The c.65-2a>g splice site mutation is associated with a mild phenotype in Danon disease due to the transcription of normal LAMP2 mrna
|
|
|
- Scot Chapman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clin Genet 2016: 90: Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2016 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd CLINICAL GENETICS doi: /cge The c.65-2a>g splice site mutation is associated with a mild phenotype in Danon disease due to the transcription of normal LAMP2 mrna Cetin H., Wöhrer A., Rittelmeyer I., Gencik M., Zulehner G., Zimprich F., Ströbel T., Zimprich A. The c.65-2a>g splice site mutation is associated with a mild phenotype in Danon disease due to the transcription of normal LAMP2 mrna. Clin Genet 2016: 90: John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2016 Danon disease (DD) is a rare X-linked multisystem disorder caused by mutations of the LAMP2 gene and characterized by intellectual disability, skeletal myopathy and cardiomyopathy. The survival time is severely reduced. Contrasting with the usual disease course, we report on a family with an exceptionally mild phenotype of DD despite having two potentially damaging LAMP2 mutations. Using RNA-Seq analysis, we showed that a c.65-2a>g splice site mutation results in the tissue-specific production of four different transcripts including the full-length mrna in muscle tissue but not in leukocytes. We confirmed our results by immunohistochemistry and immunoblotting, showing the detection of LAMP2 protein only in muscle. The second mutation (c.586a>t, p.t196s) has been reported before to have an uncertain clinical significance. In our patients, however, neither of the two mutations seem to have a high enough functional impact to cause a severe phenotype. Overall, our study reveals that alternative splicing is a potential mechanism in DD with underlying splice site mutations of the LAMP2 gene in order to rescue the full-length mrna. Moreover, our report of a mild phenotype complements the DD spectrum, which is of great importance for a rare disease suspected to be underdiagnosed. Conflict of interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. H. Cetin a,a.wöhrer b, I. Rittelmeyer c, M. Gencik c, G. Zulehner a, F. Zimprich a, T. Ströbel b and A. Zimprich a a Department of Neurology, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, b Institute of Neurology, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria, and c Center for Human Genetics, Vienna, Austria Key words: Danon disease LAMP2 myopathy storage disease tissue-specific alternative splicing Corresponding author: Hakan Cetin, MD, Department of Neurology, Medical University of Vienna, Waehringer Guertel 18-20, 1090 Vienna, Austria. Tel.: ; fax: ; hakan.cetin@meduniwien.ac.at Received 21 November 2015, revised and accepted for publication 4 January 2016 Danon disease (DD; MIM# ) is a X-linked dominant metabolic disorder with multisystem manifestations among which the clinical triad of cardiomyopathy, skeletal myopathy and intellectual disability are the most common. Men are affected earlier and more severely than women and die at an average age of approximately 20 years because of cardiac failure (1). The disorder is caused by the defects of the lysosome-associated membrane protein-2 (LAMP2; MIM# ), which is involved in the maturation of (auto)phagosomes and regulates their intracellular trafficking (2, 3). To date, 17 splice site mutations have been reported in the literature (4), most of which result in truncated mrna products. Although the majority of those transcripts are proposed to undergo post-transcriptional nonsense-mediated decay, some studies using immunoassays have detected traces of truncated LAMP2 protein (5, 6). The age at disease onset and the age of death appear not to differ between patients with splice site mutations and other mutations (4), suggesting that a full-length LAMP2 protein is crucial for its proper function. Patients with missense mutations of exon 366
2 9 (affecting the LAMP2B isoform only) experience a milder phenotype with a significantly later disease onset (7). In this study, we report a family with an unusually mild form of DD caused by a splice site mutation in intron 1 (c.65-2a>g) enabling the tissue-specific production of normal LAMP2 mrna and, presumably, LAMP2 protein. Association of c.65-2a>g with mild phenotype in Danon disease Materials and methods Ethics statement As a retrospective case report, this study does not require ethics committee approval at the Medical University of Vienna. Written informed consent was obtained from included patients to conduct the clinical and biological investigations and to publish the results. Morphological studies and western blot analysis The biopsy was obtained from the vastus lateralis muscle. LAMP2 protein expression was analyzed with two different antibodies, a mouse monoclonal anti-lamp2 (H4B4, sc-18822, 1:50, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) and a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against amino acids of human LAMP2 protein (ab101325, 1:50, Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA). The same antibodies were used as primary antibodies for western blot analyses (details provided as Supporting information). Molecular analysis Genomic DNA was extracted from leukocytes using the QIAamp DNA Mini kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Primers were designed to amplify all coding exons of LAMP2 including adjacent exon/intron boundaries. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) fragments were purified by agarose gel electrophoresis and sequenced in forward and reverse direction using the dideoxy Cy5/Cy5.5 Dye Primer cycle sequencing kit (Visible Genetics, Toronto, ON, Canada) and the OpenGene DNA sequencing system (Visible Genetics) (8). RNA-Seq analysis was performed with RNA from leukocytes (patient II-2, III-2 and control person) and from muscle tissue (patient III-2) (details provided as Supporting information). Results Index patient The 40 year old male index patient (patient III-2, Fig. 1) was initially referred to the neuromuscular outpatient clinic at the age of 33 because of elevated levels of serum creatine kinase (CK) and a generalized fatigability. The physical examination revealed no specific abnormalities, especially no muscle weakness. For the following 7 years, no deterioration was observed. Laboratory testing during this period confirmed consistently Fig. 1. Pedigree of the family presented in this study depicting the clinical status. Genetic analyses have been performed on the index patient (III-2) and his mother (II-2). His grandmother (I-2) deceased due to heart failure at the age of 35 without being tested for Danon disease. His father (II-1) died in a car accident at the age of 35. The 33 year old brother (III-1) has no symptoms and the laboratory testing was normal. elevated serum CK (up to 1100 U/l: normal <190 U/l), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (171 U/l: normal <35 U/l) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (213 U/l: normal <45 U/l) levels. All other laboratory parameters were normal. A liver biopsy had been performed on the suspicion of a hepatopathy at the age of 32 but no abnormalities could be detected. Electromyography and nerve conduction studies were normal. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and the muscles of the lower limbs were also normal. Cardiac ultrasound revealed concentric hypertrophy of the left ventricle with normal systolic function. A 24-h holter recording showed premature atrial and ventricular contractions and non-sustained runs of atrial tachycardia. Bradycardic episodes have also been reported. Neuropsychological examination revealed no relevant deficits; the patient s IQ was 85. Mother of patient III-2 The 56 year old mother (patient II-2, Fig. 1) reported no symptoms and, correspondingly, the physical examination revealed no weakness or other deficits. 367
