Histopathological and Stereological Study of the Effects of Gallic Acid Administration on Hippocampal Neuronal Density after Trimethyltin Toxication
|
|
|
- Heather Curtis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Report of Health Care Volume 4, Issue 2, 2018, p Original Article Histopathological and Stereological Study of the Effects of Gallic Acid Administration on Hippocampal Neuronal Density after Trimethyltin Toxication Heydar Aghababa 1, Mona Ghezelbash 2, Mohamad Amin Edalatmanesh 2, Shirin Dehghan 1 1. Department of Biology, Arsanjan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Arsanjan, Iran 2. Department of Biology, Shiraz Branch, Islamic Azad University, Shiraz, Iran Received: 5 February 2018 Accepted: 8 May 2018 Published online: 1 June 2018 *Corresponding author: Heydar Aghababa. Department of biology, Arsanjan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Arsanjan, Iran Phone: Fax: aqababa@iaua.ac.ir Competing interests: The authors declare that no competing interests exist. Citation: Aghababa H, Ghezelbash M, Edalatmanesh MA, Dehghan Sh. Histopathological and stereological study of the effects of gallic acid administration on hippocampal neuronal density after trimethyltin toxication. Rep Health Care. 2018; 4 (2): Abstract Introduction: Trimethyltin is a methylated organotin, which induces selective damage and neuronal death in human and rodents CNS. On the other hand, the neuroprotective effects of Gallic acid can prevent toxicity of trimethyltin. In the current study, the repairing effect of Gallic acid in cell injury caused by trimethyltin in rats was evaluated. Also, this study assessed the effects of Gallic acid on neuronal density of the different hippocampal areas of intoxicated rats with trimethyltin. Methods: 30 rats were divided in three groups: the no treatment control group, the control group, and the experimental group with intraperitoneal injection of trimethyltin (8 mg/kg) and Gallic acid solvent for 14 days. In the experimental group, after the administration of trimethyltin, 50 mg/kg of Gallic acid was injected. It was continued for 14 days. Finally, the rats were killed with transcardial perfusion. Histopathological and stereological analysis was performed on the rats. In this research, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, one-way analysis of variance, and Tukey s post-hoc test were used. Results: The results of this study showed that neuronal density of different hippocampal areas of the no treatment control group was significantly increased compared to the rats of the control and experimental groups (P<0.05), while chronic administration of Gallic acid could prevent apoptosis and protect hippocampal cells. Conclusions: According to the results, it is suggested that chronic administration of Gallic acid decreases the effects of trimethyltin and therefore, it prevents the reduction of hippocampal cells. Keywords: Hippocampus, Gallic Acid, Trimethyltin, Rat Introduction Gallic acid (3, 4, 5- trihydroxybenzoic acid) is one of the most important polyphenolic compounds in plants, and a natural product of hydrolysis of tannins. Gallic acid shows antidiabetic, anti-carcinogenic and anti-darkening effects. It prevents myocardial infarction and oxidative stress of liver and kidneys, also it protects the neurons from apoptosis induced by β-amyloid peptide (Aβ) (1, 2). Gallic acid is found in foods, pharmaceutical and cosmetic products as an antioxidant. Strawberry, pineapple, banana, lemon, red and white grapes, sumac, elm, tea leaves, oak bark, and apple skin are some of the natural products enriched with Gallic acid. Gallic acid through inhibition of tyrosine activity, induces antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities (3, 4). Relationship between damage to the hippocampus region and cognitive impairment (memory intervention and learning disorder) has been identified, which leads to the infertility of trimethyltin as an effective factor in the study of Alzheimer's disease (5). Trimethyltin affects several processes in sensitive cells. Various theories have been presented to explain the mechanism of neurotoxic trimethyltin function, which includes glutamate manifestations, increased
2 intracellular calcium, and ion transfer impairment. Oxidative stress and thermal shock protein activity are also followed by trimethyltin therapy (6). Laboratory studies have shown that impairment of memory and learning process is sought after the trimethyltin- induced death and selective death of neurons in the limbic system, and in particular the hippocampus (7, 8). Trimethyltin is known for using in laboratory animals to induce severe selective neuronal death, which is associated with microglial and astroglial activities in selective limbic areas, especially in hippocampus. Therefore, it presents a valuable method for studying hippocampal function during neurodegenerative disorders (9). Trimethyltin- induced neuronal damage in various species of rodents, is depending on different parameters such as race, age, dosage and type of administration, which leads to various consequences in metabolism and pathological toxic effects. Also it has been reported that trimethyltin can causes Alzheimer's disease (10). Laboratory findings have shown that oxidative stress could play an important role in Alzheimer s pathogenesis. Therefore, the risk of Alzheimer s disease could be reduced by consumption of the antioxidants which neutralize the adverse effects of oxidative stress (11). Methods In this experimental study, animals included 30 Sprague Dawley rats, which were selected randomly as the sample. The animals were obtained from the laboratory animal reproduction and breeding center in Shiraz, and they were kept and tested in the zoology research laboratory of Islamic Azad university of Shiraz. For absorption of urine and feces, sterile wood chips were used. The optimal temperature was 20 to 24 C and relative humidity was about 55 to 65 percent. A twelve-hour light-dark cycle was controlled accurately by salon s electronic light regulator. In this research, there was no food restriction for the animals. Rats in the study were divided into 3 groups: 1. The no treatment control group: the animals of this group did not receive any treatment. Histopathological analysis of different hippocampal areas was simultaneously performed to be compared with the other groups. 2. The control group: The animals of this group were injected with 8 mg/kg intraperitoneal trimethyltin and normal saline for 14 days. Histopathological analysis was performed to evaluate degenerative effects of this substance on hippocampal neurons during stereological analysis. And 3. The experimental group: They received 50 mg/kg of Gallic acid and 8 mg/kg of trimethyltin. After administration of trimethyltin and induction of hippocampal degeneration, the animals of this group were injected with multiple intraperitoneal Gallic acid shots during 14 days. To conduct histopathological study in the end of treatment, the animals were anaesthetized with the combination of ketamine hydrochloride (100 mg/kg) and xylazine (50 mg/kg). Then, the transcardial perfusion was performed. After the perfusion, the rats brains were extracted from their skulls and were immediately weighed with an accurate scale. Then, cerebellum tissue was prepared for slicing, and the obtained slices were stained using hematoxylin and eosin, and the microscopic imaging was conducted using a light microscope. To determine the location of different areas of hippocampus, the obtained images of the slices were matched with the atlas pictures. After assurance of location of the different hippocampal areas, the total number of questions in different hippocampal areas were estimated using hematoxylin and eosin staining. Both left and right sides of hippocampus were observed, then the mean of the obtained numbers from the different areas of hippocampus was evaluated. In this step, random sampling was used and to count DG/CA 3 /CA 2 /CA 1 the dissector counting technique was utilized. In this method, cells are counted in a counting frame. The gathered data from the measured variables were described using dispersion 23 Report of Health Care. 2018; 1 (2): 22-27
