Hyungwoo Lee, Hyoik Jang, Youn A Choi, Hyung Chan Kim, and Hyewon Chung
|
|
|
- Bertha Lewis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Retina Association Between Soluble CD14 in the Aqueous Humor and Hyperreflective Foci on Optical Coherence Tomography in Patients With Diabetic Macular Edema Hyungwoo Lee, Hyoik Jang, Youn A Choi, Hyung Chan Kim, and Hyewon Chung Department of Ophthalmology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea Correspondence: Hyewon Chung, Department of Ophthalmology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Konkuk University Medical Center, Neungdong-ro, Gwangjin-gu, Seoul, Republic of Korea 05030; hchung@kuh.ac.kr. Submitted: September 25, 2017 Accepted: January 3, 2018 Citation: Lee H, Jang H, Choi YA, Kim HC, Chung H. Association between soluble CD14 in the aqueous humor and hyperreflective foci on optical coherence tomography in patients with diabetic macular edema. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018;59: iovs PURPOSE. To investigate the associations between soluble CD14 (scd14), a cytokine released by microglia and macrophages, and hyperreflective foci (HF) and various characteristics of spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) in diabetic macular edema (DME). METHODS. Sixty-nine eyes from 51 patients with DME and 28 eyes from 28 control subjects were studied. scd14 levels in the aqueous humor (AH) were measured using ELISA before bevacizumab injection (IVB), and the associations between scd14 and visual acuity, the number of HF, retinal volume, and the DME pattern were assessed. RESULTS. scd14 levels were higher in DME patients than in the control subjects ( pg/ml versus pg/ml, P < 0.001). scd14 levels in diffuse edema were higher than those in focal edema ( pg/ml versus pg/ml, P ¼ 0.039). The number of HF in the inner retina of patients with diffuse edema was significantly higher than that in patients with focal edema ( vs , P ¼ 0.001), but no difference was found in the outer retina ( vs , P ¼ 0.25). According to multivariate analyses, elevated scd14 levels were associated with an increased inner nuclear layer volume and the total number of HF in all retinal layers on SD-OCT. Reduction of DME following IVB was correlated with reduction in the number of HF in a subset of eyes followed longitudinally in the study (n ¼ 30). CONCLUSIONS. DME patients with diffuse edema exhibit higher scd14 levels in the AH and more HF in the inner retina than patients with focal edema, indicating severe inflammation. The strong correlation between scd14 and HF in the inner retina suggests that the HF observed on SD-OCT may be due to activated microglia in DME. Keywords: CD14, hyperreflective foci, diabetic macular edema, diffuse edema type, focal edema type Diabetic macular edema (DME) is the most common cause of vision loss in diabetic retinopathy (DR). 1 The disruption of blood-retinal barriers induces the influx of fluid into the retina, resulting in DME. 2 Although the pathogenesis of DR is not fully elucidated, inflammatory reactions, including monocyte/macrophage recruitment and microglia activation, are considered among the causative factors of DME. 3 CD14 is a cytokine associated with the innate immune response and is expressed in microglia, monocytes, and macrophages. 4 CD14 exists in two forms: membrane-bound or soluble (scd14) 5 ; both forms are related to the activation of the inflammatory response. 6 In DME, the levels of scd14 are elevated in the aqueous humor (AH) and vitreous humor and are associated with increased levels of VEGF. 7 Microglia are resident immune cells in the retina that are involved in the inflammatory changes underlying DR. In DR, microglia proliferate, change their shape, release inflammatory cytokines, and aggregate near perivascular areas and areas of cystic retinal edema. 8 Although microglia are considered the primary source of scd14 in cerebrospinal fluid under pathologic conditions, 9 knowledge regarding the association between scd14 and microglia in patients with DR is scarce. Hyperreflective foci (HF) on spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) are markers of increased DME activity. 10 The origin of HF remains controversial, and activated microglia or lipoprotein exudation are among the suspected causes. 11,12 We hypothesized that scd14 in the AH is derived from activated microglia in the diabetic retina, and that if the level of this cytokine is correlated with the number of HF on SD-OCT in DME patients, HF could be indicative of activated microglia in DME patients. The degree of microglia activation could vary according to the different types of DME: focal, diffuse, or combined. We speculated that the level of scd14 and the distribution of HF could also differ depending on the type of DME because focal and diffuse edema appear to have different underlying pathophysiologies; diffuse edema is thought to result from disrupted retinal vessel integrity mainly in the inner retinal layer, whereas focal edema results from microaneurysms with pathology observed primarily in the outer retina. 13 In this study, a clear correlation was observed between the level of scd14 in the AH and either the number of HF or the level of edema in each retinal layer in DME patients. Moreover, Copyright 2018 The Authors iovs.arvojournals.org j ISSN: This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
2 Association Between scd14 and Hyperreflective Foci IOVS j February 2018 j Vol. 59 j No. 2 j 716 we also observed altered levels of scd14 and distinct local distributions of HF based on the type of DME. METHODS Subjects and AH Sample Collection AH samples were collected at the Department of Ophthalmology, Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. Between January 1, 2011, and March 31, 2017, 69 eyes from 51 patients with DME and 28 eyes from 28 control subjects were included in this study. All studied subjects were South Korean, a relatively homogeneous East Asian ethnicity. Eyes with the following characteristics were excluded: DME with epiretinal membrane or foveal traction, hard exudate at the macula, vitreous hemorrhage or pre- and subretinal hemorrhage, other retinal diseases, glaucoma, or a history of uveitis. Using a 30- gauge needle, AH samples from the eyes of the DME patients were obtained before an intravitreal injection of bevacizumab (IVB; 1.25 mg/0.05 ml); samples from the control eyes were obtained immediately before cataract surgery. At each visit, best corrected visual acuity (VA; logmar), color fundus photography, and SD-OCT were evaluated. Additional injections were conducted according to pro re nata regimen with 4 to 6 weeks when intraretinal and/or subretinal fluid remained. scd14 Measurement via ELISA The levels of scd14 in the AH were assessed using a sandwich ELISA kit (R&D systems, Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA). The color intensities were determined using a microplate reader (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). Duplicate samples were used in all assays. This study followed the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and informed written consent was obtained from all patients and control subjects. The procedure for the AH collection was approved by the institutional review boards of Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. SD-OCT Imaging A volume scan comprising 25 horizontal B-scans covering mm area of the macular region centered on the fovea was acquired using SD-OCT (Spectralis HRAþOCT; Heidelberg Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany). The eyes from the DME patients were classified into two groups according to their pattern of edema as previously described. 13 Focal edema was defined as the retinal fluid collection only in the outer retina (outer plexiform layer [OPL] to external limiting membrane [ELM]). In diffuse edema, the retinal fluid is located in the inner retina (internal limiting membrane [ILM] to inner nuclear layer [INL]). Combined edema, which fluid is observed in both the inner and outer retina, was also designated as diffuse edema. Thus, diffuse edema was defined as the retinal fluid located in the inner retina with or without retinal fluid in the outer retina. Measurements of the disrupted length of the ELM and the junction between the photoreceptor inner segment and the outer segment (IS/OS) were performed within a 3-mm area centered on the fovea in fovea-spanning horizontal B-scans. Central macular thickness (CMT) was measured within a 1-mm diameter circle centered on the fovea, and the volumes of the total retinal layers (from the ILM to the basement membrane), the INL, and the OPL plus ONL (OPL/ONL) were measured within a 3-mm diameter circle centered on the fovea. 14 The HF were manually counted within a 3-mm area using a fovea-spanning horizontal B-scan. HF were defined as discrete and well-circumscribed dots of similar reflectivity with the RPE band. The longest diameter of HF was limited to the 20- to 50- lm range. Therefore, we excluded small noise signals and large hyperreflective clumps, which are shown as hard exudates in fundus photography. Patient Data The baseline (pre-ivb) data on 69 eyes from the 51 patients with DME included demographic and clinical characteristics (i.e., age, sex, diabetes duration, presence of controlled systemic hypertension, and HbA1C) and ophthalmologic examination findings, such as best corrected VA, fluorescein angiography results, and SD-OCT results. Follow-up examinations (VA and SD-OCT) were performed in 30 eyes (11 eyes with diffuse edema and 19 eyes with focal edema) 3 months after the IVB injection (post-ivb). The VA, CMT, and the number of HF were compared to analyze the association between the level of scd14 and visual/anatomic change. The eyes were subdivided into the following three categories according to the international clinical DR severity scale: no DR, nonproliferative DR (NPDR), and proliferative DR (PDR). 15 Statistical Analysis The statistical analysis was performed using SPSS software version 17.0 for Windows (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). All values are presented as the means 6 SD or numbers (%). To compare the mean values between groups, Mann-Whitney U test were performed. The v 2 test was done to compare the ratio of variables between two groups. Wilcoxon signed-rank tests were performed to compare the means of the VA (logmar), CMT, and the number of HFs before and after the treatment. A multivariate regression analysis was performed using a stepwise selection of specific variables, with adjustments for age and sex. Spearman correlation coefficients were calculated to examine the bivariate relationships. P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. RESULTS Baseline Demographics, Baseline scd14, and Findings on SD-OCT The baseline characteristics of the subjects are listed in Table 1. The mean scd14 levels in the DME group were significantly higher than those in the control group ( vs pg/ml, respectively; P < 0.001). The HF were distributed across all retinal layers, and the numbers ranged from 1 to 27 (mean ; Table 2). The number of HF in the outer retina was higher than that in the inner retina ( vs , respectively; P < 0.001). TABLE 1. Subjects Baseline Characteristics of Patients With DME and Control Parameters DME Control P No. of eyes Age, y (SD) 55.4 (11.5) 66.8 (9.6) <0.001* Sex, male:female 55:14 13: Hypertension, n (%) 25 (36.2) 6 (21.4) 0.23 DM duration, y (SD) 7.2 (5.8) scd14, pg/ml (SD) 29.9 (41.6) 8.1 (3.6) <0.001* DM, diabetes mellitus. * Mann-Whitney U test. v 2 test.
