Reappraisal of alcoholic myopathy' Clinical and biopsy study on chronic alcoholics without muscle
|
|
|
- Rodney Carroll
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1971, 34, Reappraisal of alcoholic myopathy' Clinical and biopsy study on chronic alcoholics without muscle weakness or wasting AMIN A. FARIS2 AND MARCELINO G. REYES3 From the Division of Neurology and Department of Pathology, University of Missouri School ofmedicine at Kansas City General Hospital and Medical Center, Kansas City, Missouri, U.S.A. SUMMARY To determine if alcoholic neuropathy which causes denervation of the distal muscles of chronic alcoholics also produces a subclinical myopathy of their proximal muscles, we studied 11 chronic alcoholics who had no muscular weakness or wasting. Six patients demonstrated distal hyporeflexic (ankle jerks) sensory neuropathy on clinical examination. Four patients, one of whom was asymptomatic, had slow peroneal motor nerve conduction velocities. Patterns of neuropathy were present in the electromyograms of the proximal muscles of two patients. Muscle biopsy studies with enzyme histochemistry indicated denervation atrophy and myopathic changes in the contralateral quadriceps muscles of eight patients. As denervation atrophy was present, we concluded that these myopathic changes represented the effects of denervation of these muscles. We conclude, therefore, that the proximal subclinical alcoholic myopathy, previously described as primary by ourselves and others, is the result of denervation due to the well-known alcoholic neuropathy. Hed, Lundmark, Fahlgren, and Orell in 1962, described a reversible acute myopathy related to the excessive use of alcohol. This myopathy was characterized by proximal muscle weakness, cramps, tenderness, swelling, and, in some patients, by myoglobinuria. Histological study demonstrated vacuolation and necrosis with secondary inflammation of muscle fibres. In 1964 Ekbom, Kirstein, and Astrom studied a group of chronic alcoholics who presented with weakness and wasting of their proximal muscles. Electromyograms and muscle biopsies confirmed the presence of a myopathy. These same electromyographic and histopathological features were also present in a group of asymptomatic chronic alcoholics. In 1966 Mancall, McEntee, Hirschhorn, and Gonyea, contended, on the basis of muscle biopsy and electrodiagnostic findings, that their patients had a primary myopathy of their proximal muscles as well as an unrelated secondary 'Supported in part by U.S.P.H.S. grant NB and a grant of the Medical Staff Fund. 2Present address: Baptist Memorial Hospital, Memphis, Tennessee, U.S.A. 3Present address and for reprints: Department of Neurology, Chicago Medical School, 2020 West Ogden Street, Chicago, Illinois, U.S.A. myopathy of their distal muscles. Because the secondary myopathy resulted from denervation caused by the well-known alcoholic neuropathy, they concluded that primary alcoholic myopathy differed from alcoholic neuropathy and that both disorders may occur in the same patient. Perkoff, Hardy, and Velez-Garcia (1966) and Perkoff, Dioso, Bleisch, and Klinkerfuss (1967) demonstrated high serum creatine phosphokinase, low serum phosphorylase, and poor lactic acid response to ischaemic exercise in their patients with alcoholic myopathy. Assuming that these changes were the result of the toxic effects of alcohol on muscle, they argued for a primary alcoholic myopathy. However, most of their patients also had distal neuropathies. We presented a preliminary report on subclinical alcoholic myopathy in 1967 (Faris, Reyes, and Abrams, 1967). Twenty-four chronic alcoholics without proximal or distal muscle weakness, atrophy, fasciculations, tenderness, or cramps were studied. Neurological examination, however, showed absent or diminished ankle jerks in 20 patients who, on direct questioning, also admitted having episodes of burning feet or distal paraesthesias. Decreased conduction velocities of their distal motor and sensory nerves confirmed the presence of distal neuropathy in each of these patients. Some of them 86
2 Reappraisal of alcoholic myopathy also had electromyographic patterns of neuropathy in the muscles of their hands and feet. Electromyograms of their proximal quadriceps or biceps muscles however, did not indicate neuropathic patterns. Instead, in 18 patients we found patchily distributed low-voltage, short-duration, often polyphasic potentials and occasional paradoxical recruitment on minimal voluntary effort. These changes are consistent with a primary myopathy. Similarly, no histological signs of denervation were found in the contralateral proximal muscles of the 24 patients. Instead, 17 patients had the following abnormalities: increased numbers of sarcolemmal nuclei; internal nuclei; random variation in fibre size; occasional vacuolated, necrotic or basophilic fibres; and fatty tissue replacement of some fibres. Muscle biopsy changes such as these, in the absence of denervation atrophy, are highly indicative of primary myopathy. Our study therefore suggested that subclinical myopathy of the proximal muscles of chronic alcoholics occurs more frequently than the literature implies and that such involvement probably results from a primary myopathy. We did not, however, dismiss the possibility that the denervation associated with alcoholic neuropathy could have caused the proximal subclinical myopathy in our patients. Bauwens (1961) and Taverner (1961) found, in their patients with distal neuropathies, electromyographic patterns identical with those present in the proximal muscles of our patients. Drachman, Murphy, Nigam, and Hills (1967) demonstrated that, not infrequently, the chronically-denervated muscle will show only the classical histological signs of primary myopathy. These include, in addition to those described in our patients: fibre splitting, ring fibres, and endomysial fibrosis. None of these histological changes are, however, specific for a primary myopathy. Our studies in the hamster, and those in the cat of Engel, Brooke, and Nelson (1966), have shown that denervation can cause changes which are indistinguishable from primary myopathy except for the presence of group fibre atrophy and other enzyme histochemical signs of denervation. In other words, denervation can mimic all the histological signs of a primary mnyopathy. Therefore, to diagnose a primary myopathy, we had first to prove that the muscle biopsy changes were not the result of denervation. As denervation atrophy was absent in the biopsies of our patients, we diagnosed a primary myopathy of their proximal muscles, although they also had distal neuropathies. However, because the formalin-fixed, paraffinembedded sections we used do not allow as much clarity of histological or cytological details as do fresh-frozen sections, it is possible that we overlooked small groups of atrophic fibres in our biopsies. To eliminate this possibility, we have repeated our studies in a group of chronic alcoholics without muscle weakness or wasting, using fresh-frozen muscle biopsy techniques and enzyme histochemistry. In this manner, we are better able to judge what role denervation plays in subclinical alcoholic myopathy. PATIENTS Eleven chronic alcoholics who participated in the Rehabilitation Program of the Alcoholic Unit of Western Missouri Mental Health Center were studied. These patients, 10 males and one female, ranged in age from 39 to 65 years and had well-documented histories of chronic alcoholism of 10 to 40 years duration (measured from the time they 'lost control' of their drinking, the point that we consider differentiates the heavy social or problem drinker from the true alcoholic). Nine patients had had at least one episode of delirium tremens. None of them had any family history of neuromuscular or other neurological diseases. We found no abnormalities on physical or neurological examination with the exception of absent or diminished ankle jerks in four patients. Two of these patients also complained of occasional burning, tingling, or 'pins and needles' in their feet and hands. Two other patients complained of the distal paraesthesias only. RESULTS LABORATORY STUDIES All patients had normal CBC, FBS, BUN, Na, K, Cl, CO2, total proteins, A/G ratio, alkaline phosphatase, prothrombin time, BSP and PBI tests, except for two patients who had 8 and 32% BSP retentions at 45 minutes. Serum GOT, LDH, and CPK were normal in all but one patient whose serial electrocardiograms indicated a silent acute myocardial infarction. The other patients had normal electrocardiograms. All the patients had normal radiographs of the chest and negative serum VDRL. MUSCLE BIOPSY STUDIES We biopsied the right quadriceps muscle in each patient, placed the specimen in a moist chamber for 30 minutes to reduce its irritability, and, with a razor blade, cut out cylindrical portions, mounted them in cross-sections in cryostat chucks and froze them in chilled isopentane at C. Serial sections at 10, were cut and then stained with modified trichrome (Cunningham and Angel, 1963), nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase (NADH) (Novikoff, Shin, and Drucker, 1961), 'menadione-linked' alpha-glycerophosphate dehydrogenase (MAG) (Wattenberg and Leong, 1960), myosin adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) (Padykula and Herman, 1955), and phosphorylase (Takeuchi, 1956). 87
