSc Clinical Lecturer School of Optometry, Université de Montréal Current standards 2 According to the Canadian Diabetes
The Common Clinical Competency Framework for Non-medical Ophthalmic Healthcare Professionals in Secondary Care
 The Common Clinical Competency Framework for Non-medical Ophthalmic Healthcare Professionals in Secondary Care Medical Retina November 2016 Association of Health Professions in Ophthalmology General basic
The Common Clinical Competency Framework for Non-medical Ophthalmic Healthcare Professionals in Secondary Care Medical Retina November 2016 Association of Health Professions in Ophthalmology General basic
Diabetic Retinopathy What You Should Know. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Eye Institute
 Diabetic Retinopathy What You Should Know U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Eye Institute The National Eye Institute (NEI) conducts and supports research
Diabetic Retinopathy What You Should Know U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Eye Institute The National Eye Institute (NEI) conducts and supports research
Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology Services
 Ophthalmology Ophthalmology Services The Ophthalmology service offers the latest and most comprehensive eye care for patients. With a dedicated team of eye surgeons and consultants, we treat vision problems
Ophthalmology Ophthalmology Services The Ophthalmology service offers the latest and most comprehensive eye care for patients. With a dedicated team of eye surgeons and consultants, we treat vision problems
Patient & Family Guide. Diabetes and the Eye. Aussi disponible en français : Le diabète et les yeux (FF )
 Patient & Family Guide Diabetes and the Eye 2017 Aussi disponible en français : Le diabète et les yeux (FF85-1784) www.nshealth.ca Diabetes and the Eye What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which
Patient & Family Guide Diabetes and the Eye 2017 Aussi disponible en français : Le diabète et les yeux (FF85-1784) www.nshealth.ca Diabetes and the Eye What is diabetes? Diabetes is a disease in which
Retinal Detachment PATIENT EDUCATION
 Retinal Detachment PATIENT EDUCATION What is Retinal Detachment (RD)? Retina is the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that converts light images into nerve impulses that are relayed to the brain
Retinal Detachment PATIENT EDUCATION What is Retinal Detachment (RD)? Retina is the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that converts light images into nerve impulses that are relayed to the brain
Information for Patients undergoing Intravitreal Triamcinolone Acetonide (Kenalog) Injection
 Information for Patients undergoing Intravitreal Triamcinolone Acetonide (Kenalog) Injection Kenalog/SS/ST/04.2012/v1.1 review 05.2013 Page 1 Introduction Your doctor has found that you have leakage of
Information for Patients undergoing Intravitreal Triamcinolone Acetonide (Kenalog) Injection Kenalog/SS/ST/04.2012/v1.1 review 05.2013 Page 1 Introduction Your doctor has found that you have leakage of
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong. Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong
 Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong Co-Investigators Prof. David Wong Prof. Sarah McGhee Dr. Wico
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong Co-Investigators Prof. David Wong Prof. Sarah McGhee Dr. Wico
ROLE OF LASER PHOTOCOAGULATION VERSUS INTRAVITREAL TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE IN ANGIOGRAPHIC MACULAR EDEMA IN DIABETES MELLITUS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ROLE OF LASER PHOTOCOAGULATION VERSUS INTRAVITREAL TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE IN ANGIOGRAPHIC MACULAR EDEMA IN DIABETES MELLITUS Aggarwal Somesh VP 1, Shah Sonali N 2, Bharwada Rekha M 3,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ROLE OF LASER PHOTOCOAGULATION VERSUS INTRAVITREAL TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE IN ANGIOGRAPHIC MACULAR EDEMA IN DIABETES MELLITUS Aggarwal Somesh VP 1, Shah Sonali N 2, Bharwada Rekha M 3,
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
 Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) What is the Macula? What is Dry AMD (Age-related Macular Degeneration)? Dry AMD is an aging process that causes accumulation of waste product under the macula leading
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) What is the Macula? What is Dry AMD (Age-related Macular Degeneration)? Dry AMD is an aging process that causes accumulation of waste product under the macula leading
EYLEA. (aflibercept solution for injection) Patient Guide
