More dendritic spines, changes in shapes of dendritic spines More NT released by presynaptic membrane
|
|
|
- Russell Gregory
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LEARNING AND MEMORY (p.1) You are your learning and memory! (see movie Total Recall) L&M, two sides of the same coin learning refers more to the acquisition of new information & brain circuits (storage) memory refers more to the ability to access the above (retrieval) 1. Synaptic Mechanisms of L&M We have long-assumed a chemical/electrical event --- a structural change in NS What do we really observe? Pre- and post-synaptic membranes getting thicker Area of contact between pre- and post-synaptic membranes enlarging More pre-synaptic axon terminals making synaptic contacts on a postsynaptic area More dendritic spines, changes in shapes of dendritic spines More NT released by presynaptic membrane Long-Term Potentiation If high-frequency electrical stimulation is applied to a presynaptic neuron --- it then fires more when it is next stimulated (its response has been amplified/facilitated) Much of this research has been done on neurons in hippocampal system 1 st single, low-intensity electrical pulse is delivered to perforant path (major input to dentate gyrus) 2 nd output response is measured in the granule cells of the dentate gyrus (perforant path neurons synapse on granule cells) to get a baseline response from the granule cells 3 rd a high-intensity, high-frequency electrical pulse lasting 10 seconds is delivered to the perforant path neurons (to produce LTP) 4 th single, low-intensity electrical pulse is again delivered to perforant path and response in granule cells is again measured The response is now greatly amplified, indicating LTP has occurred. Can even delay one week between steps #3 and #4 and see LTP!
2 LEARNING AND MEMORY (cont., p.2) 1.Synaptic Mechanisms (cont.) Long-Term Potentiation (cont.) Further study of LTP on neurons in dentate gyrus How do these synapses work? Use NMDA post-synaptic receptors (N-methyl-D-aspartate) NMDA receptor must have two events occur simultaneously: Glutamate must bind to receptor +Postsynaptic neuron must already be partially depolarized which leads to more Ca++ entering the neuron so for LTP to occur, a neuron must already be primed (depolarized) when the second signal comes in (glutamate is released) --- LTP Also know that LTP depends on protein kinases (in potentiated neuron) Drugs that block protein kinases --- no LTP A primed postsynaptic neurons most likely sends a signal back to its inputting presynaptic neuron by way of sending nitric oxide back to that presynaptic neuron Note: LTP occurs not just in hippocampal neurons, but in other areas of the brain as well. Also, non-glutamate (non-nmda) systems are being discovered.
3 LEARNING AND MEMORY (cont., p3) 2. Memory a. The Case of H.M. What was known in 1953 about the hippocampus when his bilateral medial temporal lobectomy was performed? hyperactive rats But H.M. had mild retrograde amnesia (up to 2 years) and severe anterograde amnesia (from then on) Along with normal short-term memory (7 items + or 2) Poor memory for stimuli presented in any sensory system (visual, aud, etc) Showed improvement on mirror-drawing test (but no recall of doing test) Showed improvement on rotary-pursuit test (but no recall of doing test) Showed improvement on incomplete-pictures test (but no recall of doing) Could learn via classical conditioning (eye blink) (but no recall of doing) So H.M. cannot consolidate STM into LTM Does have good implicit memory (improved performance w/o conscious memory for events); does not know that he knows Does not have good explicit memory (conscious memory of doing/ knowing something) Note: H.M. must now be in his mid-70s but thinks he is 27 What must this be like?. b. Other persons with partial hippocampal (temporal lobe) damage Difficulty forming explicit LTMs, but may not completely be unable to do so Often recall general facts/information ( semantic or reference memory) but have difficulty with explicit memories for particular events or experiences ( episodic or working memory)
4 LEARNING AND MEMORY (cont., p.4) Note: Probably unconscious/implicit memory evolved first, and then conscious/explicit memory later on Evidently, must have explicit memory in order to use/transfer that memory/skill to a new situation c. Cerebral Ischemia and Hippocampal Damage Interruption of blood supply --- hippocampal damage e.g. from failed heart/lung machine (case of R.B.) e.g. from carbon monoxide poisoning often damages pyramidal cell layer of CA1 subfield in hippocampus d. Amnesia in Korsakoff s Syndrome Usually from long-term, chronic abuse of alcohol Specific cause: Symptoms: extreme confusion, personality changes, confabulation Seeming lack of awareness of deficit Damage to neocortex & cerebellum, to medial diencephalon (both thalamus and hypothalamus) Initially shows anterograde amnesia for explicit episodic/working memory Later on shows severe retrograde amnesia for explicit episodic/working and semantic/reference memory as well Failure to store new memory vs. failure to retrieve stored memories? May be somewhat similar to case of N.A. who had severe damage to the medial diencephalic areas (incl. mediodorsal nucleus of thalamus) and mammillary bodies e. Amnesia in Alzheimer s Disease Mild deterioration of memory --- severe dementia (severe amnesia) --- terminal Show more global, general memory deficits than those above Initial problems with STM & some types of implicit memory Later on LTM and explicit material is lost too
