Medicine. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. 1. Introduction. 2. Methods OPEN
|
|
|
- Juliana Meghan Walsh
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Medicine Efficacy of acid suppression therapy in gastroesophageal reflux disease-related chronic laryngitis Yue Yang, PhD a,b, Haitao Wu, PhD a,b, Jian Zhou, PhD a,b, OPEN Abstract Background: This research aims to assess the response to acid suppression therapy in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)- related chronic laryngitis (CL). Methods: Data were extracted from Web of Knowledge, Embase, and PubMed for English language article published up to March Pooled overall response rate (ORR) rates were evaluated to determine acid suppression treatment efficacy. Random effects model was used with standard approaches to sensitivity analysis, quality assessment, heterogeneity, and exploration of publication bias. Results: Pooled data from 21 reports (N = 2864, antireflux medicine: 2741; antireflux surgery: 123, study duration week) were analyzed. With the random-effect model, the ORR was 66% (95% confidence interval [CI] 54% 78%). The ORRs were 80% for antireflux surgery (95% CI 67% 93%, 3 studies, 123 patients), whereas 64% for antireflux medicine (95% CI 50% 77%, 18 studies, 2741 patients), and the ORR was 70% (95% CI 55% 85%, 15 reports, 2731 patients) for >8 weeks therapy duration, whereas 57% (95% CI 48% 65%, 6 reports, 133 patients) for 8 weeks duration of therapy. Conclusions: Acid suppression seems to be an effective therapy for GERD-related CL. There was an increase in effect among patients with surgery therapeutic method and longer therapy duration. Abbreviations: CL = Chronic laryngitis, ES = effect size, GERD = gastroesophageal reflux disease, GPR = gastropharyngeal reflux, LPR = laryngopharyngeal reflux, ORR = overall response rate, PPI = proton pump inhibitors. Keywords: antireflux surgery, chronic laryngitis, GERD, laryngopharyngeal reflux, meta-analysis, pharyngitis, proton pump inhibitor 1. Introduction In the last 2 decades, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)- induced reflux laryngitis has become a familiar finding in ear, nose, and throat. The proportion of chronic laryngitis (CL) in whole patients visiting to otolaryngology clinics in America was about 10%. [1] Therefore, acid suppression therapy is usually prescribed to these patients under the presupposition that GERD is related with signs and of CL. [2 4] It has been revealed that acid suppression improves associated upper esophageal and the gastroesophageal reflux and laryngeal Editor: Bülent Kantarçeken. The authors report no conflicts of interest. a Department of Otolaryngology, Eye Ear Nose & Throat Hospital, Fudan University, 83 Fenyang Road, b Shanghai Key Clinical Disciplines of otorhinolaryngology, Shanghai, China. Correspondence: Jian Zhou, Department of Otolaryngology, Eye Ear Nose & Throat Hospital, Fudan University, 83 Fenyang Road, Shanghai , China ( zhoujian @163.com). Copyright 2016 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives License 4.0, which allows for redistribution, commercial and non-commercial, as long as it is passed along unchanged and in whole, with credit to the author. Medicine (2016) 95:40(e4868) Received: 24 March 2016 / Received in final form: 9 August 2016 / Accepted: 23 August for instance, hoarseness and chronic cough. [5] Nevertheless, their efficacy in patients with suspected GERDrelated CL has not been definite. GERD-related extraesophageal complications can be controlled efficiently by surgery with a significantly better response than with medicine therapy. [6] We proceeded this meta-analysis to explore an estimate of the overall efficacy of acid suppression treatment (including medicine therapy and surgery therapy) in suspected GERD-related CL. 2. Methods 2.1. Ethical approval This is a study of meta-analysis, so that, ethical approval was not necessary Study Search We proceeded a systematic literature search in PubMed, Web of Knowledge, and Embase for English language article published up till March 2016 by relevant keywords and combinations such as Proton pump inhibitor, antireflux therapy, any proton pumps/antagonists & inhibitors, H(+)-K(+)-Exchanging ATPase/antagonists & inhibitors, rabeprazole, histamine H2 antagonists, pantaprazole, esomeprazole, omeprazole, lansaprazole, and laryngitis, pharyngitis, reflux laryngitis, posterior laryngitis, reflux laryngopharyngitis, reflux pharyngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR), gastropharyngeal reflux (GPR). We performed this study according 1
2 Medicine to the guidelines of PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses) Data extraction Suspected GERD-related CL was defined by the occurrence of 1 of the following : hoarseness, globus sensation, excessive phlegm, frequent throat clearing, chronic cough, and the presence of GERD-attributed signs of laryngitis on laryngoscopy-containing erythema, edema, pachydermia, granuloma, or contact ulcer. Adults aged 18 years of age or older with suspected GERD-related CL were entitled for this study. The data were collected from every eligible article: first author s surname, publication year, country of origin, methods of diagnosis of GERD, and methods of acid suppression therapy separately. All related reports were assessed independently by 2 authors, and based on consensus. We abstracted the proportion of patients who described 50% decrease in laryngeal compared with baseline. Exclusion criteria were the following: Case reports, review reports, studies not printed in English language; multiple reports providing outcomes from the same research; cohort reports; and animal researches Statistical analysis The effect size (ES), which is the OOR (%) and 95% confidence interval (95% CI), was assessed for every report. The pooled evaluation of the merged percentage was gotten by the Laid and DerSimonian method in the random effect model. Moreover, we quantified the effect of heterogeneity using I 2 = 100%(Q df)/ Q. A significant I 2 statistic (I 2 >50%) or Q statistic (P<0.10) showed heterogeneity across the reports, then the random effects model was used for the meta-analysis Evaluation of publication bias We calculated the asymmetry of the funnel plot using Begg linear regression and Egger regression test, which evaluated funnel plot asymmetry by means of the natural logarithm scale of the ES. STATA 12.0 (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX) was used in this study. 3. Results 3.1. The characteristics of the eligible reports There were 253 potential-related reports recognized with the titles, key words, and abstracts. A summary of the study results is shown in Figure 1. There were 54 potentially related full-text studies retrieved for more in-depth assessment after taking out the unrelated reports by assessment of abstract and title. Lastly, 21 separate reports were involved in this meta-analysis. All patients experienced laryngoscopic assessment to make the diagnosis of suspected GERD-related CL with, for instance, edema, granuloma, erythema, pachydermia, and/or cobblestone pattern, especially in posterior larynx. Ambulatory ph monitoring was carried out in every report, several patients also experienced esophagogastroduodenoscopy and esophageal manometry before enrollment; the primary sources of recruitment of patients in most studies were Otolaryngology clinics. As is shown in Table 1, 21 reports were involved in the metaanalysis, and the characteristics of the involved reports are displayed. Totally, 2864 patients who suspected GERD-related Figure 1. Flow diagram. CL were considered in this meta-analysis. [7 27] The involved reports were published between 1997 and The sample sizes of the reports were between 8 and Three studies chose surgical treatment, and the remainder of the studies chose acid suppression medicine treatment. [9,10,12] The duration of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) treatment ranged from 4 to108 weeks Overall effects of acid suppression therapy on GERDrelated CL Twenty-one reports that contained a total of 2864 patients were available to assess the ORR of acid suppression therapy (including medicine therapy and surgery therapy) in suspected GERD-related CL. A random-effect model was used on account of significant heterogeneity (I 2 = 97.1%, P<0.01); ORR was 66% (95% CI 54 78%) (Fig. 3) Subgroups analyses In meta regression (Table 2), there was an obvious discordance between the pooled outcomes for reports performed before 2006 (ORR: 62% [95% CI 50% 74%]) and studies performed from 2006 onwards (ORR: 70% [95% CI 51% 89%]).There was an increase in effect among the pooled outcomes for reports of patients with surgery therapeutic method (ORR: 80% [95% CI: 67% 93%]) relative to studies of patients with medicine therapeutic method (ORR: 64% [95% CI: 50% 77%]) (Table 2). When reports were compared with regard to the duration of treatment (8 week and >8 week), response to acid suppression therapy was higher in reports with longer duration of therapy (ORR: 70% [95% CI: 55% 85%] vs. ORR: 57% [95% CI: 48% 65%]) (Table 2) Evaluation of publication bias No publication bias was obvious in meta-analyses of the association between GERD-related CL and ORR of acid suppression treatment, on the basis of Egger regression test 2
