2016 Georgia Society of Health-System Pharmacists Summer Meeting CV Risk Factors: Emerging Data on Management of Type 2 Diabetes and Hypertension
|
|
|
- Warren Hudson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2016 Georgia Society of Health-System Pharmacists Summer Meeting CV Risk Factors: Emerging Data on Management of Type 2 Diabetes and Hypertension Jeff Langford, PharmD BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Cardiology University Health Care System Augusta, GA
2 Disclosure No relationships to disclose.
3 Learning Objectives 1. Describe cardiovascular (CV) outcome data for dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP 4) inhibitors and sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. 2. Optimize a treatment plan for type 2 diabetes (DM2) based on current evidence and patient specific factors. 3. Identify blood pressure (BP) treatment goals based on current clinical practice guidelines and recent evidence. 4. Select an evidence based blood pressure treatment goal based upon patient specific factors.
4 Select Abbreviations A1C = hemoglobin A1C HF = heart failure ACS = acute coronary syndrome HTN = hypertension AE = adverse events HPL = hyperlipidemia ASA = aspirin LFT = liver function test ASCVD = atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease MACE = major adverse cardiac event CAD = coronary artery disease MI = myocardial infarction CV = cardiovascular NNT = number needed to treat CVD = cardiovascular disease NS= non significant DM2 = type 2 diabetes PAD = peripheral arterial disease DPP 4 I = dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor RR = relative risk EF = ejection fraction RRR = relative risk reduction ESRD = end stage renal disease SAE = serious adverse events GFR = glomerular filtration rate SGLT2 I = sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor GIP = glucose dependent insulinotropic polypeptide TZD = thiazolidinedione GLP 1 = glucagon like peptide 1 TIA = transient ischemic attack HD = hemodialysis ULN = upper limit of normal
5 Obesity Inactivity Smoking CV Risk Factors Modifiable DM Non modifiable Risk Factors Age Gender Heredity Other contributing factors: Stress Alcohol Diet, nutrition HPL HTN Your Risk of Heart Attack_UCM_002040_Article.jsp#.V1slltIrK7A
6 Diabetes Mellitus: Epidemiology & Impact %20Sean/Documents/Fast_Facts_ a.pdf basics/statistics/cdc infographic.html
7 Diabetes Mellitus: Epidemiology & Impact 2012 Economic Burden DM in US $245 Billion $176 Billion = direct costs 90 95% have DM2 $69 Billion = indirect costs %20Sean/Documents/Fast_Facts_ a.pdf basics/statistics/cdc infographic.html
8 DM2 Hosp for MI & stroke 2 4 fold in CV Disease (CVD) Atherosclerotic CVD (ASCVD): ACS, hx of MI Stable/unstable angina Coronary/arterial revasc Stroke/TIA PAD Life expectancy 6 7 years Holman RR et al. Lancet 2014;383: Skyler JS et al. Circulation. 2009;119: American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2016; 39 (Suppl. 1):S1 S112. ASCVD in DM2: Largest cause of morbidity and mortality Largest driver of direct and indirect costs of care
9 Heart Failure: Frequent, forgotten and often fatal complication of DM DM risk of HF 2 5 fold Not neatly microvascular or macrovascular HF mortality ~ 2 x that of non diabetic population Gilbert RE et al. Lancet 2015; 385:
10 Heart Failure: Frequent, forgotten and often fatal complication of DM DM risk of HF 2 5 fold Cardiotoxic Tetrad Not neatly microvascular or macrovascular HTN Diabetic Cardiomyopathy HF mortality ~ 2 x that of non diabetic population Gilbert RE et al. Lancet 2015; 385: CAD HF in DM Extracellular Fluid Expansion
11 DM2 management is challenged by questions about CV effects related to intensity of treatment & related to drug choice. UGDP 1970 Rosiglitazone 2007 FDA 2008 DPP 4 Inhibitor Studies EMPA REG 2015 UKPDS 1998 ACCORD ADVANCE VADT 2008 Hiatt WR et al. N Engl J Med 2013; 369:
12 Effect of Intensive Glucose Lowering in DM2 UKPDS ACCORD ADVANCE VADT Microvascular Primary CV Endpoint Micro/ macrovascular events Primary CV Endpoint MI 16% (NS) At 10 year follow up: MI Mortality (NS) Mortality Macro (CV) events Mortality Mortality Skyler JS et al. Circulation. 2009; Holman RR et al. Lancet 2014;383:
13 UKPDS ACCORD ADVANCE VADT N ,251 11, Mean age, y Duration of DM, y < Sex M/F % 59/41 61/39 58/42 97/3 History of CVD % NS 35% 32% 40% Median Baseline A1C % A1C Goal < 6 vs vs local guidelines Median Followup, y A1C, % (Intensive vs Standard) < 6.0 vs planned separation of (term early) vs vs vs vs 8.5 Skyler JS et al. Circulation. 2009;
14 UKPDS ACCORD ADVANCE VADT Outcome (NF: nonfatal) Aggregate of DM related endpoint, DM related death, all cause mortality NF MI + NF stroke + CV death Microvascular + macrovascular (NF MI + NF stroke + CV death NF MI + NF stroke + CV death + Hosp HF + revascularization Primary Outcome HR (95% CI) 0.88 ( ) 0.90 ( ) 0.9 ( ) 0.88 ( ) macrovascular 0.94 ( ) Mortality HR (95% CI) 0.94 ( ) 1.22 ( ) 0.93( ) 1.07 ( ) Skyler JS et al. Circulation. 2009; Ray KK et al. Lancet 2009;373:
15 Cardiac Effects of DM2 Therapies Metformin Sulfonylureas TZDs DPP 4 Inhibitors SGLT2 Inhibitors GLP 1 Agonists α Glucosidase Inhibitors ASCVD 1 /? 2 / / 4 HF 3 / 1 ASCVD with 1 st generation agent (tolbutamide) 2 Conflicting results for rosiglitazone 3 HF with saxagliptin and trend to w/ alogliptin; sitagliptin 4 with liraglutide Data in yellow shaded boxes based on CV outcomes trials Gilbert RE et al. Lancet 2015; 385: Kumar R et al. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. doi: /ehjcvp/pvv035
16 2015 AHA/ADA: Prevention of CV Disease in DM2 Statin BP < 140/90 ASA A1C 7% Fox CS et al. Diabetes Care. doi: /dci
17 2015 AHA/ADA: Prevention of CV Disease in DM2 Moderate intensity statin High intensity statin if ASCVD risk 7.5% Statin BP< 140/90 ASA A1C 7% Fox CS et al. Diabetes Care. doi: /dci
18 2015 AHA/ADA: Prevention of CV Disease in DM2 Moderate intensity statin High intensity statin if ASCVD risk 7.5% Statin BP< 140/90 Treatment to include ACEI/ARB Select patients, SBP < 130 mm Hg ASA A1C 7% Fox CS et al. Diabetes Care. doi: /dci
19 2015 AHA/ADA: Prevention of CV Disease in DM2 Moderate intensity statin High intensity statin if ASCVD risk 7.5% Statin BP< 140/90 Treatment to include ACEI/ARB Select patients, SBP < 130 mm Hg ASA A1C 7% For select patients, A1C: < 6.5% or < 8% Fox CS et al. Diabetes Care. doi: /dci
20 2015 AHA/ADA: Prevention of CV Disease in DM2 Moderate intensity statin High intensity statin if ASCVD risk 7.5% Statin BP< 140/90 Tx to include ACEI/ARB For select patients, SBP < 130 Low dose Aspirin for: CVD risk 10% & NO risk of bleed Consider w risk 5 10% ASA A1C 7% For select patients, A1C: < 6.5% or < 8% Fox CS et al. Diabetes Care. doi: /dci
21 CV Outcomes Studies in DM2 Therapies Rosiglitazone? CV Effects 2007 Rosiglitazone Meta analysis (Cochran s Q test, P > 0.10) 43% in risk of MI (p = 0.03) 64% in risk of CV death (p = 0.06) FDA 2008 FDA Guidance for Industry Pre/post approval studies for new DM2 therapies to rule out excess CV risk Emerging CV Outcome Studies DPP 4 inhibitors and SGLT2 inhibitors More data to come Nissen SE et al. N Engl J Med 2007;356: Food and Drug Administration. Published December Accessed June 20, 2016.
