Connecting Chronic Kidney Disease: the link with Diabetes
|
|
|
- Scot Flowers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Connecting Chronic Kidney Disease: the link with Diabetes Primary Care Education Workshop This module was conceived and developed by PEAK* 1 Presented by: V0617
2 Collaborators *This Education was conceived and developed by the Primary Care Education Advisory Committee for KHA (PEAK) KHA s Primary Care Education program is proudly supported by unrestricted educational grants from: 2
3 Learning outcomes At the end of this workshop participants will be able to: State the major risk factors for developing chronic kidney disease (CKD) Determine the stage of chronic kidney disease (CKD) through accurate interpretation of kidney function test results Outline the adverse outcomes of a combined diabetes and CKD diagnosis (Diabetic Kidney Disease, DKD) Explore the nurse's role in early detection, reducing the modifiable risk factors and management of DKD Develop a system to screen at risk patients that includes CKD testing and management 3
4 What is CKD? Chronic kidney disease is defined as: Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) < 60 ml/min/1.73m 2 for 3 months with or without evidence of kidney damage. OR Evidence of kidney damage (with or without decreased GFR) for 3 months: albuminuria haematuria after exclusion of urological causes pathological abnormalities anatomical abnormalities 4 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice, 3 rd edition. Kidney Health Australia: Melbourne, 2015
5 A snapshot of kidney disease in Australia It s common 1 in 10 adults has at least one clinical sign of kidney disease 1. It s harmful In the top 10 causes of death 2. Kills more people each year than breast cancer, prostate cancer and road deaths. It s manageable If detected early and treated properly the decline in kidney function can be significantly reduced. 5 1 Australian Health Survey, Australian Bureau of Statistics, Causes of Death, 2012
6 Australians living with signs of CKD > 12% of population with signs of CKD 8-11% of population with signs of CKD < 7% of population with signs of CKD No data available 6 State of the Nation Report 2016, Kidney Health Australia
7 General chemistry results Combine egfr, albuminuria and underlying diagnosis to specify CKD stage GENERAL CHEMISTRY Sodium 144 mmol/l ( ) Pot. 4.3 mmol/l ( ) Chlor. 106 mmol/l (98-109) Bicarb. 26 mmol/l (20-32) Urea 6.5 mmol ( ) Creat. 55 µmol/l (40-85) egfr 84 ml/min/1.73m 2 Urate 0.35 mmol/l ( ) *Gluc 9.5 mmol/l (Random: ; Fasting: ) Albumin 40 g/l (35-50) 7
8 Staging CKD Combine egfr stage, albuminuria stage and underlying diagnosis to specify CKD stage e.g. stage 3b CKD with microalbuminuria secondary to diabetic kidney disease Albuminuria Stage GFR Stage GFR ml/min/1. 73m 2 Normal urine ACR mg/mmol Male: < 2.5 Female: < 3.5 Microalbuminuria urine ACR mg/mmol Male: Female: Macroalbuminuria urine ACR mg/mmol Male: > 25 Female: > Not CKD unless haematuria, structural or pathological abnormalities present 3a b X 5 <15 or on dialysis Colour-coded Clinical Action Plans in handbook and on CKD-Go! App 8 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice, 3 rd edition. Kidney Health Australia: Melbourne, 2015
9 Connecting CKD and diabetes Every second patient* you see with Type 2 diabetes WILL have CKD A patient with diabetes has CKD if they have 1 or more: Persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria An egfr < 60mL/min/1.73m 2 and/or Haematuria after exclusion of urological causes or structural abnormalities 9 *NEFRON Study 2007
10 Connecting CKD and diabetes Health care burden associated with DKD and DM- ESKD in Australia is significant and expanding Diabetes is the leading cause of incident end-stage kidney disease (DM-ESKD) The growing prevalence of T2DM in Australia, indicates the prevalence of DKD will continue to grow substantially The first priority in screening for DKD should be the detection of microalbuminuria Pharmacological intervention in DKD is stabilising the incidence of ESKD at the population level 10
11 Connecting CKD and diabetes Monitoring for kidney disease must be made a high priority for all people with type 2 diabetes Concerted effort needs to made to ensure that glucose control is optimised, blood pressure and lipids targets are met Opportunities for prevention across the entire disease continuum 11 Sarah White and Steve Chadban, Kidney Research Node Royal Prince Alfred Hospital and Charles Perkins Centre, University of Sydney April
12 An egfr less than 60mL/min/1.73m 2 indicates High risk of heart attack or stroke Decreased survival after a heart attack More common adverse drug reactions Slow wound healing Difficulty in achieving BP goals Difficult fluid control i.e. ankle swelling, fluid retention 12 *NEFRON Study 2007
13 An egfr less than 60mL/min/1.73m 2 indicates Less than 1 in every 20 patients with diabetes and CKD will live long enough to require dialysis or transplantation* Increased likelihood of fractures with falls Increased likelihood of hypoglycaemia Increased likelihood of hospitalisation in next 12 months Increased likelihood of heart failure 13 *NEFRON Study 2007
14 14 Diabetes affect on the body
15 Number of patients per year Diabetes progression to dialysis 1200 In the last 10 years there has been a 60% increase in the number of people with type 2 diabetes starting dialysis New patients with ESKD due to diabetes starting on dialysis (Australia ) Type 2 Type ANZDATA, Annual Reports. Available at
16 Rate pmp Diabetes and dialysis Diabetes is the cause of kidney failure that is largely driving the increase in dialysis patients in Australia Diabetes Gn BP Misc Uncertain PCK Reflux Analg Nx ANZDATA Registry
17 Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD) Diabetes causes damage to the kidneys; called Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD) or diabetic nephropathy Worsens other complications from diabetes such as nerve and eye damage Increases the risk of cardiovascular disease Usually has no symptoms until it is well advanced 17
18 Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD) most frequent cause of kidney failure worldwide associated with increased morbidity and mortality at all stages of CKD early detection and comprehensive management is associated with improved outcomes CKD management overlaps entirely with diabetes management and cardiovascular risk reduction 18
19 Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD) 20-40% of patients with Type 2 diabetes develop nephropathy, which classically occurs in two stages: Early nephropathy: microalbuminuria and normal to high GFR Overt nephropathy: macroalbuminuria and progressive decline in GFR 19
20 Connecting CKD and diabetes The presence of diabetes worsens the outcomes in all stages of CKD: CVD outcomes Dialysis survival Post-transplant survival 20
21 Events/100 pt/yrs CKD and diabetes, the connection Diabetes multiplies the morbidity/mortality event rate in CKD US Medicare (5% sample); Age >65, no RRT, followed 2yrs. n =1,091, D- CKD- 80% D+ CKD- 17% D- CKD+ 2.2% D+ CKD+ 1.6% ASVD CHF RRT Death ASVD, atherosclerotic vascular disease; CHF, chronic heart failure; RRT, renal replacement therapy 21 Foley et al. JASN 16: , 2005
22 Case study - Peter Background 62 years old Caucasian male Works full-time in business management Today Peter presents at your general practice with an acute cough with yellow sputum He has previously been seen at your practice when he accompanied his wife for an annual flu vaccination 22
23 History Smoker: Alcohol: Nutrition: Medical conditions: Medications: 1 packet per day for 40 years (40 pack-year history) 7-10 drinks per week Follows a diabetic diet Type 2 diabetes, diagnosed 12 months ago after presenting with thirst No regular medications, takes occasional NSAIDS for back pain 23
24 Case study - Peter Today s visit Test Blood pressure Weight Result 160/90 mmhg 102 kg BMI 31 kg/m 2 Waist circumference Chest findings 110 cm Consistent with bronchitis - no clinical signs of COPD 24
25 Case study Question Q1: Is Peter at increased risk of kidney disease? If so, why? Today s visit Peter s GP found some of his results and history concerning. The GP has asked you to review Peter s case further, particularly his potential risk for kidney disease. 25
26 Risk factors for kidney disease Diabetes Hypertension Established cardiovascular disease Family history of kidney failure Obesity (BMI >30kg/m 2 ) Smoker Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander origin History or acute kidney injury Age over 60 years Peter has 5 of the risk factors for CKD 1 in 3 Australian adults is at increased risk of CKD due to these risk factors 26 RACGP Guidelines for preventive activities in general practice 8 th edition; Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice, 3 rd edition. Kidney Health Australia: Melbourne, 2015
27 Case study Question Q1a: What does Peter s diabetes mean for his CKD risk? % of patients with Type 2 diabetes develop nephropathy, which classically* occurs in 2 stages: Early nephropathy - microalbuminuria and normal-high GFR Overt nephropathy - macroalbuminuria and progressive decline in GFR * Recent data shows that 33% individuals with diabetes with egfr <60ml/min/1.73m 2 do not have albuminuria, and for these subjects, prognosis is similar to those with albuminuria 1,2 1. Tapp RJ, Shaw J, Chadban SJ et al. Am J Kidney Dis 2004; 44: Agarwal et al, NDT 2011
28 Classical stages of diabetic kidney disease* *Those with Type 2 diabetes may have overt nephropathy at presentation GFR normal normal Albuminuria Duration of Diabetes (years)
29 Further reading KinD Report
30 Case study Question Q1b: Peter has hypertension. What does this mean for his CKD risk? Hypertension is extremely common among those with type 2 diabetes, particularly those with DKD Among those with diabetes (and without), those with hypertension are 5-8 times as likely to have albuminuria Achieving BP control is one of the most effective ways to delay the progression of kidney disease 30
31 Hypertension Adequate BP management delays the progression of CKD (reduces the GFR drop/year) 31 If Peter s BP was consistently below target, his GFR loss per year would be reduced by 71% 160/90mmHg Bakris et al., Am J Kid Disease, 2000
32 Case study Question Q1c: Peter is obese. What impact does his weight have on his risk of CKD? Overweight (BMI ) and obese (BMI >30) people are 40% and 80% more likely to develop CKD compared to normal weight individuals 1 Central obesity appears to be more important than generalised Obesity contributes to the development of albuminuria and proteinuria Obesity leads to greater difficulty in achieving glycaemic control and BP control 32 1 Wang Y et al. Association between obesity and kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2008;73:19-33.
