Pathophysiology of Experimental Glomerulonephritis in Rats
|
|
|
- Christian McCarthy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pthophysiology of Experimentl Glomerulonephritis in Rts MARJORIE E. M. ALLISON, CuRTIs B. WILSON, nd CARL W. GOrrSCHALK, with the technicl ssistnce of SARAH K. DAVIS From the Deprtment of Medicine, University of North Crolin School of Medicine, Chpel Hill, North Crolin nd the Deprtment of Experimentl Pthology, Scripps Clinic nd Reserch Foundtion, L Joll, Cliforni 9237 A B S T R A C T Micropuncture, clernce, immunofluorescence nd light microscopy techniques were used to study kidney structure nd single nephron function in rts with utologous immune complex nephritis (AICN), membrnous glomerulonephritis developing over 5 to 2 mo, in the more cute nd prolifertive glomerulr bsement membrne (GBM) nephritis nd in controls. Both models re known to hve clinicl counterprts in humn disese. Kidney functionl bnormlities correlted with the degree of rchitecturl derngement. In both AICN nd nti-gbm nephritis filtrtion frction fell in direct proportion to the fll in glomerulr filtrtion rte (GFR), renl plsm flow being unchnged. Frctionl electrolyte excretion incresed s the GFR fell. Despite mrked heterogeneity of single nephron filtrtion rte (SNGFR) (AICN, 5-93 nl/min; nti-gbm, -5 nl/min) nd of proximl tubulr hydrosttic pressure (4-48 mm Hg), ech nephron showed lmost complete glomerulotubulr blnce, bsolute rebsorption to the lte proximl convolution vrying directly with filtrtion rte. In ddition SNGFR could be relted both to proximl intrtubulr hydrosttic pressure nd to clculted glomerulr cpillry pressure (Pg), being lowest in those nephrons with the highest intrtubulr pressure. Nephrons with very high filtrtion rtes did not pprently rech filtrtion equilibrium. Men SNGFR ws significntly lower in the nti-gbm group, while clculted Pg ws the sme in both. This probbly reflects the cute nd diffuse involvement of the nti- GBM lesion with different filtrtion chrcteristics from Dr. Allison ws Creer Investigtor Fellow, Americn Hert Assocition. Her present ddress is the Renl Unit, Glsgow Royl Infirmry, Glsgow, Scotlnd. Dr. Gottschlk is Creer Investigtor, Americn Hert Assocition. Received for publiction 22 June 1973 nd in revised form 8 October the more chronic AICN disese. Tubulr dmge ws more mrked in AICN, nd extrction of p-minohippurte ws reduced in this group. INTRODUCTION Since the clssicl description by Richrd Bright in 1827 of the clinicl effects of chronic renl disese multitude of detiled studies hve been mde of whole kidney function in such ptients (1-5). The pinstking microdissection studies of Oliver (6) hve shown tht such kidneys re " heterogeneous collection of vrious nd disprte orgns, the bnorml nephrons of chronic renl disese" (7). Impressive overll functionl renl dpttion ccompnies these mrked structurl chnges (8-11 ). Informtion on the function of individul structurlly ltered nephrons, however, is sprse nd pprently contrdictory (12-17) Ẇe hve used micropuncture, clernce, immunofluorescence nd light microscopy techniques to study kidney structure nd single nephron function in rts with two forms of immunologiclly induced glomerulonephritis. Firstly, utologous immune complex or Heymnn's nephritis (AICN) 1 (18, 19) ws chosen s model resembling humn membrnous glomerulonephritis. 1Abbrevitions used in this pper: ADH, ntidiuretic hormone; AICN, utologous immune complex nephritis; nti- GBM, ntiglomerulr bsement membrne; BUN, blood ure nitrogen; C, clernce; CFA, complete Freund's djuvnt; E, extrction; EFP, effective filtrtion pressure; FF, filtrtion frction; GBM, glomerulr bsement membrne; GFR, glomerulr filtrtion rte; PAH, p-minohippurte; PAS, periodic cid-schiff; PBS,.1 M phosphtebuffered.15 M NCl, ph 7.; Pg, glomerulr cpillry hydrosttic pressure; RPF, renl plsm flow; RTA, renl tubulr ntigen; SNGRF, single nephron glomerulr filtrtion rte; TBM, tubulr bsement membrne. The Journl of Clinicl Investigtion Volume 53 My
2 Secondly, ntiglomerulr bsement membrne (Anti- GBM) nephritis (2) ws studied s more cute, prolifertive model of humn glomerulr injury. METHODS AICN. 5 1 g mle Wistr rts (Reserch Animls Inc., Brddock, P.) were given rer foot pd injections totlling 12.5 mg of prtilly purified rt renl tubulr ntigen (RTA) in.25 ml complete Freund's djuvnt (CFA) contining 2.5 mg of Mycobcterium butyricum (Difco Lbortories, Detroit, Mich.). Intrperitonel injections (18) were not used becuse we wished to void grnulomtous peritonitis with subsequent micropuncture difficulties. RTA ws prepred by slight modifiction of tht described by Edgington, Glssock, nd Dixon (21). A suspension of Wistr nd Sprgue Dwley rt renl cortex (Pel-Freez Biologicls, Inc., Rogers, Ark.) ws prepred by pssing corticl frgments through 15 mesh stinless steel screen. Bsement membrne nd cellulr frgments were removed by low speed centrifugtion (15 g). The supernte ws then centrifuged t 78, g for 3 min nd the resultnt sediment wshed two times in PBS (.1 M phosphte buffered,.15 M NCl, ph 7.) nd lyophilized. In 15 rts second dose of 12.5 mg of RTA in CFA ws given intrdermlly 51 dys (five rts), 93 dys (three rts), nd 187 dys (seven rts) lter. In 28 rts, two dditionl 12.5-mg doses were given 51 nd 16 dys (19 rts) nd 93 nd 187 dys (nine rts) fter the initil injection. 24-h urinry protein excretion rtes were used to follow the onset of overt glomerulonephritis. Determintion of urine protein concentrtion ws mde by using either the Biuret technique or slicylsulphonic cid. Clernce nd micropuncture studies were done 5-2 mo fter the first injection. Anti-GBM glomerulonephritis. Rbbit nti-rt GBM ntibody ws induced by biweekly injections (foot pds nd intrdermlly) of 1-3 mg of rt GBM (22) in CFA. Antibody production ws quntitted by the pired-lbel isotope technique (23, 24). Mle Wistr rts (1-15 g) were given ml (five rts) nd ml (five rts) rbbit nti-rt GBM ntibody contining 113 nd 13,ug of kidney fixing ntibody per ml, respectively, nd were studied 1-38 dys lter. Intensified glomerulr lesions were produced by enhncing the recipients immune response to the heterologous nti- GBM ntibody by dministering 1.8 mg of rbbit IgG in incomplete Freund's djuvnt 3 dys before receipt of nti- GBM ntibody (25). Controls. 17 mle Wistr rts, of similr ge to the AICN nimls, were used s controls. In eight tht were 4-wk old, CFA lone ws injected intrdermlly in the proportions given bove, nd injections were repeted 93 dys lter in four of them. The remining nine rts received no injections. Clernce nd micropuncture studies. Clernce nd, in most instnces, micropuncture studies were mde in 24 rts with AICN, in ll 1 rts with nti-gbm nephritis, nd in 12 control rts. All were deprived of food but not of wter overnight before study, nd were nesthetized by intrperitonel injection of sodium pentobrbitl, 5 mg/kg body wt. The rts were prepred for micropuncture s previously described (26), isotonic sline,.5%o of body wt, being given during surgery to replce fluid losses. Both ureters were cnnulted with PE 1 polyethylene tubing. Blood pressure ws recorded continuously from the crotid rtery by using Stthm P23Db trnsducer (Stthm Instruments, Inc., Oxnrd, Clif.) nd Beckmn Dynogrph recorder (Beckmn Instruments, Inc., Fullerton, Clif.). All rts were studied during hydropeni, modified Ringer's solution (NCl,.85 g/1 ml; KCl,.42 g/1 ml; CCl2,.25 g/1 ml; NHCO3,.2 g/1 ml) being given i.v. t the rte of.4 ml/1 g body wt/h, together with d-ldosterone (Cib Phrmceuticl Compny, Summit, N. J.), vsopressin (Prke, Dvis & Co., Detroit, Mich), ['H]methoxy inulin (Interntionl Chemicl nd Nucler Corportion, Burbnk, Clif.) nd in most instnces ['C]p-minohippurte (PAH) (New Englnd Nucler Corp., Boston, Mss.). In those rts in which intrrenl pressure mesurements were mde priming dose of 3 Ag of d-ldosterone, 6,uCi ['H] inulin, nd 2 GCi [CIC]PAH ws followed by infusion of d-ldosterone, 2.4,ug/h; ntidiuretic hormone (ADH),.3,g/h; ['C] PAH, 5-7,Ci/h; nd ['H]inulin t rte of 2,Ci/1 g body wt/h. When proximl tubulr F/P inulin levels were to be mesured this infusion ws incresed to 4-8,uCi [3H]- inulin/1 g body wt/h. Three consecutive timed urine collections, ech lsting pproximtely 45- min, were mde from both kidneys. Blood (<3,ul) ws obtined from the crotid rtery nd (L) renl vein t pproximtely 45-min intervls for mesurement of hemtocrit, ['H] inulin, nd ["C] PAH levels. Clernces were determined s previously described (27). Glomerulr filtrtion rte (GFR) ws clculted seprtely for the left nd right kidneys, renl plsm flow (RPF) for the left kidney only. In those rts not given ["C] PAH the left RPF ws clculted s follows: RPF = V(U-R) where V = urine flow rte nd U, A, nd R= inulin concentrtion in urine, rteril plsm, nd renl venous plsm, respectively. In those rts given ["C]PAH the RPF ws clculted s CPAH EPAH where C = clernce nd E = extrction. Two groups of micropuncture experiments were crried out In the first series (six AICN, five nti-gbm, nd three control rts) the kidney ws bthed with minerl oil heted to 36+1'C. Shrpened siliconized glss pipettes, externl tip dimeter 4-6,sm, filled with isotonic sline colored with lissmine green (K nd K Lbortories, Inc., Plinview, N. Y.) were used to puncture superficil proximl convolution, nd the free flow hydrosttic pressure ws mesured by using the "Lndis" technique (26). Simultneously the lst loop of the proximl tubule visible on the surfce of the kidney ws identified by following the pssge of the lissmine green colored sline. This lst convolution ws lter punctured with shrpened siliconized glss pipette, externl tip dimeter Am, nd minerl oil block, 4-5 tubulr dimeters in length ws injected. Tubulr fluid ws then collected, controlled suction being used to keep the oil block in plce nd the tubulr dimeter constnt if this ws t ll possible. The smple ws pulled into the stright prt of the collection pipette by using toluene, the length nd dimeter mesured by using n eyepiece micrometer, nd the volume clculted. The Pthophysiology of Experimentl Glomerulonephritis in Rts 143
3 whole smple ws then dischrged into counting fluid. The following clcultions were mde: SNGFR = F/P inulin X tubulr flow rte in nl/min Percent rebsorption to the lte proximl convolution ( F/P inulin) X Absolute rebsorption = frctionl rebsorption X SNGFR nl/min In the second group (15 AICN, five nti-gbm, nd seven control rts) the kidney ws bthed with isotonic sline heted to 36±1C in order to llow the use of n electronic servo-nulling device for mesurement of hydrosttic pressure s previously described (28). Shrpened, siliconized glss pipettes, externl tip dimeter 3-5 Aum, filled with 2 M NCl were used to mesure hydrosttic pressure in proximl tubules during free flow, in the lrge efferent rterioles or strs, in intermedite vessels, which re lrge dimeter stright vessels nd which often rise from strs, nd in the lrger peritubulr cpillries. In n ttempt to estimte glomerulr cpillry hydrosttic pressure (Pg), the stop flow hydrosttic pressure ws lso mesured (28). The Pg ws estimted s the sum of the stop flow pressure nd the fferent oncotic pressure. In four rts with AICN nd in five rts with nti-gbm disese timed collections of proximl tubulr fluid from esily ccessible proximl convolutions for clcultion of SNGFR were mde immeditely before mesuring the stop flow pressure in the sme nephron. Indvertent contmintion of the tubulr fluid smple with superficil sline is not importnt in this instnce, since we re interested only in filtrtion rte. Hence we hve SNGFR, free flow hydrosttic pressure, nd n estimte of glomerulr hydrosttic pressure in individul superficil nephrons. Efferent rteriolr protein concentrtion in these nephrons ws clculted by using the whole kidney filtrtion frction (FF) (29). Efferent rteriolr protein concentrtion Afferent rteriolr protein concentrtion 1 - whole kidney FF Arteril plsm nd serum protein concentrtions were mesured before, during, nd t the end of ech experiment by n dpttion of the Lowry technique (3) using rt serum protein stndrds. These vlues were used to clculte oncotic pressure (7r) by the Lndis nd Pppenheimer (31) eqution: 7r = 2.1P +.16P2+.9P3 In order to vlidte this eqution for rt serum the oncotic pressure ws lso mesured directly in smples from six AICN nd three control rts (G. Nvr, University of Mississippi Medicl Center, Jckson, Miss.). The clculted men vlue of 18.9±1.41 is not significntly different from tht obtined directly, 2.2±3.3 mm Hg. The fferent nd efferent effective filtrtion pressures (EFP) were clculted s follows: Afferent EFP = Pg - (ITP + ir) Efferent EFP = Pg - (ITP + 7re) where 7r is the fferent oncotic pressure, 7re the clculted efferent oncotic pressure, nd ITP the intrtubulr pressure. 144 M. E. M. Allison, C. B. Wilson, nd C. W. Gottschlk These equtions ssume tht the oncotic pressure of the tubulr fluid is so smll s to be insignificnt, sitution which is true for the norml undmged nephron (32). We hve not mesured the concentrtion of protein in the glomerulr filtrte of the disesed nephron in this study, but Lewy nd Pesco (33) nd Oken, Cotes, nd Mende (34) using nimls with minonucleoside dmged kidneys nd proteinuri hve reported n lbumin concentrtion of only mg/1 ml in the glomerulr filtrte, nd it seems unlikely tht tubulr fluid protein levels in our study were high enough to exert significnt oncotic pressure. Blood ws tken terminlly for estimtion of blood ure nitrogen (BUN), mesured on Technicon utonlyzer (Technicon Corportion, Ardsley, N. Y.) by modifiction of the crbmido-dicetyl frction s pplied to the determintion of ure nitrogen nd cholesterol. Urine nd plsm electrolytes were mesured on n IL direct reding flme photometer (Instrumenttion Lbortories Inc., Wtertown, Mss.). Frctionl electrolyte excretion ws clculted without use of the Donnn Fctor. Microinjection studies. In order to exmine the permebility of the nephrons to inulin seprte series of microinjection experiments (35) were performed in nine rts with nti-gbm nephritis nd in two with AICN, prepred s previously described. For microinjection studies they were infused with 5% mnnitol in isotonic sline t 3.1 ml/h nd PE 5 ctheters were plced in both ureters. A mesured volume ( nl) of [8H]inulin (Interntionl Chemicl nd Nucler Corportion) colored with nigrosin, ws injected slowly over 3-6 s into superficil proximl tubules, 8-min urine collections being mde from ech kidney for min therefter into liquid scintilltion counting fluid (PCS, Amershm/Serle, Arlington Heights, Ill.). The totl percentge of the mesured injectte recovered from ech kidney ws clculted. The hydrosttic pressure in ech nephron injected ws mesured by using servo-nulling pressure pprtus. Immunopthologic studies.- At the end of ech experiment, both kidneys from ech niml were weighed. The kidneys were bisected long the nterior-posterior xis so s to ssure dequte ssessment of the entire thickness of the cortex, medull, nd ppill. One hlf of the right kidney ws snp frozen (liquid nitrogen or dry ice-lcohol bth) to wit immunofluorescent studies. Cryostt sections from this kidney were overlyed with fluorescein isothiocynte-conjugted IgG frctions of ntiserum monospecific in immunodiffusion for rt IgG nd C3, for direct immunofluorescent study (36). The reminder of the kidney tissue ws fixed in Bouin's solution nd postfixed in 5%o ethyl lcohol. Sgittl sections of the entire bisected surfce were obtined fter prffin embedding. The sections were stined with hemtoxylin-eosin nd periodic cid-schiff (PAS) for light microscopy. All sections were studied s unknowns. The pttern of immunorectnt (IgG, C3) deposition ws noted nd semiquntitted by using -4 scle (37). The histologic sections were grded to 4+ for the following ctegories: glomerulr hypercellulrity, necrosis, sclerosis; GBM thickening; overll rchitecturl derngement; interstitil infiltrtion; tubulr trophy, luminl cells, csts; nd thickening of tubulr bsement membrne (TBM). The number of polymorphonucler leukocytes per glomerulus ws recorded s well s the percentge of glomeruli exhibiting crescent formtion. Vessels were grded similrly (4+) for degree of endothelil prolifertion, dupliction of the elstic nd medil hypertrophy. Perivsculr infiltrtion