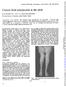
3 8888~~~~~~~Amin A. Faris and Marcelino G. Reyes In eight biopsies, the trichrome stain showed small groups of atrophic and angular fibres (Fig. 1). Each of these biopsies also had a few fibres with internal nuclei, necrotic fibres, ring fibres, and replacement of muscle cells by fat cells. We found no other morphological abnormalities but each of the eight biopsies demonstrated abnormal enzyme histochemical reactions including an increase of the oxidative enzymes NADH or MAG and loss of phosphorylase in some of the atrophic fibres (Figs. 2 and 3). Two biopsies also demonstrated selective type II reaction of the atrophic fibres (Fig. 4). Two other biopsies, one of which had targetoid fibres, also showed type grouping (Fig. 5). There were no morphological or enzyme histochemical abnormalities in three of the muscle biopsies. ELECTRODIAGNOSTIC STUDIES Electromyograms were performed on the contralateral quadriceps muscles of four patients, using a two-channel TECA machine and CT6M coaxial needles in tandem. Two of these patients had mild neuropathic patterns in patchy distribution such as mixed patterns on maximal voluntary effort, prolonged potentials on minimal effort and fibrillations at rest. Peroneal motor nerve conduction velocities in four patients were abnormally slow compared with those of an A :*...~ ~ ~ ~~~~...~~ age-matched control group of seven healthy physicians, two of whom are abstainers and the rest light social drinkers. Their mean peroneal motor nerve conduction velocity was 47-9 in/sec with a range of 45-5 to 51-6 in/sec. The results are tabulated in the Table. DISCUSSION The presence of small groups of atrophic and angular fibres in the trichrome-stained muscle biopsies of our patients was sufficient proof of denervation of their proximal muscles. That muscle wasting from cachexia or disuse can mimic this atrophy 'pattern was of no consequence as the clinical examination had excluded these possibilities. The enzyme histochemical stains further confirmed our findings; all the biopsies with denervation atrophy had some atrophic fibres with loss of phosphorylase and an increase of the oxidative enzymes NADH or MAG. Engel (1966) considered these changes 'characteristic' of the denervated fibre but not of the atrophic cachectic or disused fibre. Similarly, other corroborative enzyme histochemical signs of denervation were present: targetoid fibres, type grouping and selective type II reaction of the atrophic fibres. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry: first published as /jnnp on 1 February Downloaded from FIG. 1. Group atrophy ofthe quadriceps muscle ofa 4S year old man with a 16 year history ofchronic akcoholism. Modified trichrome, x 250. on 14 June 2018 by guest.
4 -*-s t_ 'SM4P'- _ ^Rit;_C' -. *Z-S ' Reappraisal of alcoholic myopathy 4j ~~~~~~m% ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ A FIG. 2. Atrophic fibres with increased oxidative enzymes in another area of the muscle shown in Fig. 1. NADH,x, JO. ze SE -!g i_^ -'I, FIG. 3. Atrophic fibres with loss ofphosphorylase in muscle shown in Fig. 1. Phosphorylase, x
5 90 '~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~...:... Amin A. Faris and Marcelino G. Reyes.'.. FIG. 4. Homologous area of the muscle shown in Fig. I demonstrating selective type II reaction of the atrophic fibres. A TPase, x 250. Type grouping of the quadriceps muscle ofa 45 year old man with a 20 year history of chronic FIG. 5. alcoholism. ATPase, x 35..!R-t
6 Reappraisal of alcoholic myopathy TABLE CLINICAL AND MUSCLE STUDY RESULTS Clinical Biopsy Remarks Patient Duration of DTs* Neurological signs Morphology Histochemistry Age Race/Sex alcoholism (yr) and symptoms 41 N/M 15 1 Normal Normal Normal EMG normal Peroneal CV 37-4 m/sec 65 W/M Burning feet, Grouped atrophy t Oxidative BSP 12% absent ankle internal nuclei ; Phosphorylase jerks type II atrophy 40 N/M 20 2 Normal Grouped atrophy Oxidative BSP 8% ring fibres, Phosphorylase internal nuclei 45 W/M 23 1 Normal Normal Normal 45 W/M 20 0 Burning feet Grouped atrophy f Oxidative Peroneal CV 41-2 m/sec necrotic fibres I Phosphorylase internal nuclei targetoid fibres, type grouping 42 W/M 20 3 Normal Grouped atrophy t Oxidative Developed M.I. necrotic fibres Phosphorylase 61 W/M 40 0 Absent ankle Grouped atrophy Oxidative jerks necrotic fibres Phosphorylase 39 W/F 20 1 Diminished Grouped atrophy t Oxidative EMG neuropathic ankle jerks internal nuclei t Phosphorylase Peroneal CV 39-6 m/sec type II atrophy 45 W/M 16 2 Burning feet, Grouped atrophy t Oxidative EMG neuropathic absent ankle necrotic fibres I Phosphorylase Peroneal CV 39-1 m/sec jerks fat cells type grouping 40 W/M 20 2 Burning feet Grouped atrophy t Oxidative internal nuclei I Phosphorylase 39 W/M 10 1 Normal Normal Normal EMG normal * Episodes of delirium tremens. Targetoid fibres, or the two-zoned target fibres of Engel, have a pale centre or core and a normallystained periphery. Because we have also found these fibres in the biopsies of patients with clear-cut peripheral neuropathy (as shown by clinical and electrodiagnostic studies), we agree with Engel's postulate (1966) that they may represent an unusual form of denervation. Similarly, we have seen type grouping (the segregation into contiguous groups of large numbers of fibres of the same histochemical type) in our patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and other chronic and less-defined forms of peripheral neuropathies associated with the hereditary spinocerebellar degenerations. Karpati and Engel (1968) convincingly demonstrated that section and immediate repair by suture of the guinea-pig sciatic nerve leads to type grouping of the gastrocnemius muscle. Thus, type grouping probably indicates reinnervation rather than denervation but we see no reason to discount it as a possible histochemical sign of denervation. Finally, we found selective type II reaction of the atrophic fibres, which, on the basis of our studies of the denervated quadriceps muscle of the hamster, we believe represents an intermediate phase in the progress of denervation from the time of nerve section. We also discovered histological abnormalities which we believe are secondary myopathic changes of denervation: randomly distributed fibres with internal nuclei, necrotic fibres, ring fibres, and rows of fat cells replacing muscle fibres. In our previous study, we interpreted these same changes to be primary rather than secondary because we failed to see any histological proof of denervation. In this study, however, these myopathic changes were seen in muscle biopsies with denervation atrophy, suggesting that they are indeed secondary to denervation. The electrodiagnostic studies of our patients also provided us with proof of denervation not only in their proximal muscles but also in their distal muscles. The quadriceps electromyograms showed distinct, though admittedly mild and patchily distributed, patterns of neuropathy. In four patients, including one who was asymptomatic, we found peroneal nerve conduction velocities which, when compared with an age-matched control group of 'social drinkers', appeared retarded. Almost certainly, the presence of denervation has been proved in the proximal muscles of the present group of chronic alcoholics, a group which does not differ from our previously studied group. Both groups had well-documented histories of chronic alcoholism, the absence of any muscular weakness or wasting, a high incidence of distal hyporeflexic (ankle jerks) sensory neuropathy on clinical examination, slow nerve conduction velocities of their distal 91