22 Question #1 The DPP 4 inhibitor and SGLT2 inhibitor classes for treatment of DM2 improve glycemic control and reduce CV risk. A. True B. False
23 Question #2 Which of the following DM2 medications are associated with an increased risk of HF? A. Sitagliptin B. Empagliflozin C. Saxagliptin D. All of the above
24 DPP 4 Inhibitors Agents Alogliptin Linagliptin Saxagliptin Sitagliptin
25 DPP 4 Inhibitors Agents Profile Alogliptin Linagliptin Saxagliptin Sitagliptin AIC ~ % Weight Hypoglycemia
26 DPP 4 Inhibitors Agents Alogliptin Linagliptin Saxagliptin Sitagliptin Profile AIC ~ % Weight Hypoglycemia? Pancreatitis Arthralgia Hypersensitivity AE: Adverse Effects
27 DPP 4 Inhibitors: Mechanism of Action Incretin Hormones (GLP 1 & GIP) Brain Gut Pancreas Satiety Slows Gastric emptying Insulin Glucagon Muscle Liver GLP 1: glucagon like peptide 1 GIP: glucose dependent insulinotropic polypeptide Glucose Uptake Glucose Production Jose T et al. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2012; 9(2):
28 DPP 4 Inhibitors: Mechanism of Action Incretin Hormones (GLP 1 & GIP) Brain Gut Pancreas Satiety Slows Gastric emptying Insulin Glucagon DPP 4 Inhibitors half life & bioavailability of GLP 1 and GIP Muscle Liver Glucose Uptake Glucose Production Jose T et al. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2012; 9(2):
29 Vascular Repair Slow atherosclerosis CV Effects of DPP 4 Inhibition Prevent LV dysfunction Inflammation Jose T et al. Diab Vasc Dis Res 2012; 9(2):
30 SAVOR TIMI 53 (saxagliptin) Design Subjects Exclusion Criteria Primary Endpoint Dose Randomized, double blind Saxagliptin or placebo Median follow up 2.1 years N = 16,492 Patients with DM2 & CVD or multiple risk factors Currently using incretin therapy (or within prior 6 months) ESRD/HD, renal transplant, or SCr > 6mg/dl MACE (CV death + nonfatal MI + nonfatal stroke) Saxagliptin 5mg daily (2.5mg daily if GFR 50ml/min) Scirica BM et al. N Engl J Med 2013;369: MACE: major adverse cardiac event
31 SAVOR TIMI 53: Patient Population at Baseline Mean age 65 years Male 67% Duration of DM years Mean A1C 8% Mean GFR 73 ml/min ASCVD 78% Prior HF 12.8% Scirica BM et al. N Engl J Med 2013;369:
32 % Patients w/ End Point HR % CI SAVOR TIMI 53: Results HR % CI HR % CI HR % CI Placebo Saxagliptin HR % CI MACE CV Death MI Stroke HF Hosp Scirica BM et al. N Engl J Med 2013;369:
33 SAVOR TIMI 53: Additional Considerations CV Risk Factor Management (Baseline) Glycemic Control Saxagliptin: Pancreatic Saxagliptin: Hypoglycemia Saxagliptin: Renal Saxaglipitin: ASA 75% Statin 78% ACEI 54% ARB 28% A1C 0.2% More patients with A1C < 7% Acute, chronic or pancreatic cancer Major 2.1% vs 1.7% Minor 14.2 vs 12.5% More likely to have improved albumin/ creatinine ratio Scirica BM et al. N Engl J Med 2013;369:
34 EXAMINE (alogliptin) Randomized, double blind, non inferiority (margin 1.3) Design Alogliptin or placebo Subjects Exclusion Criteria Median follow up 18 months N = 5380 Very high CV risk patients: DM2 w/ ACS in last days DM1, unstable cardiac disorder 1, HD within 14 days before screening Primary Endpoint Dose White WB et al. N Engl J Med. 2013;369: MACE (CV death + nonfatal MI + nonfatal stroke) 25mg daily (GFR 60ml/min) 12.5mg daily (GFR ml/min) 6.25mg daily (GFR < 30ml/min) 1 NYHA Class IV HF, refractory angina, uncontrolled arrhythmia, critical valvular heart disease or,severe uncontrolled HTN
35 EXAMINE: Patient Population at Baseline Median age 61 years Male 68% Median Duration of DM2 7.3 years Mean A1C 8% Median GFR 71 ml/min MI 88% HF 28% White WB et al. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:
36 % Patients with Endpoint EXAMINE: Results HR % CI 1.16 HR % CI HR % CI HR % CI Placebo Alogliptin HR % CI MACE CV Death MI Stroke HF Hosp White WB et al. N Engl J Med. 2013;369: Zannad F et al. Lancet. 2015;385:
37 EXAMINE: Additional Considerations CV Risk Factor Management (Baseline): ASA 90% Statin 90% RAAS Blocker 82% Beta Blocker 82% Glycemic Control Alogliptin: A1C 0.33% Hypoglycemia Any or serious hypoglycemia Pancreatic Acute, chronic pancreatitis No report of pancreatic cancer White WB et al. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:
38 TECOS (sitagliptin) Randomized, double blind, non inferiority (margin 1.3) Design Subjects Sitagliptin or placebo Median follow up 3.0 years N = 14,671 Patients w DM2 and established CV disease History of CAD, ischemic cerebrovascular dx or PAD Exclusion Criteria DPP 4 Inhibitor, GLP 1 agonist or TZD 1 during prior 3 months 2 episodes of hypoglycemia during previous 12 months GFR < 30ml/min Primary Endpoint Dose Green JB et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373: MACE (CV death + nonfatal MI + nonfatal stroke + hospitalization unstable angina) Sitagliptin 100mg daily Sitagliptin 50mg daily for GFR 30ml/min and < 50ml/min 1 Other than pioglitazone
39 TECOS: Patient Population at Baseline Mean age 65.5 years Male 70% Mean Duration of DM years Mean A1C 7.2% Mean GFR 75 ml/min CVD 74% (MI 43%) HF 18% Green JB et a. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:
40 12 HR % CI TECOS: Results Placebo Sitagliptin % Patients with Endpoint HR % CI HR % CI HR % CI: HR % CI MACE (3pt) CV Death MI (All) Stroke (All) HF Hospitalization Green JB et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373: doi: /nejmoa
41 TECOS: Additional Considerations CV Risk Factor Management (Baseline): ASA 78% Statin 79% ACE or ARB 78% Glycemic Control Sitagliptin: A1C 0.29% Hypoglycemia: severe Pancreatic Sitagliptin: Acute pancreatitis (NS) Pancrea c cancer (NS) Renal Sitagliptin: GFR slightly in sitagliptin group (Δ = 1.34 ml/min) Green JB et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:
42 DPP 4 Inhibitors: CV Perspective HF Risk 1 Disadvantages Advantages 1 FDA warning for HF risk w saxagliptin & alogliptin CV Neutral
43 DPP 4 Inhibitors: Individualizing Treatment Choices in DM2 ADR 2 HF Risk 1 Cost Disadvantages Advantages 1 FDA warning for HF risk w saxagliptin & alogliptin 2 ADR include? pancreatitis & hypersensitivity CV Neutral Modest A1C Low risk Hypoglycemia
44 SGLT2 Inhibitors Agents Canagliflozin Dapagliflozin Empagliflozin
45 SGLT2 Inhibitors Agents Profile Canagliflozin A1C ~ 0.5 1% Dapagliflozin Weight Empagliflozin Hypoglycemia
46 SGLT2 Inhibitors Agents Canagliflozin Profile A1C ~ 0.5 1% Bone fractures Hypotension, volume depletion Ketoacidosis Dapagliflozin Empagliflozin Weight Hypoglycemia Renal effects UTI, Genital Infections
47 SGLT2 Inhibitors Mechanism of Action Kidney Filters ~ g glucose/day Proximal Tubule Marx N et al. [Published online May 5, 2016]. Eur Heart J. SGLT1 SGLT2 10% Glucose Reabsorption 90% Glucose Reabsorption SGLT2 Inhibitors Glucose Excre on (60 100g/day) Plasma Glucose Plasma Volume Natriuresis
48 LDL 3-7 mg/dl HDL 2-5 mg/dl CV Effects of SGLT2 Inhibition Body Weight 2-3kg Uric Acid Arterial Stiffness/ Vascular Resistance SBP 3 5mmHg DPB 2mmHg Inzucchi SE et al. Diab Vasc Dis Res 2015;12(2):
49 EMPA REG OUTCOME (empagliflozin) Design Randomized, double blind, non inferiority (margin 1.3) Empagliflozin versus placebo Median follow up 3.1 years Subjects N = 7020 patients DM2, high CV risk Exclusion Criteria Exclusions: GFR < 30 ml/min, LFT > 3 x ULN, ACS, stroke or TIA within 2 months prior to consent Primary Endpoint MACE (CV death + nonfatal MI + nonfatal stroke) Dose Empagliflozin 10 or 25mg vs placebo Zinman B et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:
50 EMPA REG OUTCOME: Patient Population at Baseline Mean age 63 years Male 71% Duration of DM2 > 10 years for ~ 57% Mean A1C 8 % Mean GFR 74 ml/min CAD 76% (MI 47%) HF 10 % Zinman B et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:
51 % Patients with Endpoint HR % CI HR % CI EMPA REG OUTCOME: Results HR % CI HR % CI Placebo Empagliflozin HR % CI MACE CV Death MI Stroke HF Hosp Zinman B et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:
52 EMPA REG OUTCOME: Results Absolute Risk Reduction Relative Risk Reduction Number Needed to Treat (3.1 years) Primary Outcome 1.6% 14% 63 CV Death % 45 Any Death % 39 HF % 71 Zinman B et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:
53 EMPA REG OUTCOME: Additional Considerations CV Risk Factor Management (Baseline): ASA 83% Statin 76% ACE/ARB 80% Glycemic Control Empagliflozin: A1C 0.24% (10mg) A1C 0.36% (25mg) AE Empagliflozin: Genital infection Urosepsis AE Empagliflozin: UTI Pyelonephritis AKI DKA Fracture Volume depletion CV Weight Waist circumference Uric acid SBP& DBP HR LDL and HDL Zinman B et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:
54 Empagliflozin: CV Perspective Disadvantages Advantages HF Hosp CV Death All cause Death Improve CV risk factors
55 Empagliflozin: Individualizing Treatment Choices in DM2 AE 1 Cost Disadvantages Advantages 1 Possible AE include: Genital Infections, UTI, Fractures, Renal effects, Hypotension, Volume depletion, Ketoacidosis HF Hosp CV Death All cause Death Improve CV risk factors A1C
56 Factors in Individualizing DM2 Therapy Efficacy Quality of life Safety Cost ADR Outcomes Fox CS et al. Diabetes Care. doi: /dci
57 Hypertension Epidemiology Hypertension Prevalence US Hypertension Control Overall Age % Uncontrolled 51.8 % Controlled Race Hispanic Asian Black White
58 Impact Heart Disease & Stroke > 1000 deaths/day in US $48.6Billion / year
59 Question # 3 Based on current evidence or clinical practice guidelines which of the following BP goals would be appropriate for a 65 year old male with a medical history significant for HTN, HPL, and MI? A. < 150/90 mm Hg B. < 140/90 mm Hg C. < 120/90 mm Hg D. Any of the above may be supported by current evidence or clinical practice guidelines.