4 ws generlly included in the generl ctegory of interstitil infiltrtion. Since the micropunctures studies of necessity produced dt from superficil nephrons, creful ttention ws given ny possible vrition in immunopthologic chnges throughout the thickness of the cortex. RESULTS Generl chrcteristics We ttempted to induce AICN in totl of 5 mle Wistr rts ged pproximtely 1 mo. 48/5 rts (96%) hd histologicl evidence of glomerulonephritis when exmined 5-2 mo fter 1-3 intrdertul injections of RTA; 39 of 46 studied (85%) hd proteinuri exceeding 1 mg per dy. Only 2/17 of similrly ged control rts (13%) ultimtely developed proteinuri greter thn 1 mg per dy, when ged 17 mo s previously described (37). None of the control rts given CFA lone (8/17) developed proteinuri greter thn 6 mg per dy, lthough this hs been reported s cusing significnt proteinuri in previous studies (38, 39). Fig. 1 shows the vrying rtes of development of proteinuri in 19 rts with AICN in which this ws followed serilly nd in controls. There ws no reltionship between the totl number of ntigen injections given nd the subsequent degree of proteinuri, the gretest nd most rpidly developing proteinuri (885 mg per dy) being found in rt given single injection of RTA. All ten rts given nti-gbm ntibody nd subsequently studied by micropuncture developed significnt proteinuri, so tht when studied in the utologous phse 1-38 dys lter (men, 2 dys) ll hd proteinuri in excess of 1 mg per dy. Tble I compres the serum protein, BUN, nd cholesterol concentrtions ccording to the finl degree of proteinuri mesured in the AICN, nti-gbm, nd control rts. There ws no evidence of hypoproteinemi in the rts with AICN, even in those with proteinuri greter thn 4 mg per dy. In the more cute nti- GBM nephritis group, however, men serum protein FIGURE 1 Development of proteinuri fter one to three injections of RTA in 19 rts with AICN nd in control rts of similr ge. levels were significntly reduced below tht of the controls. The generl chrcteristics of tht portion of the totl group in which detiled clernce nd micropuncture studies were lter crried out (24 rts with AICN, mo fter initil injections; 1 rts with nti- GBM nephritis, 1-38 dys fter injection; nd 12 control nimls) were similr. Dily protein excretion rtes vried from 15 to 885 mg (men 357 mg ±238 SD) in AICN nd from 137 to 57 mg (men 356 mg ±145 SD) in nti-gbm nephritis. 24 h urine volume ws significntly incresed in AICN rts (controls 12.7 ml +4. SD, AICN 23.7 ml +-11 SD, P <.1). Men plsm protein concentrtion ws significntly reduced, however, only in the nti-gbm nephritis group (controls 5.68 g/1 ml +.36 SD, Anti-GBM SD, P <.2). None were edemtous, lthough men hemtocrits were significntly reduced (controls 48.6%±3.5 SD, AICN 44.4%+5.4 SD, P <.5; Anti-GBM 41.2%±5.6 SD, P <.1). All hd hypercholesterolemi. Men BUN concentrtion ws significntly higher thn in control rts only in nti-gbm nephritis (controls mg/1 ml, men TABLE I Reltionship of Proteinuri to Serum B UN, Cholesterol, nd Protein Concentrtions in Control nd Glomerulonephritic Rts AICN Controls Anti-GBM Age 6-21 mo Age 5-17 mo Age 2-3 mo Serum Serum Serum Proteinuri x BUN Cholesterol protein n BUN Cholesterol protein n BUN Cholesterol protein mg/dy mg/zoo ml mg/1 ml g/1 ml mg/1oo ml mg/1oo ml g/1 ml mg/foo ml mg/1 ml g/1 ml ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ±.86 m = number of rts. All figures re men4sd. Pthophysiology of Experimentl Glomerulonephritis in Rts 145
5 Woo 8 _.4 * AICN * ANTI-GBM CONTROL.3 K A A A PROTEINURIA mg/dy 6 _ 4 _ * I * *- - FILTRATION.2 FRACTION * OU C C A. 2 _ C * *:* ' * :.1 _ OS U * _* * q II& r U 6 r 5 - BUN mg/ 1 ml 3 F 5 F * ** 1 5 * 5.4 A me. * A AA 8 GFR ml/min/g kidney wt A 1.2 A % FILTERED LOAD POTASSIUM EXCRETED 4 2 F 1 * * A L--t I. A I I.4.8 GFR ml/min/g kidney wt 1.2 FIGuRE 2 Reltionship between the filtrtion rte of the left kidney nd the degree of proteinuri, BUN concentrtion, FF, nd frctionl potssium excretion in 24 rts with AICN, 1 rts with nti-gbm nephritis, nd in 12 controls... * A *A 29.8 mg/1 ml +1. SD; nti-gbm mg/1 ml, men 44.3 mg/1 ml ±13.4 SD, P<.1). Both experimentl groups hd significntly incresed men systemic blood pressure (controls: 16 mm Hg ±11 SD, AICN: 118 mm Hg ±14 SD, P<.2; nti-gbm: 126 mm Hg ±14, P <.1). Clernce studies Clernce dt re given for the (L) kidney, there being no sttisticlly significnt difference between the (R) nd (L) kidney GFR. Fig. 2 illustrtes the reltionship between kidney filtrtion rte nd the degree of proteinuri, BUN concentrtion, FF, nd potssium excretion. Quntittive proteinuri incresed s the GFR fell (AICN: r=.636, n = 24, P <.1; nti-gbm: r =.869, n = 1, P <.1). Filtrtion. frction fell in direct proportion to the fll in GFR, since the RPF, s mesured by the clernce (CPAH) nd extrction of PAH (EPAHI) or inulin, did not decrese. Frctionl excretion of sodium (not illustrted) nd potssium incresed, so tht when the GFR ws reduced to pproximtely 1% of control over.3% of the filtered lod of sodium nd 5% of the filtered lod of potssium ws excreted. Tble II compres the clernce dt in nimls with proteinuri in excess of 2 mg per dy with controls. GFR nd RPF hve been expressed in ml/min, ml/min/g kidney wt nd ml/min/1 g body wt since kidney nd body wt vried significntly between the nti-gbm rts nd the others (Tble III). Men GFR ws significntly reduced in both experimentl models irrespective of the method of presenttion. RPF, however, ws significntly incresed in the group with nti-gbm nephritis when clculted /1 g body wt. 146 M. E. M. Allison, C. B. Wilson, nd C. W. Gottschlk
6 TABLE I I Clernce Dt (Left Kidney) in Control Rts nd in Glomerulonephritic Rts with Proteinuri Greter thn 2 mg per Dy (Men+SD) AICN Control Anti-GBM n = 17 P n = 12 P n = 9 GFR ml/min 1.4±-.4 < < ml/min/g kidney wt.4-±.16 < <.1.43±-.24 ml/min/1 g body wt.16-±.6 <.1.3±-.8 < RPF ml/min 9.18±-4.1 NS NS 7.42-±1.8 ml/min/g kidney wt 3.39±-1.29 NS 3.94±-1.31 NS ml/min/1 g body wt 1.37-±.55 NS 1.23-±.41 < ±.74 FF <.1.27-±.5 <.1.11±-.5 CPAH* NS 6.56±42.17 NS 6.1±-1.5 ml/min/g kidney wt < ±.89 NS 3.88±-1.29 ml/min/1 g body wt.78±-.22 NS < CIn/CPAH.18±-.3 <.1.29±-i.7 <.1.14±-.6 EPAH.71-±.14 <.5.86±L-.6 NS.83-±.8 U/P inulin 194±-131 <.1 624±-133 <.1 225±-142 Sodium excretion Aeq/min.21±--.13 NS.18±-.24 NS.19±-.15 % Filtered lod N excreted.14±4.9 <.5.6±-.7 <.1.19±-.9 Potssium excretion ueq/min NS 1.1±-.9 NS.83±-.46 % Filtered lod K excreted < ±-2.2 < ± 18.3 P, comprison of control nd AICN or nti-gbm dt by unpired Student t test. * CPAH ws mesured in eight AICN, six control, nd seven nti-gbm rts. Men EPAH ws within norml limits (4) in nti-gbm nephritis while this ws significntly reduced in the AICN rts. Electrolyte excretion rtes nd serum electrolyte concentrtions were not significntly different in the three groups. Micropuncture studies Severely dmged kidneys from rts with either AICN or nti-gbm nephritis were enlrged, ple, nd grnulr. Microscopic exmintion of the corticl surfce of the living kidney showed mrked heterogeneity of single nephron structure, the severity of which correlted generlly with the severity of disese s judged by the whole kidney filtrtion rte. Ptches of lrge, dilted, pler proximl tubules lternted with smller res of smll trophic-looking nephrons. White specks sometimes visible on the kidney surfce were found to be tubulr csts in dilted nephrons. Smll whitish TABLE III Body Wt nd Left Kidney Wt in Glomerulonephritic Rts nd in Control Wistr Rts of Similr Age AICN AICN Proteinuri Proteinuri Control 2 mg/dy 2 mg/dy Control* Anti-GBM n = 12 n = 7 P n = 17 P n = 2 n 2 1O P Body wt NS 656 NS NS g ± ±92 ±46 ±51 Left kidney wt NS.46 < <.1 g/1 g body wt ±.4 ±.4 ±.5 ±.5 ±.17 * Dt obtined from Dr. R. Krmp. Pthophysiology of Experimentl Glomerulonephritis in Rts 147
7 A ICN 6r RATS 1 RATS 4 % 3 TUBULES 2 CONTFROL I - A _1 r--l r---n r--in r---1--a ANTI-GBM NEPHRITIS 6 5[ 41 7 RATS 1 RATS % 3 TUBULESI ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ r.t PROXIMAL INTRATUBULAR PRESSURE mm Hg SNGFR ni/min FIGURE 3 Distribution of proximl intrtubulr hydrosttic pressure nd SNGFR mesurements in 15 rts with AICN, eight rts with nti-gbm nephritis, nd in controls. pieces of mteril could t times be seen pssing down tubules or dhering to the wlls. The postglomerulr circultion ppered less plentiful, with fewer "strs" nd smller peritubulr cpillries. Less severely dmged kidneys, in nimls with proteinuri less thn 2 mg per dy, showed only occsionl ptches of dilted nephrons nd norml looking post-glomerulr vsculture. Impressive functionl heterogeneity ws reveled by single nephron studies of filtrtion rte nd proximl tubulr hydrosttic pressure in both AICN nd nti- GBM rts with proteinuri over 2 mg per dy (Fig. 3). Thus in rts with AICN, SNGFR vried overll from to lmost 1 nl/min. More importntly this pttern of functionl heterogeneity ws lso found in individul kidneys. Although the men SNGFR ws significntly lower in the smller rts with nti-gbm disese individul filtrtion rtes gin vried gretly, 148 M. E. M. Allison, C. B. Wilson, nd C. W. rnging from to 5 nl/min. These findings re to be compred with the much smller sctter found in control rts, in which over 5% of ll nephrons hd filtrtion rtes between 32 nd 4 nl/min. Similrly proximl tubulr hydrosttic pressure vried from 4 to 44 mm Hg in AICN nd from 4 to 48 mm Hg in nti-gbm disese. In generl those nephrons with high intrtubulr pressures ppered lrge nd dilted on microscopic exmintion of the living kidney. In contrst, in control rts, ll pressures recorded were between 8 nd 16 mm Hg. We hve previously shown (27) tht proximl intrtubulr pressure is the sme in norml rts weighing g nd g, similr to the weights of the nti-gbm nd AICN rts, respectively. Despite this mrked heterogeneity of single nephron filtrtion rte bsolute rebsorption to the lte proximl convolution ws in direct proportion to the filtr- Gottschlk
8 tion rte, so tht frctionl rebsorption ws uniform (Fig. 4). Thus in both forms of glomerulonephritis individul nephrons demonstrted lmost complete proximl glomerulotubulr blnce t ll levels of SNGFR. Simultneous mesurements of SNGFR nd whole kidney filtrtion rte were mde in 52 nephrons in 11 nimls with AICN, in 5 nephrons of 1 rts with nti-gbm nephritis, nd in 15 nephrons of four control rts (Tble IV). It is interesting to note tht, lthough the men whole kidney glomerulr filtrtion rte ws significntly reduced below control levels in the nimls 3-21 lop y-2.83o.42x r *.855,Pc.1 *:; AICN 8 RATS TABLE IV Comprison of Left Kidney Filtrtion Rte nd men SNGFRI Kidney in Control nd Glomerulonephritic Rts Whole kidney Group GFR SNGFR mi/mn nm/min AICN Men SD i 12.6 P <.5 NS Control Men SD i6. Anti-GBM Men SD :4-8.4 P <.1 <.1 P, comprison of GFR nd SNGFR dt by unpired Student t test. ABSOLUTE REABSORPTION TO LATE PROXIMAL CONVOLUTION nllnin _ y x r * _ U ANTI -GBM NEPHRITIS 8 RATS SNGFR nl/min 8 1 FIGuRE 4 Correltion between bsolute rebsorptive rte to the lte proximl convolution nd SNGFR in superficil nephrons of kidneys of rts with AICN nd nti- GBM disese. with AICN, men SNGFR ws not different from controls. This could be due either to smpling error in the selection of remining nephrons for puncture in the sick rts, with tendency to choose the more norml looking ones with the higher filtrtion rtes, or to fll in the whole kidney filtrtion rte in AICN resulting from the loss of substntil numbers of nephrons. We do not think tht there ws mjor smpling error, since there ws good correltion between the men SNGFR per rt nd the whole kidney filtrtion rte (Fig. 5A). For ny given level of whole kidney filtrtion rte, however, wide rnge of SNGFR ws found (Fig. 5B). Thus while the overll number of surviving nephrons ws reduced those remining were heterogeneous in function. In nti-gbm nephritis whole kidney nd single nephron filtrtion rtes were reduced to similr degree, probbly due to the cuteness nd uniformity of the injury, suggesting tht loss of more dmged nephrons hd not yet occurred. There ws no significnt difference between the men vlues found for SNGFR, F/P inulin, nd bsolute re- Pthophysiology of Experimentl Glomerulonephritis in Rts 149