 EYLEA (aflibercept solution for injection) Patient Guide Eylea is used to treat Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration (Wet AMD), macular oedema secondary to Branch and Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO
EYLEA (aflibercept solution for injection) Patient Guide Eylea is used to treat Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration (Wet AMD), macular oedema secondary to Branch and Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO
Case Report Inherent Challenges in Managing Long Standing Refractory Diabetic Macular Edema
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Case Report Inherent Challenges in Managing Long Standing Refractory Diabetic Macular Edema V Swetha E Jeganathan 1,2 * and Karen Madill 3 1 Department of Ophthalmology,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Case Report Inherent Challenges in Managing Long Standing Refractory Diabetic Macular Edema V Swetha E Jeganathan 1,2 * and Karen Madill 3 1 Department of Ophthalmology,
Guidelines for the Management of Diabetic Retinopathy for the Internist
 Visual Disorder Guidelines for the Management of Diabetic Retinopathy for the Internist JMAJ 45(1): 1 7, 2002 Sadao HORI Professor, Department of Ophthalmology, Tokyo Women s Medical University Abstract:
Visual Disorder Guidelines for the Management of Diabetic Retinopathy for the Internist JMAJ 45(1): 1 7, 2002 Sadao HORI Professor, Department of Ophthalmology, Tokyo Women s Medical University Abstract:
EyePACS Grading System (Part 3): Detecting Proliferative (Neovascular) Diabetic Retinopathy. George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD
 EyePACS Grading System (Part 3): Detecting Proliferative (Neovascular) Diabetic Retinopathy George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD Anatomy of the eye: 3 Normal Retina Retinal Arcades Macula Optic
EyePACS Grading System (Part 3): Detecting Proliferative (Neovascular) Diabetic Retinopathy George Bresnick MD MPA Jorge Cuadros OD PhD Anatomy of the eye: 3 Normal Retina Retinal Arcades Macula Optic
Retinal Tear and Detachment
 Retinal Tear and Detachment Introduction The retina is the layer of tissue in the back of the eye that is responsible for vision. It is attached to the choroid tissue, which supplies the retina with blood.
Retinal Tear and Detachment Introduction The retina is the layer of tissue in the back of the eye that is responsible for vision. It is attached to the choroid tissue, which supplies the retina with blood.
Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy. Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP
 Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP Content OCT imaging Retinal layers OCT features in Diabetes Some NON DR features
Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP Content OCT imaging Retinal layers OCT features in Diabetes Some NON DR features
Medical Retina 2011 Nicholas Lee
 Medical Retina 2011 Nicholas Lee 1 Diabetic Retinopathy Epidemiology 1000 registered blind each year 2% diabetics registered as blind (8% of all Blind Registrations) 42% with Mild Background DR will progress
Medical Retina 2011 Nicholas Lee 1 Diabetic Retinopathy Epidemiology 1000 registered blind each year 2% diabetics registered as blind (8% of all Blind Registrations) 42% with Mild Background DR will progress
eye conditions related to diabetes
 Understanding eye conditions related to diabetes RCOphth RNIB s Understanding series The Understanding series is designed to help you, your friends and family understand a little bit more about your eye
Understanding eye conditions related to diabetes RCOphth RNIB s Understanding series The Understanding series is designed to help you, your friends and family understand a little bit more about your eye
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
 THE UK GUIDE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY Everything you need to know about diabetic retinopathy Jaheed Khan BSc (Hons) MBBS MD FRCOphth Fellow of the Royal College of Ophthalmologists Association for Research
THE UK GUIDE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY Everything you need to know about diabetic retinopathy Jaheed Khan BSc (Hons) MBBS MD FRCOphth Fellow of the Royal College of Ophthalmologists Association for Research
Diabetic Retinopatathy
 Diabetic Retinopatathy Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO Financial Disclosure I have received honoraria or am on the advisory board for the following companies: Carl Zeiss Meditec Arctic DX Macula Risk Advanced
Diabetic Retinopatathy Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO Financial Disclosure I have received honoraria or am on the advisory board for the following companies: Carl Zeiss Meditec Arctic DX Macula Risk Advanced