3 Association Between scd14 and Hyperreflective Foci IOVS j February 2018 j Vol. 59 j No. 2 j 717 TABLE 2. Baseline VA and Anatomic Characteristics of Eyes From Patients With DME and Control Subjects Parameters DME Control P* No. of eyes logmar (SD) 0.33 (0.25) 0.41 (0.27) 0.53 CMT, lm (SD) (112.7) (20.8) <0.001 INL volume, mm 3 (SD) 1.3 (0.3) 1.0 (0.1) <0.001 OPL/ONL volume, mm 3 (SD) 3.5 (0.9) 2.4 (0.2) <0.001 Retinal volume, mm 3 (SD) 10.5 (1.6) 8.3 (0.3) <0.001 No. of HF in inner retina 3.2 (2.3) 0 <0.001 (SD) No. of HF in outer retina 5.3 (3.7) 0 <0.001 (SD) No. of total HF (SD) 8.5 (4.8) 0 <0.001 Control, among 28 control subjects, SD-OCT data were available in 15 eyes of 15 subjects. * Mann-Whitney U test. Associations of the scd14 Level and HF With the Type of DME Forty-six eyes exhibited focal edema, and 23 eyes exhibited diffuse edema. The levels of scd14 in the diffuse edema group were significantly higher than those in the focal edema group ( pg/ml versus pg/ml, respectively; P ¼ 0.024; Table 3). The levels of scd14 in both DME groups were higher than those in the control group (diffuse group, P < 0.001; and focal group, P < 0.001, respectively). The number of HF in the inner retina was significantly higher in the diffuse edema group than that in the focal edema group ( vs , P ¼ 0.001, Fig.). The number of HF in the entire retina was also significantly higher in the diffuse group than that in the focal edema group ( vs , P ¼ 0.02). However, the numbers of HF in the outer retina did not differ between the two edema groups ( vs ; P ¼ 0.25). Association of the scd14 Level With the Number of HF and Other Parameters on SD-OCT Positive correlations were observed between the level of scd14 and the number of HF in the inner, outer, and entire retina (r ¼ 0.506, P < 0.001; r ¼ 0.388, P ¼ 0.001; r ¼ 0.560, P < 0.001, respectively). In addition, the level of scd14 was positively correlated with the INL, OPL/ONL, and total retinal volumes (r ¼ 0.638, P < 0.001; r ¼ 0.357, P ¼ 0.003; r ¼ 0.547, P < 0.001, respectively); however, no correlation was observed between the level of scd14 and the logmar VA (r ¼ 0.204, P ¼ 0.093). The disrupted lengths of both ELM and IS/ OS were not correlated with the level of scd14 at 3 months (r ¼ 0.094, P ¼ 0.568; r ¼ 0.134, P ¼ 0.414, respectively). A univariate regression analysis was performed to identify the baseline factors that could affect the scd14 levels. The scd14 levels were positively associated with the duration of diabetes mellitus; the numbers of HF in the inner, outer, and entire retina; and the INL, OPL/ONL, and total retinal volumes (Table 4). According to the multivariate regression analysis with adjustments for age and sex, among all SD-OCT variables, the level of scd14 was associated with the number of HF across all retinal layers and the INL volume (Table 4). Changes After Treatment Thirty eyes had complete follow-up data at 3 months. The mean number of IVB injections was The numbers of HF were significantly decreased in both the inner and outer TABLE 3. Subgroup Analysis of scd14 Levels According to the Type of DME, the Degree of DR, and the Presence of Hypertension retinal layers at 3 months (inner HF to , P ¼ 0.002; outer HF to , P < 0.001; total HF to , P < 0.001) (Table 5). The scd14 level was correlated with the pre-ivb CMT and the degree of CMT change after the treatment (r ¼ 0.523, P ¼ 0.003; and r ¼ 0.471, P ¼ 0.009, respectively). In addition, higher levels of scd14 were correlated with VA improvement (logmar) (r ¼ 0.405, P ¼ 0.027). However, according to the subgroup analyses, the mean CMT was significantly decreased after treatment in the diffuse edema group (11 eyes, lm, pre-ivb versus lm, post-ivb, P ¼ 0.003), whereas no significant change was observed in the focal edema group (19 eyes, lm, pre-ivb versus lm, post-ivb, P ¼ 0.07). The VA (logmar) in the diffuse group was significantly improved after treatment ( , pre- IVB versus , post-ivb, P ¼ 0.04), whereas no significant change was observed in the focal edema group ( , pre-ivb versus , post-ivb, P ¼ 0.35). DISCUSSION Eyes, n scd14 Baseline, pg/ml P* Type of DME Diffuse edema (SD) (65.3) Focal edema (SD) (14.7) Degree of DR NPDR (SD) (49.1) PDR (SD) (14.2) Presence of hypertension Without hypertension (SD) (50.6) With hypertension (SD) (15.8) * Mann-Whitney U test. Microglia are considered important players in the initial inflammatory response in DR, but the cytokines secreted by microglia that are responsible for the pathogenesis of DR are not fully understood. 16 In histologic studies investigating DR in humans, perivascular microglia have been shown to be moderately increased in nonproliferative DR and hypertrophic in the inner retinal layers. 8 In proliferative retinopathy, dilated new vessels are surrounded by microglia. 8 Minocycline, an antibiotic that inhibits microglia, inhibits DR-induced inflammatory cytokine production and reduces the release of cytotoxins from activated microglia. 17 Therefore, activated microglia in DR negatively affect normal retinal cells by secreting proinflammatory and neurotoxic mediators. 16,18 Although the elevated levels of scd14 in the AH and vitreous humor have been reported to be correlated with the levels of cytokines, such as VEGF, 7 which suggests that scd14 could be involved in the inflammatory response in DME, information regarding the associations between scd14 and various characteristics of DME, including the type of DME and the volumetric changes in each retinal layer, is scarce. In the present study, the level of scd14 in the AH in the DME patients positively correlated with the INL, OPL/ONL, and total retinal volumes. The INL volume was most strongly associated with the level of scd14, as shown by the multivariate regression analysis. In addition, the scd14 levels were higher in diffuse edema than those in focal edema. Therefore, the level of scd14
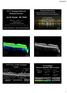
4 Association Between scd14 and Hyperreflective Foci IOVS j February 2018 j Vol. 59 j No. 2 j 718 FIGURE. SD-OCT characteristics of DME. Segmented retinal layers of fovea-spanning B-scan (blue ~ red line: INL, red ~ pink line: OPL/ONL) are depicted. (A) Patient 1: 43-year-old man with the diffuse type of DME (fluid located in both the inner and outer retina). His best corrected VA was logmar 0.40, and his scd14 level was 33.6 pg/ml. HF are observed in the inner and outer retinal layers in the inverted image. Thickening of both the INL and OPL/ONL and multiple cysts in the INL and ONL are observed in the segmented retina. Diffuse thickening of the INL and OPL/ONL is evident (white-colored pixels on the heat maps). (B) Patient 2: 46-year-old man with the diffuse type of DME. His VA was logmar 0.22, and his scd14 level was 46.3 pg/ml. HF are observed mainly in the inner retinal layers at the center and in the outer retina in the left parafoveal lesion on the inverted image. Thickening of both the INL and OPL/ONL and multiple cysts in the INL are observed in the segmented retina. Diffuse thickening of the INL and OPL/ONL is shown as white-colored pixels on the heat maps. (C) Patient 3: 51-year-old man with the focal type of DME. His VA was logmar 0.1, and his scd14 level was 9.0 pg/ml. HF are dispersed mainly in the outer retinal layer on the inverted image, and the density of the HF appears sparser than that in the patients with diffuse edema. Thickening of the OPL/ONL and multiple cysts in the ONL are observed in the segmented retina. Diffuse thickening of the OPL/ONL is prominent (white-colored pixels on the heat maps). (D) Patient 4: 49-year-old man with the focal type of DME. His VA was logmar 0.30, and his scd14 level was 15.2 pg/ml. HF are mainly observed in the outer retinal layers on the inverted image. Diffuse thickening of the OPL/ONL is observed (white-colored pixels on the heat maps).
