Chronic pharyngitis and the association with pepsin detection and reflux disease
|
|
|
- Sabina Henderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Page 1 of 8 Chronic pharyngitis and the association with pepsin detection and reflux disease Peter W. Dettmar 1, Qiuping Wang 2, Rachel M. Hodgson 1, Xiu Wang 3, Yifei Li 3, Manjie Jiang 3, Li Xu 3, Yu Lan 4, Andrew D. Woodcock 1 1 RD Biomed Limited, Castle Hill Hospital, Cottingham, UK; 2 Department of ENT, BenQ Medical Center, The Affiliated BenQ Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing , China; 3 Department of ENT, The Affiliated Jinling Hospital Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing , China; 4 Department of Gastroenterology, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Beijing , China Contributions: (I) Conception and design: Q Wang, X Wang, PW Dettmar, RM Hodgson; (II) Administrative support: RM Hodgson, Q Wang, PW Dettmar; (III) Provision of study materials or patients: Q Wang, X Wang, Y Lan, M Jiang, L Xu, Y Li; (IV) Collection and assembly of data: AD Woodcock, RM Hodgson; (V) Data analysis and interpretation: AD Woodcock, RM Hodgson, PW Dettmar; (VI) Manuscript writing: All authors; (VII) Final approval of manuscript: All authors. Correspondence to: Prof Peter W. Dettmar. RD Biomed Limited, Daisy Building, Castle Hill Hospital, Castle Road, Cottingham, HU16 5JQ, UK. peter.dettmar@technostics.com. Background: Pepsin is a biomarker for reflux disease and a major etiological factor in laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR). Do chronic pharyngitis patients have significant concentrations of pepsin present in saliva samples indicating the presence of reflux disease? Methods: Thirty-two patients with chronic pharyngitis symptoms and laryngoscopy findings from the reflux finding score (RFS), indicating chronic pharyngitis, were recruited from an Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT) department. A total of 96 patient saliva samples were analysed for the presence of pepsin. Reflux questionnaires assessed the symptoms of reflux [reflux symptom index (RSI), RFS, and reflux disease questionnaire (RDQ)] and, the non-invasive reflux diagnostic device Peptest TM was used to determine the concentration of pepsin present in the patient s saliva samples. Peptest TM uses lateral flow technology and contains two unique human anti-pepsin monoclonal antibodies fully validated and sensitive for the detection of pepsin in saliva. Results: In total, 78% of chronic pharyngitis patients had medium to high concentrations of pepsin (>75 ng/ml) in their saliva samples. In chronic pharyngitis patients 81% were found to have a positive pepsin concentration in post-prandial samples, compared to the control, where 32% were found to have a positive pepsin concentration. Conclusions: A correlation was shown between the presence of pepsin and the presence of chronic pharyngitis. 78% of chronic pharyngitis patients were shown to have medium to high concentrations of pepsin in their saliva samples and 81% had a positive pepsin concentration in post-prandial samples. Peptest TM demonstrated good diagnostic potential and as a non-invasive, rapid and easy to use test, it will play an important role as a first line reflux diagnostic. Keywords: Chronic pharyngitis; laryngopharyngeal reflux; Peptest; reflux disease; salivary pepsin Received: 25 September 2018; Accepted: 09 October 2018; Published: 19 October doi: /aoe View this article at:
2 Page 2 of 8 Annals of Esophagus, 2018 Introduction Chronic pharyngitis is more than just a sore throat ; it causes the patient long-term pain and can even lead to throat erosion and cancer (1). A survey by National Ambulatory Medical Care 1995 showed 4.3% of outpatient healthcare appointments were due to symptoms of pharyngitis, making it the 3 rd most common complaint (2). Pharyngitis can occur from a multitude of factors; viral infection being the most common cause, however some bacterial infections are often more serious (2). Typical chronic pharyngitis symptoms include inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa (3). Gastroesophageal reflux causes pepsin to reach the throat. Therefore, pepsin has been proposed as a biomarker of gastroesophageal reflux disease, and as a major etiological factor in laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR). Pepsin is used in the stomach to break-down protein; the stomach itself is not digested because of a protective mucus layer. However, during a reflux episode, pepsin and stomach acid reaching the oesophagus or throat can cause tissue erosion and inflammation. One method of inflammation was reported where pepsin induced the production of pro-inflammatory factors on the tonsil (4). They argued that inflammation can be caused directly through tissue injury or by antigenic detection of pepsin, leading to the recruitment of lymphocytes. Throat infection and pharyngitis can also occur because pepsin disturbs commensal bacteria lining the throat, allowing pathogenic bacteria to accumulate (5). It is therefore important to clarify the cause of chronic pharyngitis in patients who have been cleared of bacterial, viral and fungal infections to offer optimal therapy. Previously, the absence of any easy-to-use objective method has hindered the efforts from clinicians and researchers to prove the possible association between reflux and chronic pharyngitis. However, Peptest TM (RD Biomed Limited, Cottingham, UK) which is a non-invasive and rapid test for diagnosing the presence of salivary pepsin in clinical samples and used as a biomarker for detecting reflux disease has recently become available and has been used in the present study. Patients provided saliva samples at specific time points because changes in activity can influence the occurrence of reflux episodes. Samples from patients were collected in the morning on waking, the second sample post-prandial 60 minutes after finishing a meal and the third sample within 15 minutes of a symptom. A healthy control group without reflux disease were tested for pepsin concentration in post-prandial saliva samples. These samples were compared to the post-prandial samples in the patient group. Currently, an acceptable concentration of pepsin concentration found in the saliva of a healthy individual in the UK is <75 ng/ml, which is considered as a physiological pepsin concentration. Those which have >75 ng/ml pepsin in saliva samples are pathologically positive and would be classed as diseased and would require medical attention. The cut-off value of 76 ng/ml is in line with the specificity and sensitivity of guides obtained and previously reported (6). The aim of the present study was to establish the association between reflux and chronic pharyngitis patients. The study would also help to evaluate the diagnostic value of Peptest TM (RD Biomed Limited) for reflux diseases. Methods Subjects Thirty-two patients presenting with typical chronic pharyngitis symptoms and laryngoscopy findings indicating chronic pharyngitis were recruited from the Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT) outpatient clinic at Jinling Hospital and BenQ Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. Patient s lifestyles were also considered. No significant association was found between patients with pepsin concentrations >75 ng/ml and habits such as; smoking, drinking nor having an appetite for spicy food. Those patients were also assessed by reflux questionnaires, reflux finding score (RFS) (7), reflux symptom index (RSI) (8), and reflux disease questionnaire (RDQ) (9,10). Demographic information of patients with chronic pharyngitis is presented in Table 1, where 18 out of 32 patients completed this information. A control group of similar demographics to the patient group was used for comparison of pepsin concentration. The control group was comprised of 31 healthy individuals recruited from the Department of Gastroenterology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China. A comparison of demographics between the control group and patient group is shown in Table 2. Salivary pepsin collection Patients provided saliva which was collected into tubes containing 0.5 ml of 0.01 M citric acid. Each patient provided three salivary samples at specific time points, patients were also informed not to take any medication