5 LEARNING AND MEMORY (cont., p5) f. Amnesia in Alzheimer s Disease (cont.) Widespread loss of ACh neurons, esp. in basal forebrain (which is brain s main source of ACh axons) Note: CVAs in basal forebrain can --- amnesias ACh neurons in hippocampus are dying too Note: very early sign of Alzheimer s (prior to onset of memory problems) is a problem with memory for olfactory stimuli, what is that smell? g. Post-Concussion Amnesia Anything that interrupts the process of memory storage (consolidation) will result in complete or partial amnesia for that memory e.g. sudden blow to the head (concussion) electric shock even strong startle/fear/ trauma can have both retrograde (usually shorter) and anterograde (usually longer) effects on memory retrograde amnesia may show swiss cheese effects (islands of preserved memory within the amnesia) Initial research showed that could disrupt consolidation for minutes to an hour after the event to be remembered had occurred but now we think that memory consolidation may go on for months/years after the event Retained memories become increasingly more resistant to forgetting the more often they are recalled ( practiced ) The more often a memory is recalled and the more other memories are linked to that first memory, the easier the first memory is to recall Thus, over-learning works (studying again what you already know) Increased ease of recall, decreased retrieval problems
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory II
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory II ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html Memory Working Memory Long-term Memory Declarative Memory Procedural Memory
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory II ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html Memory Working Memory Long-term Memory Declarative Memory Procedural Memory
Learning and Memory. The Case of H.M.
 Learning and Memory Learning deals with how experience changes the brain Memory refers to how these changes are stored and later reactivated The Case of H.M. H.M. suffered from severe, intractable epilepsy
Learning and Memory Learning deals with how experience changes the brain Memory refers to how these changes are stored and later reactivated The Case of H.M. H.M. suffered from severe, intractable epilepsy
Serial model. Amnesia. Amnesia. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory. Prof. Stephan Anagnostaras. Lecture 3: HM, the medial temporal lobe, and amnesia
 Neurobiology of Learning and Memory Serial model Memory terminology based on information processing models e.g., Serial Model Prof. Stephan Anagnostaras Lecture 3: HM, the medial temporal lobe, and amnesia
Neurobiology of Learning and Memory Serial model Memory terminology based on information processing models e.g., Serial Model Prof. Stephan Anagnostaras Lecture 3: HM, the medial temporal lobe, and amnesia
Systems Neuroscience November 29, Memory
 Systems Neuroscience November 29, 2016 Memory Gabriela Michel http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html Forms of memory Different types of learning & memory rely on different brain structures
Systems Neuroscience November 29, 2016 Memory Gabriela Michel http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html Forms of memory Different types of learning & memory rely on different brain structures
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu www.cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html n Learning and Memory n Human Communication n Emotion 1 What is memory? n Working Memory:
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu www.cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html n Learning and Memory n Human Communication n Emotion 1 What is memory? n Working Memory:
CASE 49. What type of memory is available for conscious retrieval? Which part of the brain stores semantic (factual) memories?
 CASE 49 A 43-year-old woman is brought to her primary care physician by her family because of concerns about her forgetfulness. The patient has a history of Down syndrome but no other medical problems.
CASE 49 A 43-year-old woman is brought to her primary care physician by her family because of concerns about her forgetfulness. The patient has a history of Down syndrome but no other medical problems.
Ch 8. Learning and Memory
 Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Memory. Psychology 3910 Guest Lecture by Steve Smith
 Memory Psychology 3910 Guest Lecture by Steve Smith Note: Due to copyright restrictions, I had to remove the images from the Weschler Memory Scales from the slides I posted online. Wechsler Memory Scales
Memory Psychology 3910 Guest Lecture by Steve Smith Note: Due to copyright restrictions, I had to remove the images from the Weschler Memory Scales from the slides I posted online. Wechsler Memory Scales
Ch 8. Learning and Memory
 Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect 22,24,25: Memory Systems
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect 22,24,25: Memory Systems Compare Chap 31 of Purves et al., 5e Chap 24 of Bear et al., 3e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook University http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/~cse511
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect 22,24,25: Memory Systems Compare Chap 31 of Purves et al., 5e Chap 24 of Bear et al., 3e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook University http://www.cs.sunysb.edu/~cse511
Theories of memory. Memory & brain Cellular bases of learning & memory. Epileptic patient Temporal lobectomy Amnesia
 Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Theories of Sensory, short-term & long-term memories Memory & brain Cellular bases
Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Theories of Sensory, short-term & long-term memories Memory & brain Cellular bases
Summarized by. Biointelligence Laboratory, Seoul National University
 Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and db.-t. TZhang Biointelligence
Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 3 rd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2008. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and db.-t. TZhang Biointelligence
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Declarative memory conscious,
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Declarative memory conscious,
Synap&c Plas&city. long-term plasticity (~30 min to lifetime) Long-term potentiation (LTP) / Long-term depression (LTD)
 Synap&c Plas&city synaptic connectivity constantly changes in response to activity and other factors During development: provides the basic wiring of the brain s circuits Throughout rest of life: basis