3 Table 1 Characteristics of studies included in this review. Study Period of diagnosis Country Patient selection source Inclusion criteria Therapeutic method Duration, wk Outcome measured Kirch et al (2013) [7] 2006/1 2011/1 US Otolaryngology clinics LSx and LPR average duration was 1.26 years Wang et al (2012) [8] 2007/7 2009/1 China Otorhinolaryngology Clinic Laryngoscopy, and 24-h ph monitoring Ratnasingam et al (2011) [9] 2002/1 2008/7 Australia Otolaryngologist LSx, GERD at gastroscopy or 24- h ph monitoring Salminen et al (2010) [10] 1998/1 2002/8 Finland Specialist in otolaryngology and ph-monitoring-proven reflux laryngitis caused by GERD Omeprazole 20 40mg BID 8 12 Significant improvement in self-reported Rabeprazole 10mg BID 12 50% reduction after the start of therapy compared with baseline Laparoscopic Antireflux Surgery Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication 12, after surgery Significant improvement or resolution of 164, after surgery Excellent, good, or satisfactory at symptom resolution Karoui et al (2010) [11] 2009 Tunisia Specialist in otolaryngology LSx; 24-h ph monitoring pantoprazole 40mg BID 8 ENT have decreased significantly Salminen et al (2007) [12] 2002 Finland Otolaryngologist; Qua et al (2007) [13] 2004/7 2005/1 Malaysia Otorhinolaryngology Clinic and Dore et al (2007) [14] Italy Otolaryngologists Reflux laryngitis caused by GERD 24-h ph Monitoring LSx; Reflux ; 24-h ambulatory ph monitoring diagnosis of GERD; atypical laryngitis Monini et al (2006) [15] Italy Otorhinolaryngology clinical LSx; LPR on gastroscopy, ph monitoring Ahmed et al (2006) [16] To 2004/5 US ENT physicians reflux-related laryngeal signs and Vaezi et al (2005) [17] 2002/2 2003/3 US Otolaryngologists Wo et al (2005) [18] 2004 US Otolaryngology clinics and Newspaper advertisement Steward et al (2004) [19] 2004 US Otolaryngologists Eherer et al (2003) [20] 1998/4 2000/10 Austria Otolaryngologists Ulualp et al (2001) [21] 1996/ /12 US otolaryngology clinic; Hamdan et al (2001) [22] Lebanon Otolaryngolgist and gastroenterologist El-Serag et al (2001) [23] 1998/ /12 US Otolaryngologist Noordzij et al (2001) [24] US Otolaryngologists LSx for 12 wk LPR on laryngoscopy LSx for 8 wk; LPR on Laryngoscopyl ph test LSx for >4 wk LPR on laryngoscopy Hoarseness for 8 wk LPR on laryngoscopy ph test Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication 112, after surgery Significant improvement in self-reported Lansoprazole 30mg BID 8 Significant improvement in laryngeal PPI therapy BID 8-12 complete symptom resolution or had improved Omeprazole 20mg BID 12 Significant improved in laryngeal features Once daily high dose PPI 8 24 Significant improvement in self-reported Esomeprazole 40mg BID 16 50% reduction in the primary symptom Pantaprazole 40mg once a day PL who received ph monitoring H2 receptor-blocking agents or PPI LSx; GER by endoscope or by 24-h ph monitoring LSx for > 3 wk LPR on laryngoscopy LSx for 12 wk LPR on laryngoscopy ph test 12 50% reduction in global symptom score Rabeprazole 20mg BID 8 50% reduction in global symptom score Pantaprazole 40mg BID 12 Significant improvement in self-reported Pharyngeal acid reflux, total symptom scores were significantly lower pantoprazole 40mg BID 4 Vocal fatigue and vocal breaks were improved significantly Lansaprazole 30mg BID 12 Complete symptom resolution Omeprazole 40mg BID 8 50% reduction in global symptom score Langevin and Ngo (2001) [25] 2000 Canada Not known LSx for 12 wk LPR on Omeprazole 40mg once 12 50% reduction in laryngeal laryngoscopy ph test a day Havas et al (1999) [26] Australia Otolaryngologist LPR on laryngoscopy Lansaprazole 30mg BID 12 50% reduction in global symptom score Omeprazole 40mg QHS 8 Laryngeal symptom significantly improved Wo et al (1997) [27] US Otolaryngology clinics; LSx for > 1 month; LPR on amhulatory ph monitoring BID=bis in die, ENT=ears, nose, and throat, GER=gastroesophageal reflux, GERD=gastroesophageal reflux disease, LPR=laryngopharyngeal reflux, LSx=laryngeal, PL=posterior laryngitis, PPI=proton pump inhibitors, QHS=queue hora sonny. 3
4 Medicine Table 2 Sensitivity analysis of subgroup s effect of acid suppression therapy. Variable Number of trials Number of patients Estimated rate (%) 95% CI (%) I 2 (%) P for heterogeneity Year of study Before <0.01 From <0.01 Duration of therapy, wk > <0.01 Therapeutic method Medicine <0.01 Surgery Figure 2. Forest plot for effect of acid suppression success in chronic laryngitis. and Begg rank correlation test (Egger test, P=0.073; Begg test, P=0.165) (Fig. 2). 4. Discussion This research is the first study of meta-analysis offering available data on the efficacy of acid suppression therapy in GERD-related CL. Our study confirms formerly published outcomes for ORR in GERD-related CL treated with acid suppression, with ORR of up to 66%. It is well known that the base for the cure of GERD-related CL in ENT is 8 to 12 weeks double-dose PPI. [28] Nevertheless, CI=confidence interval. placebo-controlled studies showed that PPI therapy is no better than placebo in relieving GERD-related laryngopharyngeal. [29] The assumption for the comparatively poor PPIs response in the researches is a possible selection bias for the reason that GERD diagnosis was not depended on ph-metric standards at all times. Some reports have presented that about 64% to 86% of healthy people could be discovered with laryngeal abnormalities indicative of a laryngeal reflux. [30,31] Therefore, esophageal 24-hour ph watching is required to notarize GERD, particularly as the therapeutic test has not been confirmed for the duration of the ENT clinical situation. El-Serag et al [23] reported that the only predictors of fine effect to PPI were characterized when pathological acid exposure before treatment. Moreover, it is perhaps owing to the point that some patients Figure 3. Funnel plot to detect publication bias. 4
5 whose laryngeal were not caused by GERD would weaken the total study populations leading to reduced power to discover a difference between placebo and PPIs. There is a popular belief that the result of surgical treatment for reflux is best in typical reflux symptom patients. People with typical reflux and atypical throat had a good effect undergoing fundoplication; the result of these patients was similar to that of the bigger group experiencing fundoplication for typical reflux indications without throat discomfort. Farrell et al [32] assessed the ORR in people with typical against atypical (hoarseness, cough, asthma, and chest pain) after fundoplication. The authors showed that 99% of primarily reflux symptom patients were improved; in addition, 87% patients were entirely cured postoperatively. So et al [33] demonstrated that the treatment of laparoscopic fundoplication had effect on 93% of typical reflux patients, whereas only 56% atypical symptom patients improved after surgery. The ORR for laryngeal, epigastric/chest pain, and pulmonary was 78%, 48%, and 58%, respectively. Our previous study also indicated that compared to studies of patients with medicine therapeutic method (ORR: 64% [95% CI: 50% 77%]), the effect in the pooled results of patients with surgery therapeutic method was better (ORR: 80% [95% CI: 67% 93%]) (Table 2). There were some limitations of this study while illustrating the outcomes. First, the heterogeneity in this research is high, which might be rooted in statistical and clinical heterogeneity; the cause might be that the trials are from different districts and the definition of these indicators was not united. Second, a publication bias might lead to the probability of a systematic difference between larger and smaller reports; to be exact, small research possibly overestimated the effects of acid suppression therapy in terms of ORR. Likewise, asymmetry might also root in heterogeneity. Third, comparisons of ORR were hard because of absence of general agreement on the accurate characterization of result and randomization. Last, the reports involved in this study were only printed in English, signifying that a possible language bias occurred. 