3 Annals of Esophagus, 2018 Page 3 of 8 Table 1 Chronic pharyngitis patients demographics (n=18) Parameter All (n=18) Male (n=7) Female (n=11) Mean height (cm) Mean age (years) Mean weight (kg) Smoking habit (%) Drinking habit (%) Appetite for spicy food (%) A total of 18 out of 32 patients completed demographic information. Table 2 Patient and control group demographics (n=31) Parameter Chronic pharyngitis Control subjects Number of participants Male/female 14/18 15/16 Age range (years) Mean age (years) Failed to provide information 12 0 during the study period. The sample collection and analysis procedure are outlined in Figure 1. One sample was provided in the morning on waking, the second sample post-prandial 60 minutes after finishing a meal and the third sample within 15 minutes of experiencing a symptom. The healthy control group provided only post-prandial samples. All the saliva samples were analysed for the presence of pepsin using Peptest TM (RD Biomed Limited). Samples were refrigerated at 4 and analysed within 2 days of collection. Questionnaire To aid the diagnosis of the cause of the patients chronic pharyngitis, patients completed three reflux questionnaires which describe typical reflux symptoms (Table 3). The RFS is a clinician-rated endoscopic finding score based on findings from laryngoscopy (7) which were calculated by rating reflux symptoms to their corresponding number and finding the total (0 to 26), RFS >5 suggests abnormality. The RSI is a self-administered survey based on 9 questions and calculated by rating reflux symptoms from 0 to 5 and finding the total (0 to 45) (8). RSI >13 suggests abnormality. And, the RDQ is a self-rated symptom score (9-11) Collect 1 ml 1 of sample 2 Centrifuge sample for 5 minutes 3 Draw up 80 μl from clear supernatent layer Apply 80 μl sample to screwtop tube containing 240 μl migration buffer Vortex mix for 10 seconds Apply 80 μl of the mixed sample to the well of the Peptest A = Negative B = Positive C = Invalid test Figure 1 Step-by-step diagram of pepsin analysis; from collection, to the analysis of pepsin concentration on a Peptest TM device
4 Page 4 of 8 Annals of Esophagus, 2018 Table 3 Questionnaire results in 32 patients presenting with chronic pharyngitis Questionnaire calculated by rating reflux symptoms such as heartburn, dyspepsia and regurgitation within a time frame, scored from 0 to 5 and used as a classic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) diagnostic tool not considered suitable for the diagnosis of LPR. Patients experience worse symptoms if a higher RDQ total is recorded with a cut-off point of 12 for GERD diagnosis. Analysis Collection tubes were centrifuged at 4,000 rpm for 5 min and a clear supernatant was seen. Samples were centrifuged again if no supernatant was observed. 80 μl of clear supernatant was drawn up into an automated pipette. The 80 μl sample was transferred to a screw-top microtube containing 240 μl of migration buffer solution. This sample was mixed with a vortex mixer for 10 s. A second pipette was used to transfer 80 μl of the sample to the circular well of a lateral flow device (LFD) containing two unique human monoclonal antibodies; one to detect and one to capture pepsin in the saliva sample (Peptest TM, RD Biomed Limited) (Figure 1). The lower limit for detection of pepsin (as determined by the manufacturer) was set at 16 ng/ml. This value was used as a cut-off to consider a saliva sample positive for pepsin. Therefore, all samples with concentrations below this threshold were considered to have zero pepsin. Results Mean pepsin concentration (ng/ml) ± SD* RSI positive >13 (n=9) 235±149 RSI negative 13 (n=23) 208±165 RFS positive >5 (n=17) 176±150 RFS negative 5 (n=15) 261±161 RSI and RFS positive (n=7) 187±119 RSI and RFS negative (n=13) 239±158 *, mean pepsin concentration was calculated from the sample provided with the highest concentration of pepsin. RSI, reflux symptom index; RFS, reflux finding score. Patients with chronic pharyngitis and indications of chronic pharyngitis (n=32) were compared with a healthy non-gerd control group (n=31). Post-prandial saliva samples were compared for pepsin concentration. A pepsin concentration at the level >18 ng/ml displayed a visible test line on a Peptest TM (RD Biomed Limited) device and was marked positive. The absence of a test line was marked negative, a pepsin concentration <18 ng/ml. In the healthy individuals group, 10 (32%) were found to have a positive pepsin concentration and 21 (68%) were negative. In the chronic pharyngitis patient group, 25 (78%) were found to have a positive pepsin concentration and 7 (22%) were negative. Sensitivity was 78% and specificity was 68%. Positive predicted value was 71% and negative predicted value was 75%. Reflux diagnostic questionnaires result in a positive or negative determination for the presence of reflux. A Chi-square test was used to determine if the type of RDQ, namely RFS and RSI, influenced the outcome of the diagnosis. The results show that there is a significant association between the outcome of the questionnaire, depending on which questionnaire was used to determine if the patient may have reflux disease. It was more likely a patient would be diagnosed with reflux disease if the RFS questionnaire was used compared to RSI, asymptotic significance (2-sided) P= The RFS produced significantly more positive reflux disease diagnosis results than RSI. However, when averaging the pepsin concentration across the most highly concentrated samples of all patients, a positive RFS did not correlate to a higher mean pepsin concentration from the most concentrated samples from each patient. The mean maximum pepsin concentration from the three samples taken by chronic pharyngitis patients against the corresponding questionnaire results are shown in Table 3. The patient group with the highest concentration of pepsin was found when patients completed the RFS and scored a negative reflux disease diagnosis. The lowest concentration of pepsin from the patient group was found when the RFS scored positively for reflux disease diagnosis. Two sample t tests were performed to determine any significance between the outcome of the RFS and RSI on mean maximum pepsin concentration (Table 4). Two sample t tests show no significant difference between means of patients with a positive RFS or negative RFS and their corresponding concentration of pepsin. Two sample t tests show no significant difference between means of patients with a positive RSI or negative RSI and their corresponding concentration of pepsin. However, a significant difference
5 Annals of Esophagus, 2018 Page 5 of 8 Table 4 Independent samples test Statistically test applied Difference between the mean maximum pepsin concentration and RFS Difference between the mean maximum pepsin concentration and RSI Difference between the mean maximum pepsin concentration and both RFS and RSI Levene s test for equality of variances f Sig t test for equality of means t df Sig. (2 tailed) Mean difference Standard error difference Two sample t tests. Sig., significance. Table 5 Association between pepsin concentration and smoking, drinking and an appetite for spicy food Chi squared >75 ng/ml pepsin (n=18) χ 2 Smoking Drinking Appetite for spicy food Chi squared was calculated using IBM SPSS Statistics 23. occurs when the two questionnaires are used in conjunction. Two sample t tests do show a significant difference between means of patients with both a positive RFS and RSI against both a negative RFS and RSI and their corresponding concentration of pepsin P=0.452 (Table 4). Chi squared (Table 5) shows no significant association on pepsin concentrations above 75 ng/ml through smoking, drinking nor having an appetite for spicy food. No significant association between pepsin concentration >75 ng/ml and patients with a positive RSI score. Of the 32 patients diagnosed with chronic pharyngitis 41 of 96 saliva samples had a pepsin concentration above 75 ng/ml (Table 6). This corresponded to a total of 25 patients with medium to high pepsin present in their saliva sample representing 78% pepsin positivity, only 23 samples had no pepsin present and 32 samples had low pepsin present. Six patients had all three saliva samples >75 ng/ml pepsin, four patients had two saliva samples >75 ng/ml pepsin and 15 patients had one saliva sample >75 ng/ml pepsin. Seven patients had saliva samples pepsin positive but below 75 (0 to 74) ng/ml. No patients had all three saliva samples negative for pepsin. The pepsin concentration in the saliva samples provided following symptoms were significantly different (P<0.05) to the samples provided on waking. The mean pepsin concentrations were 69 (morning sample), 131 (post-prandial sample) and 150 ng/ml (sample provided following symptoms) (Figure 2). Discussion The aim of this study was to determine if patients presenting with chronic pharyngitis have a significant concentration of pepsin in their saliva samples which could be a factor causing exacerbation of their condition. Pepsin has been shown to cause tissue damage resulting in inflammation and erosion leading to pain. In the present study, a correlation has been shown between the presence of pepsin in saliva samples and patients with chronic pharyngitis. Seventyeight percent pepsin positivity was found signifying chronic pharyngitis patients are likely to be affected by pepsin indicating reflux disease. Pepsin concentrations on waking and after symptoms were significantly different (P<0.05), indicating that the patients recognize when they have refluxed and can therefore provide a sample following symptoms. This allows a more comfortable method of diagnosis than previous diagnostic methods such as phmetry or endoscopy, which are both invasive and time consuming. Through the use of Peptest TM (RD Biomed Limited) patients can be screened for the presence of pepsin