3 index and central tendency. In this research, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, one-way analysis of variance, and Tukey s post-hoc test were used. The significance level was considered as P 0.05 for all of the calculations. Results The qualitative evaluation of different hippocampal areas including CA 1 /CA 2 /CA 3 /DG showed that after administration of trimethyltin, the CA 1 neurons and cell volume were decreased, pyknosis and karyorrhexix were seen in the hippocampus. With chronic administration of Gallic acid for 14 days, these changes were less than the control group. After trimethyltin administration, the number of the neurons and cell volume were decreased and the cell wall was destructed, which indicates apoptosis. In addition to reducing the number of apoptotic neurons, Gallic acid has neuroprotective effects, therefore in the experimental group, the number and morphology of cells were closer to normal conditions. After administration of trimethyltin in CA 3, the number of neurons and cell volume were decreased, while chronic treatment with Gallic acid could preserve normal morphology of cells in this area. In DG of hippocampus, after administration of trimethyltin, a large number of control group s neurons were injured, although the injury severity was significantly lower. Treating with Gallic acid reduced the number of the injured neurons of dentate gyrus. Also, the morphology of many cells of the experimental group was similar to the control group (figure 1). The stereological results showed a significant decrease in the number and density of neurons in different hippocampal areas of the rats treated with trimethyltin. The neuronal density of the treated group with Gallic acid (the experimental group) was increased compared to the control group. The results show that neuronal density in right and left CA1 in both control and experimental groups were significantly lower than the control group without any treatment, also, it is significantly lower in the control group compared to the experimental group (P<). Moreover, there is no significant difference in neuronal density of right and left CA2 area between the groups. The results show that neuronal density of right and left CA3 area in the control group is significantly lower than the no treatment control group, also it is significantly lower in the control group compared to the experimental group (P<). The results show that there is a significant difference in neuronal density of left and right DG between the groups. The neuronal density of left and right DG in the control group was significantly lower than the no treatment control group, and it is significantly lower in the control group compared to the experimental group (P<).(Table 1). Discussion In the current study, apoptosis, neuronal necrosis, neuronal transmutation and nuclear fragmentation were seen after intoxication with Trimethyltin. In contrast, trimethyltin led to neurogenesis and neuronal regeneration. In this practical study, the dual effect of trimethyltin in different hippocampal areas was shown. Trimethyltin is an organotin compound, its neurotoxic effects occur in cerebellum, limbic system and specially in hippocampus. These effects were shown experimentally in human and animal models. Trimethyltin is used widely in hippocampal destruction models of the cognitive deficits and temporal lobe epilepsy. However, the molecular mechanisms of selective neuronal death are not known clearly (10). Trimethyltin causes selective injury of the dentate gyrus of hippocampus. Neuronal/microglial interactions play the main role in neuronal inflammation signal and trimethyltin- induced programmed neuronal death (11). Report of Health Care. 2018; 4 (2):
4 A1 B 1 C 1 D 1 A2 B 2 C 2 D 2 A3 B 3 C 3 D 3 Figure 1. A photomicrograph of hippocampal layers of the assessed groups. 400 magnification, hematoxylin and eosin staining. A, B, C, D respectively represents: the control group without any treatment (A1), the control group (A2), and the experimental group (A3) in CA 1 area. The control group without any treatment (B1), the control group (B2), and the experimental group (B3) in CA 2. The control group without any treatment (C1), the control group (C2), and the experimental group (C3) in CA 3. The control group without any treatment (D1), the control group (D2), and the experimental group (D3) in DG. Table 1. Comparison of Mean ± SE of neuronal density and one-way ANOVA analysis P value between CA1, CA2, CA3 and DG (right and left) areas in the control, sham and experimental groups. Groups (N=8) Control Sham Experi mental P Value DG ± ± ± DG ± ± ± CA3 ± ± ± CA3 ± ± ± CA2 ± ± ± CA2 ± ± ± CA1 ± ± ± CA1 ± ± ± Administration of trimethyltin was assessed in at least two animal models under laboratory conditions. trimethyltin-induced neuronal death was assessed from two different aspects. In one model of rats, acute apoptosis of dentate granule cells was observed in 48 hours after the administration, and in the other model, progressive death of pyramidal cells in CA1/CA2 during 3 weeks were seen (12). Neuronal death happens at the end of the attack (2 days after treatment), it progresses exponentially, and it will develop after 3 weeks, which is probably caused by strong adhesion of rat s hemoglobin to trimethyltin. Different studies have proved that mitochondrial dysfunction and lack of Ca 2+ homeostasis in the initial location of trimethyltin induction would led to neuronal 25 Report of Health Care. 2018; 1 (2): 22-27
5 death (10). In 2011 Funk et al. reported that two days after treating with trimethyltin, plasma levels of corticosterone were doubled, and adrenalectomy caused by trimethyltin would lead to more susceptibility to the injury (13). Mansouri et al. (2013) evaluated the protective effect of oral Gallic acid on memory disorders and brain oxidative stress in the rats with Parkinson s disease. The results of this study shows that Gallic acid has deep neuroprotective effects, which is probably explained by its significant antioxidant feature (14). The Gallic acid derivatives include 4-5- methyl gallic acid, which is reported as the main metabolite of this substance in humans and rats (15). The study of Farbood et al. (2013) has shown that gallic acid has helpful effects on behavioral disorders caused by brain injuries. The results of this study showed that gallic acid treatment will improve brain ischemia / reperfusion injuries, and it will improve antioxidant defense of the rats, therefore it will protect the brain (4). In this study, by injecting trimethyltin in animals and the stereological analysis of hippocampal neurons and comparing it with the control group, we showed that this organotin is a neurodegenerative combination. In another study, the effects of nerve protection of gallic acid as a protecting agent and antitrimethyltin in the test group were evaluated. As expected, this compound could significantly reduce the effects of trimethyltin cell cytotoxicity. A quick look into these findings once again confirmed the potential potential for nerve protection of gallic acid and the role of trimethyltin in apoptosis, cell necrosis. Conclusions According to the results of present study it appears that chronic administration of gallic acid decreases the effects of trimethyltin and therefore, it prevents the reduction of hippocampal cells. Ethical issues Not applicable. Authors contributions All authors equally contributed to the writing and revision of this paper. Acknowledgments The authors would like to thank Dr. Seyyed Ali Hosseini for contributing to the statistical analysis of this research. References 1. Besser JM, Brumbaugh WG, Brunson EL, Ingersoll CG. Acute and chronic toxicity of lead in water and diet to the amphipod hyalellaazteca. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2005; 24: Hajipour S, Sarkaki A. Effect of gallic acid on dementia type of alzheimer disease in rats: electrophysiological and histological studies. BCNJ. 2016; 7 (2): Sarkaki A, Mansouri SM. Gallic acid improves cognitive, hippocampal long term induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. US National Library Med National Inst Health. 2014: 17 (8): Farbood Y, Sarkaki A, Hashemi SH. The effects of gallic acid on pain and memory following transient global ischemia/ reperfusion in Wistar rats. Avicenna J. 2013; 25: Corvino V, Marchese E, Michetti F. Neuroprotectivestrantegics in hippocampal neuro degeneration induced by the neurotoxicant trimethylyin. Neurochem Res. 2012; 10: Shuto M, Seko K, Kuramoto N, Sugiyama C, Kawada K, Yoneyama M. Activation of c-jun N- terminal kinase cascades is involved in part of the neuronaldegeneration induced by trimethyltin in cortical neurons of mice. J Pharmacol Sci. 2009; 109: Mignini F, Nasuti C, Artico M, Giovannetti F, Fabrizi C, Fumagalli L, et al. Effects of trimethyltin on hippocampal dopaminergic markers and cognitive Report of Health Care. 2018; 4 (2):