9 8o F 6 1 SNGFR ni /min 4 SNGFR nl/min 2 _ 1oo 8 F 6 _ 4 F 2 * AICN * ANTI-GBM A CONTROL * : U 1. t LA A A 8 Om. * * * LA * *U *.. A * -- - **ge us*e Ou *-. I 1. GFR ml/min *A^ ±.4 SD). Animls with nti-gbm disese hd significntly lower SNGFR nd bsolute rebsorptive rtes thn either AICN or controls (SNGFR = 17.7 ml/ min +8.6 SD, F/P inulin = 1.81±.2 SD), finding not entirely explined by their smller size since previous studies hve shown the norml hydropenic Wistr rt kidney to hve superficil SNGFR vlues of nl/min. Men F/P inulin vlues were not sig- A nificntly different, probbly due to the smll number of observtions involved in the control group. Tble V gives the men vlues, clculted per rt, for the hydrosttic pressure in the crotid rtery, efferent rteriole, lrge peritubulr cpillry, nd proximl tubule in rts with AICN nd in controls, together with the crotid pressure nd free flow proximl tubulr pressure in rts with nti-gbm nephritis. The ltter hd significntly higher systemic nd proximl tubulr pressures thn the other two groups. No sttisticlly significnt difference in efferent rteriolr or peritubulr cpillry pressures were seen in the control nd AICN rts, lthough it should be noted tht ll A men postglomerulr hydrosttic pressures were lower in the nimls with AICN. This tendency ws even more mrked in individul severely dmged kidneys, where the lowest peritubulr cpillry pressure recorded B ws 4.5 mm Hg (lowest control 7.5 mm Hg). Men vlues for estimted glomerulr oncotic nd hydrosttic pressures, clculted per rt, in 11 nimls 2. with AICN, five with nti-gbm nephritis nd in five control rts re given in Tble VI. Animls with nti- FIGURE 5 (A) Reltionship of men SNGFRLper rt to whole kidney filtrtion rte in 11 rts with AI( CN, 1 with GBM disese hd significntly lower fferent nd efnti-gbm nephritis nd in controls. (B) Rel; tionship of ferent oncotic pressures, but significntly higher cl- filtrtion culted Pg thn the controls. Filtrtion equilibrium individul SNGFR mesurements to whole kidnley rte in the sme rts. pprently ws not reched in ny of the three groups, this being especilly mrked in the rts with nti-gbm bsorptive rte to the lte proximl convohition in the nephritis, men estimted efferent EFP being 25.1 mm AICN nd control rts (control SNGFR =41.7 nl/ Hg. min -7.2 SD, F/P inulin = 2.71+±.8 S;'D; AICN In n ttempt to determine the fctors regulting SNGFR = 47.8 nl/min ±18.5 SD, F/P iinulin = 2.4 single nephron filtrtion rte we exmined the reltion- TABLE V Hydrosttic Pressure (mm Hg) in Crotid Artery, Proximl Tubules, Efferent Arterioles, nd Peritubulr Cpillries in Control nd Glomerulonephritic Rts (Men±SD) AICN P Control P Anti-GBM Crotid rtery 119±11.3 (15)* <.2 16±11.5 (9) < ±6.8 (7) Efferent rteriole (11) < ±1. (9) Lrge peritubulr cpillry 7.6±2.8 (2) NS 1.3±2. (5) Proximl tubule 13.1±5.4 (15) NS 12.1±1.8 (9) < ±2.9 (7) P, comprison of mens by unpired Student t test. * Figures in brckets refer to number of rts M. E. M. Allison, C. B. Wilson, nd C. W. Gottschlk *
10 ship between ech nephron's mesured filtrtion rte nd intrtubulr hydrosttic pressure, clculted Pg nd fferent nd efferent EFP for tht nephron. Fig. 6 shows the reltionship between SNGFR nd free flow hydrosttic pressure. In nimls with AICN nephrons with higher intrtubulr pressures hd low filtrtion rtes. However in most instnces no reltionship ws observed between SNGFR nd pressure, fivefold difference in SNGFR being found in nephrons of similr intrtubulr pressure. In the nti-gbm group threefold difference in intrtubulr pressure ws not ssocited with ny difference in filtrtion rte. A closer reltionship ws seen between single nephron filtrtion rte nd clculted Pg (Fig. 7), the reltionship being sttisticlly significnt, however, only for the rts with nti-gbm disese. It is interesting to note tht lthough the men clculted cpillry pressure ws lmost the sme in the two groups (55.3 mm Hg in AICN nd 58. mm Hg in nti-gbm) men SNGFR ws significntly greter in the AICN group (37. nl/min in AICN, 21.6 nl/min in nti- GBM) suggesting, perhps, difference in glomerulr membrne filtrtion chrcteristics in the two disese sttes, s in permebility nd/or re. SNGFR ws lso closely relted to clculted fferent nd efferent EFP (Fig. 7). Filtrtion equilibrium ws pprently pproched only in those nephrons with very low filtrtion rtes nd the higher free flow pressures. Nephrons with higher filtrtion rtes did not pper to rech equilibrium, estimted efferent EFP being s high s mm Hg. Microinjection studies Structurl nd functionl chnges in the kidneys of the nimls used for microinjection studies were similr to those previously described. Proteinuri rnged from 133 to 55 mg per dy (men 35 mg+123 SD) nd BUN from 14 to 116 mg/1 ml (men 44.8 mg/ 1 ml ±36.4 SD). Two nimls developed gross scites nd edem with serum protein concentrtions of 1.9 nd 1.8 mg/1 ml. SNGFR nl/min SNGFR n l/min * - * 9 * -u *u * 9 Al CN 1 RATS % ANTI-GBM NEPHRITIS 8 RATS EU. U. * U.. * 5 1 ' PROXIMAL INTRATUBULAR PRESSURE rnmhg A B 35 4 FIGURE 6 Reltionship of SNGFR to proximl intrtubulr free flow hydrosttic pressure in (A) rts with AICN nd in (B) rts with nti-gbm disese. No evidence of significnt lekge of inulin ws found in those nephrons which ppered norml in vivo nd in which the intrtubulr hydrosttic pressure ws less thn 19 mm Hg. In 26 microinjected proximl tubules (2 nti-gbm, 6 AICN) hydrosttic pressure verged 13. mm Hg +2.7 SD nd inulin recovery from the injected kidneys verged 98.2%+9.1 SD. The ltter is not different from the verge vlue of SD found in seven control tubules. There ws no * m. TABLE VI Clculted Glomerulr Cpillry Hydrosttic nd Oncotic Pressures (mm Hg) in Control nd Glomerulonephritic Rts (Men±LSD) AICN Control Anti-GBM n = 11 P n =5 P n =5 Afferent oncotic pressure 16.1A1.4 NS 15.4±.96 < ±.67 FF < <.1.124±.1 Efferent oncotic pressure 2.1±1.84 < ±2.2 < ±.93 Pg 55.9±7.4 < ±-3.3 < ±9.4 Afferent EFP 24.7±8.5 NS 19.9±3.1 NS 27.6±1.9 Efferent EFP 2.3±8.7 < ±3. NS Pthophysiology of Experimentl Glomerulonephritis in Rts 1411
11 8 A 1 - C 8 _ A ICtN woo r so F E 6 SNGFR ni/min /s - 1r l ANTI-GBM NEPHRITIS B 1F D 8 _ moo r F 6 SNGFR ni/min 4 * Pg mmhg(sfp+.o) AFFERENT EFPmmHg (SFP-ITP) EFFERENT &FP mmhg (Pq-[e + ITP]) FIGuRE 7 (A nd B) Correltion between clculted Pg nd SNGFR in AICN (A, r =.362, P>.5) nd in nti-gbm nephritis (B, r =.556, P <.1). (C nd D) Correltion between clculted fferent EFP nd SNGFR in AICN (C, r.754, P <.1) nd nti- GBM nephritis (D, = r =.453, P <.1). (E nd F) Correltion between clculted efferent EFP nd SNGFR in AICN (E, r =.759, P <.1) nd in nti-gbm nephritis (F, r =.414, P <.5). ITP, intrtubulr pressure; vr, fferent oncotic pressure; 7re, efferent oncotic pressure; SFP, stop flow pressure. sttisticlly significnt excretion of inulin by the right kidney. Urine flow rte verged 13 A4/min, nd the injectte ppered in erly distl tubules.8-4 min fter proximl injection, except in one nephron where the flow rte ws very slow, 25 min elpsing before the injectte reched the erly distl segment. The eight microinjected nti-gbm nephrons with higher intrtubulr pressures (men 24.4 mm Hg ±6.2 SD) ppered dilted nd ll hd very slow flow rtes. In most the injectte remined visible in the superficil proximl tubule for 1-2 h. In three no significnt rdioctivity ws recovered from either kidney. In the other five, however, 19.8%±4.3 nd 19.6±7.2 of the microinjected inulin ws recovered in the urine from the left nd right kidneys, respectively. Although we re unble to exclude the possibility of significnt trnstubulr lekge of inulin in this circumstnce, the lekge my well hve occurred, in view of the high intrtubulr pressure nd very slow tubulr flow rte, t lest in prt, t the site of puncture nd thus hve no physiologicl significnce. Immunopthologic studies Histologiclly, the renl lesions induced either by utologous immune complex deposits or by nti-gbm ntibodies were quite chrcteristic s were the immunofluorescent findings. Vrying severities of involvement were present in both models so tht ttempts to correlte physiologic nd immunopthologic vritions were possible. AICN. The glomerulr lesions in the AICN rts developed slowly nd were typified by uniform thickening of the glomerulr bsement membrne (GBM) with only miniml glomerulr hypercellulrity nd increse in polymorphonucler leukocytes chrcteristic of membrnous glomerulonephritis. Prolifertion of Bowmn's cpsule (crescent formtion) nd glomerulr sclerosis were infrequent. The severity of glomerulr involvement ws quite uniform throughout the cortex of ech individul kidney (Fig. 8). Although the GBM ws obviously thickened in ll rts studied in this group, the degree of thickening ws extremely difficult to estimte even semi-quntittively from PAS-stined sections nd correlted poorly with the severity of either proteinuri (r =.15, n = 23) or fll in GFR (r =.245, n = 23) (Tble VII). These glomerulr lesions were ccompnied by chnges in the renl tubules nd interstitium which led to different degrees of derngement in overll renl rchitecture. This ltter prmeter, which, in ddition 1412 M. E. M. Allison, C. B. Wilson, nd C. W. Gottschlk
12 FIGUE 8 The uniformity of membrnous thickening of the GBM is shown t different levels in the cortex from rt with AICN. Virtully no prolifertion ccompnied the thickening of the GBM s seen in glomeruli ner the rcute vessels (A) in the mid-cortex (B) or in the superficil cortex (C). PAS stin. A-C, X 22. to the glomerulr pthology, ws comprised of vrying degrees of tubulr trophy nd dilttion, interstitil mononucler cell infiltrtion, tubulr csts, nd the presence of intrluminl cells confining PAS-positive mteril either singly or in multinucleted form (Fig. 9), correlted directly with the fll in GFR (r =.747, n = 23, P <.1) s well s with proteinuri (r =.711, n= 23, P <.1) (Tble VII). Similr correltions could be mde when ech component ws nlyzed seprtely. Surprisingly, for the degree of overll renl dmge, only miniml medil thickening of smll rterioles ws observed in the most hypertensive rts. Grnulr deposits of IgG nd C3 were present diffusely long the GBM (Fig. 1) in the 23 AICN rts vilble from the 24 undergoing clernce studies. This deposition correlted poorly with mounts of proteinuri nd only in generl wy with GBM thickening ssessed by light microscopy. The deposits were most cler in rts with less structurl glomerulr dmge. As glomerulr sclerosis developed, the deposition lessened in both intensity nd extent. IgG eluted (36) from these kidneys rected with ntigens present in the brush border of norml proximl renl tubules when tested by indirect immunofluorescence on norml kidney sections. Of dditionl interest, evidence from the immunofluorescent studies suggested n immune nture for some of the renl tubulr lesions observed in these nimls. IgG nd C3 were found deposited long the brush border of 8/23 of the more hevily proteinuric AICN rts studied (Fig. 11). This observtion would suggest tht ntibodies specific for rt RTA (resident in the brush border) of the proximl convoluted tubule were being filtered nd bound in vivo. This finding correlted well with the presence of chunks of IgG nd C3 within the tubulr lumens, unrelted to tubulr csts, nd the presence of cells contining PAS-positive mteril djcent to the brush borders nd free within the tubulr lumens (Fig. 9). In ddition to brush border nd occsionl intrluminl deposits of IgG nd C3 (unrelted to lbumin-contining csts) grnulr deposits of these immunorectnts were observed in Pthophysiology of Experimentl Glomerulonephritis in Rts 1413
13 the tubulr cytoplsm ner the TBM. This suggests tht immune complexes either filtered into or formed in the tubulr urine were being tken up by the tubulr cells or tht ntibody hd gined ccess to the cells to combine with intrcellulr ntigens. Similr observtions hve been mde in Sprgue Dwley rts with AICN ugmented by pertussis (41). No evidence of nti-tbm ntibodies ws found by immunofluorescence in this study. Anti-GBM glomerulonephritis. In rts with experimentl nti-gbm glomerulonephritis, the degree of GBM irregulrity, crescent formtion, nd rchitecturl derngement ssessed by light microscopy correlted well with the fll in GFR (Tble VII). The glomerulr pthology typified by incresed cellulrity, polymorphonucler leukocyte infiltrtion, prolifertion of Bowmn's cpsule (crescent formtion), nd irregulrly thickened GBM ws ccompnied by corresponding degrees of generl rchitecturl derngement including tubulr trophy nd interstitil cellulr infiltrtion. Glomerulr ltertions were quite uniform throughout the cortex (Fig. 12), possibly with slightly greter hypercellulrity in the more superficil glomeruli. Virtully no vsculr chnges were encountered, lthough the nimls hd significntly incresed men systemic blood pressure. Immunofluorescent studies reveled similr intensities of liner IgG nd C3 deposits in the nine kidneys vilble for study. In kidneys with more GBM dmge, the liner IgG nd C3 deposits were incresingly irregulr (Fig. 1) corresponding to the loss of the norml smooth, ribbon-like structure of the GBM. The pttern of deposition, however, ws lwys esily distinguishble from the grnulr immune complex deposits typifying the AICN rts. Virtully no IgG deposits were noted outside the glomeruli. Controls. Seven of the control rts hd miniml glomerulr hypercellulrity, irregulrity of the GBM, nd rchitecturl derngement. These rts lso hd mild proteinuri nd slight decreses in renl function. The histologicl nd functionl bnormlities correlted with dvncing ge but not with the dministrtion of CFA. Spontneous glomerulonephritis with dvncing ge hs been described in Wistr rts (42). The remining control rts were free of histologic or functionl bnormlities. Smll mounts of IgG nd/or C3 in segmentl grnulr pttern were found in glomeruli of the rts with histologic glomerulr bnormlities suggesting the presence of low-grde spontneous immune complex glomerulonephritis s hs been reported in mny niml species. No ttempts were mde to identify the ntigenic portion of the presumed immune complex in these nimls. Similr IgG deposits were found in two dditionl rts tht remined histologiclly nd functionlly norml. TABLE VI I Reltionship of Whole Kidney Function to Chnges Seen on Light Microscopy of Right Kidney in Control nd Glomerulonephritic Rts* Glomerulr GBM Architecturl U,/P Group hypercellulrity thickening Crescents derngementl GFR Inulin Proteinuri % glomeruli ml/min g mg/24 h kidney Wt AICN n = n = Rre Control n = o n= Anti-GBM n = n = All figures re mens. * Animls in ech group hve been subdivided on the bsis of GFR. Men glomerulr hypercellulrity, GBM thickening, nd :wiritecturl derngement were clculted from individul nimls grded on -4+ scle (see Methods) where 1 =.25, trce =.5, 1 = 1, etc. X Includes gross glomerulr chnges, tubulr trophy nd dilttion, interstitil mononucler cell infiltrtion, csts, nd intrluminl cells. Dt from four rts. Dt from nine rts. Irregulrity nd frying M. E. M. Allison, C. B. Wilson, nd C. W. Gottschlk
