Diagnosis of ocular myopathy
|
|
|
- Rodney Booker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
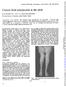
1 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 97I) 55, 633 Diagnosis of ocular myopathy MARGARET BARRIE Consultant Neurologist, St. Margaret's Hospital, Epping AND KENNETH HEATHFIELD Consultant Neurologist, Oldchurch Hospital, Ronrford Hutchinson (1897) described a disorder in which ptosis was associated with paralysis of the other extraocular muscles to which he gave the name "external ophthalmoplegia". Fuchs (I890) reported five patients with ptosis, in two of whom the disorder was familial, and Dutil (I892) and Delord (I903) published two other cases of an unusual familial form of dysphagia associated with ptosis. The prevailing opinion at the time was that external ophthalmoplegia was due to a degeneration of cranial nerve nuclei. The idea that ptosis was but a fragment of a progressive dystrophy of all striated ocular muscles was put forward by Treacher Collins (I922) and by Sandifer (I946). This opinion has gained acceptance only since the critical study of Kilch and Nevin (I95I), in which five patients with progressive muscular dystrophy with early and predominant affection of the external ocular muscles were described; they suggested that the term "ocular myopathy" be applied to these cases. Lees and Liversedge (I962) described three examples of the descending form of this disease. In their cases the ptosis and ophthalmoplegia preceded by many years the involvement of the face, pharynx, larynx, neck, shoulder, and pelvic girdles, and the course of the illness was slow and relatively benign. Victor, Hayes, and Adams (i962) called attention to a form of restricted myopathy of cranial muscles characterized by dysphagia and ptosis which they called oculopharyngeal myopathy; both familial and sporadic cases were described and firm evidence was presented that the disorder was myopathic. Roberts and Bamforth (I968) analysed 26 further patients diagnosed as cases ofocular myopathy; six of their patients had dysphagia with motility and radiographic changes suggesting that the dystrophic process also involved the smooth muscle of the oesophagus. Because of the apparent rarity and lack of general recognition of ocular myopathy, we thought it of interest to describe four cases seen over the course of one year. Case reports Case I, a 22-year-old single woman, developed drooping of the eyelids at the age of i I years. She had two operations to correct this at the ages of i i and I 5 years. Her relatives noticed that her eye movements were limited but she had not complained of double vision. She stated that if she talked or read aloud for some length of time her voice became weak. There was no family history of myopathy. Received for publication May 17, 1971 Address for reprints: Dr. M. Barrie, St. Margaret's Hospital, Epping, Essex
2 634 Margaret Barrie and Kenneth Heathfield There was severe bilateral ptosis, all eye movements were markedly restricted, those of the left eye being less affected; there was I0 of side-to-side movement, no movement above the horizontal, and only 50 downward movement. The pupils were equal and the reactions were normal. This patient also had bilateral weakness of the orbicularis oculi and ofthe lowerfacial muscles leading to a mournful expression. There was considerable wasting of the muscles of the neck and she was unable to lift her head up from the pillow. Her tongue was small but there was no myotonia; her voice was weak. Palatal movements appeared to be normal. There was considerable wasting of the muscles of the forearms on both sides. The upper limbs showed asymmetrical weakness, more marked on the right side and affecting especially the trapezii and triceps. There was also weakness of the trunk muscles and of hip flexors. All the tendon reflexes were absent in the upper limbs, but normal in the lower limbs; the plantar responses were flexor. Electromyography of the left lateral rectus was consistent with myopathy, the units on voluntary deviation being of extremely low amplitude (about 20 p.v) and rather scanty. Serum creatinine phosphokinase was I I6 mu/ml. (normal range for women 5-50 mu/ml.) but the serum aldolase at o09 mu/ml. was within the normal range o-6 mu/ml. Muscle biopsy of the deltoid (Fig. I) showed some variation in the size and staining properties of the muscle fibres with minimal degenerative changes affecting single segments rather than the whole fibre. The changes were slight but myopathic in type. It should be noted that the muscle used for biopsy was not clinically affected. FIG. I Biopsy of deltoid muscle in Case I. x 90 Case 2, a 34-year-old married woman, developed drooping of the right eyelid at the age of 25 years. For a year she had noticed blurring of vision but no true diplopia on lifting the eyelid, and she had had mild pain in the right eye, with difficulty in reading. There was no family history of myopathy. She was a pale, thin, anxious woman. There was an obvious right ptosis but the pupils were equal and reacted normally. The upward and downward movements of both eyes were full. There was moderate weakness of abduction of the right eye and slight weakness of the left and considerable weakness of adduction of the right eye. There was a little weakness of both orbicularis oculi muscles and definite weakness of the neck muscles and of the right triceps. The tendon reflexes were brisk and equal. Plantar responses were flexor. A tensilon test was negative. Serum creatinine phosphokinase was normal at 39 mu/ml. and the aldolase was within normal limits. The electromyogram was compatible with a mild myopathy.