6 behaviour. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2012; 25 (4): Park HJ, Shim HS, Ahn YH, Kim KS, Park KJ, Choi WK, et al. Tremellafuciformis enhances the neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells and restores trimethyltin- induced impairment of memory in rats via activation of CREB transcription and cholinergic systems. Behav Brain Res. 2012; 229 (1): Ogita K, Nishiyama N, Sugiyama C, Higuchi K, Yoneyama M, Yoneda Y. Regeneration of granule neurons after lesioning of hippocampal dentate gyrus: evaluation using adult mice treated with trimethyltin chloride as a model. J Neurosci Res. 2005; 82 (5): Lattanzi W, Corvino V, Di Maria V, Michetti F, Geloso MC. Gene expression profiling as a tool to investigate the molecular machinery activated during hippocampal neurodegeneration induced by trimethyltin (TMT) administration. Int J Mol Sci. 2013; 14 (8): Kikuta M, Shiba T, Yoneyama M, Kawada K, Yamaguchi T, Hinoi E, et al. Invivo and invitro treatment with edaravone promotes proliferation of neural progenitor cells generated following neuronal loss in the mouse dentate gyrus. J Pharmacol Sci. 2013; 121 (1): Lee S, Yang M, Kim J. Trimethyltininduced hippocampal neural generation: A mechanism-based review. US National Library Med National Inst Health. 2016; 125: Funk JA, Gohlke J, Kraft AD, McPherson CA, Collins JB, Jean Harry G. Voluntary exercise protects hippocampal neurons from trimethyltin injury: possible role of Interlukin-6 to modulate tumor necrosis factor receptor- mediated neurotoxicity. Brain Behav Immun. 2011; 25 (6): Mansouri TM, Farbood Y, Sameri MJ, Sarkaki A, Naghizadeh B, Rafeirad M. Neuroprotective effects of oral gallic acid against oxidative stress induced by 6- hydroxydopamine in rats. Food Chem. 2013; 138: Abdel A, Yousef AJ. Gallic acid and p- comaric acid attenuate type 2 diabetesinduced neurodegeneration in rats. US National Library Med National Inst Health. 2017; 7 (2): Report of Health Care. 2018; 1 (2): 22-27
Marzieh Moghadas, M.Sc., Mohammad Amin Edalatmanesh, Ph.D.*, Reza Robati, M.Sc.
 Original Article Histopathological Analysis from Gallic Acid Administration on Hippocampal Cell Density, Depression, and Anxiety Related Behaviors in A Trimethyltin Intoxication Model Marzieh Moghadas,
Original Article Histopathological Analysis from Gallic Acid Administration on Hippocampal Cell Density, Depression, and Anxiety Related Behaviors in A Trimethyltin Intoxication Model Marzieh Moghadas,
The Potential Effect of Caffeine and Nicotine Co-administration on the Induction of Alzheimer s disease
 The Potential Effect of Caffeine and Nicotine Co-administration on the Induction of Alzheimer s disease Azza A Ali *, Hebatalla I Ahmed * Hanan A Abd El-Samea ** Ebtehal El-Demerdash *** * Pharmacology
The Potential Effect of Caffeine and Nicotine Co-administration on the Induction of Alzheimer s disease Azza A Ali *, Hebatalla I Ahmed * Hanan A Abd El-Samea ** Ebtehal El-Demerdash *** * Pharmacology
Green Tea Polyphenol Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Attenuates Behavioral Abnormality in Hemi-Parkinsonian Rat
 Iranian Biomedical Journal 1 (4): 23-27 (October 26) Green Tea Polyphenol Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Attenuates Behavioral Abnormality in Hemi-Parkinsonian Rat Tourandokht Baluchnejadmojarad *1 and Mehrdad
Iranian Biomedical Journal 1 (4): 23-27 (October 26) Green Tea Polyphenol Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Attenuates Behavioral Abnormality in Hemi-Parkinsonian Rat Tourandokht Baluchnejadmojarad *1 and Mehrdad
Shift 1, 8 July 2018, 09:30-13:00
 Shift 1, 8 July 2018, 09:30-13:00 CNS patterning A001-A014 Stem cells: basic biology and postnatal neurogenesis - part I Development of neural systems: Molecular and genetic characterisationa Epigenetic
Shift 1, 8 July 2018, 09:30-13:00 CNS patterning A001-A014 Stem cells: basic biology and postnatal neurogenesis - part I Development of neural systems: Molecular and genetic characterisationa Epigenetic
Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing. Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2
 ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females
 The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females Samantha Pavlock (Medical Student) Pradeep Bhide and Deirdre McCarthy (Faculty
The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females Samantha Pavlock (Medical Student) Pradeep Bhide and Deirdre McCarthy (Faculty
CASE 49. What type of memory is available for conscious retrieval? Which part of the brain stores semantic (factual) memories?
 CASE 49 A 43-year-old woman is brought to her primary care physician by her family because of concerns about her forgetfulness. The patient has a history of Down syndrome but no other medical problems.
CASE 49 A 43-year-old woman is brought to her primary care physician by her family because of concerns about her forgetfulness. The patient has a history of Down syndrome but no other medical problems.
Neuroprotection in preclinical models of Parkinson disease by the NAPVSIPQ peptide
 Neuroprotection in preclinical models of Parkinson disease by the NAPVSIPQ peptide Bruce H. Morimoto, Ph.D. Executive Director, Applied Translational Medicine Microtubules Microtubules essential for neuronal
Neuroprotection in preclinical models of Parkinson disease by the NAPVSIPQ peptide Bruce H. Morimoto, Ph.D. Executive Director, Applied Translational Medicine Microtubules Microtubules essential for neuronal
Effect of chronic treatment of ketamine on hippocampus cell count of adult rats
 Quarterly of the Horizon of Medical Sciences Vol. 19, No. 1, Spr 2013 Pages: 35-39 Effect of chronic treatment of ketamine on hippocampus cell count of adult rats Downloaded from hms.gmu.ac.ir at 12:09
Quarterly of the Horizon of Medical Sciences Vol. 19, No. 1, Spr 2013 Pages: 35-39 Effect of chronic treatment of ketamine on hippocampus cell count of adult rats Downloaded from hms.gmu.ac.ir at 12:09
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 ? Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Christian S Lobsiger & Don W Cleveland (2007) Nature Neuroscience 10, 1355-1360 Astrocytes: interlinked gatekeepers of glutamate astrocytes
? Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Christian S Lobsiger & Don W Cleveland (2007) Nature Neuroscience 10, 1355-1360 Astrocytes: interlinked gatekeepers of glutamate astrocytes
A healthy blend of polyphenols from Canadian wild blueberries and french grapes COGNITIVE HEALTH
 A healthy blend of polyphenols from Canadian wild blueberries and french grapes COGNITIVE HEALTH Cerebelle TM : promoter of your brain health What is Cerebelle TM? Cerebelle TM is a standardized mixture
A healthy blend of polyphenols from Canadian wild blueberries and french grapes COGNITIVE HEALTH Cerebelle TM : promoter of your brain health What is Cerebelle TM? Cerebelle TM is a standardized mixture
The wufless-ness of glutamate!