7 92 Amin A. Faris and Marcelino G. Reyes nerves, abnormal electromyograms of their proximal muscles, and muscle biopsy abnormalities of their proximal muscles. But the two groups differ in the presence of denervation in the proximal muscles of the present group of chronic alcoholics, established by their patterns of neuropathy on electromyography and denervation atrophy on muscle biopsy. By proving denervation in their biopsies, we also proved that the accompanying myopathic changes (which were identical with those which we and others have described previously as primarily myopathic changes) are secondary to denervation. We therefore conclude that muscle biopsy abnormalities in the proximal muscles of chronic alcoholics without muscle weakness or wasting are the result of denervation due to the well-known alcoholic peripheral neuropathy. Dr. Bernard M. Abrams and Dr. Oscar E. Espinas performed the electrodiagnostic studies. REFERENCES Bauwens, P. (1961). Introduction to electrodiagnostic procedures. In Electrodiagnosis and Electromyography, pp Edited by S. Licht. Elizabeth Licht: New Haven. Drachman, D. B., Murphy, S. R., Nigam, M. P., and Hills, J. R. (1967). 'Myopathic' changes in chronically denervated muscle. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.), 16, Ekbom, K., Hed, R., Kirstein, L., and Astrom, K. (1964). Muscular affections in chronic alcoholism. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.), 10, Engel, W. K., Brooke, M. H., and Nelson, P. G. (1966). Histochemical studies of the denervated and tenotomized cat muscle: illustrating difficulties in relating experimental animal conditions to human neuromuscular diseases. In Experimental Primary Myopathies and their Relationship to Human Muscle Disease. Edited by E. Bajusz. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 138, Engel, W. K., and Cunniingham, G. C. (1963). Rapid examination of muscle tissue: an improved trichrome method for fresh-frozen biopsy sections. Neurology (Minneap.), 13, Engel, W. K. (1966). Multiplicity of pathologic reactions of human skeletal muscle. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Congress of Neuropathology (Zurich 1965), pp Edited by F. Luthy and A. Bischoff. Excerpta Medical Foundation: Amsterdam. Faris, A. A., Reyes, M. G., and Abrams, B. M. (1967). Subclinical alcoholic myopathy: electromyographic and biopsy study. Trans. Amer. neurol. Assoc., 92, Hed, R., Lundmark, C., Fahlgren, H., and Orell, S. (1962). Acute muscular syndrome in chronic alcoholism. Acta med. scand., 171, Karpati, G., and Engel, W. K. (1968). 'Type grouping' in skeletal muscles after experimental reinnervation. Neurology (Minneap.), 18, Mancall, E. L., McEntee, W. J., Hirschhorn, A. M., and Gonyea, E. F. (1966). Proximal muscular weakness and atrophy in the chronic alcoholic. (Abstract.) Neurology (Minneap.), 16, 301. Novikoff, A. B., Shin, W. Y., and Drucker, J. (1961). Mitochondrial localization of oxidative enzymes: Staining results with two tetrazolium salts. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol., 9, Padykula, H. A., and Herman, E. (1955). The specificity of the histochemical method for adenosine triphosphatase. J. Histochem. Cytochem., 3, Perkoff, G. T., Dioso, M. M., Bleisch, V., and Klinkerfuss, G. (1967). A spectrum of myopathy associated with alcoholism: I. Clinical and laboratory features. Ann. int. Med., 67, Perkoff, G. T., Hardy, P., and Velez-Garcia, E. (1966). Reversible acute muscular syndrome in chronic alcoholism. New Engl. J. Med., 274, Takeuchi, T. (1956). Histochemical demonstration of phosphorylase. (Letter to Editor.) J. Histochem. Cytochem., 4, 84. Taverner, D. (1961). Clinical applications of electromyography. In Electrodiagnosis and Electromyography, pp Edited by S. Licht. Elizabeth Licht: New Haven. Wattenberg, L. W., and Leong, J. L. (1960). Effects of coenzyme QIO and menadione on succinic dehydrogenase activity as measured by tetrazolium salt reduction. J. Histochem. Cytochem., 8, J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry: first published as /jnnp on 1 February Downloaded from on 14 June 2018 by guest.
Enzyme histochemistry of skeletal muscle
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1966, 29, 23 Enzyme histochemistry of skeletal muscle Part III Neurogenic muscular atrophies VICTOR DUBOWITZ From the Department of Child Health, University of Sheffield
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1966, 29, 23 Enzyme histochemistry of skeletal muscle Part III Neurogenic muscular atrophies VICTOR DUBOWITZ From the Department of Child Health, University of Sheffield
Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
Central nuclear counts in muscle fibres before and during treatment in hypothyroid myopathy
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 229-233 Central nuclear counts in muscle fibres before and during in hypothyroid myopathy R. 0. McKERAN",4, P. WARD2, G. SLAVIN2 3, AND E. A. PAUL5 From the Divisions
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 229-233 Central nuclear counts in muscle fibres before and during in hypothyroid myopathy R. 0. McKERAN",4, P. WARD2, G. SLAVIN2 3, AND E. A. PAUL5 From the Divisions
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists
 Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Muscle fibre type populations of human leg muscles
 HistochemicalJournal, 7 (I975), 259-266 Muscle fibre type populations of human leg muscles V. REGGIE EDGERTON, J. L. SMITH and D. R. SIMPSON Neuromuscular Research Laboratory, Brain Research Inst#ute,
HistochemicalJournal, 7 (I975), 259-266 Muscle fibre type populations of human leg muscles V. REGGIE EDGERTON, J. L. SMITH and D. R. SIMPSON Neuromuscular Research Laboratory, Brain Research Inst#ute,
Chronic alcohol excess is associated with selective but
 J Clin Pathol 1983;36:772-777 Chronic alcohol excess is associated with selective but reversible injury to type 2B muscle fibres GERARD SLAVIN, FINBARR MARTIN, PETER WARD, JONATHAN LEVI, TIMOTHY PETERS
J Clin Pathol 1983;36:772-777 Chronic alcohol excess is associated with selective but reversible injury to type 2B muscle fibres GERARD SLAVIN, FINBARR MARTIN, PETER WARD, JONATHAN LEVI, TIMOTHY PETERS
III./10.4. Diagnosis. Introduction. A.) Laboratory tests. Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques
 III./10.4. Diagnosis Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques After studying this chapter, you will become familiar with the most commonly used diagnostic
III./10.4. Diagnosis Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques After studying this chapter, you will become familiar with the most commonly used diagnostic
The Thigh Corset: Its Effects on the Quadriceps Muscle and its Role in Prosthetic Suspension
 The Thigh Corset: Its Effects on the Quadriceps Muscle and its Role in Prosthetic Suspension Joe Weiss, M.D. L. Middleton, M.D. E. Gonzalez, M.D. R.E. Lovelace, M.D. The present study aims at evaluating
The Thigh Corset: Its Effects on the Quadriceps Muscle and its Role in Prosthetic Suspension Joe Weiss, M.D. L. Middleton, M.D. E. Gonzalez, M.D. R.E. Lovelace, M.D. The present study aims at evaluating
Hereditary quadriceps myopathy
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1973, 36, 1041-1045 Hereditary quadriceps myopathy MICHAEL L. E. ESPIR AND W. B. MATTHEWS' From the Department of Neurology, Derbyshire Royal Infirmary,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1973, 36, 1041-1045 Hereditary quadriceps myopathy MICHAEL L. E. ESPIR AND W. B. MATTHEWS' From the Department of Neurology, Derbyshire Royal Infirmary,
Proceedings des 36èmes Journées Annuelles de l Association Vétérinaire Equine Française
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings des 36èmes Journées Annuelles de l Association Vétérinaire Equine Française 9-11 Octobre 2008 - Reims, France Reprinted in IVIS with the Permission
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings des 36èmes Journées Annuelles de l Association Vétérinaire Equine Française 9-11 Octobre 2008 - Reims, France Reprinted in IVIS with the Permission
ACTA HISTOCHEM. CYTOCHEM. Vol. 7, No. 4, 1974 HISTOCHEMICAL CLASSIFICATION OF SKELETAL MUSCLE FIBERS IN THE CATTLE
 ACTA HISTOCHEM. CYTOCHEM. Vol. 7, No. 4, 1974 HISTOCHEMICAL CLASSIFICATION OF SKELETAL MUSCLE FIBERS IN THE CATTLE ATSUSHI SUZUKI AND HIDEO TAMATE Laboratory of Animal Morpholog y, Faculty of Agriculture.
ACTA HISTOCHEM. CYTOCHEM. Vol. 7, No. 4, 1974 HISTOCHEMICAL CLASSIFICATION OF SKELETAL MUSCLE FIBERS IN THE CATTLE ATSUSHI SUZUKI AND HIDEO TAMATE Laboratory of Animal Morpholog y, Faculty of Agriculture.