3 Cetin et al. Laboratory testing (including CK, AST and ALT), electromyography, nerve conduction studies and a magnetic resonance imaging of the brain were normal. Cardiac ultrasound revealed mild concentric hypertrophy of the left ventricle with normal systolic function. The 24-h holter recording showed premature atrial and ventricular contractions and non-sustained runs of atrial tachycardia. The patient had an IQ of 75. Her mother (patient I-2, Fig. 1) had deceased due to heart failure at the age of 35. Unfortunately, there were no reports available. Muscle biopsy of patient III-2 The specimen showed myopathic changes with minor variability in muscle fiber size. Many fibers contained multiple cytoplasmic autophagic vacuoles that appeared as solid basophilic granules on hematoxylin and eosin staining. Muscle fibers lacked LAMP2 immunoreactivity using a monoclonal LAMP2 antibody. However, they retained positive immunoreactivity using a polyclonal antibody (Fig. 2a f). We found a predominant sarcolemmal staining and a distribution within the vacuoles. Western blot analysis Immunoblotting was performed on leukocyte extracts from the patient and his mother, on skeletal muscle just from the patient and on controls (Fig. 2g h). The monoclonal LAMP2 antibody could not detect any protein using both leukocyte and skeletal muscle extracts from the patient. In contrast, LAMP2 bands between 100 and 150 kda were present with about the same intensity in leukocytes from the patient s mother and in all controls. Performing experiments with the polyclonal LAMP2 antibody, we surprisingly detected corresponding protein bands at 105 kda in skeletal muscle extracts from the patient and in control samples, whereas there was no binding in leukocyte extracts from the patient. LAMP2 bands were present in leukocyte extracts from both his mother and controls. DNA studies After extracting DNA from leukocytes exons 1 8, 9A and9bofthe LAMP2 gene were sequenced. We detected a c.65-2a>g splice site mutation (rs ) in intron 1 affecting the splice acceptor site. In addition, two other mutations were found: the c.156a>t in exon 2 (p.v52v, rs12097) with a minor allele frequency (MAF) of designated a silent mutation and the c.586a>t in exon 5 (p.t196s, rs ) with a MAF of a missense mutation. The c.586a>t affects a position that reveals high amino acid conservation and is predicted to be possibly damaging for the protein with a PolyPhen-2 score of ( However, the variant is categorized as likely benign and with uncertain significance according to the ClinVar database. ( All three mutations have also been detected in the patient s mother. RNA studies Performing RNA-Seq analysis from blood and muscle tissue, we found four different transcripts in the patient (Fig. 3): (i) full-length normal transcripts detected in muscle but not in leukocytes, (ii) transcripts with an in-frame deletion in exon 2 leading to a predicted protein lacking 13 amino acids in blood and muscle, (iii) transcripts with skipped exon 2 and a frameshift (p.gly22glufs*14) in blood and muscle, and (iv) transcripts with skipped exons 1 and 2 in blood and muscle with an unknown effect on the protein level. The mother of the index patient processed the (i) full-length transcript and transcripts (ii) and (iii) in blood (muscle has not been examined). Control lymphocytes from a healthy male person just expressed the full-length transcript. Discussion DD is a serious lysosomal storage disorder characterized by cardiac and skeletal myopathy and a severely reduced survival time. The mean age for heart transplantation and death in male patients was reported to be 18 and 19 years, respectively. The average life expectancy in women was 35 years (1). In our study, we report on a family with an exceptionally mild phenotype although the underlying presence of two potentially hazardous mutations in the LAMP2 gene. The c.65-2a>g splice site mutation results in the tissue-specific production of four different transcripts including the full-length mrna. To our knowledge, this is the first report on a splice site mutation of the LAMP2 gene being associated with transcripts of full-length protein and, consecutively, an unusually mild phenotype. However, similar findings on splice site mutations resulting in the production of small amounts of full-length mrna, and mild phenotypes have also been published in the context of cystic fibrosis (9) and dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (10). A single patient with the c.65-2a>g mutation has been published before (5). The clinical information provided was limited, but the male patient seemed to suffer from hypertrophic cardiomyopathy without any musculoskeletal deficits or mental retardation. Using RT-PCR the mutation was reported to result in an exon 2-skipped transcript and a frameshift. This was confirmed by immunoblotting, which did not show any reaction between protein extracts from lymphocytes and fibroblasts and polyclonal LAMP2 antibodies. Muscle tissue had not been examined. These results somehow contrast with the milder phenotype of the patient in our study, which is all the more remarkable given the apparent null allele mutation. To elucidate this inconsistency, we performed RNA-Seq analyses from leukocytes and muscle tissue and identified four different transcripts in the patient. Surprisingly, we also found full-length normal transcripts, but only in muscle tissue and not in leukocytes. We confirmed our results by immunohistochemistry and western blotting, showing LAMP2 detection with predominant sarcolemmal and vacuolar distribution just in muscle tissue by a polyclonal 368
4 Association of c.65-2a>g with mild phenotype in Danon disease (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) Fig. 2. Muscle biopsy and western blot analysis. The muscle displayed moderate variation in fiber size with striking vacuoles in several muscle fibers [(a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining, 40 and insert 60; the bar represents 50 μm]. These vacuoles stain for glycogen [(b) PAS 60] and are lined by membranes, which contain sarcolemmal proteins [(c) alpha-sarkoglycan, 40]. Immunohistochemistry displays virtual absence of LAMP2 protein [(d) 40, monoclonal anti-lamp2] compared with non-diseased muscle [(e) 40], whereas protein expression is retained and showed a sarcolemmal and vacuolar distribution using a polyclonal anti-lamp2 [(f) 40]. This was reproduced in the western blot analysis. Using a polyclonal antibody, we could not detect protein in leukocytes (g) but in muscle tissue (h) from the index patient (patient III-2), whereas the monoclonal antibody failed to show a reaction. However, the exact epitope of the monoclonal antibody is unknown. Both antibodies detected LAMP2 protein in leukocytes of patient II-2 (mother). All controls showed a positive reaction. Myosin heavy chain served as a loading control. antibody. Interestingly, the vacuolar LAMP2 staining was reported before in another case of DD with a mild phenotype (with a missense mutation in exon 9 affecting the LAMP2B isoform only) (11). Overall, it rather seems that the c.65-2a>g splice site mutation results in the tissue-specific expression of full-length LAMP2 protein contributing to the mild phenotype of DD presented in our study. In contrast, the index patient s grandmother died of heart failure at the age of 35 without being tested for DD. If she was a carrier, this would rather be suggestive of a severe phenotype. However, her genetic status has not been confirmed and other factors could have contributed to her early death. There was a relatively high protein level detected by the polyclonal LAMP2 antibody in the western blot analysis (Fig. 2h) and a relatively low ratio of normal transcript in the RNA-Seq analysis of muscle tissue from the patient (5.1% of total reads, Fig. 3). A potential explanation for this apparent discrepancy might be that the RNA transcripts (ii) and (iv) are translated into detectable proteins. The polyclonal LAMP2 antibody used in our study was directed against an amino acid sequence corresponding to exons 3 5 and thus would 369