 The wufless-ness of glutamate! EXCITOTOXINS are substances, usually acidic amino acids, that react with specialized receptors in the brain in such a way as to lead to destruction of certain types of neurons.
The wufless-ness of glutamate! EXCITOTOXINS are substances, usually acidic amino acids, that react with specialized receptors in the brain in such a way as to lead to destruction of certain types of neurons.
More dendritic spines, changes in shapes of dendritic spines More NT released by presynaptic membrane
 LEARNING AND MEMORY (p.1) You are your learning and memory! (see movie Total Recall) L&M, two sides of the same coin learning refers more to the acquisition of new information & brain circuits (storage)
LEARNING AND MEMORY (p.1) You are your learning and memory! (see movie Total Recall) L&M, two sides of the same coin learning refers more to the acquisition of new information & brain circuits (storage)
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1.
 Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded
 BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
Subconvulsive Dose of Kainic Acid Transiently Increases the Locomotor Activity of Adult Wistar Rats
 Physiol. Res. 64: 263-267, 2015 SHORT COMMUNICATION Subconvulsive Dose of Kainic Acid Transiently Increases the Locomotor Activity of Adult Wistar Rats V. RILJAK 1, D. MAREŠOVÁ 1, J. POKORNÝ 1, K. JANDOVÁ
Physiol. Res. 64: 263-267, 2015 SHORT COMMUNICATION Subconvulsive Dose of Kainic Acid Transiently Increases the Locomotor Activity of Adult Wistar Rats V. RILJAK 1, D. MAREŠOVÁ 1, J. POKORNÝ 1, K. JANDOVÁ
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Functional Development of Neuronal Networks in Culture -An in vitro Assay System of Developing Brain for Endocrine Disruptors
 Functional Development of Neuronal Networks in Culture -An in vitro Assay System of Developing Brain for Endocrine Disruptors Masahiro Kawahara and Yoichiro Kuroda Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Neuroscience
Functional Development of Neuronal Networks in Culture -An in vitro Assay System of Developing Brain for Endocrine Disruptors Masahiro Kawahara and Yoichiro Kuroda Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Neuroscience
Mecanismo de acción de Souvenaid: nuevos datos preclínicos
 Mecanismo de acción de Souvenaid: nuevos datos preclínicos Dra. Sagrario Manzano Coordinadora del Grupo de Neurología de la Conducta y Demencias de la SEN. Hospital Universitario Infanta Cristina. Parla.
Mecanismo de acción de Souvenaid: nuevos datos preclínicos Dra. Sagrario Manzano Coordinadora del Grupo de Neurología de la Conducta y Demencias de la SEN. Hospital Universitario Infanta Cristina. Parla.
Neuronal Plasticity, Learning and Memory. David Keays Institute of Molecular Pathology
 Neuronal Plasticity, Learning and Memory David Keays Institute of Molecular Pathology http://keayslab.org Structure 1. What is learning and memory? 2. Anatomical basis 3. Cellular basis 4. Molecular
Neuronal Plasticity, Learning and Memory David Keays Institute of Molecular Pathology http://keayslab.org Structure 1. What is learning and memory? 2. Anatomical basis 3. Cellular basis 4. Molecular
7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY. 7.1 Introduction
 268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
Educational Background ; Fellowship in Neuroscience, The sick kids Hospital, Toronto, Canada (affiliated with the University of Toronto)
 First Name Last Name Birth Mohammad Ali Atlasi 19 th April, 1965 Degree Rank Fax Number Primary Email Secondary Email Main Area of Work Work Address PhD of Anatomical Sciences Associated Professor 0098-3615551112
First Name Last Name Birth Mohammad Ali Atlasi 19 th April, 1965 Degree Rank Fax Number Primary Email Secondary Email Main Area of Work Work Address PhD of Anatomical Sciences Associated Professor 0098-3615551112
Micro-Anatomical Effect Of Tahitian Noni Dietary Supplement On The Heart Of Caffeine-Treated SpragueDawley Rats
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 11 Number 2 Micro-Anatomical Effect Of Tahitian Noni Dietary Supplement On The Heart Of Caffeine-Treated SpragueDawley Rats R Bassey, O Yama, A Osinubi,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 11 Number 2 Micro-Anatomical Effect Of Tahitian Noni Dietary Supplement On The Heart Of Caffeine-Treated SpragueDawley Rats R Bassey, O Yama, A Osinubi,
death if the deficit is prolonged. Children and adults exposed to hypoglycaemia can develop long-term impairment of cognitive function (Blattner,
 Introduction Glucose is the primary source of fuel for the cells of the brain. Brain is dependent on a continuous supply of glucose diffusing from the blood into the interstitial tissue within the central
Introduction Glucose is the primary source of fuel for the cells of the brain. Brain is dependent on a continuous supply of glucose diffusing from the blood into the interstitial tissue within the central
Mind Altering Microbes: Role of Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Stress-Related Disorders
 Mind Altering Microbes: Role of Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Stress-Related Disorders John F. Cryan Ph.D. Professor & Chair Department of Anatomy & Neuroscience & Principal Investigator, Alimentary Pharmabiotic
Mind Altering Microbes: Role of Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Stress-Related Disorders John F. Cryan Ph.D. Professor & Chair Department of Anatomy & Neuroscience & Principal Investigator, Alimentary Pharmabiotic
PROPOSAL: Translational Safety Biomarker Assessment of Neurotoxicity
 PROPOSAL: Translational Safety Biomarker Assessment of Neurotoxicity Andreas Jeromin, PhD Chief Scientific Officer NextGen Sciences DX Boston, MA Emerging Issues Session HESI Annual Meeting 12 June 2012
PROPOSAL: Translational Safety Biomarker Assessment of Neurotoxicity Andreas Jeromin, PhD Chief Scientific Officer NextGen Sciences DX Boston, MA Emerging Issues Session HESI Annual Meeting 12 June 2012
Metal accumulation studies
 Metal accumulation studies Metal ions play a crucial role in determining the health and disease status by influencing cellular biochemical pathways. Since the uptake mechanisms of the body are not able
Metal accumulation studies Metal ions play a crucial role in determining the health and disease status by influencing cellular biochemical pathways. Since the uptake mechanisms of the body are not able
Blueberries The World^s Healthiest Food
 Blueberries The World^s Healthiest Food by William Faloon Over the past year, a record number of independent studies have confirmed the health effects of blueberries. Scientists tested blueberries against
Blueberries The World^s Healthiest Food by William Faloon Over the past year, a record number of independent studies have confirmed the health effects of blueberries. Scientists tested blueberries against
TGF-ß1 pathway as a new pharmacological target for neuroprotection in AD. Filippo Caraci