Electrodiagnosis of the carpal tunnel syndrome
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1968, 31, 23-27 FRANK KEMBLE From the Department of Neurology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham In the carpal tunnel syndrome median nerve motor conduction may be delayed
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1968, 31, 23-27 FRANK KEMBLE From the Department of Neurology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham In the carpal tunnel syndrome median nerve motor conduction may be delayed
New method for the estimation of the number of
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 1195-121 New method for the estimation of the number of motor units in a muscle 2 Duchenne, limb-girdle and facioscapulohumeral, and myotonic
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 1195-121 New method for the estimation of the number of motor units in a muscle 2 Duchenne, limb-girdle and facioscapulohumeral, and myotonic
histochemical and biochemical studies
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1983;46:248-254 Muscle wasting in chronic alcoholics: comparative histochemical and biochemical studies HD LANGOHR, H WIETHOLTER, J PEIFFER From the Department
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1983;46:248-254 Muscle wasting in chronic alcoholics: comparative histochemical and biochemical studies HD LANGOHR, H WIETHOLTER, J PEIFFER From the Department
Fibre type changes in striated muscle of alcoholics
 J Clin Pathol 1981 ;34:991-995 Fibre type changes in striated muscle of alcoholics A HANID, G SLAVIN, W MAIR, C SOWTER, P WARD, J WEBB, J LEVI From Northwick Park Hospital & Clinical Research Centre, Harrow,
J Clin Pathol 1981 ;34:991-995 Fibre type changes in striated muscle of alcoholics A HANID, G SLAVIN, W MAIR, C SOWTER, P WARD, J WEBB, J LEVI From Northwick Park Hospital & Clinical Research Centre, Harrow,
MYOPATHY IN CUSHING'S SYNDROME
 J. Neurol. iveurosurg. Psychiat., 1959, 22, 314 MYOPATHY N CUSHNG'S SYNDROME BY RAGNAR MULLER and ERC KUGELBERG From the Department of Neurology, Serafimerlasarettet, and the Department of Endocriwology,
J. Neurol. iveurosurg. Psychiat., 1959, 22, 314 MYOPATHY N CUSHNG'S SYNDROME BY RAGNAR MULLER and ERC KUGELBERG From the Department of Neurology, Serafimerlasarettet, and the Department of Endocriwology,
Please Silence Your Cell Phones. Thank You
 Please Silence Your Cell Phones Thank You From Morphology to Molecular Genetics: Role of the Pathologist in Diagnosis of Muscle Disorders Karen M. Weidenheim, M.D. Department of Pathology (Neuropathology),
Please Silence Your Cell Phones Thank You From Morphology to Molecular Genetics: Role of the Pathologist in Diagnosis of Muscle Disorders Karen M. Weidenheim, M.D. Department of Pathology (Neuropathology),
EDX in Myopathies Limitations. EDX in Myopathies Utility Causes of Myopathy. Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers
 Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
HISTOLOGICAL AND HISTOCHEMICAL CHANGES OF THE SKELETAL MUSCLE IN HUMAN CHRONIC CHAGAS' DISEASE
 HISTOLOGICAL AND HISTOCHEMICAL CHANGES OF THE SKELETAL MUSCLE IN HUMAN CHRONIC CHAGAS' DISEASE ANALIA TARATUTO Μ. A. PAGNO TERESA FUMO OLG P. SANZ R. E. P. SICA In a recent electrophysiological investigation
HISTOLOGICAL AND HISTOCHEMICAL CHANGES OF THE SKELETAL MUSCLE IN HUMAN CHRONIC CHAGAS' DISEASE ANALIA TARATUTO Μ. A. PAGNO TERESA FUMO OLG P. SANZ R. E. P. SICA In a recent electrophysiological investigation
Muscle Pathology Surgical Pathology Unknown Conference. November, 2008 Philip Boyer, M.D., Ph.D.
 Muscle Pathology Surgical Pathology Unknown Conference November, 2008 Philip Boyer, M.D., Ph.D. Etiologic Approach to Differential Diagnosis Symptoms / Signs / Imaging / Biopsy / CSF Analysis Normal Abnormal
Muscle Pathology Surgical Pathology Unknown Conference November, 2008 Philip Boyer, M.D., Ph.D. Etiologic Approach to Differential Diagnosis Symptoms / Signs / Imaging / Biopsy / CSF Analysis Normal Abnormal
Granulomatous Myositis Clinicopathologic Study of 12 Cases
 Anatomic Pathology / GRANULOMATOUS MYOSITIS Granulomatous Myositis Clinicopathologic Study of 12 Cases Richard A. Pray son, MD Key Words: Granulomas; Granulomatous myositis; Myositis; Granulomatous inflammation
Anatomic Pathology / GRANULOMATOUS MYOSITIS Granulomatous Myositis Clinicopathologic Study of 12 Cases Richard A. Pray son, MD Key Words: Granulomas; Granulomatous myositis; Myositis; Granulomatous inflammation
ELEVATION OF CREATINE KINASE IN AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS
 20 1 ELEVATION OF CREATINE KINASE IN AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS Po ten tial Confusion with Pol y m y osi ti s THOMAS M. HARRINGTON, MARC D. COHEN, JOHN D. BARTLESON, and WILLIAM W. GINSBURG Serum creatine
20 1 ELEVATION OF CREATINE KINASE IN AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS Po ten tial Confusion with Pol y m y osi ti s THOMAS M. HARRINGTON, MARC D. COHEN, JOHN D. BARTLESON, and WILLIAM W. GINSBURG Serum creatine
Original Article Pathological findings in sporadic inclusion body myositis and GNE myopathy
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(5):2907-2911 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0064777 Original Article Pathological findings in sporadic inclusion body myositis and GNE myopathy Yutong Zhang 1, Chuanqiang
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(5):2907-2911 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0064777 Original Article Pathological findings in sporadic inclusion body myositis and GNE myopathy Yutong Zhang 1, Chuanqiang
Mapping of motor units in experimentally
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1970, 33, 319-329 Mapping of motor units in experimentally reinnervated rat muscle Interpretation of histochemical and atrophic fibre patterns in neurogenic lesions ERIC
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1970, 33, 319-329 Mapping of motor units in experimentally reinnervated rat muscle Interpretation of histochemical and atrophic fibre patterns in neurogenic lesions ERIC
X-Plain Muscles Reference Summary
 X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
A/Professor Arun Aggarwal Balmain Hospital
 A/Professor Arun Aggarwal Balmain Hospital Nerve Conduction Studies Test to evaluate the function of motor / sensory nerves Evaluate Paraesthesia (numbness, tingling, burning) Weakness of arms and legs
A/Professor Arun Aggarwal Balmain Hospital Nerve Conduction Studies Test to evaluate the function of motor / sensory nerves Evaluate Paraesthesia (numbness, tingling, burning) Weakness of arms and legs
Succinic Dehydrogenase Activity of Skeltral Muscle and Its Electrophysiological Function
 26 Succinic Dehydrogenase Activity of Skeltral Muscle and Its Electrophysiological Function Shusaku TSUICAMOTO and Masahiko MORI Department of Oral Surgery, Osaka University Dental School, Osaka. Introduction
26 Succinic Dehydrogenase Activity of Skeltral Muscle and Its Electrophysiological Function Shusaku TSUICAMOTO and Masahiko MORI Department of Oral Surgery, Osaka University Dental School, Osaka. Introduction
Case 1: History of J.H. Outside Evaluation. Outside Labs. Question #1
 Case 1: History of J.H. 64 yo man seen at UCSF 6-256 25-07. 9 months ago onset progressive weakness of arms and legs, with muscle atrophy in arms. 4 months ago red scaly rash on face, back of hands and
Case 1: History of J.H. 64 yo man seen at UCSF 6-256 25-07. 9 months ago onset progressive weakness of arms and legs, with muscle atrophy in arms. 4 months ago red scaly rash on face, back of hands and
diphenylhydantoin therapy1
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1975, 38, 1235-1239 Motor nerve conduction study in patients on diphenylhydantoin therapy1 S. CHOKROVERTY2 AND Z. A. SAYEED3 From the Neurology Service
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1975, 38, 1235-1239 Motor nerve conduction study in patients on diphenylhydantoin therapy1 S. CHOKROVERTY2 AND Z. A. SAYEED3 From the Neurology Service
Amyloid neuropathy: (A) scattered Congo Red positive material in endoneurium displays apple green birefringence under polarized light.