6 Page 6 of 8 Annals of Esophagus, 2018 Table 6 Pepsin concentrations of chronic pharyngitis patients (n=32) Sample collection procedure Low pepsin concentration (ng/ml) Medium to high pepsin concentration (ng/ml) 0<16 16<75 75< < < Mean pepsin concentration n=32 SD P value Morning sample PP sample SX sample P values were calculated using unpaired t test. PP, post-prandial; SX, symptoms. Pepsin ng/ml Morning sample Chronic pharyngitis study PP sample * ** SX sample Sample collection +1 SD Figure 2 Analysed pepsin concentrations of chronic pharyngitis patients. Saliva samples were collected in the morning, PP and following SX. One SD shown. Calculated using GraphPad Prism 7. P values were calculated using unpaired t test. PP, post-prandial; SX, symptoms; SD, standard deviation. *P= **P= non-invasively. Peptest TM (RD Biomed Limited) is highly sensitive and specific (12-16) for detecting pepsin and diagnosing reflux in patients. The significance of reflux questionnaires in chronic pharyngitis patients showed significantly higher results in RSI and RFS for patients with chronic non-specific pharyngitis than in the control subjects P<0.01 (17). In the present study, when RFS and RSI were used in conjunction, there was a significant difference between the mean maximum pepsin concentration and a positive or negative result for diagnosis of reflux disease. However, if the RFS and RSI used in conjunction was the sole method of reflux diagnosis in this patient group 22% would have been diagnosed with reflux disease (Table 3). Peptest TM (RD Biomed Limited) was a better diagnostic marker because 78% of chronic pharyngitis patients were found to have a significant positive pepsin concentration in postprandial samples (>75 ng/ml) indicating reflux disease. Therefore, reflux questionnaires did not give a good indication of reflux disease as many patients were diagnosed with a false negative result. Patient demographics were shown to not have a significant impact on the results of pepsin concentrations over 75 ng/ml as shown using Chi squared test (Table 5). However, smoking did increase the number of reflux events in a previously reported study (18). Obesity, (potentially linked to weight of patients in this study) is a risk factor for GERD (19). Spicy food has also been shown to induce GERD symptoms (20). These factors may affect the likelihood of reflux disease and lifestyle factors may be adjusted accordingly. Therefore, Peptest TM (RD Biomed Limited) would be a suitable test for identifying reflux in high-risk groups of individuals and, chronic pharyngitis patients in this risk group should therefore be tested for reflux as they are at even greater risk. Limitations of this study are the relatively small sample size (n=32), small sample size of patient demographic information (n=18) and the relatively small sample size of the control group (n=31). By identifying the cause and associations with chronic pharyngitis, patients can be treated appropriately. By determining if pepsin is associated with chronic pharyngitis it reduces the over prescription of antibiotics, other treatments and invasive diagnostics. Conclusions Peptest TM (RD Biomed Limited) is a useful diagnostic tool for determining the presence of pepsin in chronic pharyngitis patients. A significant proportion (78%) of chronic pharyngitis patients had over 75 ng/ml of pepsin present in their saliva samples.
7 Annals of Esophagus, 2018 Page 7 of 8 The results showed chronic pharyngitis to be strongly associated with reflux, and patients should be identified and treated for reflux. Peptest TM (RD Biomed Limited) may play an important role in the identification of reflux in chronic pharyngitis patients. A single high positive pepsin sample out of the three samples outlined in this study, could indicate a reflux episode and could infer reflux disease. A single high pepsin concentration will have the potential to damage the throat and if repeated over periods of time, could lead to chronic pharyngitis. Peptest TM (RD Biomed Limited) was easy to use and will provide a non-invasive, rapid method for detecting pepsin in saliva samples in a selected group of patients. Future studies will need to investigate a larger sample size of patients and repeated saliva collection to assist in determining the correlation of reflux disease and chronic pharyngitis. Acknowledgements None. Footnote Conflict of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Ethical Statement: All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards (Ethical Approval ID: 2017NZKY ). Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. References 1. Issing WJ, Karkos PD. Atypical Manifestations of gastrooesophageal Reflux. J R Soc Med 2003;96: Ebell MH, Smith MA, Barry HC, et al. Does This Patient Have Strep Throat? JAMA 2000;284: Chen L, Lai Y, Dong L, et al. Polysaccharides from Citrus grandis L. Osbeck suppress inflammation and relieve chronic pharyngitis. Microb Pathog 2017;113: Kim JH, Jeong H, Kim KM, et al. Extra-Esophageal Pepsin from Stomach Refluxate Promotes Tonsil Hypertrophy. PLoS One 2016;11:e Murray RC, Chennupati SK. Chronic streptococcal and non-streptococcal pharyngitis. Infect Disord Drug Targets 2012;12: Du X, Wang F, Hu Z, et al. The diagnostic value of pepsin detection in saliva for gastro-esophageal reflux disease: a preliminary study from China. BMC Gastroenterol 2017;17: Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA. The validity and reliability of the reflux finding score (RFS). Laryngoscope 2001;111: Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA. Validity and reliability of the reflux symptom index (RSI). J Voice 2002;16: Shaw MJ, Talley NJ, Beebe TJ, et al. Initial validation of a diagnostic questionnaire for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96: Harnik IG. In the Clinic. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Ann Intern Med 2015;163:ITC Shaw M, Dent J, Beebe T, et al. The Reflux Disease Questionnaire: a measure for assessment of treatment response in clinical trials. Health Qual Life Outcomes 2008;6: Saritas Yuksel E, Hong SK, Strugala V, et al. Rapid salivary pepsin test: blinded assessment of test performance in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Laryngoscope 2012;122: Hayat JO, Yazaki E, Kang J, et al. Pepsin in Saliva and Gastroesophageal Reflux Monitoring in 100 Healthy Asymptomatic Subjects. Gastroenterology 2013;144:S de Bortoli N, Savarino E, Furnari M, et al. Use of a Non-Invasive Pepsin Diagnostic Test to Detect GERD: Correlation With MII-pH Evaluation in a Series of Suspected NERD Patients. A Pilot Study. Gastroenterology 2013;144:S Hayat JO, Yazaki E, Moore AT, et al. Objective detection of esophagopharyngeal reflux in patients with hoarseness and endoscopic signs of laryngeal inflammation. J Clin Gastroenterol 2014;48: Hayat JO, Gabieta-Somnez S, Yazaki E, et al. Pepsin in saliva for the diagnosis of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Gut 2015;64: Yazici ZM, Sayin I, Kayhan FT, et al. Laryngopharyngeal reflux might play a role on chronic nonspecific pharyngitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2010;267: Kahrilas PJ, Gupta RR. Mechanisms of acid reflux associated with cigarette smoking. Gut 1990;31: Khan A, Kim A, Sanossian C, et al. Impact of obesity
8 Page 8 of 8 Annals of Esophagus, 2018 treatment on gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J Gastroenterol 2016;22: Choe JW, Joo MK, Kim HJ, et al. Foods Inducing Typical Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Symptoms in Korea. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 2017;23: doi: /aoe Cite this article as: Dettmar PW, Wang Q, Hodgson RM, Wang X, Li Y, Jiang M, Xu L, Lan Y, Woodcock AD. Chronic pharyngitis and the association with pepsin detection and reflux disease..