14 r 11pirwr4k!T ;,-- AM m -s e FIGURE 9 Accumultions of cells were noted in the lumens of tubules in the AICN rts. The PAS-positive brush border re of the tubulr cells ppered to be stripped from segments of the lining epithelium nd phgocytized by mononucler cells which tended to become multinucleted. Mononucler cell infiltrtes were lso noted djcent to some renl tubules (D). Hemtoxylin-eosin stin (A) nd PAS stin (B-D) A nd B, X 22; C nd D, X 35. DISCUSSION This study ws designed to mesure single nephron function in histologiclly different experimentl glomerulonephritides morphologiclly resembling humn glomerulonephritis. Exmples of the two mjor immunopthogenic mechnisms of glomerulonephritis were chosen. Firstly, AICN ws used s model of immune complex (nonglomerulr ntigen-ntibody) -induced glomerulr injury, mechnism which ppers to be responsible for pproximtely 8% of humn glomerulonephritis (43). The RTA-ntibody system which typifies AICN hs recently been identified in three ptients with membrnous glomerulonephritis from Jpn (44). Secondly, nti-gbm ntibodies were used to induce glomerulr injury typified by n cute onset (within hours) of diffuse, prolifertive glomerulr lesion similr to the infrequently found (pproximtely 5%) nti-gbm ntibody-induced glomerulonephritis in mn (36). It should be noted tht, lthough AICN hs the morphology of membrnous glomerulonephritis, immune complex glomerulonephritis cn ssume virtully ny type of glomerulonephritic histologic ltertion, pprently influenced more by the intensity nd tempo of the immune rection nd the subsequent host response thn by the inciting event. Both ntibody-induced forms of glomerulr injury utilize common medition pthwys, nmely complement nd polymorphonucler leukocytes, so tht observtions mde in this study deling with diffuse prolifertive glomerulonephritis induced by nti-gbm ntibodies might lso pply to similr morphologic lesions induced by immune complexes. Mesurement of whole kidney function in our glomerulonephritic rt models reveled chnges very similr to those previously reported in extensive clinicl studies of renl function in humn glomerulonephritis. Thus whole kidney GFR nd FF fell, RPF, determined by the clernce nd extrction of PAH, remining unchnged in the more chronic AICN disese or incresing slightly in the cute, prolifertive nti-gbm Pthophysiology of Experimentl Glomerulonephritis in Rts 1415
15 FIGURE 1 Grnulr deposits of immunoglobulin were observed in the glomeruli of the AICN rts. The fine grnulrity ws present diffusely long the GBM where little thickening (A) or fter extreme thickening (B) hd occurred. Liner deposits of immunoglobulin typified the glomerulonephritis introduced by heterologous nti-gbm ntibodies. (C) The pttern ws very smooth nd continuous in kidneys with well preserved glomerulr rchitecture. (D) With greter degrees of glomerulr dmge, the immunoglobulin pttern becme incresingly irregulr with pprent frying of the GBM. Fluorescein isothiocynte-conjugted nti-rt IgG. X 25. nephritis. Such observtions hve been frequently reported in cute, subcute, nd erly chronic glomerulonephritis in humns (1, 2, 45). Absolute electrolyte excretion rtes were not significntly different from controls, but this ws chieved by n increse in the frctionl electrolyte excretion s the GFR fell, necessry dptive response previously documented in ptient studies (3, 1, 46). Only two of our rts developed edem or scites, lthough this hs been reported s often ccompnying experimentl immune complex nd nti-gbm disese in rts (18, 47). The most striking physiologicl feture in both models of experimentl glomerulonephritis ws the finding tht ech nephron studied showed lmost complete glomerulotubulr blnce, despite mrked heterogeneity of SNGFR, proximl free flow intrtubulr hydrosttic pressure, nd clculted glomerulr cpillry pressure. It might be rgued tht the heterogeneity of SNGFR could, in prt, be due to vrible loss of inulin from structurlly dmged nephrons. From our own nd other observtions, however, we do not believe tht inulin lekge contributed substntilly to our findings. No evidence of inulin lekge ws found in nephrons with intrtubulr hydrosttic pressure less thn 19 mm Hg, despite mrked heterogeneity of SNGFR in such nephrons (Fig. 6). A significnt loss of inulin ws seen in only five nephrons with high intrtubulr pressure nd very slow flow rtes, three other nephrons with high pressure nd slow flow showing no evidence of lekge fter proximl microinjection. It is techniclly very difficult to exclude the possibility of smll but significnt lekge of tubulr fluid onto the surfce of the kidney round the site of injection in nephrons with high intrtubulr pressure which might hve cused, t lest in prt, the clculted inulin lekge M. E. M. Allison, C. B. Wilson, nd C. W. Gottschlk
16 FIGURE 11 Hevy deposits of IgG (A) nd C3 (B) were observed in the re of the brush border (rrows) of foci or "islnds" of renl tubulr cells in some of the AICN rts with more extensive rchitecturl bnormlities. Fluorescein isothiocynte-conjugted nti-rt IgG (A) nd C3 (B). X 25. Moreover, even if the clculted inulin lekge resulted from the trnstubulr movement of microinjected inulin, it does not necessrily follow tht similr frction of inulin filtered in tht nephron would lek. Frctionl inulin lekge is function of contct time nd SNGFR would hve to be vnishingly smll, less thn.3 nl/min, for tubulr trnsit time to be s long, circ 1 h, s the observed contct time in these dilted nd obstructed high pressure nephrons studied by microinjection. Accepting the verge lekge observed in the five obstructed tubules nd ssuming tubulr dimeter twice norml, one cn clculte tht less thn 3% of filtered inulin would lek t n SNGFR of 5 nl/min nd less thn 1.5% t n SNGFR of 1 nl/min. In ddition, if trnstubulr inulin lekge t high intrtubulr pressure were significnt fctor one might expect to find correltion between SNGFR, lte proximl F/P inulin level, nd intrtubulr hydrosttic pressure, high pressure nephrons hving lower SNGFR nd F/P inulin vlues. No such reltionship ws observed in nti-gbm nephritis, lthough in AICN rts men SNGFR in high pressure nephrons ws significntly lower (26. nl/min ±22.4 SD) thn tht found in more norml pressure nephrons (48.6 nl/min SD, P <.5). Lte proximl F/P inulin rtios, however, were not significntly different. In recent study of experimentl glomerulonephritis produced by rbbit nti-rt kidney serum, model presumbly quite similr to our nti-gbm rts, Roch, Mrcondes, nd Mlnic (17) found tht SNGFR ws not different when clculted from proximl or distl smples nd concluded tht there ws no evidence of inulin loss from the nephritic tubules. Lstly, microinjection studies in niml models with severe tubulr dmge hve reveled no evidence of inulin lekge 3-4 wk fter the simultneous injection of potssium dichromte nd mercuric chloride (16) or 144 h fter minonucleoside dministrtion (48). In ny event only very smll number of the micropuncture collections here reported were from tubules with high pressure nd very slow flow rtes nd hence possibly suspect in regrds to trnstubulr inulin lekge. Exclusion of these few dt in no wy controverts our conclusions bout nephron heterogeneity. Structurl nd functionl heterogeneity mong nephrons in the chroniclly disesed kidney ws first described by Oliver, Bloom, nd McDowell in 1941 (12) using specific histologicl stining techniques in spontneous chronic cnine glomerulonephritis. More recently micropuncture studies in rts with chronic pyelonephritis (13), hevy metl poisoning (16), nd nti-gbm nephritis (17) hve confirmed this mrked functionl heterogeneity. From the detiled single nephron observtions reported in the present study, together with those previously described, we believe tht there cn now be no doubt tht single nephrons in the experimentl chroniclly disesed kidney show mrked heterogeneity both in function nd structure. Ech superficil nephron studied, however, demonstrted lmost the sme glomerulotubulr blnce, bsolute rebsorption to the lte proximl convolution Pthophysiology of Experimentl Glomerulonephritis in Rts 1417
17 FIGURE 12 The uniformity of glomerulr prolifertive chnges re seen t vrious levels through the cortex in rt with experimentl nti-gbm glomerulonephritis. A glomerulus djcent to n rcute rtery nd vein (A), three glomeruli in the mid-cortex (B), nd two glomeruli in the superficil cortex (C) re seen. Hemtoxylin-eosin stin. A-C, X 22. vrying in direct proportion to the nephron filtrtion rte t ll levels from 5 to 93 nl/min. Similr mintennce of single nephron glomerulotubulr blnce despite mrked heterogeneity of filtrtion rtes hs lso been found by Roch et l. (17) in rts with nti- GBM nephritis, except in those nephrons with low filtrtion rtes (25 nl/min) when F/P inulin levels were unusully high. Importnt implictions concerning the mechnism (s) regulting glomerulotubulr blnce in the disesed nephron follow from our observtions, since such mechnism(s) must obviously work on single nephron bsis. There hs recently been gret interest in the role of the so clled peritubulr physicl fctors (i.e., hydrosttic nd oncotic pressure in the tubulr environment) in controlling tubulr rebsorption. Experimentl vrition of peritubulr cpillry hydrosttic or oncotic forces cn pprently lter proximl rebsorptive rtes (49, 5). For these fctors to be importnt in the setting of glomerulotubulr blnce in single nephrons 1418 M. E. M. Allison, C. B. Wilson, nd C. W. Gottschlk in our heterogeneous disesed kidneys it must first be shown tht ech proximl tubule is surrounded only by peritubulr cpillries from its own efferent rteriole, since the oncotic pressure in ech efferent rteriole will initilly be dependent on tht nephron's FF. There re comprtively few detiled ntomicl studies of vsculr-tubulr reltionships. Some evidence of close reltionship between ech efferent rteriole nd its own proximl tubule hs been reported recently by Steinhusen, Eisenbch, nd Glske (51) in the rt kidney nd by Beeuwkes (52) in the superficil c'ortex of the dog kidney. Both gree however tht there re mny free communictions between the peritubulr cpillries. On direct microscopic exmintion of the living kidney these pper to form freely nstomotic network. Also, it might be supposed tht nephrons with high intrtubulr pressures nd low filtrtion rtes should hve djcent peritubulr cpillries with similr high hydrosttic pressures, ssuming tht this force could influence trnsport cross the proximl tubule. Inter-
18 stitil fluid pressure remins unknown, nd since it is presumbly the grdient between this comprtment nd the peritubulr cpillry on the one hnd nd the proximl tubule on the other which would determine rebsorptive rtes, bsolute peritubulr cpillry pressures my not be of importnce. Although significntly incresed vribility in efferent rteriole nd peritubulr cpillry hydrosttic pressures ws found in the disesed kidney compred with controls, the highest vlues found did not exceed norml limits. Indeed, we were impressed by the finding of postglomerulr vessels with very low hydrosttic pressures. This observtion ws predicted by Brdley (53) becuse of the mrked obstructive disese of the glomerulr vessels found in glomerulonephritis. We therefore find it difficult to ccept tht the rebsorptive rte per nephron is influenced solely by tht nephron's peritubulr "physicl" environment in the bsence of evidence tht it is specific for individul nephrons. Secondly, it hs been suggested tht SNGFR might be regulted within individul nephrons by tubulrvsculr feedbck system involving the renin-ngiotensin system, such tht n increse in sodium delivery to the mcul dens might result in incresed renin production nd hence ngiotensin relese which in turn would so lter fferent or efferent vsculr resistnce to result in fll in GFR (54-56). Recent studies hve shown tht GFR clculted from distl tubulr fluid collections re consistently lower thn those clculted from proximl tubulr fluid collections in tht nephron, when distl tubulr sodium concentrtion re presumbly very low due to the proximl oil block (57, 58). Others hve filed to substntite these findings (59). All our tubulr fluid collections were mde in proximl tubules fter plcing n oil block of t lest 4-5 tubule dimeters in length distl to the collection pipette. Despite complete blocking of the tubulr fluid flow beyond this point, however, mrked heterogeneity of single nephron filtrtion rte with mintennce of glomerulotubulr blnce ws found. One of the erliest nd simplest proposls mde to explin the phenomenon of glomerulotubulr blnce ws tht some fctor(s) relted to proximl intrluminl lod determined tubulr bsorption, completely independent of peritubulr environment (6, 61). In vitro nd in vivo single nephron microperfusion studies, however, suggested tht glomerulotubulr blnce ws not n intrinsic property of the proximl tubule, since experimentl ltertion of proximl tubule perfusion rtes with rtificil perfustes did not result in ny significnt chnge in bsolute rebsorptive rtes (62, 63). It is lso now ccepted tht intrtubulr volume (64) is not the primry determinnt of proximl rebsorptive rte (65, 66). Recently, however, Brtoli, Conger, nd Erley (59), using prtil proximl tubule collection technique, hve found tht fll in the delivery rte of norml filtrte long the proximl tubule is ssocited with decrese in the bsolute rebsorptive rte. They suggest tht this might be due either to vrition in the mixing of unstirred diffusion lyers or to chnge in the vilbility of some ultrfilterble plsm constituent with chnge in intrluminl flow rtes. Similrly in our studies it is possible tht some fctor or fctors relted to proximl intrluminl flow or lod ws responsible for pproprite lignment of bsolute rebsorptive rte in individul nephrons with widely differing filtrtion rtes. Mrked heterogeneity of SNGFR ws found in both models of glomerulonephritis, but more especilly in the AICN group. Also men SNGFR ws significntly lower in the cute prolifertive nti-gbm ntibodyinduced glomerulonephritis thn in the AICN rts with chronic membrnous glomerulonephritis. No "supernephrons" with very high filtrtion rte ws found in nti-gbm nephritis, finding similr to tht of Roch et l. (17). This probbly reflects the cute diffuse involvement of glomeruli in this model. In contrst, the much greter heterogeneity of SNGFR in AICN rts probbly ws relted to the chronicity of the experimentl model llowing dequte time for dpttion of nephron function. The primry fctors influencing individul GFR, i.e. fferent nd efferent EFP, RPF, permebility nd surfce re of glomerulr cpillry bed vilble for filtrtion, re complex nd re presumbly ltered in the disesed glomerulus. Recently, dvnces in micropuncture technology nd finding of ccessible superficil glomeruli in mutnt strin of Wistr rts hs enbled direct study of these fctors (32, 67). It hs been shown tht in the norml superficil rt glomerulus Pg re lower thn previously supposed nd tht, filtrtion equilibrium is generlly reched under vriety of experimentl conditions (68). We thve ttempted to study these fctors indirectly in the disesed nephron. Firstly, no consistent reltionship ws found between SNGFR nd proximl intrtubulr hydrosttic pressure in either AICN or nti-gbm nephritis, lthough tendency towrd lower SNGFR in nephrons with higher intrtubulr pressures ws seen in AICN rts. These ltter nephrons ppered dilted nd were presumbly blocked downstrem by fibrosis or proteinceous debris nd csts. Secondly, we found positive correltion between clculted Pg nd SNGFR, but this ws sttisticlly significnt only for nimls with nti-gbm disese. Pg ws clculted s the sum of the directly determined Pthophysiology of Experimentl Glomerulonephritis in Rts 1419