3 Diagnosis of ocular nyopathy Muscle biopsy of levator palpebrae (Figs 2 and 3) revealed that the muscles were almost completely destroyed and contained only a few surviving, apparently normal, fibres. The bulk of the specimen consisted of fibres and fatty tissue containing numerous nerve bundles. The good preservation of the latter suggested that the lesion was a myopathy. FIG. 2 Biopsy of levator palpebrae muscle in Case 2. X 120 F I G. 3 Biopsy of levator palpebrae muscle in Case 2. X I20 Treatment A surgical repair of the ptosis was made when the muscle biopsy was performed. satisfied with the result of this operation. The patient was Case 3, a 46-year-old married woman, developed drooping of the right eyelid at the age of 41 years. For the previous 6 months she had complained of aching of the right eye but there was no definite diplopia. There was no family history of myopathy. There was moderate right ptosis but the eyelid did not cover the pupil. There was also mild proptosis of the right eye. There was limitation of abduction of both eyes, and of adduction of the right. There was bilateral weakness of the orbicularis oculi and the voice was weak. The neck muscles were also weak and the patient was unable to lift her head from the pillow. The right triceps muscle was slightly weak. The reflexes were brisk and equal; the plantar responses were flexor. A tensilon test was negative. Creatinine phosphokinase was raised 63 mu/ml. Electromyography of the sternomastoid showed only a few short motor units in the right. The motor unit pattern was otherwise normal. Radioactive iodine uptake and serum protein bound iodine were both within normal limits. Muscle biopsy was not done. 635
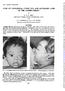
4 636 Margaret Barrie and Kenneth Heathfield Case 4, a 7x-year-old man, had developed drooping of the eyelids at 50 years of age. This had been much more marked during the last year, when he had noticed double vision on reading, images being vertically separated. He had also noticed slight weakness of the neck and shoulders. He had been diagnosed as suffering from myxoedema I0 years earlier, and had since taken thyroid tablets (I 20 mg. a day). There was a family history of ptosis and of haemophilia, as shown in Fig. 4. I II III Me affcected (ocular myopathy) (Q haemophilia unaffected FIG. 4 Case 4. Family tree He had severe bilateral ptosis (Fig. 5), two-thirds of each pupil being covered by the upper lid. All eye movements were severely restricted; there was less than 50 movement up and down and less than 100 side-to-side. The pupils were equal in size and reacted to light and accommodation. The forehead was constantly wrinkled and the eyebrows were raised above the level of the supraorbital ridges. Both orbicularis oculi muscles were weak and there was slight weakness of the lower face and of both sternomastoids and trapezii. The tendon reflexes were brisk and equal; plantar responses were flexor. Muscle biopsy of the sternomastoid is shown in Fig. 6. Br J Ophthalmol: first published as /bjo on 1 September Downloaded from FIG. 5 Case 4. Bilateral ptosis l sig..~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~.....:d... -N L FIG 6(Biopsy of sternomastoid muscle in Case 4. x T00 on 26 August 2018 by guest. Protected by
5 Diagnosis of ocular myopathy 637 A tensilon test was negative. Electromyogram of the right sternomastoid showed patches of small, short disintegrated myopathic units throughout the muscle. The right deltoid and right quadriceps showed normal activity. Serum creatinine phosphokinase was raised at 82 i.u./litre. Muscle biopsy of the sternomastoid (Fig. 6) showed a considerable increase in the amount of fibrous tissue, which contained a few remaining muscle fibres. Outside the areas of fibrosis the muscles showed no abnormality. These appearances were those of a low grade myopathy. Treatment This patient had a bilateral repair of his ptosis and was pleased with the improvement in his ability to see and in his appearance. Methods of investigation Investigation of patients with ocular myopathy is reasonably simple and the estimation of serum muscle enzymes is a useful confirmatory test, although these may not always be abnormal if the disease is restricted to a small group of muscles. Muscle biopsy of the external ocular muscles is not easy to perform and not a minor procedure, although it can be combined with correction of the ptosis. It was useful in two of these patients to perform a plastic operation on the eyelid and to take a biopsy of the levator palpebrae simultaneously. Unfortunately the state of this muscle was not entirely satisfactory from the pathological point of view, as the disease process was found to be far advanced by the time of the biopsy. In another patient, in whom a limb girdle muscle was sampled, this showed early changes of muscular dystrophy. Discussion Cases I to 3 illustrate the descending ocular myopathy of the type described by Lees and Liversedge (i 962). As in their cases, there was no family history of any similar condition. In Case i the disease was more or less symmetrical but in Cases 2 and 3 it was markedly asymmetrical. Case 2 at first glance resembled a unilateral third nerve palsy and it is of interest that this patient had been investigated as such in a Neuro-surgical Unit by means of carotid arteriograms and air studies. Case 3 had also been misdiagnosed as one of exophthalmic ophthalmoplegia because of slight unilateral proptosis. However, the weakness of the neck and shoulder girdle muscles is out of keeping with this diagnosis unless there is coexistent thyrotoxic myopathy and a definite unilateral ptosis would also be most unusual in this disease. There was no oedema of the eyelids or injection of the conjunctivae and major symptoms of ocular discomfort characteristic of exophthalmic ophthalmoplegia were absent. Case 4 illustrates a slowly progressive, familial form of this disease. The family tree suggests a dominant mode of inheritance, although the patient's parents were allegedly normal. The disease had progressed slowly over two decades to affect the face, neck, and shoulder muscles as in the other patients. The most important differential diagnosis in these patients is that of myasthenia gravis. The tensilon test usually distinguishes this condition (edrophonium chloride i o mg. intravenously). While there may not be much improvement in the power of the external ocular muscles with tensilon, the drooping of the eyelids almost invariably improves with an injection of this substance. Ophthalmologists should always be on the lookout for this neurological disorder in patients presenting to them with ptosis.