5. Conclusion This meta-analysis showed that the overall 1 rate of acid suppression therapy (including medicine therapy and surgery therapy) in suspected GERD-related CL is 66% and there was an increase in effect in the pooled outcomes for the reports of patients who underwent surgery therapeutic method (ORR: 80%) relative to studies of patients with medicine therapeutic method (ORR: 64%); moreover, response to acid suppression therapy was superior to the reports with longer period of therapy (ORR: 70% vs. 57%). References [1] Koufman JA. The otolaryngologic manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): a clinical investigation of 225 patients using ambulatory 24-hour ph monitoring and an experimental investigation of the role of acid and pepsin in the development of laryngeal injury. Laryngoscope 1991;101(4 Pt 2 Suppl 53):1 78. [2] Koufman J, Sataloff RT, Toohill R. Laryngopharyngeal reflux: consensus conference report. J Voice 1996;10: [3] Hanson DG, Jiang JJ. Diagnosis and management of chronic laryngitis associated with reflux. The Am J Med 2000;108(Suppl 4a):112s 9s. [4] Vaezi MF, Hicks DM, Abelson TI, et al. Laryngeal signs and and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): a critical assessment of cause and effect association. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol: the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association 2003;1: [5] Katz PO, Castell DO. Medical therapy of supraesophageal gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Med 2000;108(Suppl 4a):170s 7s. [6] Hinder RA, Branton SA, Floch NR. Surgical therapy for supraesophageal reflux complications of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Med 2000;108(suppl 4a):178s 80s. [7] Kirch S, Gegg R, Johns MM, et al. Globus pharyngeus: effectiveness of treatment with proton pump inhibitors and gabapentin. Ann Otol 2013;122: [8] Wang AJ, Liang MJ, Jiang AY, et al. Predictors of acid suppression success in patients with chronic laryngitis. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2012;24: e210. [9] Ratnasingam D, Irvine T, Thompson SK, et al. Laparoscopic antireflux surgery in patients with throat : a word of caution. World J Surg 2011;35: [10] Salminen P, Karvonen J, Ovaska J. Long-term outcomes after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication for reflux laryngitis. Digest Surg 2010;27: [11] Karoui S, Bibani N, Sahtout S, et al. Effect of pantoprazole in patients with chronic laryngitis and pharyngitis related to gastroesophageal reflux disease: clinical, proximal, and distal ph monitoring results. Dis Esophagus 2010;23: [12] Salminen P, Sala E, Koskenvuo J, et al. Reflux laryngitis: a feasible indication for laparoscopic antireflux surgery? Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Techn 2007;17:73 8. [13] Qua CS, Wong CH, Gopala K, et al. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in chronic laryngitis: prevalence and response to acid-suppressive therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2007;25: [14] Dore MP, Pedroni A, Pes GM, et al. Effect of antisecretory therapy on atypical in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dig Dis Sc 2007;52: [15] Monini S, Di Stadio A, Vestri A, et al. Silent reflux: ex juvantibus criteria for diagnosis and treatment of laryngeal disorders. Acta Otolaryngol 2006;126: [16] Ahmed TF, Khandwala F, Abelson TI, et al. Chronic laryngitis associated with gastroesophageal reflux: prospective assessment of differences in practice patterns between gastroenterologists and ENT physicians. Am J Gastroenterol 2006;101: [17] Vaezi MF, Richter JE, Stasney CR, et al. Treatment of chronic posterior laryngitis with esomeprazole. Laryngoscope 2006;116: [18] Wo JM, Koopman J, Harrell SP, et al. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with single-dose pantoprazole for laryngopharyngeal reflux. Am J Gastroenterol 2006;101: quiz [19] Steward DL, Wilson KM, Kelly DH, et al. Proton pump inhibitor therapy for chronic laryngo-pharyngitis: a randomized placebo-control trial. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2004;131: [20] Eherer AJ, Habermann W, Hammer HF, et al. Effect of pantoprazole on the course of reflux-associated laryngitis: a placebo-controlled doubleblind crossover study. Scand J Gastroenterol 2003;38: [21] Ulualp SO, Toohill RJ, Shaker R. Outcomes of acid suppressive therapy in patients with posterior laryngitis. Otolaryngology Head Neck Surg 2001;124: [22] Hamdan AL, Sharara AI, Younes A, et al. Effect of aggressive therapy on laryngeal and voice characteristics in patients with gastroesophageal reflux. Acta Otolaryngol 2001;121: [23] El-Serag HB, Lee P, Buchner A, et al. Lansoprazole treatment of patients with chronic idiopathic laryngitis: a placebo-controlled trial. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96: [24] Noordzij JP, Khidr A, Evans BA, et al. Evaluation of omeprazole in the treatment of reflux laryngitis: a prospective, placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study. Laryngoscope 2001;111: [25] Langevin S, Ngo H. GERD-induced ENT : A prospective placebo controlled study with omeprazole 40mg a day. Gastroenterology 2001;120:A [26] Havas T, Huang S, Levy M, et al. Posterior pharyngolaryngitis. Doubleblind randomised placebo-controlled trial of proton pump inhibitor therapy. Australian J Otolaryngol 1999;3: [27] Wo JM, Grist WJ, Gussack G, et al. Empiric trial of high-dose omeprazole in patients with posterior laryngitis: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol 1997;92: [28] Vallot T, Carella G. Medical treatment of gastroesophageal reflux with proton pump inhibitors. Gastroenterol Clin Biologique 1999;23(1 pt 2): S [29] Qadeer MA, Phillips CO, Lopez AR, et al. Proton pump inhibitor therapy for suspected GERD-related chronic laryngitis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Gastroenterol 2006;101:
6 Medicine [30] Reulbach TR, Belafsky PC, Blalock PD, et al. Occult laryngeal pathology in a community-based cohort. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2001;124: [31] Hicks DM, Ours TM, Abelson TI, et al. The prevalence of hypopharynx findings associated with gastroesophageal reflux in normal volunteers. J Voice 2002;16: [32] Farrell TM, Richardson WS, Trus TL, et al. Response of atypical of gastro-oesophageal reflux to antireflux surgery. Br J Surg 2001;88: [33] So JB, Zeitels SM, Rattner DW. Outcomes of atypical attributed to gastroesophageal reflux treated by laparoscopic fundoplication. Surgery 1998;124:
Management of laryngopharyngeal refl ux with proton pump inhibitors
 REVIEW Management of laryngopharyngeal refl ux with proton pump inhibitors Christina Reimer Peter Bytzer Department of Medical Gastroenterology, Køge University Hospital, Denmark Abstract: There is a lack
REVIEW Management of laryngopharyngeal refl ux with proton pump inhibitors Christina Reimer Peter Bytzer Department of Medical Gastroenterology, Køge University Hospital, Denmark Abstract: There is a lack
The effect of anti-reflux treatment on subjective voice measurements of patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux
 The Journal of Laryngology & Otology (2013), 127, 590 594. JLO (1984) Limited, 2013 doi:10.1017/s0022215113000832 MAIN ARTICLE The effect of anti-reflux treatment on subjective voice measurements of patients
The Journal of Laryngology & Otology (2013), 127, 590 594. JLO (1984) Limited, 2013 doi:10.1017/s0022215113000832 MAIN ARTICLE The effect of anti-reflux treatment on subjective voice measurements of patients
Lansoprazole Treatment of Patients With Chronic Idiopathic Laryngitis: A Placebo-Controlled Trial