Synap&c Plas&city synaptic connectivity constantly changes in response to activity and other factors During development: provides the basic wiring of the brain s circuits Throughout rest of life: basis
Memory Systems II How Stored: Engram and LTP. Reading: BCP Chapter 25
 Memory Systems II How Stored: Engram and LTP Reading: BCP Chapter 25 Memory Systems Learning is the acquisition of new knowledge or skills. Memory is the retention of learned information. Many different
Memory Systems II How Stored: Engram and LTP Reading: BCP Chapter 25 Memory Systems Learning is the acquisition of new knowledge or skills. Memory is the retention of learned information. Many different
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Hippocampus. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Hippocampus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Common (Distributed) Model of Memory Processes Time Course of Memory Processes Long Term Memory DECLARATIVE NON-DECLARATIVE Semantic Episodic Skills
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Hippocampus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Common (Distributed) Model of Memory Processes Time Course of Memory Processes Long Term Memory DECLARATIVE NON-DECLARATIVE Semantic Episodic Skills
LONG TERM MEMORY. Learning Objective Topics. Retrieval and the Brain. Retrieval Neuroscience of Memory. LTP Brain areas Consolidation Reconsolidation
 LONG TERM MEMORY Retrieval and the rain Learning Objective Topics Retrieval Neuroscience of Memory LTP rain areas onsolidation Reconsolidation 1 Long-term memory How does info become encoded/stored in
LONG TERM MEMORY Retrieval and the rain Learning Objective Topics Retrieval Neuroscience of Memory LTP rain areas onsolidation Reconsolidation 1 Long-term memory How does info become encoded/stored in
This Lecture: Psychology of Memory and Brain Areas Involved
 Lecture 18 (Nov 24 th ): LEARNING & MEMORY #1 Lecture Outline This Lecture: Psychology of Memory and Brain Areas Involved Next lecture: Neural Mechanisms for Memory 1) Psychology of Memory: Short Term
Lecture 18 (Nov 24 th ): LEARNING & MEMORY #1 Lecture Outline This Lecture: Psychology of Memory and Brain Areas Involved Next lecture: Neural Mechanisms for Memory 1) Psychology of Memory: Short Term
Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma
 Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma Paper: Abraham, Wickliffe C., and Anthony Robins. "Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma." Trends in neurosciences
Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma Paper: Abraham, Wickliffe C., and Anthony Robins. "Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma." Trends in neurosciences
Memory. Lynn Yen, class of 2009
 Memory Lynn Yen, class of 2009 Objectives 1. Understand the different types of memory. 2. Describe where different types of memory are stored and the CNS structures involved in storage. 3. Describe how
Memory Lynn Yen, class of 2009 Objectives 1. Understand the different types of memory. 2. Describe where different types of memory are stored and the CNS structures involved in storage. 3. Describe how
Why do we have a hippocampus? Short-term memory and consolidation
 Why do we have a hippocampus? Short-term memory and consolidation So far we have talked about the hippocampus and: -coding of spatial locations in rats -declarative (explicit) memory -experimental evidence
Why do we have a hippocampus? Short-term memory and consolidation So far we have talked about the hippocampus and: -coding of spatial locations in rats -declarative (explicit) memory -experimental evidence
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
MEMORY STORAGE. There are three major kinds of storage:
 MEMORY Jill Price was capable of remembering everything that happened last year and several years ago. Memory is the ability to store and retrieve information over time. Memories are the residue of those
MEMORY Jill Price was capable of remembering everything that happened last year and several years ago. Memory is the ability to store and retrieve information over time. Memories are the residue of those
Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory. From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Medium Spiny Neuron A Current Conception of the major memory systems in the brain Figure
Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Medium Spiny Neuron A Current Conception of the major memory systems in the brain Figure
Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory
 Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory Types and Structure of Memory Types of Memory Type of Memory Time Course Capacity Conscious Awareness Mechanism of Loss Sensory Short-Term and Working Long-Term Nondeclarative
Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory Types and Structure of Memory Types of Memory Type of Memory Time Course Capacity Conscious Awareness Mechanism of Loss Sensory Short-Term and Working Long-Term Nondeclarative
Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - -
 BRAIN PLASTICITY Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - - Recently, it was found that new neurons and glial cells are born in specific brain regions - reorganization. Brain plasticity occurs
BRAIN PLASTICITY Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - - Recently, it was found that new neurons and glial cells are born in specific brain regions - reorganization. Brain plasticity occurs
BRAIN PLASTICITY. Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - -
 BRAIN PLASTICITY Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - - Recently, it was found that new neurons and glial cells are born in specific brain regions - reorganization. Brain plasticity occurs
BRAIN PLASTICITY Neuroplasticity:. Happens in at least 3 ways: - - - Recently, it was found that new neurons and glial cells are born in specific brain regions - reorganization. Brain plasticity occurs
Memory Disorders. 1. Episodic: memory for time and places. 2. Semantic: memory for facts and knowledge (language, numbers, etc).