6 638 Margaret Barrie and Kenneth Heathfield Summary The literature of ocular myopathy is reviewed. Four cases of this condition are presented and the differential diagnosis discussed. Our thanks are due to Prof. H. Ulrich of The London Hospital for reports and photographs, Dr. N. Rudolph for electromyography, and Mr. Tom O'Driscoll for helpful comments. References COLLINS, E. TREACHER (1922) "Hereditary ocular degenerations; ophthalmic abiotrophies", in "International Congress of Ophthalmology: Washington, D.C., April 25-28, 1922", vol. I, pp. I DELORD, E. (1903) Presse mid., II, 592 DUTIL, A. (I892) Rec. Ophtal., 3e ser, I4e annee, 693 FUCHS, E. (I890) v. Graefes Arch. Ophthal., 36, 234 HUTCHINSON, J. (I879) Med-chir. Trans., 62, 307 KILOH, L. G., and NEVIN, S. (I95I) Brain, 74, I 5 LEES, F., and LIVERSEDGE, L. A. (I962) Ibid., 85, 70 I ROBERTS, A. H., and BAMFORTH, J. (I968) Neurology (Minneap.), I8, 645 SANDIFER, P. H. (1946) J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 9, 8i TAYLOR, F. W. (1915) J. nerv. ment. Dis., 42, I29 VICTOR, M., HAYES, R.,and ADAMS, R. D. (i962) New Engi. J. Med., 267, 1267 Br J Ophthalmol: first published as /bjo on 1 September Downloaded from on 26 August 2018 by guest. Protected by
PROGRESSIVE EXTERNAL OPHTHALMOPLEGIA*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1956) 40, 686. PROGRESSIVE EXTERNAL OPHTHALMOPLEGIA* BY F. D. McAULEY London THIS condition, in which the movements of the eyeballs tend progressively to diminish in amplitude, is usually
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1956) 40, 686. PROGRESSIVE EXTERNAL OPHTHALMOPLEGIA* BY F. D. McAULEY London THIS condition, in which the movements of the eyeballs tend progressively to diminish in amplitude, is usually
Hereditary quadriceps myopathy
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1973, 36, 1041-1045 Hereditary quadriceps myopathy MICHAEL L. E. ESPIR AND W. B. MATTHEWS' From the Department of Neurology, Derbyshire Royal Infirmary,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1973, 36, 1041-1045 Hereditary quadriceps myopathy MICHAEL L. E. ESPIR AND W. B. MATTHEWS' From the Department of Neurology, Derbyshire Royal Infirmary,
Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
UPPER EYELID DROOPING
 UPPER EYELID DROOPING (PTOSIS) UNDERSTAND MORE ABOUT UPPER EYELID DROOPING (PTOSIS) Upper Eyelid Drooping (Ptosis) What is ptosis? Ptosis is the medical term for drooping of the upper eyelid. It is most
UPPER EYELID DROOPING (PTOSIS) UNDERSTAND MORE ABOUT UPPER EYELID DROOPING (PTOSIS) Upper Eyelid Drooping (Ptosis) What is ptosis? Ptosis is the medical term for drooping of the upper eyelid. It is most
Congenital ocular palsy
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (1972) 56, 356 Congenital ocular palsy C. G. KEITH Queen Elizabeth Hospitalfor Children, Hackney Road, London Three patients with severe restriction of the ocular movements in one eye
Brit. j. Ophthal. (1972) 56, 356 Congenital ocular palsy C. G. KEITH Queen Elizabeth Hospitalfor Children, Hackney Road, London Three patients with severe restriction of the ocular movements in one eye
function after direct surgcal intervention for posterior communicating aneurysms
 Brit. 7. Ophthal. (I97), i i Analysis of the recovery of third nerve function after direct surgcal intervention for posterior communicating aneurysms M. C. GAYSON, S.. SONI, AND V. A. SPOONE University
Brit. 7. Ophthal. (I97), i i Analysis of the recovery of third nerve function after direct surgcal intervention for posterior communicating aneurysms M. C. GAYSON, S.. SONI, AND V. A. SPOONE University
Alleviation of myogenic ptosis by
 Brit. 7. Ophthal. ( I 973) 57, 3 1 5 Preliminary communication Alleviation of myogenic ptosis by magnetic force J. S. CONWAY.'ew End Hospital (Royal Free Hospital Group), London, N.F.3., and lvhipps Cross
Brit. 7. Ophthal. ( I 973) 57, 3 1 5 Preliminary communication Alleviation of myogenic ptosis by magnetic force J. S. CONWAY.'ew End Hospital (Royal Free Hospital Group), London, N.F.3., and lvhipps Cross
BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII
 463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
OCULAR ASPECTS OF ELECTROMYOGRAPHY*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 394. OCULAR ASPECTS OF ELECTROMYOGRAPHY*t BY SIDNEY I. DAVIDSON$ Midland Centre for Neurosurgery, Smethwick, Birmingham THE purpose of this paper is to provide simplified concepts
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 394. OCULAR ASPECTS OF ELECTROMYOGRAPHY*t BY SIDNEY I. DAVIDSON$ Midland Centre for Neurosurgery, Smethwick, Birmingham THE purpose of this paper is to provide simplified concepts
Signs: The most common sign seen by ophthalmologists are lid droop
 Myasthenia Gravis Your doctor thinks that you have Myasthenia Gravis (MG). This is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system has damaged receptors on your muscles. This results in muscle weakness
Myasthenia Gravis Your doctor thinks that you have Myasthenia Gravis (MG). This is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system has damaged receptors on your muscles. This results in muscle weakness
ADRENERGIC BLOCKING AGENTS*t A DOUBLE-BLIND TRIAL IN THE TREATMENT OF THE EYE SIGNS OF THYROID DISORDER
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 616 ADRENERGIC BLOCKING AGENTS*t A DOUBLE-BLIND TRIAL IN THE TREATMENT OF THE EYE SIGNS OF THYROID DISORDER BY A. L. CROMBIE+ Professorial Unit, Eye Department, Royal Infirmary,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 616 ADRENERGIC BLOCKING AGENTS*t A DOUBLE-BLIND TRIAL IN THE TREATMENT OF THE EYE SIGNS OF THYROID DISORDER BY A. L. CROMBIE+ Professorial Unit, Eye Department, Royal Infirmary,
Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of
 Peripheral Nervous System Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of non-insulin dependent diabetes
Peripheral Nervous System Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of non-insulin dependent diabetes
cme Combined Eyelid and Strabismus Surgery: Examining Conventional Surgical Wisdom Educational Objectives
 Article Combined Eyelid and Strabismus Surgery: Examining Conventional Surgical Wisdom Michael S. McCracken, MD; Jonathan D. del Prado, MD; David B. Granet, MD; Leah Levi, MBBS; Don O. Kikkawa, MD Abstract
Article Combined Eyelid and Strabismus Surgery: Examining Conventional Surgical Wisdom Michael S. McCracken, MD; Jonathan D. del Prado, MD; David B. Granet, MD; Leah Levi, MBBS; Don O. Kikkawa, MD Abstract
FAMILIAL MYASTHENIA GRAVIS
 Volume 34 - N. 3 Setembro de 1976 FAMILIAL MYASTHENIA GRAVIS REPORT OF FOUR CASES JOSÉ LAMARTINE DE ASSIS * MlLBERTO SCAFF ** Myasthenia gravis (MG) is considered a noninherited, sporadic and uncommon
Volume 34 - N. 3 Setembro de 1976 FAMILIAL MYASTHENIA GRAVIS REPORT OF FOUR CASES JOSÉ LAMARTINE DE ASSIS * MlLBERTO SCAFF ** Myasthenia gravis (MG) is considered a noninherited, sporadic and uncommon
OBJECTIVES. Unit 7:5 PROPERTIES OR CHARACTERISTICS OF MUSCLES. Introduction. 3 Kinds of Muscles. 3 Kinds of Muscles 4/17/2018 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
Tensilon tonography in the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis. Joel S. Closer*
 Tensilon tonography in the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis Joel S. Closer* The concomitant intravenous administration of Tensilon during tonography was performed on a group of 5 myasthenic patients and
Tensilon tonography in the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis Joel S. Closer* The concomitant intravenous administration of Tensilon during tonography was performed on a group of 5 myasthenic patients and
VISUAL REFLEXES. B. The oculomotor nucleus, Edinger-Westphal nucleus, and oculomotor nerve at level of the superior colliculus.
 Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15 HyperBrain: Ch 7 with quizzes and or Lab 7 videotape http://www-medlib.med.utah.edu/kw/hyperbrain/anim/reflex.html
Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15 HyperBrain: Ch 7 with quizzes and or Lab 7 videotape http://www-medlib.med.utah.edu/kw/hyperbrain/anim/reflex.html
Enzyme histochemistry of skeletal muscle
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1966, 29, 23 Enzyme histochemistry of skeletal muscle Part III Neurogenic muscular atrophies VICTOR DUBOWITZ From the Department of Child Health, University of Sheffield
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1966, 29, 23 Enzyme histochemistry of skeletal muscle Part III Neurogenic muscular atrophies VICTOR DUBOWITZ From the Department of Child Health, University of Sheffield
DIAGNOSIS? CASE NUMBER ONE CONVERGENCE DIFFICIENCIES. Children vs. Adults. Insufficiency vs. Paralysis CONVERGENCE INSUFFICIENCY
 CONVERGENCE DIFFICIENCIES Children vs. Adults Insufficiency vs. Paralysis CASE NUMBER ONE DIAGNOSIS? 8 year boy referred from school- headaches, reading difficulties and blurred vision MY EXAMINATION 20/20-
CONVERGENCE DIFFICIENCIES Children vs. Adults Insufficiency vs. Paralysis CASE NUMBER ONE DIAGNOSIS? 8 year boy referred from school- headaches, reading difficulties and blurred vision MY EXAMINATION 20/20-
Management of ipsilateral ptosis with hypotropia
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1986, 70, 732-736 Management of ipsilateral ptosis with hypotropia L A FICKER, J R 0 COLLIN, AND J P LEE From Moorfields Eye Hospital, London SUMMARY Thirty-one patients
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1986, 70, 732-736 Management of ipsilateral ptosis with hypotropia L A FICKER, J R 0 COLLIN, AND J P LEE From Moorfields Eye Hospital, London SUMMARY Thirty-one patients
MYOPATHY IN CUSHING'S SYNDROME
 J. Neurol. iveurosurg. Psychiat., 1959, 22, 314 MYOPATHY N CUSHNG'S SYNDROME BY RAGNAR MULLER and ERC KUGELBERG From the Department of Neurology, Serafimerlasarettet, and the Department of Endocriwology,
J. Neurol. iveurosurg. Psychiat., 1959, 22, 314 MYOPATHY N CUSHNG'S SYNDROME BY RAGNAR MULLER and ERC KUGELBERG From the Department of Neurology, Serafimerlasarettet, and the Department of Endocriwology,
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy
 Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
Case 1: History of J.H. Outside Evaluation. Outside Labs. Question #1
 Case 1: History of J.H. 64 yo man seen at UCSF 6-256 25-07. 9 months ago onset progressive weakness of arms and legs, with muscle atrophy in arms. 4 months ago red scaly rash on face, back of hands and
Case 1: History of J.H. 64 yo man seen at UCSF 6-256 25-07. 9 months ago onset progressive weakness of arms and legs, with muscle atrophy in arms. 4 months ago red scaly rash on face, back of hands and
Ophthalmoplegia in carotid cavernous sinus fistula
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1984, 68, 128-134 Ophthalmoplegia in carotid cavernous sinus fistula T. J. K. LEONARD, I. F. MOSELEY, AND M. D. SANDERS From the Departments ofneuro-ophthalmology and
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1984, 68, 128-134 Ophthalmoplegia in carotid cavernous sinus fistula T. J. K. LEONARD, I. F. MOSELEY, AND M. D. SANDERS From the Departments ofneuro-ophthalmology and
Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction
 Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Neuromuscular Junction Muscle Myastenia Gravis Eaton-Lambert Syndrome Toxic Infllammatory Denervation Atrophy
Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Neuromuscular Junction Muscle Myastenia Gravis Eaton-Lambert Syndrome Toxic Infllammatory Denervation Atrophy
Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1981, 44, 419-425 Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult N E BHARUCHA AND J A MORGAN-HUGHES From the Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London S
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1981, 44, 419-425 Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult N E BHARUCHA AND J A MORGAN-HUGHES From the Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London S
Ocular Myasthenia. a guide. myaware.org 1
 Ocular Myasthenia a guide myaware.org 1 Contents 1. What is myasthenia?...3 2. Myaware...4 3. What is ocular myasthenia?...5 4. Symptoms of ocular MG...5 5. Extraocular muscles...6 6. How do they diagnose
Ocular Myasthenia a guide myaware.org 1 Contents 1. What is myasthenia?...3 2. Myaware...4 3. What is ocular myasthenia?...5 4. Symptoms of ocular MG...5 5. Extraocular muscles...6 6. How do they diagnose
"A" AND "V" PHENOMENA*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 718 "A" AND "V" PHENOMENA*t DHANWANT SINGH, GURBUX SINGH, L. P. AGGARWAL, AND PREM CHANDRA BY From the Department of Ophthalmology, Government Medical College, Patiala, and
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 718 "A" AND "V" PHENOMENA*t DHANWANT SINGH, GURBUX SINGH, L. P. AGGARWAL, AND PREM CHANDRA BY From the Department of Ophthalmology, Government Medical College, Patiala, and
Myasthenia gravis. Page 1 of 7
 Myasthenia gravis What is myasthenia gravis? Myasthenia gravis (sometimes abbreviated to MG) is a chronic, autoimmune condition that causes muscle weakness and excessive muscle fatigue. It is rare, affecting
Myasthenia gravis What is myasthenia gravis? Myasthenia gravis (sometimes abbreviated to MG) is a chronic, autoimmune condition that causes muscle weakness and excessive muscle fatigue. It is rare, affecting
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities Volume 1 Issue 1 2015 PARINAUD'S SYNDROME A CASE REPORT Basker K Shubha Raguram K Stanley Medical College Introduction: Gaze palsies are a group
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities Volume 1 Issue 1 2015 PARINAUD'S SYNDROME A CASE REPORT Basker K Shubha Raguram K Stanley Medical College Introduction: Gaze palsies are a group
CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS PRESENTING WITH VISUAL FIELD DEFECTS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 251 CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS PRESENTING WITH VISUAL FIELD DEFECTS* BY University Department of Ophthalmology and Royal Infirmary, Edinburgh ANEURYSMS occur more frequently within
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 251 CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS PRESENTING WITH VISUAL FIELD DEFECTS* BY University Department of Ophthalmology and Royal Infirmary, Edinburgh ANEURYSMS occur more frequently within
2º ESO - PE Workbook - IES Joan Miró Physical Education Department THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
Myasthenia Gravis. Mike Gilchrist 10/30/06
 Myasthenia Gravis Mike Gilchrist 10/30/06 Overview Background Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Treatment Associated Conditions Background Severe muscle disease Most common disorder of neuromuscular