Diabetic Retinopathy Frequently Asked Questions
 Diabetic Retinopathy Frequently Asked Questions Q.Who is at risk of diabetic retinopathy? Diabetic retinopathy is a highly vascularised eye complication of both insulin dependent and non-insulin dependent
Diabetic Retinopathy Frequently Asked Questions Q.Who is at risk of diabetic retinopathy? Diabetic retinopathy is a highly vascularised eye complication of both insulin dependent and non-insulin dependent
Serious Eye diseases, New treatments. Mr. M. Usman Saeed MBBS, FRCS, FRCOphth Consultant Ophthalmologist
 Serious Eye diseases, New treatments Mr. M. Usman Saeed MBBS, FRCS, FRCOphth Consultant Ophthalmologist 5 major causes of loss of vision Cataracts Glaucoma Macular degeneration Retinal Vein occlusions
Serious Eye diseases, New treatments Mr. M. Usman Saeed MBBS, FRCS, FRCOphth Consultant Ophthalmologist 5 major causes of loss of vision Cataracts Glaucoma Macular degeneration Retinal Vein occlusions
INFORMED CONSENT FOR AVASTIN TM (BEVACIZUMAB) INTRAVITREAL INJECTION
 INFORMED CONSENT FOR AVASTIN TM (BEVACIZUMAB) INTRAVITREAL INJECTION INDICATIONS: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the leading cause of blindness in people over 50 years of age. It is caused by
INFORMED CONSENT FOR AVASTIN TM (BEVACIZUMAB) INTRAVITREAL INJECTION INDICATIONS: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the leading cause of blindness in people over 50 years of age. It is caused by
Clinical Case Presentation. Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion. Sarita M. Registered Nurse Whangarei Base Hospital
 Clinical Case Presentation on Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion Sarita M. Registered Nurse Whangarei Base Hospital Introduction Case Study Pathogenesis Clinical Features Investigations Treatment Follow-up
Clinical Case Presentation on Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion Sarita M. Registered Nurse Whangarei Base Hospital Introduction Case Study Pathogenesis Clinical Features Investigations Treatment Follow-up
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Program in the Cree Region of James Bay of Quebec
 RUIS McGILL VIRTUAL HEALTH AND SOCIAL SERVICES CENTRE (CvSSS) SIMPLIFYING TELEHEALTH! Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Program in the Cree Region of James Bay of Quebec Nurse and Imager Training Prepared
RUIS McGILL VIRTUAL HEALTH AND SOCIAL SERVICES CENTRE (CvSSS) SIMPLIFYING TELEHEALTH! Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Program in the Cree Region of James Bay of Quebec Nurse and Imager Training Prepared
Subclinical Diabetic Macular Edema Study
 Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network Subclinical Diabetic Macular Edema Study Version 2.0 March 21, 2006 Subclinical DME Protocol v2 0 3-21-06.doc Table of Contents Chapter 1. Background Information
Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network Subclinical Diabetic Macular Edema Study Version 2.0 March 21, 2006 Subclinical DME Protocol v2 0 3-21-06.doc Table of Contents Chapter 1. Background Information
Information for patients
 Information for patients Intravitreal Anti-VEGF Treatment (vascular endothelial growth factor) This leaflet gives you information that will help you decide whether to have intravitreal treatment. It also
Information for patients Intravitreal Anti-VEGF Treatment (vascular endothelial growth factor) This leaflet gives you information that will help you decide whether to have intravitreal treatment. It also
UVEITIS IN GENERAL. Information for patients UVEITIS CLINIC WHAT IS UVEITIS? MAIN CATEGORIES OF UVEITIS
 Information for patients UVEITIS CLINIC UVEITIS IN GENERAL WHAT IS UVEITIS? The uvea is a name given to the pigmented layer of tissue inside the eye. When all or part of the uvea becomes inflamed, the
Information for patients UVEITIS CLINIC UVEITIS IN GENERAL WHAT IS UVEITIS? The uvea is a name given to the pigmented layer of tissue inside the eye. When all or part of the uvea becomes inflamed, the
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA
 OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
Review of Diabetes and Diabetic Retinopathy
 1 During uncontrolled diabetes, high levels of glucose in the blood can have a damaging effect on your body and can particularly harm the tiny blood vasculature system found in your kidneys, heart, eyes,
1 During uncontrolled diabetes, high levels of glucose in the blood can have a damaging effect on your body and can particularly harm the tiny blood vasculature system found in your kidneys, heart, eyes,
Sense of Vision. Chapter 8. The Eye and Vision. The Eye Orbit. Eyebrows, Eyelids, Eyelashes. Accessory Organs 5/3/2016.