19 stop flow pressure nd the fferent oncotic pressure (69, 28). This clcultion involves three importnt ssumptions, none of which is s yet directly proven. First, glomerulr filtrtion must be completely stopped so tht the protein concentrtion in the systemic circultion cn be tken s the efferent nteriolr protein concentrtion. Secondly, ny possible effect of reduction of flow t the mcul dens fter blockge of the nephron with oil is negligible. Thirdly, pproprite ltertions in fferent/efferent rteriolr resistnce must hve occurred in order to ccommodte the incresed cpillry flow due to cesstion of filtrtion without chnge in glomerulr hydrosttic pressure. Tht the ltter cn occur under certin circumstnces hs been shown by Brenner, Troy, Dughrty, Deen, nd Robertson (68) when 1% increse in glomerulr cpillry plsm flow due to plsm volume expnsion resulted in chnge in directly mesured Pg of only 1.8 mm Hg. Vlues reported for stop flow pressures in hydropenic dult rts from different lbortories hve vried considerbly, from 26 to 29 mm Hg (17, 7) to 55 mm Hg (69), most vlues lying between 32 nd 4 mm Hg. In our studies the men vlue clculted for Pg from stop flow pressure mesurements in control rts ws 47.4 mm Hg, which is similr to thlt reported by Blntz, Isrelit, Rector, nd Seldin (67) obtined by using direct cpillry punctures in hydropenic "Munich" Wistr rts with superficil glomeruli (47.4 mm Hg), but slightly higher thn tht reported by Brenner, Troy, nd Dughrty (32) (44.4 mm Hg) in similr nimls. Clculted men Pg ws significntly higher in both AICN nd nti-gbm nephritic kidneys thn in controls, finding different thn tht of Roch et l. (17) who reported lower clculted men glomerulr cpillry pressure in rts with nti- GBM nephritis thn in control nimls. Mesurements mde by Roch et l. were t rndom points in the proximl tubule nd stop flow pressures re lower by, on verge, 7 mm Hg, when mesured in lte proximl rther thn erly proximl convolutions (28). Obviously direct mesurements of hydrosttic pressure in superficil disesed glomeruli re required. It is possible tht significnt fll in hydrosttic pressure occurs due to incresed resistnce in the dmged cpillry bed in experimentl glomerulonephritis. Furthermore, the hemodynmic chnges occurring in dmged glomerulr cpillry beds during stop flow re lso unknown nd my differ from tht seen under norml conditions. Thirdly, it seems sfe to ssume tht the filtrtion chrcteristics of the GBM my be ltered to different extents in the two histologiclly different models of glomerulr injury under study. Thus we found tht 142 M. E. M. Allison, C. B. Wilson, nd C. W. lthough the men clculted Pg ws similr in both AICN nd nti-gbm nephritis, men SNGFR ws significntly lower in those nimls with nti-gbm disese. This suggests decrese either in glomerulr permebility or in blood flow due to luminl encrochment in nti-gbm rts. Histologiclly the AICN rts hve uniformly thickened GBM nd lrge mounts of immune complex (IgG, C3) deposits in the bsence of n obvious cute phlogogenic response. By electron microscopy, these immune complex deposits pper s electron-dense msses under the fused epithelil cell foot processes, giving the GBM rther uniform thickened ppernce (71, 72). The dministrtion of nti- GBM ntibodies, on the other hnd, produced more cute prolifertive response with polymorphonucler leukocyte infiltrtion nd very erly (within hours) chnges in glomerulr permebility s mnifested by proteinuri. Indeed, gps hve been identified in the GBM by electron microscopy (73) nd frgments of the GBM hve been detected in the urine (74). Little is known bout the functionl chrcteristics of the remining somewht irregulr GBM; however, our observtions would suggest tht its usefulness s n ultrfilter is impired. Fourthly, in AICN nd nti-gbm disese there ws direct reltionship between SNGFR nd both fferent EFP, obtined by direct mesurement of stop flow pressure nd intrtubulr free flow pressure, nd clculted efferent EFP. Nephrons with high filtrtiorn rtes hd high fferent nd efferent EFP nd did not pprently rech filtrtion equilibrium. Only those with very low filtrtion rtes cme ner to equilibrium. In control rts, men efferent filtrtion pressure ws significntly lower thn in the disesed kidney, but filtrtion equilibrium did not pper to be reched. Before speculting on the significnce of these observtions it should be noted tht the clcultion of efferent EFP is dependent on estimtion of the efferent oncotic pressure which we obtined using the whole kidney FF nd the fferent protein concentrtion. Whole kidney FF in our control rt kidneys ws.22, lower thn tht generlly reported in hydropenic dult rts. Assuming tht the estimted Pg is correct, we clculte tht for these nimls to rech filtrtion equilibrium n FF of pproximtely.38 would be required. In the disesed rts whole kidney FF were much lower. FF of individul glomeruli were not mesured. If one ssumes firly constnt glomerulr cpillry plsm flow per nephron, then nephrons with high filtrtion rtes would hve significntly higher FF thn those with low SNGFR, perhps resulting in smller disequilibrium t the end of the glomerulr cpillry bed. More likely, however, both plsm flows nd FF in Gottschlk
20 individul glomeruli re vrible in the disesed kidney. Resolution of these problems obviously wits mesurements of single nephron FF in disesed glomeruli. Finlly, the possible contribution of immunologic tubulr dmge to derngement of single nephron function should be considered. Previous morphologic studies hve described tubulr bnormlities in AICN (4), nd tubulr bnormlities often considered secondry to glomerulr dmge re universl in dvncing experimentl nd humn glomerulonephritis. No clercut immunologic role hs been estblished for these lesions; however, certin observtions would suggest tht immune tubulr s well s glomerulr injury does occur in these diseses. Tubulr deposits of immunoglobulin nd complement hve been observed in experimentl nd humn renl disese (75-77). Humn nti- GBM nephritis frequently hs liner deposits of IgG in the TBM suggesting the presence of nti-tbm ntibodies s well. We hve in ddition observed the presence of nti-tbm ntibodies in renl llogrfts with specificity restricted to the TBM on elution studies (Wilson, unpublished observtions). Irregulr grnulr deposits of IgG nd C3 re commonly seen in renl tubules (often ssocited with the TBM) of ptients with immune complex glomerulonephritis, prticulrly when nering endstge (Wilson, unpublished observtions). The significnce of these deposits is s yet unknown. It is not surprising therefore tht immunopthologic tubulr bnormlities would be present in our experimentl models. The AICN rts hd evidence of IgG nd C3 deposits on the brush border s well s intrcellulrly ccompnied by pprent stripping of the PAS-positive brush border of the proximl tubules by cells within the tubulr lumen, suggesting immunopthologiclly induced tubulr injury. No direct immunofluorescent evidence of immune deposits ws found in the nti-gbm rts. These observtions correlted directly with the difference in PAH extrction observed in the two models in which only the. AICN rts hd significnt decrese in this monitor of tubulr function. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This study ws supported by grnt-in-id from the Americn Hert Assocition, by grnt HE-2334 from the Ntionl Institutes of Helth, by Public Helth Service Contrct PH nd by U. S. Public Helth Service grnt A Scripps Publiction Number 72. REFERENCES 1. Erle, D. P., Jr., J. V. Tggrt, nd J. A. Shnnon Glomerulonephritis. A survey of the functionl orgniztion of the kidney in vrious stges of diffuse glomerulonephritis. J. Clin. Invest. 23: Brdley, S. E., G. P. Brdley, C. J. Tyson, J. J. Curry, nd W. D. Blke Renl function in renl diseses. Am. J. Med. 9: Kleemn, C. R., R. Okun, nd R. J. Heller The renl regultion of sodium nd potssium in ptients with chronic renl filure (CRF) nd the effect of diuretics on the excretion of these ions. Ann. N. Y. Acd. Sci. 139: Brod, J Study of renl function in the differentil dignosis of kidney disese. Br. Med. J. 3: Lewy, J. E., L. Slins-Mdrigl, P. B. Herdson, C. L. Pirni, nd J. Metcoff Clinico-pthologic correltions in cute post streptococcl glomerulonephritis. Medicine (Bltimore). 5: Oliver, J Architecture of the kidney in chronic Bright's disese. Pul B. Hoeber Inc., New York Oliver, J When is the kidney not kidney? J. Urol. 63: Pltt, R Structurl nd functionl dpttion in renl dmge. Br. Med. J. 1: 1313 nd Pitts, R. F Physiology of the kidney nd body fluids. Yer Book Medicl Publishers, Chicgo. 1st edition. 1. Bricker, N. S., S. Klhr, H. Lubowitz, nd R. E. Rieselbch Renl function in chronic renl disese. Medicine (Bltimore). 44: Gottschlk, C. W Function of the chroniclly disesed kidney. The dptive nephron. Circ. Res. 11 Suppl. II: Oliver, J., F. Bloom, nd M. McDowell Structurl nd functionl trnsformtions in the tubulr epithelium of the dog's kidney in chronic Bright's disese nd their reltion to mechnisms of renl compenstion nd filure. J. Exp. Med. 73: Bnk, N., H. S. Aynedjin Individul nephron function in experimentl bilterl pyelonephritis. I. Glomerulr filtrtion rte nd proximl tubulr sodium, potssium nd wter rebsorption. J. Lb. Clin. Med. 68: Lubowitz, H., M. L. Purkerson, nd N. S. Bricker Investigtion of single nephrons in the chroniclly disesed (pyelonephritic) kidney of the rt using micropuncture techniques. Nephron. 3: Lubowitz, H., M. L. Purkerson, M. Sugit, nd N. S. Bricker GFR per nephron nd per kidney in chroniclly disesed (pyelonephritic) kidney of the rt. Am. J. Physiol. 217: Krmp, R., C. W. Gottschlk, J. Oliver, nd M. Mc- Dowell Micropuncture nd microdissection studies of dmged rt kidneys. Clin. Res. 18: Roch, A., M. Mrcondes, nd G. Mlnic Micropuncture study in rts with experimentl glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 3: Heymnn, W., D. B. Hckel, S., Hrwood, S. G. F. Wilson, nd J. L. P. Hunter Production of nephrotic syndrome in rts by Freund's djuvnts nd rt kidney suspensions. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med..1: Edgington, T. S., R. J. Glssock, nd F. J. Dixon Autologous immune-complex pthogenesis of experimentl llergic glomerulonephritis. Science (Wsh. D. C.). 155: Unnue, E. R., nd F. J. Dixon Experimentl glomerulonephritis: immunologicl events nd pthogenetic mechnisms. Adv. Immunol. 6: 1. Pthophysiology of Experimentl Glomerulonephritis in Rts 1421
21 21. Edgington, T. S., R. J. Glssock, nd F. J. Dixon Autologous immune complex nephritis induced with renl tubulr ntigen. I. Identifiction nd isoltion of the pthogenic ntigen. J. Exp. Med. 127: Krkower, C. A., nd S. A. Greenspon Locliztion of the nephrotoxic ntigen within the isolted renl glomerulus. Arch. Pthol. 51: Pressmn, D., E. D. Dy, nd M. Blu The use of pired lbeling in the determintions of tumorloclizing ntibodies. Cncer Res. 17: Unnue, E. R., nd F. J. Dixon Experimentl glomerulonephritis. V. Studies on the interction of nephrotoxic ntibodies with tissues of the rt. J. Exp. Med. 121: Unnue, E. R., nd F. J. Dixon Experimentl glomerulonephritis. VI. The utologous phse of nephrotoxic serum nephritis. J. Exp. Med. 121: Gottschlk, C. W., nd M. Mylle Micropuncture study of pressures in proximl tubules nd peritubulr cpillries of the rt kidney nd their reltion to ureterl nd venous pressures. Am. J. Physiol. 185: Allison, M. E. M., E. M. Liphm, W. E. Lssiter, nd C. W. Gottschlk The cutely reduced kidney. Kidney Int. 3: Allison, M. E. M., E. M. Liphm, nd C. W. Gottschlk Hydrosttic pressure in the rt kidney. Am. J. Physiol. 223: Dughrty, T. M., I. F. Ueki, D. P. Nichols, nd B. M. Brenner Comprtive renl effects of isoncotic nd colloid-free volume expnsion in the rt. Am. J. Physiol. 222: Brenner, B. M., K. H. Flchuk, R. I. Keimowitz, nd R. W. Berliner The reltionship between peritubulr cpillry protein concentrtion nd fluid rebsorption by the renl proximl tubule. J. Clin. Invest. 48: 15, Lndis, E. M., nd J. R. Pppenheimer Exchnge of substnces through cpillry wlls. Hndb. Physiol. Sect. 2 (Circultion). 2: Brenner, B. M., J. L. Troy, nd T. M. Dughrty The dynmics of glomerulr ultrfiltrtion in the rt. J. Clin. Invest. 5: Lewy, J. E., nd A. Pesco Micropuncture study of lbumin trnsfer in minonucleoside nephrosis in the rt. Peditr. Res. 7: Oken, D. E., S. C. Cotes, nd C. W. Mende Micropuncture study of tubulr trnsport of lbumin in rts with minonucleoside nephrosis. Kidney Int. 1: Gottschlk, C. W., F. Morel, nd M. Mylle Trcer microinjection studies of renl tubulr permebility. Am. J. Physiol. 29: Wilson, C. B., nd F. J. Dixon Anti-glomerulr bsement membrne ntibody-induced glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 3: Wilson, C. B., nd F. J. Dixon Antigen quntittion in experimentl immune complex glomerulonephritis. I. Acute serum sickness. J. Immunol. 15: Perry, S. W Proteinuri in the Wistr rt. J. Pthol. Bcteriol. 89: Hess, E. V., C. T. Ashworth, nd M. Ziff Nephrosis in the rt induced by rt kidney extrcts. Ann. N. Y. Acd. Sci. 124: Cortney, M. A., M. Mylle, W. E. Lssiter, nd C. W. Gottschlk Renl tubulr trnsport of wter, 1422 M. E. M. Allison, C. B. Wilson, nd C. W. Gottschlk solute nd PAH in rts loded with isotonic sline. Am. J. Physiol. 29: Klssen, J., T. Sugiski, F. Milgrom, nd R. T. Mc- Cluskey. '1971. Studies on multiple renl lesions in Heymn's nephritis. Lb. Invest. 25: Berg, B. N Longevity studies in rts. II. Pthology of geing rts. In Pthology of Lbortory Rts nd Mice. E. Cotchin nd F. J. C. Roe, editors. F. A. Dvis Co., Phildelphi Wilson, C. B., nd F. J. Dixon Immunologic mechnisms in the pthogenesis of glomerulonephritis. In Controversy in Internl Medicine II. F. J. Ingelfinger, M. Finlnd, A. S. Relmn, nd R. H. Ebert, editors. W. B. Sunders Co., Phildelphi Nruse, T., K. Kitmur, Y. Miykw, nd S. Shibt Deposition of renl tubulr epithelil ntigen long the glomerulr cpillry wlls of ptients with membrnous glomerulonephritis. J. Immunol. 11: Brun, C., T. Hilden, nd F. Rschou Physiology of disesed kidney: determintion of glomerulr filtrtion, renl blood flow nd mximl tubulr excretory cpcity nd their contribution to the understnding of function of disesed kidney. Act Med. Scnd. Suppl. 234: Allison, M. E. M., nd A. C. Kennedy Diuretics in chronic renl disese. A study of high dosge frusemide. Clin. Sci. (Oxf.). 41: Heymnn, W., nd H. Z. Lund Nephrotic syndrome in rts. Peditrics. 7: Lewy, J. E., nd A. Pesce Microinjection study of inulin nd lbumin trnsfer in minonucleoside nephrosis in the rt. Am. Soc. Nephrology Lewy, J. E., nd E. E. Windhger Peritubulr control of proximl tubulr fluid rebsorption in the rt. Am. J. Physiol. 214: Brenner, B. M., nd J. L. Troy Postglomerulr vsculr protein concentrtion: evidence for cusl role in governing fluid rebsorption nd glomerulotubulr blnce by the renl proximl tubule. J. Clin. Invest. 5: Steinhusen, M., G. M. Eisenbch, nd R. Glske Countercurrent system in the renl cortex of rts. Science (Wsh. D. C.). 167: Beeuwkes, R., III Efferent vsculr ptterns nd erly vsculr-tubulr reltions in the dog kidney. Am. J. Physiol. 221: Brdley, S. E Medicl progress. Modern concepts of renl structure nd function in chronic Bright's disese. N. Engl. J. Med. 231: Thuru, K., nd J. Schnermnn Die Ntriumkonzentrtion n den Mcul dens-zellen ls regulierender Fktor fur ds Glomerulumfiltrt (Mikropunktionsversuche). Klin. Wochenschr. 43: Schnermnn, J., A. E. G. Persson, nd B. Agerup Tubuloglomerulr feedbck. Nonliner reltion between glomerulr hydrosttic pressure nd loop of Henle perfusion rte. J. Clin. Invest. 52: Schnermnn, J., F. S. Wright, J. M. Dvis, W. V. Stckelberg, nd G. Grill Regultion of superficil nephron filtrtion rte by tubulo-glomerulr feedbck. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 318: Schnermnn, J., J. M. Dvis, P. Wunderlich, D. Z. Levine, nd M. Horster Technicl problems in the micropuncture determintion of nephron filtrtion