Myasthenia Gravis Mike Gilchrist 10/30/06 Overview Background Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Treatment Associated Conditions Background Severe muscle disease Most common disorder of neuromuscular
A NEW OPERATION FOR CONGENITAL AND PARALYTIC PTOSIS. By M. SARWAR, M.B., B.S., D.O.M.S. Ophthalmologist, United Oxford Hospitals
 A NEW OPERATION FOR CONGENITAL AND PARALYTIC PTOSIS By M. SARWAR, M.B., B.S., D.O.M.S. Ophthalmologist, United Oxford Hospitals THE various remedies for ptosis have never been really satisfactory, as is
A NEW OPERATION FOR CONGENITAL AND PARALYTIC PTOSIS By M. SARWAR, M.B., B.S., D.O.M.S. Ophthalmologist, United Oxford Hospitals THE various remedies for ptosis have never been really satisfactory, as is
Pupil Exams and Visual Fields
 Pupil Exams and Visual Fields A Closer Look at Cranial Nerves No Financial Interests Amy Jost does not have any financial interests related to this presentation AMY JOST, BS, COMT, CCRC, OSC CINCINNATI
Pupil Exams and Visual Fields A Closer Look at Cranial Nerves No Financial Interests Amy Jost does not have any financial interests related to this presentation AMY JOST, BS, COMT, CCRC, OSC CINCINNATI
Eye Movements. Geometry of the Orbit. Extraocular Muscles
 Eye Movements Geometry of the Orbit The eye (oculus) is located in the anterior aspect of the orbit: the equator of the eye (defined by a coronal plane passing through its middle) lies at the margin of
Eye Movements Geometry of the Orbit The eye (oculus) is located in the anterior aspect of the orbit: the equator of the eye (defined by a coronal plane passing through its middle) lies at the margin of
HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY PRACTICE QUESTIONS
 HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. A patient complains that he has lost sensation on his face and that the skin of his face feels numb. The physician tests tactile acuity by touching the forehead
HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. A patient complains that he has lost sensation on his face and that the skin of his face feels numb. The physician tests tactile acuity by touching the forehead
Electromyography of extraocular muscles
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (I972) 56, 594 Electromyography of extraocular muscles in Duane's syndrome I. M. STRACHAN AND B. H. BROWN Hallamshire Hospital, Sheffield The electromyographic (EMG) study of patients
Brit. j. Ophthal. (I972) 56, 594 Electromyography of extraocular muscles in Duane's syndrome I. M. STRACHAN AND B. H. BROWN Hallamshire Hospital, Sheffield The electromyographic (EMG) study of patients
Graves Ophthalmopathy Overview. Graves Disease Hyperthyroidism TSIgs (anti-tsh-receptor-abs) Graves Disease 10/22/2010
 Graves Disease Robert Graves Graves Ophthalmopathy Overview Robert C. Kersten Dept. of Ophthalmology UCSF Triad Hyperthyroidism Eye findings Pretibial Myxedema (phalangeal acropachy-1%) Most common auto-immune
Graves Disease Robert Graves Graves Ophthalmopathy Overview Robert C. Kersten Dept. of Ophthalmology UCSF Triad Hyperthyroidism Eye findings Pretibial Myxedema (phalangeal acropachy-1%) Most common auto-immune
Clinical and Radiological Aspects of Myopathies
 J.A.L.Bulcke A.L.Baert Clinical and Radiological Aspects of Myopathies CT Scanning EMG Radioisotopes With 151 Figures and 30 Tables Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg GmbH Dr. JAN A. L BULCKE K. U. Leuven,
J.A.L.Bulcke A.L.Baert Clinical and Radiological Aspects of Myopathies CT Scanning EMG Radioisotopes With 151 Figures and 30 Tables Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg GmbH Dr. JAN A. L BULCKE K. U. Leuven,
O unaffected siblings. MYOTONIA CONGENITA (THOMSEN'S DISEASE) 1N A CHINESE FAMILY
 Vol. 10, No. 2. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL 111 June, 1969. MYOTONIA CONGENITA (THOMSEN'S DISEASE) 1N A CHINESE FAMILY By J. S. Cheah, M.B., B.S., M.R.A.C.P. and B. H. Toh, Ms., B.S., (Department of Medicine,
Vol. 10, No. 2. SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL 111 June, 1969. MYOTONIA CONGENITA (THOMSEN'S DISEASE) 1N A CHINESE FAMILY By J. S. Cheah, M.B., B.S., M.R.A.C.P. and B. H. Toh, Ms., B.S., (Department of Medicine,
MYASTHENIA GRAVIS. Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer
 MYASTHENIA GRAVIS Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer OUTLINE Background Anatomy Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Treatment BACKGROUND Acquired autoimmune disorder Clinically characterized by: Weakness
MYASTHENIA GRAVIS Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer OUTLINE Background Anatomy Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Treatment BACKGROUND Acquired autoimmune disorder Clinically characterized by: Weakness
Surgical management of Duane's
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I974) 58, 30 I Surgical management of Duane's syndrome M. H. GOBIN ljniversity Eye Clinic, Leyden, IHolland Ten years ago I introduced a surgical technique for the correction of Duane's
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I974) 58, 30 I Surgical management of Duane's syndrome M. H. GOBIN ljniversity Eye Clinic, Leyden, IHolland Ten years ago I introduced a surgical technique for the correction of Duane's
Myasthenia Gravis What is Myasthenia Gravis? Who is at risk of developing MG? Is MG hereditary? What are the symptoms of MG? What causes MG?
 Myasthenia Gravis What is Myasthenia Gravis? Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a chronic, autoimmune disease that causes muscle weakness and excessive muscle fatigue. It is uncommon, affecting about 15 in every
Myasthenia Gravis What is Myasthenia Gravis? Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a chronic, autoimmune disease that causes muscle weakness and excessive muscle fatigue. It is uncommon, affecting about 15 in every
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Neurological Assessment Part 1
 Neurological Assessment Part 1 MOTOR EXAMINATION: Look at bulk, contour and symmetry of individual muscles: muscles of face upper arm arm thigh lower leg Look for atrophy--may help to localize the site
Neurological Assessment Part 1 MOTOR EXAMINATION: Look at bulk, contour and symmetry of individual muscles: muscles of face upper arm arm thigh lower leg Look for atrophy--may help to localize the site
UNILATERAL PARALYSIS OF THE ELEVATORS OF SUPRANUCLEAR ORIGIN*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955) 39, 73. UNILATERAL PARALYSIS OF THE ELEVATORS OF SUPRANUCLEAR ORIGIN* BY ENRIQUE MALBRAN AND ATILIO LUIS NORBIS Buenos Aires UNILATERAL paralysis of the elevators (inferior oblique
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955) 39, 73. UNILATERAL PARALYSIS OF THE ELEVATORS OF SUPRANUCLEAR ORIGIN* BY ENRIQUE MALBRAN AND ATILIO LUIS NORBIS Buenos Aires UNILATERAL paralysis of the elevators (inferior oblique
Ptosis (drooping) of the upper eyelid (1) What is Ptosis? Ptosis describes a drooping of one or both upper eyelids. (2) What are the causes of ptosis?
