How to Reduce CVD Complications in Diabetes?
|
|
|
- Tyler Curtis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 How to Reduce CVD Complications in Diabetes? Chaicharn Deerochanawong M.D. Diabetes and Endocrinology Unit Department of Medicine Rajavithi Hospital, Ministry of Public Health
2 Framingham Heart Study 30-Year Follow-up CVD Events in Patients With Diabetes Compared with non-diabetes Subjects (Ages 35-64) RR Men Women Total CVD CHD Cardiac failure Intermittent Claudication Stroke Wilson PWF. Diabetes and Vascular Disease. Oxford;1992
3 Mortality Rate is Twice as Great in Patients with Diabetes 35 Ratio 2.5 Ratio 2.2 Ratio 2.1 Mortality rate (deaths per 1,000 patient years) Control Diabetes 0 Whitehall Study Paris Prospective Helsinki Study Policemen Study Balkau B, et al. Lancet 1997; 350:1680.
4 Causes of Mortality in Patients With Diabetes Malignant Neoplasms 13% Pneumonia/ Influenza 13% Other 4% 5% 10% Heart Disease 55% Diabetes Cerebrovascular Disease Geiss LS, et al. In: Diabetes in America. 2nd ed. NIH Publication No :
5 Type 2 Diabetes and CHD : 7 Year Incidence of Fatal/Nonfatal MI P<0.001 (East West Study) Nondiabetic N=1373 Diabetic N=1059 P< No prior M I M I No Prior M I M I Haffner.NEJM1998:339;229-34
6 Diabetes, Metabolic syndrome and prevalence of CHD 25 CHD prevalence % 13.9% 7.5% 19.2% 0 No MS / No DM MS / No DM DM / No MS DM / MS % of population 54.2% 28.7% 2.3% 14.6% Charles M. Diabetes 2003;52:1210-4
7 Diabetes & Cardiovascular Risks 65% of people with diabetes die from heart disease or stroke. 1 3X more cardiovascular mortality in type 2 DM 2 Risk for heart attack 2, 3 Middle-aged patients with type 2 DM = Patients without DM with history of heart attack. Heart attacks occur at an earlier age in people with DM 4 1.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Diabetes Surveillance Report, Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, Haffner SM, Lehto S, Ronnemaa T, Pyorala K, Laakso M. N Engl J Med 1998; 339: Grundy SM, Benjamin IJ, Burke GL, et al. Circulation 1999; 100: Wingard DL, Barrett-Connor E. Heart disease and diabetes. In: National Diabetes Data Group, ed. Diabetes in America. Washington, DC: National Institutes of Health, NIDDK, NIH publication no , 1995.
8 Why Type 2 Diabetes has Excessive Premature Atherosclerosis? Hyperglycemia : AGE proteins, Oxidative stress Insulin Resistance Atherogenic dyslipidemia Hypertension Haemostatic abnormalities
9 How to reduce cardiovascular complications in diabetes? Holistic treatment Or Multiple Risks Management
10 Goals of Therapy in Diabetes Glycemic goal Blood pressure goal ACEI in albuminuria or CVD or CVD risk factor Lipid goal Aspirin in selected cases Quit smoking Approach desriable body weight
11 Glycemic Control - Intervention Studies Micro and Macrovascular Complications Reduction in risk with intensive therapy Retinopathy Nephropathy Neuropathy Cardiovascular disease DCCT (Type 1) 63% 54% 60% 41%* (p=0.06) Kumamoto (Type 2) 69% 70% - - UKPDS (Type 2) 17-21% 24-33% - 16%* (p=0.052) DCCT Research Group. N Engl J Med ;329: Ohkubo Y, et al. Diabetes Res Clin Pract ;28: UKPDS 33: Lancet 1998; 352,
12 UKPDS Risk Reduction:Glucose Control Study Mean HbA1c 7.8% vs 8.5% and FU PSM 5yr = 8.0% During Study Including PSM Any DM related end pt. 12%, p= %, p=0.033 DM related death 10%, p= %, p=0.028 All cause mortality 6%, p= %, p=0.071 Myocardial infarction 16%, p= %, p=0.042 Stroke +11%, p= %, p=0.660 PVD 35%, p= %, p=0.089 Microvascular dis. 25%, p= %. P=0.001
13 Goals of Glycemic Control ADA ACCE EASD IDF HbA1c ( %) < 7.0% 6.5% 6.5% 6.5% FPG (preprandial( preprandial)< Postprandial <
14 Is Lower the Better of Glycemic control in Diabetes? There is no lower limit of HbA1c at which further lowering does not reduce risk of complications, at the risk of increased hypoglycemia The risks and benefits of an HbA1c goal of < 6% are currently tested in type 2 diabetes ( ACCORD )
15 Compare Met vs Intens. vs Conv. in Overweight pts. Any diabetes related endpoint Metformin Intensive Diabetes related deaths Metformin Intensive All cause mortality Metformin Intensive Myocardial infarction Metformin Intensive M v Int RR p p= p=0.11 p=0.021 p= RR (95% CI) Favours metformin or intensive favours conventional
16 Goals of Therapy in Diabetes Glycemic goal Blood pressure goal ACEI in albuminuria or CVD or CVD risk factor Lipid goal Aspirin in selected cases Quit smoking Approach desriable body weight
17 The goal of BP in DM is < 130/80mmHg
18 Major CV events in patients with diabetes at randomisation in relation to target blood pressure groups Major CV events/ 1000 patient years p=0.005 for trend HOT STUDY < 90 < 85 < 80 Target DBP mm Hg
19 Association of Systolic BP and Cardiovascular Death in Type 2 DM Cardiovascular 175 mortality rate/10, person-yr Nondiabetic Diabetic < > 200 Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) Stamler J et al. Diabetes Care 1993;16:
20 Number of Antihypertensive Drugs Therapy Requirement in UKPDS number of antihypertensive agents None one two > two 100 LessTight Control Policy Tight Control Policy % of patients Years from randomisation
21 Effects of Antihypertensive Drugs on Cardiovascular dis.. in Diabetic Patients Comparative drugs in Diabetes patients ABCD and FACET : ACEI vs DCCB CAPP : ACEI vs conventional UKPDS : ACEI vs Beta Blocker STOP2 : ACEI vs DCCB vs convent. LIFE : ARB vs Beta Blocker ALLHAT : Diuretic vs ACEI vs DCCB RENALL : ARB vs convent. IDNT : ARB vs CCB
22 Goals of Therapy in Diabetes Glycemic goal Blood pressure goal ACEI in albuminuria or CVD or CVD risk factor Lipid goal Aspirin in selected cases Quit smoking Approach desriable body weight
23 MICRO-HOPE or HOPE STUDY DIABETES SUBGROUP ( Lancet 2000;355: )
24 MICRO-HOPE - Objective Does the addition of ramipril and/or vitamin E to the ongoing medication of 'high-risk' diabetic patients reduce the risk of renal and CV events?