5 Association Between scd14 and Hyperreflective Foci IOVS j February 2018 j Vol. 59 j No. 2 j 719 FIGURE. Continued. is associated with edema across all retinal layers in DME and is particularly associated with inner retinal changes. Coscas et al. 11 suggested that the origin of the HF could be activated microglia associated with the inflammatory environment in age-related macular degeneration. In DME, anti-vegf treatment is associated with a reduction in HF, and the presence of HF has been considered a marker of active disease status. 19 Interestingly, microglia and HF share common characteristics. Both microglia and HF are primarily found in the inner retina in DR without edema 10,20 and show an extended distribution into the outer retina in DME. Vujosevic et al. 21 reported that compared with healthy subjects, diabetic patients showed an increase in the number of HF in the inner retinal layer, suggesting that HF may represent aggregates of activated microglial cells. These authors insisted that HF are distinct in nature from lipoprotein exudates because only patients at the initial stages of DR or without DR were included in their study. Microglia have been observed in the outer retina and subretinal space as DME progresses, 8 and this finding is consistent with our results in which the HF were distributed across all retinal layers. Moreover, following their activation, the cell bodies of microglia become larger and are therefore more likely to be detected as bright dots on SD-OCT. 8,22 In addition to these common characteristics, a positive correlation was observed between the level of scd14 and the number of HF, indicating that HF in most patients with DME, if not in all, could represent activated microglia. After dividing the patients into two groups according to the DME type, the level of scd14 and the total number of HF were higher in the diffuse edema group than those in the focal edema group. The number of inner retinal HF in diffuse edema was significantly higher than that in focal edema, whereas the numbers of HF in the outer retinal layer did not differ between the two DME groups. The higher levels of scd14 and number
6 Association Between scd14 and Hyperreflective Foci IOVS j February 2018 j Vol. 59 j No. 2 j 720 TABLE 4. Regression Analyses for the Factors Associated With scd14 Levels Univariate Regression Analysis Multivariate Regression Analysis Variables Estimate SE P Estimate SE P Age, n ¼ Sex, n ¼ DM duration, n ¼ <0.001 logmar, n ¼ HbA1C, n ¼ No. of HF at inner retina, n ¼ No. of HF at outer retina, n ¼ No. of HF total, n ¼ CMT, n ¼ <0.001 INL volume, n ¼ < OPL/ONL volume, n ¼ Total retina volume, n ¼ <0.001 Age and sex were adjusted in the multivariate regression analysis. of INL HF in diffuse edema might imply that there is a more severe inflammatory reaction and concomitant increase in activated microglia in the inner retina. Diffuse edema is known to be induced by the generalized breakdown of the inner blood-retinal barrier. 23 When diffuse leakage occurs in the inner retina, fluid collects mainly in the INL, resulting in a diffuse edema pattern. 13 Compared with focal edema, diffuse edema is associated with a more extensive area of leakage, 13 and the activated microglia also could be more extensively distributed around areas of extensive leakage. However, in focal edema, microaneurysms are the major source of the focal fluid accumulation in the outer retina. Bolz et al. 12 described that HF located around microaneurysm walls were likely to consist of extravasated lipoproteins. Indeed, hard exudates are commonly found around microaneurysms but are not typically observed in diffuse DME. Therefore, the increase in both the number of HF and the level of scd14 in diffuse edema in the present study supports our hypothesis that HF in the inner retina represent activated microglia rather than lipoprotein exudates. This finding raises the question of the origin of HF in the outer retina. Do HF consist of migrated microglia or extravasated lipoprotein from microaneurysms? The following clues suggest that many outer retinal HF could also represent activated microglia. Compared with the control eyes, the level of scd14 in the eyes with focal edema and cysts mainly distributed in the OPL/ONL was significantly increased. In addition, no difference was observed in the number of outer retinal HF between the edema subtypes. Hard exudates are thought to form from microaneurysms, which is the major source of leakage in focal edema. If most HF observed on OCT in DME patients consist of lipoprotein exudates, outer retinal HF should be more abundant in focal edema, which was not the case in the present study. However, aggregates of HF in the outer retina have been visualized as hard exudates in fundus photography 12 ; thus, we cannot fully exclude the possibility that lipoprotein exudates could be the origin of some HF. Further immunohistologic studies of microglia and concomitant OCT imaging using donor eyeballs might be needed to answer this intriguing question. The higher baseline scd14 levels were correlated with decreased CMT and VA improvement after the anti-vegf treatment, which is consistent with previous reports in which anti-vegf treatment reduced the number of microglia and their activity. 24 The decreased microglial activity following the anti-vegf treatment could contribute to the reduced loads of inflammatory cytokines, resulting in the reduction of CMT and the number of HF and VA improvement. Concordantly, CMT was significantly decreased in the diffuse edema group, whose baseline scd14 was higher, while CMT in the focal edema group did not decrease. The favorable anatomic response in the diffuse edema group to the anti-vegf treatment is consistent with previous reports. 25 We speculate that the favorable response to the anti-vegf treatment in the diffuse edema group might be due to the remarkable deactivation of microglia by anti-vegf antibodies. Altogether, the level of scd14 could be a new biomarker of functional and anatomic responses to anti-vegf treatment or other drugs targeting the inflammatory microenvironment in DME. This study has several limitations. First, direct evidence supporting increased microglia activation in the eyes with elevated scd14 levels could not be obtained. Although knowledge regarding the scd14 levels in animal models of DME is limited, correlating the level of scd14 to visualized microglia using an immunohistologic approach might provide evidence regarding their direct relationship. Second, we could not directly show that HF on SD-OCT represent activated microglia. Thus, donor eyes from patients with DME should be scanned using SD-OCT to visualize the HF, and the HF should be colocalized with the same retinal tissue immunostained by microglial markers. Third, the association of the changes in the scd14 levels post-ivb with other clinical parameters could not be shown in the present study due to the lack of measurement of scd14 levels post-ivb. Thus, a future longitudinal study including the association of the changes in the scd14 levels and HF after the treatment of DME is needed. Finally, the numbers of DME patients and control subjects were relatively small and their ages and sexes were not matched well (with younger ages and more males in the DME group than in the control group), which could affect the measurement value of scd14. There is little information about the age and sex TABLE 5. Changes in VA and SD-OCT Parameters in Patients With DME Pre-IVB, n ¼ 30 Post-IVB, n ¼ 30 P* logmar (SD) 0.32 (0.18) 0.39 (0.31) 0.07 CMT, lm (SD) (68.9) (85.3) No. of HF in inner retina (SD) 3.2 (2.5) 1.5 (1.1) No. of HF in outer retina (SD) 5.8 (3.2) 2.2 (1.9) <0.001 No. of total HF (SD) 9.0 (4.8) 3.7 (2.3) <0.001 Pre-IVB, before the first intravitreal bevacizumab injection; Post- IVB, 3 months after the first intravitreal bevacizumab injection. * Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
7 Association Between scd14 and Hyperreflective Foci IOVS j February 2018 j Vol. 59 j No. 2 j 721 predilection of microglial activation or elevated scd14 in DR or DME, although CD14 has been known to be elevated more in older individuals or males than in younger individuals or females in a neurodegenerative disease of the brain or chronic intermittent hypoxia, respectively. 26,27 Further elucidation with a larger study group without bias might be needed to show direct relationships between microglial activation and HF on OCT in DME. In conclusion, this study demonstrated that the level of scd14 in the AH from eyes with DME is significantly higher than that in the control eyes. A positive correlation was observed between the level of scd14 and the number of HF on OCT. Higher scd14 levels were strongly correlated with increases in both the number of HF in the inner retina and the INL volume. Additionally, higher scd14 levels were markedly correlated with an increased number of HF in the inner retinas of patients with diffuse edema, who presented an increased INL volume. Further immunohistologic studies using animal models and donor eyeballs from patients with DME might be needed to obtain definitive answers as to whether HF originate from activated microglia and whether elevated scd14 in DME is due primarily to activated microglia. Acknowledgments Supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, which is funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare (Grant HI14C1872). Disclosure: H. Lee, None; H. Jang, None; Y.A. Choi, None; H.C. Kim, None; H. Chung, None References 1. Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE, Davis MD, DeMets DL. The Wisconsin epidemiologic study of diabetic retinopathy. IV. Diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology. 1984;91: Bhagat N, Grigorian RA, Tutela A, Zarbin MA. Diabetic macular edema: pathogenesis and treatment. Surv Ophthalmol. 2009;54: Omri S, Behar-Cohen F, de Kozak Y, et al. Microglia/ macrophages migrate through retinal epithelium barrier by a transcellular route in diabetic retinopathy: role of PKC f in the Goto Kakizaki rat model. Am J Pathol. 2011;179: Landmann R, Müller B, Zimmerli W. CD14, new aspects of ligand and signal diversity. Microbes Infect. 2000;2: Sohn EJ, Paape MJ, Bannerman DD, Connor EE, Fetterer RH, Peters RR. Shedding of scd14 by bovine neutrophils following activation with bacterial lipopolysaccharide results in down-regulation of IL-8. Vet Res. 2007;38: Frey EA, Miller DS, Jahr TG, et al. Soluble CD14 participates in the response of cells to lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1992; 176: Umazume K, Usui Y, Wakabayashi Y, Okunuki Y, Kezuka T, Goto H. Effects of soluble CD14 and cytokine levels on diabetic macular edema and visual acuity. Retina. 2013;33: Zeng HY, Green WR, Tso MO. Microglial activation in human diabetic retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 2008;126: Yin GN, Jeon H, Lee S, Lee HW, Cho JY, Suk K. Role of soluble CD14 in cerebrospinal fluid as a regulator of glial functions. J Neurosci Res. 2009;87: Kang JW, Chung H, Kim HC. Correlation of optical coherence tomographic hyperreflective foci with visual outcomes in different patterns of diabetic macular edema. Retina. 2016; 36: Coscas G, De Benedetto U, Coscas F, et al. Hyperreflective dots: a new spectral-domain optical coherence tomography entity for follow-up and prognosis in exudative age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmologica. 2013;229: Bolz M, Schmidt-Erfurth U, Deak G, et al. Optical coherence tomographic hyperreflective foci: a morphologic sign of lipid extravasation in diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology. 2009;116: Byeon SH, Chu YK, Hong YT, Kim M, Kang HM, Kwon OW. New insights into the pathoanatomy of diabetic macular edema: angiographic patterns and optical coherence tomography. Retina. 2012;32: Ji B, Lim D, Kim J, Kim HC, Chung H. Increased levels of dickkopf 3 in the aqueous humor of patients with diabetic macular edema. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;57: Wilkinson CP, Ferris FL III, Klein RE, et al. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology. 2003;110: Ibrahim AS, El-Remessy AB, Matragoon S, et al. Retinal microglial activation and inflammation induced by amadoriglycated albumin in a rat model of diabetes. Diabetes. 2011; 60: Krady JK, Basu A, Allen CM, et al. Minocycline reduces proinflammatory cytokine expression, microglial activation, and caspase-3 activation in a rodent model of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes. 2005;54: Zeng XX, Ng YK, Ling EA. Neuronal and microglial response in the retina of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Vis Neurosci. 2000;17: Framme C, Schweizer P, Imesch M, Wolf S, Wolf-Schnurrbusch U. Behavior of SD-OCT-detected hyperreflective foci in the retina of anti-vegf-treated patients with diabetic macular edema. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53: Uji A, Murakami T, Nishijima K, et al. Association between hyperreflective foci in the outer retina, status of photoreceptor layer, and visual acuity in diabetic macular edema. Am J Ophthalmol. 2012;153: Vujosevic S, Bini S, Midena G, Berton M, Pilotto E, Midena E. Hyperreflective intraretinal spots in diabetics without and with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy: an in vivo study using spectral domain OCT. J Diabetes Res. 2013;2013: Yu Y, Chen H, Su SB. Neuroinflammatory responses in diabetic retinopathy. J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12: Bresnick GH. Diabetic maculopathy. A critical review highlighting diffuse macular edema. Ophthalmology. 1983; 90: Couturier A, Bousquet E, Zhao M, et al. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor acts on retinal microglia/macrophage activation in a rat model of ocular inflammation. Mol Vis. 2014;20: Kim M, Lee P, Kim Y, Yu SY, Kwak HW. Effect of intravitreal bevacizumab based on optical coherence tomography patterns of diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmologica. 2011; 226: Von Bernhardi R, Eugenín-von Bernhardi L, Eugenín J. Microglial cell dysregulation in brain aging and neurodegeneration. Front Aging Neurosci. 2015;7: Kimyon R, Smith S, Watters J. Sex differences in microglial responses to chronic intermittent hypoxia (E-Abstract ). FASEB J. 2015;29.