 Sense of Vision Chapter 8 Special Senses The Eye and Vision 70 percent of all sensory receptors are in the eyes Each eye has over 1 million nerve fibers Protection for the eye Most of the eye is enclosed
Sense of Vision Chapter 8 Special Senses The Eye and Vision 70 percent of all sensory receptors are in the eyes Each eye has over 1 million nerve fibers Protection for the eye Most of the eye is enclosed
Ophthalmology. Juliette Stenz, MD
 Ophthalmology Juliette Stenz, MD Required Slide Disclosures NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Required Slide At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1.
Ophthalmology Juliette Stenz, MD Required Slide Disclosures NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Required Slide At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1.
For details on measurement and recording of visual acuity, refer to Annex 1. VISION INTERPRETING RESULTS ABSTRACT
 management update on functional decline in older adults 2012 Unit No. 5 VISION Dr Au Eong Kah Guan, Ms Yulianti, Ms Fifiana ABSTRACT Among Singaporean adults of Chinese origin aged 40 to 79 years old,
management update on functional decline in older adults 2012 Unit No. 5 VISION Dr Au Eong Kah Guan, Ms Yulianti, Ms Fifiana ABSTRACT Among Singaporean adults of Chinese origin aged 40 to 79 years old,
NEPTUNE RED BANK BRICK
 NEPTUNE RED BANK BRICK Diabetes & The Eye Diabetics are more likely to develop Cataracts at a younger age. Diabetics are twice as likely to develop Glaucoma when compared to non-diabetics. The primary
NEPTUNE RED BANK BRICK Diabetes & The Eye Diabetics are more likely to develop Cataracts at a younger age. Diabetics are twice as likely to develop Glaucoma when compared to non-diabetics. The primary
New Developments in the treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy
 New Developments in the treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy B. Jeroen Klevering University Medical Centre Nijmegen - The Netherlands Topics Management of diabetic retinopathy Interventions a. primary (prevention)
New Developments in the treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy B. Jeroen Klevering University Medical Centre Nijmegen - The Netherlands Topics Management of diabetic retinopathy Interventions a. primary (prevention)
Flashers and Floaters
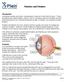 Flashers and Floaters Introduction Sometimes people see small, moving spots or specks in their field of vision. These sensations are called floaters. About 7 out of 10 people experience floaters at some
Flashers and Floaters Introduction Sometimes people see small, moving spots or specks in their field of vision. These sensations are called floaters. About 7 out of 10 people experience floaters at some
Measures have been taken, by the Utah Department of Health, Bureau of Health Promotions, to ensure no conflict of interest in this activity.
 Measures have been taken, by the Utah Department of Health, Bureau of Health Promotions, to ensure no conflict of interest in this activity. CNE/CPE/CEU s are available for this live webinar. You must
Measures have been taken, by the Utah Department of Health, Bureau of Health Promotions, to ensure no conflict of interest in this activity. CNE/CPE/CEU s are available for this live webinar. You must
Cataract. What is a Cataract?