25 METHODS 3,577 people with diabetes ( 98% type 2 ) Age > 55 years Had a previous cardiovascular event or At least one other cardiovascular risk factor 1. TC > 200 mg/dl, HDL < 35 mg/dl 2. Hypertension (>160/90) 3. Known microalbuminuria 4. Current smoking No clinical proteinuria, heart failure or low EF Randomly assigned Ramipril 10 mg or placebo
26 MICRO-HOPE (ramipril( ramipril) - baseline characteristics Variable Ramipril (n = 1808) Placebo (n = 1769) Men/women 1112 (62%)/696 (38%) 1143 (65%)/626 (35%) Age (years)* SBP/DBP (mm Hg)* ± 19.5/79.3 BMI (kg/m2) * Waist-hip ratio* Waist circumference (cm)* History of CAD 1046 (58%) 1093 (62%) Stroke/endarterectomy 124 (7%) 150 (8%) PVD 311 (17%) 361 (20%) No history of CV disease 604 (33%) 515 (29%) Hypertension 1045 (58%) 951 (54%) Type 2 diabetes 1774 (98%) 1722 (97%) Duration of diabetes (years) * 11.1 ± ± 10.7 Current smokers 274 (15%) 270 (15%) Elevated total cholesterol level 1174 (65%) 1161 (66%) Serum creatinine ([m]mol/l)* MA 553 (31%) 587 (33%)
27 MicroHOPE: : Benefit of Ramipril in DM patient Effects Beyond Baseline Therapy %RR Stroke 33%* CV Death 37%* Nonfatal MI 22%* Overt Kidney Disease 24% * P =
28 0.16 MICRO-HOPE (ramipril( ramipril) All causes mortality RRR 24% p= Placebo Placebo Kaplan-Meier rates Ramipril HOPE Study Investigators Lancet 2000;355: Duration of follow up (days)
29
30 Goals of Therapy in Diabetes Glycemic goal Blood pressure goal ACEI in albuminuria or CVD or CVD risk factor Lipid goal Aspirin in selected cases Quit smoking Approach desriable body weight
31 Lipid Goals NCEP & ADA 2007 LDL-C < 100 mg/dl ( < 70 mg/dl in CAD pts. ) Triglycerides < 150 mg/dl Non HDL-C < 130 mg/dl HDL-C > 40 mg/dl
32 ACP 2004 Recommendations Do not recommend a specific LDL-C target level No strong evidence support exact thresholds for initiating treatment or treating to specific target LDL-C or TC in type 2 diabetic patients HPS and CARDS study showed benefit of statin in diabetic patients Ann Intern Med 2004;140:650-8
33 Treatment Effect on the Primary Endpoint by Subgroup Subgroup* Placebo** Atorva** Hazard Ratio Risk Reduction (CI) LDL-C (9.5) 44 (6.1) 38% (9-58) LDL-C < (8.5) 39 (5.6) 37% (6-58) p=0.96 HDL-C (8.4) 36 (5.2) 41% (11-61) HDL-C < (9.6) 47 (6.4) 35% (5-55) p=0.71 Trig (9.6) 40 (5.5) 44% (18-62) Trig. < (8.4) 43 (6.1) 29% (-5-52) p= * units in mmol/l (mg/dl) ** N (% of randomised) Favours Atorvastatin Favours Placebo
34 ACP 2004 Recommendations All adults with type 2 diabetes and CAD should receive statins All adults with type 2 diabetes and other cardiovascular risk factors, including HT, smoking, LVH, age > 55 yr, should receive statins Statin should take at least moderate dose Patients with low LDL-C and low HDL-C, fibrate may be used as first line therapy Ann Intern Med 2004;140:650-8
35 Goals of Therapy in Diabetes Glycemic goal Blood pressure goal ACEI in albuminuria or CVD or CVD risk factor Lipid goal Aspirin in selected cases Quit smoking Approach desriable body weight
36 Aspirin therapy in Diabetes Use aspirin therapy ( mg/day ) in all adult patients with diabetes and macrovascular disease. Consider beginning aspirin therapy ( mg/dl ) for primary prevention in patients > 40 years of age with diabetes and one or more other cardiovascular risk factors Patients at ages below 30 years, when the risk of CVD is low, there is no evidence of benefit of aspirin for primary prevention
37 Goals of Therapy in Diabetes Glycemic goal Blood pressure goal ACEI in albuminuria or CVD or CVD risk factor Lipid goal Aspirin in selected cases Quit smoking Approach desriable body weight
38 INTERHEART:Risk of AMI with Multiple Risk Factors OR (99% CI) Smk DM HTN APoB/A all4 +O +PS All RFs
39 INTERHEART: Decreased Risk of AMI with Avoidance of Smoking; Daily Fruits/Veg Veg, Reg Phys Activity & Alcohol OR (99% CI) no smk Frt/Veg Exer Alc Nosmk+fvg +exer +alc
40 Modest weight loss has beneficial health effects Modest weight loss of >5% in obese individuals with type 2 diabetes, hypertension or hyperlipidaemia resulted in: Improved glycaemic control Reduced blood pressure Improved lipid profile 20% reduction in premature mortality in overweight women with obesity-related health conditions Goldstein DJ. Int J Obesity 1991; 16:
41 Multifactorial Intervention and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 DM ( STENO 2 ) Peter Gaede et al. NEJM 2003; 348:
42 STENO 2 Randomized study to evaluate effect on CVD of an intensified, targeted, multifactorial intervention in type 2 diabetes with microalbuminuria 160 patients follow up means 7.8 years Interventions: dietary, exercise, ACEI, vitamin mineral supplement, 150 mg ASA, tight glycemic, BP and lipid control
43 Treatment Goals Variable Conventional Therapy Intensive Therapy Systolic blood pressure (mmhg) <160 <135 <145 <130 Diastolic blood pressure (mmhg) <95 <85 <85 <80 Glycosylated hemoglobin (%) <7.5 <6.5 <6.5 <6.5 Fasting serum total cholesterol (mg/dl) <250 <190 <190 <175 Fasting serum triglycerides (mg/dl) <195 <180 <150 <150 Treatment with ACE inhibitor irrespective of blood pressure Aspirin therapy No Yes Yes Yes For patients with known ischemia Yes Yes Yes Yes For patients peripheral vascular dis No No Yes Yes For patients without coronary heart disease or peripheral vascular disease No No No Yes
44 Percentage of patients who reached the intensive-treatment goals at a mean of 7.8 yr Patients % P <0.001 intensive therapy P =0.19 P =0.001 Conventional therapy P = P= G Hb < 6.5% Cholesterol <175 mg/dl Triglycerides <150 mg/dl Systolic BP <130 mmhg Diastolic BP <80 mmhg
45 Primary Composite End Point (%) No. at Risk Conventional80 therapy Intensive 80 therapy P=0.007 Hazard ratio = 0.47 NNT = 5 patients to prevent 1 CVD event Months of Follow-up Conventional therapy Intensive therapy
46 STENO 2 A long term, targerted, intensive intervention involving multiple risk factors with continued patient education and motivation reduces the risk of both cardiovascular and microvascular events by about 50 percent among patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria Such patients may represent about 1/3 of the population of patients with type 2 DM
47 Conclusions CVD is very common in diabetes and is the leading cause of death in type 2 diabetes To reduce the cardiovascular complications of diabetes need long term targeted intensive multiple risk factors intervention ACEI, Ramipril, proved to reduce CVD complications in diabetes with CVD or with CVD risk factor
48
Diabetes Mellitus: A Cardiovascular Disease
 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cardiovascular Disease Nestoras Mathioudakis, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, & Metabolism September 30, 2013 1 The ABCs of cardiovascular
Diabetes Mellitus: A Cardiovascular Disease Nestoras Mathioudakis, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, & Metabolism September 30, 2013 1 The ABCs of cardiovascular
Eugene Barrett M.D., Ph.D. University of Virginia 6/18/2007. Diagnosis and what is it Glucose Tolerance Categories FPG
 Diabetes Mellitus: Update 7 What is the unifying basis of this vascular disease? Eugene J. Barrett, MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine and Pediatrics Director, Diabetes Center and GCRC Health System
Diabetes Mellitus: Update 7 What is the unifying basis of this vascular disease? Eugene J. Barrett, MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine and Pediatrics Director, Diabetes Center and GCRC Health System