60 HTN Goals (mm Hg): Comparison of Guideline Recommendations Uncomplicated HTN Diabetes CV Disease Chronic Kidney Disease Older Adults JNC 7 (2003) < 140/90 <130/80 <140/90 <130/80 Not specified JNC 8 (2014) < 140/90 <140/90 <140/90 <150/90, age 60 yr ASH/ISH (2013) <140/90 <140/90 <140/90 <140/90 <150/90, age 80 yr CHEP (2016) <140/90 1 < 130/80 <140/90 1 <140/90 1 <150/90, age 80 yr ESH/ESC (2013) <140/90 <140/85 <140/90 <140/90 <150/90, age 80 yr JNC: Joint National Committee ASH/ISH: American Society of Hypertension, International Society of Hypertension CHEP: Canadian Hypertension Education Program ESH/ESC: European Society of Hypertension, European Society of Cardiology McConnnell KJ et al. Pharmacotherapy Self Assessment Program, 2016 Book 1. Cardiology. 2016:7 27. Leung et al. Can J Cardiol. 2016;32: For high risk patients, age 50 years, with SBP 130, consider target SBP 120. Patient selection recommended; caution for certain high risk groups.
61 HTN Goals (mm Hg): Comparison of Disease Specific Guideline Recommendations Uncomplicated HTN Diabetes CV Disease Chronic Kidney Disease ADA (2016) <140/90 < 130/80 for select patients ACC/AHA (2015) <140/90 <150/90 for age 80 yr KDIGO (2012) <140/90 <130/80 w/ proteinuria Older Adults ADA: American Diabetes Association ACC/AHA: American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association KDIGO: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outocmes American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes Diabetes Care 2016; 39 (Suppl. 1):S1 S112. McConnnell KJ et al. Pharmacotherapy Self Assessment Program, 2016 Book 1. Cardiology. 2016:7 27.
62 SPRINT: Intensive vs Standard BP Control Randomized, controlled, open label Design Subjects Exclusion Criteria SBP target < 120 mm Hg (intensive) vs < 140 mm Hg (standard) Median follow up: 3.26 years (terminated early) N = 9361 Pa ents with CV Risk but without DM At least 50 yo, SBP mm Hg DM, prior stroke, GFR < 20 ml/min or ESRD, EF <35% Primary Endpoint Treatment. Wright JT et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373: MI + ACS + Stroke +HF + CV Death HTN meds: All major classes included Encouraged use of drug classes w/ strongest evidence for CV outcomes
63 SPRINT: Patient Population at Baseline Mean age 68 years Male 64% BP 140/78 mm HG GFR 72 ml/min 10 yr CV Risk Score 20% # of BP Meds 1.8 Wright JT et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:
64 SPRINT: Treatment Algorithms INTENSTIVE STANDARD Start with 2 3 drug regimen If SBP 160 (or 140 last 2 visits): Titrate or add therapy If SBP 120: Titrate or add therapy and see monthly If DBP 100 (or 90 last 2 visits): Titrate or add therapy Follow up: Monthly x 3 months, then every 3 months; adjust meds monthly for SBP < 120 If DBP 100 (or 90 last 2 visits): Titrate or add therapy If SBP < 130 (or < 135 last 2 visits): Step down Follow up: Monthly x 3 months, then every 3 months; Follow in 1 month if SBP 160 Wright JT et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:
65 SPRINT: Antihypertensive Utilization Number of Agents Intensive (%) Standard (%) Class Intensive (%) Standard (%) ACEI/ARB Thiazide diuretic Calcium channel blocker DHP Beta blocker Alpha 1 blocker Average (#) Wright JT et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373: Aldosterone receptor blocker DHP: Dihydropyridine
66 SPRINT: Antihypertensive Utilization Number of Agents Intensive (%) Standard (%) Class Intensive (%) Standard (%) ACEI/ARB Thiazide diuretic Calcium channel blocker DHP Beta blocker Alpha 1 blocker Average (#) Wright JT et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373: Aldosterone receptor blocker DHP: Dihydropyridine
67 SPRINT: Antihypertensive Utilization Number of Agents Intensive (%) Standard (%) Class Intensive (%) Standard (%) ACEI/ARB Thiazide diuretic Calcium channel blocker DHP Beta blocker Alpha 1 blocker Average (#) Wright JT et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373: Aldosterone receptor blocker DHP: Dihydropyridine
68 % Patients with Endpoint HR % CI HR % CI SPRINT: Results HR % CI Standard Intensive HR % CI HR % CI Primary CV Outcome CV Death MI Stroke HF Wright JT et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:
69 SPRINT: Results Absolute Risk Reduction Relative Risk Reduction Number Needed to Treat (3.26 years) Primary CV 1.6% 25% 63 Outcome CV Death 0.6% 43% 167 Any Death 1.2% 27% 83 HF 0.8% 38% 125 Wright JT et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:
70 SPRINT: Subgroup Analysis Primary Outcome Age 75 Male Non black No Prior CV Disease SBP 132 Age < 75 Female Black Prior CV Disease SBP > 132 Intensive Better No Difference Standard Better Wright JT et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:
71 SPRINT: Additional Considerations CV Risk Factor Management (Baseline): ASA ~ 50% Statin 43% Δin BP at Year 1: SBP 14.8 mm Hg DBP 7.6 mm Hg AE Intensive: Injurious falls Bradycardia Orthostatic hypotension AE Intensive: Hypotension Syncope Electrolyte abnormalities AKI Patient Perceived Health Status Wright JT et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373: Berlowitz D et al. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2016;10(4):e4 e5.
72 SPRINT Analysis Outcome Age 75 CV Event Mortality HF AE AE results show trenddifferences not statistically significant Syncope AKI Hypotension Falls Williamson JD et al. JAMA. [Published online May 19, 2016]. doi: /jama
73 % Patients with Endpoint/year HR % CI HR % CI SPRINT Age 75 Years: Results HR % CI HR % CI Standard Intensive HR % CI Primary CV Outcome CV Death MI Stroke HF Williamson JD et al. JAMA. [Published online May 19, 2016]. doi: /jama
74 Intensive Blood Pressure Control: Individualizing Treatment Targets in HTN AE 1 Monitoring Pill Burden & Cost Populations excluded from SPRINT 2 Disadvantages Advantages 1 AE include: AKI, Hypotension, Syncope, Electrolyte Abnormalities 2 DM, Stroke, GFR < 20, EF < 35%, Recent MI 3 Benefits maintained in age 75 Primary CV Outcome 3 CV Death All cause Death 3 HF 3
75 Factors in Selecting Appropriate BP Target Age Access for follow up Comorbidity Compliance Risk of ADR
76 CV Risk Factors: Emerging Data on Management of DM2 & HTN DPP 4 Inhibitors CV Neutral Some agents HF risk Modest A1C Empagliflozin (SGLT2 Inhibitor) MACE, CV death, HF Modest A1C Potential AEs require careful patient selection Intensive BP Control Primary CV Outcome, Mortality, HF Benefit similar in patients 75 yo Careful patient selection required (AE, compliance, monitoring, certain populations excluded)
77 Question #1 The DPP 4 inhibitor and SGLT2 inhibitor classes for treatment of DM2 improve glycemic control and reduce CV risk. A. True B. False
78 Question #2 Which of the following DM2 medications are associated with an increased risk of HF? A. Sitagliptin B. Empagliflozin C. Saxagliptin D. All of the above
79 Question # 3 Based on current evidence or clinical practice guidelines which of the following BP goals would be appropriate for a 65 yo male with a medical history significant for HTN, HPL, and MI? A. < 150/90 mm Hg B. < 140/90 mm Hg C. < 120/90 mm Hg D. Any of the above may be supported by current evidence or clinical practice guidelines.