5 Cetin et al. Fig. 3. Next generation sequencing-based RNA-Seq analysis was used to sequence LAMP2 transcripts in leucocytes (index patient and mother) and muscle tissue (index patient). The c.65-2a>g splice site mutation in intron 1 resulted in four different transcripts: full-length normal transcripts (i), transcripts with a 39 bp in-frame deletion in exon 2 (ii), transcripts with skipped exon 2 and a frameshift (iii) and transcripts with skipped exons 1 and 2(iv). have also detected transcripts (ii) and (iv) (which lacked 39 bp in exon 2 and exons 1 and 2, respectively). Moreover, as a semi-quantitative method NGS does not measure the absolute amount of a specific transcript but rather displays the relative amount of one transcript to another. Thus, even though the normal full-length transcript constitutes for just about 5% of all NGS reads, this might suffice for adequate amounts of full-length protein. Surprisingly, we have not detected any protein by immunohistochemistry or western blotting using a commercial monoclonal LAMP2 antibody, for which the specific epitope is not known. This could be explained by the fact that the family presented in this study had another mutation in exon 5 (c.586a>t), which might have been affecting the interaction between the LAMP2 protein with the monoclonal antibodies in our experiments. In conclusion, our study shows that the c.65-2a>g splice site mutation produces different transcripts including the full-length mrna. The pattern of transcription seems to be tissue-specific with normal protein being expressed in muscle tissue. This might explain the exceptionally mild phenotype in our patients. Our findings also convey important clinical implications. In patients with splice site mutations, prognostic predictions seem to be more accurate using muscle tissue instead of leukocytes for genetic analyses. Moreover, our report of a mild phenotype complements the DD spectrum, which is of great importance for a rare disease suspected to be underdiagnosed (12). Supporting Information Additional supporting information may be found in the online version of this article at the publisher s web-site. Acknowledgements The authors are very thankful to the patients for their cooperation. References 1. Boucek D, Jirikowic J, Taylor M. Natural history of Danon disease. Genet Med 2011: 13: Saftig P, Beertsen W, Eskelinen EL. LAMP-2: a control step for phagosome and autophagosome maturation. Autophagy 2008: 4: Saftig P, Klumperman J. Lysosome biogenesis and lysosomal membrane proteins: trafficking meets function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009: 10: D Souza RS, Levandowski C, Slavov D et al. Danon disease: clinical features, evaluation, and management. Circ Heart Fail 2014: 7: Arad M, Maron BJ, Gorham JM et al. Glycogen storage diseases presenting as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med 2005: 352:
6 Association of c.65-2a>g with mild phenotype in Danon disease 6. Cottinet SL, Bergemer-Fouquet AM, Toutain A et al. Danon disease: intrafamilial phenotypic variability related to a novel LAMP-2 mutation. J Inherit Metab Dis 2011: 34: Hong D, Shi Z, Wang Z, Yuan Ye. Danon disease caused by two novel mutations of the LAMP2 gene: implications for two ends of the clinical spectrum. Clin Neuropathol 2012: 31: Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1977: 74: Highsmith WE, Burch LH, Zhou Z et al. A novel mutation in the cystic fibrosis gene in patients with pulmonary disease but normal sweat chloride concentrations. N Engl J Med 1994: 331: Hamada T, Fukuda S, Ishii N et al. Genotype-phenotype correlation in non-hallopeau-siemens recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: the splice site mutation c g> in the COL7A1 gene results in aberrant and normal splicings. J Dermatol Sci 2008: 50: van der Kooi AJ, van Langen IM, Aronica E et al. Extension of the clinical spectrum of Danon disease. Neurology 2008: 70: Yang Z, McMahon CJ, Smith LR et al. Danon disease as an underrecognized cause of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in children. Circulation 2005: 112:
A 12 year-old-boy with proximal muscle weakness and cardiomyopathy
 A 12 year-old-boy with proximal muscle weakness and cardiomyopathy Samra Vazirian, M.D.*, Kara Jones, M.D. Ph.D.#, Steven Moore, M.D. Ph.D.#, Perry B. Shieh, M.D. Ph.D.* *University of California, Los
A 12 year-old-boy with proximal muscle weakness and cardiomyopathy Samra Vazirian, M.D.*, Kara Jones, M.D. Ph.D.#, Steven Moore, M.D. Ph.D.#, Perry B. Shieh, M.D. Ph.D.* *University of California, Los
DMD Genetics: complicated, complex and critical to understand
 DMD Genetics: complicated, complex and critical to understand Stanley Nelson, MD Professor of Human Genetics, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and Psychiatry Co Director, Center for Duchenne Muscular
DMD Genetics: complicated, complex and critical to understand Stanley Nelson, MD Professor of Human Genetics, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and Psychiatry Co Director, Center for Duchenne Muscular
Differentiation-induced Changes of Mediterranean Fever Gene (MEFV) Expression in HL-60 Cell
 Differentiation-induced Changes of Mediterranean Fever Gene (MEFV) Expression in HL-60 Cell Wenxin Li Department of Biological Sciences Fordham University Abstract MEFV is a human gene that codes for an
Differentiation-induced Changes of Mediterranean Fever Gene (MEFV) Expression in HL-60 Cell Wenxin Li Department of Biological Sciences Fordham University Abstract MEFV is a human gene that codes for an
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_duchenne_and_becker_muscular_dystrophy
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_duchenne_and_becker_muscular_dystrophy
variant led to a premature stop codon p.k316* which resulted in nonsense-mediated mrna decay. Although the exact function of the C19L1 is still
 157 Neurological disorders primarily affect and impair the functioning of the brain and/or neurological system. Structural, electrical or metabolic abnormalities in the brain or neurological system can
157 Neurological disorders primarily affect and impair the functioning of the brain and/or neurological system. Structural, electrical or metabolic abnormalities in the brain or neurological system can
Novel LAMP-2 Mutation in a Family With Danon Disease Presenting With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
 CASE REPORT Circ J 2009; 73: 376 380 Novel LAMP-2 Mutation in a Family With Danon Disease Presenting With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Nobuhiro Dougu, MD*, ; Shuji Joho, MD**, ; Lishen Shan, MD, ; Takuya
CASE REPORT Circ J 2009; 73: 376 380 Novel LAMP-2 Mutation in a Family With Danon Disease Presenting With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Nobuhiro Dougu, MD*, ; Shuji Joho, MD**, ; Lishen Shan, MD, ; Takuya
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Identification and characterization of multiple splice variants of Cdc2-like kinase 4 (Clk4)
 Identification and characterization of multiple splice variants of Cdc2-like kinase 4 (Clk4) Vahagn Stepanyan Department of Biological Sciences, Fordham University Abstract: Alternative splicing is an
Identification and characterization of multiple splice variants of Cdc2-like kinase 4 (Clk4) Vahagn Stepanyan Department of Biological Sciences, Fordham University Abstract: Alternative splicing is an
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29354 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Straathof, Chiara Title: dystrophinopathies : heterogeneous clinical aspects of
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29354 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Straathof, Chiara Title: dystrophinopathies : heterogeneous clinical aspects of
SALSA MLPA KIT P060-B2 SMA
 SALSA MLPA KIT P6-B2 SMA Lot 111, 511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot 11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). Please note that, in contrast to the
SALSA MLPA KIT P6-B2 SMA Lot 111, 511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot 11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). Please note that, in contrast to the
Muscular Dystrophy. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
TITLE: CYP1B1 Polymorphism as a Risk Factor for Race-Related Prostate Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0579 TITLE: CYP1B1 Polymorphism as a Risk Factor for Race-Related Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yuichiro Tanaka, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Northern California