THE KIDNEY AND THE CONCEPT OF CLEARANCE*
 THE KIDNEY AND THE CONCEPT OF CLEARANCE* I. The Antomy of the Mmmlin Kidney A. Gross ntomy: 1. The outer region of the kidney = the CORTEX 2. Inner region = the MEDULLA 3. The re where ll of the urine
THE KIDNEY AND THE CONCEPT OF CLEARANCE* I. The Antomy of the Mmmlin Kidney A. Gross ntomy: 1. The outer region of the kidney = the CORTEX 2. Inner region = the MEDULLA 3. The re where ll of the urine
Comparison of three simple methods for the
 J. clin. Pth. (1967), 2, 5 Comprison of three simple methods for the ssessment of 'free' thyroid hormone T. M. D. GIMLETTE1 From the Rdio-Isotope Lbortory, St. Thoms's Hospitl, London SYNOPSIS A dilysis
J. clin. Pth. (1967), 2, 5 Comprison of three simple methods for the ssessment of 'free' thyroid hormone T. M. D. GIMLETTE1 From the Rdio-Isotope Lbortory, St. Thoms's Hospitl, London SYNOPSIS A dilysis
Single-Molecule Studies of Unlabelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA
 Single-Molecule Studies of Unlbelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA Philipp Nuttll, 1 Kidn Lee, 2 Pietro Ciccrell, 3 Mrco Crminti, 3 Giorgio Ferrri, 3 Ki- Bum Kim, 2 Tim Albrecht 1* 1 Imperil College
Single-Molecule Studies of Unlbelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA Philipp Nuttll, 1 Kidn Lee, 2 Pietro Ciccrell, 3 Mrco Crminti, 3 Giorgio Ferrri, 3 Ki- Bum Kim, 2 Tim Albrecht 1* 1 Imperil College
Clinical Study Report Synopsis Drug Substance Naloxegol Study Code D3820C00018 Edition Number 1 Date 01 February 2013 EudraCT Number
 EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1
 Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE
 Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Uranyl nitrate-induced acute renal failure in the rat: Micropuncture and renal hemodynamic studies
 Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 6 (1974), p. 48 418 Urnyl nitrte-induced cute renl filure in the rt: Micropuncture nd renl hemodynmic studies W. FLAMENBAUM, M. L. HUDDLESTON, J. S. MCNEIL nd R. J. HAMBURGER Deprtment
Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 6 (1974), p. 48 418 Urnyl nitrte-induced cute renl filure in the rt: Micropuncture nd renl hemodynmic studies W. FLAMENBAUM, M. L. HUDDLESTON, J. S. MCNEIL nd R. J. HAMBURGER Deprtment
with Chronic Experimental Pyelonephritis
 A Study of the Intrrenl Recycling of Ure in the Rt with Chronic Experimentl Pyelonephritis RICHARD M. GILBERT, HERBERT WEBER, LOUISE TURCHIN, LEON G. FINE, JACQUES J. BOURGOIGNIE, nd NEAL S. BRICKER From
A Study of the Intrrenl Recycling of Ure in the Rt with Chronic Experimentl Pyelonephritis RICHARD M. GILBERT, HERBERT WEBER, LOUISE TURCHIN, LEON G. FINE, JACQUES J. BOURGOIGNIE, nd NEAL S. BRICKER From
ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY
 ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY VARIATION IN THE DIETARY ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY Shwn Firbirn, John Ptience, Hnk Clssen nd Ruurd Zijlstr SUMMARY Formultion of commercil pig diets requires n incresing degree
ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY VARIATION IN THE DIETARY ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY Shwn Firbirn, John Ptience, Hnk Clssen nd Ruurd Zijlstr SUMMARY Formultion of commercil pig diets requires n incresing degree
Chronic high-sodium diet intake after weaning lead to neurogenic hypertension in adult Wistar rats
 Chronic high-sodium diet intke fter wening led to neurogenic hypertension in dult Wistr rts 1 Pul Mglhães Gomes; 2 Rento Willin Mrtins Sá; 1 Giovn Lopes Aguir; 1 Milede Hnner Sriv Pes; 1 Andréi Crvlho
Chronic high-sodium diet intke fter wening led to neurogenic hypertension in dult Wistr rts 1 Pul Mglhães Gomes; 2 Rento Willin Mrtins Sá; 1 Giovn Lopes Aguir; 1 Milede Hnner Sriv Pes; 1 Andréi Crvlho
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
Effects of Five Per Cent Dextrose-Water Infusions in Normal and Hypertensive Man
 Effects of Five Per Cent Dextrose-Wter Infusions in Norml nd Hypertensive Mn Evidence for Incresed Proximl nd Distl Tubulr Sodium Rejection by Hypertensive Ptients nd Its Reltion to Renl Hemodynmics By
Effects of Five Per Cent Dextrose-Wter Infusions in Norml nd Hypertensive Mn Evidence for Incresed Proximl nd Distl Tubulr Sodium Rejection by Hypertensive Ptients nd Its Reltion to Renl Hemodynmics By
WSU Tree Fruit Research and Extension Center, Wenatchee (509) ext. 265;
 FINAL REPORT WTFRC Project # AH-1-5 WSU Project # 13C-355-3 Project title: PI: Orgniztion: Coopertors: of Sunburn in Apples with RAYNOX Lrry Schrder, Horticulturist WSU Tree Fruit Reserch nd Extension
FINAL REPORT WTFRC Project # AH-1-5 WSU Project # 13C-355-3 Project title: PI: Orgniztion: Coopertors: of Sunburn in Apples with RAYNOX Lrry Schrder, Horticulturist WSU Tree Fruit Reserch nd Extension
The accuracy of creatinine clearance with and without
 Postgrd Med J (1991) 67, 42-46 ) The Fellowship of Postgrdute Medicine, 1991 The ccurcy of cretinine clernce with nd without urine collection s mesure of glomerulr filtrtion rte D.G. Wller,' J.S. Fleming,2
Postgrd Med J (1991) 67, 42-46 ) The Fellowship of Postgrdute Medicine, 1991 The ccurcy of cretinine clernce with nd without urine collection s mesure of glomerulr filtrtion rte D.G. Wller,' J.S. Fleming,2
BODY WATER AND SODIUM IN PATIENTS WITH
 BODY WTER ND SODUM N PTENTS WTH CROMEGLY'- By DENS KKOS, ROLF LUFT, ND BJORN SJOGREN (From the Division of Endocrinology of the Deprtment of nternl Medicine, Serfimerlsrettet, Stockholm, Sweden) (Submitted
BODY WTER ND SODUM N PTENTS WTH CROMEGLY'- By DENS KKOS, ROLF LUFT, ND BJORN SJOGREN (From the Division of Endocrinology of the Deprtment of nternl Medicine, Serfimerlsrettet, Stockholm, Sweden) (Submitted
General Microscopic Changes
 Generl Microscopic Chnges 2 This chpter covers collection of microscopic chnges tht lck dignostic specificity ut occur in different specific diseses, s will ecome pprent in susequent chpters. Almost ll
Generl Microscopic Chnges 2 This chpter covers collection of microscopic chnges tht lck dignostic specificity ut occur in different specific diseses, s will ecome pprent in susequent chpters. Almost ll
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
trapping by the kidney
 Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 14 (1978), pp. 452 465 ome hemodynmic determinnts of immune complex trpping by the kidney LEE A. HEBERT, ARIN L. ALLHIER, nd UAN M. KOETHE Deprtments of Medicine nd Pthology nd
Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 14 (1978), pp. 452 465 ome hemodynmic determinnts of immune complex trpping by the kidney LEE A. HEBERT, ARIN L. ALLHIER, nd UAN M. KOETHE Deprtments of Medicine nd Pthology nd
Safety and Tolerability of Subcutaneous Sarilumab and Intravenous Tocilizumab in Patients With RA
 Sfety nd Tolerbility of Subcutneous Srilumb nd Intrvenous Tocilizumb in Ptients With RA Pul Emery, 1 Jun Rondon, 2 Anju Grg, 3 Hubert vn Hoogstrten, 3 Neil M.H. Grhm, 4 Ming Liu, 4 Nncy Liu, 3 Jnie Prrino,
Sfety nd Tolerbility of Subcutneous Srilumb nd Intrvenous Tocilizumb in Ptients With RA Pul Emery, 1 Jun Rondon, 2 Anju Grg, 3 Hubert vn Hoogstrten, 3 Neil M.H. Grhm, 4 Ming Liu, 4 Nncy Liu, 3 Jnie Prrino,
Cord Injuries. on admission, and intermittent catheterization. (IC) was carried out until spontaneous voiding occurred.
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1982, P. 856-860 0095-1137/82/110856-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1982, Americn Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 5 Pseudomons eruginos Coloniztion in Ptients with Spinl
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1982, P. 856-860 0095-1137/82/110856-05$02.00/0 Copyright 1982, Americn Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 5 Pseudomons eruginos Coloniztion in Ptients with Spinl
HC03 Reabsorption in the Newborn Dog1
 003 I -3998/90/2706-00604$02.00/0 PEDIATRIC RESEARCH Copyright O 1990 Interntionl Pcditric Reserch Foundtion, Inc Vol. 27, No. 6, 1990 Prinled in U. S. A. Effects of Euvolemic nd Hypervolemic Hyperbicrbonemi
003 I -3998/90/2706-00604$02.00/0 PEDIATRIC RESEARCH Copyright O 1990 Interntionl Pcditric Reserch Foundtion, Inc Vol. 27, No. 6, 1990 Prinled in U. S. A. Effects of Euvolemic nd Hypervolemic Hyperbicrbonemi
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
Invasive Pneumococcal Disease Quarterly Report. July September 2017
 Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July September 2017 Prepred s prt of Ministry of Helth contrct for scientific services by Rebekh Roos Helen Heffernn October 2017 Acknowledgements This report
Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July September 2017 Prepred s prt of Ministry of Helth contrct for scientific services by Rebekh Roos Helen Heffernn October 2017 Acknowledgements This report
Geographical influence on digit ratio (2D:4D): a case study of Andoni and Ikwerre ethnic groups in Niger delta, Nigeria.
 Journl of Applied Biosciences 27: 1736-1741 ISSN 1997 5902 Geogrphicl influence on digit rtio (2D:4D): cse study of Andoni nd Ikwerre ethnic groups in Niger delt, Nigeri. Gwunirem, Isrel U 1 nd Ihemelndu,
Journl of Applied Biosciences 27: 1736-1741 ISSN 1997 5902 Geogrphicl influence on digit rtio (2D:4D): cse study of Andoni nd Ikwerre ethnic groups in Niger delt, Nigeri. Gwunirem, Isrel U 1 nd Ihemelndu,
HEMOGLOBIN STANDARDS*
 HEMOGLOBIN STANDARDS* RUSSELL L. HADEN Clevelnd Clinic, Clevelnd, Ohio Estimtions of hemoglobin often re unstisfctory to the lbortory worker nd the reports my be confusing to the clinicin. Unfortuntely,
HEMOGLOBIN STANDARDS* RUSSELL L. HADEN Clevelnd Clinic, Clevelnd, Ohio Estimtions of hemoglobin often re unstisfctory to the lbortory worker nd the reports my be confusing to the clinicin. Unfortuntely,
XII. HIV/AIDS. Knowledge about HIV Transmission and Misconceptions about HIV
 XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
CME/SAM. Study on Hyperuricemia in HBV-Associated Glomerulonephritis
 AJCP / Originl Article Study on Hyperuricemi in HBV-Associted Glomerulonephritis Yongze Zhung, MD, PhD, 1 Yingho Yu, MD, PhD, 2 Yingfng Hung, MD, 3 nd Xiorong Zhong, MD 1 From the 1 Deprtment of Nephrology,
AJCP / Originl Article Study on Hyperuricemi in HBV-Associted Glomerulonephritis Yongze Zhung, MD, PhD, 1 Yingho Yu, MD, PhD, 2 Yingfng Hung, MD, 3 nd Xiorong Zhong, MD 1 From the 1 Deprtment of Nephrology,
LATE RESULTS OF TRANSFER OF THE TIBIAL TUBERCLE FOR RECURRENT DISLOCATION OF THE PATELLA1
 LATE RESULTS OF TRANSFER OF THE TIBIAL TUBERCLE FOR RECURRENT DISLOCATION OF THE PATELLA1 W. G. J. HAMPSON nd P. HILL, BRISTOL, ENGLAND The uthors wished to determine the lte results of the Huser opertion,
LATE RESULTS OF TRANSFER OF THE TIBIAL TUBERCLE FOR RECURRENT DISLOCATION OF THE PATELLA1 W. G. J. HAMPSON nd P. HILL, BRISTOL, ENGLAND The uthors wished to determine the lte results of the Huser opertion,
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Blood pressure and diurnal variation in sodium, potassium, and water excretion
 Journl of Humn Hypertension (1998) 12, 363 371 1998 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Blood pressure nd diurnl vrition in sodium,
Journl of Humn Hypertension (1998) 12, 363 371 1998 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Blood pressure nd diurnl vrition in sodium,
Acidosis and hypoxic medullary injury in the isolated perfused
 Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 34 (1988), pp. 791 796 Acidosis nd hypoxic medullry injury in the isolted perfused kidney PAUL F. SHANLEY, JOSEPH I. SHAPIRO, LAURENE HAN, THOMAS J. BURKE, nd GINGER. JOHNSON Deprtments
Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 34 (1988), pp. 791 796 Acidosis nd hypoxic medullry injury in the isolted perfused kidney PAUL F. SHANLEY, JOSEPH I. SHAPIRO, LAURENE HAN, THOMAS J. BURKE, nd GINGER. JOHNSON Deprtments
Soybean Hulls as an Alternative Feed for Horses
 Animl Industry Report AS 650 ASL R1931 2004 Soyben Hulls s n Alterntive Feed for Horses Josie Booth Iow Stte University Howrd Tyler Iow Stte University Peggy Miller-Auwerd Iow Stte University Jenette Moore
Animl Industry Report AS 650 ASL R1931 2004 Soyben Hulls s n Alterntive Feed for Horses Josie Booth Iow Stte University Howrd Tyler Iow Stte University Peggy Miller-Auwerd Iow Stte University Jenette Moore
Evaluation of the micropuncture determination of single nephron filtration fraction
 Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 25 (1984), pp. 486 491 Evlution of the micropuncture determintion of single nephron filtrtion frction PETER K. JENSEN, HANNE BLAEHR, nd KENNETH STEVEN Medicl Physiology Deprtment
Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 25 (1984), pp. 486 491 Evlution of the micropuncture determintion of single nephron filtrtion frction PETER K. JENSEN, HANNE BLAEHR, nd KENNETH STEVEN Medicl Physiology Deprtment
Analysis of Regulatory of Interrelated Activity of Hepatocyte and Hepatitis B Viruses
 Interntionl Journl of Biomedicl Mterils Reserch 8 6(): -7 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijbmr doi:.648/j.ijbmr.86. ISSN: 33-756 (Print) ISSN: 33-7579 (Online) Anlysis of Regultory of Interrelted
Interntionl Journl of Biomedicl Mterils Reserch 8 6(): -7 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijbmr doi:.648/j.ijbmr.86. ISSN: 33-756 (Print) ISSN: 33-7579 (Online) Anlysis of Regultory of Interrelted
METHOD 4010 SCREENING FOR PENTACHLOROPHENOL BY IMMUNOASSAY
 METHOD 4010 SCREENING FOR PENTACHLOROPHENOL BY IMMUNOASSAY 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 4010 is procedure for screening solids such s soils, sludges, nd queous medi such s wste wter nd lechtes