 Cataract What is a Cataract? We all have a lens in our eye. This is positioned just behind the iris, which is the coloured ring in the eye that gives your eye its colour. The lens function is to focus
Cataract What is a Cataract? We all have a lens in our eye. This is positioned just behind the iris, which is the coloured ring in the eye that gives your eye its colour. The lens function is to focus
Recognising and managing diabetic retinopathy
 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT Recognising and managing diabetic retinopathy Former Head of Department of Ophthalmology, Kilimanjaro Christian Medical Centre, Tanzania. Email: abhall@kcco.net Key learning points
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT Recognising and managing diabetic retinopathy Former Head of Department of Ophthalmology, Kilimanjaro Christian Medical Centre, Tanzania. Email: abhall@kcco.net Key learning points
Glaucoma. Cornea. Iris
 Glaucoma Introduction Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to blindness if not treated. Openangle glaucoma, the most common form of glaucoma, affects about 3 million Americans. Half of those
Glaucoma Introduction Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to blindness if not treated. Openangle glaucoma, the most common form of glaucoma, affects about 3 million Americans. Half of those
Test Bank for Medical Surgical Nursing An Integrated Approach 3rd Edition by White
 Test Bank for Medical Surgical Nursing An Integrated Approach 3rd Edition by White Link full download : http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-medical-surgical-nursing-anintegrated-approach-3rd-edition-by-white/
Test Bank for Medical Surgical Nursing An Integrated Approach 3rd Edition by White Link full download : http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-medical-surgical-nursing-anintegrated-approach-3rd-edition-by-white/
UNDERSTAND MORE ABOUT UVEITIS UVEITIS
 UNDERSTAND MORE ABOUT UVEITIS UVEITIS Uveitis What is uveitis? Uveitis is inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of your eye. The eye is shaped much like a tennis ball, with three different layers
UNDERSTAND MORE ABOUT UVEITIS UVEITIS Uveitis What is uveitis? Uveitis is inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of your eye. The eye is shaped much like a tennis ball, with three different layers
Grand Rounds: Interesting and Exemplary Cases From Guanajuato and Djibouti
 Learning Community: January 25, 2015 Grand Rounds: Interesting and Exemplary Cases From Guanajuato and Djibouti JORGE CUADROS, OD, PHD EyePACS In Guanajuato Program started in 2007 Cameras go from clinic
Learning Community: January 25, 2015 Grand Rounds: Interesting and Exemplary Cases From Guanajuato and Djibouti JORGE CUADROS, OD, PHD EyePACS In Guanajuato Program started in 2007 Cameras go from clinic
Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO Cedar Springs Eye Clinic
 Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO Cedar Springs Eye Clinic 25.6 million adults 11.3% of the adult population 10.9 million adults 65 years and older 26.9% of this age population 79 million people are Pre-diabetic!!
Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO Cedar Springs Eye Clinic 25.6 million adults 11.3% of the adult population 10.9 million adults 65 years and older 26.9% of this age population 79 million people are Pre-diabetic!!
Management of diabetic eye disease: an overview
 Peter Blows Photographic screening for diabetic eye disease can identify patients who will benefit from laser treatment. BOTSWANA MANAGEMENT Management of diabetic eye disease: an overview Laser for DR
Peter Blows Photographic screening for diabetic eye disease can identify patients who will benefit from laser treatment. BOTSWANA MANAGEMENT Management of diabetic eye disease: an overview Laser for DR
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
 DIABETIC RETINOPATHY C. L. B. Canny, MD FRCSC Diabetic retinopathy is the most serious eye manifestation of diabetes and is responsible for most of the blindness caused by diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY C. L. B. Canny, MD FRCSC Diabetic retinopathy is the most serious eye manifestation of diabetes and is responsible for most of the blindness caused by diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy
Torbay Children s Diabetes Service
 Torbay Children s Diabetes Service Preventing Diabetes Complications Retinopathy Stroke Gum Disease Nephropathy Cardiovascular disease Neuropathy Diabetes Complications Thinking and talking about the possibility
Torbay Children s Diabetes Service Preventing Diabetes Complications Retinopathy Stroke Gum Disease Nephropathy Cardiovascular disease Neuropathy Diabetes Complications Thinking and talking about the possibility
Rapid Visual Loss. Dr Michael Johnson PhD FCOptom DipOrth DipGlauc DipTp(IP) Independent Prescribing Optometrist
 Rapid Visual Loss Dr Michael Johnson PhD FCOptom DipOrth DipGlauc DipTp(IP) Independent Prescribing Optometrist Outline Pathophysiology Differential diagnosis. Patient scenarios in community practice:
Rapid Visual Loss Dr Michael Johnson PhD FCOptom DipOrth DipGlauc DipTp(IP) Independent Prescribing Optometrist Outline Pathophysiology Differential diagnosis. Patient scenarios in community practice:
Ophthalmology. Caring For Your Eyes. Jurong Medical Centre
 Ophthalmology Caring For Your Eyes Jurong Medical Centre Your eyes and you At Jurong Medical Centre, we have a dedicated team of ophthalmologists that specialise in treating a wide range of acute and chronic
Ophthalmology Caring For Your Eyes Jurong Medical Centre Your eyes and you At Jurong Medical Centre, we have a dedicated team of ophthalmologists that specialise in treating a wide range of acute and chronic