 Department of Clinical and Molecular Biomedicine Section of Pharmacology and Biochemistry Department of Educational Sciences University of Catania TGF-ß1 pathway as a new pharmacological target for neuroprotection
Department of Clinical and Molecular Biomedicine Section of Pharmacology and Biochemistry Department of Educational Sciences University of Catania TGF-ß1 pathway as a new pharmacological target for neuroprotection
Cellular PSP Ultra-Structure
 Cellular PSP is the trademark of ingredients containing a unique functional and cellular food formulation of nutrients that are essential for bodily functions. Cellular PSP contains all of these naturally
Cellular PSP is the trademark of ingredients containing a unique functional and cellular food formulation of nutrients that are essential for bodily functions. Cellular PSP contains all of these naturally
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70%
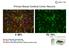 Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Neurogenesis in Adult Central Nervous System: Death of a Dogma
 Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece, Nov. 2007 Neurogenesis in Adult Central Nervous System: Death of a Dogma Anton B. Tonchev Division of Cell Biology, Varna University of Medicine, Bulgaria
Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece, Nov. 2007 Neurogenesis in Adult Central Nervous System: Death of a Dogma Anton B. Tonchev Division of Cell Biology, Varna University of Medicine, Bulgaria
Neuroprotective properties of GLP-1 - a brief overview. Michael Gejl Jensen, MD Dept. Of Pharmacology, AU
 Neuroprotective properties of GLP-1 - a brief overview Michael Gejl Jensen, MD Dept. Of Pharmacology, AU mg@farm.au.dk Agenda Glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) GLP-1 and neuronal activity GLP-1 in disease-specific
Neuroprotective properties of GLP-1 - a brief overview Michael Gejl Jensen, MD Dept. Of Pharmacology, AU mg@farm.au.dk Agenda Glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) GLP-1 and neuronal activity GLP-1 in disease-specific
Ph D THESIS ABSTRACT
 ALEXANDRU IOAN CUZA UNIVERSITY IAŞI FACULTY OF BIOLOGY THE STUDY OF CHANGES FOR SEVERAL BIOCHEMICAL PARAMETERS OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN ANIMAL MODELS FOR NEUROPSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Ph D THESIS ABSTRACT Scientific
ALEXANDRU IOAN CUZA UNIVERSITY IAŞI FACULTY OF BIOLOGY THE STUDY OF CHANGES FOR SEVERAL BIOCHEMICAL PARAMETERS OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN ANIMAL MODELS FOR NEUROPSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Ph D THESIS ABSTRACT Scientific
Received 20/11/2013 Accepted 27/12/2013
 Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 3 () January 4: 69-74 4 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 77-88 Journal s URL:http://www.bepls.com
Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 3 () January 4: 69-74 4 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 77-88 Journal s URL:http://www.bepls.com
Systems Neuroscience CISC 3250
 Systems Neuroscience CISC 325 Memory Types of Memory Declarative Non-declarative Episodic Semantic Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 328A Hippocampus (MTL) Cerebral cortex Basal ganglia Motor
Systems Neuroscience CISC 325 Memory Types of Memory Declarative Non-declarative Episodic Semantic Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 328A Hippocampus (MTL) Cerebral cortex Basal ganglia Motor
epilepticus (SE) or trauma. Between this injury and the emergence of recurrent
 Introduction Epilepsy is one of the oldest medical disorders known. The word epilepsy derived from the Greek word epilamhanein, meaning to be seized or to be overwhelmed by surprise. Epilepsy is one of
Introduction Epilepsy is one of the oldest medical disorders known. The word epilepsy derived from the Greek word epilamhanein, meaning to be seized or to be overwhelmed by surprise. Epilepsy is one of
Alcohol Abuse in Mothers during Gravidity and Breastfeeding Brings Changes of Hippocampal Neurons in their Offspring
 103) Alcohol Abuse in Mothers during Gravidity and Breastfeeding Brings Changes of Hippocampal Neurons in their Offspring Milotová M., Riljak V., Jandová K., Langmeier M., Marešová D., Pokorný J., Trojan
103) Alcohol Abuse in Mothers during Gravidity and Breastfeeding Brings Changes of Hippocampal Neurons in their Offspring Milotová M., Riljak V., Jandová K., Langmeier M., Marešová D., Pokorný J., Trojan
EFFECTS OF GALLIC ACID ON EXPLORATORY BEHAVIOR AND LOCOMOTOR ACTIVITY IN RATS
 Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 13, Suppl. 2, pp 29-33, 2015 Copyright 2015 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) doi:10.15547/tjs.2015.s.02.007 ISSN 1313-3551
Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 13, Suppl. 2, pp 29-33, 2015 Copyright 2015 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) doi:10.15547/tjs.2015.s.02.007 ISSN 1313-3551
TARGETING MITOCHONDRIA DESIGN, SYNTHESIS AND APPLICATION OF GS-NITROXIDES. Tanja Krainz Wipf Group Research Topic Seminar 16 th May, 2015
 TARGETING MITOCHONDRIA DESIGN, SYNTHESIS AND APPLICATION OF GS-NITROXIDES Tanja Krainz Wipf Group Research Topic Seminar 16 th May, 2015 Tanja Krainz @ Wipf Group Page 1 of 26 5/20/2015 Mitochondria as
TARGETING MITOCHONDRIA DESIGN, SYNTHESIS AND APPLICATION OF GS-NITROXIDES Tanja Krainz Wipf Group Research Topic Seminar 16 th May, 2015 Tanja Krainz @ Wipf Group Page 1 of 26 5/20/2015 Mitochondria as
The Effect of Gallic Acid on Histopathologic Evaluation of Cerebellum in Valproic Acid-Induced Autism Animal Models
 Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 6:164-171 The Effect of Gallic Acid on Histopathologic Evaluation of Cerebellum
Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 6:164-171 The Effect of Gallic Acid on Histopathologic Evaluation of Cerebellum
Embargoed until Oct. 18, 10:30 a.m. CDT Contacts: Kat Snodgrass, (202) Press Room, Oct : (312) Sarah Bates, (202)
 Embargoed until Oct. 18, 10:30 a.m. CDT Contacts: Kat Snodgrass, (202) 962-4090 Press Room, Oct. 17 21: (312) 791-6619 Sarah Bates, (202) 962-4087 RUN FOR YOUR LIFE: NEW STUDIES SHOW BENEFITS OF EXERCISE
Embargoed until Oct. 18, 10:30 a.m. CDT Contacts: Kat Snodgrass, (202) 962-4090 Press Room, Oct. 17 21: (312) 791-6619 Sarah Bates, (202) 962-4087 RUN FOR YOUR LIFE: NEW STUDIES SHOW BENEFITS OF EXERCISE
SCIRF Award #2016 I-03 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Neuron-specific Enolase and SCI
 SCIRF Award #2016 I-03 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Neuron-specific Enolase and SCI 10-month Technical Progress Report Enolase is a multifunctional glycolytic enzyme involved in growth control, hypoxia,
SCIRF Award #2016 I-03 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Neuron-specific Enolase and SCI 10-month Technical Progress Report Enolase is a multifunctional glycolytic enzyme involved in growth control, hypoxia,