 Ptosis (drooping) of the upper eyelid (1) What is Ptosis? Ptosis describes a drooping of one or both upper eyelids. (2) What are the causes of ptosis? Ptosis may be present at birth (congenital ptosis)
Ptosis (drooping) of the upper eyelid (1) What is Ptosis? Ptosis describes a drooping of one or both upper eyelids. (2) What are the causes of ptosis? Ptosis may be present at birth (congenital ptosis)
TUMOURS IN THE REGION OF FORAMEN MAGNUM
 TUMOURS IN THE REGION OF FORAMEN MAGNUM Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 119 To 122 Naim-ur-Rahman ( Department of Neurosurgery, Rawalpindi Medical College, Rawalpindi. ) A very unusual case
TUMOURS IN THE REGION OF FORAMEN MAGNUM Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 119 To 122 Naim-ur-Rahman ( Department of Neurosurgery, Rawalpindi Medical College, Rawalpindi. ) A very unusual case
EFFICACY OF A SINGLE SUBCONJUNCTIVAL INJECTION WITH DISPORT FOR LID RETRACTION TREATMENT
 Original Article EFFICACY OF A SINGLE SUBCONJUNCTIVAL INJECTION WITH DISPORT FOR LID RETRACTION TREATMENT Khataminia Gh R 1, Moosavian J 2 ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of dysport
Original Article EFFICACY OF A SINGLE SUBCONJUNCTIVAL INJECTION WITH DISPORT FOR LID RETRACTION TREATMENT Khataminia Gh R 1, Moosavian J 2 ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of dysport
CHRONIC RETROBULBAR AND CHIASMAL NEURITIS*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 51, 698 CHRONIC RETROBULBAR AND CHIASMAL NEURITIS*t BY From the Department of Medicine, University of Bristol, and the United Bristol Hospitals AcuTE retrobulbar neuritis is a
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 51, 698 CHRONIC RETROBULBAR AND CHIASMAL NEURITIS*t BY From the Department of Medicine, University of Bristol, and the United Bristol Hospitals AcuTE retrobulbar neuritis is a
ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE NORMAL OPHTHALMIC
 Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 473. ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE NORMAL OPHTHALMIC ARTERY AND CHOROIDAL PLEXUS OF THE EYE* BY P. H. SCHURR From the Department of Neurosurgery, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford THE ophthalmic
Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 473. ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE NORMAL OPHTHALMIC ARTERY AND CHOROIDAL PLEXUS OF THE EYE* BY P. H. SCHURR From the Department of Neurosurgery, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford THE ophthalmic
EDX in Myopathies Limitations. EDX in Myopathies Utility Causes of Myopathy. Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers
 Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
frontalis muscle while the patient makes an attempt to open the eye. With the first and third classes I am not now concerned, except
 OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIs 741 AN OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIS* BY R. AFFLECK GREEVES LONDON CASES of congenital ptosis may be conveniently divided, clinically, into
OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIs 741 AN OPERATION FOR THE RELIEF OF CONGENITAL PTOSIS* BY R. AFFLECK GREEVES LONDON CASES of congenital ptosis may be conveniently divided, clinically, into
Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives
 Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives Know the locations of cranial nerve motor nuclei Describe the effects of motor cranial nerve lesions Describe how the corticobulbar tract innervates
Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives Know the locations of cranial nerve motor nuclei Describe the effects of motor cranial nerve lesions Describe how the corticobulbar tract innervates
UNIOCULAR APLASIA OF THE OPTIC NERVE*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 51. UNIOCULAR APLASIA OF THE OPTIC NERVE* BY FROMA SOMERVILLE London APLASIA of the optic nerve occurring as an isolated abnormality in an eye of normal external appearance
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 51. UNIOCULAR APLASIA OF THE OPTIC NERVE* BY FROMA SOMERVILLE London APLASIA of the optic nerve occurring as an isolated abnormality in an eye of normal external appearance
X-Plain Muscles Reference Summary
 X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Fall, 2015
 1 Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Fall, 2015 Name: Nursing Case Study: Muscle Weakness Chief Complaint: A 26-year-old woman with muscle weakness in the face. Patient Presentation: A 26-year-old woman
1 Human Physiology Lab (Biol 236L) Fall, 2015 Name: Nursing Case Study: Muscle Weakness Chief Complaint: A 26-year-old woman with muscle weakness in the face. Patient Presentation: A 26-year-old woman
Energy for Muscle Contractions: Direct phosphorylation. Creatine phosphate loses a phosphate to ADP to create ATP
 Energy for Muscle Contractions: Direct phosphorylation Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration (lactic acid fermentation) Creatine phosphate loses a phosphate to ADP to create ATP Requires oxygen to
Energy for Muscle Contractions: Direct phosphorylation Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration (lactic acid fermentation) Creatine phosphate loses a phosphate to ADP to create ATP Requires oxygen to
LESIONS OF THE CILIARY GANGLION AS A CAUSE OF
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 471. LESIONS OF THE CILIARY GANGLION AS A CAUSE OF ARGYLL ROBERTSON AND ADIE PUPILS* BY MALCOLM E. Brisbane CAMERON MANY and varied are the lesions postulated for the Argyll
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 471. LESIONS OF THE CILIARY GANGLION AS A CAUSE OF ARGYLL ROBERTSON AND ADIE PUPILS* BY MALCOLM E. Brisbane CAMERON MANY and varied are the lesions postulated for the Argyll
A ptosis repair of aponeurotic defects by the posterior approach
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1979, 63, 586-590 A ptosis repair of aponeurotic defects by the posterior approach J. R. 0. COLLIN From the Department of Clinical Ophthalmology, Moorfields Eye Hospital,
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1979, 63, 586-590 A ptosis repair of aponeurotic defects by the posterior approach J. R. 0. COLLIN From the Department of Clinical Ophthalmology, Moorfields Eye Hospital,
PATHWAY OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES IN THE HUMAN
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 246 PATHWAY OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES IN THE HUMAN OPTIC NERVE, CHIASM, AND TRACT*t BY J. REIMER WOL-TER AND ROMAN R. KNOBLICH From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Pathology
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 246 PATHWAY OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES IN THE HUMAN OPTIC NERVE, CHIASM, AND TRACT*t BY J. REIMER WOL-TER AND ROMAN R. KNOBLICH From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Pathology
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09a Lab Activity
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: http://www.fallingpixel.com/products/33817/mains/0000-malemuscular_1.jpg The Muscular System The main function of the muscular
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: http://www.fallingpixel.com/products/33817/mains/0000-malemuscular_1.jpg The Muscular System The main function of the muscular
1/28/2019. OSF HealthCare INI Care Center Team. Neuromuscular Disease: Muscular Dystrophy. OSF HealthCare INI Care Center Team: Who are we?