The Metabolic Syndrome: Is It A Valid Concept? YES
 The Metabolic Syndrome: Is It A Valid Concept? YES Congress on Diabetes and Cardiometabolic Health Boston, MA April 23, 2013 Edward S Horton, MD Joslin Diabetes Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA
The Metabolic Syndrome: Is It A Valid Concept? YES Congress on Diabetes and Cardiometabolic Health Boston, MA April 23, 2013 Edward S Horton, MD Joslin Diabetes Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA
Treatment to reduce cardiovascular risk: multifactorial management
 Treatment to reduce cardiovascular risk: multifactorial management Matteo Anselmino, MD PhD Assistant Professor San Giovanni Battista Hospital Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine University
Treatment to reduce cardiovascular risk: multifactorial management Matteo Anselmino, MD PhD Assistant Professor San Giovanni Battista Hospital Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine University
Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease. Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010
 Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010 Relationships Between Diabetes and Ischemic Heart Disease Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Different Categories
Ischemic Heart and Cerebrovascular Disease Harold E. Lebovitz, MD, FACE Kathmandu November 2010 Relationships Between Diabetes and Ischemic Heart Disease Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Different Categories
The Diabetes Link to Heart Disease
 The Diabetes Link to Heart Disease Anthony Abe DeSantis, MD September 18, 2015 University of WA Division of Metabolism, Endocrinology and Nutrition Oswald Toosweet Case #1 68 yo M with T2DM Diagnosed DM
The Diabetes Link to Heart Disease Anthony Abe DeSantis, MD September 18, 2015 University of WA Division of Metabolism, Endocrinology and Nutrition Oswald Toosweet Case #1 68 yo M with T2DM Diagnosed DM
Disclosures. Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management. Learning Objectives. Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
 Disclosures Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Tony Hampton, MD, MBA Medical Director Advocate Aurora Operating System Advocate Aurora Healthcare Downers Grove, IL No conflicts or disclosures
Disclosures Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Tony Hampton, MD, MBA Medical Director Advocate Aurora Operating System Advocate Aurora Healthcare Downers Grove, IL No conflicts or disclosures
Cedars Sinai Diabetes. Michael A. Weber
 Cedars Sinai Diabetes Michael A. Weber Speaker Disclosures I disclose that I am a Consultant for: Ablative Solutions, Boston Scientific, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Forest, Medtronics, Novartis, ReCor
Cedars Sinai Diabetes Michael A. Weber Speaker Disclosures I disclose that I am a Consultant for: Ablative Solutions, Boston Scientific, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Forest, Medtronics, Novartis, ReCor
Diabetes Guidelines in View of Recent Clinical Trials Are They Still Applicable?
 Diabetes Guidelines in View of Recent Clinical Trials Are They Still Applicable? Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of
Diabetes Guidelines in View of Recent Clinical Trials Are They Still Applicable? Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of
Treating Hypertension in Individuals with Diabetes
 Treating Hypertension in Individuals with Diabetes Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or by any
Treating Hypertension in Individuals with Diabetes Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or by any
A Fork in the Road: Navigating Through New Terrain
 A Fork in the Road: Navigating Through New Terrain Carol Hatch Wysham, MD Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine University of Washington School of Medicine Section Head, Rockwood Center for Diabetes
A Fork in the Road: Navigating Through New Terrain Carol Hatch Wysham, MD Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine University of Washington School of Medicine Section Head, Rockwood Center for Diabetes
Optimizing risk assessment of total cardiovascular risk What are the tools? Lars Rydén Professor Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden
 Optimizing risk assessment of total cardiovascular risk What are the tools? Lars Rydén Professor Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Cardiovascular Disease Prevention (CVD) Three Strategies for CVD
Optimizing risk assessment of total cardiovascular risk What are the tools? Lars Rydén Professor Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Cardiovascular Disease Prevention (CVD) Three Strategies for CVD
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
 ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
The Clinical Unmet need in the patient with Diabetes and ACS
 The Clinical Unmet need in the patient with Diabetes and ACS Professor Kausik Ray (UK) BSc(hons), MBChB, MD, MPhil, FRCP (lon), FRCP (ed), FACC, FESC, FAHA Diabetes is a global public health challenge
The Clinical Unmet need in the patient with Diabetes and ACS Professor Kausik Ray (UK) BSc(hons), MBChB, MD, MPhil, FRCP (lon), FRCP (ed), FACC, FESC, FAHA Diabetes is a global public health challenge
Diabete: terapia nei pazienti a rischio cardiovascolare
 Diabete: terapia nei pazienti a rischio cardiovascolare Giorgio Sesti Università Magna Graecia di Catanzaro Cardiovascular mortality in relation to diabetes mellitus and a prior MI: A Danish Population
Diabete: terapia nei pazienti a rischio cardiovascolare Giorgio Sesti Università Magna Graecia di Catanzaro Cardiovascular mortality in relation to diabetes mellitus and a prior MI: A Danish Population
Complications of Diabetes: Screening and Prevention. Dr Martin McIntyre Consultant Physician Royal Alexandra Hospital Paisley
 Complications of Diabetes: Screening and Prevention Dr Martin McIntyre Consultant Physician Royal Alexandra Hospital Paisley Diabetic Complications Microvascular: Retinopathy Nephropathy Neuropathy Macrovascular:
Complications of Diabetes: Screening and Prevention Dr Martin McIntyre Consultant Physician Royal Alexandra Hospital Paisley Diabetic Complications Microvascular: Retinopathy Nephropathy Neuropathy Macrovascular:
Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications
 Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications Estimates of Diagnosed Diabetes in Adults, 2005 Alka M. Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine UCSF, Primary Care CME October
Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications Estimates of Diagnosed Diabetes in Adults, 2005 Alka M. Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine UCSF, Primary Care CME October
ADVANCE post trial ObservatioNal Study
 Hot Topics in Diabetes 50 th EASD, Vienna 2014 ADVANCE post trial ObservatioNal Study Sophia Zoungas The George Institute The University of Sydney Rationale and Study Design Sophia Zoungas The George Institute
Hot Topics in Diabetes 50 th EASD, Vienna 2014 ADVANCE post trial ObservatioNal Study Sophia Zoungas The George Institute The University of Sydney Rationale and Study Design Sophia Zoungas The George Institute
Reducing CVD globally through combination approaches to prevention: the polypill. Salim Yusuf
 Reducing CVD globally through combination approaches to prevention: the polypill. Salim Yusuf Disclosure None Polypill & CVD Prevention 1. Why do we need a polypill? 2. What components in the polypill?