 I. Types of memory: A. Declarative memory: Memory Disorders 1. Episodic: memory for time and places. 2. Semantic: memory for facts and knowledge (language, numbers, etc). B. Procedural memory: - examples:
I. Types of memory: A. Declarative memory: Memory Disorders 1. Episodic: memory for time and places. 2. Semantic: memory for facts and knowledge (language, numbers, etc). B. Procedural memory: - examples:
Increasing the amount of information that can be held in short-term memory by grouping related items together into a single unit, or chunk.
 chunking Increasing the amount of information that can be held in short-term memory by grouping related items together into a single unit, or chunk. clustering Organizing items into related groups during
chunking Increasing the amount of information that can be held in short-term memory by grouping related items together into a single unit, or chunk. clustering Organizing items into related groups during
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
The Nervous System. Neuron 01/12/2011. The Synapse: The Processor
 The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140
 Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140 Second midterm is next Tuesday!! Covers lectures 7-12 (Synaptic transmission, NT & receptors, intracellular signaling & synaptic plasticity). Review session is on Monday (Nov
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140 Second midterm is next Tuesday!! Covers lectures 7-12 (Synaptic transmission, NT & receptors, intracellular signaling & synaptic plasticity). Review session is on Monday (Nov
The motor regulator. 2) The cerebellum
 The motor regulator 2) The cerebellum Motor control systems outside the cortex Cerebellum -controls neural programs for the executionl of skilled movements Feed-back and feed-forward control circuits By
The motor regulator 2) The cerebellum Motor control systems outside the cortex Cerebellum -controls neural programs for the executionl of skilled movements Feed-back and feed-forward control circuits By
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change
 How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter06.html http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter06.html http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of
Morris water maze: standard test for spatial memory in rodents
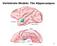 Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 34 Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 35 Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 36 Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 37 Animal Models of Learning (Vertebrates) Morris water
Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 34 Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 35 Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 36 Vertebrate Models: The Hippocampus 37 Animal Models of Learning (Vertebrates) Morris water
Why is dispersion of memory important*
 What is memory* It is a web of connections Research has shown that people who lose their memory also lose the ability to connect things to each other in their mind It is these connections that let us understand
What is memory* It is a web of connections Research has shown that people who lose their memory also lose the ability to connect things to each other in their mind It is these connections that let us understand
Memory: Computation, Genetics, Physiology, and Behavior. James L. McClelland Stanford University
 Memory: Computation, Genetics, Physiology, and Behavior James L. McClelland Stanford University A Playwright s Take on Memory What interests me a great deal is the mistiness of the past Harold Pinter,
Memory: Computation, Genetics, Physiology, and Behavior James L. McClelland Stanford University A Playwright s Take on Memory What interests me a great deal is the mistiness of the past Harold Pinter,
October 2, Memory II. 8 The Human Amnesic Syndrome. 9 Recent/Remote Distinction. 11 Frontal/Executive Contributions to Memory
 1 Memory II October 2, 2008 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 The Human Amnesic Syndrome Impaired new learning (anterograde amnesia), exacerbated by increasing retention delay Impaired recollection of events learned prior
1 Memory II October 2, 2008 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 The Human Amnesic Syndrome Impaired new learning (anterograde amnesia), exacerbated by increasing retention delay Impaired recollection of events learned prior
Do all these faces look familiar? Can you name them all? Why is it difficult to recall names even though you can recognize them? More generally, why
 Do all these faces look familiar? Can you name them all? Why is it difficult to recall names even though you can recognize them? More generally, why do we forget things? Learning Causes Forgetting: Interference
Do all these faces look familiar? Can you name them all? Why is it difficult to recall names even though you can recognize them? More generally, why do we forget things? Learning Causes Forgetting: Interference
The motor regulator. 2) The cerebellum
 The motor regulator 2) The cerebellum Motor control systems outside the cortex Cerebellum -controls neural programs for the executionl of skilled movements Cerebellar Peduncles Atlas Fig. 2-31 Atlas Fig.
The motor regulator 2) The cerebellum Motor control systems outside the cortex Cerebellum -controls neural programs for the executionl of skilled movements Cerebellar Peduncles Atlas Fig. 2-31 Atlas Fig.