pat hways Medtech innovation briefing Published: 22 May 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib31
 pat hways Peptest for diagnosing gastro-oesophageal reflux Medtech innovation briefing Published: 22 May 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib31 Summary The Peptest is designed to help diagnose gastro-oesophageal
pat hways Peptest for diagnosing gastro-oesophageal reflux Medtech innovation briefing Published: 22 May 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib31 Summary The Peptest is designed to help diagnose gastro-oesophageal
The effect of dietary intake, physical activity and posture on pepsin concentrations detected in the saliva of free-living, healthy individuals
 The effect of dietary intake, physical activity and posture on pepsin concentrations detected in the saliva of free-living, healthy individuals Authors Richard Khaw 1, Naomi Slater 2, Ellie Smith 2, Chi
The effect of dietary intake, physical activity and posture on pepsin concentrations detected in the saliva of free-living, healthy individuals Authors Richard Khaw 1, Naomi Slater 2, Ellie Smith 2, Chi
Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease. Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)*
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 3, September 2011 Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)* Objective: To evaluate the efficacy
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 3, September 2011 Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)* Objective: To evaluate the efficacy
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion
 Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Idiopathic Laryngitis ABSTRACT
 THAI J 28 GASTROENTEROL Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Original Idiopathic Laryngitis Article A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic
THAI J 28 GASTROENTEROL Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Original Idiopathic Laryngitis Article A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic
GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications
 GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications Esophageal Syndromes Extra - esophageal Syndromes Symptomatic Syndromes Typical reflux
GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications Esophageal Syndromes Extra - esophageal Syndromes Symptomatic Syndromes Typical reflux
Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of the Literature
 International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 291472, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/291472 Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of
International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 291472, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/291472 Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of
The Throat. Image source:
 The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
The effect of anti-reflux treatment on subjective voice measurements of patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux
 The Journal of Laryngology & Otology (2013), 127, 590 594. JLO (1984) Limited, 2013 doi:10.1017/s0022215113000832 MAIN ARTICLE The effect of anti-reflux treatment on subjective voice measurements of patients
The Journal of Laryngology & Otology (2013), 127, 590 594. JLO (1984) Limited, 2013 doi:10.1017/s0022215113000832 MAIN ARTICLE The effect of anti-reflux treatment on subjective voice measurements of patients
GERD. Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the. stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the
 GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT DISCLOSURES 4/18/2018
 GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. or dysphagia may alert a physician to the possibility of LPR. 1,2 Laryngeal findings
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Clinical Value of Pharyngeal ph Monitoring Using a Double-Probe, Triple-Sensor Catheter in Patients With Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Togay Muderris, MD; M. Kursat Gokcan, MD; Irfan Yorulmaz,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Clinical Value of Pharyngeal ph Monitoring Using a Double-Probe, Triple-Sensor Catheter in Patients With Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Togay Muderris, MD; M. Kursat Gokcan, MD; Irfan Yorulmaz,
The Impact of Gender on the Symptom Presentation and Life Quality of Patients with Erosive Esophagitis and Non-Erosive Reflux Disease
 ARC Journal of Hepatology and Gastroenterology Volume 1, Issue 1, 2016, PP 3-8 www.arcjournals.org The Impact of Gender on the Symptom Presentation and Life Quality of Patients with Erosive Esophagitis
ARC Journal of Hepatology and Gastroenterology Volume 1, Issue 1, 2016, PP 3-8 www.arcjournals.org The Impact of Gender on the Symptom Presentation and Life Quality of Patients with Erosive Esophagitis
Patient information. Laryngopharyngeal Reflux ( LPR) Ear Nose and Throat Directorate PIF 1423/V4
 Patient information Laryngopharyngeal Reflux ( LPR) Ear Nose and Throat Directorate PIF 1423/V4 You have been diagnosed with laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR), otherwise known as extra-oesophageal reflux
Patient information Laryngopharyngeal Reflux ( LPR) Ear Nose and Throat Directorate PIF 1423/V4 You have been diagnosed with laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR), otherwise known as extra-oesophageal reflux
A Clinical Assessment of Throat Manifestations of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease with Special Reference to Video Endoscopic Findings
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. VII (June. 2017), PP 57-62 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Assessment of Throat Manifestations
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. VII (June. 2017), PP 57-62 www.iosrjournals.org A Clinical Assessment of Throat Manifestations
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
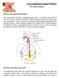 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do?
 Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do? Philip O. Katz, MD, FACG Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia,
Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do? Philip O. Katz, MD, FACG Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc 2 and Marcelo F. Vela MD, MSCR 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Einstein
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc 2 and Marcelo F. Vela MD, MSCR 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Einstein
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)?
 WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
Role of Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score in Evaluation of Treatment Outcome in Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
 Original Article Role of RSI and RFS in Evaluation of Treatment 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1141 Outcome in Patients with LPR Role of Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score in Evaluation of Treatment
Original Article Role of RSI and RFS in Evaluation of Treatment 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1141 Outcome in Patients with LPR Role of Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score in Evaluation of Treatment
Silent Reflux. Adult Speech & Language Therapy Macclesfield District General Hospital
 Silent Reflux Adult Speech & Language Therapy 01625 661067 Macclesfield District General Hospital @EastCheshireNHS Leaflet Ref: 11067 Published: Jan 2019 Review: 31/12/2021 Page 1 Introduction Reflux is
Silent Reflux Adult Speech & Language Therapy 01625 661067 Macclesfield District General Hospital @EastCheshireNHS Leaflet Ref: 11067 Published: Jan 2019 Review: 31/12/2021 Page 1 Introduction Reflux is
Evaluation of Risk Factors for Laryngopharyngeal Reflux among Sikkimese Population Kesari SP, Chakraborty S, Sharma B
 Original Article VOL. 15 NO. 1 ISSUE 57 JAN.-MARCH 2017 Evaluation of Risk Factors for Laryngopharyngeal Reflux among Sikkimese Population Kesari SP, Chakraborty S, Sharma B ABSTRACT Background Department
Original Article VOL. 15 NO. 1 ISSUE 57 JAN.-MARCH 2017 Evaluation of Risk Factors for Laryngopharyngeal Reflux among Sikkimese Population Kesari SP, Chakraborty S, Sharma B ABSTRACT Background Department
Barrett s Oesophagus Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Barrett s Oesophagus Barrett s Oesophagus is the term used for a pre-cancerous condition where the normal
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Barrett s Oesophagus Barrett s Oesophagus is the term used for a pre-cancerous condition where the normal
Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons:
 Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons: http://dspace.flinders.edu.au/dspace/ This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: Fox M, Omari T, Rommel N. Supraesophageal Reflux Disease: Solving
Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons: http://dspace.flinders.edu.au/dspace/ This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: Fox M, Omari T, Rommel N. Supraesophageal Reflux Disease: Solving
Silent reflux (also known as LPR or EOR)
 ENT - Information for patients Silent reflux (also known as LPR or EOR) Introduction This leaflet explains what your condition is, why it happens, what the symptoms are and how it can be managed. If there
ENT - Information for patients Silent reflux (also known as LPR or EOR) Introduction This leaflet explains what your condition is, why it happens, what the symptoms are and how it can be managed. If there
DOI: / ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;79(5):589-93. DOI: 10.5935/1808-8694.20130105 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of signs and symptoms of laryngopharyngeal reflux in snorers with suspected obstructive sleep apnea
Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;79(5):589-93. DOI: 10.5935/1808-8694.20130105 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of signs and symptoms of laryngopharyngeal reflux in snorers with suspected obstructive sleep apnea
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice
 Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
GERD. gastroesophageal reflux disease : GERD. Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease : LPRD GERD GERD GERD LPRD GERD. gastroesophageal reflux ; GER GERD
 114114 2011 : GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease : GERD Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease : LPRD GERD GERD GERD GERD LPRD QOL GERD LPRD QOL LPRD : gastroesophageal reflux ; GER gastroesophageal reflux
114114 2011 : GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease : GERD Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease : LPRD GERD GERD GERD GERD LPRD QOL GERD LPRD QOL LPRD : gastroesophageal reflux ; GER gastroesophageal reflux
ACID REFLUX & GERD: The Unsettling Reality in Canada
 ACID REFLUX & GERD: The Unsettling Reality in Canada gerd fact 1 see page 8 Canadian Society of Intestinal Research On average, ARD patients wait over two years before seeking care 1. 1 gerd fact 2 see
ACID REFLUX & GERD: The Unsettling Reality in Canada gerd fact 1 see page 8 Canadian Society of Intestinal Research On average, ARD patients wait over two years before seeking care 1. 1 gerd fact 2 see
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: esophageal_ph_monitoring 4/2011 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Acid reflux is the
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: esophageal_ph_monitoring 4/2011 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Acid reflux is the
Gastroesophageal and extraesophageal symptoms in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: An endoscopy-based study in Albania
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Gastroesophageal and extraesophageal symptoms in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: An endoscopy-based study in Albania Indrit Kellici 1,2, Bledar Kraja 1,3,4, Rozana Aleksi
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Gastroesophageal and extraesophageal symptoms in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: An endoscopy-based study in Albania Indrit Kellici 1,2, Bledar Kraja 1,3,4, Rozana Aleksi
Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease. (GERD) is often accompanied
 ...PRESENTATIONS... Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease Based on a presentation by Peter J. Kahrilas, MD Presentation Summary Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) accompanied by regurgitation
...PRESENTATIONS... Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease Based on a presentation by Peter J. Kahrilas, MD Presentation Summary Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) accompanied by regurgitation
LARYNGO-PHARYNGEAL REFLUX A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL
 LARYNGO-PHARYNGEAL REFLUX A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL A randomized, open label, three arm parallel design, single-site study, comparing the effects of esomeprazole and alginate on top of lifestyle guidance
LARYNGO-PHARYNGEAL REFLUX A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL A randomized, open label, three arm parallel design, single-site study, comparing the effects of esomeprazole and alginate on top of lifestyle guidance
ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:612 619 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT Regurgitation Is Less Responsive to Acid Suppression Than Heartburn in Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:612 619 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT Regurgitation Is Less Responsive to Acid Suppression Than Heartburn in Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux
Patient-reported Outcomes
 3 Patient-reported Outcomes Ingela Wiklund Key points Many gastrointestinal diseases are symptomdriven, so the patient s perspective is particularly important in this area. Patient-reported outcomes (PROs)
3 Patient-reported Outcomes Ingela Wiklund Key points Many gastrointestinal diseases are symptomdriven, so the patient s perspective is particularly important in this area. Patient-reported outcomes (PROs)
Hiatus Hernia. Endoscopy Department. Patient information leaflet
 Hiatus Hernia Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with a hiatus hernia. The information below outlines normal anatomy, conditions,
Hiatus Hernia Endoscopy Department Patient information leaflet You will only be given this leaflet if you have been diagnosed with a hiatus hernia. The information below outlines normal anatomy, conditions,
Relationship between Psychological Factors and Quality of Life in Subtypes of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 3, No. 4, December 2009, pp. 259-265 original article Relationship between Psychological Factors and Quality of Life in Subtypes of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Jung-Hwan Oh*, Tae-Suk
Gut and Liver, Vol. 3, No. 4, December 2009, pp. 259-265 original article Relationship between Psychological Factors and Quality of Life in Subtypes of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Jung-Hwan Oh*, Tae-Suk
ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.6.EN2 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease. Santhana Krishna Kumar. B 1, Sivasankari. L 1 1 Assistant
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.6.EN2 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease. Santhana Krishna Kumar. B 1, Sivasankari. L 1 1 Assistant
Gastroesophageal reflux disease. The case for improving patient education in primary care
 Original Research Gastroesophageal reflux disease: The case for improving patient education in primary care This study reveals that something as simple as knowing when to take GERD medication is compromised
Original Research Gastroesophageal reflux disease: The case for improving patient education in primary care This study reveals that something as simple as knowing when to take GERD medication is compromised
The Risk Factors and Quality of Life in Patients with Overlapping Functional Dyspepsia or Peptic Ulcer Disease with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 8, No. 2, March 2014, pp. 160-164 ORiginal Article The Risk Factors and Quality of Life in Patients with Overlapping Functional Dyspepsia or Peptic Ulcer Disease with Gastroesophageal
Gut and Liver, Vol. 8, No. 2, March 2014, pp. 160-164 ORiginal Article The Risk Factors and Quality of Life in Patients with Overlapping Functional Dyspepsia or Peptic Ulcer Disease with Gastroesophageal
Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation. Introduction. Predisposing factor. Introduction.
 Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) JUSTIN CHE-YUEN WU, et. al. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Gastroenterology,
Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) JUSTIN CHE-YUEN WU, et. al. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Gastroenterology,
GERD: A linical Clinical Clinical Update Objectives
 GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
Dysphagia Questionnaire. Referring Doctor:
 Dysphagia Questionnaire Name: Date of Birth: Address: Referring Doctor: Diagnosis: Phone number: Email: What are your complaints regarding your swallowing: Date and onset of swallowing problems: Please
Dysphagia Questionnaire Name: Date of Birth: Address: Referring Doctor: Diagnosis: Phone number: Email: What are your complaints regarding your swallowing: Date and onset of swallowing problems: Please
Gastroesophageal and Extraesophageal Reflux Symptoms: Similarities and Differences
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Gastroesophageal and Extraesophageal Reflux Symptoms: Similarities and Differences Michael Drinnan, PhD;
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Gastroesophageal and Extraesophageal Reflux Symptoms: Similarities and Differences Michael Drinnan, PhD;
Management of laryngopharyngeal refl ux with proton pump inhibitors
 REVIEW Management of laryngopharyngeal refl ux with proton pump inhibitors Christina Reimer Peter Bytzer Department of Medical Gastroenterology, Køge University Hospital, Denmark Abstract: There is a lack
REVIEW Management of laryngopharyngeal refl ux with proton pump inhibitors Christina Reimer Peter Bytzer Department of Medical Gastroenterology, Køge University Hospital, Denmark Abstract: There is a lack
TBURN TBURN BURN ARTBURN EARTBURN EART HEARTBURN: HOW TO GET IT OFF YOUR CHEST
 TBURN BURN TBURN ARTBURN. EARTBURN EART N EARTBURN HEARTBURN: HOW TO GET IT OFF YOUR CHEST Do you sometimes wake up at night with a sharp, burning sensation in your chest? Does this sometimes happen during
TBURN BURN TBURN ARTBURN. EARTBURN EART N EARTBURN HEARTBURN: HOW TO GET IT OFF YOUR CHEST Do you sometimes wake up at night with a sharp, burning sensation in your chest? Does this sometimes happen during
GERD: How to. Failures
 GERD: How to Manage Treatment Failures John Fang MD University of Utah Introduction GERD: condition of reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/complications Refractory GERD: poor response
GERD: How to Manage Treatment Failures John Fang MD University of Utah Introduction GERD: condition of reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/complications Refractory GERD: poor response
The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
The prevalence of upper respiratory symptoms in a cohort of adults presenting with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
 The prevalence of upper respiratory symptoms in a cohort of adults presenting with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease D L Amarasiri 1, A Pathmeswaran 2, A S Dassanayake 3, A P de Silva 4, M
The prevalence of upper respiratory symptoms in a cohort of adults presenting with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease D L Amarasiri 1, A Pathmeswaran 2, A S Dassanayake 3, A P de Silva 4, M
Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease in the Greek general population, prevalence and risk factors
 Spantideas et al. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders (2015) 15:7 DOI 10.1186/s12901-015-0020-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease in the Greek general population, prevalence and risk factors
Spantideas et al. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders (2015) 15:7 DOI 10.1186/s12901-015-0020-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease in the Greek general population, prevalence and risk factors
Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Refractoriness to Optimal Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy in Non-erosive Reflux Disease
 www.medscape.com Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Refractoriness to Optimal Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy in Non-erosive Reflux Disease Mentore Ribolsi; Michele Cicala; Patrizia Zentilin; Matteo
www.medscape.com Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Refractoriness to Optimal Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy in Non-erosive Reflux Disease Mentore Ribolsi; Michele Cicala; Patrizia Zentilin; Matteo
Unmet Needs in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Unmet Needs in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ronnie Fass MD Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Esophageal
Unmet Needs in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ronnie Fass MD Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Esophageal
Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors in the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
 IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul Aug 2018), PP 54-61 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn:2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul Aug 2018), PP 54-61 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitors
Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness in Children and Adults
 Page 1 of 9 Main Algorithm Annotations 1. Patient Reports Some Combination of Symptoms Patients may present for an appointment, call into a provider to schedule an appointment or nurse line presenting
Page 1 of 9 Main Algorithm Annotations 1. Patient Reports Some Combination of Symptoms Patients may present for an appointment, call into a provider to schedule an appointment or nurse line presenting
1. Introduction. Correspondence should be addressed to Wei-Chen Tai; Received 29 May 2013; Accepted 5 July 2013
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 480325, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/480325 Clinical Study The Frequencies of Gastroesophageal and Extragastroesophageal Symptoms
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2013, Article ID 480325, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/480325 Clinical Study The Frequencies of Gastroesophageal and Extragastroesophageal Symptoms
127 Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3
 CHAPTER 8 Summary Summary 127 In Chapter 1, a general introduction on the principles and applications of intraluminal impedance monitoring in esophageal disorders is provided. Intra-esophageal impedance
CHAPTER 8 Summary Summary 127 In Chapter 1, a general introduction on the principles and applications of intraluminal impedance monitoring in esophageal disorders is provided. Intra-esophageal impedance
Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia
 Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Objectives Understand the means of diagnosing functional heartburn
Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Objectives Understand the means of diagnosing functional heartburn
Outline. Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology Management With an emphasis on recent developments
 Chronic Dyspepsia Eamonn M M Quigley MD FRCP FACP MACG FRCPI Lynda K and David M Underwood Center for Digestive Disorders Houston Methodist Hospital Houston, Texas Outline Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology
Chronic Dyspepsia Eamonn M M Quigley MD FRCP FACP MACG FRCPI Lynda K and David M Underwood Center for Digestive Disorders Houston Methodist Hospital Houston, Texas Outline Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology
James Paget University Hospitals. NHS Foundation Trust. Hiatus hernia. Patient Information
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Hiatus hernia Patient Information What is a hiatus hernia? A hiatus hernia can cause highly irritating stomach contents, such as acid, to move up into
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Hiatus hernia Patient Information What is a hiatus hernia? A hiatus hernia can cause highly irritating stomach contents, such as acid, to move up into
GUIDELINES FOR CLINICIANS. Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults. Reflux Disease. 4th Edition Digestive Health Foundation
 GUIDELINES FOR CLINICIANS Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults Reflux Disease 4th Edition 2008 Digestive Health Foundation Digestive Health Foundation Table of contents Page 4 Gastro-oesophageal
GUIDELINES FOR CLINICIANS Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults Reflux Disease 4th Edition 2008 Digestive Health Foundation Digestive Health Foundation Table of contents Page 4 Gastro-oesophageal
Lansoprazole Treatment of Patients With Chronic Idiopathic Laryngitis: A Placebo-Controlled Trial
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 4, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02244-4 Lansoprazole Treatment
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 4, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02244-4 Lansoprazole Treatment
Understanding GERD. & Stretta Therapy. GERD (gĕrd): Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Understanding GERD & Stretta Therapy GERD (gĕrd): Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease What is GERD? When the muscle between your stomach and esophagus is weak, stomach contents like acid or bile can reflux
Understanding GERD & Stretta Therapy GERD (gĕrd): Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease What is GERD? When the muscle between your stomach and esophagus is weak, stomach contents like acid or bile can reflux
What causes abnormal secretions?