 Neuromuscular Disease: Muscular Dystrophy Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) and OSF HealthCare Illinois Neurological Institute (INI) Care Center Team The Neuromuscular clinic is a designated MDA Care
Neuromuscular Disease: Muscular Dystrophy Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) and OSF HealthCare Illinois Neurological Institute (INI) Care Center Team The Neuromuscular clinic is a designated MDA Care
What was going on. Thyroid Related Orbitopathy. Pathophysiology. Definition GALLO EYE AND FACIAL PLASTIC SURGERY 3/16/2017
 GALLO EYE AND FACIAL PLASTIC SURGERY What was going on A. She found out the increase to her Premium and Deductible for employee health care next year B. She is getting an over agressive Physical Exam by
GALLO EYE AND FACIAL PLASTIC SURGERY What was going on A. She found out the increase to her Premium and Deductible for employee health care next year B. She is getting an over agressive Physical Exam by
WITH REPORT OF A PEDIGREE*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955), 39, 374. HEREDITARY POSTERIOR POLAR CATARACT WITH REPORT OF A PEDIGREE* BY C. G. TULLOH London K HEREDITARY, developmental, posterior polar cataract has been encountered in a
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955), 39, 374. HEREDITARY POSTERIOR POLAR CATARACT WITH REPORT OF A PEDIGREE* BY C. G. TULLOH London K HEREDITARY, developmental, posterior polar cataract has been encountered in a
Apraxia of eyelid opening: Clinical features and therapy
 E u ropean Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 16 no. 2, 2006 / pp. 2 0 4-2 0 8 Apraxia of eyelid opening: Clinical features and therapy E. KERT Y 1, K. EIDAL 2 1 Department of Neuro l o g y, Rikshospitalet,
E u ropean Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 16 no. 2, 2006 / pp. 2 0 4-2 0 8 Apraxia of eyelid opening: Clinical features and therapy E. KERT Y 1, K. EIDAL 2 1 Department of Neuro l o g y, Rikshospitalet,
Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression. Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre
 Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre Outline of talk Mononeuropathies median and anterior interosseous nerve ulnar nerve
Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre Outline of talk Mononeuropathies median and anterior interosseous nerve ulnar nerve
HISTORY TAKING ON NERVOUS SYSTEM. Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal
 HISTORY TAKING ON NERVOUS SYSTEM Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal General points History of neurological symptoms should also be taken from patient and close relative or friend Memory loss, intoxication, aphasia Patient
HISTORY TAKING ON NERVOUS SYSTEM Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal General points History of neurological symptoms should also be taken from patient and close relative or friend Memory loss, intoxication, aphasia Patient
A Patient Presenting with Ptosis, Ophthalmoplegia, and Decreased Periorbital Sensations and Facial Droop in Tolosa-Hunt Syndrome
 A Patient Presenting with Ptosis, Ophthalmoplegia, and Decreased Periorbital Sensations and Facial Droop in Tolosa-Hunt Syndrome medicine2.missouri.edu/jahm/patient-presenting-ptosis-ophthalmoplegia-decreased-periorbital-sensations-facial-drooptolosa-hunt-syndrome/
A Patient Presenting with Ptosis, Ophthalmoplegia, and Decreased Periorbital Sensations and Facial Droop in Tolosa-Hunt Syndrome medicine2.missouri.edu/jahm/patient-presenting-ptosis-ophthalmoplegia-decreased-periorbital-sensations-facial-drooptolosa-hunt-syndrome/
Clinical Manifestation of Ocular Motor Nerve Palsies in a Tertiary Eye Hospital of Kathmandu, Nepal
 72 Original article Clinical Manifestation of Ocular Motor Nerve Palsies in a Tertiary Eye Hospital of Kathmandu, Nepal Sitaula S 1, Sharma AK 1, Shrestha GB 1, Gajurel BP 2, Shrestha GS 1 1 Department
72 Original article Clinical Manifestation of Ocular Motor Nerve Palsies in a Tertiary Eye Hospital of Kathmandu, Nepal Sitaula S 1, Sharma AK 1, Shrestha GB 1, Gajurel BP 2, Shrestha GS 1 1 Department
INSERTION* SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE LEVATOR PALPEBRAE. impossible to dissect and separate these layers. That the levator aponeurosis
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 503. SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE LEVATOR PALPEBRAE INSERTION* BY EDWARD EPSTEIN Johannesburg, Union of South Africa THE text-book description of the anatomy of the upper eyelid
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 503. SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE LEVATOR PALPEBRAE INSERTION* BY EDWARD EPSTEIN Johannesburg, Union of South Africa THE text-book description of the anatomy of the upper eyelid
High Yield Neurological Examination
 High Yield Neurological Examination Vanja Douglas, MD Sara & Evan Williams Foundation Endowed Neurohospitalist Chair Director, Neurohospitalist Division Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF Department
High Yield Neurological Examination Vanja Douglas, MD Sara & Evan Williams Foundation Endowed Neurohospitalist Chair Director, Neurohospitalist Division Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF Department
Investigations. The blood count was normal with an erythrocyte. sedimentation rate of 5 mm. ist hr, and negative Waaler-
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I975) 59, 149 Tolosa-Hunt syndrome The dangers of an eponym T. J. FOWLER, C. J. EARL, V. L. McALLISTER, AND W. I. McDONALD From the Institute of Neurology, National Hospitalfor Nervous
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I975) 59, 149 Tolosa-Hunt syndrome The dangers of an eponym T. J. FOWLER, C. J. EARL, V. L. McALLISTER, AND W. I. McDONALD From the Institute of Neurology, National Hospitalfor Nervous
ELECTROMYOGRAPHIC STUDIES ON THE
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1954), 38, 605. ELECTROMYOGRAPHIC STUDIES ON THE COORDINATION OF ANTAGONISTIC MUSCLES IN CASES OF ABDUCENS AND FACIAL PALSY* BY AKE BJORK From the Department of Clinical Neurophysiology,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1954), 38, 605. ELECTROMYOGRAPHIC STUDIES ON THE COORDINATION OF ANTAGONISTIC MUSCLES IN CASES OF ABDUCENS AND FACIAL PALSY* BY AKE BJORK From the Department of Clinical Neurophysiology,
GNK485 The eye and related structures. Prof MC Bosman 2012
 GNK485 The eye and related structures Prof MC Bosman 2012 Surface anatomy Bony orbit Eyeball and Lacrimal apparatus Extra-ocular muscles Movements of the eye Innervation Arterial supply and venous drainage
GNK485 The eye and related structures Prof MC Bosman 2012 Surface anatomy Bony orbit Eyeball and Lacrimal apparatus Extra-ocular muscles Movements of the eye Innervation Arterial supply and venous drainage
Assessment Instruments for Your Patients with Myasthenia Gravis (MG)
 Assessment Instruments for Your Patients with Myasthenia Gravis (MG) Table of Contents Reported by patient Myasthenia Gravis Activities of Daily Living (MG-ADL): ~10 minutes 8-item outcome measure that
Assessment Instruments for Your Patients with Myasthenia Gravis (MG) Table of Contents Reported by patient Myasthenia Gravis Activities of Daily Living (MG-ADL): ~10 minutes 8-item outcome measure that
C19. Pediatric Neuro-ophthalmology: Dilemmas in clinical practice. 12 June, :15 15:45. Room 115 HAND-OUTS
 C19 Pediatric Neuro-ophthalmology: Dilemmas in clinical practice 12 June, 2017 14:15 15:45 Room 115 HAND-OUTS Is this strabismus really harmful? Karl Golnik, MD, MEd University of Cincinnati, USA Childhood
C19 Pediatric Neuro-ophthalmology: Dilemmas in clinical practice 12 June, 2017 14:15 15:45 Room 115 HAND-OUTS Is this strabismus really harmful? Karl Golnik, MD, MEd University of Cincinnati, USA Childhood
Imaging Orbit/Periorbital Injury
 Imaging Orbit/Periorbital Injury 9 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2016 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Fireworks Topics to Cover Struts