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0579 TITLE: CYP1B1 Polymorphism as a Risk Factor for Race-Related Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yuichiro Tanaka, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Northern California
READ ORPHA.NET WEBSITE ABOUT BETA-SARCOGLYOCANOPATHY LIMB-GIRDLE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES
 READ ORPHA.NET WEBSITE ABOUT BETA-SARCOGLYOCANOPATHY LIMB-GIRDLE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES (LGMD) Limb-girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMD) are a heterogeneous group of genetically determined disorders with a
READ ORPHA.NET WEBSITE ABOUT BETA-SARCOGLYOCANOPATHY LIMB-GIRDLE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES (LGMD) Limb-girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMD) are a heterogeneous group of genetically determined disorders with a
Clinical Genetics in Cardiomyopathies
 Clinical Genetics in Cardiomyopathies Γεώργιος Κ Ευθυμιάδης Αναπληρωτής Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας ΑΠΘ No conflict of interest Genetic terms Proband: The first individual diagnosed in a family Mutation: A
Clinical Genetics in Cardiomyopathies Γεώργιος Κ Ευθυμιάδης Αναπληρωτής Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας ΑΠΘ No conflict of interest Genetic terms Proband: The first individual diagnosed in a family Mutation: A
Identification of a novel duplication mutation in the VHL gene in a large Chinese family with Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome
 Identification of a novel duplication mutation in the VHL gene in a large Chinese family with Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome L.H. Cao 1, B.H. Kuang 2, C. Chen 1, C. Hu 2, Z. Sun 1, H. Chen 2, S.S. Wang
Identification of a novel duplication mutation in the VHL gene in a large Chinese family with Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome L.H. Cao 1, B.H. Kuang 2, C. Chen 1, C. Hu 2, Z. Sun 1, H. Chen 2, S.S. Wang
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Yatsenko AN, Georgiadis AP, Röpke A, et al. X-linked TEX11
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Yatsenko AN, Georgiadis AP, Röpke A, et al. X-linked TEX11
Reporting TP53 gene analysis results in CLL
 Reporting TP53 gene analysis results in CLL Mutations in TP53 - From discovery to clinical practice in CLL Discovery Validation Clinical practice Variant diversity *Leroy at al, Cancer Research Review
Reporting TP53 gene analysis results in CLL Mutations in TP53 - From discovery to clinical practice in CLL Discovery Validation Clinical practice Variant diversity *Leroy at al, Cancer Research Review
A guide to understanding variant classification
 White paper A guide to understanding variant classification In a diagnostic setting, variant classification forms the basis for clinical judgment, making proper classification of variants critical to your
White paper A guide to understanding variant classification In a diagnostic setting, variant classification forms the basis for clinical judgment, making proper classification of variants critical to your
Identifying Mutations Responsible for Rare Disorders Using New Technologies
 Identifying Mutations Responsible for Rare Disorders Using New Technologies Jacek Majewski, Department of Human Genetics, McGill University, Montreal, QC Canada Mendelian Diseases Clear mode of inheritance
Identifying Mutations Responsible for Rare Disorders Using New Technologies Jacek Majewski, Department of Human Genetics, McGill University, Montreal, QC Canada Mendelian Diseases Clear mode of inheritance
JULY 21, Genetics 101: SCN1A. Katie Angione, MS CGC Certified Genetic Counselor CHCO Neurology
 JULY 21, 2018 Genetics 101: SCN1A Katie Angione, MS CGC Certified Genetic Counselor CHCO Neurology Disclosures: I have no financial interests or relationships to disclose. Objectives 1. Review genetic
JULY 21, 2018 Genetics 101: SCN1A Katie Angione, MS CGC Certified Genetic Counselor CHCO Neurology Disclosures: I have no financial interests or relationships to disclose. Objectives 1. Review genetic
2011 HCM Guideline Data Supplements
 Data Supplement 1. Genetics Table Study Name/Author (Citation) Aim of Study Quality of life and psychological distress quality of life and in mutation psychological carriers: a crosssectional distress
Data Supplement 1. Genetics Table Study Name/Author (Citation) Aim of Study Quality of life and psychological distress quality of life and in mutation psychological carriers: a crosssectional distress
The Human Major Histocompatibility Complex
 The Human Major Histocompatibility Complex 1 Location and Organization of the HLA Complex on Chromosome 6 NEJM 343(10):702-9 2 Inheritance of the HLA Complex Haplotype Inheritance (Family Study) 3 Structure
The Human Major Histocompatibility Complex 1 Location and Organization of the HLA Complex on Chromosome 6 NEJM 343(10):702-9 2 Inheritance of the HLA Complex Haplotype Inheritance (Family Study) 3 Structure
Introduction to Genetics
 Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation
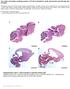 The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation Anita Becker-Heck#, Irene Zohn#, Noriko Okabe#, Andrew Pollock#, Kari Baker Lenhart,
The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation Anita Becker-Heck#, Irene Zohn#, Noriko Okabe#, Andrew Pollock#, Kari Baker Lenhart,
CANCER GENETICS PROVIDER SURVEY
 Dear Participant, Previously you agreed to participate in an evaluation of an education program we developed for primary care providers on the topic of cancer genetics. This is an IRB-approved, CDCfunded
Dear Participant, Previously you agreed to participate in an evaluation of an education program we developed for primary care providers on the topic of cancer genetics. This is an IRB-approved, CDCfunded
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 19;
 SALSA MLPA probemix P6-B2 SMA Lot B2-712, B2-312, B2-111, B2-511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot B1-11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). SPINAL
SALSA MLPA probemix P6-B2 SMA Lot B2-712, B2-312, B2-111, B2-511: As compared to the previous version B1 (lot B1-11), the 88 and 96 nt DNA Denaturation control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). SPINAL
AIDS - Knowledge and Dogma. Conditions for the Emergence and Decline of Scientific Theories Congress, July 16/ , Vienna, Austria
 AIDS - Knowledge and Dogma Conditions for the Emergence and Decline of Scientific Theories Congress, July 16/17 2010, Vienna, Austria Reliability of PCR to detect genetic sequences from HIV Juan Manuel
AIDS - Knowledge and Dogma Conditions for the Emergence and Decline of Scientific Theories Congress, July 16/17 2010, Vienna, Austria Reliability of PCR to detect genetic sequences from HIV Juan Manuel
NGS panels in clinical diagnostics: Utrecht experience. Van Gijn ME PhD Genome Diagnostics UMCUtrecht
 NGS panels in clinical diagnostics: Utrecht experience Van Gijn ME PhD Genome Diagnostics UMCUtrecht 93 Gene panels UMC Utrecht Cardiovascular disease (CAR) (5 panels) Epilepsy (EPI) (11 panels) Hereditary
NGS panels in clinical diagnostics: Utrecht experience Van Gijn ME PhD Genome Diagnostics UMCUtrecht 93 Gene panels UMC Utrecht Cardiovascular disease (CAR) (5 panels) Epilepsy (EPI) (11 panels) Hereditary
Concurrent Practical Session ACMG Classification
 Variant Effect Prediction Training Course 6-8 November 2017 Prague, Czech Republic Concurrent Practical Session ACMG Classification Andreas Laner / Anna Benet-Pagès 1 Content 1. Background... 3 2. Aim
Variant Effect Prediction Training Course 6-8 November 2017 Prague, Czech Republic Concurrent Practical Session ACMG Classification Andreas Laner / Anna Benet-Pagès 1 Content 1. Background... 3 2. Aim
Genome - Wide Linkage Mapping
 Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Genome - Wide Linkage Mapping Introduction This activity is based on the work of Dr. Christine Seidman et al that was published in Circulation, 1998, vol 97, pgs 2043-2048.
Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Genome - Wide Linkage Mapping Introduction This activity is based on the work of Dr. Christine Seidman et al that was published in Circulation, 1998, vol 97, pgs 2043-2048.
NGS in tissue and liquid biopsy
 NGS in tissue and liquid biopsy Ana Vivancos, PhD Referencias So, why NGS in the clinics? 2000 Sanger Sequencing (1977-) 2016 NGS (2006-) ABIPrism (Applied Biosystems) Up to 2304 per day (96 sequences
NGS in tissue and liquid biopsy Ana Vivancos, PhD Referencias So, why NGS in the clinics? 2000 Sanger Sequencing (1977-) 2016 NGS (2006-) ABIPrism (Applied Biosystems) Up to 2304 per day (96 sequences
Supplementary methods:
 Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
IVF Michigan, Rochester Hills, Michigan, and Reproductive Genetics Institute, Chicago, Illinois
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 80, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 Copyright 2003 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS Preimplantation
FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 80, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2003 Copyright 2003 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. CASE REPORTS Preimplantation
Beta Thalassemia Case Study Introduction to Bioinformatics
 Beta Thalassemia Case Study Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA sami.khuri@sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline v Hemoglobin v Alpha
Beta Thalassemia Case Study Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA sami.khuri@sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline v Hemoglobin v Alpha
Muscle Metabolism. Dr. Nabil Bashir
 Muscle Metabolism Dr. Nabil Bashir Learning objectives Understand how skeletal muscles derive energy at rest, moderate exercise, and strong exercise. Recognize the difference between aerobic and anaerobic
Muscle Metabolism Dr. Nabil Bashir Learning objectives Understand how skeletal muscles derive energy at rest, moderate exercise, and strong exercise. Recognize the difference between aerobic and anaerobic
Genetic Cardiomyopathies
 2017 HFCT Annual Scientific Meeting The Heart Failure Crosstalk Genetic Cardiomyopathies Teerapat Yingchoncharoen M.D. Ramathibodi Hospital Cardiomyopathy Group of diseases of the myocardium associated
2017 HFCT Annual Scientific Meeting The Heart Failure Crosstalk Genetic Cardiomyopathies Teerapat Yingchoncharoen M.D. Ramathibodi Hospital Cardiomyopathy Group of diseases of the myocardium associated
MEDICAL GENOMICS LABORATORY. Non-NF1 RASopathy panel by Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of SPRED1 (NNP-NG)
 Non-NF1 RASopathy panel by Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of SPRED1 (NNP-NG) Ordering Information Acceptable specimen types: Blood (3-6ml EDTA; no time limitations associated with
Non-NF1 RASopathy panel by Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of SPRED1 (NNP-NG) Ordering Information Acceptable specimen types: Blood (3-6ml EDTA; no time limitations associated with
Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3. Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented in our
 1 2 Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3 Mutations 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented
1 2 Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3 Mutations 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented
Patient Identification: Patient Name (first, middle, last)
 Patient Identification: Patient Name (first, middle, last) Patient s USIDNET Registry Number assigned after online enrollment Date of Birth / / (mm/dd/yyyy) or Year of Birth Gender: male [ ], female [
Patient Identification: Patient Name (first, middle, last) Patient s USIDNET Registry Number assigned after online enrollment Date of Birth / / (mm/dd/yyyy) or Year of Birth Gender: male [ ], female [
HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report
 Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders
 Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
The Organism as a system
 The Organism as a system PATIENT 1: Seven-year old female with a history of normal development until age two. At this point she developed episodic vomiting, acidosis, epilepsy, general weakness, ataxia
The Organism as a system PATIENT 1: Seven-year old female with a history of normal development until age two. At this point she developed episodic vomiting, acidosis, epilepsy, general weakness, ataxia
Proteins. Length of protein varies from thousands of amino acids to only a few insulin only 51 amino acids
 Proteins Protein carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and often sulphur Length of protein varies from thousands of amino acids to only a few insulin only 51 amino acids During protein synthesis, amino acids
Proteins Protein carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and often sulphur Length of protein varies from thousands of amino acids to only a few insulin only 51 amino acids During protein synthesis, amino acids
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Loeys-Dietz Syndrome OMIM number for disease 609192; 608967; 610380; 610168 Disease
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Loeys-Dietz Syndrome OMIM number for disease 609192; 608967; 610380; 610168 Disease
Preclinical Data on RP-A501, the First Gene Therapy to Treat a Monogenic Heart Failure Syndrome. Company Webcast November 26, 2018
 Preclinical Data on RP-A501, the First Gene Therapy to Treat a Monogenic Heart Failure Syndrome Company Webcast November 26, 2018 Attendees Speakers Gaurav Shah, M.D., Chief Executive Officer & President
Preclinical Data on RP-A501, the First Gene Therapy to Treat a Monogenic Heart Failure Syndrome Company Webcast November 26, 2018 Attendees Speakers Gaurav Shah, M.D., Chief Executive Officer & President
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Leber congenital amaurosis OMIM number for disease 204000 Disease alternative
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Leber congenital amaurosis OMIM number for disease 204000 Disease alternative
BIOCHEMICAL INVESTIGATIONS IN THE DIAGNOSTICS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS. As. MARUSHCHAK M.I.