Cardiovascular Benefits of Two Classes of Antihyperglycemic Medications
 Cardiovascular Benefits of Two Classes of Antihyperglycemic Medications Nathan Woolever, Pharm.D., Resident Pharmacist Pharmacy Grand Rounds November 6 th, 2018 Franciscan Healthcare La Crosse, WI 2017
Cardiovascular Benefits of Two Classes of Antihyperglycemic Medications Nathan Woolever, Pharm.D., Resident Pharmacist Pharmacy Grand Rounds November 6 th, 2018 Franciscan Healthcare La Crosse, WI 2017
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials Tom Blevins MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, Texas
 Management of Type 2 Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials 2018 Tom Blevins MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, Texas Speaker Disclosure Dr. Blevins has disclosed that he has received grant support
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials 2018 Tom Blevins MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, Texas Speaker Disclosure Dr. Blevins has disclosed that he has received grant support
LATE BREAKING STUDIES IN DM AND CAD. Will this change the guidelines?
 LATE BREAKING STUDIES IN DM AND CAD Will this change the guidelines? Objectives 1. Discuss current guidelines for prevention of CHD in diabetes. 2. Discuss the FDA Guidance for Industry regarding evaluating
LATE BREAKING STUDIES IN DM AND CAD Will this change the guidelines? Objectives 1. Discuss current guidelines for prevention of CHD in diabetes. 2. Discuss the FDA Guidance for Industry regarding evaluating
Updates in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Management: Are You Making the Link?
 Updates in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Management: Are You Making the Link? Denise Kolanczyk, PharmD, BCPS AQ Cardiology 1 Erika Hellenbart, PharmD, BCPS 2 Jennifer D Souza, PharmD, CDE, BC ADM
Updates in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Management: Are You Making the Link? Denise Kolanczyk, PharmD, BCPS AQ Cardiology 1 Erika Hellenbart, PharmD, BCPS 2 Jennifer D Souza, PharmD, CDE, BC ADM
Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy
 Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 7, 2012 VanderbiltHeart.com Outline
Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 7, 2012 VanderbiltHeart.com Outline
CANVAS Program Independent commentary
 CANVAS Program Independent commentary Cliff Bailey Aston University, Birmingham, UK 2017 Disclosures and disclaimers Clifford J Bailey CJB has attended advisory boards, undertaken ad hoc consultancy, received
CANVAS Program Independent commentary Cliff Bailey Aston University, Birmingham, UK 2017 Disclosures and disclaimers Clifford J Bailey CJB has attended advisory boards, undertaken ad hoc consultancy, received
Top HF Trials to Impact Your Practice
 Top HF Trials to Impact Your Practice Biykem Bozkurt, MD, FACC The Mary and Gordon Cain Chair & Professor of Medicine Medical Care Line Executive, DeBakey VA Medical Center, Director, Winters Center for
Top HF Trials to Impact Your Practice Biykem Bozkurt, MD, FACC The Mary and Gordon Cain Chair & Professor of Medicine Medical Care Line Executive, DeBakey VA Medical Center, Director, Winters Center for
The Flozins Quest for Clarity?
 The Flozins Quest for Clarity? Choosing Wisely with Academic Detailing 2018 ARE THEY THE REAL DEAL Disclosure statements The Academic Detailing Service is operated by Dalhousie Continuing Professional
The Flozins Quest for Clarity? Choosing Wisely with Academic Detailing 2018 ARE THEY THE REAL DEAL Disclosure statements The Academic Detailing Service is operated by Dalhousie Continuing Professional
The Death of Sulfonylureas? A Review of New Diabetes Medications
 The Death of Sulfonylureas? A Review of New Diabetes Medications Kelly Hoenig, Pharm.D., BCPS Cedar Rapids Family Medicine Residency 2/4/17 Objectives Review GLP-1 Agonists, DPP-IV Inhibitors and SGLT-2
The Death of Sulfonylureas? A Review of New Diabetes Medications Kelly Hoenig, Pharm.D., BCPS Cedar Rapids Family Medicine Residency 2/4/17 Objectives Review GLP-1 Agonists, DPP-IV Inhibitors and SGLT-2
Blood Pressure Targets: Where are We Now?
 Blood Pressure Targets: Where are We Now? Diana Cao, PharmD, BCPS-AQ Cardiology Assistant Professor Department of Clinical & Administrative Sciences California Northstate University College of Pharmacy
Blood Pressure Targets: Where are We Now? Diana Cao, PharmD, BCPS-AQ Cardiology Assistant Professor Department of Clinical & Administrative Sciences California Northstate University College of Pharmacy
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
 ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
01/09/2017. Outline. SGLT 2 inhibitor? Diabetes Patients: Complex and Heterogeneous. Association between diabetes and cardiovascular events
 MICROVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS Incidence of outcome g 1 Cardioprotective Effects of SGLT2s Relevant for Which T2 Diabetes Patient? SGLT 2 inhibitor? 58 year old, waist circumference 5 cm, PMH: IHD On statin,
MICROVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS Incidence of outcome g 1 Cardioprotective Effects of SGLT2s Relevant for Which T2 Diabetes Patient? SGLT 2 inhibitor? 58 year old, waist circumference 5 cm, PMH: IHD On statin,
Medical therapy advances London/Manchester RCP February/June 2016
 Medical therapy advances London/Manchester RCP February/June 2016 Advances in medical therapies for diabetes mellitus Duality of interest: The speaker or institutions with which he is associated has received
Medical therapy advances London/Manchester RCP February/June 2016 Advances in medical therapies for diabetes mellitus Duality of interest: The speaker or institutions with which he is associated has received
2019 Update on Recent Guideline Releases for Diabetes, Hypertension, and Dyslipidemia: Can We, Please, All Just Get on the Same Page?!
 2019 Update on Recent Guideline Releases for Diabetes, Hypertension, and Dyslipidemia: Can We, Please, All Just Get on the Same Page?! Jeremy L. Johnson, PharmD, BCACP, CDE, BC-ADM Assistant Professor,
2019 Update on Recent Guideline Releases for Diabetes, Hypertension, and Dyslipidemia: Can We, Please, All Just Get on the Same Page?! Jeremy L. Johnson, PharmD, BCACP, CDE, BC-ADM Assistant Professor,
Diabete: terapia nei pazienti a rischio cardiovascolare
 Diabete: terapia nei pazienti a rischio cardiovascolare Giorgio Sesti Università Magna Graecia di Catanzaro Cardiovascular mortality in relation to diabetes mellitus and a prior MI: A Danish Population
Diabete: terapia nei pazienti a rischio cardiovascolare Giorgio Sesti Università Magna Graecia di Catanzaro Cardiovascular mortality in relation to diabetes mellitus and a prior MI: A Danish Population
Hypertension in 2015: SPRINT-ing ahead of JNC-8. MAJ Charles Magee, MD MPH FACP Director, WRNMMC Hypertension Clinic
 Hypertension in 2015: SPRINT-ing ahead of JNC-8 MAJ Charles Magee, MD MPH FACP Director, WRNMMC Hypertension Clinic Conflits of interest? None Disclaimer The opinions contained herein are not to be considered
Hypertension in 2015: SPRINT-ing ahead of JNC-8 MAJ Charles Magee, MD MPH FACP Director, WRNMMC Hypertension Clinic Conflits of interest? None Disclaimer The opinions contained herein are not to be considered
No Increased Cardiovascular Risk for Lixisenatide in ELIXA
 ON ISSUES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES JUNE 2015 Coverage of data from ADA 2015, June 5 9 in Boston, Massachusetts No Increased Cardiovascular Risk for Lixisenatide in ELIXA First Cardiovascular
ON ISSUES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES JUNE 2015 Coverage of data from ADA 2015, June 5 9 in Boston, Massachusetts No Increased Cardiovascular Risk for Lixisenatide in ELIXA First Cardiovascular
Diabetes and New Meds for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction. F. Dwight Chrisman, MD, FACC. Disclosures: BI Boehringer Ingelheim speaker
 Diabetes and New Meds for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction F. Dwight Chrisman, MD, FACC Disclosures: BI Boehringer Ingelheim speaker 1 Prevalence of DM DM state specific prevalence 2006 4%-6% 6-8% 8-10% 10-12%
Diabetes and New Meds for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction F. Dwight Chrisman, MD, FACC Disclosures: BI Boehringer Ingelheim speaker 1 Prevalence of DM DM state specific prevalence 2006 4%-6% 6-8% 8-10% 10-12%
egfr > 50 (n = 13,916)
 Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
The ABCs (A1C, BP and Cholesterol) of Diabetes
 The ABCs (A1C, BP and Cholesterol) of Diabetes Gregg Simonson, PhD Director, Professional Training and Consulting International Diabetes Center; Adjunct Assistant Professor, University of Minnesota Department
The ABCs (A1C, BP and Cholesterol) of Diabetes Gregg Simonson, PhD Director, Professional Training and Consulting International Diabetes Center; Adjunct Assistant Professor, University of Minnesota Department
Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Denise M. Kolanczyk, PharmD, BCPS-AQ Cardiology
 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Denise M. Kolanczyk, PharmD, BCPS-AQ Cardiology Disclosures In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American Diabetes Association requires the
Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Denise M. Kolanczyk, PharmD, BCPS-AQ Cardiology Disclosures In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American Diabetes Association requires the
Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitors Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol
 Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitors Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medicaid P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has
Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitors Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medicaid P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has
NEW DIABETES CARE MEDICATIONS
 NEW DIABETES CARE MEDICATIONS James Bonucchi DO, ECNU, FACE Adult Medicine and Endocrinology Specialists Disclosures Speakers bureau Sanofi AZ BI Diabetes Diabetes cost ADA 2017 data Ever increasing disorder.