Imaging Orbit/Periorbital Injury 9 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2016 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Fireworks Topics to Cover Struts
Muscles Unit TEST and Final Exam Study Guide May 2017
 Muscles Unit TEST and Final Exam Study Guide May 2017 Part 1 of final exam is pictures, see bottom of the study guide Part 2 of the final exam is only going to cover muscles unit. If you do this study
Muscles Unit TEST and Final Exam Study Guide May 2017 Part 1 of final exam is pictures, see bottom of the study guide Part 2 of the final exam is only going to cover muscles unit. If you do this study
Unit 4: The Muscular System REVIEW GUIDE
 NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List the three functions of the muscular system. Unit 4: The Muscular System REVIEW GUIDE 2) What are the four characteristics of muscle tissue? Briefly
NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List the three functions of the muscular system. Unit 4: The Muscular System REVIEW GUIDE 2) What are the four characteristics of muscle tissue? Briefly
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. 1) Skeletal 2) Smooth 3) Cardiac 2 Walls of blood vessels. 2 Walls of digestive tract
 S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems
 Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Chapter(2):the lid page (1) THE LID
 Chapter(2):the lid page (1) THE LID Anatomy of the lid: * Check movie anatomy of the lid model The eyelids are two movable muco-cutaneous folds which protect the eye on closure. The are joined temporary
Chapter(2):the lid page (1) THE LID Anatomy of the lid: * Check movie anatomy of the lid model The eyelids are two movable muco-cutaneous folds which protect the eye on closure. The are joined temporary
Importance of Developmental Kinesiology for Manual Medicine
 Importance of Developmental Kinesiology for Manual Medicine Pavel Kolá!, 1996 Dpt. of Rehabilitation, University Hospital Motol, Prague, Czech Republic (Czech Journal of Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy)
Importance of Developmental Kinesiology for Manual Medicine Pavel Kolá!, 1996 Dpt. of Rehabilitation, University Hospital Motol, Prague, Czech Republic (Czech Journal of Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy)
Clinical Observation on Oculomotor Nerve Palsy Treated by Moxibustion
 2003. Vol. 24. No. 4. 149-153 Korean Journal of Oriental Medicine Original Articles Clinical Observation on Oculomotor Nerve Palsy Treated by Moxibustion Hyun-Su Woo, Dong-Min Seo, Jong-Deog Kim, Sang-Min
2003. Vol. 24. No. 4. 149-153 Korean Journal of Oriental Medicine Original Articles Clinical Observation on Oculomotor Nerve Palsy Treated by Moxibustion Hyun-Su Woo, Dong-Min Seo, Jong-Deog Kim, Sang-Min
Lab Exercise 8. BIOPAC Exercise. Muscle Tissue. Muscles. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 8 BIOPAC Exercise Muscle Tissue Muscles Textbook Reference: See Chapters 9 & 10 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to answer questions covering
Lab Exercise 8 BIOPAC Exercise Muscle Tissue Muscles Textbook Reference: See Chapters 9 & 10 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to answer questions covering
Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping
 Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping filaments within the muscle cell. Skeletal muscle can be consciously
Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping filaments within the muscle cell. Skeletal muscle can be consciously
Title. CitationInternal Medicine, 46(8): Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information
 Title Scapular Winging as a Symptom of Cervical Flexion My Author(s)Yaguchi, Hiroaki; Takahashi, Ikuko; Tashiro, Jun; Ts CitationInternal Medicine, 46(8): 511-514 Issue Date 2007-04-17 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/20467
Title Scapular Winging as a Symptom of Cervical Flexion My Author(s)Yaguchi, Hiroaki; Takahashi, Ikuko; Tashiro, Jun; Ts CitationInternal Medicine, 46(8): 511-514 Issue Date 2007-04-17 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/20467
m ':~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~N
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 622. EPIPHORA A SYMPTOM OF EARLY HYPOTHYROIDISM* BY W. HAMILTON SMITH, K. G. HOWSAM, and J. J. BILLINGS Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital, Melbourne, Australia AMONG the many
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 622. EPIPHORA A SYMPTOM OF EARLY HYPOTHYROIDISM* BY W. HAMILTON SMITH, K. G. HOWSAM, and J. J. BILLINGS Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital, Melbourne, Australia AMONG the many
Author: Ida Lucy Iacobucci, 2015
 Author: Ida Lucy Iacobucci, 2015 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 4.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
Author: Ida Lucy Iacobucci, 2015 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-Share Alike 4.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
CRANIAL NERVES. Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
 CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
CASE OF CONGENITAL CYSTIC EYE AND ACCESSORY LIMB OF THE LOWER EYELID*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 409 CASE OF CONGENITAL CYSTIC EYE AND ACCESSORY LIMB OF THE LOWER EYELID* BY N. S. C. RICE Department ofpathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, London, AND S. P. MINWALLA AND
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 409 CASE OF CONGENITAL CYSTIC EYE AND ACCESSORY LIMB OF THE LOWER EYELID* BY N. S. C. RICE Department ofpathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, London, AND S. P. MINWALLA AND
How to Think like a Neurologist Review of Exam Process and Assessment Findings
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Myasthenia gravis. David Hilton-Jones Oxford Neuromuscular Centre
 Myasthenia gravis David Hilton-Jones Oxford Neuromuscular Centre SWIM, Taunton, 2018 Myasthenia gravis Autoimmune disease Nature of Role of thymus Myasthenia gravis Autoimmune disease Nature of Role of
Myasthenia gravis David Hilton-Jones Oxford Neuromuscular Centre SWIM, Taunton, 2018 Myasthenia gravis Autoimmune disease Nature of Role of thymus Myasthenia gravis Autoimmune disease Nature of Role of
Cervical Spine Exercise and Manual Therapy for the Autonomous Practitioner
 Cervical Spine Exercise and Manual Therapy for the Autonomous Practitioner Eric Chaconas PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Assistant Professor and Assistant Program Director Doctor of Physical Therapy Program Eric
Cervical Spine Exercise and Manual Therapy for the Autonomous Practitioner Eric Chaconas PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Assistant Professor and Assistant Program Director Doctor of Physical Therapy Program Eric
Ann Senisi Scott & Elizabeth Fong: Body Structures & Functions 11 th Edition
 Chapter 7: Muscular System Theory Lecture Outline Objectives 1. Describe the function of muscle 2. Describe each of the muscle groups 3. List the characteristics of muscle 4. Describe how pairs of muscles
Chapter 7: Muscular System Theory Lecture Outline Objectives 1. Describe the function of muscle 2. Describe each of the muscle groups 3. List the characteristics of muscle 4. Describe how pairs of muscles
sheath syndrome Bilateral superior oblique tendon of uniovular twins Occurrence and spontaneous recovery in one Brit. J. Ophthal.
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I969) 53, 466 Bilateral superior oblique tendon sheath syndrome Occurrence and spontaneous recovery in one of uniovular twins RONALD F. LOWE Melbourne, Australia Brown (I950) defined
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I969) 53, 466 Bilateral superior oblique tendon sheath syndrome Occurrence and spontaneous recovery in one of uniovular twins RONALD F. LOWE Melbourne, Australia Brown (I950) defined