 BIOCHEMICAL INVESTIGATIONS IN THE DIAGNOSTICS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS As. MARUSHCHAK M.I. Heart attack symptoms Acute MI Measurement of cardiac enzyme levels Measure cardiac enzyme levels at regular
BIOCHEMICAL INVESTIGATIONS IN THE DIAGNOSTICS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS As. MARUSHCHAK M.I. Heart attack symptoms Acute MI Measurement of cardiac enzyme levels Measure cardiac enzyme levels at regular
Mutations and Disease Mutations in the Myosin Gene
 Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Mutations and Disease Mutations in the Myosin Gene Goals Explore how mutations can lead to disease using the myosin gene as a model system. Explore how changes in the
Biological Sciences Initiative HHMI Mutations and Disease Mutations in the Myosin Gene Goals Explore how mutations can lead to disease using the myosin gene as a model system. Explore how changes in the
Molecular Characterization of the NF2 Gene in Korean Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type 2: A Report of Four Novel Mutations
 Korean J Lab Med 2010;30:190-4 DOI 10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.2.190 Original Article Diagnostic Genetics Molecular Characterization of the NF2 Gene in Korean Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type 2: A Report
Korean J Lab Med 2010;30:190-4 DOI 10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.2.190 Original Article Diagnostic Genetics Molecular Characterization of the NF2 Gene in Korean Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type 2: A Report
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Choroideremia OMIM number for disease 303100 Disease alternative names please
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Choroideremia OMIM number for disease 303100 Disease alternative names please
SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1]
![SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1] SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1]](/thumbs/72/67086153.jpg) SMA OVERVIEW SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1] Autosomal recessive genetic inheritance 1 in 50 people (approximately 6 million Americans) are carriers [2] 1 in 6,000 to 1 in 10,000 children born
SMA OVERVIEW SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1] Autosomal recessive genetic inheritance 1 in 50 people (approximately 6 million Americans) are carriers [2] 1 in 6,000 to 1 in 10,000 children born
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
 Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy From Genetics to ECHO Alexandra A Frogoudaki Second Cardiology Department ATTIKON University Hospital Athens University Athens, Greece EUROECHO 2010, Copenhagen, 11/12/2010
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy From Genetics to ECHO Alexandra A Frogoudaki Second Cardiology Department ATTIKON University Hospital Athens University Athens, Greece EUROECHO 2010, Copenhagen, 11/12/2010
Declaration of conflict of interest. I have nothing to disclose.
 Declaration of conflict of interest I have nothing to disclose. Left Bundle branch block in HF: DO GENETICS MATTER? Silvia Giuliana Priori Cardiovascular Genetics, Langone Medical Center, New York University
Declaration of conflict of interest I have nothing to disclose. Left Bundle branch block in HF: DO GENETICS MATTER? Silvia Giuliana Priori Cardiovascular Genetics, Langone Medical Center, New York University
A rare variant in MYH6 confers high risk of sick sinus syndrome. Hilma Hólm ESC Congress 2011 Paris, France
 A rare variant in MYH6 confers high risk of sick sinus syndrome Hilma Hólm ESC Congress 2011 Paris, France Disclosures I am an employee of decode genetics, Reykjavik, Iceland. Sick sinus syndrome SSS is
A rare variant in MYH6 confers high risk of sick sinus syndrome Hilma Hólm ESC Congress 2011 Paris, France Disclosures I am an employee of decode genetics, Reykjavik, Iceland. Sick sinus syndrome SSS is
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II
 MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names Osteogenesis Imperfecta
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Kidney Int. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 September 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2011 March ; 79(6): 691 692. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.514. The case: Familial occurrence of retinitis pigmentosa, deafness
RISK OF FMF DEVELOPMENT AMONG HETEROZYGOUS PATIENTS IN ARMENIAN POPULATION
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE YEREVAN STATE UNIVERSITY C h e m i s t r y a n d B i o l o g y 2016, 3, p. 48 52 RISK OF FMF DEVELOPMENT AMONG HETEROZYGOUS PATIENTS IN ARMENIAN POPULATION B i o l o g y H. S. HAYRAPETYAN
PROCEEDINGS OF THE YEREVAN STATE UNIVERSITY C h e m i s t r y a n d B i o l o g y 2016, 3, p. 48 52 RISK OF FMF DEVELOPMENT AMONG HETEROZYGOUS PATIENTS IN ARMENIAN POPULATION B i o l o g y H. S. HAYRAPETYAN
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 A S100A4: SFLGKRTDEAAFQKLMSNLDSNRDNEVDFQEYCVFLSCIAMMCNEFFEGFPDK Overlap: SF G DE KLM LD N D VDFQEY VFL I M N FF G PD S100A2: SFVGEKVDEEGLKKLMGSLDENSDQQVDFQEYAVFLALITVMCNDFFQGCPDR
Supplemental Figure 1 A S100A4: SFLGKRTDEAAFQKLMSNLDSNRDNEVDFQEYCVFLSCIAMMCNEFFEGFPDK Overlap: SF G DE KLM LD N D VDFQEY VFL I M N FF G PD S100A2: SFVGEKVDEEGLKKLMGSLDENSDQQVDFQEYAVFLALITVMCNDFFQGCPDR
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Table S1. Primers and PCR protocols for mutation screening of MN1, NF2, KREMEN1 and ZNRF3.