NEW DIABETES CARE MEDICATIONS James Bonucchi DO, ECNU, FACE Adult Medicine and Endocrinology Specialists Disclosures Speakers bureau Sanofi AZ BI Diabetes Diabetes cost ADA 2017 data Ever increasing disorder.
The Diabetes Link to Heart Disease
 The Diabetes Link to Heart Disease Anthony Abe DeSantis, MD September 18, 2015 University of WA Division of Metabolism, Endocrinology and Nutrition Oswald Toosweet Case #1 68 yo M with T2DM Diagnosed DM
The Diabetes Link to Heart Disease Anthony Abe DeSantis, MD September 18, 2015 University of WA Division of Metabolism, Endocrinology and Nutrition Oswald Toosweet Case #1 68 yo M with T2DM Diagnosed DM
Blood Pressure Treatment Goals
 Blood Pressure Treatment Goals Kenneth Izuora, MD, MBA, FACE Associate Professor UNLV School of Medicine November 18, 2017 Learning Objectives Discuss the recent studies on treating hypertension Review
Blood Pressure Treatment Goals Kenneth Izuora, MD, MBA, FACE Associate Professor UNLV School of Medicine November 18, 2017 Learning Objectives Discuss the recent studies on treating hypertension Review
Update on Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcome Trials
 Update on Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcome Trials Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of Miami Miller School of Medicine
Update on Diabetes Cardiovascular Outcome Trials Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of Miami Miller School of Medicine
The EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial: Design and results. David Fitchett, MD University of Toronto, Canada
 The EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial: Design and results David Fitchett, MD University of Toronto, Canada Asian Cardio Diabetes Forum April 23 24, 2016 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Life Expectancy Is Reduced by ~12 Years
The EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial: Design and results David Fitchett, MD University of Toronto, Canada Asian Cardio Diabetes Forum April 23 24, 2016 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Life Expectancy Is Reduced by ~12 Years
Disclosures. Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management. Learning Objectives. Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
 Disclosures Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Tony Hampton, MD, MBA Medical Director Advocate Aurora Operating System Advocate Aurora Healthcare Downers Grove, IL No conflicts or disclosures
Disclosures Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Tony Hampton, MD, MBA Medical Director Advocate Aurora Operating System Advocate Aurora Healthcare Downers Grove, IL No conflicts or disclosures
CV outcomes Studies and Implications for diabetes management. Seraj Abualnaja, MD, FRCPC Consultant Interventional cardiologist DSFH
 CV outcomes Studies and Implications for diabetes management Seraj Abualnaja, MD, FRCPC Consultant Interventional cardiologist DSFH Case 49 y female with the following medical problems DM typ2 Hypertension
CV outcomes Studies and Implications for diabetes management Seraj Abualnaja, MD, FRCPC Consultant Interventional cardiologist DSFH Case 49 y female with the following medical problems DM typ2 Hypertension
Clinical Relevance of Blood Pressure Lowering Effect of Modern Antidiabetic Drugs
 Clinical Relevance of Blood Pressure Lowering Effect of Modern Antidiabetic Drugs Professor Guntram Schernthaner Medical University of Vienna, Austria guntram.schernthaner@meduniwien.ac.at Agenda Glucose
Clinical Relevance of Blood Pressure Lowering Effect of Modern Antidiabetic Drugs Professor Guntram Schernthaner Medical University of Vienna, Austria guntram.schernthaner@meduniwien.ac.at Agenda Glucose
Case Studies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials
 Case Studies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials Louis Kuritzky MD Clinical Assistant Professor Emeritus Department of Community Health and Family Medicine College of Medicine
Case Studies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials Louis Kuritzky MD Clinical Assistant Professor Emeritus Department of Community Health and Family Medicine College of Medicine
Drug Class Monograph
 Drug Class Monograph Class: Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitors Drugs: Farxiga (dapagliflozin), Invokamet (canagliflozin/metformin), Invokana (canagliflozin), Jardiance (empagliflozin),
Drug Class Monograph Class: Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT-2) Inhibitors Drugs: Farxiga (dapagliflozin), Invokamet (canagliflozin/metformin), Invokana (canagliflozin), Jardiance (empagliflozin),
Causes of death in Diabetes
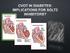 Rates of CV events in Diabetes patients Respiratory4.2 Cancer 7.6 Diabetes 1.3 CV disease 17.3 Causes of death in Diabetes 250 200 150 100 50 0 per 10,000 person-years 97 151 243 Framingham 5 X increase
Rates of CV events in Diabetes patients Respiratory4.2 Cancer 7.6 Diabetes 1.3 CV disease 17.3 Causes of death in Diabetes 250 200 150 100 50 0 per 10,000 person-years 97 151 243 Framingham 5 X increase
Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications
 Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications Estimates of Diagnosed Diabetes in Adults, 2005 Alka M. Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine UCSF, Primary Care CME October
Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications Estimates of Diagnosed Diabetes in Adults, 2005 Alka M. Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine UCSF, Primary Care CME October
Side Effects of: GLP-1 agonists DPP-4 inhibitors SGLT-2 inhibitors. Bryce Fukunaga PharmD April 25, 2018
 Side Effects of: GLP-1 agonists DPP-4 inhibitors SGLT-2 inhibitors Bryce Fukunaga PharmD April 25, 2018 Objectives For each drug class: Identify the overall place in therapy Explain the mechanism of action
Side Effects of: GLP-1 agonists DPP-4 inhibitors SGLT-2 inhibitors Bryce Fukunaga PharmD April 25, 2018 Objectives For each drug class: Identify the overall place in therapy Explain the mechanism of action
Pharmacology Update for the Adult Patient - Newer Oral Medications for Diabetes
 Pharmacology Update for the Adult Patient - Newer Oral Medications for Diabetes Brooke Hudspeth, PharmD, CDE, MLDE Director of Diabetes Prevention, Kroger Pharmacy Adjunct Assistant Professor, University
Pharmacology Update for the Adult Patient - Newer Oral Medications for Diabetes Brooke Hudspeth, PharmD, CDE, MLDE Director of Diabetes Prevention, Kroger Pharmacy Adjunct Assistant Professor, University
Hypertension Update Clinical Controversies Regarding Age and Race
 Hypertension Update Clinical Controversies Regarding Age and Race Allison Helmer, PharmD, BCACP Assistant Clinical Professor Auburn University Harrison School of Pharmacy July 22, 2017 DISCLOSURE/CONFLICT
Hypertension Update Clinical Controversies Regarding Age and Race Allison Helmer, PharmD, BCACP Assistant Clinical Professor Auburn University Harrison School of Pharmacy July 22, 2017 DISCLOSURE/CONFLICT
DISCLOSURE PHARMACIST OBJECTIVES 9/30/2014 JNC 8: A REVIEW OF THE LONG-AWAITED/MUCH-ANTICIPATED HYPERTENSION GUIDELINES. I have nothing to disclose.