Introduction to Long-Term Memory
 Introduction to Long-Term Memory Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/26/2018: Lecture 05-4 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
Introduction to Long-Term Memory Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/26/2018: Lecture 05-4 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
MEMORY. Announcements. Practice Question 2. Practice Question 1 10/3/2012. Next Quiz available Oct 11
 Announcements Next Quiz available Oct 11 Due Oct 16 MEMORY Practice Question 1 Practice Question 2 What type of operant conditioning is Stewie using to get attention from his mom? A rercer that acquires
Announcements Next Quiz available Oct 11 Due Oct 16 MEMORY Practice Question 1 Practice Question 2 What type of operant conditioning is Stewie using to get attention from his mom? A rercer that acquires
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Memory 2/15/2017. The Three Systems Model of Memory. Process by which one encodes, stores, and retrieves information
 Chapter 6: Memory Memory Process by which one encodes, stores, and retrieves information The Three Systems Model of Memory Each system differs in terms of span and duration 1 The Three Systems Model of
Chapter 6: Memory Memory Process by which one encodes, stores, and retrieves information The Three Systems Model of Memory Each system differs in terms of span and duration 1 The Three Systems Model of
Henry Molaison. Biography. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 Henry Molaison From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Henry Gustav Molaison (February 26, 1926 December 2, 2008), known widely as H.M., was an American memory disorder patient who had a bilateral medial
Henry Molaison From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Henry Gustav Molaison (February 26, 1926 December 2, 2008), known widely as H.M., was an American memory disorder patient who had a bilateral medial
Cerebral Cortex: Association Areas and Memory Tutis Vilis
 97 Cerebral Cortex: Association Areas and Memory Tutis Vilis a) Name the 5 main subdivisions of the cerebral cortex. Frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal, and limbic (on the medial side) b) Locate the
97 Cerebral Cortex: Association Areas and Memory Tutis Vilis a) Name the 5 main subdivisions of the cerebral cortex. Frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal, and limbic (on the medial side) b) Locate the
memory Examples: Obama is president, PSYC 2 is in Price Center Theater, my 21st birthday was a disaster
 PSYC 2: Biological Foundations - Fall 2012 - Professor Claffey Notes: Cognition 2 Version: 11/18/12 - original version Memory Classifications A note on memory classifications Definitions developed from
PSYC 2: Biological Foundations - Fall 2012 - Professor Claffey Notes: Cognition 2 Version: 11/18/12 - original version Memory Classifications A note on memory classifications Definitions developed from
Psychology 320: Topics in Physiological Psychology Lecture Exam 2: March 19th, 2003
 Psychology 320: Topics in Physiological Psychology Lecture Exam 2: March 19th, 2003 Name: Student #: BEFORE YOU BEGIN!!! 1) Count the number of pages in your exam. The exam is 8 pages long; if you do not
Psychology 320: Topics in Physiological Psychology Lecture Exam 2: March 19th, 2003 Name: Student #: BEFORE YOU BEGIN!!! 1) Count the number of pages in your exam. The exam is 8 pages long; if you do not
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Perceptual Learning. Motor Learning. Stimulus-Response Learning. Relational Learning
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu www.cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html Learning and Memory Human Communication Emotion 1 Working Memory: What is memory? Limited
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu www.cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html Learning and Memory Human Communication Emotion 1 Working Memory: What is memory? Limited
Consciousness Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 6, Part 1
 Consciousness Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 6, Part 1 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A March 11, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 Consciousness Moment-by-moment awareness
Consciousness Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 6, Part 1 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A March 11, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 Consciousness Moment-by-moment awareness
Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy
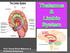 Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: Describe the anatomy and main functions of the thalamus. Name and identify different nuclei
Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: Describe the anatomy and main functions of the thalamus. Name and identify different nuclei
Prior Knowledge and Memory Consolidation Expanding Competitive Trace Theory
 Prior Knowledge and Memory Consolidation Expanding Competitive Trace Theory Anna Smith Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Background in Memory Models Models of Consolidation The Hippocampus Competitive Trace Theory
Prior Knowledge and Memory Consolidation Expanding Competitive Trace Theory Anna Smith Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Background in Memory Models Models of Consolidation The Hippocampus Competitive Trace Theory
Chapter 23: Wiring the Brain
 Chapter 23: Wiring the Brain Introduction Operation of the brain Precise interconnections among 100 billion neurons Brain development Begins as a tube Neurogenesis, synaptogenesis, pathway formation, connections
Chapter 23: Wiring the Brain Introduction Operation of the brain Precise interconnections among 100 billion neurons Brain development Begins as a tube Neurogenesis, synaptogenesis, pathway formation, connections
NST II Psychology NST II Neuroscience (Module 5)
 NST II Psychology NST II Neuroscience (Module 5) Brain Mechanisms of Memory and Cognition 4 Forms of memory. Neural basis of memory (1): amnesia, the hippocampus Rudolf Cardinal Department of Experimental
NST II Psychology NST II Neuroscience (Module 5) Brain Mechanisms of Memory and Cognition 4 Forms of memory. Neural basis of memory (1): amnesia, the hippocampus Rudolf Cardinal Department of Experimental
Synaptic plasticityhippocampus. Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity. Outline. Synaptic plasticity hypothesis
 Synaptic plasticityhippocampus Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity Outline Synaptic plasticity hypothesis Long term potentiation in the hippocampus How it s measured What it looks like Mechanisms
Synaptic plasticityhippocampus Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity Outline Synaptic plasticity hypothesis Long term potentiation in the hippocampus How it s measured What it looks like Mechanisms
Cortex and Mind Chapter 5. Memory is stored knowledge about the internal and external environments; it includes perceptual and motor knowledge.