Reducing CVD globally through combination approaches to prevention: the polypill. Salim Yusuf Disclosure None Polypill & CVD Prevention 1. Why do we need a polypill? 2. What components in the polypill?
Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Denise M. Kolanczyk, PharmD, BCPS-AQ Cardiology
 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Denise M. Kolanczyk, PharmD, BCPS-AQ Cardiology Disclosures In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American Diabetes Association requires the
Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Denise M. Kolanczyk, PharmD, BCPS-AQ Cardiology Disclosures In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American Diabetes Association requires the
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour
 ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
CV Risk Management in Diabetes Mellitus
 CV Risk Management in Diabetes Mellitus J R Minkoff MD, FACP Endocrinology Clinical Professor of Family and Community Medicine University of California, San Francisco Mr. B 40 y/o Latino male c/o fatigue,
CV Risk Management in Diabetes Mellitus J R Minkoff MD, FACP Endocrinology Clinical Professor of Family and Community Medicine University of California, San Francisco Mr. B 40 y/o Latino male c/o fatigue,
Macrovascular Residual Risk. What risk remains after LDL-C management and intensive therapy?
 Macrovascular Residual Risk What risk remains after LDL-C management and intensive therapy? Defining Residual Vascular Risk The risk of macrovascular events and microvascular complications which persists
Macrovascular Residual Risk What risk remains after LDL-C management and intensive therapy? Defining Residual Vascular Risk The risk of macrovascular events and microvascular complications which persists
Metformin should be considered in all patients with type 2 diabetes unless contra-indicated
 November 2001 N P S National Prescribing Service Limited PPR fifteen Prescribing Practice Review PPR Managing type 2 diabetes For General Practice Key messages Metformin should be considered in all patients
November 2001 N P S National Prescribing Service Limited PPR fifteen Prescribing Practice Review PPR Managing type 2 diabetes For General Practice Key messages Metformin should be considered in all patients
Cardiovascular Management of a Patient with Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Management of a Patient with Diabetes Dr Jeremy Krebs Clinical Leader Endocrinology and Diabetes Wellington Hospital Summary People with diabetes take a lot of medication Compliance and
Cardiovascular Management of a Patient with Diabetes Dr Jeremy Krebs Clinical Leader Endocrinology and Diabetes Wellington Hospital Summary People with diabetes take a lot of medication Compliance and
Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes
 VBWG Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes Nicola Abate, M.D., F.N.L.A. Professor and Chief Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston, Texas Coronary
VBWG Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes Nicola Abate, M.D., F.N.L.A. Professor and Chief Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston, Texas Coronary
The Burden of the Diabetic Heart
 The Burden of the Diabetic Heart Dr. Ghaida Kaddaha (MBBS, MRCP-UK, FRCP-london) Diabetes Unit Rashid Hospital Dubai U.A.E Risk of CVD in Diabetes Morbidity and mortality from CVD is 2-4 fold higher than
The Burden of the Diabetic Heart Dr. Ghaida Kaddaha (MBBS, MRCP-UK, FRCP-london) Diabetes Unit Rashid Hospital Dubai U.A.E Risk of CVD in Diabetes Morbidity and mortality from CVD is 2-4 fold higher than
Hypertension Management in Diabetic Patients
 Hypertension Management in Diabetic Patients Park, Chang G, MD, PhD Cardiovascular Center, Guro Hospital, Korea University Medical School Contents (Treatment of 2 Cases) Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Hypertension
Hypertension Management in Diabetic Patients Park, Chang G, MD, PhD Cardiovascular Center, Guro Hospital, Korea University Medical School Contents (Treatment of 2 Cases) Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Hypertension
Diabetic Dyslipidemia
 Diabetic Dyslipidemia Dr R V S N Sarma, M.D., (Internal Medicine), M.Sc., (Canada), Consultant Physician Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a significant cause of illness, disability, and death among individuals
Diabetic Dyslipidemia Dr R V S N Sarma, M.D., (Internal Medicine), M.Sc., (Canada), Consultant Physician Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a significant cause of illness, disability, and death among individuals
The target blood pressure in patients with diabetes is <130 mm Hg
 Controversies in hypertension, About Diabetes diabetes and and metabolic Cardiovascular syndrome Risk ESC annual congress August 29, 2011 The target blood pressure in patients with diabetes is
Controversies in hypertension, About Diabetes diabetes and and metabolic Cardiovascular syndrome Risk ESC annual congress August 29, 2011 The target blood pressure in patients with diabetes is
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. A Fork in the Road: Navigating Through New Terrain. Diabetes Standards of Care Then and Now
 Slide 1 A Fork in the Road: Navigating Through New Terrain Carol Hatch Wysham, MD Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine University of Washington School of Medicine Section Head, Rockwood Center for
Slide 1 A Fork in the Road: Navigating Through New Terrain Carol Hatch Wysham, MD Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine University of Washington School of Medicine Section Head, Rockwood Center for
Cardiovascular Risk Reduction and Other Co-Morbidities in Type 2 Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Risk Reduction and Other Co-Morbidities in Type 2 Diabetes Following this presentation, you will be able to: Describe the relationship between major CV risk factors and CVD outcomes Select
Cardiovascular Risk Reduction and Other Co-Morbidities in Type 2 Diabetes Following this presentation, you will be able to: Describe the relationship between major CV risk factors and CVD outcomes Select
Update on CVD and Microvascular Complications in T2D
 Update on CVD and Microvascular Complications in T2D Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of Miami Miller School of Medicine
Update on CVD and Microvascular Complications in T2D Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of Miami Miller School of Medicine
Prevention And Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy. MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 3/2006 Dr Stephen Chew Tec Huan
 Prevention And Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 3/2006 Dr Stephen Chew Tec Huan Prevention Tight glucose control reduces the development of diabetic nephropathy Progression
Prevention And Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 3/2006 Dr Stephen Chew Tec Huan Prevention Tight glucose control reduces the development of diabetic nephropathy Progression
John J.P. Kastelein MD PhD Professor of Medicine Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medial Center / University of Amsterdam
 Latest Insights from the JUPITER Study John J.P. Kastelein MD PhD Professor of Medicine Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medial Center / University of Amsterdam Inflammation, hscrp, and Vascular Prevention
Latest Insights from the JUPITER Study John J.P. Kastelein MD PhD Professor of Medicine Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medial Center / University of Amsterdam Inflammation, hscrp, and Vascular Prevention
Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients
 2012 international Conference on Diabetes and metabolism (ICDM) Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients Nan Hee Kim, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University
2012 international Conference on Diabetes and metabolism (ICDM) Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients Nan Hee Kim, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University