 JNC 8: A REVIEW OF THE LONG-AWAITED/MUCH-ANTICIPATED HYPERTENSION GUIDELINES Tiffany Dickey, PharmD Assistant Professor, UAMS COP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Mercy Hospital Northwest AR DISCLOSURE I
JNC 8: A REVIEW OF THE LONG-AWAITED/MUCH-ANTICIPATED HYPERTENSION GUIDELINES Tiffany Dickey, PharmD Assistant Professor, UAMS COP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Mercy Hospital Northwest AR DISCLOSURE I
Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2
 EARN 3 FREE CPD POINTS diabetes Leader in digital CPD for Southern African healthcare professionals Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes Introduction People with type 2 diabetes
EARN 3 FREE CPD POINTS diabetes Leader in digital CPD for Southern African healthcare professionals Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes Introduction People with type 2 diabetes
Empagliflozin: Role in Treatment Options for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Diabetes Ther (2017) 8:33 53 DOI 10.1007/s13300-016-0211-x REVIEW Empagliflozin: Role in Treatment Options for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus John E. Anderson. Eugene E. Wright Jr.. Charles F.
Diabetes Ther (2017) 8:33 53 DOI 10.1007/s13300-016-0211-x REVIEW Empagliflozin: Role in Treatment Options for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus John E. Anderson. Eugene E. Wright Jr.. Charles F.
Evaluating the Cardiovascular Benefits of Antidiabetic Medications
 Evaluating the Cardiovascular Benefits of Antidiabetic Medications Target Audience: Pharmacists ACPE#: 0202-0000-18-054-L01-P Activity Type: Application-based Disclosures Stuart T. Haines has no relevant
Evaluating the Cardiovascular Benefits of Antidiabetic Medications Target Audience: Pharmacists ACPE#: 0202-0000-18-054-L01-P Activity Type: Application-based Disclosures Stuart T. Haines has no relevant
The Clinical Unmet need in the patient with Diabetes and ACS
 The Clinical Unmet need in the patient with Diabetes and ACS Professor Kausik Ray (UK) BSc(hons), MBChB, MD, MPhil, FRCP (lon), FRCP (ed), FACC, FESC, FAHA Diabetes is a global public health challenge
The Clinical Unmet need in the patient with Diabetes and ACS Professor Kausik Ray (UK) BSc(hons), MBChB, MD, MPhil, FRCP (lon), FRCP (ed), FACC, FESC, FAHA Diabetes is a global public health challenge
Overview T2DM medications. Winnie Ho
 Overview T2DM medications Winnie Ho Diabetes in Australia 1.7 million Australians with diabetes, of these 85% have T2DM 2-fold excess risk CV death in patients with diabetes Risk factor for progression
Overview T2DM medications Winnie Ho Diabetes in Australia 1.7 million Australians with diabetes, of these 85% have T2DM 2-fold excess risk CV death in patients with diabetes Risk factor for progression
Diabetes Management in CAD Patients. Stuart R. Chipkin, MD Research Professor School of Public Health and Health Sciences University of Massachusetts
 Diabetes Management in CAD Patients Stuart R. Chipkin, MD Research Professor School of Public Health and Health Sciences University of Massachusetts Disclosure Stuart R. Chipkin, MD, FACE Nothing to disclose
Diabetes Management in CAD Patients Stuart R. Chipkin, MD Research Professor School of Public Health and Health Sciences University of Massachusetts Disclosure Stuart R. Chipkin, MD, FACE Nothing to disclose
Diabetes and the Elderly: Medication Considerations When Determining Benefits and Risks
 Diabetes and the Elderly: Medication Considerations When Determining Benefits and Risks Gretchen M. Ray, PharmD, PhC, BCACP, CDE Associate Professor UNM College of Pharmacy September 7 th, 2018 DISCLOSURES
Diabetes and the Elderly: Medication Considerations When Determining Benefits and Risks Gretchen M. Ray, PharmD, PhC, BCACP, CDE Associate Professor UNM College of Pharmacy September 7 th, 2018 DISCLOSURES
Type 2 Diabetes: Where Do We Start with Treatment? DIABETES EDUCATION. Diabetes Mellitus: Complications and Co-Morbid Conditions
 Diabetes Mellitus: Complications and Co-Morbid Conditions ADA Guidelines for Glycemic Control: 2016 Retinopathy Between 2005-2008, 28.5% of patients with diabetes 40 years and older diagnosed with diabetic
Diabetes Mellitus: Complications and Co-Morbid Conditions ADA Guidelines for Glycemic Control: 2016 Retinopathy Between 2005-2008, 28.5% of patients with diabetes 40 years and older diagnosed with diabetic
Treating Hypertension in 2018: What Makes the Most Sense Today?
 Treating Hypertension in 2018: What Makes the Most Sense Today? Daniel Blanchard, MD Professor of Medicine UC San Diego Cardiovascular Center La Jolla, California 1 2 Speaker Disclosures Consultant and/or
Treating Hypertension in 2018: What Makes the Most Sense Today? Daniel Blanchard, MD Professor of Medicine UC San Diego Cardiovascular Center La Jolla, California 1 2 Speaker Disclosures Consultant and/or
Diabetes Guidelines in View of Recent Clinical Trials Are They Still Applicable?
 Diabetes Guidelines in View of Recent Clinical Trials Are They Still Applicable? Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of
Diabetes Guidelines in View of Recent Clinical Trials Are They Still Applicable? Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of
Help the Heart. An Update on GLP-1 Agonists and SGLT2 Inhibitors. Tara Hawley, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Mayo Clinic Health System Eau Claire
 Help the Heart An Update on GLP-1 Agonists and SGLT2 Inhibitors Tara Hawley, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Mayo Clinic Health System Eau Claire Mayo Clinic Grand Rounds May 16, 2017 2017 MFMER slide-1
Help the Heart An Update on GLP-1 Agonists and SGLT2 Inhibitors Tara Hawley, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Mayo Clinic Health System Eau Claire Mayo Clinic Grand Rounds May 16, 2017 2017 MFMER slide-1
Can We Reduce Heart Failure by Treating Diabetes? CVOT Data on SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1Receptor Agonists
 Can We Reduce Heart Failure by Treating Diabetes? CVOT Data on SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1Receptor Agonists Robert R. Henry, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Diego Relevant Conflict
Can We Reduce Heart Failure by Treating Diabetes? CVOT Data on SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1Receptor Agonists Robert R. Henry, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Diego Relevant Conflict
In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American Diabetes Association requires the following disclosure to the participants:
 In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American Diabetes Association requires the following disclosure to the participants: Entity Activity Financial Consideration Comments Novo Nordisk
In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American Diabetes Association requires the following disclosure to the participants: Entity Activity Financial Consideration Comments Novo Nordisk
Cardiologists and HbA1c: Novel Diabetes Drugs and Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes
 Biomarkers 2018 Cardiologists and HbA1c: Novel Diabetes Drugs and Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHFSA Elliot Corday Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine UCLA Division
Biomarkers 2018 Cardiologists and HbA1c: Novel Diabetes Drugs and Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, FACC, FAHA, FHFSA Elliot Corday Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine UCLA Division
IMPROVED DIAGNOSIS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES AND TAILORING MEDICATIONS
 IMPROVED DIAGNOSIS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES AND TAILORING MEDICATIONS Dr Bidhu Mohapatra, MBBS, MD, FRACP Consultant Physician Endocrinology and General Medicine Introduction 382 million people affected by diabetes
IMPROVED DIAGNOSIS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES AND TAILORING MEDICATIONS Dr Bidhu Mohapatra, MBBS, MD, FRACP Consultant Physician Endocrinology and General Medicine Introduction 382 million people affected by diabetes
Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone
 Index Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication GAD glutamic acid decarboxylase GLP-1 glucagon-like peptide 1 NPH neutral
Index Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication GAD glutamic acid decarboxylase GLP-1 glucagon-like peptide 1 NPH neutral
Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide NOVEMBER 2017
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide Introduction NOVEMBER 2017 This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2017 KP National Diabetes Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide Introduction NOVEMBER 2017 This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2017 KP National Diabetes Guideline.