 Cơ vân Cơ vân Cơ vân (cắt dọc) Amyloid neuropathy: (A) scattered Congo Red positive material in endoneurium displays apple green birefringence under polarized light. (A, Congo Red). Amyloid neuropathy:
Cơ vân Cơ vân Cơ vân (cắt dọc) Amyloid neuropathy: (A) scattered Congo Red positive material in endoneurium displays apple green birefringence under polarized light. (A, Congo Red). Amyloid neuropathy:
Sensory conduction of the sural nerve in polyneuropathy'
 Jourtial of Neurology, Neurosurgery, anid Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 647-652 Sensory conduction of the sural nerve in polyneuropathy' DAVID BURKE, NEVELL F. SKUSE, AND A. KEITH LETHLEAN From the Unit of Clinical
Jourtial of Neurology, Neurosurgery, anid Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 647-652 Sensory conduction of the sural nerve in polyneuropathy' DAVID BURKE, NEVELL F. SKUSE, AND A. KEITH LETHLEAN From the Unit of Clinical
Alcoholic Skeletal Myopathy, A Clinical and Pathological Study
 Quarterly Journal of Medicine, New Series 55, No. 218, pp. 233-251, June 1985 Alcoholic Skeletal Myopathy, A Clinical and Pathological Study F. MARTIN, K. WARD, G. SLAVIN, J. LEVI and T. J. PETERS From
Quarterly Journal of Medicine, New Series 55, No. 218, pp. 233-251, June 1985 Alcoholic Skeletal Myopathy, A Clinical and Pathological Study F. MARTIN, K. WARD, G. SLAVIN, J. LEVI and T. J. PETERS From
Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease. Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine
 Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Nerves 1. Anterior Horn Cell 2. Dorsal root ganglion cell 3.
Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Nerves 1. Anterior Horn Cell 2. Dorsal root ganglion cell 3.
Motor neurone disease
 Motor neurone disease n abnormality of nerve metabolism J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1969, 32, 1-5 HGWN SHHNI* ND W. RITCHIE RUSSELL From the Department of Neurology, Churchill Hospital, Oxford Recent
Motor neurone disease n abnormality of nerve metabolism J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1969, 32, 1-5 HGWN SHHNI* ND W. RITCHIE RUSSELL From the Department of Neurology, Churchill Hospital, Oxford Recent
Electromyography in nutritional osteomalacic
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 686-693 Electromyography in nutritional osteomalacic myopathy P. F. IRANI From the Department ofneurology, J.J. Group ofhospitals, Byculla,
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 686-693 Electromyography in nutritional osteomalacic myopathy P. F. IRANI From the Department ofneurology, J.J. Group ofhospitals, Byculla,
Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Welander distal myopathy
 orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Welander distal myopathy Disease name: Welander distal myopathy ICD 10: G71.0 Synonyms: late adult onset type 1 distal myopathy;
orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Welander distal myopathy Disease name: Welander distal myopathy ICD 10: G71.0 Synonyms: late adult onset type 1 distal myopathy;
Correlation of Electromyogram and Muscle Biopsy in Myopathy of Young Age
 780 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation of and Muscle Biopsy in of Young Age Jihoon Chang, MD, Yoon Ghil Park, MD, PhD, Young-chul Choi, MD, PhD, Jung Hwa Choi, MD, Jae Ho Moon, MD ABSTRACT. Chang JH, Park YG,
780 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation of and Muscle Biopsy in of Young Age Jihoon Chang, MD, Yoon Ghil Park, MD, PhD, Young-chul Choi, MD, PhD, Jung Hwa Choi, MD, Jae Ho Moon, MD ABSTRACT. Chang JH, Park YG,
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
"INSERTION ACTIVITY" IN ELECTROMYOGRAPHY
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1949, 12, 268. "INSERTION ACTIVITY" IN ELECTROMYOGRAPHY WITH NOTES ON DENERVATED MUSCLE RESPONSE TO CONSTANT CURRENT BY ERIC KUGELBERG and INGEMAR PETERSEN From the Department
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1949, 12, 268. "INSERTION ACTIVITY" IN ELECTROMYOGRAPHY WITH NOTES ON DENERVATED MUSCLE RESPONSE TO CONSTANT CURRENT BY ERIC KUGELBERG and INGEMAR PETERSEN From the Department
Responses to electrical stimulation of denervated human muscle fibres recorded with single fibre EMG
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1983;46:305-309 Responses to electrical stimulation of denervated human muscle fibres recorded with single fibre EMG JOZE TRONTELJ, ERIK STALBERG From
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1983;46:305-309 Responses to electrical stimulation of denervated human muscle fibres recorded with single fibre EMG JOZE TRONTELJ, ERIK STALBERG From
stimulation with a magnetic coil. This approach has the great advantage of being relatively painless. We
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1989;52:767-772 Magnetic stimulation in the diagnosis of lumbosacral radiculopathy S CHOKROVERTY, R SACHDEO, J DILULLO, R C DUVOISIN From the Department
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1989;52:767-772 Magnetic stimulation in the diagnosis of lumbosacral radiculopathy S CHOKROVERTY, R SACHDEO, J DILULLO, R C DUVOISIN From the Department
Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1981, 44, 419-425 Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult N E BHARUCHA AND J A MORGAN-HUGHES From the Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London S
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1981, 44, 419-425 Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult N E BHARUCHA AND J A MORGAN-HUGHES From the Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London S
Comparison of Sudomotor and Sensory Nerve Testing in Painful Sensory Neuropathies
 138 Original Article Comparison of Sudomotor and Sensory Nerve Testing in Painful Sensory Neuropathies James M. Killian, MD,* Shane Smyth, MD,* Rudy Guerra, PhD, Ishan Adhikari, MD,* and Yadollah Harati,
138 Original Article Comparison of Sudomotor and Sensory Nerve Testing in Painful Sensory Neuropathies James M. Killian, MD,* Shane Smyth, MD,* Rudy Guerra, PhD, Ishan Adhikari, MD,* and Yadollah Harati,
Femoral nerve conduction in diabetes and chronic
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1968, 31, 28-33 Femoral nerve conduction in diabetes and chronic occlusive vascular disease J. S. CHOPR1 ND L. J. HURWITZ From the Department of Neurology and the Metabolic
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1968, 31, 28-33 Femoral nerve conduction in diabetes and chronic occlusive vascular disease J. S. CHOPR1 ND L. J. HURWITZ From the Department of Neurology and the Metabolic
Disorders of Muscle. Disorders of Muscle. Muscle Groups Involved in Myopathy. Needle Examination of EMG. History. Muscle Biopsy
 Disorders of Muscle Disorders of Muscle Zakia Bell, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology and Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Virginia Commonwealth University Cardinal symptom of diseases of the muscle
Disorders of Muscle Disorders of Muscle Zakia Bell, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology and Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Virginia Commonwealth University Cardinal symptom of diseases of the muscle
Muscle morphology and metabolism in hypothyroid
 J Clin Pathol 1983;36:519-526 Muscle morphology and metabolism in hypothyroid myopathy: effects of treatment AL A KHALEEL, K GOHL, G McPHAL, JM ROUND, RHT EDWARDS From the Department of Medicine, University
J Clin Pathol 1983;36:519-526 Muscle morphology and metabolism in hypothyroid myopathy: effects of treatment AL A KHALEEL, K GOHL, G McPHAL, JM ROUND, RHT EDWARDS From the Department of Medicine, University
Electrodiagnostics for Back & Neck Pain. Steven Andersen, MD Providence Physiatry Clinic
