Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Fellowship Examination. Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 1
|
|
|
- Alberta Merritt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Fellowship Examination June 2016 Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 1 Perusal time: Twenty (20) minutes Time allowed: Four (4) hours after perusal Section A: Answer ONE (1) question Section B: Answer ALL FIVE (5) questions Section C: Answer ALL TEN (10) questions 2016 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists ABN This publication is copyright. Other than for the purposes of and subject to the conditions prescribed under the Copyright Act, no part of it may in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, microcopying, photocopying, recording or otherwise) be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted without prior written permission. Enquiries should be addressed to the Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Section A: Answer ONE essay-style question worth 60 marks... total 60 marks Section B: Answer FIVE short-answer questions each worth 24 marks... total 120 marks Section C: Answer TEN short-answer questions each worth 6 marks... total 60 marks Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 1 Page 1 of 7
2 Paper 1: Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Section A: Answer ONE (1) essay-style question 1. Answer all parts of this question: a) Define the systemic inflammatory response syndrome, sepsis, severe sepsis, septic shock, and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome using current veterinary terminology and clinical criteria in dogs. (15 marks) b) Briefly compare and contrast the pathophysiology of the initial immune response to non-infectious versus infectious insults, giving examples of specific insults and molecular patterns sensed by the host. (5 marks) c) Describe the innate immune response to gram negative bacterial infection including key mediators of the subsequent clinical syndrome. (20 marks) d) Draw a diagram showing determinants of oxygen delivery (DO 2 ), then work through the algorithm discussing in detail the parameters affected by sepsis, and how each may be affected. (10 marks) e) Outline your treatment approach to septic shock in dogs; be specific with drugs and doses, and compare your approach to current guidelines in human medicine. Do not include the general management strategies for sepsis (i.e. antibiotics or source control) in your answer. Include second line therapies, monitoring and/or end-points. (10 marks) Section B starts over page Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 1 Page 2 of 7
3 Section B: Answer ALL five (5) short-answer questions 1. Answer all parts of this question: a) Define and outline the components of cerebral perfusion pressure. (2 marks) b) Draw and explain the cerebral compliance curve including a description of the Monroe-Kellie doctrine. Explain the implications of this pathophysiology for a head trauma patient. (6 marks) c) Describe the two (2) main mechanisms by which intracranial pressure (ICP) is regulated. (3 marks) d) The modified Glasgow coma scale (MGCS) score is used as a somewhat objective means to grade the severity of head injury in dogs. Identify the three (3) categories of the MGCS score, describe the neurologic signs associated with the lowest MGCS score, and state the lowest possible score (x out of y). (6 marks) e) Explain your approach to managing increased ICP. For pharmacologic therapies include information on dosing and mechanisms of action. (7 marks) 2. Answer all parts of this question: a) Compare and contrast pre-synaptic and post-synaptic neurotoxins from Elapid snakes with regard to their mechanism of action and therapeutic implications. (4 marks) b) Compare and contrast the predominant diseases that are differential diagnoses for ascending flaccid paralysis in Australia with regard to their clinical syndrome, and the diagnostic approach. (16 marks) c) Based on analysis of the current veterinary literature, briefly discuss the prognosis for animals with ascending flaccid paralysis requiring mechanical ventilation. (4 marks) Continued over page Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 1 Page 3 of 7
4 3. Answer all parts of this question: a) Identify the components of Virchow s triad and provide examples of diseases that cause each of its components. (8 marks) b) Compare and contrast arterial versus venous thrombi and explain how these differences might influence thromboprophylaxis. (4 marks) c) For each of the following drugs, outline the mode of action and rationale for use in the management of patients with thromboembolic disease: (8 marks) i. unfractionated heparin (UFH) ii. low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) iii. tissue plasminogen activator (tpa) iv. warfarin. d) For each of the anticoagulant drugs (not tpa) in 3 c), briefly state how you would monitor therapy and identify the specific therapeutic target that you aim to reach. (4 marks) 4. Answer all parts of this question: a) Write out the Starling-Landis equation, including a description of each component of the equation. (7 marks) b) Describe the recent modification of our understanding of the Starling equation. (3 marks) c) Describe at least three (3) factors that protect against the development of oedema in nondistensible tissues such as the lung. (6 marks) d) List and explain the two (2) main pathophysiologic forms of pulmonary oedema with reference to the equation outlined in 4a). (4 marks) e) List and explain the other three (3) recognised pathophysiologic mechanisms of oedema formation and provide examples of predisposing conditions for each. (4 marks) Continued over page Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 1 Page 4 of 7
5 5. Answer all parts of this question: a) In order of occurrence, identify the three (3) most common arrest rhythms in small animal patients and state the additional rhythm that has been recognised in humans. (2 marks) b) State the equation that denotes myocardial perfusion pressure, and explain how this influences the decision to administer intravenous fluids during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). (4 marks) c) Describe in detail the two (2) theories by which cardiac output is achieved during CPR and explain how these are associated with compression technique. (6 marks) d) Explain the 3-phase model of ischaemia during ventricular fibrillation (VF), and how the duration of VF prior to defibrillation influences your approach to defibrillation. (7 marks) e) Assuming other components of basic and advanced life support are occurring appropriately, describe the technique specifically for performing open chest CPR. (5 marks) Section C starts over page Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 1 Page 5 of 7
6 Section C: Answer ALL ten (10) short-answer questions 1. Describe the features of the Berlin definition of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), including how the severity of ARDS is incorporated into this definition. (6 marks) 2. Answer all parts of this question: a) State the most common cause for brown coloured mucous membranes. (1 mark) b) List three (3) disease processes which can cause this abnormality, including examples where appropriate. (4 marks) c) Explain how this condition can be quantified. (1 mark) 3. Using figures, explain the Bohr and Haldane effects. Include in your answer information about the chloride shift. (6 marks) 4. Describe the Fenton and Haber-Weiss reactions and explain their pathophysiologic significance. (6 marks) 5. Answer all parts of this question: a) Define and describe a bacterial biofilm. (2 marks) b) Give four (4) examples of common locations and situations where biofilms may develop and become problematic in small animal patients. (2 marks) c) List two (2) management strategies to reduce the clinical impact of bacterial biofilms. (2 marks) Continued over page Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 1 Page 6 of 7