American Diabetes Association 2018 Guidelines Important Notable Points
 American Diabetes Association 2018 Guidelines Important Notable Points The Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018 by ADA include the most current evidencebased recommendations for diagnosing and treating
American Diabetes Association 2018 Guidelines Important Notable Points The Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018 by ADA include the most current evidencebased recommendations for diagnosing and treating
American Academy of Insurance Medicine
 American Academy of Insurance Medicine October 2012 Dr. Alison Moy Liberty Mutual Dr. John Kirkpatrick Thrivent Financial for Lutherans 1 59 year old male, diagnosed with T2DM six months ago Nonsmoker
American Academy of Insurance Medicine October 2012 Dr. Alison Moy Liberty Mutual Dr. John Kirkpatrick Thrivent Financial for Lutherans 1 59 year old male, diagnosed with T2DM six months ago Nonsmoker
Complications of Diabetes: Screening and Prevention
 Complications of Diabetes: Screening and Prevention Dr Steve Cleland Consultant Physician GGH and QEUH Diabetes Staff Education Course June 17 Diabetic Complications Microvascular: Retinopathy Nephropathy
Complications of Diabetes: Screening and Prevention Dr Steve Cleland Consultant Physician GGH and QEUH Diabetes Staff Education Course June 17 Diabetic Complications Microvascular: Retinopathy Nephropathy
Established Risk Factors for Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
 Getting Patients to Make Small Lifestyle Changes That Result in SIGNIFICANT Improvements in Health - Prevention of Diabetes and Obesity for Better Health Maureen E. Mays, MD, MS, FACC Director ~ Portland
Getting Patients to Make Small Lifestyle Changes That Result in SIGNIFICANT Improvements in Health - Prevention of Diabetes and Obesity for Better Health Maureen E. Mays, MD, MS, FACC Director ~ Portland
Diabetes and the Heart
 Diabetes and the Heart Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 6, 2012 Outline Screening for diabetes in patients with CAD Screening for CAD in patients with
Diabetes and the Heart Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 6, 2012 Outline Screening for diabetes in patients with CAD Screening for CAD in patients with
Causes of death in Diabetes
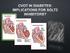 Rates of CV events in Diabetes patients Respiratory4.2 Cancer 7.6 Diabetes 1.3 CV disease 17.3 Causes of death in Diabetes 250 200 150 100 50 0 per 10,000 person-years 97 151 243 Framingham 5 X increase
Rates of CV events in Diabetes patients Respiratory4.2 Cancer 7.6 Diabetes 1.3 CV disease 17.3 Causes of death in Diabetes 250 200 150 100 50 0 per 10,000 person-years 97 151 243 Framingham 5 X increase
T. Suithichaiyakul Cardiomed Chula
 T. Suithichaiyakul Cardiomed Chula The cardiovascular (CV) continuum: role of risk factors Endothelial Dysfunction Atherosclerosis and left ventricular hypertrophy Myocardial infarction & stroke Endothelial
T. Suithichaiyakul Cardiomed Chula The cardiovascular (CV) continuum: role of risk factors Endothelial Dysfunction Atherosclerosis and left ventricular hypertrophy Myocardial infarction & stroke Endothelial
Cardiovascular Risk Reduction and Other Co-morbidities in Type 2 Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Risk Reduction and Other Co-morbidities in Type 2 Diabetes Following this presentation, you will be able to: Describe the relationship between major CV risk factors and CVD outcomes Select
Cardiovascular Risk Reduction and Other Co-morbidities in Type 2 Diabetes Following this presentation, you will be able to: Describe the relationship between major CV risk factors and CVD outcomes Select
Diabetic Nephropathy. Objectives:
 There are, in truth, no specialties in medicine, since to know fully many of the most important diseases a man must be familiar with their manifestations in many organs. William Osler 1894. Objectives:
There are, in truth, no specialties in medicine, since to know fully many of the most important diseases a man must be familiar with their manifestations in many organs. William Osler 1894. Objectives:
1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease. albuminuria
 1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease albuminuria Cardio-renal continuum REGRESS Target organ damage Asymptomatic CKD New risk factors Atherosclerosis Target organ damage
1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease albuminuria Cardio-renal continuum REGRESS Target organ damage Asymptomatic CKD New risk factors Atherosclerosis Target organ damage
Review. Hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia and hypertension in older people with diabetes: the benefits of cardiovascular risk reduction
 Review Hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia and hypertension in older people with diabetes: the benefits of cardiovascular risk reduction Diabetes mellitus is increasingly recognized as an essentially vascular
Review Hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia and hypertension in older people with diabetes: the benefits of cardiovascular risk reduction Diabetes mellitus is increasingly recognized as an essentially vascular
Macrovascular Disease in Diabetes
 Macrovascular Disease in Diabetes William R. Hiatt, MD Professor of Medicine/Cardiology University of Colorado School of Medicine President, CPC Clinical Research Conflicts CPC Clinical Research (University-based
Macrovascular Disease in Diabetes William R. Hiatt, MD Professor of Medicine/Cardiology University of Colorado School of Medicine President, CPC Clinical Research Conflicts CPC Clinical Research (University-based
BRFSS, , *BMI
 The Epidemic of Obesity, Diabetes, and the Metabolic Syndrome Holly Novak, MD, FACC Obesity Trends* Among US Adults BRFSS, 1985 BRFSS=Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. *Body Mass Index (BMI)
The Epidemic of Obesity, Diabetes, and the Metabolic Syndrome Holly Novak, MD, FACC Obesity Trends* Among US Adults BRFSS, 1985 BRFSS=Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. *Body Mass Index (BMI)
The Latest Generation of Clinical
 The Latest Generation of Clinical Guidelines: HTN and HLD Dave Brackett Clinical Guideline Purpose Uniform approach Awareness of key details Diagnosis Treatment Monitoring Evidence based approach Inform
The Latest Generation of Clinical Guidelines: HTN and HLD Dave Brackett Clinical Guideline Purpose Uniform approach Awareness of key details Diagnosis Treatment Monitoring Evidence based approach Inform
Dyslipidaemia. Is there any new information? Dr. A.R.M. Saifuddin Ekram
 Dyslipidaemia Is there any new information? Dr. A.R.M. Saifuddin Ekram PhD,FACP,FCPS(Medicine) Professor(c.c.) & Head Department of Medicine Rajshahi Medical College Rajshahi-6000 New features of ATP III
Dyslipidaemia Is there any new information? Dr. A.R.M. Saifuddin Ekram PhD,FACP,FCPS(Medicine) Professor(c.c.) & Head Department of Medicine Rajshahi Medical College Rajshahi-6000 New features of ATP III
Metabolic Syndrome: Why Should We Look For It?
 021-CardioCase 29/05/06 15:04 Page 21 Metabolic Syndrome: Why Should We Look For It? Dafna Rippel, MD, MHA and Andrew Ignaszewski, MD, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Andy s fatigue Andy, 47, comes to you
021-CardioCase 29/05/06 15:04 Page 21 Metabolic Syndrome: Why Should We Look For It? Dafna Rippel, MD, MHA and Andrew Ignaszewski, MD, FRCPC CardioCase presentation Andy s fatigue Andy, 47, comes to you
Case Presentation. Rafael Bitzur The Bert W Strassburger Lipid Center Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer
 Case Presentation Rafael Bitzur The Bert W Strassburger Lipid Center Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer Case Presentation 50 YO man NSTEMI treated with PCI 1 month ago Medical History: Obesity: BMI 32,
Case Presentation Rafael Bitzur The Bert W Strassburger Lipid Center Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer Case Presentation 50 YO man NSTEMI treated with PCI 1 month ago Medical History: Obesity: BMI 32,
Why is Earlier and More Aggressive Treatment of T2 Diabetes Better?