 Electrodiagnostics for Back & Neck Pain Steven Andersen, MD Providence Physiatry Clinic Electrodiagnostics Electromyography (EMG) Needle EMG exam (NEE) Nerve conduction studies (NCS) Motor Sensory Late
Electrodiagnostics for Back & Neck Pain Steven Andersen, MD Providence Physiatry Clinic Electrodiagnostics Electromyography (EMG) Needle EMG exam (NEE) Nerve conduction studies (NCS) Motor Sensory Late
CNEMG. Myopathy, Stålberg. At rest denervation and spec spontaneous activity (myotonia, CRD, neuromyotonia) MUP number of fibres in recorded area
 clincial heredity biochem MYOPATHY biopsy Erik Stålberg Uppsala, Sweden imaging genetics Electrodes A B C MU D E Conc EMG signals from 2-15 muscle fibres CNEMG At rest denervation and spec spontaneous
clincial heredity biochem MYOPATHY biopsy Erik Stålberg Uppsala, Sweden imaging genetics Electrodes A B C MU D E Conc EMG signals from 2-15 muscle fibres CNEMG At rest denervation and spec spontaneous
Central core disease of muscle with focal wasting
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1965, 28, 432 VICTOR DUBOWITZ AND MARGARET PLATTS From the Department of Child Health and the Department of Medicine, University of Sheffield In 1956 Shy and Magee described
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1965, 28, 432 VICTOR DUBOWITZ AND MARGARET PLATTS From the Department of Child Health and the Department of Medicine, University of Sheffield In 1956 Shy and Magee described
The near-nerve sensory nerve conduction in tarsal tunnel syndrome
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1985;48: 999-1003 The near-nerve sensory nerve conduction in tarsal tunnel syndrome SHN J OH, HYUN S KM, BASHRUDDN K AHMAD From the Department ofneurology,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1985;48: 999-1003 The near-nerve sensory nerve conduction in tarsal tunnel syndrome SHN J OH, HYUN S KM, BASHRUDDN K AHMAD From the Department ofneurology,
Computer method for the analysis of evoked
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1975, 38, 417-428 Computer method for the analysis of evoked motor unit potentials 2. Duchenne, limb-girdle, facioscapulohumeral and myotonic muscular
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1975, 38, 417-428 Computer method for the analysis of evoked motor unit potentials 2. Duchenne, limb-girdle, facioscapulohumeral and myotonic muscular
Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG
 Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG Drs R Arunachalam Consultant Clinical Neurophysiologist Wessex Neurological Centre Southampton University Hospital EMG/NCS EMG machine For the assessment of patients
Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG Drs R Arunachalam Consultant Clinical Neurophysiologist Wessex Neurological Centre Southampton University Hospital EMG/NCS EMG machine For the assessment of patients
MALIGNANT HYPERTHERMIA: A DISEASE OF SPECIFIC MYOFIBER TYPE?
 MALIGNANT HYPERTHERMIA: A DISEASE OF SPECIFIC MYOFIBER TYPE? THOMAS E. NELSON AND SYDNEY S. ScltOCHgT, JR. ABSTRACT The present study attempts to determine if malignant hyperthermia susceptibility () is
MALIGNANT HYPERTHERMIA: A DISEASE OF SPECIFIC MYOFIBER TYPE? THOMAS E. NELSON AND SYDNEY S. ScltOCHgT, JR. ABSTRACT The present study attempts to determine if malignant hyperthermia susceptibility () is
CLASSIFICATION OF PERIPHERAL NERVE DISEASES
 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF NEUROGENIC DISORDERS & MYOPATHIES NEUROPATHY MYOPATHY Weakness distal proximal Sensory loss + 0 Loss of reflexes early late CSF protein elevated normal Electromyography neurogenic
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF NEUROGENIC DISORDERS & MYOPATHIES NEUROPATHY MYOPATHY Weakness distal proximal Sensory loss + 0 Loss of reflexes early late CSF protein elevated normal Electromyography neurogenic
Diagnosis of McArdle's disease in an elderly patient: Case report and review of literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurology Volume 9 Number 1 Diagnosis of McArdle's disease in an elderly patient: Case report and review of literature R Makary, A Berger, N Talpur, S Shuja Citation R
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurology Volume 9 Number 1 Diagnosis of McArdle's disease in an elderly patient: Case report and review of literature R Makary, A Berger, N Talpur, S Shuja Citation R
muscle biopsy How to do it
 How to do it muscle biopsy Gillian Hall Department of Clinical Neurosciences, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh EH4 2XU. Email: ghall@skull.dcn.ed.ac.uk INTRODUCTION Good clinical evaluation remains
How to do it muscle biopsy Gillian Hall Department of Clinical Neurosciences, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh EH4 2XU. Email: ghall@skull.dcn.ed.ac.uk INTRODUCTION Good clinical evaluation remains
Pediatric Aspects of EDX
 Pediatric Aspects of EDX Albert C. Clairmont, MD Associate Professor-Clinical The Ohio State University February 25, 2013 Objectives Overview of Pediatric Electrodiagnosis (EDX) Understand the different
Pediatric Aspects of EDX Albert C. Clairmont, MD Associate Professor-Clinical The Ohio State University February 25, 2013 Objectives Overview of Pediatric Electrodiagnosis (EDX) Understand the different
Sciatic nerve motor conduction velocity studyt
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1967, 30, 233 Sciatic nerve motor conduction velocity studyt C.-B. YAP AND T. HIROTA From the Department of Neurology and Psychiatry, Northwestern University Medical School,
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1967, 30, 233 Sciatic nerve motor conduction velocity studyt C.-B. YAP AND T. HIROTA From the Department of Neurology and Psychiatry, Northwestern University Medical School,
GLYCOGEN LOSS IN RAT MUSCLES DURING LOCOMOTION ON DIFFERENT INCLINES
 J. exp. Biol. 176, 135 144 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 135 GLYCOGEN LOSS IN RAT MUSCLES DURING LOCOMOTION ON DIFFERENT INCLINES R. B. ARMSTRONG and C. R. TAYLOR
J. exp. Biol. 176, 135 144 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 135 GLYCOGEN LOSS IN RAT MUSCLES DURING LOCOMOTION ON DIFFERENT INCLINES R. B. ARMSTRONG and C. R. TAYLOR
Clinical and electrophysiological study of the
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1964, 27. 351 Clinical and electrophysiological study of the pattern of conduction times in the distribution of the sciatic nerve M. M. GASSEL AND W. TROJABORG From the
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1964, 27. 351 Clinical and electrophysiological study of the pattern of conduction times in the distribution of the sciatic nerve M. M. GASSEL AND W. TROJABORG From the
A Histological and Histochemical Study of the Brown and Yellow Adipose Tissue of the Bat, Hipposideros speoris
 369 A Histological and Histochemical Study of the Brown and Yellow Adipose Tissue of the Bat, Hipposideros speoris By J. C. GEORGE and J. EAPEN {From the Laboratories of Animal Physiology and Histochemistry,
369 A Histological and Histochemical Study of the Brown and Yellow Adipose Tissue of the Bat, Hipposideros speoris By J. C. GEORGE and J. EAPEN {From the Laboratories of Animal Physiology and Histochemistry,
DSS-1. No financial disclosures
 DSS-1 No financial disclosures Clinical History 9 year old boy with past medical history significant for cerebral palsy, in-turning right foot, left clubfoot that was surgically corrected at 3 years of
DSS-1 No financial disclosures Clinical History 9 year old boy with past medical history significant for cerebral palsy, in-turning right foot, left clubfoot that was surgically corrected at 3 years of
Keywords. Introduction. Use of 4-aminopyridine for Motor Weakness Due to Charcot- Marie - Tooth Hereditary Motor Sensory Neuropathy.