Drug Class Review Newer Diabetes Medications and Combinations
 Drug Class Review Newer Diabetes Medications and Combinations Final Update 2 Report July 2016 The purpose reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness and harms
Drug Class Review Newer Diabetes Medications and Combinations Final Update 2 Report July 2016 The purpose reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness and harms
Cardiovascular Outcomes With Newer Diabetes Drugs: Results From The EMPA-REG and LEADER Trials
 Cardiovascular Outcomes With Newer Diabetes Drugs: Results From The EMPA-REG and LEADER Trials Rajiv Roy, MD Endocrinology Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group Background Between 1990 and 2010: Incidence of
Cardiovascular Outcomes With Newer Diabetes Drugs: Results From The EMPA-REG and LEADER Trials Rajiv Roy, MD Endocrinology Sharp Rees-Stealy Medical Group Background Between 1990 and 2010: Incidence of
The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities
 The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities Question #1 Which of the following is a risk factor for increased hypoglycemia in older patients that may suggest the need to relax hyperglycemia treatment
The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities Question #1 Which of the following is a risk factor for increased hypoglycemia in older patients that may suggest the need to relax hyperglycemia treatment
SGLT2 Inhibitors Improve CardioRenal Outcomes in DM2-Get Rid of the Sugar
 SGLT2 Inhibitors Improve CardioRenal Outcomes in DM2-Get Rid of the Sugar David Balis, MD University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Internal Medicine Grand Rounds 10/6/17 This is to acknowledge that
SGLT2 Inhibitors Improve CardioRenal Outcomes in DM2-Get Rid of the Sugar David Balis, MD University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center Internal Medicine Grand Rounds 10/6/17 This is to acknowledge that
Drug Class Monograph
 Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drug Class Monograph Drugs: alogliptin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin), Jentadueto (linagliptin/metformin),
Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drug Class Monograph Drugs: alogliptin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin), Jentadueto (linagliptin/metformin),
The Latest Generation of Clinical
 The Latest Generation of Clinical Guidelines: HTN and HLD Dave Brackett Clinical Guideline Purpose Uniform approach Awareness of key details Diagnosis Treatment Monitoring Evidence based approach Inform
The Latest Generation of Clinical Guidelines: HTN and HLD Dave Brackett Clinical Guideline Purpose Uniform approach Awareness of key details Diagnosis Treatment Monitoring Evidence based approach Inform
Cardiovascular Impact of Medications for Treating Type 2 Diabetes
 Friday CME Breakfast Lecture Cardiovascular Impact of Medications for Treating Type 2 Diabetes Thomas Blevins, MD Endocrinologist, Private Practice Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, Texas Educational
Friday CME Breakfast Lecture Cardiovascular Impact of Medications for Treating Type 2 Diabetes Thomas Blevins, MD Endocrinologist, Private Practice Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, Texas Educational
JNC 8 -Controversies. Sagren Naidoo Nephrologist CMJAH
 JNC 8 -Controversies Sagren Naidoo Nephrologist CMJAH Joint National Committee (JNC) Panel appointed by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) First guidelines (JNC-1) published in 1977
JNC 8 -Controversies Sagren Naidoo Nephrologist CMJAH Joint National Committee (JNC) Panel appointed by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) First guidelines (JNC-1) published in 1977
Drug Class Monograph
 Drug Class Monograph Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drugs: alogliptin, alogliptin/metformin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin),
Drug Class Monograph Class: Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drugs: alogliptin, alogliptin/metformin, Januvia (sitagliptin), Janumet (sitagliptin/metformin), Janumet XR (sitagliptin/metformin),
MANAGING DIABETES IN 2016 WHAT TO ADD, WHEN AND WHY?
 MANAGING DIABETES IN 2016 WHAT TO ADD, WHEN AND WHY? Faculty: Maria Wolfs MD, MHSc, FRCPC Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Staff Endocrinologist, St. Michael's Hospital Relationships with commercial
MANAGING DIABETES IN 2016 WHAT TO ADD, WHEN AND WHY? Faculty: Maria Wolfs MD, MHSc, FRCPC Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Staff Endocrinologist, St. Michael's Hospital Relationships with commercial
Hypertension Controversies: SPRINTing to New Goals
 Hypertension Controversies: SPRINTing to New Goals Diana Isaacs, PharmD, BCPS, BC-ADM, CDE Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Cleveland Clinic Lauren Wolfe, PharmD Primary Care Clinical Specialist Cleveland
Hypertension Controversies: SPRINTing to New Goals Diana Isaacs, PharmD, BCPS, BC-ADM, CDE Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Cleveland Clinic Lauren Wolfe, PharmD Primary Care Clinical Specialist Cleveland
Review of FDA Guidance on Cardiovascular Outcomes for Diabetes Medication Trials and Application to Clinical Management
 Katherine S. O Neal Pharm.D., MBA, BCACP, CDE, BC-ADM, AE-C Associate Professor The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center College of Pharmacy Department of Internal Medicine Oklahoma City, OK Member,
Katherine S. O Neal Pharm.D., MBA, BCACP, CDE, BC-ADM, AE-C Associate Professor The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center College of Pharmacy Department of Internal Medicine Oklahoma City, OK Member,
Diabetes new challenges, new agents, new order
 Diabetes new challenges, new agents, new order Ken Earle St Georges University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Overview Cardiovascular disease unmet needs Treating evident and residual risk Integrating
Diabetes new challenges, new agents, new order Ken Earle St Georges University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Overview Cardiovascular disease unmet needs Treating evident and residual risk Integrating
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC Choosing the Right Agent for your Patient with diabetes: Individualizing type 2 diabetes management in light of the expanding therapies
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC Choosing the Right Agent for your Patient with diabetes: Individualizing type 2 diabetes management in light of the expanding therapies
LEADER Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes
 LEADER Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes Presented at DSBS seminar on mediation analysis August 18 th Søren Rasmussen, Novo Nordisk. LEADER CV outcome study To determine the effect
LEADER Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes Presented at DSBS seminar on mediation analysis August 18 th Søren Rasmussen, Novo Nordisk. LEADER CV outcome study To determine the effect
GLP 1 agonists Winning the Losing Battle. Dr Bernard SAMIA. KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration
 GLP 1 agonists Winning the Losing Battle Dr Bernard SAMIA KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email: kcardiacs@gmail.com Web: www.kenyacardiacs.org Disclosures I have
GLP 1 agonists Winning the Losing Battle Dr Bernard SAMIA KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email: kcardiacs@gmail.com Web: www.kenyacardiacs.org Disclosures I have
The New Hypertension Guidelines
 The New Hypertension Guidelines Joseph Saseen, PharmD Professor and Vice Chair, Department of Clinical Pharmacy University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus Disclosure Joseph Saseen reports no conflicts
The New Hypertension Guidelines Joseph Saseen, PharmD Professor and Vice Chair, Department of Clinical Pharmacy University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus Disclosure Joseph Saseen reports no conflicts
Learning and Earning with Gateway Professional Education CME/CEU Webinar Series. Diabetes Update July 6, :00pm 1:00pm
 Learning and Earning with Gateway Professional Education CME/CEU Webinar Series Diabetes Update July 6, 2017 12:00pm 1:00pm Jennifer Pennock Holst, MD Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism AHN Center for
Learning and Earning with Gateway Professional Education CME/CEU Webinar Series Diabetes Update July 6, 2017 12:00pm 1:00pm Jennifer Pennock Holst, MD Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism AHN Center for
Managing Hypertension in Diabetes Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park.
 Managing Hypertension in Diabetes 2015 Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park Case Scenario Mike M is a 59 year old man with type 2 diabetes managed
Managing Hypertension in Diabetes 2015 Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park Case Scenario Mike M is a 59 year old man with type 2 diabetes managed
Treating Hypertension in Individuals with Diabetes
 Treating Hypertension in Individuals with Diabetes Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or by any
Treating Hypertension in Individuals with Diabetes Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or by any
Preventing Serious Health Consequences of Type 2 Diabetes
 Preventing Serious Health Consequences of Type 2 Diabetes The Evidence Hertzel C. Gerstein MD MSc FRCPC Professor and Population Health Institute Chair in Diabetes Research McMaster University and Hamilton
Preventing Serious Health Consequences of Type 2 Diabetes The Evidence Hertzel C. Gerstein MD MSc FRCPC Professor and Population Health Institute Chair in Diabetes Research McMaster University and Hamilton
Newer Diabetes Treatments Drug Class Update with New Drug Evaluation: Semaglutide and Ertugliflozin
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Hypertension. Does it Matter What Medications We Use? Nishant K. Sekaran, M.D. M.Sc. Intermountain Heart Institute
 Hypertension Does it Matter What Medications We Use? Nishant K. Sekaran, M.D. M.Sc. Intermountain Heart Institute Hypertension 2017 Classification BP Category Systolic Diastolic Normal 120 and 80 Elevated
Hypertension Does it Matter What Medications We Use? Nishant K. Sekaran, M.D. M.Sc. Intermountain Heart Institute Hypertension 2017 Classification BP Category Systolic Diastolic Normal 120 and 80 Elevated
PROTECTING YOUR SWEET HEART
 PROTECTING YOUR SWEET HEART Cardiovascular risk reducdon in diabetes too many choices and so much confusion! Dr. Arden Barry, BSc, BSc(Pharm), PharmD, ACPR Clinical Pharmacy and Research Specialist, Chilliwack
PROTECTING YOUR SWEET HEART Cardiovascular risk reducdon in diabetes too many choices and so much confusion! Dr. Arden Barry, BSc, BSc(Pharm), PharmD, ACPR Clinical Pharmacy and Research Specialist, Chilliwack
DISCLOSURES. Learning objectives NAVIGATING THE TREATMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES: WHAT S NEW? Investigator Initiated Trial Support:
 NAVIGATING THE TREATMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES: WHAT S NEW? Jane E-B Reusch MD Professor of Medicine, Biochemistry and Bioengineering Associate Director Center for Women s Health Research University of Colorado
NAVIGATING THE TREATMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES: WHAT S NEW? Jane E-B Reusch MD Professor of Medicine, Biochemistry and Bioengineering Associate Director Center for Women s Health Research University of Colorado
Update on Cardiovascular Outcome Trials in Diabetes. Rury R. Holman, FMedSci NIHR Senior Investigator 11 th February 2013
 Update on Cardiovascular Outcome Trials in Diabetes Rury R. Holman, FMedSci NIHR Senior Investigator 11 th February 2013 Residual Vascular Risk in People with Diabetes 2 Analyses based on 530,083 participants
Update on Cardiovascular Outcome Trials in Diabetes Rury R. Holman, FMedSci NIHR Senior Investigator 11 th February 2013 Residual Vascular Risk in People with Diabetes 2 Analyses based on 530,083 participants
Antihyperglycemic Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes: What's Guiding Pharmacotherapy Choice?