 Blood glucose (mmol/l) Why is Earlier and More Aggressive Treatment of T2 Diabetes Better? Disclosures Dr Kennedy has provided CME, been on advisory boards or received travel or conference support from:
Blood glucose (mmol/l) Why is Earlier and More Aggressive Treatment of T2 Diabetes Better? Disclosures Dr Kennedy has provided CME, been on advisory boards or received travel or conference support from:
2003 World Health Organization (WHO) / International Society of Hypertension (ISH) Statement on Management of Hypertension.
 2003 World Health Organization (WHO) / International Society of Hypertension (ISH) Statement on Management of Hypertension Writing Group: Background Hypertension worldwide causes 7.1 million premature
2003 World Health Organization (WHO) / International Society of Hypertension (ISH) Statement on Management of Hypertension Writing Group: Background Hypertension worldwide causes 7.1 million premature
Eyes on Korean Data: Lipid Management in Korean DM Patients
 Eyes on Korean Data: Lipid Management in Korean DM Patients ICDM Luncheon Symposium Sung Rae Kim MD PhD Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The Catholic University of Korea Causes of Death in People
Eyes on Korean Data: Lipid Management in Korean DM Patients ICDM Luncheon Symposium Sung Rae Kim MD PhD Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The Catholic University of Korea Causes of Death in People
Hypertension in 2015: SPRINT-ing ahead of JNC-8. MAJ Charles Magee, MD MPH FACP Director, WRNMMC Hypertension Clinic
 Hypertension in 2015: SPRINT-ing ahead of JNC-8 MAJ Charles Magee, MD MPH FACP Director, WRNMMC Hypertension Clinic Conflits of interest? None Disclaimer The opinions contained herein are not to be considered
Hypertension in 2015: SPRINT-ing ahead of JNC-8 MAJ Charles Magee, MD MPH FACP Director, WRNMMC Hypertension Clinic Conflits of interest? None Disclaimer The opinions contained herein are not to be considered
( Diabetes mellitus, DM ) ( Hyperlipidemia ) ( Cardiovascular disease, CVD )
 005 6 69-74 40 mg/dl > 50 mg/dl) (00 mg/dl < 00 mg/dl(.6 mmol/l) 30-40% < 70 mg/dl 40 mg/dl 00 9 mg/dl fibric acid derivative niacin statin fibrate statin niacin ( ) ( Diabetes mellitus,
005 6 69-74 40 mg/dl > 50 mg/dl) (00 mg/dl < 00 mg/dl(.6 mmol/l) 30-40% < 70 mg/dl 40 mg/dl 00 9 mg/dl fibric acid derivative niacin statin fibrate statin niacin ( ) ( Diabetes mellitus,
Blood Pressure Targets in Diabetes
 Stockholm, 29 th August 2010 ESC Meeting Blood Pressure Targets in Diabetes Peter M Nilsson, MD, PhD Department of Clinical Sciences University Hospital, Malmö Sweden Studies on BP in DM2 ADVANCE RCT (Lancet
Stockholm, 29 th August 2010 ESC Meeting Blood Pressure Targets in Diabetes Peter M Nilsson, MD, PhD Department of Clinical Sciences University Hospital, Malmö Sweden Studies on BP in DM2 ADVANCE RCT (Lancet
Practical Diabetes. Nic Crook. (and don t use so many charts) Kuirau Specialists 1239 Ranolf Street Rotorua. Rotorua Hospital Private Bag 3023 Rotorua
 Practical Diabetes (and don t use so many charts) Nic Crook Rotorua Hospital Private Bag 3023 Rotorua Kuirau Specialists 1239 Ranolf Street Rotorua Worldwide rates of diabetes mellitus: predictions 80
Practical Diabetes (and don t use so many charts) Nic Crook Rotorua Hospital Private Bag 3023 Rotorua Kuirau Specialists 1239 Ranolf Street Rotorua Worldwide rates of diabetes mellitus: predictions 80
A factorial randomized trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes
 A factorial randomized trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes Hypotheses: Among individuals with type 2 diabetes, the risks of major microvascular
A factorial randomized trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in 11,140 patients with type 2 diabetes Hypotheses: Among individuals with type 2 diabetes, the risks of major microvascular
Module 2. Global Cardiovascular Risk Assessment and Reduction in Women with Hypertension
 Module 2 Global Cardiovascular Risk Assessment and Reduction in Women with Hypertension 1 Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored,
Module 2 Global Cardiovascular Risk Assessment and Reduction in Women with Hypertension 1 Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored,
Diabetes and Hypertension
 Diabetes and Hypertension William C. Cushman, MD, FAHA, FACP, FASH Chief, Preventive Medicine, Veterans Affairs Medical Center Professor, Preventive Medicine, Medicine, and Physiology University of Tennessee
Diabetes and Hypertension William C. Cushman, MD, FAHA, FACP, FASH Chief, Preventive Medicine, Veterans Affairs Medical Center Professor, Preventive Medicine, Medicine, and Physiology University of Tennessee
Individualized Treatment Goals for Optimal Long-Term Health Outcomes among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 1 Dissertation Title Page: Individualized Treatment Goals for Optimal Long-Term Health Outcomes among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Qian Shi, MPH, PhD candidate Department of Global Health Management
1 Dissertation Title Page: Individualized Treatment Goals for Optimal Long-Term Health Outcomes among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Qian Shi, MPH, PhD candidate Department of Global Health Management
Hyperlipidemia and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
 ...PRESENTATIONS... Hyperlipidemia and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Based on a presentation by Ronald B. Goldberg, MD Presentation Summary Atherosclerosis accounts for approximately
...PRESENTATIONS... Hyperlipidemia and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Based on a presentation by Ronald B. Goldberg, MD Presentation Summary Atherosclerosis accounts for approximately
Tailored Statin Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes. Han, Ki Hoon Asan Medical Center University of Ulsan
 Tailored Statin Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes Han, Ki Hoon Asan Medical Center University of Ulsan 1 Cardiovascular disease ; No1. death (2001) respiratory tract infection Other NCD S HIV/AIDS deaths during
Tailored Statin Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes Han, Ki Hoon Asan Medical Center University of Ulsan 1 Cardiovascular disease ; No1. death (2001) respiratory tract infection Other NCD S HIV/AIDS deaths during
Hypertension targets: sorting out the confusion. Brian Rayner, Division of Nephrology and Hypertension, University of Cape Town
 Hypertension targets: sorting out the confusion Brian Rayner, Division of Nephrology and Hypertension, University of Cape Town Historical Perspective The most famous casualty of this approach was the
Hypertension targets: sorting out the confusion Brian Rayner, Division of Nephrology and Hypertension, University of Cape Town Historical Perspective The most famous casualty of this approach was the
Diabetes Mellitus: Evaluation and Care Management
 Diabetes Mellitus: Evaluation and Care Management Michael King, MD Assistant Professor Residency Program Director University of Kentucky Dept. of Family & Community Medicine Learning Objectives 1. Review
Diabetes Mellitus: Evaluation and Care Management Michael King, MD Assistant Professor Residency Program Director University of Kentucky Dept. of Family & Community Medicine Learning Objectives 1. Review
Blood Pressure Treatment Goals