Hyperreflective foci (HFs) have been frequently observed
 Multidisciplinary Ophthalmic Imaging Behavior of SD-OCT Detected Hyperreflective Foci in the Retina of Anti-VEGF Treated Patients with Diabetic Macular Edema Carsten Framme, Paul Schweizer, Manfred Imesch,
Multidisciplinary Ophthalmic Imaging Behavior of SD-OCT Detected Hyperreflective Foci in the Retina of Anti-VEGF Treated Patients with Diabetic Macular Edema Carsten Framme, Paul Schweizer, Manfred Imesch,
Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City
 Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City Disclosures Consulted for Novo Nordisk 2017,2018. Will be discussing
Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy Blake Cooper MD Ophthalmologist Vitreoretinal Surgeon Retina Associates Kansas City Disclosures Consulted for Novo Nordisk 2017,2018. Will be discussing
A retrospective nonrandomized study was conducted at 3
 Department of Ophthalmology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University College of Medicine 1, Seoul, Korea Hangil Eye Hospital 2, Incheon, Korea Seoul National University Bundang Hospital 3, Seongnam,
Department of Ophthalmology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University College of Medicine 1, Seoul, Korea Hangil Eye Hospital 2, Incheon, Korea Seoul National University Bundang Hospital 3, Seongnam,
Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction
 Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction Lawrence Iu FRCSEd (Ophth), FCOphthHK, FHKAM (Ophthalmology) Department of Ophthalmology, Grantham Hospital & Queen Mary Hospital Background Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Diabetic and the Eye: An Introduction Lawrence Iu FRCSEd (Ophth), FCOphthHK, FHKAM (Ophthalmology) Department of Ophthalmology, Grantham Hospital & Queen Mary Hospital Background Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy. Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP
 Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP Content OCT imaging Retinal layers OCT features in Diabetes Some NON DR features
Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetic Retinopathy Mrs Samantha Mann Consultant Ophthalmologist Clinical Lead of SEL-DESP Content OCT imaging Retinal layers OCT features in Diabetes Some NON DR features
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME)
 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
OCT Assessment of the Vitreoretinal Relationship in CSME
 December 2007 Sonia Rani John et al. - IFIS 375 ORIGINAL ARTICLE OCT Assessment of the Vitreoretinal Relationship in CSME Dr. Manoj S. DNB FRCS, Dr. Unnikrishnan Nair MS DO FRCS, Dr. Gargi Sathish MS Introduction
December 2007 Sonia Rani John et al. - IFIS 375 ORIGINAL ARTICLE OCT Assessment of the Vitreoretinal Relationship in CSME Dr. Manoj S. DNB FRCS, Dr. Unnikrishnan Nair MS DO FRCS, Dr. Gargi Sathish MS Introduction
PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY
 PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY General Anatomy At Ora Serrata At Optic Nerve Head Fundoscopic View Of Normal Retina What Is So Special About Diabetic Retinopathy? The WHO definition of blindness is
PART 1: GENERAL RETINAL ANATOMY General Anatomy At Ora Serrata At Optic Nerve Head Fundoscopic View Of Normal Retina What Is So Special About Diabetic Retinopathy? The WHO definition of blindness is
The Quick Guide to OCT Mastery 50 Real Cases with Expert Analysis
 OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY The Quick Guide to OCT Mastery 50 Real Cases with Expert Analysis VOL 1 Sanjay Sharma, MD, FRCS, MSc (Epid), MBA Ophthalmologist, Epidemiologist Queen s University, Canada
OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY The Quick Guide to OCT Mastery 50 Real Cases with Expert Analysis VOL 1 Sanjay Sharma, MD, FRCS, MSc (Epid), MBA Ophthalmologist, Epidemiologist Queen s University, Canada
The Natural History of Diabetic Retinopathy and How Primary Care Makes A Difference
 The Natural History of Diabetic Retinopathy and How Primary Care Makes A Difference We will discuss - How exactly does blood sugar control affect retinopathy? - What are other factors that we measure in
The Natural History of Diabetic Retinopathy and How Primary Care Makes A Difference We will discuss - How exactly does blood sugar control affect retinopathy? - What are other factors that we measure in
Is OCT-A Needed As An Investigative Tool During The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema
 Is OCT-A Needed As An Investigative Tool During The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema Ayman M Khattab MD, FRCS Professor of Ophthalmology Cairo University Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) Diabetic macular
Is OCT-A Needed As An Investigative Tool During The Management Of Diabetic Macular Edema Ayman M Khattab MD, FRCS Professor of Ophthalmology Cairo University Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) Diabetic macular
Diabetic Management beyond traditional risk factors and LDL-C control: Can we improve macro and microvascular risks?
 Retinopathy Diabetes has a negative effect on eyes in many ways, increasing the risk of cataracts for example, but the most common and serious ocular complication of diabetes is retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy
Retinopathy Diabetes has a negative effect on eyes in many ways, increasing the risk of cataracts for example, but the most common and serious ocular complication of diabetes is retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy
An A to Z guide on Epiretinal Membranes (ERMs) Paris Tranos PhD,ICO,FRCS OPHTHALMICA Vitreoretinal & Uveitis Department
 An A to Z guide on Epiretinal Membranes (ERMs) Paris Tranos PhD,ICO,FRCS OPHTHALMICA Vitreoretinal & Uveitis Department Types of ERM Natural history OCT prognostic factors ERM with co-existing pathology
An A to Z guide on Epiretinal Membranes (ERMs) Paris Tranos PhD,ICO,FRCS OPHTHALMICA Vitreoretinal & Uveitis Department Types of ERM Natural history OCT prognostic factors ERM with co-existing pathology
Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient
 Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient Rova Virgana FK Unpad Pusat Mata Nasional RS Mata Cicendo Bandung Eye Center (Hospital and Clinic) PIT IDI Jabar 2018 Keys Facts from WHO
Eyes on Diabetics: How to Avoid Blindness in Diabetic Patient Rova Virgana FK Unpad Pusat Mata Nasional RS Mata Cicendo Bandung Eye Center (Hospital and Clinic) PIT IDI Jabar 2018 Keys Facts from WHO
Optical Coherence Tomograpic Features in Idiopathic Retinitis, Vasculitis, Aneurysms and Neuroretinitis (IRVAN)
 Columbia International Publishing Journal of Ophthalmic Research (2014) Research Article Optical Coherence Tomograpic Features in Idiopathic Retinitis, Vasculitis, Aneurysms and Neuroretinitis (IRVAN)
Columbia International Publishing Journal of Ophthalmic Research (2014) Research Article Optical Coherence Tomograpic Features in Idiopathic Retinitis, Vasculitis, Aneurysms and Neuroretinitis (IRVAN)
ANGIO OCT IMAGING OF MACULAR VASCULATURE IN DIABETIC MACULAR EDEMA BEFORE AND AFTER MACULAR SURGERY
 17th EVRS Meeting September 14-17, 2017 Teatro della Pergola FLORENCE - ITALY ANGIO OCT IMAGING OF MACULAR VASCULATURE IN DIABETIC MACULAR EDEMA BEFORE AND AFTER MACULAR SURGERY G. Macrì, G. Pacelli, V.
17th EVRS Meeting September 14-17, 2017 Teatro della Pergola FLORENCE - ITALY ANGIO OCT IMAGING OF MACULAR VASCULATURE IN DIABETIC MACULAR EDEMA BEFORE AND AFTER MACULAR SURGERY G. Macrì, G. Pacelli, V.
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 12 Page December 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.39 Central Macular Thickness analysis
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.39 Central Macular Thickness analysis
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) in Uveitis Piergiorgio Neri, BMedSc, MD, PhD Head Ocular Immunology Unit
 The Eye Clinic Polytechnic University of Marche Head: Prof Alfonso Giovannini November, 1991 Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) in Uveitis Piergiorgio Neri, BMedSc, MD, PhD Head Ocular Immunology Unit
The Eye Clinic Polytechnic University of Marche Head: Prof Alfonso Giovannini November, 1991 Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) in Uveitis Piergiorgio Neri, BMedSc, MD, PhD Head Ocular Immunology Unit
ZEISS AngioPlex OCT Angiography. Clinical Case Reports
 Clinical Case Reports Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) Case Report 969 PROLIFERATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY 1 1-year-old diabetic female presents for follow-up of proliferative diabetic retinopathy
Clinical Case Reports Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR) Case Report 969 PROLIFERATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY 1 1-year-old diabetic female presents for follow-up of proliferative diabetic retinopathy
Andrew J. Barkmeier, MD; Benjamin P. Nicholson, MA; Levent Akduman, MD
 c l i n i c a l s c i e n c e Effectiveness of Laser Photocoagulation in Clinically Significant Macular Edema With Focal Versus Diffuse Parafoveal Thickening on Optical Coherence Tomography Andrew J. Barkmeier,
c l i n i c a l s c i e n c e Effectiveness of Laser Photocoagulation in Clinically Significant Macular Edema With Focal Versus Diffuse Parafoveal Thickening on Optical Coherence Tomography Andrew J. Barkmeier,
Optical Coherence Tomography: Pearls for the Anterior Segment Surgeon Basic Science Michael Stewart, M.D.