 Table S1. Primers and PCR protocols for mutation screening of MN1, NF2, KREMEN1 and ZNRF3. MN1 (Accession No. NM_002430) MN1-1514F 5 -GGCTGTCATGCCCTATTGAT Exon 1 MN1-1882R 5 -CTGGTGGGGATGATGACTTC Exon
Table S1. Primers and PCR protocols for mutation screening of MN1, NF2, KREMEN1 and ZNRF3. MN1 (Accession No. NM_002430) MN1-1514F 5 -GGCTGTCATGCCCTATTGAT Exon 1 MN1-1882R 5 -CTGGTGGGGATGATGACTTC Exon
Diagnostic difficulties in prevention and control program for thalassemia in Thailand: atypical thalassemia carriers
 Diagnostic difficulties in prevention and control program for thalassemia in Thailand: atypical thalassemia carriers Pranee Winichagoon Fucharoen Thalassemia Research Center Institute of Molecular Biosciences
Diagnostic difficulties in prevention and control program for thalassemia in Thailand: atypical thalassemia carriers Pranee Winichagoon Fucharoen Thalassemia Research Center Institute of Molecular Biosciences
Index. derm.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesion and migration, the diverse functions of the laminin a3 subunit, 79 87 Alopecia in epidermolysis bullosa, 165 169 Amblyopia and inherited
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesion and migration, the diverse functions of the laminin a3 subunit, 79 87 Alopecia in epidermolysis bullosa, 165 169 Amblyopia and inherited
Introduction. Introduction
 Introduction We are leveraging genome sequencing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) to more accurately define mutated and stable genes and dysregulated metabolic pathways in solid tumors. These efforts
Introduction We are leveraging genome sequencing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) to more accurately define mutated and stable genes and dysregulated metabolic pathways in solid tumors. These efforts
Name Animal source Vendor Cat # Dilutions
 Supplementary data Table S1. Primary and Secondary antibody sources Devi et al, TXNIP in mitophagy A. Primary Antibodies Name Animal source Vendor Cat # Dilutions 1. TXNIP mouse MBL KO205-2 1:2000 (WB)
Supplementary data Table S1. Primary and Secondary antibody sources Devi et al, TXNIP in mitophagy A. Primary Antibodies Name Animal source Vendor Cat # Dilutions 1. TXNIP mouse MBL KO205-2 1:2000 (WB)
Paula Clemens NS-065/NCNP-01 Study Chair
 A Phase II, Dose Finding Study to Assess the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of NS-065/NCNP-01 in Boys with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) Paula Clemens NS-065/NCNP-01 Study
A Phase II, Dose Finding Study to Assess the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of NS-065/NCNP-01 in Boys with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) Paula Clemens NS-065/NCNP-01 Study
MEDICAL GENOMICS LABORATORY. Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of NF1 Only (NF1-NG)
 Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of NF1 Only (NF1-NG) Ordering Information Acceptable specimen types: Fresh blood sample (3-6 ml EDTA; no time limitations associated with receipt)
Next-Gen Sequencing and Deletion/Duplication Analysis of NF1 Only (NF1-NG) Ordering Information Acceptable specimen types: Fresh blood sample (3-6 ml EDTA; no time limitations associated with receipt)
Genotype-Phenotype in Egyptian Patients with Nephropathic Cystinosis. (December 2012 report)
 Genotype-Phenotype in Egyptian Patients with Nephropathic Cystinosis (December 2012 report) This is the first study of the genotype of Nephropathic Cystinosis (NC) patients in Egypt and the region of North
Genotype-Phenotype in Egyptian Patients with Nephropathic Cystinosis (December 2012 report) This is the first study of the genotype of Nephropathic Cystinosis (NC) patients in Egypt and the region of North
BIOCHEMICAL AND MOLECULAR HETEROGENEITY IN CARNITINE PALMITOYLTRANSFERASE II DEFICIENCY
 BIOCHEMICAL AND MOLECULAR HETEROGENEITY IN CARNITINE PALMITOYLTRANSFERASE II DEFICIENCY Carmen Sousa, Helena Fonseca, Hugo Rocha, Ana Marcão, Laura Vilarinho, Luísa Diogo, Sílvia Sequeira, Cristina Costa,
BIOCHEMICAL AND MOLECULAR HETEROGENEITY IN CARNITINE PALMITOYLTRANSFERASE II DEFICIENCY Carmen Sousa, Helena Fonseca, Hugo Rocha, Ana Marcão, Laura Vilarinho, Luísa Diogo, Sílvia Sequeira, Cristina Costa,
Kit Components Product # EP42720 (24 preps) MDx 2X PCR Master Mix 350 µl Cryptococcus neoformans Primer Mix 70 µl Cryptococcus neoformans Positive
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cryptococcus neoformans End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42720 Product
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cryptococcus neoformans End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42720 Product
What do you think of when you here the word genome?
 What do you think of when you here the word genome? What do you think of when you here the word genome? Personal Genomics Outline Review of pre-lab work Genomics and Medicine Case Overview & Assignment
What do you think of when you here the word genome? What do you think of when you here the word genome? Personal Genomics Outline Review of pre-lab work Genomics and Medicine Case Overview & Assignment
The Meaning of Genetic Variation
 Activity 2 The Meaning of Genetic Variation Focus: Students investigate variation in the beta globin gene by identifying base changes that do and do not alter function, and by using several CD-ROM-based
Activity 2 The Meaning of Genetic Variation Focus: Students investigate variation in the beta globin gene by identifying base changes that do and do not alter function, and by using several CD-ROM-based
Ambient temperature regulated flowering time
 Ambient temperature regulated flowering time Applications of RNAseq RNA- seq course: The power of RNA-seq June 7 th, 2013; Richard Immink Overview Introduction: Biological research question/hypothesis
Ambient temperature regulated flowering time Applications of RNAseq RNA- seq course: The power of RNA-seq June 7 th, 2013; Richard Immink Overview Introduction: Biological research question/hypothesis
What Clinicians Need to Know About Genetic Testing for Patients and Families with HCM
 What Clinicians Need to Know About Genetic Testing for Patients and Families with HCM Sharon Cresci, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Assistant Professor of Genetics Cardiovascular Division Washington
What Clinicians Need to Know About Genetic Testing for Patients and Families with HCM Sharon Cresci, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Assistant Professor of Genetics Cardiovascular Division Washington
Basic Definitions. Dr. Mohammed Hussein Assi MBChB MSc DCH (UK) MRCPCH
 Basic Definitions Chromosomes There are two types of chromosomes: autosomes (1-22) and sex chromosomes (X & Y). Humans are composed of two groups of cells: Gametes. Ova and sperm cells, which are haploid,
Basic Definitions Chromosomes There are two types of chromosomes: autosomes (1-22) and sex chromosomes (X & Y). Humans are composed of two groups of cells: Gametes. Ova and sperm cells, which are haploid,
Gene therapy and genome editing technologies for the study and potential treatment of :
 WORKSHOP ON GENOME EDITING Gene therapy and genome editing technologies for the study and potential treatment of : Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy by Dr France Piétri-Rouxel, Institut de Myologie Centre de
WORKSHOP ON GENOME EDITING Gene therapy and genome editing technologies for the study and potential treatment of : Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy by Dr France Piétri-Rouxel, Institut de Myologie Centre de
Glycogen Storage Disease Type III also known as Cori or Forbe s Disease/Debrancher Enzyme Deficiency
 Glycogen Storage Disease Type III also known as Cori or Forbe s Disease/Debrancher Enzyme Deficiency What is GSDIII? Glycogen Storage Disease type 3 is an inherited condition caused by a defect in a gene
Glycogen Storage Disease Type III also known as Cori or Forbe s Disease/Debrancher Enzyme Deficiency What is GSDIII? Glycogen Storage Disease type 3 is an inherited condition caused by a defect in a gene
What favorite organism of geneticists is described in the right-hand column?