 CASE REPORT Use of 4-aminopyridine for Motor Weakness Due to Charcot- Marie - Tooth Hereditary Motor Sensory Neuropathy Jay M. Meythaler* and Jean Peduzzi-Nelson* Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation,
CASE REPORT Use of 4-aminopyridine for Motor Weakness Due to Charcot- Marie - Tooth Hereditary Motor Sensory Neuropathy Jay M. Meythaler* and Jean Peduzzi-Nelson* Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation,
Abnormal EMG Patterns in Disease. Amanda C. Peltier, MD MS October 12, 2013
 Abnormal EMG Patterns in Disease Amanda C. Peltier, MD MS October 12, 2013 Disclosures I have no financial relationships to disclose that are relative to the content of my presentation. Basic Tenets of
Abnormal EMG Patterns in Disease Amanda C. Peltier, MD MS October 12, 2013 Disclosures I have no financial relationships to disclose that are relative to the content of my presentation. Basic Tenets of
ICU Acquired Weakness Mobilisation Nutrition. ICU Acquired Weakness CRITICALLY ILL 20/10/2017. X. Wittebole Critical Care Department
 ICU Acquired Weakness Mobilisation Nutrition X. Wittebole Critical Care Department CRITICALLY ILL 2 ICU Acquired Weakness 1915: Sr W. OSLER The Principles of Medicine VIIIth Edition «Neuromuscular Dysfunction
ICU Acquired Weakness Mobilisation Nutrition X. Wittebole Critical Care Department CRITICALLY ILL 2 ICU Acquired Weakness 1915: Sr W. OSLER The Principles of Medicine VIIIth Edition «Neuromuscular Dysfunction
Hereditary distal spinal muscular atrophy
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1980, 43, 413-418 Hereditary distal spinal muscular atrophy with vocal cord paralysis I D YOUNG AND P S HARPER From the Section ofmedical Genetics, Department
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1980, 43, 413-418 Hereditary distal spinal muscular atrophy with vocal cord paralysis I D YOUNG AND P S HARPER From the Section ofmedical Genetics, Department
A family study of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
 Joturnal of Medical Genetics, 1982, 19, 88-93 A family study of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease A P BROOKS* AND A E H EMERY From the University Department of Human Genetics, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh
Joturnal of Medical Genetics, 1982, 19, 88-93 A family study of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease A P BROOKS* AND A E H EMERY From the University Department of Human Genetics, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh
The Internist s Approach to Neuropathy
 The Internist s Approach to Neuropathy VOLKAN GRANIT, MD, MSC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY NEUROMUSCU LAR DIVISION UNIVERSITY OF MIAMI, MILLER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE RELEVANT DECLARATIONS Financial disclosures:
The Internist s Approach to Neuropathy VOLKAN GRANIT, MD, MSC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY NEUROMUSCU LAR DIVISION UNIVERSITY OF MIAMI, MILLER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE RELEVANT DECLARATIONS Financial disclosures:
NEUROPATHY IN PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE 1
 267 616.833-02:616.13-005 NEUROPATHY IN PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE 1 Its Bearing on Diabetic Neuropathy BY E. C. HUTCHINSON AND L. A. LIVERSKDGE (From the Department of Neurology, Manchester Royal Infirmary)
267 616.833-02:616.13-005 NEUROPATHY IN PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE 1 Its Bearing on Diabetic Neuropathy BY E. C. HUTCHINSON AND L. A. LIVERSKDGE (From the Department of Neurology, Manchester Royal Infirmary)
Possible neurogenic factor in muscular dystrophy:
 Joutrnal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1973, 36, 399-410 Possible neurogenic factor in muscular dystrophy: its similarity to denervation atrophy' DARAB K. DASTUR AND ZOHRA A. RAZZAK From
Joutrnal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1973, 36, 399-410 Possible neurogenic factor in muscular dystrophy: its similarity to denervation atrophy' DARAB K. DASTUR AND ZOHRA A. RAZZAK From
Central core disease in one of identical twins
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 659-663 Central core disease in one of identical twins MICHAEL E. COHEN, PATRICIA K. DUFFNER, AND REID HEFFNER From the Division of Child Neurology
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 659-663 Central core disease in one of identical twins MICHAEL E. COHEN, PATRICIA K. DUFFNER, AND REID HEFFNER From the Division of Child Neurology
Increased motor unit fibre density in the external
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1980, 43, 343-347 Increased motor unit fibre density in the external anal sphincter muscle in ano-rectal incontinence: a single fibre EMG study M E NEILL
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1980, 43, 343-347 Increased motor unit fibre density in the external anal sphincter muscle in ano-rectal incontinence: a single fibre EMG study M E NEILL
Role of Quantitative Electromyography in Detecting Subclinical Skeletal Myopathy in Patients with Idiopathic Dilated Cardiomyopathy
 World Journal of Medical Sciences 8 (4): 334-338, 2013 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2013 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2013.8.4.754 Role of Quantitative Electromyography in Detecting Subclinical Skeletal
World Journal of Medical Sciences 8 (4): 334-338, 2013 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2013 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2013.8.4.754 Role of Quantitative Electromyography in Detecting Subclinical Skeletal
Motor and sensory nerve conduction studies
 3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 2 Assessment of peripheral nerves function and structure in suspected peripheral neuropathies
3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 2 Assessment of peripheral nerves function and structure in suspected peripheral neuropathies
Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM. Andrzej Sladkowski
 Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM Andrzej Sladkowski Potential causes of weakness in the ICU-1 Muscle disease Critical illness myopathy Inflammatory myopathy Hypokalemic
Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM Andrzej Sladkowski Potential causes of weakness in the ICU-1 Muscle disease Critical illness myopathy Inflammatory myopathy Hypokalemic
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of One Hundred Pediatric Muscle Biopsies During A 2-Year Period in Mofid Children And Toos Hospitals
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of One Hundred Pediatric Muscle Biopsies During A 2-Year Period in Mofid Children And Toos Hospitals How to Cite This Article: : Nilipor Y, Shariatmadari F, Abdollah gorji F,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of One Hundred Pediatric Muscle Biopsies During A 2-Year Period in Mofid Children And Toos Hospitals How to Cite This Article: : Nilipor Y, Shariatmadari F, Abdollah gorji F,
Shalini Mahajan, M.D. Director, LA Neuromuscular Center (LANMC) Attune Health, Beverly Hills, CA
 Shalini Mahajan, M.D. Director, LA Neuromuscular Center (LANMC) Attune Health, Beverly Hills, CA Business Address LA Neuromuscular Center Attune Health 8750 Wilshire Blvd, Ste 350, Beverly Hills, CA 90211
Shalini Mahajan, M.D. Director, LA Neuromuscular Center (LANMC) Attune Health, Beverly Hills, CA Business Address LA Neuromuscular Center Attune Health 8750 Wilshire Blvd, Ste 350, Beverly Hills, CA 90211
Autosomal recessive distal myopathy
 J Clin Pathol 1988;41:188-194 Autosomal recessive distal myopathy H ISAACS, MARGARET E BADENHORST, T WHISTLER From the Neuromuscular Research Laboratory, Department of Physiology, Witwatersrand University
J Clin Pathol 1988;41:188-194 Autosomal recessive distal myopathy H ISAACS, MARGARET E BADENHORST, T WHISTLER From the Neuromuscular Research Laboratory, Department of Physiology, Witwatersrand University
Tibial and Common Peroneal Nerve Compression in The Popliteal Fossa: A Case Report and Literature Review
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Tibial and Common Peroneal Nerve Compression in The Popliteal Fossa: A Case Report and Literature D Reichner, G Evans Citation D Reichner,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Tibial and Common Peroneal Nerve Compression in The Popliteal Fossa: A Case Report and Literature D Reichner, G Evans Citation D Reichner,
Myopathy in Whipple's disease
 Gut, 1977, 18, 800-804 Myopathy in Whipple's disease M. SWASH, M. S. SCHWARTZ, M. J. VANDENBURG, AND D. J. POLLOCK From the Departments of Medicine and Pathology, The London Hospital, London SUMMARY We
Gut, 1977, 18, 800-804 Myopathy in Whipple's disease M. SWASH, M. S. SCHWARTZ, M. J. VANDENBURG, AND D. J. POLLOCK From the Departments of Medicine and Pathology, The London Hospital, London SUMMARY We