 Optical Coherence Tomography: Pearls for the Anterior Segment Surgeon Basic Science Michael Stewart, M.D. Disclosure OCT Optical Coherence Tomography No relevant financial relationships I will refer to
Optical Coherence Tomography: Pearls for the Anterior Segment Surgeon Basic Science Michael Stewart, M.D. Disclosure OCT Optical Coherence Tomography No relevant financial relationships I will refer to
Optical Coherence Tomographic Reflectivity of Photoreceptors beneath Cystoid Spaces in Diabetic Macular Edema
 Retina Optical Coherence Tomographic Reflectivity of Photoreceptors beneath in Diabetic Macular Edema Tomoaki Murakami, Kazuaki Nishijima, Tadamichi Akagi, Akihito Uji, Takahiro Horii, Naoko Ueda-Arakawa,
Retina Optical Coherence Tomographic Reflectivity of Photoreceptors beneath in Diabetic Macular Edema Tomoaki Murakami, Kazuaki Nishijima, Tadamichi Akagi, Akihito Uji, Takahiro Horii, Naoko Ueda-Arakawa,
Ellabban, Abdallah A; Yoshimura, Na.
 Association between hyperreflective Titlestatus of photoreceptor layer, and macular edema. Uji, Akihito; Murakami, Tomoaki; Ni Author(s) Tadamichi; Horii, Takahiro; Arakawa Ellabban, Abdallah A; Yoshimura,
Association between hyperreflective Titlestatus of photoreceptor layer, and macular edema. Uji, Akihito; Murakami, Tomoaki; Ni Author(s) Tadamichi; Horii, Takahiro; Arakawa Ellabban, Abdallah A; Yoshimura,
Fundus Autoflu ores cence Findings Pre and Post Intravitreal Bevacizumab Injection in Patients with Diabetic Macular Edema
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 1, September: 1093-1100, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Fundus Autoflu ores cence Findings Pre and Post Intravitreal Bevacizumab Injection in Patients with
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 1, September: 1093-1100, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Fundus Autoflu ores cence Findings Pre and Post Intravitreal Bevacizumab Injection in Patients with
In its initial report, the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy. A Severity Scale for Diabetic Macular Edema Developed from ETDRS Data
 A Severity Scale for Diabetic Macular Edema Developed from ETDRS Data Ronald E. Gangnon, 1,2 Matthew D. Davis, 3 Larry D. Hubbard, 3 Lloyd M. Aiello, 4 Emily Y. Chew, 5 Frederick L. Ferris III, 5 Marian
A Severity Scale for Diabetic Macular Edema Developed from ETDRS Data Ronald E. Gangnon, 1,2 Matthew D. Davis, 3 Larry D. Hubbard, 3 Lloyd M. Aiello, 4 Emily Y. Chew, 5 Frederick L. Ferris III, 5 Marian
Hyperreflective foci (HF) are discrete, well-circumscribed
 Retina Correlation Between Hyperreflective Foci and Clinical Outcomes in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration After Switching to Aflibercept Kaveh Abri Aghdam, 1,2 Amelie Pielen, 1 Carsten Framme,
Retina Correlation Between Hyperreflective Foci and Clinical Outcomes in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration After Switching to Aflibercept Kaveh Abri Aghdam, 1,2 Amelie Pielen, 1 Carsten Framme,
Kyungmin Lee, Heeyoung Chung, Youngsuk Park, Joonhong Sohn. HanGil Eye Hospital, Incheon, Korea
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2014;28(4):298-305 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2014.28.4.298 Original Article Efficacy of Intravitreal Anti-vascular Endothelial Growth Factor or
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2014;28(4):298-305 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2014.28.4.298 Original Article Efficacy of Intravitreal Anti-vascular Endothelial Growth Factor or
EFFICACY OF ANTI-VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR AGENTS IN RETINAL DISORDER FOR BETTER VISUAL ACUITY
 EFFICACY OF ANTI-VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR AGENTS IN RETINAL DISORDER FOR BETTER VISUAL ACUITY Diwakar chaudhary *1, 2, Hu shuqiong, Long Yuan and Xiong kun 1 Yangtze University, 1 Nanhuan Road
EFFICACY OF ANTI-VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR AGENTS IN RETINAL DISORDER FOR BETTER VISUAL ACUITY Diwakar chaudhary *1, 2, Hu shuqiong, Long Yuan and Xiong kun 1 Yangtze University, 1 Nanhuan Road
OCT Image Analysis System for Grading and Diagnosis of Retinal Diseases and its Integration in i-hospital
 Progress Report for1 st Quarter, May-July 2017 OCT Image Analysis System for Grading and Diagnosis of Retinal Diseases and its Integration in i-hospital Milestone 1: Designing Annotation tool extraction
Progress Report for1 st Quarter, May-July 2017 OCT Image Analysis System for Grading and Diagnosis of Retinal Diseases and its Integration in i-hospital Milestone 1: Designing Annotation tool extraction
OCT in Diabetic Macular Edema and its Correlation with Flourescein Angiography
 Uvea OCT in Diabetic Macular Edema and its Correlation with Flourescein Angiography Kirti Jaisingh MS Kirti Jaisingh MS, Yashpal Goel* MS, Kshitij Aditya** DO * Guru Nanak Eye Centre, New Delhi ** Baba
Uvea OCT in Diabetic Macular Edema and its Correlation with Flourescein Angiography Kirti Jaisingh MS Kirti Jaisingh MS, Yashpal Goel* MS, Kshitij Aditya** DO * Guru Nanak Eye Centre, New Delhi ** Baba
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes can be classified into type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus, formerly known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and non-insulin diabetes mellitus, respectively.
Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes can be classified into type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus, formerly known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and non-insulin diabetes mellitus, respectively.
The Human Eye. Cornea Iris. Pupil. Lens. Retina
 The Retina Thin layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (the film of the camera). Light rays are focused on the retina then transmitted to the brain. The macula is the very small area in
The Retina Thin layer of light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (the film of the camera). Light rays are focused on the retina then transmitted to the brain. The macula is the very small area in
Study of clinical significance of optical coherence tomography in diagnosis & management of diabetic macular edema
 Original Research Article Study of clinical significance of optical coherence tomography in diagnosis & management of diabetic macular edema Neha Kantilal Desai 1,*, Somesh Vedprakash Aggarwal 2, Sonali
Original Research Article Study of clinical significance of optical coherence tomography in diagnosis & management of diabetic macular edema Neha Kantilal Desai 1,*, Somesh Vedprakash Aggarwal 2, Sonali
Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public
 Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public Ray M. Balyeat, MD The Eye Institute Tulsa, Oklahoma The Healthy Eye Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, pupil and lens. These light rays are
Diabetic Retinopathy A Presentation for the Public Ray M. Balyeat, MD The Eye Institute Tulsa, Oklahoma The Healthy Eye Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, pupil and lens. These light rays are
Measuring of the fovea and foveola using line scans and 3D Macular scans obtained with spectral domain optical coherent tomography.
 Measuring of the fovea and foveola using line scans and 3D Macular scans obtained with spectral domain optical coherent tomography. Vakhrameeva O.A. 1, Moiseenko G.A. 1, Maltsev D.S. 2, Sukhinin M.V. 2,
Measuring of the fovea and foveola using line scans and 3D Macular scans obtained with spectral domain optical coherent tomography. Vakhrameeva O.A. 1, Moiseenko G.A. 1, Maltsev D.S. 2, Sukhinin M.V. 2,
OCT Angiography in Primary Eye Care
 OCT Angiography in Primary Eye Care An Image Interpretation Primer Julie Rodman, OD, MS, FAAO and Nadia Waheed, MD, MPH Table of Contents Diabetic Retinopathy 3-6 Choroidal Neovascularization 7-9 Central
OCT Angiography in Primary Eye Care An Image Interpretation Primer Julie Rodman, OD, MS, FAAO and Nadia Waheed, MD, MPH Table of Contents Diabetic Retinopathy 3-6 Choroidal Neovascularization 7-9 Central
EFFICACY OF INTRAVITREAL TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE FOR THE TREATMENT OF DIABETIC MACULAR EDEMA
 Basrah Journal Of Surgery EFFICACY OF INTRAVITREAL TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE FOR THE TREATMENT OF DIABETIC MACULAR EDEMA Salah Zuhair Abed Al-Asadi MB,ChB, FICMS, Lecturer, Department of Surgery, College
Basrah Journal Of Surgery EFFICACY OF INTRAVITREAL TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE FOR THE TREATMENT OF DIABETIC MACULAR EDEMA Salah Zuhair Abed Al-Asadi MB,ChB, FICMS, Lecturer, Department of Surgery, College
Why Is Imaging Critical in My Uveitis Practice?