 Cortex and Mind Chapter 5 Memory is stored knowledge about the internal and external environments; it includes perceptual and motor knowledge. Review of classical classification of learning and memory
Cortex and Mind Chapter 5 Memory is stored knowledge about the internal and external environments; it includes perceptual and motor knowledge. Review of classical classification of learning and memory
1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or to the head TA (jcolas).
 Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
Neuronal Plasticity, Learning and Memory. David Keays Institute of Molecular Pathology
 Neuronal Plasticity, Learning and Memory David Keays Institute of Molecular Pathology http://keayslab.org Structure 1. What is learning and memory? 2. Anatomical basis 3. Cellular basis 4. Molecular
Neuronal Plasticity, Learning and Memory David Keays Institute of Molecular Pathology http://keayslab.org Structure 1. What is learning and memory? 2. Anatomical basis 3. Cellular basis 4. Molecular
Feedback Education and Neuroscience. Pankaj Sah
 Feedback Education and Neuroscience Pankaj Sah Science of Learning Learning The process of acquiring a skill or knowledge that leads to a change in behaviour Memory The ability to retain and recover information
Feedback Education and Neuroscience Pankaj Sah Science of Learning Learning The process of acquiring a skill or knowledge that leads to a change in behaviour Memory The ability to retain and recover information
Name: Per:_ Advanced Placement Psychology Semester 1 Final Exam Study Guide
 Name: Per:_ Advanced Placement Psychology Semester 1 Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 1: Foundations & History 1. Describe the following perspectives of psychology. Behavioral Perspective Evolutionary Perspective
Name: Per:_ Advanced Placement Psychology Semester 1 Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 1: Foundations & History 1. Describe the following perspectives of psychology. Behavioral Perspective Evolutionary Perspective
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
MODULE 32 MEMORY STORAGE AND RETRIEVAL
 MODULE 32 MEMORY STORAGE AND RETRIEVAL ARE OUR LONG TERM MEMORIES PROCESSED AND STORED IN SPECIFIC LOCATIONS? Our memories are flexible and superimposable, a panoramic blackboard with an endless supply
MODULE 32 MEMORY STORAGE AND RETRIEVAL ARE OUR LONG TERM MEMORIES PROCESSED AND STORED IN SPECIFIC LOCATIONS? Our memories are flexible and superimposable, a panoramic blackboard with an endless supply
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Synapses and synaptic plasticity. Lubica Benuskova Lecture 8 How neurons communicate How do we learn and remember
 Synapses and synaptic plasticity Lubica Benuskova Lecture 8 How neurons communicate How do we learn and remember 1 Brain is comprised of networks of neurons connected and communicating via synapses ~10
Synapses and synaptic plasticity Lubica Benuskova Lecture 8 How neurons communicate How do we learn and remember 1 Brain is comprised of networks of neurons connected and communicating via synapses ~10
Body control systems. Let s start at the top: the human brain. The Cerebrum. The human brain. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
Anatomy of the Hippocampus
 Anatomy of the Hippocampus Lecture 3.2 David S. Touretzky September, 2015 Human Hippocampus 2 Human Hippocampus 3 Hippocampus Means Seahorse Dissected human hippocampus next to a specimen of hippocampus
Anatomy of the Hippocampus Lecture 3.2 David S. Touretzky September, 2015 Human Hippocampus 2 Human Hippocampus 3 Hippocampus Means Seahorse Dissected human hippocampus next to a specimen of hippocampus
Long-Term Potentiation and Memory
 Physiol Rev 84: 87 136, 2004; 10.1152/physrev.00014.2003. Long-Term Potentiation and Memory M. A. LYNCH Trinity College Institute of Neuroscience, Department of Physiology, Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland
Physiol Rev 84: 87 136, 2004; 10.1152/physrev.00014.2003. Long-Term Potentiation and Memory M. A. LYNCH Trinity College Institute of Neuroscience, Department of Physiology, Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland
NEOCORTICAL CIRCUITS. specifications
 NEOCORTICAL CIRCUITS specifications where are we coming from? human-based computing using typically human faculties associating words with images -> labels for image search locating objects in images ->
NEOCORTICAL CIRCUITS specifications where are we coming from? human-based computing using typically human faculties associating words with images -> labels for image search locating objects in images ->
Synaptic plasticity and hippocampal memory
 Synaptic plasticity and hippocampal memory Tobias Bast School of Psychology, University of Nottingham tobias.bast@nottingham.ac.uk Synaptic plasticity as the neurophysiological substrate of learning Hebb
Synaptic plasticity and hippocampal memory Tobias Bast School of Psychology, University of Nottingham tobias.bast@nottingham.ac.uk Synaptic plasticity as the neurophysiological substrate of learning Hebb
10/24/2017. Medial Temporal Lobes. Autobiographical Memory. Episodic and Semantic Memory. Arlo Clark-Foos, Ph.D.