Extending Injury- and Disease-Tolerant Phenotypes by Repetitive Conditioning
 Extending Injury- and Disease-Tolerant Phenotypes by Repetitive Conditioning Promoting Long-Lasting Protection in the CNS Jeff Gidday PhD Neurosurgery Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences Cell Biology & Physiology
Extending Injury- and Disease-Tolerant Phenotypes by Repetitive Conditioning Promoting Long-Lasting Protection in the CNS Jeff Gidday PhD Neurosurgery Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences Cell Biology & Physiology
The Marmoset Monkey as Model for Neurological Disorders
 The Marmoset Monkey as Model for Neurological Disorders Jan Langermans and Ingrid Philippens From Laboratory to Clinic Disease models neuroscience: Parkinson, Sleep, Stress, Alzheimer, MS MS Models: rhmog
The Marmoset Monkey as Model for Neurological Disorders Jan Langermans and Ingrid Philippens From Laboratory to Clinic Disease models neuroscience: Parkinson, Sleep, Stress, Alzheimer, MS MS Models: rhmog
Convergent and Divergent Mechanisms in Aging and Cancer
 Convergent and Divergent Mechanisms in Aging and Cancer Mariana S. De Lorenzo, PhD Department of Cell Biology & Molecular Medicine delorems@umdnj.edu LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. To identify convergent and divergent
Convergent and Divergent Mechanisms in Aging and Cancer Mariana S. De Lorenzo, PhD Department of Cell Biology & Molecular Medicine delorems@umdnj.edu LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. To identify convergent and divergent
Contribution of microglia to tissue injury and repair in MS
 Contribution of microglia to tissue injury and repair in MS MS disease course histologic features Courtesy of Samuel Ludwin I ACUTE CHRONIC s ACTIVE CHRONIC Clinical Course Intra CNS Extra CNS Imaging
Contribution of microglia to tissue injury and repair in MS MS disease course histologic features Courtesy of Samuel Ludwin I ACUTE CHRONIC s ACTIVE CHRONIC Clinical Course Intra CNS Extra CNS Imaging
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II. Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy
 Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
processes in the central nervous system (CNS), affecting many of the during the course of ethanol treatment. Ethanol stimulates the release of
 INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION Neuroscience research is essential for understanding the biological basis of ethanol-related brain alterations and for identifying the molecular targets for therapeutic compounds
INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION Neuroscience research is essential for understanding the biological basis of ethanol-related brain alterations and for identifying the molecular targets for therapeutic compounds
Imaging ischemic strokes: Correlating radiological findings with the pathophysiological evolution of an infarct
 Imaging ischemic strokes: Correlating radiological findings with the pathophysiological evolution of an infarct Jay Chyung,, PhD, HMS III Patient A: history 91 y.o. woman Acute onset R sided weakness and
Imaging ischemic strokes: Correlating radiological findings with the pathophysiological evolution of an infarct Jay Chyung,, PhD, HMS III Patient A: history 91 y.o. woman Acute onset R sided weakness and
Abstracts and affiliations
 Dopamine Discovery Day August 30, 2012 Rikshospitalet Store auditorium, Oslo, Norway Organized by Linda H. Bergersen & Vidar Gundersen Institute of Basic Medical Sciences & Centre for Molecular Biology
Dopamine Discovery Day August 30, 2012 Rikshospitalet Store auditorium, Oslo, Norway Organized by Linda H. Bergersen & Vidar Gundersen Institute of Basic Medical Sciences & Centre for Molecular Biology
HOW NUTRITION CHANGES THE AGING BRAIN. Nafisa Jadavji, PhD
 HOW NUTRITION CHANGES THE AGING BRAIN Nafisa Jadavji, PhD NafisaJadavji@carleton.ca Lecture Outline Introduction Brain Nutrition Peer Review Questions BREAK Dementia and Alzheimer's disease Parkinson s
HOW NUTRITION CHANGES THE AGING BRAIN Nafisa Jadavji, PhD NafisaJadavji@carleton.ca Lecture Outline Introduction Brain Nutrition Peer Review Questions BREAK Dementia and Alzheimer's disease Parkinson s
Dietary Flavonoids: Modulators of Brain Ageing?
 MLECULAR NUTRITIN GRUP Established 2004 Dietary Flavonoids: Modulators of Brain Ageing? Jeremy P E Spencer School of Food Biosciences University of Reading, UK The Sensitivity of the Brain to xidative
MLECULAR NUTRITIN GRUP Established 2004 Dietary Flavonoids: Modulators of Brain Ageing? Jeremy P E Spencer School of Food Biosciences University of Reading, UK The Sensitivity of the Brain to xidative
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Fakulti Perubatan dan Sains Kesihatan, Universiti Putra Malaysia.
 Academic Sciences International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 4, Issue 4, 2012 Research Article CRESYL VIOLET STAINING TO ASSESS NEUROPROTECTIVE AND NEUROREGENERATIVE
Academic Sciences International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN- 0975-1491 Vol 4, Issue 4, 2012 Research Article CRESYL VIOLET STAINING TO ASSESS NEUROPROTECTIVE AND NEUROREGENERATIVE
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Personal Information. Academic Background. M.S.c Thesis
 Personal Information Name: Surname: Jalal hassanshahi Date of Birth: December, 25th, 1987 City of Birth: Nationality: Religion: Pre-University: Email: Rafsanjan Iranian Islam Educated from Emam Ali High
Personal Information Name: Surname: Jalal hassanshahi Date of Birth: December, 25th, 1987 City of Birth: Nationality: Religion: Pre-University: Email: Rafsanjan Iranian Islam Educated from Emam Ali High
LIST OF FIGURES AND TABLES
 ii LIST OF FIGURES AND TABLES GENERAL INTRODUCTION Fig. 1 Effect of Pb on antioxidant enzymes and cofactors leading to inactivation of enzyme activity Fig. 2 Rationale between Pb exposures among low SES
ii LIST OF FIGURES AND TABLES GENERAL INTRODUCTION Fig. 1 Effect of Pb on antioxidant enzymes and cofactors leading to inactivation of enzyme activity Fig. 2 Rationale between Pb exposures among low SES
THE ROLE OF INSULIN RECEPTOR SIGNALING IN THE BRAIN. COGS 163 By: Pranav Singh Alexandra Villar
 THE ROLE OF INSULIN RECEPTOR SIGNALING IN THE BRAIN COGS 163 By: Pranav Singh Alexandra Villar INTRODUCTION Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas by the islets of Langerhans that regulates the
THE ROLE OF INSULIN RECEPTOR SIGNALING IN THE BRAIN COGS 163 By: Pranav Singh Alexandra Villar INTRODUCTION Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas by the islets of Langerhans that regulates the
HYPERTENSIVE ENCEPHALOPATHY
 HYPERTENSIVE ENCEPHALOPATHY Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome Cause Renal disease Pheochromocytoma Disseminated vasculitis Eclampsia Acute toxemia Medications & illicit drugs (cocaine)