 Blood Pressure Treatment Goals Kenneth Izuora, MD, MBA, FACE Associate Professor UNLV School of Medicine November 18, 2017 Learning Objectives Discuss the recent studies on treating hypertension Review
Blood Pressure Treatment Goals Kenneth Izuora, MD, MBA, FACE Associate Professor UNLV School of Medicine November 18, 2017 Learning Objectives Discuss the recent studies on treating hypertension Review
Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD INTRODUCTION
 2 Hyperlipidemia Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION RISK CATEGORIES AND TARGET LDL-CHOLESTEROL TREATMENT OF LDL-CHOLESTEROL SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS OLDER AND YOUNGER ADULTS ADDITIONAL
2 Hyperlipidemia Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION RISK CATEGORIES AND TARGET LDL-CHOLESTEROL TREATMENT OF LDL-CHOLESTEROL SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS OLDER AND YOUNGER ADULTS ADDITIONAL
Predicting and changing the future for people with CKD
 Predicting and changing the future for people with CKD I. David Weiner, M.D. Co-holder, C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University
Predicting and changing the future for people with CKD I. David Weiner, M.D. Co-holder, C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University
Welcome and Introduction
 Welcome and Introduction This presentation will: Define obesity, prediabetes, and diabetes Discuss the diagnoses and management of obesity, prediabetes, and diabetes Explain the early risk factors for
Welcome and Introduction This presentation will: Define obesity, prediabetes, and diabetes Discuss the diagnoses and management of obesity, prediabetes, and diabetes Explain the early risk factors for
Environmental. Vascular / Tissue. Metabolics
 Global Risk Reduction--WINS Picking Mom and Dad-2016 Environmental Vascular / Tissue Metabolics Stop smoking-1b Physical activity-1b Weight control-1b Chelation therapy-3c Influenza vaccination-1b Blood
Global Risk Reduction--WINS Picking Mom and Dad-2016 Environmental Vascular / Tissue Metabolics Stop smoking-1b Physical activity-1b Weight control-1b Chelation therapy-3c Influenza vaccination-1b Blood
Diabetes Control and Complications in Public Hospitals in Malaysia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diabetes Control and Complications in Public Hospitals in Malaysia Mafauzy M. FRCP For the Diabcare-Malaysia Study Group, Health Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 16150 Kubang Kerian,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diabetes Control and Complications in Public Hospitals in Malaysia Mafauzy M. FRCP For the Diabcare-Malaysia Study Group, Health Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 16150 Kubang Kerian,
Complications of Diabetes mellitus. Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015
 Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
Cardiovascular Risk Reduction and Other Co-morbidities in Type 2 Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Risk Reduction and Other Co-morbidities in Type 2 Diabetes Following this presentation, you will be able to: Describe the relationship between major CV risk factors and CVD outcomes Select
Cardiovascular Risk Reduction and Other Co-morbidities in Type 2 Diabetes Following this presentation, you will be able to: Describe the relationship between major CV risk factors and CVD outcomes Select
Firenze 22 settembre 2007
 Istituto di di medicina dello sport di di Firenze AMES Prevenzione cardiovascolare e cambiamenti negli stili di vita Firenze 22 settembre 2007 Orientamenti attuali per un intervento farmacologico e non
Istituto di di medicina dello sport di di Firenze AMES Prevenzione cardiovascolare e cambiamenti negli stili di vita Firenze 22 settembre 2007 Orientamenti attuali per un intervento farmacologico e non
hypertension Head of prevention and control of CVD disease office Ministry of heath
 hypertension t. Samavat MD,Cadiologist,MPH Head of prevention and control of CVD disease office Ministry of heath RECOMMENDATIONS FOR HYPERTENSION DIAGNOSIS, ASSESSMENT, AND TREATMENT Definition of hypertension
hypertension t. Samavat MD,Cadiologist,MPH Head of prevention and control of CVD disease office Ministry of heath RECOMMENDATIONS FOR HYPERTENSION DIAGNOSIS, ASSESSMENT, AND TREATMENT Definition of hypertension
Total risk management of Cardiovascular diseases Nobuhiro Yamada
 Nobuhiro Yamada The worldwide burden of cardiovascular diseases (WHO) To prevent cardiovascular diseases Beyond LDL Multiple risk factors With common molecular basis The Current Burden of CVD CVD is responsible
Nobuhiro Yamada The worldwide burden of cardiovascular diseases (WHO) To prevent cardiovascular diseases Beyond LDL Multiple risk factors With common molecular basis The Current Burden of CVD CVD is responsible
Prevention of MACROvascular Complications of Diabetes
 Prevention of MACROvascular Complications of Diabetes Matt Bouchonville, MD, CDE Endocrinology Division University of New Mexico School of Medicine July 12, 2018 Conflicts of Interest None Objectives 1.
Prevention of MACROvascular Complications of Diabetes Matt Bouchonville, MD, CDE Endocrinology Division University of New Mexico School of Medicine July 12, 2018 Conflicts of Interest None Objectives 1.
Marshall Tulloch-Reid, MD, MPhil, DSc, FACE Epidemiology Research Unit Tropical Medicine Research Institute The University of the West Indies, Mona,
 Marshall Tulloch-Reid, MD, MPhil, DSc, FACE Epidemiology Research Unit Tropical Medicine Research Institute The University of the West Indies, Mona, Jamaica At the end of this presentation the participant
Marshall Tulloch-Reid, MD, MPhil, DSc, FACE Epidemiology Research Unit Tropical Medicine Research Institute The University of the West Indies, Mona, Jamaica At the end of this presentation the participant
Epidemiology of Diabetes, Impaired Glucose Homeostasis and Cardiovascular Risk. Eberhard Standl
 Epidemiology of Diabetes, Impaired Glucose Homeostasis and Cardiovascular Risk Eberhard Standl European Heart House Sophia Antipolis Thursday, June 17, 2010 IDF Diabetes Atlas 2009: Global Numbers Still
Epidemiology of Diabetes, Impaired Glucose Homeostasis and Cardiovascular Risk Eberhard Standl European Heart House Sophia Antipolis Thursday, June 17, 2010 IDF Diabetes Atlas 2009: Global Numbers Still
Strategies for the prevention of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease
 European Heart Journal Supplements (2005) 7 (Supplement D), D18 D22 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/sui025 Strategies for the prevention of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease Jaakko Tuomilehto 1,2,3 *, Jaana
European Heart Journal Supplements (2005) 7 (Supplement D), D18 D22 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/sui025 Strategies for the prevention of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease Jaakko Tuomilehto 1,2,3 *, Jaana
HYPERTENSION GUIDELINES WHERE ARE WE IN 2014
 HYPERTENSION GUIDELINES WHERE ARE WE IN 2014 Donald J. DiPette MD FACP Special Assistant to the Provost for Health Affairs Distinguished Health Sciences Professor University of South Carolina University
HYPERTENSION GUIDELINES WHERE ARE WE IN 2014 Donald J. DiPette MD FACP Special Assistant to the Provost for Health Affairs Distinguished Health Sciences Professor University of South Carolina University