7 6. How is dead space ventilation subdivided/classified? Provide a brief explanation of each type of dead space. With respect to ventilation, define and differentiate different classification or types of dead space. (6 marks) 7. Outline how burns are classified based on the depth of tissue destruction scheme. Include layers involved, wound characteristics and details of healing. (6 marks) 8. Answer all parts of this question: a) Define abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS). (2 marks) b) Differentiate among primary, secondary and tertiary ACS using examples. (3 marks) c) Give one (1) example of a method or technique that you could use to quantify the intra-abdominal pressure in a veterinary ICU patient. (1 mark) 9. Compare and contrast the toxic syndromes of carbamates and organophosphates with specific focus on which clinical signs are attributable to toxin binding at which receptor sites. (6 marks) 10. Answer both parts of this question: a) Define ScvO 2, explain its biological significance and state how it is measured. (3 marks) b) Identify the two (2) broad categories by which ScvO 2 can be decreased and name two (2) examples within each category. (3 marks) End of paper Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 1 Page 7 of 7
8 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Fellowship Examination June 2016 Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 2 Perusal time: Twenty (20) minutes Time allowed: Four (4) hours after perusal Answer ALL FIVE (5) questions All five questions are of equal value. Answer FIVE questions each worth 48 marks... total 240 marks Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 2 Page 1 of 7
9 Paper 2: Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Answer all five (5) questions 1. Answer all parts of this question: a) Describe the pathophysiology of vomiting. (10 marks) b) List three (3) anti-emetic drugs of different classes, describe their mechanism of action, dosing regimen, and any unique features. (9 marks) c) Name two (2) additional drugs that could potentially be used as prokinetics in a patient with regurgitation and/or gastrointestinal ileus. Describe their mechanism of action, dosing regimen, and any unique features. (6 marks) d) Discuss the arguments for and against early and delayed enteral nutrition in pancreatitis. (7 marks) e) List advantages and disadvantages of four (4) enteral feeding tube options. Do not include comparisons of cost in your answer. (16 marks) Continued over page Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 2 Page 2 of 7
10 2. Answer all parts of this question: a) Explain how mean arterial pressure (MAP) is calculated using the systolic arterial blood pressure (SAP) and diastolic arterial blood pressure (DAP). (2 marks) b) Explain how accuracy of this MAP calculation is affected by patient heart rate. (1 mark) c) Using an appropriate diagram, describe how to perform a square wave test, explain what this is for, and how overdamping and underdamping would be identified. (5 marks) d) Identify cause(s) of underdamped and overdamped fluid-filled monitoring systems. (4 marks) e) Define pulse pressure and use an equation to relate the two (2) main factors that determine pulse pressure. (2 marks) f) List two (2) causes each of a narrow pulse pressure and a high (wide) pulse pressure. (4 marks) g) Describe the theory behind, and potential clinical utility of, pulse pressure variation (PPV) in anaesthetised patients. (4 marks) h) List four (4) techniques specifically used for measurement of cardiac output (CO). Describe how each technique is performed and provide one (1) limitation for each methodology listed (do not list the same limitation for multiple methodologies). (16 marks) i) Once the cardiac output is measured, oxygen delivery (DO 2 ) and oxygen consumption (VO 2 ) can be calculated. State the formulas for calculating these two oxygen-derived variables. (3 marks) j) Define systemic vascular resistance (SVR) and provide a formula for its calculation following determination of patient CO. (2 marks) k) Define pulmonary artery occlusion pressure, how is it measured, and how can it be helpful in assessment of critically ill patients? Include four (4) factors that could result in deviation of pulmonary artery occlusion pressure from normal, and the nature of that deviation. (5 marks) Continued over page Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 2 Page 3 of 7
11 3. Answer all parts of this question: a) Discuss glucagon s role in the pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). (6 marks) b) Describe synthetic pathways of each of the ketones. Include in your answer the names of the three (3) ketones. (3 marks) c) The nitroprusside reaction test is used to detect ketones in blood, plasma and urine. Explain how the nitroprusside reaction test can be negative despite the presence of ketones in the sample. (2 marks) d) Patients with diabetic ketoacidosis are described as having a high anion gap (normochloraemic) metabolic acidosis. Answer all parts of this sub-question: i. Provide the formula for anion gap. (1 mark) ii. Serum bicarbonate is expected to decrease in the presence of elevated serum anions. Explain why this occurs. (1 mark) iii. List four (4) other causes of high anion gap metabolic acidosis. (4 marks) e) Describe the pathophysiology of pseudohyponatraemia. Include in your answer, the expected degree of decrease in sodium, relative to increase in glucose. (6 marks) f) You are treating a dog with diabetic ketoacidosis with the following laboratory values: Na + : 132 mmol/l Cl - : 106 mmol/l K + : 5.2 mmol/l blood glucose: 38.5 mmol/l For this patient, calculate the following two values. Show all workings: i. corrected sodium (3 marks) ii. corrected chloride. (3 marks) Question 3 continued over page Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 2 Page 4 of 7
12 g) List four (4) reasons for hyperkalaemia associated with diabetic ketoacidosis. (2 marks) h) Discuss the mechanisms by which insulin therapy and fluid therapy decreases serum potassium and phosphorus. (2 marks) i) Severe hypophosphataemia (< 0.3 mmol/l) is a possible complication of the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis. Answer both parts of this sub-question: i. Describe two (2) effects of severe hypophosphataemia on the red blood cells and the possible clinical consequences. (2 marks) ii. List two (2) effects of severe hypophosphataemia on the neuromuscular system. (1 mark) j) Outline a general approach to initial fluid therapy and potassium supplementation in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis. Include in your answer the type(s) of fluid you would use (for example, isotonic). (7 marks) k) Outline a general approach to insulin therapy in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis. (5 marks) Continued over page Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 2 Page 5 of 7
13 4. Answer all parts of this question: a) Regarding von Willebrand disease (vwd): i. Outline the pathophysiology of the disease. (4 marks) ii. Briefly explain how the disease is classified. List at least two (2) dog breeds predisposed to each type of vwd. (4 marks) iii. State the typical pattern of bleeding for dogs with vwd. (1 mark) iv. Name the definitive diagnostic test for vwd. (1 mark) v. Identify the pharmacologic therapy that can be used for dogs with vwd and briefly explain how is it used. (2 marks) vi. Name the blood component that is most efficient for the treatment of vwd and explain how it is made. (2 marks) b) Regarding haemophilia A: i. State the aetiology of the disease. (2 marks) ii. Briefly explain how the disease is classified. (2 marks) iii. State the typical pattern of bleeding for dogs with haemophilia A. (2 marks) iv. Name the definitive diagnostic test for haemophilia A. (1 mark) c) Regarding Glanzmann s thrombasthenia: i. Outline the pathophysiology of the disease. (2 marks) ii. List one (1) dog breed predisposed to Glanzmann s thrombasthenia. (1 mark) iii. State the typical pattern of bleeding for dogs with Glanzmann s. (1 mark) iv. Name the definitive diagnostic test for Glanzmann s thrombasthenia. (1 mark) Question 4 continued over page Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 2 Page 6 of 7