 Post-Nasal Drip Glands in your nose and throat continually produce mucus (one to two quarts a day). Mucus moistens and cleans the nasal membranes, humidifies air, traps and clears inhaled foreign matter,
Post-Nasal Drip Glands in your nose and throat continually produce mucus (one to two quarts a day). Mucus moistens and cleans the nasal membranes, humidifies air, traps and clears inhaled foreign matter,
ORIGINAL STUDY MANAGEMENT OF PHARYNGOLARYNGEAL REFLUX AT VOICE PROFESSIONALS
 MEDICINĂ, no 2, 2011 ORIGINAL STUDY MANAGEMENT OF PHARYNGOLARYNGEAL REFLUX AT VOICE PROFESSIONALS Monica Voineag 1,2, Vasile Costinescu 3, Mihail Dan Cobzeanu 3 1 University of Medicine and Pharmacy Gr
MEDICINĂ, no 2, 2011 ORIGINAL STUDY MANAGEMENT OF PHARYNGOLARYNGEAL REFLUX AT VOICE PROFESSIONALS Monica Voineag 1,2, Vasile Costinescu 3, Mihail Dan Cobzeanu 3 1 University of Medicine and Pharmacy Gr
Alginates Extended Abstract
 Alginates Extended Abstract III) Clinical practice guidelines: DeVault KR, Castell DO; American College of Gastroenterology. Updated guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux
Alginates Extended Abstract III) Clinical practice guidelines: DeVault KR, Castell DO; American College of Gastroenterology. Updated guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux
Oesophageal manometry and 24 hour PH tests
 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Oesophageal manometry and 24 hour PH tests This leaflet has been produced to reiterate the information given by the consultant. It is designed to answer some of the questions you
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Oesophageal manometry and 24 hour PH tests This leaflet has been produced to reiterate the information given by the consultant. It is designed to answer some of the questions you
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Association between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and gastroesophageal reflux disease: a meta-analysis
 Association between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and gastroesophageal reflux disease: a meta-analysis David Bédard Méthot, MD, Internal Medicine Resident Evelyne Leblanc, MD, Internal Medicine Resident
Association between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and gastroesophageal reflux disease: a meta-analysis David Bédard Méthot, MD, Internal Medicine Resident Evelyne Leblanc, MD, Internal Medicine Resident
Review article: identifying the causes of reflux events and symptoms new approaches
 Review article: identifying the causes of reflux events and symptoms new approaches M. Fox Nottingham Digestive Diseases Centre and Biomedical Research Unit, Queen s Medical Centre, University Hospital,
Review article: identifying the causes of reflux events and symptoms new approaches M. Fox Nottingham Digestive Diseases Centre and Biomedical Research Unit, Queen s Medical Centre, University Hospital,
Accepted Article. Questionnaires for the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease: are they really useful? Constanza Ciriza de los Ríos
 Accepted Article Questionnaires for the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease: are they really useful? Constanza Ciriza de los Ríos DOI: 10.17235/reed.2016.4267/2016 Link: PDF Please cite this article
Accepted Article Questionnaires for the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease: are they really useful? Constanza Ciriza de los Ríos DOI: 10.17235/reed.2016.4267/2016 Link: PDF Please cite this article
JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
 ㅋ JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 17 No. 1 January, 2011 DOI: 10.5056/jnm.2011.17.1.54 Original Article Relationship Between Gastroesophageal Reflux Symptoms
ㅋ JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 17 No. 1 January, 2011 DOI: 10.5056/jnm.2011.17.1.54 Original Article Relationship Between Gastroesophageal Reflux Symptoms
Extraesophageal GERD: Fact or Fiction?
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/gi-insights/extraesophageal-gerd-fact-or-fiction/4157/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/gi-insights/extraesophageal-gerd-fact-or-fiction/4157/
PREPARING FOR REFLUX TESTING. Digitrapper Reflux Testing System
 PREPARING FOR REFLUX TESTING Digitrapper Reflux Testing System An innovative solution to evaluate your gastroesophageal reflux symptoms on or off anti-reflux therapy WHY TEST FOR GERD? Do you have frequent
PREPARING FOR REFLUX TESTING Digitrapper Reflux Testing System An innovative solution to evaluate your gastroesophageal reflux symptoms on or off anti-reflux therapy WHY TEST FOR GERD? Do you have frequent
Validation of a Four-Graded Scale for Severity of Heartburn in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Volume 11 Number 4 2008 VALUE IN HEALTH Validation of a Four-Graded Scale for Severity of Heartburn in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ola Junghard, PhD, 1 Ingela Wiklund, PhD
Volume 11 Number 4 2008 VALUE IN HEALTH Validation of a Four-Graded Scale for Severity of Heartburn in Patients with Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ola Junghard, PhD, 1 Ingela Wiklund, PhD
What is an Upper GI Endoscopy?
 What is an Upper GI Endoscopy? An upper GI endoscopy is a test your doctor does to see inside part of your digestive system. Your doctor will look at the inside of your esophagus (the tube that links your
What is an Upper GI Endoscopy? An upper GI endoscopy is a test your doctor does to see inside part of your digestive system. Your doctor will look at the inside of your esophagus (the tube that links your
Original Article. K Semmanaselvan 1, Qayum I Mukaddam 2, Manoj Naik 3. Abstract
 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 63 July 2015 27 Original Article An Open Label, Prospective, Single Centre Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Fixed Dose Combination of
Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 63 July 2015 27 Original Article An Open Label, Prospective, Single Centre Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Fixed Dose Combination of
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/acid-reflux-gastroesophageal-reflux-disease-in-adults-...