Accelerated atherosclerosis begins years prior to the diagnosis of diabetes
 Joslin Diabetes Forum 211: Optimizing Care for the Practicing Clinician Risk for atherosclerosis is 2 4 times greater in patients with diabetes CVD accounts for 65% of diabetic mortality >5% of patients
Joslin Diabetes Forum 211: Optimizing Care for the Practicing Clinician Risk for atherosclerosis is 2 4 times greater in patients with diabetes CVD accounts for 65% of diabetic mortality >5% of patients
Educational and behavioral interventions hitherto published
 Treatment of High-Risk Patients with Diabetes: Motivation and Teaching Intervention: A Randomized, Prospective 8-Year Follow-Up Study Rita Rachmani, Inna Slavacheski, Maya Berla, Ronni Frommer-Shapira,
Treatment of High-Risk Patients with Diabetes: Motivation and Teaching Intervention: A Randomized, Prospective 8-Year Follow-Up Study Rita Rachmani, Inna Slavacheski, Maya Berla, Ronni Frommer-Shapira,
Management of Hypertension in the Diabetic Patient:
 Management of Hypertension in the Diabetic Patient: Nicolas W. Shammas, MS, MD Research Director, Cardiovascular Medicine, PC Presentation Objectives To review: The relationship between HTN, insulin resistance
Management of Hypertension in the Diabetic Patient: Nicolas W. Shammas, MS, MD Research Director, Cardiovascular Medicine, PC Presentation Objectives To review: The relationship between HTN, insulin resistance
CANADIAN STROKE BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS. Prevention of Stroke Evidence Tables Diabetes Management
 CANADIAN STROKE BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS Diabetes Management Coutts S, Wein T (Writing Group Chairs) on Behalf of the PREVENTION of STROKE Writing Group 2014 Heart and Stroke Foundation November 2014
CANADIAN STROKE BEST PRACTICE RECOMMENDATIONS Diabetes Management Coutts S, Wein T (Writing Group Chairs) on Behalf of the PREVENTION of STROKE Writing Group 2014 Heart and Stroke Foundation November 2014
ASSeSSing the risk of fatal cardiovascular disease
 ASSeSSing the risk of fatal cardiovascular disease «Systematic Cerebrovascular and coronary Risk Evaluation» think total vascular risk Assess the risk Set the targets Act to get to goal revised; aupril
ASSeSSing the risk of fatal cardiovascular disease «Systematic Cerebrovascular and coronary Risk Evaluation» think total vascular risk Assess the risk Set the targets Act to get to goal revised; aupril
Cardiovascular Complications in Diabetes
 What is all the fuss about? Cardiovascular Complications in Diabetes Dina Shrestha MD Consultant Endocrinologist Norvic International Hospital and Medical College Hospital for Advanced Medicine and Surgery
What is all the fuss about? Cardiovascular Complications in Diabetes Dina Shrestha MD Consultant Endocrinologist Norvic International Hospital and Medical College Hospital for Advanced Medicine and Surgery
Management of Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes
 Management of Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Radha J. Sarma, MBBS, FACP. FACC. FAHA. FASE Professor of Internal Medicine Western University of Health Sciences. Director, Heart and Vascular Center Western
Management of Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Radha J. Sarma, MBBS, FACP. FACC. FAHA. FASE Professor of Internal Medicine Western University of Health Sciences. Director, Heart and Vascular Center Western
Diabetes new challenges, new agents, new order
 Diabetes new challenges, new agents, new order Ken Earle St Georges University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Overview Cardiovascular disease unmet needs Treating evident and residual risk Integrating
Diabetes new challenges, new agents, new order Ken Earle St Georges University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Overview Cardiovascular disease unmet needs Treating evident and residual risk Integrating
ACCORD, ADVANCE & VADT. Now what do I do in my practice?
 ACCORD, ADVANCE & VADT Now what do I do in my practice? Richard M. Bergenstal, MD International Diabetes Center Park Nicollet Health Services University of Minnesota Minneapolis, MN richard.bergenstal@parknicollet.com
ACCORD, ADVANCE & VADT Now what do I do in my practice? Richard M. Bergenstal, MD International Diabetes Center Park Nicollet Health Services University of Minnesota Minneapolis, MN richard.bergenstal@parknicollet.com
Traitements associés chez l hypertendu: Statines, Aspirine
 Traitements associés chez l hypertendu: Statines, Aspirine Pr Jean-Jacques Mourad CHU Avicenne, Université Paris 13, Bobigny DU HTA, Mars 2012 jean-jacques.mourad@avc.aphp.fr Global Mortality 2000: Impact
Traitements associés chez l hypertendu: Statines, Aspirine Pr Jean-Jacques Mourad CHU Avicenne, Université Paris 13, Bobigny DU HTA, Mars 2012 jean-jacques.mourad@avc.aphp.fr Global Mortality 2000: Impact
Preventive Cardiology Scientific evidence
 Preventive Cardiology Scientific evidence Professor David A Wood Garfield Weston Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine International Centre for Circulatory Health Imperial College London Primary prevention
Preventive Cardiology Scientific evidence Professor David A Wood Garfield Weston Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine International Centre for Circulatory Health Imperial College London Primary prevention
Diabetes: Use of Adjunctive Therapy ACEs, ARBs, ASA & STATINs --Oh My! Veronica J. Brady, PhD, FNP-BC, BC-ADM, CDE Project ECHO April 19, 2018
 Diabetes: Use of Adjunctive Therapy ACEs, ARBs, ASA & STATINs --Oh My! Veronica J. Brady, PhD, FNP-BC, BC-ADM, CDE Project ECHO April 19, 2018 Points to Ponder ASCVD is the leading cause of morbidity
Diabetes: Use of Adjunctive Therapy ACEs, ARBs, ASA & STATINs --Oh My! Veronica J. Brady, PhD, FNP-BC, BC-ADM, CDE Project ECHO April 19, 2018 Points to Ponder ASCVD is the leading cause of morbidity
egfr > 50 (n = 13,916)
 Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
BEST PRACTICE MANAGEMENT: CARDIOVASCULAR RISKS
 BEST PRACTICE MANAGEMENT: CARDIOVASCULAR RISKS Neil R Poulter ICCH, Imperial College London BHIVA: October 10th, 2008 Background CVD is the biggest single killer in the world CVD rates are increasing High
BEST PRACTICE MANAGEMENT: CARDIOVASCULAR RISKS Neil R Poulter ICCH, Imperial College London BHIVA: October 10th, 2008 Background CVD is the biggest single killer in the world CVD rates are increasing High
The American Diabetes Association estimates
 DYSLIPIDEMIA, PREDIABETES, AND TYPE 2 DIABETES: CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS OF THE VA-HIT SUBANALYSIS Frank M. Sacks, MD* ABSTRACT The most serious and common complication in adults with diabetes is cardiovascular
DYSLIPIDEMIA, PREDIABETES, AND TYPE 2 DIABETES: CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS OF THE VA-HIT SUBANALYSIS Frank M. Sacks, MD* ABSTRACT The most serious and common complication in adults with diabetes is cardiovascular
How would you manage Ms. Gold
 How would you manage Ms. Gold 32 yo Asian woman with dyslipidemia Current medications: Simvastatin 20mg QD Most recent lipid profile: TC = 246, TG = 100, LDL = 176, HDL = 50 What about Mr. Williams? 56
How would you manage Ms. Gold 32 yo Asian woman with dyslipidemia Current medications: Simvastatin 20mg QD Most recent lipid profile: TC = 246, TG = 100, LDL = 176, HDL = 50 What about Mr. Williams? 56