14 d) Regarding acute traumatic coagulopathy: i. Describe the epidemiology and pathophysiology of the disease in human patients. (9 marks) ii. Discuss the prevailing clinical approach to treating acute traumatic coagulopathy in human medicine, including consideration of evidence for the use of antifibrinolytic drugs. (6 marks) iii. Summarise the evidence regarding the potential existence of acute traumatic coagulopathy in veterinary patients. (7 marks) 5. A two-year-old male neutered cat is presented for evaluation of a two-day history of lethargy and inappetence. Screening laboratory tests reveal marked azotaemia and isosthenuria with inactive urine sediment, prompting a diagnosis of acute kidney injury (AKI). Answer all parts of this question: a) List at least four (4) broad categories of possible underlying conditions/aetiologies for AKI in this cat, and give examples under each category to include at least ten (10) specific examples. (7 marks) b) Describe the pathophysiology of AKI. (10 marks) c) Compare and contrast two (2) grading schemes for AKI that are used in human medicine. (10 marks) d) Compare and contrast two (2) grading schemes for AKI that are specifically described in veterinary patients. (8 marks) e) Define the term biomarker and identify two (2) novel urinary biomarkers that have been evaluated in veterinary patients. (3 marks) f) During hospitalisation, the cat s urine output drops precipitously. Describe at least three (3) pharmacologic interventions that could be used to improve urine output. Include specific mechanism of action for each drug and potential adverse effects. (10 marks) End of paper Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 2 Page 7 of 7
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Membership Examination. Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care Paper 1
 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2017 Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2017 Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Membership Examination. Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care Paper 1
 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2018 Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2018 Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Membership Examination. Small Animal Medicine Paper 1
 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2018 Small Animal Medicine Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal Answer
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2018 Small Animal Medicine Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal Answer
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Membership Examination. Small Animal Medicine Paper 1
 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2017 Small Animal Medicine Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal Answer
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2017 Small Animal Medicine Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal Answer
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Fellowship Examination. Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 1
 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Fellowship Examination June 2015 Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 1 Perusal time: Twenty (20) minutes Time allowed: Four
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Fellowship Examination June 2015 Veterinary Emergency Medicine and Critical Care Paper 1 Perusal time: Twenty (20) minutes Time allowed: Four
2017 ACCP/SCCM Critical Care Preparatory Review and Recertification Course Learning Objectives
 2017 ACCP/SCCM Critical Care Preparatory Review and Recertification Course Learning Objectives Shock Syndromes and Sepsis, Pulmonary Disorders, Hepatic Failure/GI/Endocrine Emergencies, Supportive and
2017 ACCP/SCCM Critical Care Preparatory Review and Recertification Course Learning Objectives Shock Syndromes and Sepsis, Pulmonary Disorders, Hepatic Failure/GI/Endocrine Emergencies, Supportive and
ACCP/SCCM Critical Care Preparatory Review and Recertification Course Learning Objectives
 ACCP/SCCM Critical Care Preparatory Review and Recertification Course Learning Objectives Module 1 Critical Care Pharmacy Evolution and Validation, Practice Standards, Training, and Professional Development,
ACCP/SCCM Critical Care Preparatory Review and Recertification Course Learning Objectives Module 1 Critical Care Pharmacy Evolution and Validation, Practice Standards, Training, and Professional Development,
Staging Sepsis for the Emergency Department: Physician
 Staging Sepsis for the Emergency Department: Physician Sepsis Continuum 1 Sepsis Continuum SIRS = 2 or more clinical criteria, resulting in Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Sepsis = SIRS + proven/suspected
Staging Sepsis for the Emergency Department: Physician Sepsis Continuum 1 Sepsis Continuum SIRS = 2 or more clinical criteria, resulting in Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Sepsis = SIRS + proven/suspected
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Accelerated intravascular coagulation and fibrinolysis (AICF) in liver disease, 390 391 Acid suppression in liver disease, 403 404 ACLF.
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Accelerated intravascular coagulation and fibrinolysis (AICF) in liver disease, 390 391 Acid suppression in liver disease, 403 404 ACLF.
Blood transfusions in sepsis, the elderly and patients with TBI
 Blood transfusions in sepsis, the elderly and patients with TBI Shabbir Alekar MICU, CH Baragwanath Academic Hospital & The University of the Witwatersrand CCSSA Congress 11 June 2015 Packed RBC - complications
Blood transfusions in sepsis, the elderly and patients with TBI Shabbir Alekar MICU, CH Baragwanath Academic Hospital & The University of the Witwatersrand CCSSA Congress 11 June 2015 Packed RBC - complications
New Strategies in the Management of Patients with Severe Sepsis
 New Strategies in the Management of Patients with Severe Sepsis Michael Zgoda, MD, MBA President, Medical Staff Medical Director, ICU CMC-University, Charlotte, NC Factors of increases in the dx. of severe
New Strategies in the Management of Patients with Severe Sepsis Michael Zgoda, MD, MBA President, Medical Staff Medical Director, ICU CMC-University, Charlotte, NC Factors of increases in the dx. of severe
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis Definition: Diabetic Ketoacidosis is one of the most serious acute complications of diabetes. It s more common in young patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. It s usually characterized
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Definition: Diabetic Ketoacidosis is one of the most serious acute complications of diabetes. It s more common in young patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. It s usually characterized
Sepsis Wave II Webinar Series. Sepsis Reassessment
 Sepsis Wave II Webinar Series Sepsis Reassessment Presenters Nova Panebianco, MD Todd Slesinger, MD Fluid Reassessment in Sepsis Todd L. Slesinger, MD, FACEP, FCCM, FCCP, FAAEM Residency Program Director
Sepsis Wave II Webinar Series Sepsis Reassessment Presenters Nova Panebianco, MD Todd Slesinger, MD Fluid Reassessment in Sepsis Todd L. Slesinger, MD, FACEP, FCCM, FCCP, FAAEM Residency Program Director
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!!
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
Hyperglycaemic Emergencies GRI EDUCATION
 Hyperglycaemic Emergencies GRI EDUCATION LEARNING OUTCOMES Develop and describe your system of blood gas interpretation and recognise common patterns of acid-base abnormality. Describe the pathophysiology
Hyperglycaemic Emergencies GRI EDUCATION LEARNING OUTCOMES Develop and describe your system of blood gas interpretation and recognise common patterns of acid-base abnormality. Describe the pathophysiology
Manual Defibrillation. CPR AGE: 18 years LOA: Altered HR: N/A RR: N/A SBP: N/A Other: N/A
 ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
Australian College of Veterinary Scientists. Membership Examinationn. Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care Paper 1
 Australian College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examinationn June 2011 Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal
Australian College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examinationn June 2011 Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal
4. Which survey program does your facility use to get your program designated by the state?
 TRAUMA SURVEY Please complete one survey for each TCD designation you have in your facility. There would be a maximum of three surveys completed if your facility was designated as a trauma, stroke and
TRAUMA SURVEY Please complete one survey for each TCD designation you have in your facility. There would be a maximum of three surveys completed if your facility was designated as a trauma, stroke and
Supplemental Digital Content: Definitions Based on the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification
 Supplemental Digital Content: Definitions Based on the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) Diagnose and Procedures Codes 1. ICD-9-CM definition of
Supplemental Digital Content: Definitions Based on the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) Diagnose and Procedures Codes 1. ICD-9-CM definition of
CEDR 2018 QCDR Measures for CMS 2018 MIPS Performance Year Reporting
 ACEP19 Emergency Department Utilization of CT for Minor Blunt Head Trauma for Aged 18 Years and Older Percentage of visits for aged 18 years and older who presented with a minor blunt head trauma who had
ACEP19 Emergency Department Utilization of CT for Minor Blunt Head Trauma for Aged 18 Years and Older Percentage of visits for aged 18 years and older who presented with a minor blunt head trauma who had
Skills: Recall the incidence of seizures Recall the causes of seizures Describe types of seizures List signs and symptoms of seizure patients
 Medical 1 Resuscitation Describe the morbidity and mortality associated with sudden cardiac arrest List the chain of survival for sudden cardiac arrest as identified by the American Heart Association Discuss
Medical 1 Resuscitation Describe the morbidity and mortality associated with sudden cardiac arrest List the chain of survival for sudden cardiac arrest as identified by the American Heart Association Discuss
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency
 Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Advanced Resuscitation - Child
 C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
THE COLLEGES OF MEDICINE OF SOUTH AFRICA Incorporated Association not for gain Reg No/Nr 1955/000003/08
 THE COLLEGES OF MEDICINE OF SOUTH AFRICA Incorporated Association not for gain Reg No/Nr 1955/000003/08 DCH(SA) Examination for the Diploma in Child Health of the College of Paediatricians of South Africa
THE COLLEGES OF MEDICINE OF SOUTH AFRICA Incorporated Association not for gain Reg No/Nr 1955/000003/08 DCH(SA) Examination for the Diploma in Child Health of the College of Paediatricians of South Africa
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Membership Examination. Veterinary Pathology Paper 1
 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2014 Veterinary Pathology Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal Answer
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2014 Veterinary Pathology Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal Answer
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdomen, and aorta, as causes of shock, point-of-care ultrasonography in assessment of, 915 917 Abdominal compartment syndrome, trauma patient
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdomen, and aorta, as causes of shock, point-of-care ultrasonography in assessment of, 915 917 Abdominal compartment syndrome, trauma patient
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Fellowship Examination. Veterinary Radiology Paper 1
 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Fellowship Examination June 2014 Veterinary Radiology Paper 1 Perusal time: Twenty (20) minutes Time allowed: Three (3) hours after perusal Section
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Fellowship Examination June 2014 Veterinary Radiology Paper 1 Perusal time: Twenty (20) minutes Time allowed: Three (3) hours after perusal Section
High-Acuity Nursing. Global edition. Global edition. Kathleen Dorman Wagner Melanie G. Hardin-Pierce
 High-Acuity Nursing For these Global Editions, the editorial team at Pearson has collaborated with educators across the world to address a wide range of subjects and requirements, equipping students with
High-Acuity Nursing For these Global Editions, the editorial team at Pearson has collaborated with educators across the world to address a wide range of subjects and requirements, equipping students with
Advanced Resuscitation - Adult
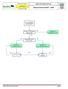 C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Quality & Hospital Acquired Conditions
 Quality & Hospital Acquired Conditions Rebecca Armbruster, DO, MS, FACOI Medical Director Resource Management Patricia Heys, BS Director of Infection Prevention & Control Sally Hinkle, DNP, MPA, RN Director
Quality & Hospital Acquired Conditions Rebecca Armbruster, DO, MS, FACOI Medical Director Resource Management Patricia Heys, BS Director of Infection Prevention & Control Sally Hinkle, DNP, MPA, RN Director
Lecture. ALS Algorithm
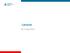 Lecture ALS Algorithm 1 Learning outcomes The ALS algorithm Treatment of shockable and non-shockable rhythms Potentially reversible causes of cardiac arrest 2 Adult ALS Algorithm 3 To confirm cardiac arrest
Lecture ALS Algorithm 1 Learning outcomes The ALS algorithm Treatment of shockable and non-shockable rhythms Potentially reversible causes of cardiac arrest 2 Adult ALS Algorithm 3 To confirm cardiac arrest
Please inform the Diabetes Nurse Specialist that this patient has been admitted within 24hrs of admission.
 Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis Care Bundle (V1. Issued October 2014 Review October 2015) Improving patient care This pack includes: DKA Management Guideline Name: (Patient Addressograph) DOB: Hospital No:
Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis Care Bundle (V1. Issued October 2014 Review October 2015) Improving patient care This pack includes: DKA Management Guideline Name: (Patient Addressograph) DOB: Hospital No:
CDE Exam Preparation Presented by Wendy Graham RD CDE May 4, 2017
 CDE Exam Preparation Presented by Wendy Graham RD CDE May 4, 2017 DKA at organ level 3 Diabetic Ketoacidosis Characteristics Ketones positive Anion Gap > 12 (High) Blood Sugar > 14 (High) Bicarbonate
CDE Exam Preparation Presented by Wendy Graham RD CDE May 4, 2017 DKA at organ level 3 Diabetic Ketoacidosis Characteristics Ketones positive Anion Gap > 12 (High) Blood Sugar > 14 (High) Bicarbonate
Written Guidelines for Laboratory Testing in Intensive Care - Still Effective After 3 Years
 Written Guidelines for Laboratory Testing in Intensive Care - Still Effective After 3 Years S. M. MEHARI, J. H. HAVILL Intensive Care Unit, Waikato Hospital, Hamilton, NEW ZEALAND ABSTRACT Objective: The
Written Guidelines for Laboratory Testing in Intensive Care - Still Effective After 3 Years S. M. MEHARI, J. H. HAVILL Intensive Care Unit, Waikato Hospital, Hamilton, NEW ZEALAND ABSTRACT Objective: The
Case TWO. Vital Signs: Temperature 36.6degC BP 137/89 HR 110 SpO2 97% on Room Air
 Mr N is a 64year old Chinese gentleman who is a heavy drinker, still actively drinking, and chronic smoker of >40pack year history. He has a past medical history significant for Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia,
Mr N is a 64year old Chinese gentleman who is a heavy drinker, still actively drinking, and chronic smoker of >40pack year history. He has a past medical history significant for Hypertension, Hyperlipidemia,
R Adams Cowley Founder of the R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center and Maryland EMS System in Baltimore, Maryland.