33 Case study Question Q1d: How does smoking increase Peter s risk of CKD? Among individuals with diabetes, those who smoke are more likely to get albuminuria and among those with diabetic kidney disease, smoking accelerates progression to failure 1,2 Even among the normal Australian population, smoking has been associated with kidney damage 3 33 [1] Gambaro et al. Diabetes Nutr Metab 2001;14:337. [2] Orth & Hallan. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol [3] Briganti et al. Am J Kidney Dis 2002;40:704.
34 Case study Question Q1e: Does Peter s occasional NSAID use increase his risk of CKD? Probably not Chronic use of NSAIDs have not been proven to lead to CKD in humans NSAID ingestion can aggravate underlying kidney disease and hypertension and risk of vascular events NSAIDs should be avoided in this setting 34
35 Case study Question Q1f: Will Peter s chest infection contribute to his likelihood of CKD? No Chest infection by itself has no relationship to CKD Recurrent chest infections are more common in smokers With his history of smoking Peter is highly likely to develop COPD in the future 35
36 CVD risk Australian Absolute Cardiovascular Disease Risk Calculator 36 **Peter is at increased risk of kidney disease and therefore also at risk of having a cardiovascular event.
37 CVD risk anyone with egfr < 45 ml/min/1.73m 2 or persistent proteinuria Diabetes and microalbuminuria Diabetes and age > 60 years Established cardiovascular disease Familial hypercholesterolemia or total cholesterol above 7.5 Severe hypertension Systolic 180 mmhg or greater Diastolic 110 mmhg or greater 37 is already at the highest risk of a cardiovascular event, therefore the calculator should not be used Guidelines for the management of Absolute cardiovascular disease risk: National Vascular Prevention Alliance.
38 Cardiovascular risk reduction in CKD CKD is one of the most potent known risk factors for cardiovascular disease It is essential to clinically determine the risk of CKD before using the Australian absolute cardiovascular risk tool ( ) to accurately calculate cardiovascular risk Individuals with CKD have a 2-3 fold greater risk of cardiac death than individuals without CKD People with CKD are at least 20 times more likely to die from cardiovascular disease than survive to need dialysis or transplant 38 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice, 3rd edition. Kidney Health Australia: Melbourne, 2015
39 Resources Guidelines for the assessment and management of Absolute Cardiovascular Disease Risk National Vascular Disease Prevention Alliance Available at 39
40 Checking for kidney damage Q2: What test results would you use as evidence of kidney damage? Peter is at increased risk of kidney disease and you decide to test him for evidence of kidney damage.? urine dipstick for blood and protein? spot urine albumin/creatinine ratio (ACR)? 24 hour urine protein? serum creatinine? egfr? renal ultrasound (kidney outline and size) 40
41 Checking for kidney damage? urine dipstick for blood and protein spot urine albumin/creatinine ratio (ACR)? 24 hour urine protein serum creatinine egfr? renal ultrasound (kidney outline and size) 41
42 Urine albumin /creatinine ratio (ACR) The preferred urine test in all diabetics is to look for microalbuminuria This is best tested by a urine albumin:creatinine ratio (ACR) Preferably 1st morning void but a random sample can also be used ACR result Test results range Recommended follow -up Normal Females <3.5 mg/mmol Males <2.5 mg/mmol Re-test annually 42 Microalbuminuria Macroalbuminuria (also called proteinuria) Females mg/mmol Males mg/mmol Females >35 mg/mmol Males >25 mg/mmol Repeat 2 times over 3 months Confirm microalbuminuria if 2 out of 3 tests are positive Do a protein:creatinine ratio (PCR) or 24 hour urine protein (to quantify protein excretion) NHMRC Guidelines 2009
43 Glomerular filtration rate Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) best measure of kidney function Can be estimated (egfr) from serum creatinine egfr automatically provided by pathology laboratories when a creatinine is ordered (for adults over 18 yrs) Reported as an actual numerical value or > 90mL/min/1.73m 2 egfr is accurate at values <60 ml/min/1.73m 2 Tends to underestimate GFR in those with diabetes with true GFR > 60 ml/min/1.73m 2 Creatinine alone will commonly under-estimate the degree of reduction in kidney function, particularly in small elderly women 43 Australasian Proteinuria Consensus Group, 2012 Chudleigh et al, Diabetes Care 2007;30:300-5.