 Why Is Imaging Critical in My Uveitis Practice? Dilraj S. Grewal, MD Developed in collaboration Imaging Is the Backbone of Uveitis Workup and Monitoring Treatment Response FP FAF B- scan Multimodal Imaging
Why Is Imaging Critical in My Uveitis Practice? Dilraj S. Grewal, MD Developed in collaboration Imaging Is the Backbone of Uveitis Workup and Monitoring Treatment Response FP FAF B- scan Multimodal Imaging
Neural Retinal Disorganization as a Robust Marker of Visual Acuity in Current and Resolved Diabetic Macular Edema
 2560 Diabetes Volume 64, July 2015 Jennifer K. Sun, 1,2 Salma H. Radwan, 3,4 Ahmed Z. Soliman, 4,5 Jan Lammer, 6 Michael M. Lin, 7 Sonja G. Prager, 6 Paolo S. Silva, 1,2 Lloyd Bryce Aiello, 1 and Lloyd
2560 Diabetes Volume 64, July 2015 Jennifer K. Sun, 1,2 Salma H. Radwan, 3,4 Ahmed Z. Soliman, 4,5 Jan Lammer, 6 Michael M. Lin, 7 Sonja G. Prager, 6 Paolo S. Silva, 1,2 Lloyd Bryce Aiello, 1 and Lloyd
3/6/2014. Hoda MH Mostafa MD Associate Professor of Ophthalmology Cairo University. The author has no proprietary interest. Today s Objectives
 Hoda MH Mostafa MD Associate Professor of Ophthalmology Cairo University The author has no proprietary interest Today s Objectives Identify the CLINICAL SCENARIOS IN MACULAR EDEMA where OCT plays a MAJOR
Hoda MH Mostafa MD Associate Professor of Ophthalmology Cairo University The author has no proprietary interest Today s Objectives Identify the CLINICAL SCENARIOS IN MACULAR EDEMA where OCT plays a MAJOR
Quantitative Reduction in Central Foveal Thickness After First Anti-VEGF Injection as a Predictor of Final Outcome in BRVO Patients
 Original clinical study Quantitative Reduction in Central Foveal Thickness After First Anti-VEGF Injection as a Predictor of Final Outcome in BRVO Patients Rupak Roy, MS, Kumar Saurabh, MS, Avirupa Ghose,
Original clinical study Quantitative Reduction in Central Foveal Thickness After First Anti-VEGF Injection as a Predictor of Final Outcome in BRVO Patients Rupak Roy, MS, Kumar Saurabh, MS, Avirupa Ghose,
INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS Introduction of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a potentially blinding complication of diabetes. It is defined as presence of one or more definite
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION AND SYMPTOMS Introduction of Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a potentially blinding complication of diabetes. It is defined as presence of one or more definite
Diabetes Care 24: , 2001
 Pathophysiology/Complications O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Prevalence and Significance of Retinopathy in Subjects With Type 1 Diabetes of Less Than 5 Years Duration Screened for the Diabetes Control and
Pathophysiology/Complications O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Prevalence and Significance of Retinopathy in Subjects With Type 1 Diabetes of Less Than 5 Years Duration Screened for the Diabetes Control and
CSME BCVA. OCT Bevacizumab CMT CMT BCVA. BCVA LogMAR. p CMT NPDR PDR PDR. Bevacizumab PDR FDA. Ranibizumab. Bevacizumab.
 email: rezaj76@yahoo.com Bevacizumab FDA mg Ranibizumab - Bevacizumab NPDR PDR PDR PDR CSME FAZFA BCVA CMT OCT Bevacizumab BCVA CMT BCVA LogMAR p CMT p CSME CRVO CSME BRVO CRVOBRVO (fovea avascular zone)
email: rezaj76@yahoo.com Bevacizumab FDA mg Ranibizumab - Bevacizumab NPDR PDR PDR PDR CSME FAZFA BCVA CMT OCT Bevacizumab BCVA CMT BCVA LogMAR p CMT p CSME CRVO CSME BRVO CRVOBRVO (fovea avascular zone)
OCT Angiography The Next Frontier
 Choroid Retina avascular 5/13/2017 OCT Angiography The Next Frontier Pierce Kenworthy OD, FAAO June 9, 2017 OCT Angiography (OCTA) 2016 Non-invasive, motion contrast imaging Represents erythrocyte movement
Choroid Retina avascular 5/13/2017 OCT Angiography The Next Frontier Pierce Kenworthy OD, FAAO June 9, 2017 OCT Angiography (OCTA) 2016 Non-invasive, motion contrast imaging Represents erythrocyte movement
Clinical Study Choroidal Thickness in Eyes with Unilateral Ocular Ischemic Syndrome
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 215, Article ID 62372, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/62372 Clinical Study Choroidal Thickness in Eyes with Unilateral Ocular Ischemic
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 215, Article ID 62372, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/62372 Clinical Study Choroidal Thickness in Eyes with Unilateral Ocular Ischemic
Diabetic Retinopathy and Peripapillary Retinal Thickness
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2010;24(1):16-22 DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2010.24.1.16 Original Article Diabetic Retinopathy and Peripapillary Retinal Thickness Hee Yoon Cho 1, Dong Hoon
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2010;24(1):16-22 DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2010.24.1.16 Original Article Diabetic Retinopathy and Peripapillary Retinal Thickness Hee Yoon Cho 1, Dong Hoon
Scott M. Pfahler D.O. Dayton Vitreo-Retinal Associates AOCOO-HNS Palm Springs, CA 2012
 Scott M. Pfahler D.O. Dayton Vitreo-Retinal Associates AOCOO-HNS Palm Springs, CA 2012 Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Laser Treatments Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Diabetic Macular Edema Laser
Scott M. Pfahler D.O. Dayton Vitreo-Retinal Associates AOCOO-HNS Palm Springs, CA 2012 Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Laser Treatments Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Diabetic Macular Edema Laser
Clinical Trial Endpoints for Macular Diseases
 Clinical Trial Endpoints for Macular Diseases Developed in collaboration Learning Objective Upon completion, participants should be able to: Summarize types of biomarkers of progression and treatment response
Clinical Trial Endpoints for Macular Diseases Developed in collaboration Learning Objective Upon completion, participants should be able to: Summarize types of biomarkers of progression and treatment response
Flore De Bats, 1 Benjamin Wolff, 2,3 Martine Mauget-Faÿsse, 2 Claire Scemama, 2 and Laurent Kodjikian Introduction
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 260237, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/260237 Case Report B-Scan and En-Face Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging for the Diagnosis
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 260237, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/260237 Case Report B-Scan and En-Face Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging for the Diagnosis
Soluble Lutein (Lutemax2020 ) Prevents Retinal Damage in Streptozotocin (STZ)- induced Diabetic Rats
 Soluble Lutein (Lutemax2020 ) Prevents Retinal Damage in Streptozotocin (STZ)- induced Diabetic Rats Vijaya Juturu, Ph.D., F.A.C.N. OmniActive Health Technologies, Inc. Morristown, NJ Acknowledgements
Soluble Lutein (Lutemax2020 ) Prevents Retinal Damage in Streptozotocin (STZ)- induced Diabetic Rats Vijaya Juturu, Ph.D., F.A.C.N. OmniActive Health Technologies, Inc. Morristown, NJ Acknowledgements
Intravitreal versus Posterior Subtenon Injection of Triamcinolone Acetonide for Diabetic Macular Edema
 Intravitreal versus Posterior Subtenon Injection of Triamcinolone Acetonide for Diabetic Macular Edema Young Jae Choi, MD, In Kyung Oh, MD, Jae Ryung Oh, MD, PhD, Kuhl Huh, MD, PhD Department of Ophthalmology,
Intravitreal versus Posterior Subtenon Injection of Triamcinolone Acetonide for Diabetic Macular Edema Young Jae Choi, MD, In Kyung Oh, MD, Jae Ryung Oh, MD, PhD, Kuhl Huh, MD, PhD Department of Ophthalmology,
CLINICALCASE PROVOST J, SEKFALI R, AMOROSO F, ZAMBROWSKI O, MIERE A
 CLINICALCASE PROVOST J, SEKFALI R, AMOROSO F, ZAMBROWSKI O, MIERE A Department of ophthalmology, Souied E. (MD,PhD) Centre Hospitalier Intercommunal de Créteil Université Paris Est HISTORY 13 years old
CLINICALCASE PROVOST J, SEKFALI R, AMOROSO F, ZAMBROWSKI O, MIERE A Department of ophthalmology, Souied E. (MD,PhD) Centre Hospitalier Intercommunal de Créteil Université Paris Est HISTORY 13 years old
THE ROLE OF anti-vegf IN DIABETIC RETINOPATHY AND AGE RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION
 THE ROLE OF anti-vegf IN DIABETIC RETINOPATHY AND AGE RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION MOESTIDJAB DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AIRLANGGA UNIVERSITY DR SOETOMO HOSPITAL SURABAYA INTRODUCTION
THE ROLE OF anti-vegf IN DIABETIC RETINOPATHY AND AGE RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION MOESTIDJAB DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AIRLANGGA UNIVERSITY DR SOETOMO HOSPITAL SURABAYA INTRODUCTION
Longitudinal Changes of Retinal Thicknesses in Branch Retinal Artery Occlusion: Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Study METHODS.