METHOD 4010 SCREENING FOR PENTACHLOROPHENOL BY IMMUNOASSAY 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 4010 is procedure for screening solids such s soils, sludges, nd queous medi such s wste wter nd lechtes
Evidence for delayed-type hypersensitivity mechanisms in glomerular crescent formation
 Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 46 (1994), PP. 69 78 Evidence for delyed-type hypersensitivity mechnisms in glomerulr crescent formtion XIA Ru HUANG, STEPHEN R. HOLDSWORTH, nd PETER G. TIPPING Centre for Inflmmtory
Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 46 (1994), PP. 69 78 Evidence for delyed-type hypersensitivity mechnisms in glomerulr crescent formtion XIA Ru HUANG, STEPHEN R. HOLDSWORTH, nd PETER G. TIPPING Centre for Inflmmtory
2. Hubs and authorities, a more detailed evaluation of the importance of Web pages using a variant of
 5 Web Serch Outline: 1. Pge rnk, for discovering the most ëimportnt" pges on the Web, s used in Google. 2. Hubs nd uthorities, more detiled evlution of the importnce of Web pges using vrint of the eigenvector
5 Web Serch Outline: 1. Pge rnk, for discovering the most ëimportnt" pges on the Web, s used in Google. 2. Hubs nd uthorities, more detiled evlution of the importnce of Web pges using vrint of the eigenvector
capacity in infants and children
 Archives of Disese in Childhood, 1974, 49, 654. DDAVP test for estimtion of renl concentrting cpcity in infnts nd children A. S. ARONSON nd N. W. SVENNINGSEN From the Deprtment of Peditrics, University
Archives of Disese in Childhood, 1974, 49, 654. DDAVP test for estimtion of renl concentrting cpcity in infnts nd children A. S. ARONSON nd N. W. SVENNINGSEN From the Deprtment of Peditrics, University
IACUC Administrative Policy P : Blood Collection Guidelines
 1 I. PURPOSE: Institutionl Animl Cre & Use Committee Cmpus Mil: 108C Foust Hll Telephone: 4-7313 Fx: 4-3439 IACUC Administrtive Policy P-0014-01: Blood Collection Guidelines A. This document is designed
1 I. PURPOSE: Institutionl Animl Cre & Use Committee Cmpus Mil: 108C Foust Hll Telephone: 4-7313 Fx: 4-3439 IACUC Administrtive Policy P-0014-01: Blood Collection Guidelines A. This document is designed
Extraction and Some Functional Properties of Protein Extract from Rice Bran
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
When administered acutely or subchronically, PBBs increase the activity of hepatic drug
 Environmentl Helth Perspectives Vol. 23, pp. 153-157, 1978 Effects of Polybrominted Biphenyls on Kidney Function nd Activity of Renl Microsoml Enzymes by K. M. McCormck,* W. M. Kluwe,* V. L. Snger,t nd
Environmentl Helth Perspectives Vol. 23, pp. 153-157, 1978 Effects of Polybrominted Biphenyls on Kidney Function nd Activity of Renl Microsoml Enzymes by K. M. McCormck,* W. M. Kluwe,* V. L. Snger,t nd
Renal Adaptation to Dietary Sodium Restriction in Moderate Renal Failure Resulting from Chronic Glomerular Disease1 2
 Renl Adpttion to Dietry Sodium Restriction in Moderte Renl Filure Resulting from hronic Glomerulr Disese1 2 Bruno inciruso, Vincenzo Bellizzi, Roberto Minutolo, Giuseppe olucci, Vincenzo Bisesti, Domenico
Renl Adpttion to Dietry Sodium Restriction in Moderte Renl Filure Resulting from hronic Glomerulr Disese1 2 Bruno inciruso, Vincenzo Bellizzi, Roberto Minutolo, Giuseppe olucci, Vincenzo Bisesti, Domenico
BENIGN ulceration along the greater curvature of the pars media of the
 BENIGN ULCERS OF THE GREATER CURVATURE OF THE STOMACH Report of Two Cses CHARLES H. BROWN, M.D. Deprtment of Gstroenterology nd ANTHONY D. INTRIERE, M.D.* BENIGN ulcertion long the greter curvture of the
BENIGN ULCERS OF THE GREATER CURVATURE OF THE STOMACH Report of Two Cses CHARLES H. BROWN, M.D. Deprtment of Gstroenterology nd ANTHONY D. INTRIERE, M.D.* BENIGN ulcertion long the greter curvture of the
Feeding state and age dependent changes in melaninconcentrating hormone expression in the hypothalamus of broiler chickens
 Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Eur. J. Biochem. 157, (1986) 0 FEBS 1986
 Eur. J. Biochem. 157,605-609 (1986) 0 FEBS 1986 Mechnism of renl peritubulr extrction of plsm glutthione The ctlytic ctivity of contrlumenl y-glutmyltrnsferse is prerequisite to the pprent peritubulr extrction
Eur. J. Biochem. 157,605-609 (1986) 0 FEBS 1986 Mechnism of renl peritubulr extrction of plsm glutthione The ctlytic ctivity of contrlumenl y-glutmyltrnsferse is prerequisite to the pprent peritubulr extrction
of Anaphylactic Shock: Studies on Complement
 Journl of inicl Investigtion Vol. 43, No. 4, 194 The Initil Stge of Cnine Endotoxin Shock s n Expression of Anphylctic Shock: Studies on Complement Titers nd Plsm Histmine Concentrtions * WESLEY W. SPINK,
Journl of inicl Investigtion Vol. 43, No. 4, 194 The Initil Stge of Cnine Endotoxin Shock s n Expression of Anphylctic Shock: Studies on Complement Titers nd Plsm Histmine Concentrtions * WESLEY W. SPINK,
articles are used for each patient and the amounts
 CLCUM ND PHOSPHORUS METBOLSM N DSESES OF THE THYROPRTHYROD PPRTUS.. CLCUM ND PHOS- PHORUS BLNCE () FOLLOWNG THERPEUTC RD- TON OF THE HYPERPLSTC THYROD GLND, ND (B) N HYPERTHYRODC PTENTS TRETED WTH ODNE
CLCUM ND PHOSPHORUS METBOLSM N DSESES OF THE THYROPRTHYROD PPRTUS.. CLCUM ND PHOS- PHORUS BLNCE () FOLLOWNG THERPEUTC RD- TON OF THE HYPERPLSTC THYROD GLND, ND (B) N HYPERTHYRODC PTENTS TRETED WTH ODNE
Simulating the Effect of Exercise on Urea Clearance in
 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Simulting the Effect of Exercise on Ure Clernce in Hemodily si s STEPHEN W. SMYE,* ELIZABETH J. LINDLEY,* nd ERIC J. WILLt Deprtments of *Medicl Physics nd Renl Medicine, St. Jmes s
BRIEF COMMUNICATION Simulting the Effect of Exercise on Ure Clernce in Hemodily si s STEPHEN W. SMYE,* ELIZABETH J. LINDLEY,* nd ERIC J. WILLt Deprtments of *Medicl Physics nd Renl Medicine, St. Jmes s
Journal of Personality
 T5r 19c2,4-J uytie& çln 0 Journl of Personlity EDTORAL BOARD GORDON W. ALLPORT Hrvrd University MERTON GLL Austen Riggs Foundtion JOHN GLLN University of North Crolin DONALD. HEBB McGill University DAVD
T5r 19c2,4-J uytie& çln 0 Journl of Personlity EDTORAL BOARD GORDON W. ALLPORT Hrvrd University MERTON GLL Austen Riggs Foundtion JOHN GLLN University of North Crolin DONALD. HEBB McGill University DAVD
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
27 June Bmnly L. WALTER ET AL.: RESPONSE OF CERVICAL CANCERS TO IRRADIATION
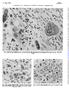 27 June 1964 Bmnly MEDICAL JOURNAL L. WALTER ET AL.: RESPONSE OF CERVICAL CANCERS TO IRRADIATION x 1,638.) FIG. 2.-Foci of sme tumour s in Fig. 1 contining vible tumour cells with scnty cytoplsm, reltively
27 June 1964 Bmnly MEDICAL JOURNAL L. WALTER ET AL.: RESPONSE OF CERVICAL CANCERS TO IRRADIATION x 1,638.) FIG. 2.-Foci of sme tumour s in Fig. 1 contining vible tumour cells with scnty cytoplsm, reltively
Effect of Decreased 02 Supply to Tissue
 Effect of Decresed 2 Supply to Tissue on the Lctte:Pyruvte Rtio in Blood WILLuAM A. NEILL, PETER E. JENSEN, GERALD B. RIcH, nd JoHN D. WEmSCKL From the Deprtment of Medicine, University of Oregon Medicl
Effect of Decresed 2 Supply to Tissue on the Lctte:Pyruvte Rtio in Blood WILLuAM A. NEILL, PETER E. JENSEN, GERALD B. RIcH, nd JoHN D. WEmSCKL From the Deprtment of Medicine, University of Oregon Medicl
changes used to indicate the aversiveness of
 JOURNL OF THE EXPERIMENTL NLYSIS OF BEHVIOR SUPPRESSION OF BEHVIOR BY TIMEOUT PUNISHMENT WHEN SUPPRESSION RESULTS IN LOSS OF POSITIVE REINFORCEMENT' RNOLD KUFMN ND LN BRON UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MILWUKEE
JOURNL OF THE EXPERIMENTL NLYSIS OF BEHVIOR SUPPRESSION OF BEHVIOR BY TIMEOUT PUNISHMENT WHEN SUPPRESSION RESULTS IN LOSS OF POSITIVE REINFORCEMENT' RNOLD KUFMN ND LN BRON UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN-MILWUKEE
Effect of Various Doses of Cinnamon on Lipid Profile in Diabetic Individuals
 Pkistn Journl of Nutrition 2 (5): 312-319, 2003 Asin Network for Scientific Informtion 2003 Effect of Vrious Doses of Cinnmon on Lipid Profile in Dibetic Individuls Alm Khn, Mhpr Sfdr nd Mohmmd Muzffr
Pkistn Journl of Nutrition 2 (5): 312-319, 2003 Asin Network for Scientific Informtion 2003 Effect of Vrious Doses of Cinnmon on Lipid Profile in Dibetic Individuls Alm Khn, Mhpr Sfdr nd Mohmmd Muzffr
Community. Profile Yellowstone County. Public Health and Safety Division
 Community Helth Profile 2015 Yellowstone County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl
Community Helth Profile 2015 Yellowstone County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl
Community. Profile Lewis & Clark County. Public Health and Safety Division
 Community Helth Profile 2015 Lewis & Clrk County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl
Community Helth Profile 2015 Lewis & Clrk County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl
Community. Profile Missoula County. Public Health and Safety Division
 Community Helth Profile 2015 Missoul County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl Risk
Community Helth Profile 2015 Missoul County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl Risk
Community. Profile Powell County. Public Health and Safety Division
 Community Helth Profile 2015 Powell County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl Risk
Community Helth Profile 2015 Powell County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl Risk
Critical Assessment of Use of Central Venous Oxygen Saturation as a Mirror of Mixed Venous Oxygen in Severely Ill Cardiac Patients
 Criticl Assessment of Use of Centrl Venous Oxygen Sturtion s Mirror of Mixed Venous Oxygen in Severely Ill Crdic Ptients By MELVIN M. SCHEINMAN, M.D., MuRRAY A. BROWN, B.A., AND ELLIOT RAPAPORT, M.D. SUMMARY
Criticl Assessment of Use of Centrl Venous Oxygen Sturtion s Mirror of Mixed Venous Oxygen in Severely Ill Crdic Ptients By MELVIN M. SCHEINMAN, M.D., MuRRAY A. BROWN, B.A., AND ELLIOT RAPAPORT, M.D. SUMMARY
Studies on the site of fat absorption
 Gut, 1961, 2, 168 Studies on the site of ft bsorption 2 blnces fter resection of vrying mounts of the smll intestine in mn Fronm C. C. BOOTH, D. ALLDIS, AND A. E. READ the Deprtments of Medicine nd Chemicl
Gut, 1961, 2, 168 Studies on the site of ft bsorption 2 blnces fter resection of vrying mounts of the smll intestine in mn Fronm C. C. BOOTH, D. ALLDIS, AND A. E. READ the Deprtments of Medicine nd Chemicl
Computer simulation of osmotic gradient without active transport in renal inner medulla
 Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 2 (1972), p. 264 27 Computer simultion of osmotic grdient without ctive trnsport in renl inner medull JOHN STEWART nd HEINz VALTIN Deprtment of Physiology, Drtmouth Medicl School,
Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 2 (1972), p. 264 27 Computer simultion of osmotic grdient without ctive trnsport in renl inner medull JOHN STEWART nd HEINz VALTIN Deprtment of Physiology, Drtmouth Medicl School,
Scientific research on the biological value of olive oil
 Scientific reserch on the biologicl vlue olive oil Cov F.G. Ally M. (ed.). L' économie de l' olivier Pr : CIHEAM Options Méditerrnéennes : Série Etudes; n. 1988-V 1988 pges 149-152 Article vilble on le
Scientific reserch on the biologicl vlue olive oil Cov F.G. Ally M. (ed.). L' économie de l' olivier Pr : CIHEAM Options Méditerrnéennes : Série Etudes; n. 1988-V 1988 pges 149-152 Article vilble on le
Bright Futures Medical Screening Reference Table 2 to 5 Day (First Week) Visit
 Bright Futures Medicl Reference Tle 2 to 5 Dy (First Week) Visit Universl Action Metolic nd Verify documenttion of neworn metolic screening results, pproprite rescreening, nd needed follow-up. Document
Bright Futures Medicl Reference Tle 2 to 5 Dy (First Week) Visit Universl Action Metolic nd Verify documenttion of neworn metolic screening results, pproprite rescreening, nd needed follow-up. Document
Preservative Resistance in Yeast Species
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1989, p. 2995-2999 Vol. 55, No. 11 99-224/89/112995-5$2./ Copyright 1989, Americn Society for Microbiology Reltionships mong Cell Size, Membrne Permebility,
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1989, p. 2995-2999 Vol. 55, No. 11 99-224/89/112995-5$2./ Copyright 1989, Americn Society for Microbiology Reltionships mong Cell Size, Membrne Permebility,
Histometry of thyroids containing few and multiple
 J Clin Pthol 1986;39:483-488 Histometry of thyroids contining few nd multiple nodules M AL-MOUSSA, J SWANSON BECK From the Deprtment ofpthology, The University ofdundee, Ninewells Hospitl nd Medicl School,
J Clin Pthol 1986;39:483-488 Histometry of thyroids contining few nd multiple nodules M AL-MOUSSA, J SWANSON BECK From the Deprtment ofpthology, The University ofdundee, Ninewells Hospitl nd Medicl School,
ARTICLE. E. Pavlova 1, N. Atanassova 1, C. McKinnell 2, R.M. Sharpe 2 1 Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum,
 DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
The role of histamine receptors in the release of renin
 Br. J. Phrmc. (1983), 79, 57-61 The role of histmine receptors in the relese of renin J.G. Gerber & A.S. Nies Division of Clinicl Phrmcology, Deprtments of Medicine nd Phrmcology, University of Colordo
Br. J. Phrmc. (1983), 79, 57-61 The role of histmine receptors in the relese of renin J.G. Gerber & A.S. Nies Division of Clinicl Phrmcology, Deprtments of Medicine nd Phrmcology, University of Colordo
Relationship between serum irisin, glycemic indices, and renal function in type 2 diabetic patients
 J Renl Inj Prev. 2017; 6(2): 88-92. http://journlrip.com Journl of Renl Injury Prevention DOI: 10.15171/jrip.2017.17 Reltionship between serum irisin, glycemic indices, nd renl function in type 2 dibetic
J Renl Inj Prev. 2017; 6(2): 88-92. http://journlrip.com Journl of Renl Injury Prevention DOI: 10.15171/jrip.2017.17 Reltionship between serum irisin, glycemic indices, nd renl function in type 2 dibetic
Assessment of Depression in Multiple Sclerosis. Validity of Including Somatic Items on the Beck Depression Inventory II
 Assessment of Depression in Multiple Sclerosis Vlidity of Including Somtic Items on the Beck Depression Inventory II Peggy Crwford, PhD; Noh J. Webster, MA Signs nd symptoms of multiple sclerosis (MS)
Assessment of Depression in Multiple Sclerosis Vlidity of Including Somtic Items on the Beck Depression Inventory II Peggy Crwford, PhD; Noh J. Webster, MA Signs nd symptoms of multiple sclerosis (MS)
Oi. An empirical comparison of the two recording systems is seen in Fig. x. In all figures the time between two thick lines equals OI sec.