HYPERTENSIVE ENCEPHALOPATHY Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome Cause Renal disease Pheochromocytoma Disseminated vasculitis Eclampsia Acute toxemia Medications & illicit drugs (cocaine)
Jurnal Teknologi. Full Paper. *Corresponding author
 Jurnal Teknologi DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION LENGTH OF CENTELLA ASIATICA (L.) URBAN DECREASE THE LEVEL OF SOD AND MDA AND IMPROVE BRAIN HISTOLOGICAL CONDITION OF RATS Bayyinatul Muchtaromah *, Mujahidin
Jurnal Teknologi DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION LENGTH OF CENTELLA ASIATICA (L.) URBAN DECREASE THE LEVEL OF SOD AND MDA AND IMPROVE BRAIN HISTOLOGICAL CONDITION OF RATS Bayyinatul Muchtaromah *, Mujahidin
Nitric oxide damages neuronal mitochondria and induces apoptosis in neurons
 Nitric oxide damages neuronal mitochondria and induces apoptosis in neurons WEI Taotao, CHEN Chang, HOU Jingwu, ZHAO Baolu & XIN Wenjuan Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101,
Nitric oxide damages neuronal mitochondria and induces apoptosis in neurons WEI Taotao, CHEN Chang, HOU Jingwu, ZHAO Baolu & XIN Wenjuan Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101,
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations
 Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
A new approach to Common Sporadic Alzheimer s, Post-Traumatic Alzheimer s, and CTE:
 A new approach to Common Sporadic Alzheimer s, Post-Traumatic Alzheimer s, and CTE: Roles of Aβ, Tau, ApoE, and Regulatory Signaling in Elucidating Pathogenesis and Experimental Therapeutics Sam Gandy,
A new approach to Common Sporadic Alzheimer s, Post-Traumatic Alzheimer s, and CTE: Roles of Aβ, Tau, ApoE, and Regulatory Signaling in Elucidating Pathogenesis and Experimental Therapeutics Sam Gandy,
Targeting the p75 Receptor to Inhibit Degenerative Signaling and Tau Phosphorylation/Misfolding/ Missorting: Preclinical through Phase 1
 Targeting the p75 Receptor to Inhibit Degenerative Signaling and Tau Phosphorylation/Misfolding/ Missorting: Preclinical through Phase 1 ADC Directors Meeting, April 18 th 2015 Frank M. Longo, Stanford
Targeting the p75 Receptor to Inhibit Degenerative Signaling and Tau Phosphorylation/Misfolding/ Missorting: Preclinical through Phase 1 ADC Directors Meeting, April 18 th 2015 Frank M. Longo, Stanford
Science & Technologies COMPARISON THE EFFECTS OF TACRINE AND GALANTAMINE ON ACTIVE AVOIDANCE TEST IN RATS WITH DIAZEPAM-AMNESIA MODEL
 COMPARISON THE EFFECTS OF TACRINE AND GALANTAMINE ON ACTIVE AVOIDANCE TEST IN RATS WITH DIAZEPAM-AMNESIA MODEL Darinka Dimitrova, Damianka Getova Medical University Plovdiv, Medical Faculty, 4002 Plovdiv,
COMPARISON THE EFFECTS OF TACRINE AND GALANTAMINE ON ACTIVE AVOIDANCE TEST IN RATS WITH DIAZEPAM-AMNESIA MODEL Darinka Dimitrova, Damianka Getova Medical University Plovdiv, Medical Faculty, 4002 Plovdiv,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Alzheimer's Disease A mind in darkness awaiting the drink of a gentle color.
 Alzheimer's Disease A mind in darkness awaiting the drink of a gentle color. Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Gabriel García Márquez One Hundred Years of Solitude Alois Alzheimer
Alzheimer's Disease A mind in darkness awaiting the drink of a gentle color. Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Gabriel García Márquez One Hundred Years of Solitude Alois Alzheimer
Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury
 Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D., Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Kenichiro Yahata, M.D.,
Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D., Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Kenichiro Yahata, M.D.,
Supplementary Figure 1. Western blot of hippocampal lysates from WT and Adcy1 KO mice demonstrates the specificity of the ADCY1 antibody.
 ADCY1 13 kda β-actin 45 kda Supplementary Figure 1. Western blot of hippocampal lysates from and mice demonstrates the specificity of the ADCY1 antibody. a DHPG perk1/2 ERK1/2 Relative level min 1.6 *
ADCY1 13 kda β-actin 45 kda Supplementary Figure 1. Western blot of hippocampal lysates from and mice demonstrates the specificity of the ADCY1 antibody. a DHPG perk1/2 ERK1/2 Relative level min 1.6 *
Subject Index. Band of Giacomini 22 Benton Visual Retention Test 66 68
 Subject Index Adams, R.D. 4 Addenbrooke s Cognitive Examination 101 Alzheimer s disease clinical assessment histological imaging 104 neuroimaging 101 104 neuropsychological assessment 101 clinical presentation
Subject Index Adams, R.D. 4 Addenbrooke s Cognitive Examination 101 Alzheimer s disease clinical assessment histological imaging 104 neuroimaging 101 104 neuropsychological assessment 101 clinical presentation
Pharmacologyonline 2: 471:479 (2008)
 SERUM ZINC AND COPPER LEVELS IN UNTREATED EPILEPTIC PATIENTS Habib Allah Nemati Karimooy*, Mosa- Alreza Hajzadeh 1, Raheleh Haidari 2, Mahmoud Hosseini 1 *Dept of Physiology, School of medicine, Mashhad
SERUM ZINC AND COPPER LEVELS IN UNTREATED EPILEPTIC PATIENTS Habib Allah Nemati Karimooy*, Mosa- Alreza Hajzadeh 1, Raheleh Haidari 2, Mahmoud Hosseini 1 *Dept of Physiology, School of medicine, Mashhad
Fernando Gomez-Pinilla, Ph.D. UCLA
 Regaining homeostasis with diet (and exercise) Fernando Gomez-Pinilla, Ph.D. Professor Dept Neurosurgery, and Integrative Biology and Physiology UCLA Brain Injury Research Center UCLA Brain Injury Research
Regaining homeostasis with diet (and exercise) Fernando Gomez-Pinilla, Ph.D. Professor Dept Neurosurgery, and Integrative Biology and Physiology UCLA Brain Injury Research Center UCLA Brain Injury Research
NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update
 NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update 1 Overview The natural growth factor IGF-1 is broken down in the body to IGF-1[1-3] NNZ-2566 is an analogue of IGF-1[1-3] developed
NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update 1 Overview The natural growth factor IGF-1 is broken down in the body to IGF-1[1-3] NNZ-2566 is an analogue of IGF-1[1-3] developed
Stress and the aging brain
 Stress and the aging brain Stress and the aging brain: What are the issues? Aging makes us less able to adjust to change Reactions of elderly to change generate stress Stress response involves acute reactions
Stress and the aging brain Stress and the aging brain: What are the issues? Aging makes us less able to adjust to change Reactions of elderly to change generate stress Stress response involves acute reactions
Rhodiola rosea L- Standardized Extract on Passive
 Research Article ISSN: 0976-5700 Rhodiola rosea L- Standardized Extract on Passive Avoidance in Rats Liliya Vl Vasileva 1,2,3*, Damyanka P Getova 3 1Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology,
Research Article ISSN: 0976-5700 Rhodiola rosea L- Standardized Extract on Passive Avoidance in Rats Liliya Vl Vasileva 1,2,3*, Damyanka P Getova 3 1Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology,
Leading the way to a healthier old age.