 R Adams Cowley 1917 -- 1991 Founder of the R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center and Maryland EMS System in Baltimore, Maryland. ...That the primary purpose of medicine was to save lives, that every critically
R Adams Cowley 1917 -- 1991 Founder of the R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center and Maryland EMS System in Baltimore, Maryland. ...That the primary purpose of medicine was to save lives, that every critically
Reverse (fluid) resuscitation Should we be doing it? NAHLA IRTIZA ISMAIL
 Reverse (fluid) resuscitation Should we be doing it? NAHLA IRTIZA ISMAIL 65 Male, 60 kg D1 in ICU Admitted from OT intubated Diagnosis : septic shock secondary to necrotising fasciitis of the R lower limb
Reverse (fluid) resuscitation Should we be doing it? NAHLA IRTIZA ISMAIL 65 Male, 60 kg D1 in ICU Admitted from OT intubated Diagnosis : septic shock secondary to necrotising fasciitis of the R lower limb
DKA : Diabetic Ketoacidosis & HHS: Hyperlgycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome Protocol. Glycemic Task Force September 2014
 DKA : Diabetic Ketoacidosis & HHS: Hyperlgycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome Protocol Glycemic Task Force September 2014 Hyperglycemic Crises: Pathophysiology DKA HHS Hyperglycemia DKA HHS Umpierrez, In Shoemaker,
DKA : Diabetic Ketoacidosis & HHS: Hyperlgycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome Protocol Glycemic Task Force September 2014 Hyperglycemic Crises: Pathophysiology DKA HHS Hyperglycemia DKA HHS Umpierrez, In Shoemaker,
Thrombolysis administration
 Thrombolysis administration Liz Mackey Stroke Nurse Practitioner Western Health Sunshine & Footscray Hospital, Melbourne Thanks ASNEN committee members Skye Coote, Acute Stroke Nurse, Eastern Health (slide
Thrombolysis administration Liz Mackey Stroke Nurse Practitioner Western Health Sunshine & Footscray Hospital, Melbourne Thanks ASNEN committee members Skye Coote, Acute Stroke Nurse, Eastern Health (slide
DIABETES MELLITUS. IAP UG Teaching slides
 DIABETES MELLITUS 1 DIABETES MELLITUS IN CHILDREN Introduction, Definition Classification, pathogenesis Clinical features Investigations and diagnosis Therapy and follow up Complications Carry home message
DIABETES MELLITUS 1 DIABETES MELLITUS IN CHILDREN Introduction, Definition Classification, pathogenesis Clinical features Investigations and diagnosis Therapy and follow up Complications Carry home message
Electrolytes by case examples. Graham Bilbrough, European Medical Affairs Manager
 Electrolytes by case examples Graham Bilbrough, European Medical Affairs Manager 1 Acid-bases disturbances Generally result from one of the following: 1. damage to an organ such as the kidneys or lungs
Electrolytes by case examples Graham Bilbrough, European Medical Affairs Manager 1 Acid-bases disturbances Generally result from one of the following: 1. damage to an organ such as the kidneys or lungs
Supplement Table 1. Definitions for Causes of Death
 Supplement Table 1. Definitions for Causes of Death 3. Cause of Death: To record the primary cause of death. Record only one answer. Classify cause of death as one of the following: 3.1 Cardiac: Death
Supplement Table 1. Definitions for Causes of Death 3. Cause of Death: To record the primary cause of death. Record only one answer. Classify cause of death as one of the following: 3.1 Cardiac: Death
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AKI) ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) ADVANCED DIRECTIVE LIMITING CARE...91 AGE...9 AGE UNITS...
 ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AKI)...122 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS)...124 ADVANCED DIRECTIVE LIMITING CARE...91 AGE...9 AGE UNITS...10 AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT...30 AIS PREDOT CODE...118 AIS SEVERITY...119
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY (AKI)...122 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS)...124 ADVANCED DIRECTIVE LIMITING CARE...91 AGE...9 AGE UNITS...10 AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT...30 AIS PREDOT CODE...118 AIS SEVERITY...119
The Septic Patient. Dr Arunraj Navaratnarajah. Renal SpR Imperial College NHS Healthcare Trust
 The Septic Patient Dr Arunraj Navaratnarajah Renal SpR Imperial College NHS Healthcare Trust Objectives of this session Define SIRS / sepsis / severe sepsis / septic shock Early recognition of Sepsis The
The Septic Patient Dr Arunraj Navaratnarajah Renal SpR Imperial College NHS Healthcare Trust Objectives of this session Define SIRS / sepsis / severe sepsis / septic shock Early recognition of Sepsis The
Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent
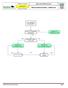 C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Membership Examination. Animal Nutrition (Ruminant) Paper 1
 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2017 Animal Nutrition (Ruminant) Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2017 Animal Nutrition (Ruminant) Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal
Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016
 Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016 Mitchell M. Levy MD, MCCM Professor of Medicine Chief, Division of Pulmonary, Sleep, and Critical Care
Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016 Mitchell M. Levy MD, MCCM Professor of Medicine Chief, Division of Pulmonary, Sleep, and Critical Care
IV fluid administration in sepsis. Dr David Inwald Consultant in PICU St Mary s Hospital, London CATS, London
 IV fluid administration in sepsis Dr David Inwald Consultant in PICU St Mary s Hospital, London CATS, London The talk What is septic shock? What are the recommendations? What is the evidence? Do we follow
IV fluid administration in sepsis Dr David Inwald Consultant in PICU St Mary s Hospital, London CATS, London The talk What is septic shock? What are the recommendations? What is the evidence? Do we follow
Sepsis Bundle Project (SEP) Kathy Wonderly RN, MSEd, CPHQ Consultant Developed: April 2015 Most recent Revision: December 2018
 Sepsis Bundle Project (SEP) Kathy Wonderly RN, MSEd, CPHQ Consultant Developed: April 2015 Most recent Revision: December 2018 Objectives 1. To identify the symptom of severe sepsis and septic shock syndrome.
Sepsis Bundle Project (SEP) Kathy Wonderly RN, MSEd, CPHQ Consultant Developed: April 2015 Most recent Revision: December 2018 Objectives 1. To identify the symptom of severe sepsis and septic shock syndrome.