44 Serum creatinine Comparing creatinine and egfr CKD 3bCKD 3a CKD 1 & 2 CKD 4 CKD Dialysis GFR ml/min Albuminuria 44 Normal Serum Creatinine level Actual Serum Creatinine level
45 Screening for CKD Indications for assessment* Diabetes Hypertension Established cardiovascular disease ** Family history of kidney failure Obesity (BMI 30 kg/m 2 ) Smoker Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander origin aged 30 years History of acute kidney injury Recommended assessments Urine ACR, egfr, blood pressure If urine ACR positive repeat twice over 3 months (preferably first morning void) If egfr < 60mL/min/1.73m 2 repeat within 7 days See recommendations in booklet Frequency Every 1-2 *Whilst being aged 60 years of age or over is considered to be a risk factor for CKD, in the absence of other risk factors it is not necessary to routinely assess these individuals for kidney disease. **Established cardiovascular disease is defined as a previous diagnosis of coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease or peripheral vascular disease. Annually for individuals with diabetes or hypertension. Refer to booklet for more details regarding recommendations for testing in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples. years 1 in 3 Australia n adults is at increased risk of CKD due to these risk factors 45 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice, 3rd edition. Kidney Health Australia: Melbourne, 2015
46 Kidney Health Check Kidney Health Check Blood Test Urine Test BP Check egfr calculated from serum creatinine Albumin / Creatinine Ratio (ACR) check for albuminuria Blood pressure maintain consistently below BP goal CKD screening should be undertaken as a part of every chronic disease & cardiovascular risk assessment 46 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice, 3 rd edition. Kidney Health Australia: Melbourne, 2015
47 Case study - Peter You identify Peter as being at increased risk for CKD and request he be recalled for further tests. Peter's test results show the following: Test Creatinine Result 135 µmol/l egfr 46 ml/min/1.73m 2 Urine ACR HbA1c Blood pressure 44 mg/mmol (macroalbuminuria) 9.6% / 81 mmol/mol 160/90 mmhg 47
48 Case study - Peter Q3: What can be done to improve Peter s control of his diabetes? Good glycaemic control slows progression of kidney failure* Prescribe exercise and diet 44% of patients are on a sulphonylurea Metformin okay to use in reduced doses when egfr is between 30 and 60 ml/min - avoid use if GFR below 30 ml/min, due to risk of acidosis Consider referral to endocrinologist and diabetes education centre See Diabetes Australia website for guidelines: 48 *UKPDS. Lancet 1998;352:837-53
49 Drug therapy recommendations for non-insulin hypoglycaemic drug therapy for patients with stages 3b 5 CKD CLASS CKD Complications Biguanide (Metformin) Second generation sulphonylurea Reduce dose Contraindicated GFR <60ml/min (PI) <30ml/min (RACGP) Contraindicated GFR<30ml/min Lactic acidosis Hypoglycaemia - glucosidase inhibitors SCr > 2 mg/dl: Avoid Hepatic toxicity TZDs Metiglinides GLP1 analogue Gliptins (DPP4 inhibitors) No dose adjustment No dose adjustment Contraindicated GFR<30ml/min Dose adjustment / use is variable depending on agent Volume retention, CHF?nil 49
50 Drug class target sites Liver Hepatic glucose overproduction Pancreas -cell dysfunction Biguanide TZDs Sulphonylureas Meglitinides GLP-1 analogs DPP 4 inhibitors Muscle and fat Insulin resistance Glucose level Kidney Renal glucose transport Biguanides TZDs SGLT2 Inhibitors -Glucosidase inhibitors 50 Gut Glucose absorption
51 Case study Peter Q4: What can be implemented to reduce Peter s blood pressure? a) Lifestyle modification? b) Medications? ACE-inhibitor, ARB or other drugs? Other? c) Do more tests? d) Refer on to an endocrinologist, nephrologist? 51
52 Hypertension in diabetes Lifestyle approaches are the first consideration in all people with diabetes and high blood pressure - the key elements are: SNAP - smoking, nutrition, alcohol, physical activity Stop smoking A low salt diet A reduction in his alcohol intake An exercise program A low calorie diet to reduce his BMI 52 For more details General Practice Management of Type 2 diabetes 2014/15
53 53 Lifestyle effects on BP Modification Weight reduction Dietary sodium restriction DASH diet Physical activity Moderate alcohol consumption only Recommendation BMI kg/m 2 Reduce dietary sodium intake to no more than 2.4g sodium (or 6g salt) Fruit, vegies, low saturated and total fat Aerobic activity for 30-60mins/day, 3-5 days/week No more than 2 drinks per day (men) or 1 drink per day (women) 4.4mmHg (for 5.1kg weight lost) 4-7mmHg (for reduction by 6g in daily salt intake) mmHg (5.5 for normotensives 11.4 for hypertensives) 5mmHg 3mmHg (for 67% reduction from baseline of 3-6 drinks per day) Tiberio MFrisoli et al Beyond salt; lifestyle modifications and blood pressure: European Heart Journal (2011) 32, doi: /eurheartj/ehr379
54 Hypertension in Diabetes 54 Medications may be needed to lower blood pressure to target levels The preferred anti-hypertensive agents in diabetes are an ACEinhibitor or ARB These agents may also slow progression of CKD Any other anti-hypertensive agent that lowers blood pressure will improve the patient s disease progression
55 Case study - Peter Peter has stage 3b CKD with macroalbuminuria and diabetes, so at high risk of a CVD event automatically and his blood pressure should be maintained consistently below 130/80mmHg Flag with his GP to consider: Starting a clinical action plan Lifestyle modification Pharmacotherapy to treat his hypertension Monitor 6-12 weekly until sufficient improvement People with... Maintain BP consistently BELOW (mmhg) Albuminuria <130/80 Diabetes <130/80 Chronic Kidney Disease <140/90 55
56 Orange Clinical Action Plan egfr ml/min/1.73m 2 with microalbuminuria OR egfr ml/min/1.73m 2 with normoalbuminuria Goals of management Investigations to determine underlying cause Reduce progression of kidney disease Assessment of Absolute Cardiovascular Risk Avoidance of nephrotoxic medications or volume depletion Early detection and management of complications Adjustment of medication doses to levels appropriate for kidney function Appropriate referral to a nephrologist when indicated 56 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice, 3 rd edition. Kidney Health Australia: Melbourne, 2015
57 Orange Clinical Action Plan Frequency of monitoring Clinical assessment Laboratory assessment 3 to 6 months Blood pressure Weight Urine ACR egfr Biochemical profile including urea, creatinine, electrolytes HbA1c (for people with diabetes) Fasting lipids Full blood count Calcium and phosphate Parathyroid hormone (6-12 monthly if egfr <45 ml/min/1.73m 2 ) 57 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice, 3 rd edition. Kidney Health Australia: Melbourne, 2015
58 Orange Clinical Action Plan egfr ml/min/1.73m 2 with microalbuminuria OR egfr ml/min/1.73m 2 with normoalbuminuria It is also important to consider Absolute Cardiovascular Risk Assessment ( Lifestyle modification Blood pressure reduction Lipid lowering treatments Glycaemic control 58 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice, 3 rd edition. Kidney Health Australia: Melbourne, 2015
59 Screening and assessments Screening - search* for patients at risk and invite patients for a health check Health Assessments (Items 701, 703, 705, 707, 715) Screen those at risk Assessments Health Checks 59 Diabetes Family history of kidney failure Established CVD High blood pressure Obese (BMI >30kg/m 2 Smoker Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander origin For more information visit A type 2 diabetes risk evaluation for people aged years (inclusive) with a high risk of developing type 2 diabetes as determined by the Australian Type 2 Diabetes Risk Assessment Tool once every 3 years to eligible patients A health assessment for people aged years (inclusive) who are at risk of developing chronic disease once only to an eligible patient *Use data management tools such as PEN CAT to help find patients at risk
60 Annual diabetes cycle of care Item 2517 Twice every 12 months At least once every 12 months Every 12 months Once every 2 years Weight Height Total Cholesterol Triglycerides Self Care education Diet Comprehensive eye examination BMI HDL-C Physical activity BP HbA1c Smoking evaluation Feet examination Microalbuminuria Medication Review egfr For more information visit 60 Diabetes Management in General Practice 14/15
61 Chronic disease management Medicare Australia has provided remuneration for chronic disease management by the following item numbers: GP Management Plan Other Items Items 721, 729 & 732 Items 723, 10997, For patient and GP management of chronic disease Incorporates patients goals, needs, achievements and references to resources Item 715 for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Health Assessments Involves collaboration with other health professionals in patient care Electronic templates for specific conditions are available CKD template available at 61
62 Monitoring and support Item / For provision of monitoring and support to people with a chronic disease by a practice nurse or registered Aboriginal Health Worker, on behalf of a GP. Available for people who have a GPMP / TCA at a maximum of 5 services can be claimed per patient per calendar year. With 15 services available to Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islanders with a Health Assessment. The item may be used to provide: Checks on clinical progress - egfrs, ACR, BP Monitoring medication compliance - BP medication(s) Self management advice - personal goals Collection of information to support GP reviews of care plans For more information visit 62
63 Resources CKD patient fact sheets Available along with more kidney health fact sheets at 63
64 Case study Peter Q5: Who could you involve in Peter s management through a Team Care Arrangement? 64