 Leading the way to a healthier old age. enhances the quality of life in ageing dogs. Not only does it increase oxygenation, but it also improves cardiovascular function and neurological performance. We
Leading the way to a healthier old age. enhances the quality of life in ageing dogs. Not only does it increase oxygenation, but it also improves cardiovascular function and neurological performance. We
KA Toulis, K. Dovas, M. Tsolaki. The endocrine facets of Alzheimer s disease and dementia-related disorders
 KA Toulis, K. Dovas, M. Tsolaki The endocrine facets of Alzheimer s disease and dementia-related disorders Sex hormones Calcium metabolism GH/IGF-I Thyroid axis Metabolic hormones + dementia Sex hormones
KA Toulis, K. Dovas, M. Tsolaki The endocrine facets of Alzheimer s disease and dementia-related disorders Sex hormones Calcium metabolism GH/IGF-I Thyroid axis Metabolic hormones + dementia Sex hormones
TNS Journal Club: Interneurons of the Hippocampus, Freund and Buzsaki
 TNS Journal Club: Interneurons of the Hippocampus, Freund and Buzsaki Rich Turner (turner@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk) Gatsby Unit, 22/04/2005 Rich T. Introduction Interneuron def = GABAergic non-principal cell Usually
TNS Journal Club: Interneurons of the Hippocampus, Freund and Buzsaki Rich Turner (turner@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk) Gatsby Unit, 22/04/2005 Rich T. Introduction Interneuron def = GABAergic non-principal cell Usually
The effect of ETS exposure on the BDNF protein. In America, it is common knowledge that smoking cigarettes is bad for one s health;
 The effect of ETS exposure on the BDNF protein Introduction: In America, it is common knowledge that smoking cigarettes is bad for one s health; however, it is less well known that secondhand smoke exposure
The effect of ETS exposure on the BDNF protein Introduction: In America, it is common knowledge that smoking cigarettes is bad for one s health; however, it is less well known that secondhand smoke exposure
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
METABOLIC SYNDROME, NEUROINFLAMMATION AND COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT: STATE OF LEVEL OUTPATIENT CLINIC IN ITALY
 METABOLIC SYNDROME, NEUROINFLAMMATION AND COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT: STATE OF THE ART AND DATA FROM A SECOND LEVEL OUTPATIENT CLINIC IN ITALY Valeria Calsolaro Post graduating school on Geriatric medicine University
METABOLIC SYNDROME, NEUROINFLAMMATION AND COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT: STATE OF THE ART AND DATA FROM A SECOND LEVEL OUTPATIENT CLINIC IN ITALY Valeria Calsolaro Post graduating school on Geriatric medicine University
HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS
 12 Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 1 12-21 2002 Research Report HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS YM Shivarajashankara, a AR Shivashankara, a P Gopalakrishna Bhat, b S Muddanna
12 Fluoride Vol. 35 No. 1 12-21 2002 Research Report HISTOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE BRAIN OF YOUNG FLUORIDE-INTOXICATED RATS YM Shivarajashankara, a AR Shivashankara, a P Gopalakrishna Bhat, b S Muddanna
Impact of vitamins & nutrients on neurological function. B-vitamins and aging. Nafisa Jadavji, PhD
 Impact of vitamins & nutrients on neurological function B-vitamins and aging Nafisa Jadavji, PhD nafisa.jadavji@carleton.ca Lecture Outline Answer to questions from last class Homocysteine Vitamin B9:
Impact of vitamins & nutrients on neurological function B-vitamins and aging Nafisa Jadavji, PhD nafisa.jadavji@carleton.ca Lecture Outline Answer to questions from last class Homocysteine Vitamin B9:
Rapamycin Attenuates the Development of Posttraumatic Epilepsy in a Mouse Model of Traumatic Brain Injury.
 Current Literature In Basic Science Prophylaxis for Post-Traumatic Epilepsy: Can Your Kinase Do That? Rapamycin Attenuates the Development of Posttraumatic Epilepsy in a Mouse Model of Traumatic Brain
Current Literature In Basic Science Prophylaxis for Post-Traumatic Epilepsy: Can Your Kinase Do That? Rapamycin Attenuates the Development of Posttraumatic Epilepsy in a Mouse Model of Traumatic Brain
Delirium & Dementia. Nicholas J. Silvestri, MD
 Delirium & Dementia Nicholas J. Silvestri, MD Outline Delirium vs. Dementia Neural pathways relating to consciousness Encephalopathy Stupor Coma Dementia Delirium vs. Dementia Delirium Abrupt onset Lasts
Delirium & Dementia Nicholas J. Silvestri, MD Outline Delirium vs. Dementia Neural pathways relating to consciousness Encephalopathy Stupor Coma Dementia Delirium vs. Dementia Delirium Abrupt onset Lasts
Improvement of Peripheral Regeneration with G-CSF in a Rat Model of Sciatic Nerve Repair
 Improvement of Peripheral Regeneration with G-CSF in a Rat Model of Sciatic Nerve Repair YENFU CHEN, MD 1, YAO-LUNG KUO, MD 2,3,4, I-Ming Jou, Prof, 3. 1 Department of Orthopaedics, National Cheng Kung
Improvement of Peripheral Regeneration with G-CSF in a Rat Model of Sciatic Nerve Repair YENFU CHEN, MD 1, YAO-LUNG KUO, MD 2,3,4, I-Ming Jou, Prof, 3. 1 Department of Orthopaedics, National Cheng Kung
STROKE & DIETARY INFLUENCES ON COGNITION IN AGING
 How Nutrition Changes the Aging Brain STROKE & DIETARY INFLUENCES ON COGNITION IN AGING Nafisa Jadavji, PhD nafisa.jadavji@carleton.ca REMINDER! Purpose of Course To present information about how nutrition
How Nutrition Changes the Aging Brain STROKE & DIETARY INFLUENCES ON COGNITION IN AGING Nafisa Jadavji, PhD nafisa.jadavji@carleton.ca REMINDER! Purpose of Course To present information about how nutrition
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2+ cells in different brain regions.
 Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Heyam Awad
 number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
GFP/Iba1/GFAP. Brain. Liver. Kidney. Lung. Hoechst/Iba1/TLR9!
 Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Advanced Nutritional Strategies for Optimal Health and Performance in Warfighters
 Advanced Nutritional Strategies for Optimal Health and Performance in Warfighters Primary Funding Department of Defense - Combat Feeding Program, Natick, MA DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Project Agency)
Advanced Nutritional Strategies for Optimal Health and Performance in Warfighters Primary Funding Department of Defense - Combat Feeding Program, Natick, MA DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Project Agency)
Formation of New Inhibitory Circuits for Treating Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
 Formation of New Inhibitory Circuits for Treating Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Janice R. Naegele, Ph.D. Department of Biology Program in Neuroscience Wesleyan University Neurology and Neurosurgery Grand Rounds
Formation of New Inhibitory Circuits for Treating Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Janice R. Naegele, Ph.D. Department of Biology Program in Neuroscience Wesleyan University Neurology and Neurosurgery Grand Rounds
Neuropharmacology NOTES
 Neuropharmacology NOTES Contents Topic Page # Lecture 1- Intro to Neurochemical Transmission & Neuromodulation 2 Lecture 2- Serotonin & Noradrenaline 7 Lecture 3- Acetylcholine & Dopamine 14 Lecture 4-
Neuropharmacology NOTES Contents Topic Page # Lecture 1- Intro to Neurochemical Transmission & Neuromodulation 2 Lecture 2- Serotonin & Noradrenaline 7 Lecture 3- Acetylcholine & Dopamine 14 Lecture 4-
Role of TDP-43 in Non-Alzheimer s and Alzheimer s Neurodegenerative Diseases
 Role of TDP-43 in Non-Alzheimer s and Alzheimer s Neurodegenerative Diseases Keith A. Josephs, MD, MST, MSc Professor of Neurology 13th Annual Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) Symposium: Alzheimer and Non-Alzheimer
Role of TDP-43 in Non-Alzheimer s and Alzheimer s Neurodegenerative Diseases Keith A. Josephs, MD, MST, MSc Professor of Neurology 13th Annual Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) Symposium: Alzheimer and Non-Alzheimer