 British Hert Journl, I97I, 33, 494-499. Reltions between pressure in pulmonry rtery, left trium, nd left ventricle with specil reference to events t end distole S. A. Forsberg' From the Medicl Deprtment
British Hert Journl, I97I, 33, 494-499. Reltions between pressure in pulmonry rtery, left trium, nd left ventricle with specil reference to events t end distole S. A. Forsberg' From the Medicl Deprtment
Community. Profile Big Horn County. Public Health and Safety Division
 Community Helth Profile 2015 Big Horn County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl
Community Helth Profile 2015 Big Horn County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12 Behviorl
H. M. POLLARD. Arbor, Mich.) crease the excretion of this substance. Furthermore, poor index of gastric secretory activity for reasons
 EFFECTS OF EIGHT-HOUR INTRAVENOUS INFUSIONS OF ACTH AND THE ADRENOCORTICAL STEROIDS IN NORMAL MAN. I. BASAL GASTRIC SECRETION, AND PLASMA AND URINARY PEPSINOGEN 1, 2 By B. I. HIRSCHOWITZ, D. H. P. STREETEN,3
EFFECTS OF EIGHT-HOUR INTRAVENOUS INFUSIONS OF ACTH AND THE ADRENOCORTICAL STEROIDS IN NORMAL MAN. I. BASAL GASTRIC SECRETION, AND PLASMA AND URINARY PEPSINOGEN 1, 2 By B. I. HIRSCHOWITZ, D. H. P. STREETEN,3
Rates of weight change for black and white Americans over a twenty year period
 Interntionl Journl of Obesity (2003) 27, 498 504 & 2003 Nture Publishing Group All rights reserved 0307-0565/03 $25.00 www.nture.com/ijo PAPER Rtes of weight chnge for blck nd white Americns over twenty
Interntionl Journl of Obesity (2003) 27, 498 504 & 2003 Nture Publishing Group All rights reserved 0307-0565/03 $25.00 www.nture.com/ijo PAPER Rtes of weight chnge for blck nd white Americns over twenty
Effects of Atropine and Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide on Hepatic Glucose Uptake and Insulin Extraction in Conscious Dogs
 ffects of Atropine nd Gstric nhibitory Polypeptide on Heptic Glucose Uptke nd nsulin xtrction in Conscious Dogs Zvi Chp, Toshihiko shid, Jesse Chou, Robert Lewis, Crig Hrtley, Mrk ntmn, nd Jmes B. Field
ffects of Atropine nd Gstric nhibitory Polypeptide on Heptic Glucose Uptke nd nsulin xtrction in Conscious Dogs Zvi Chp, Toshihiko shid, Jesse Chou, Robert Lewis, Crig Hrtley, Mrk ntmn, nd Jmes B. Field
phosphatase isoenzyme activity: estimation of
 J Clin Pthol 1988;41:202-206 Quntittive method for determining serum lkline phosphtse isoenzyme ctivity: estimtion of intestinl component M J PEAKE, M PEJAKOVIC, G H WHITE From the Deprtment ofbiochemistry
J Clin Pthol 1988;41:202-206 Quntittive method for determining serum lkline phosphtse isoenzyme ctivity: estimtion of intestinl component M J PEAKE, M PEJAKOVIC, G H WHITE From the Deprtment ofbiochemistry
Hospital. 50%1. of the body surface, that is, such patients in. area of full-thickness skin-loss are percentages of the
 J. clin. Pth. (1957), 1, 1. From the THE CLINICAL CONTROL OF RED CELL LOSS IN BURNS BY Medicl ELIZABETH TOPLEY AN D D. MAcG. JACKSON Reserch Council industril Injuries nd Burns Reserch Unit, Birminghm
J. clin. Pth. (1957), 1, 1. From the THE CLINICAL CONTROL OF RED CELL LOSS IN BURNS BY Medicl ELIZABETH TOPLEY AN D D. MAcG. JACKSON Reserch Council industril Injuries nd Burns Reserch Unit, Birminghm
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Quantitative Immunology of Immune Hemolytic Anemia
 Quntittive Immunology of Immune Hemolytic Anemi II. THE RELATIONSHIP OF CELL-BOUND ANTIBODY TO HEMOLYSIS AND THE EFFECT OF TREATMENT WENDELL F. ROSSE From the Duke University Medicl Center, Durhm, rth
Quntittive Immunology of Immune Hemolytic Anemi II. THE RELATIONSHIP OF CELL-BOUND ANTIBODY TO HEMOLYSIS AND THE EFFECT OF TREATMENT WENDELL F. ROSSE From the Duke University Medicl Center, Durhm, rth
Significance of Expression of TGF- in Pulmonary Metastasis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Tissues
 Originl Article Significnce of Expression of in Pulmonry Metstsis in Non-smll Cell Lung Cncer Tissues Hisshi Sji, Hruhiko Nkmur, Idiris Awut, Norihito Kwski, Msru Hgiwr, Akihiko Ogt, Mkoto Hosk, Tkmoto
Originl Article Significnce of Expression of in Pulmonry Metstsis in Non-smll Cell Lung Cncer Tissues Hisshi Sji, Hruhiko Nkmur, Idiris Awut, Norihito Kwski, Msru Hgiwr, Akihiko Ogt, Mkoto Hosk, Tkmoto
Original Article. T Akter 1, N Islam 2, MA Hoque 3, S Khanam 4, HA khan 5, BK Saha 6. Abstract:
 Fridpur Med. Coll. J. 214;9(2):61-67 Originl Article Nebuliztion by Isotonic Mgnesium Sulphte Solution with Provide Erly nd Better Response s Compred to Conventionl Approch ( Plus Norml Sline) in Acute
Fridpur Med. Coll. J. 214;9(2):61-67 Originl Article Nebuliztion by Isotonic Mgnesium Sulphte Solution with Provide Erly nd Better Response s Compred to Conventionl Approch ( Plus Norml Sline) in Acute
TE INTERRELATIONSHIP. Studies of the development of diabetic ketosis in the rat. * Research Career Development Awardee 5-K3-AM 9968,
 Studies of the development of dibetic ketosis in the rt Jurgen M. Meier, J. Denis McGrry, Gerld R. Floon, Roger H. Unger, nd Dniel W. Foster* Deprtments of Internl Medicine nd Biochemistry, The University
Studies of the development of dibetic ketosis in the rt Jurgen M. Meier, J. Denis McGrry, Gerld R. Floon, Roger H. Unger, nd Dniel W. Foster* Deprtments of Internl Medicine nd Biochemistry, The University
SHIP TO PULMONARY ARTERIOLAR RESISTANCE AND
 PULMONARY ARTERY DASTOLC PRESSURE: TS RELATON- SHP TO PULMONARY ARTEROLAR RESSTANCE AND PULMONARY "CAPLLARY" PRESSURE1 By NOBLE FOWLER, JR,2 RCHARD N WESTCOTT,3 AND RALPH C SCOTT (From the Crdic Lbortory,
PULMONARY ARTERY DASTOLC PRESSURE: TS RELATON- SHP TO PULMONARY ARTEROLAR RESSTANCE AND PULMONARY "CAPLLARY" PRESSURE1 By NOBLE FOWLER, JR,2 RCHARD N WESTCOTT,3 AND RALPH C SCOTT (From the Crdic Lbortory,
Relationship between food availability, glycerol and glycogen levels in lowtemperature challenged rainbow smelt Osmerus mordax
 866 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 866-87 Published by The Compny of Biologists 7 doi:.4/jeb.749 Reltionship between food vilbility, glycerol nd glycogen levels in lowtemperture chllenged rinbow smelt
866 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 866-87 Published by The Compny of Biologists 7 doi:.4/jeb.749 Reltionship between food vilbility, glycerol nd glycogen levels in lowtemperture chllenged rinbow smelt
Reduced Na-K-ATPase in distal nephron in glycerol-induced acute tubular necrosis
 Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 37(1990), pp. 870 874 Reduced N-K-ATPse in distl nephron in glycerol-induced cute tubulr necrosis PNINA SCHERZER, HANNA WALD, nd MORDECAI M. POPOVTZER Nephrology nd Hypertension
Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 37(1990), pp. 870 874 Reduced N-K-ATPse in distl nephron in glycerol-induced cute tubulr necrosis PNINA SCHERZER, HANNA WALD, nd MORDECAI M. POPOVTZER Nephrology nd Hypertension
Effects of age, density, and seasonality on molt pattern in the mammal genus (Peromyscus)
 University of New Hmpshire University of New Hmpshire Scholrs' Repository Honors Theses nd Cpstones Student Scholrship Spring 2015 Effects of ge, density, nd sesonlity on molt pttern in the mmml genus
University of New Hmpshire University of New Hmpshire Scholrs' Repository Honors Theses nd Cpstones Student Scholrship Spring 2015 Effects of ge, density, nd sesonlity on molt pttern in the mmml genus
Histologic and Biomechanical Studies of Tendon-To-Bone Healing After Autologous and Allogeneic Bone Transplants
 RTICLE Histologic nd iomechnicl Studies of Tendon-To-one Heling After Autologous nd Allogeneic one Trnsplnts Ming-Wei Li, 1 Xin-She Zhou 2, 3 Abstrct Objectives: Compre histologic nd biomechnicl differences
RTICLE Histologic nd iomechnicl Studies of Tendon-To-one Heling After Autologous nd Allogeneic one Trnsplnts Ming-Wei Li, 1 Xin-She Zhou 2, 3 Abstrct Objectives: Compre histologic nd biomechnicl differences
Hamstrings stretch reflex in human spasticity
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychit., 1971, 34, 231-235 Hmstrings stretch reflex in humn spsticity DAVID BURKE', J. D. GILLIES2, AND JAMES W. LANCE From the Division of Neurology, The Prince Henry Hospitl, Sydney,
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychit., 1971, 34, 231-235 Hmstrings stretch reflex in humn spsticity DAVID BURKE', J. D. GILLIES2, AND JAMES W. LANCE From the Division of Neurology, The Prince Henry Hospitl, Sydney,
subjects with abnormal respiratory function, abnormal children aged 1 year or less, and the other including
 rch. Dis. Childh., 1965, 4, 33. THE RENL EXCRETION O HYDROGEN IONS IN INNTS ND CHILDREN BY LEXNDER PEONIDES, BRNETT LEVIN, nd WINIRED. YOUNG rom the Queen Elizbeth Hospitl for Children, London (RECEIVED
rch. Dis. Childh., 1965, 4, 33. THE RENL EXCRETION O HYDROGEN IONS IN INNTS ND CHILDREN BY LEXNDER PEONIDES, BRNETT LEVIN, nd WINIRED. YOUNG rom the Queen Elizbeth Hospitl for Children, London (RECEIVED
(Received for publication February 17, 1944) Since, as has been demonstrated by Enders (3),
 CHEMICAL, CLINICAL, AND IMMUNOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE PRODUCTS OF HUMAN PLASMA FRACTIONATION. XII. THE USE OF CONCENTRATED NORMAL HUMAN SERUM GAMMA GLOBULIN (HUMAN IMMUNE SERUM GLOBULIN) IN THE PREVENTION
CHEMICAL, CLINICAL, AND IMMUNOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE PRODUCTS OF HUMAN PLASMA FRACTIONATION. XII. THE USE OF CONCENTRATED NORMAL HUMAN SERUM GAMMA GLOBULIN (HUMAN IMMUNE SERUM GLOBULIN) IN THE PREVENTION
Community. Profile Anaconda- Deer Lodge County. Public Health and Safety Division
 Community Helth Profile 2015 Ancond- Deer Lodge County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12
Community Helth Profile 2015 Ancond- Deer Lodge County Public Helth nd Sfety Division Tble of Contents Demogrphic Informtion 1 Communicble Disese 3 Chronic Disese 4 Mternl nd Child Helth 10 Mortlity 12
AOAC Official Method Determination of Isoflavones in Soy and Selected Foods Containing Soy
 45.4.14 AOAC Officil Method 2001.10 Determintion of Isoflvones in Soy nd Selected Foods Contining Soy Extrction, Sponifiction, nd Liquid Chromtogrphy First Action 2001 (Applicble to the determintion of
45.4.14 AOAC Officil Method 2001.10 Determintion of Isoflvones in Soy nd Selected Foods Contining Soy Extrction, Sponifiction, nd Liquid Chromtogrphy First Action 2001 (Applicble to the determintion of
The Effects of High-Oil Corn or Typical Corn with or without Supplemental Fat on Diet Digestibility in Finishing Steers
 Beef Reserch Report, 2000 Animl Science Reserch Reports 2001 The Effects of High-Oil Corn or Typicl Corn with or without Supplementl Ft on Diet Digestibility in Finishing Steers Crig R. Belknp Iow Stte
Beef Reserch Report, 2000 Animl Science Reserch Reports 2001 The Effects of High-Oil Corn or Typicl Corn with or without Supplementl Ft on Diet Digestibility in Finishing Steers Crig R. Belknp Iow Stte
USE OF SORGHUM-BASED DISTILLERS GRAINS IN DIETS FOR NURSERY AND FINISHING PIGS
 Swine Dy 1996 USE OF SORGHUM-BASED DISTILLERS GRAINS IN DIETS FOR NURSERY AND FINISHING PIGS B. W. Senne, J. D. Hncock, I. Mvromichlis, S. L. Johnston, P. S. Sorrell, I. H. Kim, nd R. H. Hines Summry Two
Swine Dy 1996 USE OF SORGHUM-BASED DISTILLERS GRAINS IN DIETS FOR NURSERY AND FINISHING PIGS B. W. Senne, J. D. Hncock, I. Mvromichlis, S. L. Johnston, P. S. Sorrell, I. H. Kim, nd R. H. Hines Summry Two
Glomerular Function in Pima Indians with Noninsulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus of Recent Onset
 Glomerulr Function in Pim Indins with Noninsulin-dependent Dibetes Mellitus of Recent Onset Bryn D. Myers,* Robert G. Nelson,* George W. Willims,* Peter H. Bennett,$ Sterling A. Hrdy,* Richrd L. Berg,*
Glomerulr Function in Pim Indins with Noninsulin-dependent Dibetes Mellitus of Recent Onset Bryn D. Myers,* Robert G. Nelson,* George W. Willims,* Peter H. Bennett,$ Sterling A. Hrdy,* Richrd L. Berg,*
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
of comorbid conditions, interventions Diagnosis and treatment, treatment reduction of risk factors for CVD to slow disease progression,
 Tble 5.1. NKF Clssifiction of Chronic Kidney Disese nd Clinicl Fetures Stge Description GFR (ml/ min/1.73 m 2 ) U.S. Prevlence, b # Affected (%) Clinicl Fetures Action Pln c At incresed risk for CKD >60
Tble 5.1. NKF Clssifiction of Chronic Kidney Disese nd Clinicl Fetures Stge Description GFR (ml/ min/1.73 m 2 ) U.S. Prevlence, b # Affected (%) Clinicl Fetures Action Pln c At incresed risk for CKD >60
Influence of the vagus nerve upon the reflex control of the lower oesophageal sphincter
 Gut, 1984, 2, 23-28 Influence of the vgus nerve upon the reflex control of the lower oesophgel sphincter L OGILVIE* ND M TKINSON From University Hospitl, Queen's Medicl Centre, Nottinghm SUMMRY In 24 control
Gut, 1984, 2, 23-28 Influence of the vgus nerve upon the reflex control of the lower oesophgel sphincter L OGILVIE* ND M TKINSON From University Hospitl, Queen's Medicl Centre, Nottinghm SUMMRY In 24 control