65 Multidisciplinary Care Team May include, but is not limited to: Exercise Physiologist Dietitian Family Members / carers Community Health -weight and diet programs specific to local community Nephrologist Optometrist/ Ophthalmologist Endocrinologist Diabetes Specialist Renal Nurse Nurse Practitioner Pharmacist Podiatrist Social Worker Vascular/ Transplant Surgeon Cardiologist *N.B not all listed here are eligible for TCA inclusion. 65
66 Peter's management Q6: What will you review at Peter s next visit and when? The recommended period for a GPMP review is every 3-6 months. 66
67 Management reviews History Examination Investigation Review SNAP Patient s record of home testing Foot symptoms Weight Waist circ. Height HbA1c Intercurrent illnesses Goals BP 67 Diabetes Management in General Practice 14/15
68 Nurse role in CKD Reduce the impact of CKD Screen for risks Manage disease Monitor patient progress Using Kidney Health Check Diabetes Hypertension Cardiovascular using Absolute CVD Risk Calculator* Other CKD risk factors Using health checks & item numbers Using care plans and item numbers Promote self management Diabetes Hypertension CKD Symptoms Using item numbers Adherence to treatment Nephrotoxic medications *Refer to slide 36 68
69 Summary Optimal management of DKD Everyone with diabetes should have a kidney health check every year Targets of therapy and management change in those with DKD e.g. blood pressure, glycaemia etc. Major role for practice nurse in coordinating a multidisciplinary approach Kidney disease is an integral part of chronic disease management Overlap with diabetes management and CVD risk reduction Encourage self management 69 Potential to halve the number of patients presenting with kidney failure
70 Resources CKD management in General Practice 2015 guidelines handbook Available at health-professionals 70
71 Resources CKD-GO! Phone App Rated a must have App by Medical Observer Available on itunes and Google Play app stores All the best bits of the CKD Management in General Practice handbook now in a handy app! 71
72 Resources My Kidneys, My Health Handbook & App Free resource for patients newly diagnosed with early stage CKD App available on itunes and Google Play app stores 72 Hardcopy books available to order visit
73 Factsheet Resources Healthshare fact sheets Chronic Kidney Disease fact sheets for patients. Available for Medical Director and Best Practice software Urinary tract infections How to look after your kidneys Kidney Health Check up GP only Chronic Kidney Disease All about Chronic Kidney Disease Looking after yourself with CKD Kidney stones Kidney transplant Peritoneal dialysis Consent and kidney tests Kidney health tests Kidney cysts Access for dialysis Kidney cancer Treating kidney disease Homes haemodialysis Haemodialysis Life with a single kidney All about GFR 73
74 Resources Kidney Health Information Service Free call information service for people living with / affected by kidney disease Kidney Community Members receive a monthly newsletter from KHA allowing you to access: Information and invitations to KHA's education and support activities Updates on medical research in kidney disease Information on advocacy opportunities and government relations issues Information on community and corporate events held by Kidney Health Australia 74 To join the kidney community, community@kidney.org.au
75 Thankyou for participating in this workshop Please complete your evaluation form before leaving. 75
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS
 KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
Management of early chronic kidney disease
 Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer. Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC
 Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC Presented at the University of Calgary s CME and Professional Development 2006-2007
Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC Presented at the University of Calgary s CME and Professional Development 2006-2007
Chronic kidney disease screening and assessment
 Care map information Information resources for patients and carers Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders DEFINITION OF CKD egfr
Care map information Information resources for patients and carers Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders DEFINITION OF CKD egfr
This information is intended to be used with the help of a relevant health professional, and is available as a booklet to download.
 Goals of management Goals of management is a guide to assist you in managing your diabetes. It is important when you have your health checks you have an understanding of what the numbers signify and how
Goals of management Goals of management is a guide to assist you in managing your diabetes. It is important when you have your health checks you have an understanding of what the numbers signify and how
Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective
 Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective DR SARAH DAVIES GP PARTNER WITH SPECIAL INTEREST IN DIABETES, CARDIFF DUK CLINICAL CHAMPION NB MEDICAL HOT TOPICS PRESENTER AND DIABETES
Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective DR SARAH DAVIES GP PARTNER WITH SPECIAL INTEREST IN DIABETES, CARDIFF DUK CLINICAL CHAMPION NB MEDICAL HOT TOPICS PRESENTER AND DIABETES
Type 2 Diabetes. Stopping Smoking. Consider referral to smoking cessation. Consider referring for weight management advice.
 Type 2 Diabetes Stopping Smoking Consider referral to smoking cessation BMI > 25 kg m² Set a weight loss target of a 5-10% reduction Consider referring for weight management advice Control BP to
Type 2 Diabetes Stopping Smoking Consider referral to smoking cessation BMI > 25 kg m² Set a weight loss target of a 5-10% reduction Consider referring for weight management advice Control BP to
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus
 Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Diabetes and Kidney Disease. Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018
 Diabetes and Kidney Disease Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018 Aims Develop an understanding of Chronic Kidney Disease Understand how diabetes impacts on your kidneys Be able to recognise the risk
Diabetes and Kidney Disease Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018 Aims Develop an understanding of Chronic Kidney Disease Understand how diabetes impacts on your kidneys Be able to recognise the risk
Wendy Washington & Anne Graham. Nephrology Nurse Practitioners
 Wendy Washington & Anne Graham Nephrology Nurse Practitioners Eight major risk factors for CKD Diabetes High blood pressure Age over 60 years Smoking Obesity Family history of kidney disease Aboriginal
Wendy Washington & Anne Graham Nephrology Nurse Practitioners Eight major risk factors for CKD Diabetes High blood pressure Age over 60 years Smoking Obesity Family history of kidney disease Aboriginal
Professor Suetonia Palmer
 Professor Suetonia Palmer Department of Medicine Nephrologist Christchurch Hospital Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #108: The Kidney Test - When To Test and When to Refer ( and When Not To) 15:05-16:00 WS
Professor Suetonia Palmer Department of Medicine Nephrologist Christchurch Hospital Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #108: The Kidney Test - When To Test and When to Refer ( and When Not To) 15:05-16:00 WS
Key Clinical Tips KIDNEY HEALTH AUSTRALIA
 Key Clinical Tips A measured or estimated GFR < 60 ml/min/1.73 m 2 is associated with increased risks of adverse renal, cardiovascular and other clinical outcomes, irrespective of age. For people with
Key Clinical Tips A measured or estimated GFR < 60 ml/min/1.73 m 2 is associated with increased risks of adverse renal, cardiovascular and other clinical outcomes, irrespective of age. For people with
Diabetes in Renal Patients. Contents. Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
CKDinform: A PCP s Guide to CKD Detection and Delaying Progression
 CKDinform: A PCP s Guide to CKD Detection and Delaying Progression Learning Objectives Describe suitable screening tools, such as GFR and ACR, for proper utilization in clinical practice related to the
CKDinform: A PCP s Guide to CKD Detection and Delaying Progression Learning Objectives Describe suitable screening tools, such as GFR and ACR, for proper utilization in clinical practice related to the
Diabetes and Hypertension
 Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Metformin should be considered in all patients with type 2 diabetes unless contra-indicated
 November 2001 N P S National Prescribing Service Limited PPR fifteen Prescribing Practice Review PPR Managing type 2 diabetes For General Practice Key messages Metformin should be considered in all patients
November 2001 N P S National Prescribing Service Limited PPR fifteen Prescribing Practice Review PPR Managing type 2 diabetes For General Practice Key messages Metformin should be considered in all patients
Absolute cardiovascular disease risk management
 Quick reference guide for health professionals Absolute cardiovascular disease risk management This quick reference guide is for use by health professionals for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease
Quick reference guide for health professionals Absolute cardiovascular disease risk management This quick reference guide is for use by health professionals for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease
Diabetes Mellitus. Eiman Ali Basheir. Mob: /1/2019
 Diabetes Mellitus Eiman Ali Basheir Mob: 091520385 27/1/2019 Learning Outcomes Discuss the WHO criteria for Diabetes Mellitus diagnosis Describe the steps taken to confirm diagnosis Interpret GTT. Discuss
Diabetes Mellitus Eiman Ali Basheir Mob: 091520385 27/1/2019 Learning Outcomes Discuss the WHO criteria for Diabetes Mellitus diagnosis Describe the steps taken to confirm diagnosis Interpret GTT. Discuss
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009
 The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
Appendix This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors.