Conventional needle electromyography
 3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 5 Electromyography: Surface, needle conventional and single fiber - Level 1-2 Conventional
3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 5 Electromyography: Surface, needle conventional and single fiber - Level 1-2 Conventional
Lipid changes in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1972, 35, 658-663 B. P. HUGHES From the Muscular Dystrophy Research Laboratory, Institute of Neurology, The National Hospital, London SUMMARY Thin layer
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1972, 35, 658-663 B. P. HUGHES From the Muscular Dystrophy Research Laboratory, Institute of Neurology, The National Hospital, London SUMMARY Thin layer
Pathology of Neuromuscular Disease Part 1: muscle
 Pathology of Neuromuscular Disease Part 1: muscle Zarife Sahenk, MD. PhD. Research Institute at Nationwide Children s Hospital Center for gene therapy, Neuromuscular Program Experimental & Clinical Neuromuscular
Pathology of Neuromuscular Disease Part 1: muscle Zarife Sahenk, MD. PhD. Research Institute at Nationwide Children s Hospital Center for gene therapy, Neuromuscular Program Experimental & Clinical Neuromuscular
Diagnosis of ocular myopathy
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 97I) 55, 633 Diagnosis of ocular myopathy MARGARET BARRIE Consultant Neurologist, St. Margaret's Hospital, Epping AND KENNETH HEATHFIELD Consultant Neurologist, Oldchurch Hospital,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 97I) 55, 633 Diagnosis of ocular myopathy MARGARET BARRIE Consultant Neurologist, St. Margaret's Hospital, Epping AND KENNETH HEATHFIELD Consultant Neurologist, Oldchurch Hospital,
Carcinoid myopathy and treatment with cyproheptadine (Periactin)
 Gut, 1974, 15, 34-38 Carcinoid myopathy and treatment with cyproheptadine (Periactin) ELLIOT M. BERRY', CAROLINE MAUNDER, AND MARIE WILSON From the Royal Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Hospital,
Gut, 1974, 15, 34-38 Carcinoid myopathy and treatment with cyproheptadine (Periactin) ELLIOT M. BERRY', CAROLINE MAUNDER, AND MARIE WILSON From the Royal Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Hospital,
EMG CASE No. 61, April 2003
 EMG CASE No. 61, April 2003 Presenting Symptom(s): Progressive left arm weakness, cramping, and muscle twitching. Case prepared by: Ann A. Little, M.D. James W. Teener, M.D. University of Michigan Department
EMG CASE No. 61, April 2003 Presenting Symptom(s): Progressive left arm weakness, cramping, and muscle twitching. Case prepared by: Ann A. Little, M.D. James W. Teener, M.D. University of Michigan Department
A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL
 A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL CASE HISTORY Nine year old male child Second born Born
A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL CASE HISTORY Nine year old male child Second born Born
(From the Division of Animal Physiology and Histochemistry, Department of Zoology, M.S. University of Baroda, Baroda, India) With i plate (fig.
 Histochemical demonstration of certain DPN-linked dehydrogenases and of aldolase in the red and white fibres of pigeon breast-muscle By J. C. GEORGE and C. L. TALESARA (From the Division of Animal Physiology
Histochemical demonstration of certain DPN-linked dehydrogenases and of aldolase in the red and white fibres of pigeon breast-muscle By J. C. GEORGE and C. L. TALESARA (From the Division of Animal Physiology
Prognosis of alcoholic peripheral neuropathy
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1984;47:699-703 Prognosis of alcoholic peripheral neuropathy MATTI HILLBOM,* ARNE WENNBERGt From the Department of Clinical Alcohol and Drug Research,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1984;47:699-703 Prognosis of alcoholic peripheral neuropathy MATTI HILLBOM,* ARNE WENNBERGt From the Department of Clinical Alcohol and Drug Research,
Hoffmann s syndrome: An atypical neurological manifestation of hypothyroidism
 Case report Hoffmann s syndrome: An atypical neurological manifestation of hypothyroidism Dr. Prinesh Varghese, Dr. Keni Ravish Rajiv, Dr. Uthaya Sankar Department of General Medicine, Sri Manakula Vinayagar
Case report Hoffmann s syndrome: An atypical neurological manifestation of hypothyroidism Dr. Prinesh Varghese, Dr. Keni Ravish Rajiv, Dr. Uthaya Sankar Department of General Medicine, Sri Manakula Vinayagar
Shoulder abduction fatiguability
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1987;5:423-427 J NICKLIN, Y KARNI, C M WILES From the Departments of Clinical Neurophysiology and Physiotherapy, The National Hospitalfor Nervous Diseases,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1987;5:423-427 J NICKLIN, Y KARNI, C M WILES From the Departments of Clinical Neurophysiology and Physiotherapy, The National Hospitalfor Nervous Diseases,
Median-ulnar nerve communications and carpal tunnel syndrome
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1977, 40, 982-986 Median-ulnar nerve communications and carpal tunnel syndrome LUDWIG GUTMANN From the Department of Neurology, West Virginia University,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1977, 40, 982-986 Median-ulnar nerve communications and carpal tunnel syndrome LUDWIG GUTMANN From the Department of Neurology, West Virginia University,
Measure #1a: Essential Components of Electrodiagnostic (EDX) Evaluation for Median Neuropathy at the Wrist
 Measure #1a: Essential Components of Electrodiagnostic (EDX) Evaluation for Median Neuropathy at the Wrist Measure Description Percentage of patients referred for EDX evaluation of CTS who had adequate
Measure #1a: Essential Components of Electrodiagnostic (EDX) Evaluation for Median Neuropathy at the Wrist Measure Description Percentage of patients referred for EDX evaluation of CTS who had adequate
Voháňka S., Vytopil M., *Lukáš Z., **Dušek L. Toman J***
 Quantitative analysis of motor unit action potentials as a non-invasive technique assessing subclinical skeletal muscle involvement in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy and conduction system disease.
Quantitative analysis of motor unit action potentials as a non-invasive technique assessing subclinical skeletal muscle involvement in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy and conduction system disease.
Appearance in Slow Muscle Sarcolemma of Specializations Characteristic of Fast Muscle after Reinnervation by a Fast Muscle Nerve
 EXPERIMENTAL NEUROLOGY 58, 59-67 (1978) Appearance in Slow Muscle Sarcolemma of Specializations Characteristic of Fast Muscle after Reinnervation by a Fast Muscle Nerve MAKK H. ELLISMAN, MICHAEL H. BKOOKE,
EXPERIMENTAL NEUROLOGY 58, 59-67 (1978) Appearance in Slow Muscle Sarcolemma of Specializations Characteristic of Fast Muscle after Reinnervation by a Fast Muscle Nerve MAKK H. ELLISMAN, MICHAEL H. BKOOKE,
CIDP + MMN - how to diagnose and treat. Dr Hadi Manji
 CIDP + MMN - how to diagnose and treat Dr Hadi Manji Outline Introduction CIDP Diagnosis Clinical features MRI Nerve conduction tests Lumbar puncture Nerve biopsy Treatment IV Ig Steroids Plasma Exchnage
CIDP + MMN - how to diagnose and treat Dr Hadi Manji Outline Introduction CIDP Diagnosis Clinical features MRI Nerve conduction tests Lumbar puncture Nerve biopsy Treatment IV Ig Steroids Plasma Exchnage
Compound Nerve Action Potential of Common Peroneal Nerve and Sural Nerve Action Potential in Common Peroneal Neuropathy
 J Korean Med Sci 2008; 23: 117-21 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.1.117 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Compound Nerve Action Potential of Common Peroneal Nerve and Sural Nerve
J Korean Med Sci 2008; 23: 117-21 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.1.117 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Compound Nerve Action Potential of Common Peroneal Nerve and Sural Nerve
electrophysiological and nerve biopsy study
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1984;47:543-548 Delayed neuropathy after organophosphorus insecticide (Dipterex) poisoning: a clinical, electrophysiological and nerve biopsy study C
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1984;47:543-548 Delayed neuropathy after organophosphorus insecticide (Dipterex) poisoning: a clinical, electrophysiological and nerve biopsy study C
American Academy of Neurology Neuromuscular Section Resident Core Curriculum
 American Academy of Neurology Neuromuscular Section Resident Core Curriculum 10/03/01 1. Introduction: Neuromuscular disorders are a significant component of the diseases of the nervous system that neurologists
American Academy of Neurology Neuromuscular Section Resident Core Curriculum 10/03/01 1. Introduction: Neuromuscular disorders are a significant component of the diseases of the nervous system that neurologists