 Retina Longitudinal Changes of Retinal Thicknesses in Branch Retinal Artery Occlusion: Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Study Min-Su Kim, 1 Kyeung-Min Kim, 1 Hyung-Bin Lim, 1,2 Young-Joon Jo,
Retina Longitudinal Changes of Retinal Thicknesses in Branch Retinal Artery Occlusion: Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Study Min-Su Kim, 1 Kyeung-Min Kim, 1 Hyung-Bin Lim, 1,2 Young-Joon Jo,
Yasser R. Serag, MD Tamer Wasfi, MD El- Saied El-Dessoukey, MD Magdi S. Moussa, MD Anselm Kampik, MD
 Microperimetric Evaluation of Brilliant Blue G- assisted Internal Limiting Membrane Peeling By Yasser R. Serag, MD Tamer Wasfi, MD El- Saied El-Dessoukey, MD Magdi S. Moussa, MD Anselm Kampik, MD The internal
Microperimetric Evaluation of Brilliant Blue G- assisted Internal Limiting Membrane Peeling By Yasser R. Serag, MD Tamer Wasfi, MD El- Saied El-Dessoukey, MD Magdi S. Moussa, MD Anselm Kampik, MD The internal
Macular Hole Associated with Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Disease at the Acute Uveitic Stage
 Published online: September 15, 2015 2015 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 1663 2699/15/0063 0328$39.50/0 This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0
Published online: September 15, 2015 2015 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 1663 2699/15/0063 0328$39.50/0 This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0
OCT Interpretation in Retinal Disease
 OCT Interpretation in Retinal Disease Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO Financial Disclosure I have received honoraria or am on the advisory board for the following companies: Carl Zeiss Meditec Advanced Ocular
OCT Interpretation in Retinal Disease Jay M. Haynie, OD, FAAO Financial Disclosure I have received honoraria or am on the advisory board for the following companies: Carl Zeiss Meditec Advanced Ocular
Fundus Fluorescein Angiography in Diabetic Retinopathy: Correlation of Angiographic Findings to the Clinical Maculopathy Abstract: Purpose:
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. XII (Feb. 2016), PP 80-88 www.iosrjournals.org Fundus Fluorescein Angiography in Diabetic
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. XII (Feb. 2016), PP 80-88 www.iosrjournals.org Fundus Fluorescein Angiography in Diabetic
R&M Solutions
 Mohamed Hosny El-Bradey, MD., Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology, Tanta University. Wael El Haig, MD., Professor of Ophthalmology. Zagazeeg University. 1 Myopic CNV is considered the most common vision
Mohamed Hosny El-Bradey, MD., Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology, Tanta University. Wael El Haig, MD., Professor of Ophthalmology. Zagazeeg University. 1 Myopic CNV is considered the most common vision
연령연관황반변성에서망막혈관종성증식과동반된망막색소상피박리의임상양상과일차적인광역학치료의결과
 연령연관황반변성에서망막혈관종성증식과동반된망막색소상피박리의임상양상과일차적인광역학치료의결과 40 Table. Clinical characteristics and results of patients undergoing photodynamic therapy for retinal angiomatous proliferation Patients No. Age/ sex Eye
연령연관황반변성에서망막혈관종성증식과동반된망막색소상피박리의임상양상과일차적인광역학치료의결과 40 Table. Clinical characteristics and results of patients undergoing photodynamic therapy for retinal angiomatous proliferation Patients No. Age/ sex Eye
Diabetic macular edema (DME) is the primary cause of
 Retina Quantification of External Limiting Membrane Disruption Caused by Diabetic Macular Edema from SD-OCT Xinjian Chen,*,1 Li Zhang, 1 Elliott H. Sohn, 2,3 Kyungmoo Lee, 1 Meindert Niemeijer, 1,3 John
Retina Quantification of External Limiting Membrane Disruption Caused by Diabetic Macular Edema from SD-OCT Xinjian Chen,*,1 Li Zhang, 1 Elliott H. Sohn, 2,3 Kyungmoo Lee, 1 Meindert Niemeijer, 1,3 John
Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Diabetic Retinopathy
 Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Diabetic Retinopathy Vincent Reppucci, MD Director, Retina Service Mt. Sinai St. Luke s-roosevelt Hospital Attending Physician, Retina Service New York Eye and Ear Infirmary
Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Diabetic Retinopathy Vincent Reppucci, MD Director, Retina Service Mt. Sinai St. Luke s-roosevelt Hospital Attending Physician, Retina Service New York Eye and Ear Infirmary
Diabetic macular edema (DME) is the most common cause. Effect of Diabetic Macular Edema on Peripapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Profiles
 Retina Effect of Diabetic Macular Edema on Peripapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Profiles Duck Jin Hwang, 1,2 Eun Ji Lee, 1 Sang Yoon Lee, 3 Kyu Hyung Park, 1 and Se Joon Woo 1 1 Department
Retina Effect of Diabetic Macular Edema on Peripapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Profiles Duck Jin Hwang, 1,2 Eun Ji Lee, 1 Sang Yoon Lee, 3 Kyu Hyung Park, 1 and Se Joon Woo 1 1 Department
EPIRETINAL MEMBRANE & VITREOMACULAR TRACTION
 EPIRETINAL MEMBRANE & VITREOMACULAR TRACTION Management of ERM and VMT K.V.Chalam,MD,PhD,MBA,FACS Professor and Director of Retina Loma Linda Eye Institute Los Angeles, USA REVIEW ANATOMY The vitreous
EPIRETINAL MEMBRANE & VITREOMACULAR TRACTION Management of ERM and VMT K.V.Chalam,MD,PhD,MBA,FACS Professor and Director of Retina Loma Linda Eye Institute Los Angeles, USA REVIEW ANATOMY The vitreous
You can C-ME after Uveitis
 You can C-ME after Uveitis Abstract: Approximately 50% of uveitis patients will present with vision loss secondary to cystoid macular edema[1]. Two patients with uveitis present with a constant decrease
You can C-ME after Uveitis Abstract: Approximately 50% of uveitis patients will present with vision loss secondary to cystoid macular edema[1]. Two patients with uveitis present with a constant decrease
Effectiveness of Intravitreal Ranibizumab for Diabetic Macular Edema with Serous Retinal Detachment
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 2018 July 17. [Epub ahead of print] https://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2017.0117 Original Article Effectiveness of Intravitreal Ranibizumab for Diabetic Macular Edema with Serous
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 2018 July 17. [Epub ahead of print] https://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2017.0117 Original Article Effectiveness of Intravitreal Ranibizumab for Diabetic Macular Edema with Serous
Abdullah Ozkaya, MD, Mehmet Ozveren, MD, Okkes Baz, MD, Hatice Nur Tarakcioglu, MD, 1 1
 Original Article Diabetic Macular Edema Patients with Poor Baseline Visual Acuity Treated with Ranibizumab in Real Life and Optical Coherence Tomography Based Predictor Factors for Visual Outcomes 1 1
Original Article Diabetic Macular Edema Patients with Poor Baseline Visual Acuity Treated with Ranibizumab in Real Life and Optical Coherence Tomography Based Predictor Factors for Visual Outcomes 1 1
Clinical Study Spectral Domain OCT: An Aid to Diagnosis and Surgical Planning of Retinal Detachments
 Ophthalmology Volume 2011, Article ID 725362, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/725362 Clinical Study Spectral Domain OCT: An Aid to Diagnosis and Surgical Planning of Retinal Detachments Graham Auger and Stephen
Ophthalmology Volume 2011, Article ID 725362, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/725362 Clinical Study Spectral Domain OCT: An Aid to Diagnosis and Surgical Planning of Retinal Detachments Graham Auger and Stephen
Neuropathy (NAION) and Avastin. Clinical Assembly of the AOCOO-HNS Foundation May 9, 2013
 Non Arteritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NAION) and Avastin Shalom Kelman, MD Clinical Assembly of the AOCOO-HNS Foundation May 9, 2013 Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Acute, painless, visual loss,
Non Arteritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NAION) and Avastin Shalom Kelman, MD Clinical Assembly of the AOCOO-HNS Foundation May 9, 2013 Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Acute, painless, visual loss,
Diabetic Macular Edema Treatment in the 21st Century
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Diabetic maculopathy 11/ An update on. Miss Vasuki Sivagnanavel
 Miss Vasuki Sivagnanavel Consultant Ophthalmologist An update on Diabetic maculopathy Despite advances in the management of diabetes, diabetic retinopathy is already the commonest cause of blindness among
Miss Vasuki Sivagnanavel Consultant Ophthalmologist An update on Diabetic maculopathy Despite advances in the management of diabetes, diabetic retinopathy is already the commonest cause of blindness among
Clinical Case Presentation. Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion. Sarita M. Registered Nurse Whangarei Base Hospital
 Clinical Case Presentation on Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion Sarita M. Registered Nurse Whangarei Base Hospital Introduction Case Study Pathogenesis Clinical Features Investigations Treatment Follow-up
Clinical Case Presentation on Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion Sarita M. Registered Nurse Whangarei Base Hospital Introduction Case Study Pathogenesis Clinical Features Investigations Treatment Follow-up
Clinical Outcomes After Intravitreal Bevacizumab Injection for Diabetic Macular Edema
 Original Article Clinical Outcomes After Intravitreal Bevacizumab Injection for Diabetic Macular Edema Karen Joyce G. Castro, MD, Marie Joan V. Loy, MD International Eye Institute St. Luke s Medical Center
Original Article Clinical Outcomes After Intravitreal Bevacizumab Injection for Diabetic Macular Edema Karen Joyce G. Castro, MD, Marie Joan V. Loy, MD International Eye Institute St. Luke s Medical Center
Optical coherence tomography in diabetic macular edema: patterns and related risk factors
 Original article Optical coherence tomography in diabetic macular edema: patterns and related risk factors Mohammadreza Ahmadpour-Baghdadabad Masoudreza Manaviat Ahmad Shojaoddiny-Ardekani Yazd Diabetes
Original article Optical coherence tomography in diabetic macular edema: patterns and related risk factors Mohammadreza Ahmadpour-Baghdadabad Masoudreza Manaviat Ahmad Shojaoddiny-Ardekani Yazd Diabetes
ROLE OF LASER PHOTOCOAGULATION VERSUS INTRAVITREAL TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE IN ANGIOGRAPHIC MACULAR EDEMA IN DIABETES MELLITUS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ROLE OF LASER PHOTOCOAGULATION VERSUS INTRAVITREAL TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE IN ANGIOGRAPHIC MACULAR EDEMA IN DIABETES MELLITUS Aggarwal Somesh VP 1, Shah Sonali N 2, Bharwada Rekha M 3,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ROLE OF LASER PHOTOCOAGULATION VERSUS INTRAVITREAL TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE IN ANGIOGRAPHIC MACULAR EDEMA IN DIABETES MELLITUS Aggarwal Somesh VP 1, Shah Sonali N 2, Bharwada Rekha M 3,
Use of the Free Electron Laser for the Noninvasive Determination of Retinal Oxyhemoglobin Saturation by Near Infrared Reflectance Spectrophotometry