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 4, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02244-4 Lansoprazole Treatment
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 4, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02244-4 Lansoprazole Treatment
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is implicated
 Donald O. Castell, M.D., Series Editor Chronic Laryngitis and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease by Jonathan A. Schneider and Michael F. Vaezi INTRODUCTION Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is implicated
Donald O. Castell, M.D., Series Editor Chronic Laryngitis and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease by Jonathan A. Schneider and Michael F. Vaezi INTRODUCTION Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is implicated
GERD. gastroesophageal reflux disease : GERD. Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease : LPRD GERD GERD GERD LPRD GERD. gastroesophageal reflux ; GER GERD
 114114 2011 : GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease : GERD Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease : LPRD GERD GERD GERD GERD LPRD QOL GERD LPRD QOL LPRD : gastroesophageal reflux ; GER gastroesophageal reflux
114114 2011 : GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease : GERD Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease : LPRD GERD GERD GERD GERD LPRD QOL GERD LPRD QOL LPRD : gastroesophageal reflux ; GER gastroesophageal reflux
Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of the Literature
 International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 291472, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/291472 Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of
International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 291472, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/291472 Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of
Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease. (GERD) is often accompanied
 ...PRESENTATIONS... Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease Based on a presentation by Peter J. Kahrilas, MD Presentation Summary Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) accompanied by regurgitation
...PRESENTATIONS... Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease Based on a presentation by Peter J. Kahrilas, MD Presentation Summary Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) accompanied by regurgitation
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in chronic laryngitis: prevalence and response to acid-suppressive therapy
 Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in chronic laryngitis: prevalence and response to acid-suppressive therapy C.S.QUA*,C.H.WONG*,K.GOPALA &K.L.GOH* *Division of Gastroenterology
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in chronic laryngitis: prevalence and response to acid-suppressive therapy C.S.QUA*,C.H.WONG*,K.GOPALA &K.L.GOH* *Division of Gastroenterology
A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Idiopathic Laryngitis ABSTRACT
 THAI J 28 GASTROENTEROL Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Original Idiopathic Laryngitis Article A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic
THAI J 28 GASTROENTEROL Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Original Idiopathic Laryngitis Article A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic
The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications
 GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications Esophageal Syndromes Extra - esophageal Syndromes Symptomatic Syndromes Typical reflux
GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications Esophageal Syndromes Extra - esophageal Syndromes Symptomatic Syndromes Typical reflux
Role of Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score in Evaluation of Treatment Outcome in Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
 Original Article Role of RSI and RFS in Evaluation of Treatment 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1141 Outcome in Patients with LPR Role of Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score in Evaluation of Treatment
Original Article Role of RSI and RFS in Evaluation of Treatment 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1141 Outcome in Patients with LPR Role of Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score in Evaluation of Treatment
Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease. Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)*
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 3, September 2011 Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)* Objective: To evaluate the efficacy
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 3, September 2011 Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)* Objective: To evaluate the efficacy
Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease; how to evaluate
 Open Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 20; (): 5- Published online December 20, 20 (http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/osjcm) Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease; how to evaluate IRFAN IQBAL, *,
Open Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 20; (): 5- Published online December 20, 20 (http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/osjcm) Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease; how to evaluate IRFAN IQBAL, *,
Association between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and gastroesophageal reflux disease: a meta-analysis
 Association between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and gastroesophageal reflux disease: a meta-analysis David Bédard Méthot, MD, Internal Medicine Resident Evelyne Leblanc, MD, Internal Medicine Resident
Association between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and gastroesophageal reflux disease: a meta-analysis David Bédard Méthot, MD, Internal Medicine Resident Evelyne Leblanc, MD, Internal Medicine Resident
Epidemiology Classic Symptoms of GERD
 Definitions LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX AND ITS ROLE IN PEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGY Wendy Mackey, APRN, CORLN SOHN Congress Meeting Washington, DC September 2012 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Retrograde movement
Definitions LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX AND ITS ROLE IN PEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGY Wendy Mackey, APRN, CORLN SOHN Congress Meeting Washington, DC September 2012 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Retrograde movement
Gastro-oesophageal reflux treatment for prolonged nonspecific cough in children and adults (Review)
 Gastro-oesophageal reflux treatment for prolonged nonspecific cough in children and adults (Review) Chang AB, Lasserson TJ, Gaffney J, Connor FL, Garske LA This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared
Gastro-oesophageal reflux treatment for prolonged nonspecific cough in children and adults (Review) Chang AB, Lasserson TJ, Gaffney J, Connor FL, Garske LA This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared
Review article: extraoesophageal manifestations of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 22 (Suppl. 1): 70 80. Review article: extraoesophageal manifestations of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease J. E. RICHTER Department of Medicine, Temple University School of
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 22 (Suppl. 1): 70 80. Review article: extraoesophageal manifestations of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease J. E. RICHTER Department of Medicine, Temple University School of
Predictors of Outcome in an Open Label, Therapeutic Trial of High-Dose Omeprazole in Laryngitis
 American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2004 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.04151.x Published by Blackwell Publishing ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTIONS Predictors of
American Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270 C 2004 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.04151.x Published by Blackwell Publishing ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTIONS Predictors of
Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do?
 Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do? Philip O. Katz, MD, FACG Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia,
Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do? Philip O. Katz, MD, FACG Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. or dysphagia may alert a physician to the possibility of LPR. 1,2 Laryngeal findings
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Clinical Value of Pharyngeal ph Monitoring Using a Double-Probe, Triple-Sensor Catheter in Patients With Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Togay Muderris, MD; M. Kursat Gokcan, MD; Irfan Yorulmaz,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Clinical Value of Pharyngeal ph Monitoring Using a Double-Probe, Triple-Sensor Catheter in Patients With Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Togay Muderris, MD; M. Kursat Gokcan, MD; Irfan Yorulmaz,
Acid reflux treatment for hoarseness (Review)
 Hopkins C, Yousaf U, Pedersen M This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 2007, Issue 3 http://www.thecochranelibrary.com
Hopkins C, Yousaf U, Pedersen M This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 2007, Issue 3 http://www.thecochranelibrary.com
Acid reflux treatment for hoarseness (Protocol)
 Hopkins C, Yousaf U, Pedersen M This is a reprint of a Cochrane protocol, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 200, Issue 2 http://www.thecochranelibrary.com
Hopkins C, Yousaf U, Pedersen M This is a reprint of a Cochrane protocol, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 200, Issue 2 http://www.thecochranelibrary.com
NEGATIVE ENDOSCOPY, What is the Diagnosis and Treatment?
 NEGATIVE ENDOSCOPY, PPI REFRACTORY REFLUX: What is the Diagnosis and Treatment? Michael F. Vaezi, MD, PhD, MSc, FACG Professor of Medicine Clinical Director Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and
NEGATIVE ENDOSCOPY, PPI REFRACTORY REFLUX: What is the Diagnosis and Treatment? Michael F. Vaezi, MD, PhD, MSc, FACG Professor of Medicine Clinical Director Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc 2 and Marcelo F. Vela MD, MSCR 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Einstein
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc 2 and Marcelo F. Vela MD, MSCR 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Einstein
Gastro-oesophageal reflux treatment for prolonged nonspecific cough in children and adults (Review)
 Gastro-oesophageal reflux treatment for prolonged nonspecific cough in children and adults (Review) Chang AB, Lasserson TJ, Gaffney J, Connor FL, Garske LA This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared
Gastro-oesophageal reflux treatment for prolonged nonspecific cough in children and adults (Review) Chang AB, Lasserson TJ, Gaffney J, Connor FL, Garske LA This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared
The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.4, December 2000 The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality Saleh Mohsen
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.4, December 2000 The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality Saleh Mohsen
Unmet Needs in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Unmet Needs in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ronnie Fass MD Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Esophageal
Unmet Needs in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ronnie Fass MD Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Esophageal
Patient information. Laryngopharyngeal Reflux ( LPR) Ear Nose and Throat Directorate PIF 1423/V4
 Patient information Laryngopharyngeal Reflux ( LPR) Ear Nose and Throat Directorate PIF 1423/V4 You have been diagnosed with laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR), otherwise known as extra-oesophageal reflux
Patient information Laryngopharyngeal Reflux ( LPR) Ear Nose and Throat Directorate PIF 1423/V4 You have been diagnosed with laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR), otherwise known as extra-oesophageal reflux
Mucosal Changes in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Prevalence, Sensitivity, Specificity and Assessment
 The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Contemporary Review Mucosal Changes in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Prevalence, Sensitivity, Specificity and
The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Contemporary Review Mucosal Changes in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Prevalence, Sensitivity, Specificity and
ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.6.EN2 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease. Santhana Krishna Kumar. B 1, Sivasankari. L 1 1 Assistant
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.6.EN2 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease. Santhana Krishna Kumar. B 1, Sivasankari. L 1 1 Assistant
Original Article. K Semmanaselvan 1, Qayum I Mukaddam 2, Manoj Naik 3. Abstract
 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 63 July 2015 27 Original Article An Open Label, Prospective, Single Centre Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Fixed Dose Combination of
Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 63 July 2015 27 Original Article An Open Label, Prospective, Single Centre Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Fixed Dose Combination of
4/24/2015. History of Reflux Surgery. Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux
 Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux Scott Carpenter, DO, FACOS, FACS Mercy Hospital Ardmore Ardmore, OK History of Reflux Surgery - 18 th century- first use of term heartburn - 1934-
Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux Scott Carpenter, DO, FACOS, FACS Mercy Hospital Ardmore Ardmore, OK History of Reflux Surgery - 18 th century- first use of term heartburn - 1934-
JPoelmans,JTack RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL PRACTICE EXTRAOESOPHAGEAL MANIFESTATIONS OF GASTRO- OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX
 1492 See end of article for authors affiliations Correspondence to: Dr J Tack, Centre for Gastroenterological Research, Catholic University of Leuven, Herestraat 49, B-3000 Leuven, Belgium; Jan.Tack@ med.kuleuven.ac.be
1492 See end of article for authors affiliations Correspondence to: Dr J Tack, Centre for Gastroenterological Research, Catholic University of Leuven, Herestraat 49, B-3000 Leuven, Belgium; Jan.Tack@ med.kuleuven.ac.be
Composite ph Predicts Esomeprazole Response in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Without Typical Reflux Syndrome
 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Composite ph Predicts Esomeprazole Response in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Without Typical Reflux Syndrome Han-Chung
The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Composite ph Predicts Esomeprazole Response in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Without Typical Reflux Syndrome Han-Chung
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
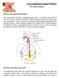 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
Effective Health Care
 Effective Health Care Comparative Effectiveness of Management Strategies for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Executive Summary Background Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), defined as weekly heartburn
Effective Health Care Comparative Effectiveness of Management Strategies for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Executive Summary Background Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), defined as weekly heartburn
Intragastric acidity during treatment with esomeprazole 40 mg twice daily or pantoprazole 40 mg twice daily a randomized, two-way crossover study
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 21: 963 967. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02432.x Intragastric acidity during treatment with esomeprazole 40 mg twice daily or pantoprazole 40 mg twice daily a randomized,
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 21: 963 967. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02432.x Intragastric acidity during treatment with esomeprazole 40 mg twice daily or pantoprazole 40 mg twice daily a randomized,
GERD: 2014 Dilemmas and Solutions. Ronnie Fass MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University
 GERD: 2014 Dilemmas and Solutions Ronnie Fass MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University How to Maximize Your PPI Treatment? Improve compliance and adherance Fass R. Am J Gastroenterol.
GERD: 2014 Dilemmas and Solutions Ronnie Fass MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University How to Maximize Your PPI Treatment? Improve compliance and adherance Fass R. Am J Gastroenterol.