Shock is defined as a state of cellular and tissue hypoxia due to : reduced oxygen delivery and/or increased oxygen consumption or inadequate oxygen
 Shock is defined as a state of cellular and tissue hypoxia due to : reduced oxygen delivery and/or increased oxygen consumption or inadequate oxygen utilization The effects of shock are initially reversible
Shock is defined as a state of cellular and tissue hypoxia due to : reduced oxygen delivery and/or increased oxygen consumption or inadequate oxygen utilization The effects of shock are initially reversible
Icu-cpr PICTURE QUIZ march 2014
 Department of surgery Icu-cpr PICTURE QUIZ march 2014 Prepared by Dr. Karam Kamal Younis Assistant professor and consultant surgeon Convener of the Department of Surgery College of Medicine University
Department of surgery Icu-cpr PICTURE QUIZ march 2014 Prepared by Dr. Karam Kamal Younis Assistant professor and consultant surgeon Convener of the Department of Surgery College of Medicine University
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
NEONATAL HYPOXIC-ISCHAEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY (HIE) & COOLING THERAPY
 Background NEONATAL HYPOXIC-ISCHAEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY (HIE) & COOLING THERAPY A perinatal hypoxic-ischaemic insult may present with varying degrees of neonatal encephalopathy, neurological disorder and
Background NEONATAL HYPOXIC-ISCHAEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY (HIE) & COOLING THERAPY A perinatal hypoxic-ischaemic insult may present with varying degrees of neonatal encephalopathy, neurological disorder and
Maternal Collapse Guideline
 Maternal Collapse Guideline Guideline Number: 664 Supersedes: Classification Clinical Version No: Date of EqIA: Approved by: Date Approved: Date made active: Review Date: 1 Obstetric Written Documentation
Maternal Collapse Guideline Guideline Number: 664 Supersedes: Classification Clinical Version No: Date of EqIA: Approved by: Date Approved: Date made active: Review Date: 1 Obstetric Written Documentation
No conflicts of interest
 Robert M. Rodriguez, MD FAAEM Clinical Professor of Medicine and Emergency Medicine, UCSF No conflicts of interest Major Points Most ICU patients start in ED Chain of critical care starting in field and
Robert M. Rodriguez, MD FAAEM Clinical Professor of Medicine and Emergency Medicine, UCSF No conflicts of interest Major Points Most ICU patients start in ED Chain of critical care starting in field and
7/4/2015. diffuse lung injury resulting in noncardiogenic pulmonary edema due to increase in capillary permeability
 Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Objectives Identify the 5 criteria for the diagnosis of ARDS. Discuss the common etiologies
Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Objectives Identify the 5 criteria for the diagnosis of ARDS. Discuss the common etiologies
Fluids in Sepsis: How much and what type? John Fowler, MD, FACEP Kent Hospital, İzmir Eisenhower Medical Center, USA American Hospital Dubai, UAE
 Fluids in Sepsis: How much and what type? John Fowler, MD, FACEP Kent Hospital, İzmir Eisenhower Medical Center, USA American Hospital Dubai, UAE In critically ill patients: too little fluid Low preload,
Fluids in Sepsis: How much and what type? John Fowler, MD, FACEP Kent Hospital, İzmir Eisenhower Medical Center, USA American Hospital Dubai, UAE In critically ill patients: too little fluid Low preload,
M5 BOARD REVIEW. Q s. Q s. Q s. Q s. Q s. Equations. Be Brilliant Today. Respiratory ( ) Alveolar Gas Equation. Dead Space (Bohr Equation)
 Be Brilliant Today Respiratory Alveolar Gas Equation Dead Space (Bohr Equation) PA O2 FI O2 ( P ATM P H2 O ) Pa CO2 / RQ V D V T P a P ECO CO2 2 P a CO 2 PA O2 Alveolar partial pressure of oxygen P a CO
Be Brilliant Today Respiratory Alveolar Gas Equation Dead Space (Bohr Equation) PA O2 FI O2 ( P ATM P H2 O ) Pa CO2 / RQ V D V T P a P ECO CO2 2 P a CO 2 PA O2 Alveolar partial pressure of oxygen P a CO
Early lactate clearance rate is an indicator of Outcome in severe sepsis and septic shock
 Early lactate clearance rate is an indicator of Outcome in severe sepsis and septic shock Sultana R, Ahsan ASMA, Fatema K, Ahmed F, Hamid T, Saha DK, Saha M, Nazneen S, Dr. Rozina Sultana FCPS (Medicine)
Early lactate clearance rate is an indicator of Outcome in severe sepsis and septic shock Sultana R, Ahsan ASMA, Fatema K, Ahmed F, Hamid T, Saha DK, Saha M, Nazneen S, Dr. Rozina Sultana FCPS (Medicine)
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 26 Caring for Clients with Coronary Heart Disease and Dysrhythmias Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Leading
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 26 Caring for Clients with Coronary Heart Disease and Dysrhythmias Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Leading
Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines
 Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines www.circ.ahajournals.org Elham Pishbin. M.D Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine MUMS C H E S Advanced Life Support
Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines www.circ.ahajournals.org Elham Pishbin. M.D Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine MUMS C H E S Advanced Life Support
Small Animal Benchmark May 2013
 Small Animal Benchmark May 2013 A 5-year-old MC yellow Laborador Retriever (35 kg) is referred for management of the burn injury depicted below. This injury was suspected to have been sustained from prolonged
Small Animal Benchmark May 2013 A 5-year-old MC yellow Laborador Retriever (35 kg) is referred for management of the burn injury depicted below. This injury was suspected to have been sustained from prolonged
EMT. Chapter 14 Review
 EMT Chapter 14 Review Review 1. All of the following are common signs and symptoms of cardiac ischemia, EXCEPT: A. headache. B. chest pressure. C. shortness of breath. D. anxiety or restlessness. Review
EMT Chapter 14 Review Review 1. All of the following are common signs and symptoms of cardiac ischemia, EXCEPT: A. headache. B. chest pressure. C. shortness of breath. D. anxiety or restlessness. Review
PARAMEDIC RECERT PROPOSAL (NCCP standards)
 PARAMEDIC RECERT PROPOSAL (NCCP standards) Module I TOPIC Airway, Respiration, Ventilation and Neurotological Management Ventilation ETCO2 Automated Transport Ventilators Oxygenation CPAP Capnography Neurological
PARAMEDIC RECERT PROPOSAL (NCCP standards) Module I TOPIC Airway, Respiration, Ventilation and Neurotological Management Ventilation ETCO2 Automated Transport Ventilators Oxygenation CPAP Capnography Neurological
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Solution for cardiac perfusion in viaflex plastic container
 CARDIOPLEGIA SOLUTION A Solution for cardiac perfusion in viaflex plastic container DESCRIPTION Cardioplegia Solution A is a sterile, non-pyrogenic solution in a Viaflex bag. It is used to induce cardiac
CARDIOPLEGIA SOLUTION A Solution for cardiac perfusion in viaflex plastic container DESCRIPTION Cardioplegia Solution A is a sterile, non-pyrogenic solution in a Viaflex bag. It is used to induce cardiac
Pediatric emergencies (SHOCK & COMA) Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University
 Pediatric emergencies (SHOCK & COMA) Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University SHOCK Definition: Shock is a syndrome = inability to provide sufficient oxygenated blood to tissues. Oxygen
Pediatric emergencies (SHOCK & COMA) Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University SHOCK Definition: Shock is a syndrome = inability to provide sufficient oxygenated blood to tissues. Oxygen
Resuscitating neonatal and infant organs and preserving function. GI Tract and Kidneys
 Resuscitating neonatal and infant organs and preserving function GI Tract and Kidneys Australian and New Zealand Resuscitation Council Joint Guidelines Outline Emphasis on the infant - PICU Kidney Gastrointestinal
Resuscitating neonatal and infant organs and preserving function GI Tract and Kidneys Australian and New Zealand Resuscitation Council Joint Guidelines Outline Emphasis on the infant - PICU Kidney Gastrointestinal
Contents. page xii. .'" Tom E. Peck. Section 1. Mathematical principles. Section 2. Physical principles
 i ~:kj owledgements "dace r \\'ord to the second edition P-l{e,sor Peter Hutton Clr word to the first edition.'" Tom E. Peck page xii xiii xv xvii '1troduction Section 1. Mathematical principles. lathematical
i ~:kj owledgements "dace r \\'ord to the second edition P-l{e,sor Peter Hutton Clr word to the first edition.'" Tom E. Peck page xii xiii xv xvii '1troduction Section 1. Mathematical principles. lathematical
SHOCK AETIOLOGY OF SHOCK (1) Inadequate circulating blood volume ) Loss of Autonomic control of the vasculature (3) Impaired cardiac function