 Use of the Free Electron Laser for the Noninvasive Determination of Retinal Oxyhemoglobin Saturation by Near Infrared Reflectance Spectrophotometry Ref: Eye, M.C. Escher, 1946 Ref: Eye, M.C. Escher, 1946
Use of the Free Electron Laser for the Noninvasive Determination of Retinal Oxyhemoglobin Saturation by Near Infrared Reflectance Spectrophotometry Ref: Eye, M.C. Escher, 1946 Ref: Eye, M.C. Escher, 1946
Efficacy of Anti-VEGF Agents in the Treatment of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
 Efficacy of Anti-VEGF Agents in the Treatment of Age-Related Macular Degeneration Marilita M. Moschos Abstract- Purpose: To evaluate by OCT and mf-erg the macular function in eyes with CNV due to ARMD
Efficacy of Anti-VEGF Agents in the Treatment of Age-Related Macular Degeneration Marilita M. Moschos Abstract- Purpose: To evaluate by OCT and mf-erg the macular function in eyes with CNV due to ARMD
Yoshiro Minami 1*, Taiji Nagaoka 2, Akihiro Ishibazawa 1,2 and Akitoshi Yoshida 2
 Minami et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:90 DOI 10.1186/s12886-017-0485-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Correlation between short- and long-term effects of intravitreal ranibizumab therapy on macular edema
Minami et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:90 DOI 10.1186/s12886-017-0485-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Correlation between short- and long-term effects of intravitreal ranibizumab therapy on macular edema
A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy 840 Walnut Street, Philadelphia PA 19107 www.willseye.org Diabetic Retinopathy 1. Definition Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes
Diabetic Retinopathy A Patient s Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy 840 Walnut Street, Philadelphia PA 19107 www.willseye.org Diabetic Retinopathy 1. Definition Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes
Case report 12/10/2014. Delphine Lam ; Dr Mayer Srour Service d ophtalmologie Professeur E.Souied Université Paris Est
 Case report 12/10/2014 Delphine Lam ; Dr Mayer Srour Service d ophtalmologie Professeur E.Souied Medical history Man, 75 years old Complaint: Vision loss in left eye in June 2014 Past ophthalmologic history:
Case report 12/10/2014 Delphine Lam ; Dr Mayer Srour Service d ophtalmologie Professeur E.Souied Medical history Man, 75 years old Complaint: Vision loss in left eye in June 2014 Past ophthalmologic history:
Thesis Submitted by. Moataz Hamed Mohamed. M.B.B.Ch, M.Sc. (Ophthalmology) In Partial Fulfillment of MD Degree in Ophthalmology Under Supervision of
 Prospective randomized study comparing micropulse diode laser photocoagulation and argon green laser photocoagulation for treatment of clinically significant diabetic macular oedema Thesis Submitted by
Prospective randomized study comparing micropulse diode laser photocoagulation and argon green laser photocoagulation for treatment of clinically significant diabetic macular oedema Thesis Submitted by
Use of Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscope Microperimetry in Clinically Significant Macular Edema in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Use of Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscope Microperimetry in Clinically Significant Macular Edema in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Fumihiko Mori, Satoshi Ishiko, Norihiko Kitaya, Taiichi Hikichi, Eiichi Sato, Akira
Use of Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscope Microperimetry in Clinically Significant Macular Edema in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Fumihiko Mori, Satoshi Ishiko, Norihiko Kitaya, Taiichi Hikichi, Eiichi Sato, Akira
Intravitreal bevacizumab for pediatric exudative retinal diseases
 Saudi Journal of Ophthalmology (2011) 25, 193 197 King Saud University Saudi Journal of Ophthalmology www.saudiophthaljournal.com www.ksu.edu.sa www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Intravitreal bevacizumab
Saudi Journal of Ophthalmology (2011) 25, 193 197 King Saud University Saudi Journal of Ophthalmology www.saudiophthaljournal.com www.ksu.edu.sa www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Intravitreal bevacizumab
7.1 Grading Diabetic Retinopathy
 Chapter 7 DIABETIC RETINOPATHYGRADING -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- A consistent approach to the
Chapter 7 DIABETIC RETINOPATHYGRADING -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- A consistent approach to the
황반부부종을동반한분지망막정맥폐쇄의치료에있어서유리체강내베바시주맙의반응을예측하는인자
 Journal of Retina 2018;3(1):20-25 ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 2508-1926 eissn 2508-3589 황반부부종을동반한분지망막정맥폐쇄의치료에있어서유리체강내베바시주맙의반응을예측하는인자 Predictive Factors for a Favorable Response to Intravitreal Bevacizumab for
Journal of Retina 2018;3(1):20-25 ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 2508-1926 eissn 2508-3589 황반부부종을동반한분지망막정맥폐쇄의치료에있어서유리체강내베바시주맙의반응을예측하는인자 Predictive Factors for a Favorable Response to Intravitreal Bevacizumab for
Acquired vitelliform detachment in patients with subretinal drusenoid deposits (reticular pseudodrusen)
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2011 Acquired vitelliform detachment in patients with subretinal drusenoid
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2011 Acquired vitelliform detachment in patients with subretinal drusenoid
Optical Coherence Tomography Features of Active and Inactive. Retinal Neovascularization in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
 1 Optical Coherence Tomography Features of Active and Inactive Retinal Neovascularization in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Sara Vaz-Pereira, MD, 1,3 Javier Zarranz-Ventura, MD, PhD, FEBO, 1,4 Dawn
1 Optical Coherence Tomography Features of Active and Inactive Retinal Neovascularization in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Sara Vaz-Pereira, MD, 1,3 Javier Zarranz-Ventura, MD, PhD, FEBO, 1,4 Dawn
The Distribution of Leakage on Fluorescein Angiography in Diabetic Macular Edema: A New Approach to Its Etiology
 Retina The Distribution of Leakage on Fluorescein Angiography in Diabetic Macular Edema: A New Approach to Its Etiology Bilal Haj Najeeb, 1 Christian Simader, 1 Gabor Deak, 1 Clemens Vass, 2 Jutta Gamper,
Retina The Distribution of Leakage on Fluorescein Angiography in Diabetic Macular Edema: A New Approach to Its Etiology Bilal Haj Najeeb, 1 Christian Simader, 1 Gabor Deak, 1 Clemens Vass, 2 Jutta Gamper,
Combined treatment for Coats disease: retinal laser photocoagulation combined with intravitreal bevacizumab injection was effective in two cases
 Kodama et al. BMC Ophthalmology 2014, 14:36 CASE REPORT Open Access Combined treatment for Coats disease: retinal laser photocoagulation combined with intravitreal bevacizumab injection was effective in
Kodama et al. BMC Ophthalmology 2014, 14:36 CASE REPORT Open Access Combined treatment for Coats disease: retinal laser photocoagulation combined with intravitreal bevacizumab injection was effective in
Disease-Specific Fluorescein Angiography
 Ruth E. Picchiottino, CRA Disease-Specific Fluorescein Angiography 15 Disease-Specific Fluorescein Angiography Recommendations for tailoring retinal fluorescein angiography to diabetic retinopathy, macular
Ruth E. Picchiottino, CRA Disease-Specific Fluorescein Angiography 15 Disease-Specific Fluorescein Angiography Recommendations for tailoring retinal fluorescein angiography to diabetic retinopathy, macular
ATLAS OF OCT. Retinal Anatomy in Health & Pathology by Neal A. Adams, MD. Provided to you by:
 ATLAS OF OCT Retinal Anatomy in Health & Pathology by Neal A. Adams, MD Provided to you by: Atlas of OCT The OCT Atlas is written by Neal A. Adams, MD, and produced by Heidelberg Engineering, Inc. to help
ATLAS OF OCT Retinal Anatomy in Health & Pathology by Neal A. Adams, MD Provided to you by: Atlas of OCT The OCT Atlas is written by Neal A. Adams, MD, and produced by Heidelberg Engineering, Inc. to help
Guidelines for the Management of Diabetic Retinopathy for the Internist
 Visual Disorder Guidelines for the Management of Diabetic Retinopathy for the Internist JMAJ 45(1): 1 7, 2002 Sadao HORI Professor, Department of Ophthalmology, Tokyo Women s Medical University Abstract:
Visual Disorder Guidelines for the Management of Diabetic Retinopathy for the Internist JMAJ 45(1): 1 7, 2002 Sadao HORI Professor, Department of Ophthalmology, Tokyo Women s Medical University Abstract:
Macular Morphology and Visual Acuity in the Comparison of Age-related Macular Degeneration Treatments Trials
 Macular Morphology and Visual Acuity in the Comparison of Age-related Macular Degeneration Treatments Trials Glenn J. Jaffe, MD, 1 Daniel F. Martin, MD, 2 Cynthia A. Toth, MD, 1 Ebenezer Daniel, MPH, PhD,
Macular Morphology and Visual Acuity in the Comparison of Age-related Macular Degeneration Treatments Trials Glenn J. Jaffe, MD, 1 Daniel F. Martin, MD, 2 Cynthia A. Toth, MD, 1 Ebenezer Daniel, MPH, PhD,
IN NICU OCT UTILIZES A CONCEPT KNOWN AS INTERFEROMETRY APPLICATIONS FOR OCT THE PRIMARY USE IN THE EYE - RETINA
 2016 25 YEARS OF OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY IN NICU Marcin Stopa, MD, PhD, FEBO Department of Ophthalmology, Chair of Ophthalmology and Optometry. Poznan University of Medical
2016 25 YEARS OF OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY IN NICU Marcin Stopa, MD, PhD, FEBO Department of Ophthalmology, Chair of Ophthalmology and Optometry. Poznan University of Medical
Ji Soo Shin, Young Hoon Lee. Department of Ophthalmology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2017;31(6):497-507 https://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.0108 Original Article Changes in Macular Retinal Layers and Peripapillary Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2017;31(6):497-507 https://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.0108 Original Article Changes in Macular Retinal Layers and Peripapillary Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness
 measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
Citation BioMed Research International, 2015, v. 2015, article no Creative Commons: Attribution 3.0 Hong Kong License
 Title Relationship between Outer Retinal Layers Thickness and Visual Acuity in Diabetic Macular Edema Author(s) Wong, RLM; Lee, JWY; Yau, GSK; Wong, IYH Citation BioMed Research International, 2015, v.
Title Relationship between Outer Retinal Layers Thickness and Visual Acuity in Diabetic Macular Edema Author(s) Wong, RLM; Lee, JWY; Yau, GSK; Wong, IYH Citation BioMed Research International, 2015, v.
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong. Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong
 Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong Co-Investigators Prof. David Wong Prof. Sarah McGhee Dr. Wico
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening in Hong Kong Dr. Rita Gangwani M.S, FRCS (Ophth), FCOphth(HK), FHKAM Eye Institute, The University of Hong Kong Co-Investigators Prof. David Wong Prof. Sarah McGhee Dr. Wico