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons:
 Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons: http://dspace.flinders.edu.au/dspace/ This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: Fox M, Omari T, Rommel N. Supraesophageal Reflux Disease: Solving
Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons: http://dspace.flinders.edu.au/dspace/ This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: Fox M, Omari T, Rommel N. Supraesophageal Reflux Disease: Solving
Extraesophageal presentations of gastroesophageal reflux disease: the case for aggressive diagnosis and treatment
 JOEL E. RICHTER, MD Dr. Richter is chairman of the Department of Gastroenterology at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, specializing in esophageal diseases with particular interest in GERD, achalasia, and
JOEL E. RICHTER, MD Dr. Richter is chairman of the Department of Gastroenterology at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, specializing in esophageal diseases with particular interest in GERD, achalasia, and
LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX
 CLINICAL REVIEW CLINICIAN S CORNER Evaluation and Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Charles N. Ford, MD LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX (LPR) is the result of retrograde flow of gastric contents to the laryngopharynx,
CLINICAL REVIEW CLINICIAN S CORNER Evaluation and Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Charles N. Ford, MD LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX (LPR) is the result of retrograde flow of gastric contents to the laryngopharynx,
The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation
 The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation James P. Dworkin, Ph.D. Jayme Dowdall, M.D. Adam Folbe, M.D. Tom Willis, M.S. Richard Culatta, Ph.D. Wayne
The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation James P. Dworkin, Ph.D. Jayme Dowdall, M.D. Adam Folbe, M.D. Tom Willis, M.S. Richard Culatta, Ph.D. Wayne
Mapping Regional Laryngopharyngeal Mechanoreceptor Response
 Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 7, No. 4: 319-323, December 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2014.7.4.319 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Mapping Regional Laryngopharyngeal
Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 7, No. 4: 319-323, December 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2014.7.4.319 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Mapping Regional Laryngopharyngeal
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: esophageal_ph_monitoring 4/2011 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Acid reflux is the
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: esophageal_ph_monitoring 4/2011 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Acid reflux is the
Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children
 Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children Jose Luis Martinez, M.D. Associate Professor University of California San Francisco Director Endoscopy Unit Children s Hospital Central California Overview
Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children Jose Luis Martinez, M.D. Associate Professor University of California San Francisco Director Endoscopy Unit Children s Hospital Central California Overview
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is among the
 New Developments in Extraesophageal Reflux Disease Elif Saritas Yuksel, MD, and Michael F. Vaezi, MD, PhD, MSc (Epi) Dr. Saritas Yuksel is a Research Assistant in the Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology,
New Developments in Extraesophageal Reflux Disease Elif Saritas Yuksel, MD, and Michael F. Vaezi, MD, PhD, MSc (Epi) Dr. Saritas Yuksel is a Research Assistant in the Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology,
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is the most prevalent
 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux and Functional Laryngeal Disorder: Perspective and Common Practice of the General Gastroenterologist Dhyanesh A. Patel, MD, Michael Blanco, MD, and Michael F. Vaezi, MD, PhD Dr
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux and Functional Laryngeal Disorder: Perspective and Common Practice of the General Gastroenterologist Dhyanesh A. Patel, MD, Michael Blanco, MD, and Michael F. Vaezi, MD, PhD Dr
Research Article Postthyroidectomy Throat Pain and Swallowing: Do Proton Pump Inhibitors Make a Difference?
 ISRN Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 135978, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/135978 Research Article Postthyroidectomy Throat Pain and Swallowing: Do Proton Pump Inhibitors Make a Difference?
ISRN Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 135978, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/135978 Research Article Postthyroidectomy Throat Pain and Swallowing: Do Proton Pump Inhibitors Make a Difference?
Hoarseness and Laryngopharyngeal Reflux A Survey of Primary Care Physician Practice Patterns
 Research Original Investigation A Survey of Primary Care Physician Practice Patterns Ryan Ruiz, BA; Seema Jeswani, MD; Kenneth Andrews, MD; Benjamin Rafii, MD; Benjamin C. Paul, MD; Ryan C. Branski, PhD;
Research Original Investigation A Survey of Primary Care Physician Practice Patterns Ryan Ruiz, BA; Seema Jeswani, MD; Kenneth Andrews, MD; Benjamin Rafii, MD; Benjamin C. Paul, MD; Ryan C. Branski, PhD;
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice
 Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
Drug Class Review on Proton Pump Inhibitors
 Drug Class Review on Proton Pump Inhibitors Final Report Update 4 July 2006 Original Report Date: November 2002 Update 1 Report Date: April 2003 Update 2 Report Date: April 2004 Update 3 Report Date: May
Drug Class Review on Proton Pump Inhibitors Final Report Update 4 July 2006 Original Report Date: November 2002 Update 1 Report Date: April 2003 Update 2 Report Date: April 2004 Update 3 Report Date: May
ORIGINAL STUDY MANAGEMENT OF PHARYNGOLARYNGEAL REFLUX AT VOICE PROFESSIONALS
 MEDICINĂ, no 2, 2011 ORIGINAL STUDY MANAGEMENT OF PHARYNGOLARYNGEAL REFLUX AT VOICE PROFESSIONALS Monica Voineag 1,2, Vasile Costinescu 3, Mihail Dan Cobzeanu 3 1 University of Medicine and Pharmacy Gr
MEDICINĂ, no 2, 2011 ORIGINAL STUDY MANAGEMENT OF PHARYNGOLARYNGEAL REFLUX AT VOICE PROFESSIONALS Monica Voineag 1,2, Vasile Costinescu 3, Mihail Dan Cobzeanu 3 1 University of Medicine and Pharmacy Gr
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) often is implicated
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:433 441 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Surgical Fundoplication in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Unresponsive to Aggressive Acid Suppression: A Controlled Study JASON SWOGER,*
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:433 441 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Surgical Fundoplication in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Unresponsive to Aggressive Acid Suppression: A Controlled Study JASON SWOGER,*
Hold the Wrap! There is so much more to be done!
 Hold the Wrap! There is so much more to be done! (Well, a few things that can be done.) (Well, not all that much, really ) (But Blair has never killed anyone with a PPI!) Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center
Hold the Wrap! There is so much more to be done! (Well, a few things that can be done.) (Well, not all that much, really ) (But Blair has never killed anyone with a PPI!) Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center
Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors in the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
 IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul Aug 2018), PP 54-61 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul Aug 2018), PP 54-61 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion
 Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
Reliability of Echocardiography Measurement of Patent Ductus Arteriosus Minimum Diameter: A Meta-analysis
 International Journal of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease 4(): 15-19, 016 DOI: 10.13189/ijccd.016.04001 http://www.hrpub.org Reliability of Echocardiography Measurement of Patent Ductus Arteriosus
International Journal of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease 4(): 15-19, 016 DOI: 10.13189/ijccd.016.04001 http://www.hrpub.org Reliability of Echocardiography Measurement of Patent Ductus Arteriosus
CYP2C19-Proton Pump Inhibitors
 CYP2C19-Proton Pump Inhibitors Cameron Thomas, Pharm.D. PGY2 Clinical Pharmacogenetics Resident St. Jude Children s Research Hospital February 1, 2018 Objectives: CYP2C19-PPI Implementation Review the
CYP2C19-Proton Pump Inhibitors Cameron Thomas, Pharm.D. PGY2 Clinical Pharmacogenetics Resident St. Jude Children s Research Hospital February 1, 2018 Objectives: CYP2C19-PPI Implementation Review the
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Effects of Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication on Chronic GERD Patients: 12-Month Prospective Multicenter Experience Erik B. Wilson, MD, FACS,* William E. Barnes, MD, FACS,w Peter
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Effects of Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication on Chronic GERD Patients: 12-Month Prospective Multicenter Experience Erik B. Wilson, MD, FACS,* William E. Barnes, MD, FACS,w Peter
GERD: Pitfalls and Pearls
 GERD: Pitfalls and Pearls Gary W. Falk, M.D., M.S. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Perelman School of Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania Conflicts of Interest Nothing to disclose
GERD: Pitfalls and Pearls Gary W. Falk, M.D., M.S. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Perelman School of Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania Conflicts of Interest Nothing to disclose
Burning Issues in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 3:45 4:45pm Burning Issues in GERD SPEAKER Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP,
3:45 4:45pm Burning Issues in GERD SPEAKER Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Correlation of Findings at Direct Laryngoscopy and Bronchoscopy With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Children
 Correlation of Findings at Direct Laryngoscopy and Bronchoscopy With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Children A Prospective Study ORIGINAL ARTICLE Michele M. Carr, DDS, MD, MEd, FRCSC; Mark L. Nagy,
Correlation of Findings at Direct Laryngoscopy and Bronchoscopy With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Children A Prospective Study ORIGINAL ARTICLE Michele M. Carr, DDS, MD, MEd, FRCSC; Mark L. Nagy,
A Clinical Assessment of Throat Manifestations of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease with Special Reference to Video Endoscopic Findings
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. VII (June. 2017), PP 57-62 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Assessment of Throat Manifestations
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. VII (June. 2017), PP 57-62 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Assessment of Throat Manifestations
Validation of a Four-Graded Scale for Severity of Heartburn in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Volume 11 Number 4 2008 VALUE IN HEALTH Validation of a Four-Graded Scale for Severity of Heartburn in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ola Junghard, PhD, 1 Ingela Wiklund, PhD
Volume 11 Number 4 2008 VALUE IN HEALTH Validation of a Four-Graded Scale for Severity of Heartburn in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ola Junghard, PhD, 1 Ingela Wiklund, PhD
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) Produced by the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination Copyright 2017 University of York.