 SHOCK Shock is a condition in which the metabolic needs of the body are not met because of an inadequate cardiac output. If tissue perfusion can be restored in an expeditious fashion, cellular injury may
SHOCK Shock is a condition in which the metabolic needs of the body are not met because of an inadequate cardiac output. If tissue perfusion can be restored in an expeditious fashion, cellular injury may
Bedside assessment of fluid status
 Bedside assessment of fluid status 2nd AKI Academy October 18 th 2014 David Treacher Guy s & St Thomas NHS Trust Assessing the circulation - the 3 key questions v Is my patient adequately filled? v What
Bedside assessment of fluid status 2nd AKI Academy October 18 th 2014 David Treacher Guy s & St Thomas NHS Trust Assessing the circulation - the 3 key questions v Is my patient adequately filled? v What
ICU treatment of the trauma patient. Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre Nijmegen
 ICU treatment of the trauma patient Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre Nijmegen Christian Kleber Surgical Intensive Care Unit - The trauma surgery Perspective Langenbecks
ICU treatment of the trauma patient Intensive Care Training Program Radboud University Medical Centre Nijmegen Christian Kleber Surgical Intensive Care Unit - The trauma surgery Perspective Langenbecks
ENDPOINTS OF RESUSCITATION
 ENDPOINTS OF RESUSCITATION Fred Pieracci, MD, MPH Acute Care Surgeon Denver Health Medical Center Assistant Professor of Surgery University of Colorado Health Science Center OUTLINE Recognition and characterization
ENDPOINTS OF RESUSCITATION Fred Pieracci, MD, MPH Acute Care Surgeon Denver Health Medical Center Assistant Professor of Surgery University of Colorado Health Science Center OUTLINE Recognition and characterization
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid base balance pregnancy-related changes to, 640 Acquired heart disease, 731 Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP), 618 Acute kidney
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid base balance pregnancy-related changes to, 640 Acquired heart disease, 731 Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP), 618 Acute kidney
With Dr. Sarah Reid and Dr. Sarah Curtis
 5. Headaches 6. Known diabetes 7. Specific high risk groups (ie. Teenagers, children on insulin pumps and those from lower socio-economic status). Episode 63 Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis With Dr. Sarah
5. Headaches 6. Known diabetes 7. Specific high risk groups (ie. Teenagers, children on insulin pumps and those from lower socio-economic status). Episode 63 Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis With Dr. Sarah
TOO SWEET TOO STORMY. CONSULTANTS: Dr. Saji James Dr. J. Dhivyalakshmi Dr. P. N. Vinoth. PRESENTOR: Dr. Abhinaya PG I (M.D Paeds)
 TOO SWEET TOO STORMY PRESENTOR: Dr. Abhinaya PG I (M.D Paeds) CONSULTANTS: Dr. Saji James Dr. J. Dhivyalakshmi Dr. P. N. Vinoth Unit IV, Dept. Of Paediatrics, SRMC & RI 14year old female complaints of
TOO SWEET TOO STORMY PRESENTOR: Dr. Abhinaya PG I (M.D Paeds) CONSULTANTS: Dr. Saji James Dr. J. Dhivyalakshmi Dr. P. N. Vinoth Unit IV, Dept. Of Paediatrics, SRMC & RI 14year old female complaints of
diabetes in adults Metabolic complications of
 Metabolic complications of diabetes in adults Dimitri MARGETIS MD ICU St ANTOINE PARIS Definition Diabetic acidoketosis Serious complication in type I diabetes : Hyperglycemia Metabolic acidosis Acidic
Metabolic complications of diabetes in adults Dimitri MARGETIS MD ICU St ANTOINE PARIS Definition Diabetic acidoketosis Serious complication in type I diabetes : Hyperglycemia Metabolic acidosis Acidic
Cardiac anaesthesia. Simon May
 Cardiac anaesthesia Simon May Contents Cardiac: Principles of peri-operative management for cardiac surgery Cardiopulmonary bypass, cardioplegia and off pump cardiac surgery Cardiac disease and its implications
Cardiac anaesthesia Simon May Contents Cardiac: Principles of peri-operative management for cardiac surgery Cardiopulmonary bypass, cardioplegia and off pump cardiac surgery Cardiac disease and its implications
ACID/BASE. A. What is her acid-base disorder, what is her anion gap, and what is the likely cause?
 These fluid and electrolyte problems are modified from those in a previous textbook for this sequence, Renal Pathophysiology edited by James A. Shayman M.D., Professor of Internal Medicine, University
These fluid and electrolyte problems are modified from those in a previous textbook for this sequence, Renal Pathophysiology edited by James A. Shayman M.D., Professor of Internal Medicine, University
Printed copies of this document may not be up to date, obtain the most recent version from
 Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Septic Shock Document Control Information Author Claire Fraser P.Ramnarayan Author Position tanp CATS Consultant Document Owner E. Polke Document
Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Septic Shock Document Control Information Author Claire Fraser P.Ramnarayan Author Position tanp CATS Consultant Document Owner E. Polke Document
Learning Station Competency Checklists
 Learning Station Competency Checklists Cardiac Arrest: Shockable Rhythm Team Dynamics Practice Demonstrates effective team dynamics (see, below) Performs manual maneuvers to open airway* Initiates assisted
Learning Station Competency Checklists Cardiac Arrest: Shockable Rhythm Team Dynamics Practice Demonstrates effective team dynamics (see, below) Performs manual maneuvers to open airway* Initiates assisted
Evidence- Based Medicine Fluid Therapy
 Evidence- Based Medicine Fluid Therapy Ndidi Musa M.D. Assosciate Professor of Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin/ Children s Hospital of Wisconsin Disclosures A. I have no relevant financial relationships
Evidence- Based Medicine Fluid Therapy Ndidi Musa M.D. Assosciate Professor of Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin/ Children s Hospital of Wisconsin Disclosures A. I have no relevant financial relationships
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults
 Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults Fatma Özdemir, MD Emergency Deparment of Uludag University Faculty of Medicine OVERVIEW Introduction Pathophysiology BLS algorithm ALS algorithm Post resuscitation
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Adults Fatma Özdemir, MD Emergency Deparment of Uludag University Faculty of Medicine OVERVIEW Introduction Pathophysiology BLS algorithm ALS algorithm Post resuscitation
SEPSIS AND SEPTIC SHOCK INTERNATIONAL GUIDLINES 2016
 SEPSIS AND SEPTIC SHOCK INTERNATIONAL GUIDLINES 2016 Sepsis is defined as organ dysfunction due to excessive reaction to infection It is a consequence of sepsis Needs vasoactive drug administration for
SEPSIS AND SEPTIC SHOCK INTERNATIONAL GUIDLINES 2016 Sepsis is defined as organ dysfunction due to excessive reaction to infection It is a consequence of sepsis Needs vasoactive drug administration for
Trauma, Shock, Multiple Organ Dysfunction. Class 14 Objectives
 Trauma, Shock, Multiple Organ Dysfunction University of San Francisco Dr. M. Maag 2003 Margaret Maag Class 14 Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, the student will be able to apply the previously
Trauma, Shock, Multiple Organ Dysfunction University of San Francisco Dr. M. Maag 2003 Margaret Maag Class 14 Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, the student will be able to apply the previously
SECTION 1: INCLUSION/EXCLUSION CRITERIA INCLUSION CRITERIA Please put a cross in the Yes or No box for each question
 Site Number Patient s Initials SECTION 1: INCLUSION/EXCLUSION CRITERIA INCLUSION CRITERIA Please put a cross in the Yes or No box for each question Yes No 1.1 Is the patient receiving invasive mechanical
Site Number Patient s Initials SECTION 1: INCLUSION/EXCLUSION CRITERIA INCLUSION CRITERIA Please put a cross in the Yes or No box for each question Yes No 1.1 Is the patient receiving invasive mechanical
Acid and Base Balance
 Acid and Base Balance 1 2 The Body and ph Homeostasis of ph is tightly controlled Extracellular fluid = 7.4 Blood = 7.35 7.45 < 7.35: Acidosis (acidemia) > 7.45: Alkalosis (alkalemia) < 6.8 or > 8.0: death
Acid and Base Balance 1 2 The Body and ph Homeostasis of ph is tightly controlled Extracellular fluid = 7.4 Blood = 7.35 7.45 < 7.35: Acidosis (acidemia) > 7.45: Alkalosis (alkalemia) < 6.8 or > 8.0: death
Pediatric advanced life support. Management of decreased conscious level in children. Virgi ija Žili skaitė 2017
 Pediatric advanced life support. Management of decreased conscious level in children Virgi ija Žili skaitė 2017 Life threatening conditions: primary assessment, differential diagnostics and emergency care.