 What favorite organism of geneticists is described in the right-hand column? Model Organism fruit fly?? Generation time 12 days ~ 5000 days Size 2 mm 1500-1800mm Brood size hundreds a couple dozen would
What favorite organism of geneticists is described in the right-hand column? Model Organism fruit fly?? Generation time 12 days ~ 5000 days Size 2 mm 1500-1800mm Brood size hundreds a couple dozen would
Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8
 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
THE ROLE OF CFTR MUTATIONS IN CAUSING CYSTIC FIBROSIS (CF)
 THE ROLE OF CFTR MUTATIONS IN CAUSING CYSTIC FIBROSIS (CF) Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated, 50 Northern Avenue, Boston, MA 02210. Vertex and the Vertex triangle logo are registered trademarks for Vertex
THE ROLE OF CFTR MUTATIONS IN CAUSING CYSTIC FIBROSIS (CF) Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated, 50 Northern Avenue, Boston, MA 02210. Vertex and the Vertex triangle logo are registered trademarks for Vertex
How many disease-causing variants in a normal person? Matthew Hurles
 How many disease-causing variants in a normal person? Matthew Hurles Summary What is in a genome? What is normal? Depends on age What is a disease-causing variant? Different classes of variation Final
How many disease-causing variants in a normal person? Matthew Hurles Summary What is in a genome? What is normal? Depends on age What is a disease-causing variant? Different classes of variation Final
Pedigree Analysis. A = the trait (a genetic disease or abnormality, dominant) a = normal (recessive)
 Pedigree Analysis Introduction A pedigree is a diagram of family relationships that uses symbols to represent people and lines to represent genetic relationships. These diagrams make it easier to visualize
Pedigree Analysis Introduction A pedigree is a diagram of family relationships that uses symbols to represent people and lines to represent genetic relationships. These diagrams make it easier to visualize
Section Chapter 14. Go to Section:
 Section 12-3 Chapter 14 Go to Section: Content Objectives Write these Down! I will be able to identify: The origin of genetic differences among organisms. The possible kinds of different mutations. The
Section 12-3 Chapter 14 Go to Section: Content Objectives Write these Down! I will be able to identify: The origin of genetic differences among organisms. The possible kinds of different mutations. The
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Contribution of genetics for sudden death risk stratification in dilated cardiomyopathy
 Contribution of genetics for sudden death risk stratification in dilated cardiomyopathy Pr Philippe Charron Centre de Référence pour les maladies cardiaques héréditaires (1) Hôpital Ambroise Paré, Boulogne
Contribution of genetics for sudden death risk stratification in dilated cardiomyopathy Pr Philippe Charron Centre de Référence pour les maladies cardiaques héréditaires (1) Hôpital Ambroise Paré, Boulogne
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. showed that all three replicates had similar growth trends (Figure 4.1) (p<0.05; p=0.0000)
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
Case Report GNE Myopathy in Turkish Sisters with a Novel Homozygous Mutation
 Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 8647645, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8647645 Case Report GNE Myopathy in Turkish Sisters with a Novel Homozygous Mutation Gulden
Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 8647645, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8647645 Case Report GNE Myopathy in Turkish Sisters with a Novel Homozygous Mutation Gulden
We have addressed each of the reviewers comments point by point below, and marked all changes to the revised manuscript in red.
 Author s response to reviews Title: A novel frameshift GRN mutation results in frontotemporal lobar degeneration with a distinct clinical phenotype in two siblings: case report and literature review Authors:
Author s response to reviews Title: A novel frameshift GRN mutation results in frontotemporal lobar degeneration with a distinct clinical phenotype in two siblings: case report and literature review Authors:
Lab Activity Report: Mendelian Genetics - Genetic Disorders
 Name Date Period Lab Activity Report: Mendelian Genetics - Genetic Disorders Background: Sometimes genetic disorders are caused by mutations to normal genes. When the mutation has been in the population
Name Date Period Lab Activity Report: Mendelian Genetics - Genetic Disorders Background: Sometimes genetic disorders are caused by mutations to normal genes. When the mutation has been in the population
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of alternative-cassette-exon engagement with the ribosome is consistent across data from multiple human cell types and from mouse stem cells. Box plots showing AS frequency
Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of alternative-cassette-exon engagement with the ribosome is consistent across data from multiple human cell types and from mouse stem cells. Box plots showing AS frequency
MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS for X-LINKED INTELLECTUAL DISABILITY
 MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS for X-LINKED INTELLECTUAL DISABILITY Intellectual disability (ID) or mental retardation is characterized by significant limitations in cognitive abilities and social/behavioral adaptive
MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS for X-LINKED INTELLECTUAL DISABILITY Intellectual disability (ID) or mental retardation is characterized by significant limitations in cognitive abilities and social/behavioral adaptive
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Invasive Prenatal (Fetal) Diagnostic Testing File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: invasive_prenatal_(fetal)_diagnostic_testing 12/2014 3/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Invasive Prenatal (Fetal) Diagnostic Testing File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: invasive_prenatal_(fetal)_diagnostic_testing 12/2014 3/2018
Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation
 Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation The number of mechanisms that are known to be involved in splicing regulation approximates the number of splicing decisions that have been analyzed in detail.
Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation The number of mechanisms that are known to be involved in splicing regulation approximates the number of splicing decisions that have been analyzed in detail.
Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 9: Genetics of Cancer Worksheet
 Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 9: Genetics of Cancer Worksheet All cancer is due to genetic mutations. However, in cancer that clusters in families (familial cancer) at least one of these mutations
Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 9: Genetics of Cancer Worksheet All cancer is due to genetic mutations. However, in cancer that clusters in families (familial cancer) at least one of these mutations
Iowa Wellstone Center Muscle Tissue and Cell Culture Repository
 Iowa Wellstone Center Muscle Tissue and Cell Culture Repository Steven A. Moore, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Iowa Department of Pathology and Iowa Wellstone Muscular Dystrophy Cooperative Research Center
Iowa Wellstone Center Muscle Tissue and Cell Culture Repository Steven A. Moore, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Iowa Department of Pathology and Iowa Wellstone Muscular Dystrophy Cooperative Research Center
Familial DilatedCardiomyopathy Georgios K Efthimiadis, MD
 Familial DilatedCardiomyopathy Georgios K Efthimiadis, MD Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dilated LV/RV, reduced EF, in the absence of CAD valvulopathy pericardial disease Prevalence:40/100.000 persons Natural
Familial DilatedCardiomyopathy Georgios K Efthimiadis, MD Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dilated LV/RV, reduced EF, in the absence of CAD valvulopathy pericardial disease Prevalence:40/100.000 persons Natural
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier/Additional Provider
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier/Additional Provider TEST DISORDER/CONDITION POPULATION TRIAD Submitting laboratory: Exeter RGC Approved: Sept 2013 1. Disorder/condition
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier/Additional Provider TEST DISORDER/CONDITION POPULATION TRIAD Submitting laboratory: Exeter RGC Approved: Sept 2013 1. Disorder/condition