 Antihyperglycemic Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes: What's Guiding Pharmacotherapy Choice? Zach Weber, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CDE Live Activity Handout 4 slides per page Antihyperglycemic Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes:
Antihyperglycemic Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes: What's Guiding Pharmacotherapy Choice? Zach Weber, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CDE Live Activity Handout 4 slides per page Antihyperglycemic Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes:
Disclosures. Type 2 Diabetes. The New Epidemic: How Did We Get Here and What's to Come? Summary:
 Type 2. The New Epidemic: How Did We Get Here and What's to Come? Robert J. Rushakoff, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco None Disclosures robert.rushakoff@ucsf.edu Type 2.
Type 2. The New Epidemic: How Did We Get Here and What's to Come? Robert J. Rushakoff, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco None Disclosures robert.rushakoff@ucsf.edu Type 2.
Hypertension and Diabetes Should we be SPRINTING or Reaching an ACCORD?
 Hypertension and Diabetes Should we be SPRINTING or Reaching an ACCORD? Suzanne Oparil, MD Distinguished Professor of Medicine, Professor of Cell, Developmental and Integrative Biology Director, Vascular
Hypertension and Diabetes Should we be SPRINTING or Reaching an ACCORD? Suzanne Oparil, MD Distinguished Professor of Medicine, Professor of Cell, Developmental and Integrative Biology Director, Vascular
Invokana (canagliflozin) NEW INDICATION REVIEW
 Invokana (canagliflozin) NEW INDICATION REVIEW Introduction Brand name: Invokana Generic name: Canagliflozin Pharmacological class: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor Strength and Formulation:
Invokana (canagliflozin) NEW INDICATION REVIEW Introduction Brand name: Invokana Generic name: Canagliflozin Pharmacological class: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor Strength and Formulation:
UPDATES IN AMBULATORY MEDICINE ERIK RIESSEN, MD, FACP INTERMOUNTAIN MEDICAL CENTER OUTPATIENT INTERNAL MEDICINE RESIDENCY CLINIC
 UPDATES IN AMBULATORY MEDICINE ERIK RIESSEN, MD, FACP INTERMOUNTAIN MEDICAL CENTER OUTPATIENT INTERNAL MEDICINE RESIDENCY CLINIC DISCLOSURES: I have no conflict-of-interest disclosures UPDATES: THE STRUGGLE
UPDATES IN AMBULATORY MEDICINE ERIK RIESSEN, MD, FACP INTERMOUNTAIN MEDICAL CENTER OUTPATIENT INTERNAL MEDICINE RESIDENCY CLINIC DISCLOSURES: I have no conflict-of-interest disclosures UPDATES: THE STRUGGLE
Glycemic control a matter of life and death
 Glycemic control a matter of life and death Linda Garcia Mellbin MD PhD Specialist in Cardiology & Internal medicine Dep of Cardiology Karolinska University Hospital /Karolinska Institutet Mortality (%)
Glycemic control a matter of life and death Linda Garcia Mellbin MD PhD Specialist in Cardiology & Internal medicine Dep of Cardiology Karolinska University Hospital /Karolinska Institutet Mortality (%)
What s New in Type 2 Diabetes? 2018 Diabetes Updates
 What s New in Type 2 Diabetes? 2018 Diabetes Updates Gretchen Ray, PharmD, PhC, BCACP, CDE Associate Professor, UNM College of Pharmacy January 28, 2018 gray@salud.unm.edu OBJECTIVES Describe the most
What s New in Type 2 Diabetes? 2018 Diabetes Updates Gretchen Ray, PharmD, PhC, BCACP, CDE Associate Professor, UNM College of Pharmacy January 28, 2018 gray@salud.unm.edu OBJECTIVES Describe the most
Updates in Diabetes Care
 Updates in Diabetes Care Disclosures Nothing to disclose Pharmacist Objectives 1. List strategies for improving diabetes care 2. Understand benefits and risks associated with newer pharmacotherapeutic
Updates in Diabetes Care Disclosures Nothing to disclose Pharmacist Objectives 1. List strategies for improving diabetes care 2. Understand benefits and risks associated with newer pharmacotherapeutic
Hypertension Management in Diabetic Patients
 Hypertension Management in Diabetic Patients Park, Chang G, MD, PhD Cardiovascular Center, Guro Hospital, Korea University Medical School Contents (Treatment of 2 Cases) Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Hypertension
Hypertension Management in Diabetic Patients Park, Chang G, MD, PhD Cardiovascular Center, Guro Hospital, Korea University Medical School Contents (Treatment of 2 Cases) Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Hypertension
What s In the New Hypertension Guidelines?
 American College of Physicians Ohio/Air Force Chapters 2018 Scientific Meeting Columbus, OH October 5, 2018 What s In the New Hypertension Guidelines? Max C. Reif, MD, FACP Objectives: At the end of the
American College of Physicians Ohio/Air Force Chapters 2018 Scientific Meeting Columbus, OH October 5, 2018 What s In the New Hypertension Guidelines? Max C. Reif, MD, FACP Objectives: At the end of the
Hypertension Management Controversies in the Elderly Patient
 Hypertension Management Controversies in the Elderly Patient Juan Bowen, MD Geriatric Update for the Primary Care Provider November 17, 2016 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure No financial relationships No
Hypertension Management Controversies in the Elderly Patient Juan Bowen, MD Geriatric Update for the Primary Care Provider November 17, 2016 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure No financial relationships No
Eugene Barrett M.D., Ph.D. University of Virginia 6/18/2007. Diagnosis and what is it Glucose Tolerance Categories FPG
 Diabetes Mellitus: Update 7 What is the unifying basis of this vascular disease? Eugene J. Barrett, MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine and Pediatrics Director, Diabetes Center and GCRC Health System
Diabetes Mellitus: Update 7 What is the unifying basis of this vascular disease? Eugene J. Barrett, MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine and Pediatrics Director, Diabetes Center and GCRC Health System
JNC Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults
 JNC 8 2014 Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults Table of Contents Why Do We Treat Hypertension? Blood Pressure Treatment Goals Initial Therapy Strength of Recommendation
JNC 8 2014 Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults Table of Contents Why Do We Treat Hypertension? Blood Pressure Treatment Goals Initial Therapy Strength of Recommendation
Disclaimers 22/03/2018. Role of DPP-4 Inhibitors, GLP-1 Agonists, and SGLT-2 Inhibitors in the treatment of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
 Disclaimers Role of DPP-4 Inhibitors, GLP-1 Agonists, and SGLT-2 Inhibitors in the treatment of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 I have not received money or gifts from medical device companies or from the pharmaceutical
Disclaimers Role of DPP-4 Inhibitors, GLP-1 Agonists, and SGLT-2 Inhibitors in the treatment of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 I have not received money or gifts from medical device companies or from the pharmaceutical
What s New in Diabetes Medications. Jena Torpin, PharmD
 What s New in Diabetes Medications Jena Torpin, PharmD 1 Objectives Discuss new medications in the management of diabetes Understand the mechanism of the medications discussed Understand the side effects
What s New in Diabetes Medications Jena Torpin, PharmD 1 Objectives Discuss new medications in the management of diabetes Understand the mechanism of the medications discussed Understand the side effects
Diabetes Drugs and Cardiac Disease. Disclosures
 Diabetes Drugs and Cardiac Disease Robert J. Rushakoff, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco robert.rushakoff@ucsf.edu Disclosures None 1 Written Comments As I have said every
Diabetes Drugs and Cardiac Disease Robert J. Rushakoff, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco robert.rushakoff@ucsf.edu Disclosures None 1 Written Comments As I have said every
Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol
 Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medicaid P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has been developed
Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medicaid P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has been developed
Cardiovascular Consequences of Diabetes Mellitus
 Cardiovascular Consequences of Diabetes Mellitus William J. Elliott, M.D., Ph.D. 05 MAY 18 Disclosure Statement The speaker s research and educational activities have been supported in the past (but NOT
Cardiovascular Consequences of Diabetes Mellitus William J. Elliott, M.D., Ph.D. 05 MAY 18 Disclosure Statement The speaker s research and educational activities have been supported in the past (but NOT
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