 Medial Temporal Lobes Henry Molaison (HM) (1926-2008) Arlo Clark-Foos, Ph.D. Consequences of bilateral removal Episodic and Semantic Memory Endel Tulving on Declarative (Explicit) Memories Autobiographical
Medial Temporal Lobes Henry Molaison (HM) (1926-2008) Arlo Clark-Foos, Ph.D. Consequences of bilateral removal Episodic and Semantic Memory Endel Tulving on Declarative (Explicit) Memories Autobiographical
Arlo Clark-Foos, Ph.D.
 Arlo Clark-Foos, Ph.D. Medial Temporal Lobes Henry Molaison (HM) (1926-2008) Consequences of bilateral removal Episodic and Semantic Memory Endel Tulving on Declarative (Explicit) Memories Episodic Memory
Arlo Clark-Foos, Ph.D. Medial Temporal Lobes Henry Molaison (HM) (1926-2008) Consequences of bilateral removal Episodic and Semantic Memory Endel Tulving on Declarative (Explicit) Memories Episodic Memory
Introduction to Systems Neuroscience. Nov. 28, The limbic system. Daniel C. Kiper
 Introduction to Systems Neuroscience Nov. 28, 2017 The limbic system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html LIMBIC SYSTEM The term limbic system mean
Introduction to Systems Neuroscience Nov. 28, 2017 The limbic system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html LIMBIC SYSTEM The term limbic system mean
Motor systems III: Cerebellum April 16, 2007 Mu-ming Poo
 Motor systems III: Cerebellum April 16, 2007 Mu-ming Poo Population coding in the motor cortex Overview and structure of cerebellum Microcircuitry of cerebellum Function of cerebellum -- vestibulo-ocular
Motor systems III: Cerebellum April 16, 2007 Mu-ming Poo Population coding in the motor cortex Overview and structure of cerebellum Microcircuitry of cerebellum Function of cerebellum -- vestibulo-ocular
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change
 How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter06.html https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D.
How Synapses Integrate Information and Change Rachel Stewart class of 2016 https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter06.html https://nba.uth.tmc.edu/neuroscience/s1/chapter07.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D.
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
PHYSIOLOGY of LIMBIC SYSTEM
 PHYSIOLOGY of LIMBIC SYSTEM By Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi (MBBS, M.Phil.) Assistant Professor Physiology Limbic system: (shown in dark pink) Limbic = border Definition: limbic system means the entire neuronal
PHYSIOLOGY of LIMBIC SYSTEM By Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi (MBBS, M.Phil.) Assistant Professor Physiology Limbic system: (shown in dark pink) Limbic = border Definition: limbic system means the entire neuronal
Lisa M. Giocomo & Michael E. Hasselmo
 Mol Neurobiol (2007) 36:184 200 DOI 10.1007/s12035-007-0032-z Neuromodulation by Glutamate and Acetylcholine can Change Circuit Dynamics by Regulating the Relative Influence of Afferent Input and Excitatory
Mol Neurobiol (2007) 36:184 200 DOI 10.1007/s12035-007-0032-z Neuromodulation by Glutamate and Acetylcholine can Change Circuit Dynamics by Regulating the Relative Influence of Afferent Input and Excitatory
Nervous System Review
 Nervous System Review Name: Block: 1. Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z? A. exocytosis and diffusion B. endocytosis and diffusion C. exocytosis and facilitated
Nervous System Review Name: Block: 1. Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z? A. exocytosis and diffusion B. endocytosis and diffusion C. exocytosis and facilitated
Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory. From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Definitions Learning: The acquisition of an altered behavioral response due to an environmental
Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Definitions Learning: The acquisition of an altered behavioral response due to an environmental
Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
The Nervous System. B. The Components: 1) Nerve Cells Neurons are the cells of the body and are specialized to carry messages through an process.