 A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of five strategies for the prevention of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: a systematic review with economic modelling Brown
A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of five strategies for the prevention of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: a systematic review with economic modelling Brown
Committee Approval Date: October 14, 2014 Next Review Date: October 2015
 Medication Policy Manual Topic: esomeprazole-containing medications: - Nexium - Vimovo - esomeprazole strontium Policy No: dru039 Date of Origin: May 2001 Committee Approval Date: October 14, 2014 Next
Medication Policy Manual Topic: esomeprazole-containing medications: - Nexium - Vimovo - esomeprazole strontium Policy No: dru039 Date of Origin: May 2001 Committee Approval Date: October 14, 2014 Next
Refractory GERD. Kenneth R. DeVault, MD, FACG President American College of Gastroenterology Chair Department of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida
 Refractory GERD Kenneth R. DeVault, MD, FACG President American College of Gastroenterology Chair Department of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida Objectives Define the terminology associated with refractory
Refractory GERD Kenneth R. DeVault, MD, FACG President American College of Gastroenterology Chair Department of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida Objectives Define the terminology associated with refractory
The Expression of Beclin-1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Non-Tumor Liver Tissue: A Meta-Analysis
 The Expression of Beclin-1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Non-Tumor Liver Tissue: A Meta-Analysis Zhiqiang Qin¹, Xinjuan Yu², Jinkun Wu¹, Mei Lin¹ 1 Department of Pathology, School of Basic Medicine,
The Expression of Beclin-1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Non-Tumor Liver Tissue: A Meta-Analysis Zhiqiang Qin¹, Xinjuan Yu², Jinkun Wu¹, Mei Lin¹ 1 Department of Pathology, School of Basic Medicine,
GERD. Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the. stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the
 GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
Review article: gastric acidity ) comparison of esomeprazole with other proton pump inhibitors
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17 (Suppl. 1): 10 15. Review article: gastric acidity ) comparison of esomeprazole with other proton pump inhibitors J. G. HATLEBAKK Department of Medicine, Haukeland Sykehus,
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17 (Suppl. 1): 10 15. Review article: gastric acidity ) comparison of esomeprazole with other proton pump inhibitors J. G. HATLEBAKK Department of Medicine, Haukeland Sykehus,
Four-Day Bravo ph Capsule Monitoring With and Without Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:1083 1088 Four-Day Bravo ph Capsule Monitoring With and Without Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy IKUO HIRANO, QING ZHANG, JOHN E. PANDOLFINO, and PETER J. KAHRILAS
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:1083 1088 Four-Day Bravo ph Capsule Monitoring With and Without Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy IKUO HIRANO, QING ZHANG, JOHN E. PANDOLFINO, and PETER J. KAHRILAS
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, barium esophagography for, 57 58 Acid pocket, 18 19 Acid-sensing ion, 20 Acupuncture, 128 Adiponectin, in obesity, 166 ADX10059 metabotropic
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, barium esophagography for, 57 58 Acid pocket, 18 19 Acid-sensing ion, 20 Acupuncture, 128 Adiponectin, in obesity, 166 ADX10059 metabotropic
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Paraesophageal Hernias &
 530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
Gastroesophageal Reflux Evaluation in Patients Affected by Chronic Cough: Restech Versus Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance/pH Metry
 The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Gastroesophageal Reflux Evaluation in Patients Affected by Chronic Cough: Restech Versus Multichannel Intraluminal
The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Gastroesophageal Reflux Evaluation in Patients Affected by Chronic Cough: Restech Versus Multichannel Intraluminal
Keywords transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF), EsophyX, extraesophageal GERD symptoms, regurgitation, proton pump inhibitor (PPI), heartburn
 526788SRIXXX10.1177/1553350614526788Surgical InnovationTrad et al research-article2014 Original Clinical Science Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication Effective in Eliminating GERD Symptoms in Partial
526788SRIXXX10.1177/1553350614526788Surgical InnovationTrad et al research-article2014 Original Clinical Science Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication Effective in Eliminating GERD Symptoms in Partial
Altman et al.: A Review of Clinical Practice Guidelines for Reflux Disease
 The Laryngoscope VC 2011 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Contemporary Review A Review of Clinical Practice Guidelines for Reflux Disease: Toward Creating a Clinical
The Laryngoscope VC 2011 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Contemporary Review A Review of Clinical Practice Guidelines for Reflux Disease: Toward Creating a Clinical
Traditional Reflux Parameters and Not Impedance Monitoring Predict Outcome After Fundoplication in Extraesophageal Reflux
 The Laryngoscope VC 2011 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Traditional Reflux Parameters and Not Impedance Monitoring Predict Outcome After Fundoplication in Extraesophageal
The Laryngoscope VC 2011 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Traditional Reflux Parameters and Not Impedance Monitoring Predict Outcome After Fundoplication in Extraesophageal
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Information for patients UHN Read this handout to learn about: What gastroesohageal reflux (GERD) is Signs and symptoms How your doctor will know if you have it Tests
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Information for patients UHN Read this handout to learn about: What gastroesohageal reflux (GERD) is Signs and symptoms How your doctor will know if you have it Tests
Original Policy Date
 MP 2.04.38 Genetic Testing for Helicobacter pylori Treatment Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return
MP 2.04.38 Genetic Testing for Helicobacter pylori Treatment Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return
DOI: / ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;79(5):589-93. DOI: 10.5935/1808-8694.20130105 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of signs and symptoms of laryngopharyngeal reflux in snorers with suspected obstructive sleep apnea
Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;79(5):589-93. DOI: 10.5935/1808-8694.20130105 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of signs and symptoms of laryngopharyngeal reflux in snorers with suspected obstructive sleep apnea
Extraesophageal manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease*
 150 Gurski RR, Rosa ARP, Valle E, Borba MA, Valiati AA Review Article Extraesophageal manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease* RICHARD RICACHENEVSKI GURSKI 1, ANDRÉ RICARDO PEREIRA DA ROSA 2,
150 Gurski RR, Rosa ARP, Valle E, Borba MA, Valiati AA Review Article Extraesophageal manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease* RICHARD RICACHENEVSKI GURSKI 1, ANDRÉ RICARDO PEREIRA DA ROSA 2,
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies (MOOSE): Checklist.
 Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies (MOOSE): Checklist. MOOSE Checklist Infliximab reduces hospitalizations and surgery interventions in patients with inflammatory bowel disease:
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies (MOOSE): Checklist. MOOSE Checklist Infliximab reduces hospitalizations and surgery interventions in patients with inflammatory bowel disease:
Diverged Otorhinolaryngological Manifestations of Reflux Disease in Indian Condition: A Base Line Data Generation
 Suddhasheel Roy, Rajiv Kumar Jain Original Article 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1114 Diverged Otorhinolaryngological Manifestations of Reflux Disease in Indian Condition: A Base Line Data Generation 1 Suddhasheel
Suddhasheel Roy, Rajiv Kumar Jain Original Article 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1114 Diverged Otorhinolaryngological Manifestations of Reflux Disease in Indian Condition: A Base Line Data Generation 1 Suddhasheel
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Patients with Eustachian Tube Catarrh
 IJOPL Original article Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1107 Patients with Eustachian Tube Catarrh Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Patients with Eustachian Tube Catarrh 1
IJOPL Original article Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1107 Patients with Eustachian Tube Catarrh Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Patients with Eustachian Tube Catarrh 1
Mette Pedersen * The Medical Centre, Voice Unit, Østergade 18, 3, 1100 Copenhagen, Denmark
 Journal of Rhinolaryngo-Otologies, 2014, 2, 67-73 67 Acoustical Voice Measurements did Change after Treatment in Patients with Laryngo-Pharyngeal Reflux: A Prospective Randomized Study Including MDVP (Laryngograph
Journal of Rhinolaryngo-Otologies, 2014, 2, 67-73 67 Acoustical Voice Measurements did Change after Treatment in Patients with Laryngo-Pharyngeal Reflux: A Prospective Randomized Study Including MDVP (Laryngograph
Rpts. GENERAL General Schedule (Code GE) Program Prescriber type: Dental Medical Practitioners Nurse practitioners Optometrists Midwives
 Esomeprazole 20mg Name, Restriction, Manner of esomeprazole 20 mg enteric tablet, 30 (8886Q) (029W) Gastric ulcer Peptic ulcer Treatment Phase: Initial treatment The therapy must be for initial treatment
Esomeprazole 20mg Name, Restriction, Manner of esomeprazole 20 mg enteric tablet, 30 (8886Q) (029W) Gastric ulcer Peptic ulcer Treatment Phase: Initial treatment The therapy must be for initial treatment
Posterior laryngitis: a study of persisting symptoms and health-related quality of life.
 Posterior laryngitis: a study of persisting symptoms and health-related quality of life. Pendleton, Hillevi; Ahlner Elmqvist, Marianne; Jannert, Magnus; Ohlsson, Bodil Published in: European Archives of
Posterior laryngitis: a study of persisting symptoms and health-related quality of life. Pendleton, Hillevi; Ahlner Elmqvist, Marianne; Jannert, Magnus; Ohlsson, Bodil Published in: European Archives of
Disclosures. Proton Pump Inhibitors Deprescribing? Deprescribing PPI Objectives. Deprescribing. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI) 5/28/2018.
 Proton Pump Inhibitors Deprescribing? None Disclosures Chad Burski, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine UAB Gastroenterology Deprescribing PPI Objectives AR Why? Who? How? The mechanism of action of Proton
Proton Pump Inhibitors Deprescribing? None Disclosures Chad Burski, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine UAB Gastroenterology Deprescribing PPI Objectives AR Why? Who? How? The mechanism of action of Proton
Heartburn is a common symptom among adults in
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:553 563 Early Heartburn Relief With Proton Pump Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Clinical Trials KENNETH R. MCQUAID*, and LOREN LAINE
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:553 563 Early Heartburn Relief With Proton Pump Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Clinical Trials KENNETH R. MCQUAID*, and LOREN LAINE
Study population The study population comprised a hypothetical cohort of patients with confirmed reflux oesophagitis.
 Cost effectiveness of esomeprazole compared with omeprazole in the acute treatment of patients with reflux oesophagitis in the UK Wahlqvist P, Junghard O, Higgins A, Green J Record Status This is a critical
Cost effectiveness of esomeprazole compared with omeprazole in the acute treatment of patients with reflux oesophagitis in the UK Wahlqvist P, Junghard O, Higgins A, Green J Record Status This is a critical
GERD: A linical Clinical Clinical Update Objectives
 GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
Number of studies. Endoscopic finding. Number of subjects. Pooled prevalence 95% CI
 Clinical Approach to the Patient t with Dyspepsia William D. Chey, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Prevalence of Endoscopic Findings in Individuals with Dyspepsia Systematic Review
Clinical Approach to the Patient t with Dyspepsia William D. Chey, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Prevalence of Endoscopic Findings in Individuals with Dyspepsia Systematic Review
235 60th Street, West New York, NJ T: (201) F: (201) Main Street, Hackensack, NJ T: (201)
 235 60th Street, West New York, NJ 07093 T: (201) 854-4646 F: (201) 854-4647 810 Main Street, Hackensack, NJ 07601 T: (201) 488-0095 Barrett's Esophagus WHAT IS BARRETTT'S ESOPHAGUS? Barrett's esophagus
235 60th Street, West New York, NJ 07093 T: (201) 854-4646 F: (201) 854-4647 810 Main Street, Hackensack, NJ 07601 T: (201) 488-0095 Barrett's Esophagus WHAT IS BARRETTT'S ESOPHAGUS? Barrett's esophagus
Chronic pharyngitis and the association with pepsin detection and reflux disease
 Original Article Page 1 of 8 Chronic pharyngitis and the association with pepsin detection and reflux disease Peter W. Dettmar 1, Qiuping Wang 2, Rachel M. Hodgson 1, Xiu Wang 3, Yifei Li 3, Manjie Jiang
Original Article Page 1 of 8 Chronic pharyngitis and the association with pepsin detection and reflux disease Peter W. Dettmar 1, Qiuping Wang 2, Rachel M. Hodgson 1, Xiu Wang 3, Yifei Li 3, Manjie Jiang
11/19/2012. Comparison between PPIs G CELL. Risk ratio (95% CI) Patient subgroup. gastrin. S-form of omeprazole. Acid sensitive. coated.
 REGULATION OF GASTRIC ACID SECRETION Comparison between PPIs Omeprazole Lansoprazole Rabeprazole Pantoprazole Esomeprazole gastrin G CELL + Acid sensitive Yes T1/2 30-60 minutes Main elimination Enteric
REGULATION OF GASTRIC ACID SECRETION Comparison between PPIs Omeprazole Lansoprazole Rabeprazole Pantoprazole Esomeprazole gastrin G CELL + Acid sensitive Yes T1/2 30-60 minutes Main elimination Enteric
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT DISCLOSURES 4/18/2018
 GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
Review article: pharmacology of esomeprazole and comparisons with omeprazole
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17 (Suppl. 1): 5 9. Review article: pharmacology of esomeprazole and comparisons with omeprazole J. DENT Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and General Medicine, Royal
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17 (Suppl. 1): 5 9. Review article: pharmacology of esomeprazole and comparisons with omeprazole J. DENT Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and General Medicine, Royal
Gastroesophageal reflux disease. The case for improving patient education in primary care
 Original Research Gastroesophageal reflux disease: The case for improving patient education in primary care This study reveals that something as simple as knowing when to take GERD medication is compromised
Original Research Gastroesophageal reflux disease: The case for improving patient education in primary care This study reveals that something as simple as knowing when to take GERD medication is compromised