 Appendix This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. Appendix to: Banks E, Crouch SR, Korda RJ, et al. Absolute risk of cardiovascular
Appendix This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. Appendix to: Banks E, Crouch SR, Korda RJ, et al. Absolute risk of cardiovascular
Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD
 Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD Develop patient treatment plan according to level of severity. Source: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012
Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD Develop patient treatment plan according to level of severity. Source: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012
The Pursuit of Prevention of Renal failure in an imperfect world-is it possible in the 21 st century?
 The Pursuit of Prevention of Renal failure in an imperfect world-is it possible in the 21 st century? By: Baskar, WDHB, Renal Service Auckland New Zealand Presented at : 4 th International Conference on
The Pursuit of Prevention of Renal failure in an imperfect world-is it possible in the 21 st century? By: Baskar, WDHB, Renal Service Auckland New Zealand Presented at : 4 th International Conference on
Morbidity & Mortality from Chronic Kidney Disease
 Morbidity & Mortality from Chronic Kidney Disease Dr. Lam Man-Fai ( 林萬斐醫生 ) Honorary Clinical Assistant Professor MBBS, MRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM, PDipID (HK), FRCP (Edin, Glasg) Hong Kong Renal Registry Report
Morbidity & Mortality from Chronic Kidney Disease Dr. Lam Man-Fai ( 林萬斐醫生 ) Honorary Clinical Assistant Professor MBBS, MRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM, PDipID (HK), FRCP (Edin, Glasg) Hong Kong Renal Registry Report
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Afkarian M, Zelnick L, Hall YN, et al. Clinical manifestations of kidney disease among US adults with diabetes, 1988-2014. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.10924 emethods efigure
Supplementary Online Content Afkarian M, Zelnick L, Hall YN, et al. Clinical manifestations of kidney disease among US adults with diabetes, 1988-2014. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.10924 emethods efigure
Case study: Lean adult with no complications, newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes
 Case study: Lean adult with no complications, newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes Authored by Clifford Bailey and James LaSalle on behalf of the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management. The
Case study: Lean adult with no complications, newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes Authored by Clifford Bailey and James LaSalle on behalf of the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management. The
Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
 Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant
 Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant Onset at 5-15 years of T1DM Can be present at diagnosis of T2DM Detect in regular MA/Cr screening (2X first urine sample, no UTI, no other causes) Contributing Factors
Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant Onset at 5-15 years of T1DM Can be present at diagnosis of T2DM Detect in regular MA/Cr screening (2X first urine sample, no UTI, no other causes) Contributing Factors
Kidney Failure- Are you at risk?? ( 腎功能衰竭 - 你是在高危險群嗎?)
 Kidney Failure- Are you at risk?? ( 腎功能衰竭 - 你是在高危險群嗎?) Dr Goh Heong Keong, Penang www.passpaces.com/kidney.htm Outline of Lecture Introduction( 介紹 ) Definition of Chronic kidney disease( 慢性肾脏病的定义 ) Stages
Kidney Failure- Are you at risk?? ( 腎功能衰竭 - 你是在高危險群嗎?) Dr Goh Heong Keong, Penang www.passpaces.com/kidney.htm Outline of Lecture Introduction( 介紹 ) Definition of Chronic kidney disease( 慢性肾脏病的定义 ) Stages
DIABETES MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW
 2014 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: DIABETES MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2014 PQRS MEASURES IN DIABETES MEASURES GROUP: #1. Diabetes: Hemoglobin A1c Poor Control #2. Diabetes: Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL-C)
2014 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: DIABETES MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2014 PQRS MEASURES IN DIABETES MEASURES GROUP: #1. Diabetes: Hemoglobin A1c Poor Control #2. Diabetes: Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL-C)
New Hypertension Guideline Recommendations for Adults July 7, :45-9:30am
 Advances in Cardiovascular Disease 30 th Annual Convention and Reunion UERM-CMAA, Inc. Annual Convention and Scientific Meeting July 5-8, 2018 New Hypertension Guideline Recommendations for Adults July
Advances in Cardiovascular Disease 30 th Annual Convention and Reunion UERM-CMAA, Inc. Annual Convention and Scientific Meeting July 5-8, 2018 New Hypertension Guideline Recommendations for Adults July
Outcomes of diabetes care in England and Wales. A summary of findings from the National Diabetes Audit : Complications and Mortality reports
 Outcomes of diabetes care in England and Wales A summary of findings from the National Diabetes Audit 2015 16: Complications and Mortality reports About this report This report is for people with diabetes
Outcomes of diabetes care in England and Wales A summary of findings from the National Diabetes Audit 2015 16: Complications and Mortality reports About this report This report is for people with diabetes
Addressing Chronic Kidney Disease in People with Multiple Chronic Conditions
 Addressing Chronic Kidney Disease in People with Multiple Chronic Conditions Andrew S Narva, MD Na/onal Kidney Disease Educa/on Program U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institute of
Addressing Chronic Kidney Disease in People with Multiple Chronic Conditions Andrew S Narva, MD Na/onal Kidney Disease Educa/on Program U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institute of
Hypertension Clinical case scenarios for primary care
 Hypertension Clinical case scenarios for primary care Implementing NICE guidance August 2011 NICE clinical guideline 127 What this presentation covers Five clinical case scenarios, including: presentation
Hypertension Clinical case scenarios for primary care Implementing NICE guidance August 2011 NICE clinical guideline 127 What this presentation covers Five clinical case scenarios, including: presentation
CKD & HT. Anne-Marie Angus
 CKD & HT Anne-Marie Angus Hypertension definitions Persisting BP >140/90 and HBPM >135/85 Stage 1 >140/90 (HBPM >135/85) Stage 2 >160/100 (HBPM >150/90) Severe >180/100 White coat HT Why treat? A major
CKD & HT Anne-Marie Angus Hypertension definitions Persisting BP >140/90 and HBPM >135/85 Stage 1 >140/90 (HBPM >135/85) Stage 2 >160/100 (HBPM >150/90) Severe >180/100 White coat HT Why treat? A major
Australian general practitioners current practice for chronic kidney disease (CKD) detection and management
 Australian general practitioners current practice for chronic kidney disease (CKD) detection and management Marie Ludlow 1, Timothy Mathew 1, Timothy Usherwood 2, Shanthi Ramanathan 3, Ivor Katz 4, Katherine
Australian general practitioners current practice for chronic kidney disease (CKD) detection and management Marie Ludlow 1, Timothy Mathew 1, Timothy Usherwood 2, Shanthi Ramanathan 3, Ivor Katz 4, Katherine
Office Management of Reduced GFR Practical advice for the management of CKD
 Office Management of Reduced GFR Practical advice for the management of CKD CKD Online Education CME for Primary Care April 27, 2016 Monica Beaulieu, MD FRCPC MHA CHAIR PROVINCIAL KIDNEY CARE COMMITTEE
Office Management of Reduced GFR Practical advice for the management of CKD CKD Online Education CME for Primary Care April 27, 2016 Monica Beaulieu, MD FRCPC MHA CHAIR PROVINCIAL KIDNEY CARE COMMITTEE
Diabetic Nephropathy. Objectives:
 There are, in truth, no specialties in medicine, since to know fully many of the most important diseases a man must be familiar with their manifestations in many organs. William Osler 1894. Objectives:
There are, in truth, no specialties in medicine, since to know fully many of the most important diseases a man must be familiar with their manifestations in many organs. William Osler 1894. Objectives:
Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes. April 2010
 Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes April 2010 Foreword The guidelines were devised by the Diabetes Day Centre in Beaumont Hospital in consultation with a number
Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes April 2010 Foreword The guidelines were devised by the Diabetes Day Centre in Beaumont Hospital in consultation with a number
Heart health CHD management gaps in general practice