 The Nervous System A. The Divisions: 1) The Central Nervous System includes the and. The brain contains billions of nerve cells called, and trillions of support cells called. 2) The Peripheral Nervous
The Nervous System A. The Divisions: 1) The Central Nervous System includes the and. The brain contains billions of nerve cells called, and trillions of support cells called. 2) The Peripheral Nervous
Telecommunications & Health Science
 Telecommunications & Health Science Dr. Sheila Johnston Neuroscience Consultant, London WHO EMF PROJECT A. Industry Health Spokesperson Michaela Reeh 1997-2000 B. Industry Association FMK C. Independent
Telecommunications & Health Science Dr. Sheila Johnston Neuroscience Consultant, London WHO EMF PROJECT A. Industry Health Spokesperson Michaela Reeh 1997-2000 B. Industry Association FMK C. Independent
Storage: Retaining Information
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Storage: Retaining Information Module 26 2 Storage: Retaining Information Storage: Retaining Information Sensory
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Storage: Retaining Information Module 26 2 Storage: Retaining Information Storage: Retaining Information Sensory
Butter Food Eat Sandwich Rye Jam Milk Flour Jelly Dough Crust Slice Wine Loaf Toast
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ /~ksweeney/psy260.html Comments on your comments Thank you! Some things that I can change NOW: Slow
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ /~ksweeney/psy260.html Comments on your comments Thank you! Some things that I can change NOW: Slow
Meds 371, Systems Neuroscience University of Connecticut Health Center. Memory and Learning. Srdjan Antic, M.D. Department of Neuroscience
 Meds 371, Systems Neuroscience University of Connecticut Health Center Memory and Learning Srdjan Antic, M.D. Department of Neuroscience Sources: Purves Textbook: Chapter 31, Memory Review article: Lisman
Meds 371, Systems Neuroscience University of Connecticut Health Center Memory and Learning Srdjan Antic, M.D. Department of Neuroscience Sources: Purves Textbook: Chapter 31, Memory Review article: Lisman
Linda Lušić Research fellow Department of neuroscience School of medicine. University of Split
 Linda Lušić Research fellow Department of neuroscience School of medicine University of Split Nonassociative? Associative? Nonassociative learning when an animal or a person is exposed once or repeatedly
Linda Lušić Research fellow Department of neuroscience School of medicine University of Split Nonassociative? Associative? Nonassociative learning when an animal or a person is exposed once or repeatedly
Neural plasticity in infants - relevance to baby swimming. Morten Overgaard
 Neural plasticity in infants - relevance to baby swimming Morten Overgaard Programme What is neuroscience? Totally superficial neuroanatomy Paradoxes of functional localization Mechanisms of neural plasticity
Neural plasticity in infants - relevance to baby swimming Morten Overgaard Programme What is neuroscience? Totally superficial neuroanatomy Paradoxes of functional localization Mechanisms of neural plasticity
You submitted this quiz on Sun 19 May :32 PM IST (UTC +0530). You got a score of out of
 Feedback Ex6 You submitted this quiz on Sun 19 May 2013 9:32 PM IST (UTC +0530). You got a score of 10.00 out of 10.00. Question 1 What is common to Parkinson, Alzheimer and Autism? Electrical (deep brain)
Feedback Ex6 You submitted this quiz on Sun 19 May 2013 9:32 PM IST (UTC +0530). You got a score of 10.00 out of 10.00. Question 1 What is common to Parkinson, Alzheimer and Autism? Electrical (deep brain)
2/22/2012. Cerebrum CNS
 Chapter 8 outline CNS: Consists of???? Structural organization of the brain Cerebrum Diencephalon Midbrain and hindbrain Spinal cord tracts Cranial and spinal nerves Receives input from???? neurons Directs
Chapter 8 outline CNS: Consists of???? Structural organization of the brain Cerebrum Diencephalon Midbrain and hindbrain Spinal cord tracts Cranial and spinal nerves Receives input from???? neurons Directs
Biological Psychology 2012 Spring 2005 Patterson
 Final Exam Biological Psychology 2012 Spring 2005 Patterson There are two versions of this exam. You have version A. Before starting the exam, mark A on question 60. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative
Final Exam Biological Psychology 2012 Spring 2005 Patterson There are two versions of this exam. You have version A. Before starting the exam, mark A on question 60. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative
Cognitive Neuroscience Structure and Function
 Phylogeny of the cortex Cognitive Neuroscience Structure and Function The neocortex of mammals developed out of the primordial neopallium, which, like that of certain present-day amphibians, consisted
Phylogeny of the cortex Cognitive Neuroscience Structure and Function The neocortex of mammals developed out of the primordial neopallium, which, like that of certain present-day amphibians, consisted
Importance of Deficits
 Importance of Deficits In complex systems the parts are often so integrated that they cannot be detected in normal operation Need to break the system to discover the components not just physical components
Importance of Deficits In complex systems the parts are often so integrated that they cannot be detected in normal operation Need to break the system to discover the components not just physical components
Let me begin by telling a little story.
 Chapter 19 Learning and Memory Let me begin by telling a little story. When I was a graduate student we had to take an exam that Cornell does in an interesting way. They put you in a swivelchair surrounded
Chapter 19 Learning and Memory Let me begin by telling a little story. When I was a graduate student we had to take an exam that Cornell does in an interesting way. They put you in a swivelchair surrounded
Exam 2 PSYC Fall (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
 Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Psych 136S Review Questions, Summer 2015
 Psych 136S Review Questions, Summer 2015 For each paper you should be able to briefly summarize the methods and results and explain why the results are important. The guided summary for the Roediger et
Psych 136S Review Questions, Summer 2015 For each paper you should be able to briefly summarize the methods and results and explain why the results are important. The guided summary for the Roediger et
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Behavioral Neuroscience: Fear thou not. Rony Paz
 Behavioral Neuroscience: Fear thou not Rony Paz Rony.paz@weizmann.ac.il Thoughts What is a reward? Learning is best motivated by threats to survival Threats are much better reinforcers Fear is a prime
Behavioral Neuroscience: Fear thou not Rony Paz Rony.paz@weizmann.ac.il Thoughts What is a reward? Learning is best motivated by threats to survival Threats are much better reinforcers Fear is a prime