 Page 1 of 10 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Page 1 of 10 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Heartburn Overview. Causes & Risk Factors
 Return to Web version Heartburn Overview What is heartburn? Despite its name, heartburn doesn't affect the heart. Heartburn is a burning feeling in the lower chest, along with a sour or bitter taste in
Return to Web version Heartburn Overview What is heartburn? Despite its name, heartburn doesn't affect the heart. Heartburn is a burning feeling in the lower chest, along with a sour or bitter taste in
Definition: gas tro e soph a ge al re f lux dis ease (GERD) from Stedman's Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing
 Topic Page: Gastroesophageal reflux Definition: gas tro e soph a ge al re f lux dis ease (GERD) from Stedman's Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing (gas trō-ĕ-sof ă-jē ăl rē flŭks
Topic Page: Gastroesophageal reflux Definition: gas tro e soph a ge al re f lux dis ease (GERD) from Stedman's Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing (gas trō-ĕ-sof ă-jē ăl rē flŭks
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57:
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 258-265 Original Evaluation of the likelihood of reflux developing in patients with recurrent upper respiratory infections, recurrent sinusitis or recurrent
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 258-265 Original Evaluation of the likelihood of reflux developing in patients with recurrent upper respiratory infections, recurrent sinusitis or recurrent
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Paraesophageal Hernias &
 530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
4/24/2015. History of Reflux Surgery. Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux
 Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux Scott Carpenter, DO, FACOS, FACS Mercy Hospital Ardmore Ardmore, OK History of Reflux Surgery - 18 th century- first use of term heartburn - 1934-
Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux Scott Carpenter, DO, FACOS, FACS Mercy Hospital Ardmore Ardmore, OK History of Reflux Surgery - 18 th century- first use of term heartburn - 1934-
The challenge of making an accurate diagnosis. The online Cough Clinic: developing guideline-based diagnosis and advice
 Eur Respir J 2009; 34: 819 824 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00126908 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2009 The online Cough Clinic: developing guideline-based diagnosis and advice P.W. Dettmar*, V. Strugala*, H. Fathi
Eur Respir J 2009; 34: 819 824 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00126908 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2009 The online Cough Clinic: developing guideline-based diagnosis and advice P.W. Dettmar*, V. Strugala*, H. Fathi
LINX. A new, FDA approved treatment for GERD
 LINX A new, FDA approved treatment for GERD What Causes Reflux? Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), also called reflux, is a chronic, often progressive disease caused by a weak lower esophageal sphincter
LINX A new, FDA approved treatment for GERD What Causes Reflux? Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), also called reflux, is a chronic, often progressive disease caused by a weak lower esophageal sphincter
What Is Barrett s Esophagus?
 What Is Barrett s Esophagus? Having Barrett s esophagus means the cells lining the esophagus (the tube that links the mouth and the stomach) have changed into types of intestinal cells that are not normal
What Is Barrett s Esophagus? Having Barrett s esophagus means the cells lining the esophagus (the tube that links the mouth and the stomach) have changed into types of intestinal cells that are not normal
instrument. When 13C-UBT positive value is greater than or equal to / - 0.4, the the subject can be 1. Data and methods details are as follows:
 Application of 13 C-urea breath test in screening helicobacter pylori infection during health examination in Chengdu, Sichuan YANG Yan-hua. LIU Yu-ping. CHENG You-fu, SHUAI Ping. LU Qiao. ZHENG Xiao-xia,
Application of 13 C-urea breath test in screening helicobacter pylori infection during health examination in Chengdu, Sichuan YANG Yan-hua. LIU Yu-ping. CHENG You-fu, SHUAI Ping. LU Qiao. ZHENG Xiao-xia,
The Degree of Disease Knowledge in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Multi-center Prospective Study in Korea
 JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 23 No. 3 July, 2017 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm16123 Original Article The Degree of Disease Knowledge in Patients with Gastroesophageal
JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 23 No. 3 July, 2017 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm16123 Original Article The Degree of Disease Knowledge in Patients with Gastroesophageal
ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT INDIGESTION FUNDING RESEARCH INTO DISEASES OF THE GUT, LIVER & PANCREAS
 ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT INDIGESTION FUNDING RESEARCH INTO DISEASES OF THE GUT, LIVER & PANCREAS THIS FACTSHEET IS ABOUT INDIGESTION Indigestion (also known as dyspepsia) is a term used to describe unpleasant
ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT INDIGESTION FUNDING RESEARCH INTO DISEASES OF THE GUT, LIVER & PANCREAS THIS FACTSHEET IS ABOUT INDIGESTION Indigestion (also known as dyspepsia) is a term used to describe unpleasant
Accepted Manuscript. CGH Editorial: Sound the Alarm for Barrett s Screening! Tarek Sawas, M.D., M.P.H., David A. Katzka, M.D
 Accepted Manuscript CGH Editorial: Sound the Alarm for Barrett s Screening! Tarek Sawas, M.D., M.P.H., David A. Katzka, M.D PII: S1542-3565(18)31093-0 DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.10.010 Reference: YJCGH 56132
Accepted Manuscript CGH Editorial: Sound the Alarm for Barrett s Screening! Tarek Sawas, M.D., M.P.H., David A. Katzka, M.D PII: S1542-3565(18)31093-0 DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.10.010 Reference: YJCGH 56132
Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 2.01.17 Esophageal ph Monitoring Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Subsection Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
MP 2.01.17 Esophageal ph Monitoring Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Subsection Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
Epidemiology Classic Symptoms of GERD
 Definitions LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX AND ITS ROLE IN PEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGY Wendy Mackey, APRN, CORLN SOHN Congress Meeting Washington, DC September 2012 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Retrograde movement
Definitions LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX AND ITS ROLE IN PEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGY Wendy Mackey, APRN, CORLN SOHN Congress Meeting Washington, DC September 2012 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Retrograde movement
Nexium 24HR Pharmacy Training
 Nexium 24HR Pharmacy Training Your pharmacist's advice is required. Always read the label. Use only as directed. If symptoms persist, consult your doctor/ healthcare professional. Pfizer Consumer Healthcare
Nexium 24HR Pharmacy Training Your pharmacist's advice is required. Always read the label. Use only as directed. If symptoms persist, consult your doctor/ healthcare professional. Pfizer Consumer Healthcare
INTERNAL MEDICINE - PEDIATRICS
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2013 vol. 117, no. 3 INTERNAL MEDICINE - PEDIATRICS ORIGINAL PAPERS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX AND METABOLIC SYNDROME Mihaela-Aura Mocanu 1, M. Diculescu 2, Monica Dumitrescu
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2013 vol. 117, no. 3 INTERNAL MEDICINE - PEDIATRICS ORIGINAL PAPERS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX AND METABOLIC SYNDROME Mihaela-Aura Mocanu 1, M. Diculescu 2, Monica Dumitrescu
Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease; how to evaluate
 Open Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 20; (): 5- Published online December 20, 20 (http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/osjcm) Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease; how to evaluate IRFAN IQBAL, *,
Open Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 20; (): 5- Published online December 20, 20 (http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/osjcm) Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease; how to evaluate IRFAN IQBAL, *,
and Gastro-oesophageal Reflux What symptoms might I expect?
 In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Heartburn and Gastro-oesophageal Reflux www.corecharity.org.uk Why does reflux happen? Does reflux always cause symptoms?
In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Heartburn and Gastro-oesophageal Reflux www.corecharity.org.uk Why does reflux happen? Does reflux always cause symptoms?
Gastroesophageal Reflux Evaluation in Patients Affected by Chronic Cough: Restech Versus Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance/pH Metry
 The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Gastroesophageal Reflux Evaluation in Patients Affected by Chronic Cough: Restech Versus Multichannel Intraluminal
The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Gastroesophageal Reflux Evaluation in Patients Affected by Chronic Cough: Restech Versus Multichannel Intraluminal