 professional practice Nancy Huang MBBS, DipRACOG, MPH, is National Manager Clinical Programs, Heart Foundation, Melbourne, Victoria. nancy.huang@heartfoundation.org.au Marcus Daddo BSc(Hons), is Manager
professional practice Nancy Huang MBBS, DipRACOG, MPH, is National Manager Clinical Programs, Heart Foundation, Melbourne, Victoria. nancy.huang@heartfoundation.org.au Marcus Daddo BSc(Hons), is Manager
Chronic Kidney Disease: Optimal and Coordinated Management
 Chronic Kidney Disease: Optimal and Coordinated Management Michael Copland, MD, FRCPC Presented at University of British Columbia s 42nd Annual Post Graduate Review in Family Medicine Conference, Vancouver,
Chronic Kidney Disease: Optimal and Coordinated Management Michael Copland, MD, FRCPC Presented at University of British Columbia s 42nd Annual Post Graduate Review in Family Medicine Conference, Vancouver,
An Introduction to HIV Shared Care for GPs
 An Introduction to HIV Shared Care for GPs Managing HIV as a chronic condition With effective antiretroviral therapy (ART), HIV infection is now considered a chronic condition and people living with HIV
An Introduction to HIV Shared Care for GPs Managing HIV as a chronic condition With effective antiretroviral therapy (ART), HIV infection is now considered a chronic condition and people living with HIV
CKD FOR INTERNISTS. Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College
 CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
Identifying and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: A Practical Approach
 Identifying and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: A Practical Approach S. Neil Finkle, MD, FRCPC Associate Professor Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Dalhousie University Program Director,
Identifying and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: A Practical Approach S. Neil Finkle, MD, FRCPC Associate Professor Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Dalhousie University Program Director,
PLEASE REMEMBER TO BRING TO EACH APPOINTMENT
 PLEASE REMEMBER TO BRING TO EACH APPOINTMENT Conversion table for HbA1c% to mmol/mol Old DCCT aligned HbA1c(%) New IFCC HbA1c (mmol/mol) 4.0 20 5.0 31 6.0 42 6.5 48 7.0 53 7.5 59 8.0 64 9.0 75 10.0 86
PLEASE REMEMBER TO BRING TO EACH APPOINTMENT Conversion table for HbA1c% to mmol/mol Old DCCT aligned HbA1c(%) New IFCC HbA1c (mmol/mol) 4.0 20 5.0 31 6.0 42 6.5 48 7.0 53 7.5 59 8.0 64 9.0 75 10.0 86
TREAT THE KIDNEY TO SAVE THE HEART. Leanna Tyshler, MD Chronic Kidney Disease Medical Advisor Northwest Kidney Centers February 2 nd, 2009
 TREAT THE KIDNEY TO SAVE THE HEART Leanna Tyshler, MD Chronic Kidney Disease Medical Advisor Northwest Kidney Centers February 2 nd, 2009 1 ESRD Prevalent Rates in 1996 per million population December
TREAT THE KIDNEY TO SAVE THE HEART Leanna Tyshler, MD Chronic Kidney Disease Medical Advisor Northwest Kidney Centers February 2 nd, 2009 1 ESRD Prevalent Rates in 1996 per million population December
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and egfr: Decision and Dilemma. Dr Bhavna K Pandya Consultant Nephrologist University Hospital Aintree
 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and egfr: Decision and Dilemma Dr Bhavna K Pandya Consultant Nephrologist University Hospital Aintree Topics CKD background egfr background Patient with egfr Referral Guidelines
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and egfr: Decision and Dilemma Dr Bhavna K Pandya Consultant Nephrologist University Hospital Aintree Topics CKD background egfr background Patient with egfr Referral Guidelines
Have you seen a patient like Elaine *?
 (linagliptin) 5mg tablets Have you seen a patient like Elaine *? *Hypothetical patient profile Elaine * : 60 years old Housewife *Hypothetical patient profile ELAINE*: T2D Patient with early signs of kidney
(linagliptin) 5mg tablets Have you seen a patient like Elaine *? *Hypothetical patient profile Elaine * : 60 years old Housewife *Hypothetical patient profile ELAINE*: T2D Patient with early signs of kidney
Dept of Diabetes Main Desk
 Dept of Diabetes Main Desk 01202 448060 Glucose management in Type 2 Diabetes in Adults The natural history of type 2 diabetes is for HbA1c to deteriorate with time. A stepwise approach to treatment is
Dept of Diabetes Main Desk 01202 448060 Glucose management in Type 2 Diabetes in Adults The natural history of type 2 diabetes is for HbA1c to deteriorate with time. A stepwise approach to treatment is
Chronic Kidney Disease
 Chronic Kidney Disease Presence of kidney damage or decreased kidney function for three or more months, - necessary to distinguish CKD from acute kidney disease. Ascertained either by kidney biopsy or
Chronic Kidney Disease Presence of kidney damage or decreased kidney function for three or more months, - necessary to distinguish CKD from acute kidney disease. Ascertained either by kidney biopsy or
Chronic kidney disease management primary care
 Care map information Information resources for patients and carers Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders DEFINITION OF CKD egfr
Care map information Information resources for patients and carers Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islanders DEFINITION OF CKD egfr
Joslin Diabetes Center Joslin Diabetes Forum 2013: The Impact of Comorbidities on Glucose Control Scenario 2: Reduced Renal Function
 Scenario 2: Reduced Renal Function 62 y.o. white man with type 2 diabetes for 18 years Hypertension and hypercholesterolemia Known proliferative retinopathy Current medications: Metformin 1000 mg bid Glyburide
Scenario 2: Reduced Renal Function 62 y.o. white man with type 2 diabetes for 18 years Hypertension and hypercholesterolemia Known proliferative retinopathy Current medications: Metformin 1000 mg bid Glyburide
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERENCE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
Personal Diabetes Passport
 Personal Diabetes Passport Contact information: Name: Physician: Diabetes Education Centre: Dietitian: Ophthalmologist: Chiropodist: Type of Diabetes: Type 1 (T1DM) Increased risk for diabetes Type 2(T2DM)
Personal Diabetes Passport Contact information: Name: Physician: Diabetes Education Centre: Dietitian: Ophthalmologist: Chiropodist: Type of Diabetes: Type 1 (T1DM) Increased risk for diabetes Type 2(T2DM)
Evaluation of Chronic Kidney Disease KDIGO. Paul E de Jong University Medical Center Groningen The Netherlands
 Evaluation of Chronic Kidney Disease Paul E de Jong University Medical Center Groningen The Netherlands Evaluation and Management of CKD 1. Definition and classification of CKD 2. Definition and impact
Evaluation of Chronic Kidney Disease Paul E de Jong University Medical Center Groningen The Netherlands Evaluation and Management of CKD 1. Definition and classification of CKD 2. Definition and impact
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour
 ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
Diabetes Renal Disease Management. Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital
 Diabetes Renal Disease Management Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital 0 Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is a clinical syndrome characterised by the following: Persistent albuminuria
Diabetes Renal Disease Management Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital 0 Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is a clinical syndrome characterised by the following: Persistent albuminuria
SIGN 149 Risk estimation and the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Quick Reference Guide July Evidence
 SIGN 149 Risk estimation and the prevention of cardiovascular disease Quick Reference Guide July 2017 Evidence ESTIMATING CARDIOVASCULAR RISK R Individuals with the following risk factors should be considered
SIGN 149 Risk estimation and the prevention of cardiovascular disease Quick Reference Guide July 2017 Evidence ESTIMATING CARDIOVASCULAR RISK R Individuals with the following risk factors should be considered
Chronic Kidney Disease due to Diabetes (Diabetic Nephropathy)
 Chronic Kidney Disease due to Diabetes (Diabetic Nephropathy) Patient information Oxford Kidney Unit If you have been told you have chronic kidney disease (CKD) due to diabetic nephropathy this leaflet
Chronic Kidney Disease due to Diabetes (Diabetic Nephropathy) Patient information Oxford Kidney Unit If you have been told you have chronic kidney disease (CKD) due to diabetic nephropathy this leaflet
Section 1: 1: Trends. Section 2: 2: Comparisons to to Overall Portland Area Area Results for for
 Section 1: 1: Trends 1 Patients in the Diabetes Register 2 Gender of Patients with Diabetes 2 Age of Patients with Diabetes 3 Diabetes Type 3 Duration of Diabetes 4 Weight Control 5 Hemoglobin A1c 6 Blood