Pediatric advanced life support. Management of decreased conscious level in children Virgi ija Žili skaitė 2017 Life threatening conditions: primary assessment, differential diagnostics and emergency care.
AMI Talking Points. Provide appropriate treatment to Acute MI patients with these core measures:
 AMI Provide appropriate treatment to Acute MI patients with these core measures: Aspirin received within 24 hours of arrival or contraindication documented Primary PCI Received Within 90 Minutes of Hospital
AMI Provide appropriate treatment to Acute MI patients with these core measures: Aspirin received within 24 hours of arrival or contraindication documented Primary PCI Received Within 90 Minutes of Hospital
Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies. CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED
 Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED THREE FAMILIAR CARDIAC CONDITIONS Angina Pectoris Acute Myocardial Infarction Congestive Heart Failure ANGINA PECTORIS Chest
Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED THREE FAMILIAR CARDIAC CONDITIONS Angina Pectoris Acute Myocardial Infarction Congestive Heart Failure ANGINA PECTORIS Chest
Contents. Contributors. Reviewers. Acknowledgements I CARDIOVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS
 Contributors Reviewers Acknowledgements Preface xii xvi xvii xviii I CARDIOVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS 1 Cardiac Complications of Cancer and Anticancer Treatment 3 Introduction 3 Malignant Pericardial Effusion
Contributors Reviewers Acknowledgements Preface xii xvi xvii xviii I CARDIOVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS 1 Cardiac Complications of Cancer and Anticancer Treatment 3 Introduction 3 Malignant Pericardial Effusion
Extracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO) Guidelines for Pediatric Respiratory Failure
 Extracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO) Guidelines for Pediatric Respiratory Failure Introduction This pediatric respiratory failure guideline is a supplement to ELSO s General Guidelines for all
Extracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO) Guidelines for Pediatric Respiratory Failure Introduction This pediatric respiratory failure guideline is a supplement to ELSO s General Guidelines for all
Table 1. Common precipitating events of DKA.
 Update in Anaesthesia Diabetic ketoacidosis Claire Preedy and William English Correspondence Email: englishwilliam@hotmail.com DEFINITION Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a medical emergency. It is classified
Update in Anaesthesia Diabetic ketoacidosis Claire Preedy and William English Correspondence Email: englishwilliam@hotmail.com DEFINITION Diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA) is a medical emergency. It is classified
Deep vein thrombosis and its prevention in critically ill adults Attia J, Ray J G, Cook D J, Douketis J, Ginsberg J S, Geerts W H
 Deep vein thrombosis and its prevention in critically ill adults Attia J, Ray J G, Cook D J, Douketis J, Ginsberg J S, Geerts W H Authors' objectives To systematically review the incidence of deep vein
Deep vein thrombosis and its prevention in critically ill adults Attia J, Ray J G, Cook D J, Douketis J, Ginsberg J S, Geerts W H Authors' objectives To systematically review the incidence of deep vein
Adult Basic Life Support
 Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
COMPLIANCE WITH THIS DOCUMENT IS MANDATORY
 COVER SHEET `NAME OF DOCUMENT TYPE OF DOCUMENT at Shoalhaven Hospital Group Critical Care Procedure DOCUMENT NUMBER DATE OF PUBLICATION February 2018 RISK RATING Medium REVIEW DATE February 2021 FORMER
COVER SHEET `NAME OF DOCUMENT TYPE OF DOCUMENT at Shoalhaven Hospital Group Critical Care Procedure DOCUMENT NUMBER DATE OF PUBLICATION February 2018 RISK RATING Medium REVIEW DATE February 2021 FORMER
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Fellowship Examination. Veterinary Ophthalmology Paper 1
 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Fellowship Examination June 2014 Veterinary Ophthalmology Paper 1 Perusal time: Twenty (20) minutes Time allowed: Three (3) hours after perusal
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Fellowship Examination June 2014 Veterinary Ophthalmology Paper 1 Perusal time: Twenty (20) minutes Time allowed: Three (3) hours after perusal
Nurse Driven Fluid Optimization Using Dynamic Assessments
 Nurse Driven Fluid Optimization Using Dynamic Assessments 2016 1 WHAT WE BELIEVE We believe that clinicians make vital fluid and drug decisions every day with limited and inconclusive information Cheetah
Nurse Driven Fluid Optimization Using Dynamic Assessments 2016 1 WHAT WE BELIEVE We believe that clinicians make vital fluid and drug decisions every day with limited and inconclusive information Cheetah
SAFE approach. Unresponsive? Shout or call for help. Open Airway. Not Breathing normally? 30 chest compressions. 2 rescue breaths
 Basic Life Support Dial 2222 Chin lift, head tilt jaw thrust Look, listen, feel For 10 seconds Rate 100/min *Lateral tilt* SAFE approach Unresponsive? Shout or call for help Open Airway Not Breathing normally?
Basic Life Support Dial 2222 Chin lift, head tilt jaw thrust Look, listen, feel For 10 seconds Rate 100/min *Lateral tilt* SAFE approach Unresponsive? Shout or call for help Open Airway Not Breathing normally?
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
 October 2015 Michael T. McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Case History HPI: 24 yo man with recent 8 lb. weight loss, increased thirst and frequent
October 2015 Michael T. McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Case History HPI: 24 yo man with recent 8 lb. weight loss, increased thirst and frequent