Section 1: 1: Trends 1 Patients in the Diabetes Register 2 Gender of Patients with Diabetes 2 Age of Patients with Diabetes 3 Diabetes Type 3 Duration of Diabetes 4 Weight Control 5 Hemoglobin A1c 6 Blood
CLINICAL AUDIT. Laboratory Testing in. Diabetes. in Primary Care
 CLINICAL AUDIT Laboratory Testing in Diabetes in Primary Care Valid to November 2013 bpac nz better medicin e Background Regular health checks are essential for people with diabetes to reduce the frequency
CLINICAL AUDIT Laboratory Testing in Diabetes in Primary Care Valid to November 2013 bpac nz better medicin e Background Regular health checks are essential for people with diabetes to reduce the frequency
5.2 Key priorities for implementation
 5.2 Key priorities for implementation From the full set of recommendations, the GDG selected ten key priorities for implementation. The criteria used for selecting these recommendations are listed in detail
5.2 Key priorities for implementation From the full set of recommendations, the GDG selected ten key priorities for implementation. The criteria used for selecting these recommendations are listed in detail
National Collaborative Wave 2 (Wave 9): National Diabetes Prevention and Management Wave, Month 9 Diabetes Management: Diabetes Register
 National Collaborative Wave 2 (Wave 9): National Diabetes Prevention and Management Wave, Month 9 Diabetes Management: Diabetes Register The above graph shows a decrease in the number of patients on the
National Collaborative Wave 2 (Wave 9): National Diabetes Prevention and Management Wave, Month 9 Diabetes Management: Diabetes Register The above graph shows a decrease in the number of patients on the
The National Quality Standards for Chronic Kidney Disease
 The National Quality Standards for Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Robert Lewis Chief of Service, Wessex Kidney Centre, Portsmouth Specialist Committee Member Quality Standard for Chronic Kidney Disease, NICE
The National Quality Standards for Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Robert Lewis Chief of Service, Wessex Kidney Centre, Portsmouth Specialist Committee Member Quality Standard for Chronic Kidney Disease, NICE
egfr > 50 (n = 13,916)
 Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Prediction in Indigenous Australians
 Cardiovascular Disease Risk Prediction in Indigenous Australians ELIZABETH LM BARR (MPH, PHD) NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION POST-DOC FELLOW Cardiac Care in the NT Annual Workshop 2017 is proudly supported
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Prediction in Indigenous Australians ELIZABETH LM BARR (MPH, PHD) NATIONAL HEART FOUNDATION POST-DOC FELLOW Cardiac Care in the NT Annual Workshop 2017 is proudly supported
CKD and risk management : NICE guideline
 CKD and risk management : NICE guideline 2008-2014 Shahed Ahmed Consultant Nephrologist shahed.ahmed@rlbuht.nhs.uk Key points : Changing parameters of CKD and NICE guidance CKD and age related change of
CKD and risk management : NICE guideline 2008-2014 Shahed Ahmed Consultant Nephrologist shahed.ahmed@rlbuht.nhs.uk Key points : Changing parameters of CKD and NICE guidance CKD and age related change of
1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease. albuminuria
 1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease albuminuria Cardio-renal continuum REGRESS Target organ damage Asymptomatic CKD New risk factors Atherosclerosis Target organ damage
1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease albuminuria Cardio-renal continuum REGRESS Target organ damage Asymptomatic CKD New risk factors Atherosclerosis Target organ damage
NORTHERN IRELAND GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 NORTHERN IRELAND GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Practical points for use of estimated GFR + quality outcome framework indicators Developed by GAIN and the Northern Ireland Nephrology
NORTHERN IRELAND GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Practical points for use of estimated GFR + quality outcome framework indicators Developed by GAIN and the Northern Ireland Nephrology
DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin and
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin and
Case study for CME Diabetes up-to-date management
 Case study for CME Diabetes up-to-date management Dr Ole Schmiedel, MRCP MD FRACP Physician and Endocrinologist Service Clinical Director Auckland Diabetes Centre GP referral to Auckland Diabetes Centre
Case study for CME Diabetes up-to-date management Dr Ole Schmiedel, MRCP MD FRACP Physician and Endocrinologist Service Clinical Director Auckland Diabetes Centre GP referral to Auckland Diabetes Centre
Faculty/Presenter Disclosure
 CSI for CKD Unravelling the myths surrounding chronic kidney disease Practical Evidence for Informed Practice Oct 21 2016 Dr. Scott Klarenbach University of Alberta Slide 1: Option B (Presenter with NO
CSI for CKD Unravelling the myths surrounding chronic kidney disease Practical Evidence for Informed Practice Oct 21 2016 Dr. Scott Klarenbach University of Alberta Slide 1: Option B (Presenter with NO
Guest Speaker Evaluations Viewer Call-In Thanks to our Sponsors: Phone: Fax: Public Health Live T 2 B 2
 Public Health Live T 2 B 2 Chronic Kidney Disease in Diabetes: Early Identification and Intervention Guest Speaker Joseph Vassalotti, MD, FASN Chief Medical Officer National Kidney Foundation Thanks to
Public Health Live T 2 B 2 Chronic Kidney Disease in Diabetes: Early Identification and Intervention Guest Speaker Joseph Vassalotti, MD, FASN Chief Medical Officer National Kidney Foundation Thanks to
Online clinical pathway for chronic kidney disease (CKD) in primary care. February 27, 2015 Dr. Kerry McBrien University of Calgary
 Online clinical pathway for chronic kidney disease (CKD) in primary care February 27, 2015 Dr. Kerry McBrien University of Calgary FACULTY/PRESENTER DISCLOSURE Faculty: Kerry McBrien Relationships with
Online clinical pathway for chronic kidney disease (CKD) in primary care February 27, 2015 Dr. Kerry McBrien University of Calgary FACULTY/PRESENTER DISCLOSURE Faculty: Kerry McBrien Relationships with
Summary of Recommendation Statements Kidney International Supplements (2013) 3, 5 14; doi: /kisup
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 DIGO Summary of Recommendation Statements idney International Supplements (2013) 3, 5 14; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.77 Chapter 1: Definition and classification of
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 DIGO Summary of Recommendation Statements idney International Supplements (2013) 3, 5 14; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.77 Chapter 1: Definition and classification of
Renal Protection Staying on Target
 Update Staying on Target James Barton, MD, FRCPC As presented at the University of Saskatchewan's Management of Diabetes & Its Complications (May 2004) Gwen s case Gwen, 49, asks you to take on her primary
Update Staying on Target James Barton, MD, FRCPC As presented at the University of Saskatchewan's Management of Diabetes & Its Complications (May 2004) Gwen s case Gwen, 49, asks you to take on her primary
Hypertension in 2015: SPRINT-ing ahead of JNC-8. MAJ Charles Magee, MD MPH FACP Director, WRNMMC Hypertension Clinic
 Hypertension in 2015: SPRINT-ing ahead of JNC-8 MAJ Charles Magee, MD MPH FACP Director, WRNMMC Hypertension Clinic Conflits of interest? None Disclaimer The opinions contained herein are not to be considered
Hypertension in 2015: SPRINT-ing ahead of JNC-8 MAJ Charles Magee, MD MPH FACP Director, WRNMMC Hypertension Clinic Conflits of interest? None Disclaimer The opinions contained herein are not to be considered
Key Elements in Managing Diabetes
 Key Elements in Managing Diabetes Presentor Disclosure No conflicts of interest to disclose Presented by Susan Cotey, RN, CDE Lennon Diabetes Center Stephanie Tubbs Jones Health Center Cleveland Clinic
Key Elements in Managing Diabetes Presentor Disclosure No conflicts of interest to disclose Presented by Susan Cotey, RN, CDE Lennon Diabetes Center Stephanie Tubbs Jones Health Center Cleveland Clinic
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. Protein Restriction to prevent the progression of diabetic nephropathy GUIDELINES
 Protein Restriction to prevent the progression of diabetic nephropathy Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES a. A small volume of evidence suggests
Protein Restriction to prevent the progression of diabetic nephropathy Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES a. A small volume of evidence suggests
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice
 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice Guidance and clinical tips to help identify, manage and refer patients with CKD in your practice 3rd Edition 2015 www.kcat.org.au Prevent, Detect,
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management in General Practice Guidance and clinical tips to help identify, manage and refer patients with CKD in your practice 3rd Edition 2015 www.kcat.org.au Prevent, Detect,
Irish Practice Nurses Association Annual Conference Tullamore Court Hotel OCTOBER 6 th 2012
 Irish Practice Nurses Association Annual Conference Tullamore Court Hotel OCTOBER 6 th 2012 Susan McKenna Renal Clinical Nurse Specialist Cavan General Hospital Renal patient population ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Irish Practice Nurses Association Annual Conference Tullamore Court Hotel OCTOBER 6 th 2012 Susan McKenna Renal Clinical Nurse Specialist Cavan General Hospital Renal patient population ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Diabetes Passport. East Coast Area Diabetes Integrated Care
 Diabetes Passport East Coast Area Diabetes Integrated Care Personal Details Name: Address: Developed by East Coast Area Diabetes Programme (ECAD), 2014. Thanks to Beaumont Hospital for allowing us to use
Diabetes Passport East Coast Area Diabetes Integrated Care Personal Details Name: Address: Developed by East Coast Area Diabetes Programme (ECAD), 2014. Thanks to Beaumont Hospital for allowing us to use
Modified version focused on CCNC Quality Measures and Feedback Processes
 Executive Summary: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2010 Modified version focused on CCNC Quality Measures and Feedback Processes See http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/33/supplement_1/s11.full
Executive Summary: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2010 Modified version focused on CCNC Quality Measures and Feedback Processes See http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/33/supplement_1/s11.full
Outline. Outline CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW 7/23/2013. Question 1: Which of these patients has CKD?
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
Quality ID #119 (NQF 0062): Diabetes: Medical Attention for Nephropathy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Quality ID #119 (NQF 0062): Diabetes: Medical Attention for Nephropathy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process
Quality ID #119 (NQF 0062): Diabetes: Medical Attention for Nephropathy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process
The organs of the human body were created to perform ten functions among which is the function of the kidney to furnish the human being with thought.
 The organs of the human body were created to perform ten functions among which is the function of the kidney to furnish the human being with thought. Leviticus Rabba 3 Talmud Berochoth 6 1 b Outline &
The organs of the human body were created to perform ten functions among which is the function of the kidney to furnish the human being with thought. Leviticus Rabba 3 Talmud Berochoth 6 1 b Outline &
Primary Care Approach to Management of CKD
 Primary Care Approach to Management of CKD This PowerPoint was developed through a collaboration between the National Kidney Foundation and ASCP. Copyright 2018 National Kidney Foundation and ASCP Low
Primary Care Approach to Management of CKD This PowerPoint was developed through a collaboration between the National Kidney Foundation and ASCP. Copyright 2018 National Kidney Foundation and ASCP Low
Kidneys and Women s health. Monica NYAKURGWA CNE /CNC Renal service Leanne O GRADY CNC Renal Services 7 th March 2018
 Kidneys and Women s health Presenters - Monica NYAKURGWA CNE /CNC Renal service Leanne O GRADY CNC Renal Services 7 th March 2018 Objectives World kidney week/ kidney day/ International women's day dates
Kidneys and Women s health Presenters - Monica NYAKURGWA CNE /CNC Renal service Leanne O GRADY CNC Renal Services 7 th March 2018 Objectives World kidney week/ kidney day/ International women's day dates
Nice CKD Clinical Guidelines 2014 The challenges and benefits they may bring toprimary care
 Nice CKD Clinical Guidelines 2014 The challenges and benefits they may bring toprimary care Paula D Souza Senior CKD Nurse Specialist Royal Devon and Exeter Healthcare Trust Introduction Background What
Nice CKD Clinical Guidelines 2014 The challenges and benefits they may bring toprimary care Paula D Souza Senior CKD Nurse Specialist Royal Devon and Exeter Healthcare Trust Introduction Background What
HIV AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE. Understanding GFR
 HIV AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Understanding GFR in PEOPLE WITH HIV contents Introduction... 4 Chronic Kidney Disease... 5 What are kidneys and what do they do?... 5 What is glomerular filtration rate
HIV AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Understanding GFR in PEOPLE WITH HIV contents Introduction... 4 Chronic Kidney Disease... 5 What are kidneys and what do they do?... 5 What is glomerular filtration rate
2013 Hypertension Measure Group Patient Visit Form
 Please complete the form below for 20 or more unique patients meeting patient sample criteria for the measure group for the current reporting year. A majority (11 or more) patients must be Medicare Part
Please complete the form below for 20 or more unique patients meeting patient sample criteria for the measure group for the current reporting year. A majority (11 or more) patients must be Medicare Part
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
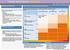 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
Challenges in type 2 diabetes control: slipping control and weight gain
 control Earn 3 CPD Points online Case study Challenges in type 2 diabetes control: slipping control and weight gain Presenter Dr Sedeshan Govender Specialist Physician, Endocrinologist and Diabetologists
control Earn 3 CPD Points online Case study Challenges in type 2 diabetes control: slipping control and weight gain Presenter Dr Sedeshan Govender Specialist Physician, Endocrinologist and Diabetologists
Hypertension Management Controversies in the Elderly Patient
 Hypertension Management Controversies in the Elderly Patient Juan Bowen, MD Geriatric Update for the Primary Care Provider November 17, 2016 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure No financial relationships No
Hypertension Management Controversies in the Elderly Patient Juan Bowen, MD Geriatric Update for the Primary Care Provider November 17, 2016 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure No financial relationships No
6/10/2014. Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care. Management of CKD according to stage (KDOQI 2002)
 Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care Dr Nathalie Demoulin, Prof Michel Jadoul Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc Université Catholique de Louvain What should and can be done
Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care Dr Nathalie Demoulin, Prof Michel Jadoul Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc Université Catholique de Louvain What should and can be done
2019 COLLECTION TYPE: MIPS CLINICAL QUALITY MEASURES (CQMS) MEASURE TYPE: Process
 Quality ID #119 (NQF 0062): Diabetes: Medical Attention for Nephropathy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care Meaningful Measure Area: Management of Chronic Conditions 2019 COLLECTION
Quality ID #119 (NQF 0062): Diabetes: Medical Attention for Nephropathy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care Meaningful Measure Area: Management of Chronic Conditions 2019 COLLECTION
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
Objectives. Kidney Complications With Diabetes. Case 10/21/2015
 Objectives Kidney Complications With Diabetes Brian Boerner, MD Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism University of Nebraska Medical Center Review screening for, and management of, albuminuria Review
Objectives Kidney Complications With Diabetes Brian Boerner, MD Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism University of Nebraska Medical Center Review screening for, and management of, albuminuria Review
Supplement: Summary of Recommendation Statements CHAPTER 1: DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF CKD
 Supplement: Summary of Recommendation Statements CHAPTER 1: DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF CKD 1.1 DEFINITION OF CKD 1.1.1: CKD is defined as abnormalities of kidney structure or function, present for
Supplement: Summary of Recommendation Statements CHAPTER 1: DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF CKD 1.1 DEFINITION OF CKD 1.1.1: CKD is defined as abnormalities of kidney structure or function, present for
