Arterial supply of the olfactory trigone and the anterior perforated substance in macrosmatic and microsmatic animals
|
|
|
- Britton Cross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 O R I G I N A L ARTICLE Folia Morphol. Vol. 61, No. 4, pp Copyright 2002 Via Medica ISSN Arterial supply of the olfactory trigone and the anterior perforated substance in macrosmatic and microsmatic animals Ewa Nachman, Mirosław Topol Independent Laboratory of Angiology, Department of Normal Anatomy, Medical University, Łódź, Poland [Received 26 September 2002; Revised 15 October 2002; Accepted 15 October 2002] An investigation was conducted into the differences between macrosmatic and microsmatic animals of arterial supply in the area of the olfactory trigone and the anterior perforated substance. A brain of domestic cat was taken as an example of a macrosmatic animal and a brain of baboon as an example of a microsmatic animal. The cerebral blood vessels of the cadavers of 30 cats and 11 baboons were filled with latex and, after fixation in acid alcohol by means of microscopic operation, the cortical and deep branches of the anterior and middle cerebral arteries were dissected. We discovered that there were differences between these two groups of animals in the places of arising of deep branches and in their course. In the cat the deep branches running through the area of the olfactory trigone arose from the beginning part of the middle cerebral artery in numbers 5 10 and entered the brain in the olfactory tubercle. In the baboon the deep branches arose from two sources: the middle cerebral artery and the anterior cerebral artery. The branches of the middle cerebral artery went through the anterior perforated substance, forming two groups of branches: lateral and medial. key words: olfactory trigone, anterior perforated substance, arterial supply, cat, baboon INTRODUCTION The aim of the study was to investigate the differences between macrosmatic and microsmatic animals in arterial supply of the area of the olfactory trigone and the anterior perforated substance. The brain of domestic cat was taken as an example of a macrosmatic animal and the brain of baboon as an example of a microsmatic animal. In articles which have been published up until now concerning arterial supply of the brain of the cat and some other macrosmatic animals, i.e., dog, sheep, rabbit or fox [1 8, 11, 16 18], the topography of the vessels of the arterial circle and the range of supplying of the main arterial stems running on the surface of the cerebral hemispheres have been described. However, in the available literature there have been differences between the results of the research works into arterial supplying of the olfactory trigone and anterior perforated substance either in a cat or a baboon [2 5, 9, 12 15]. MATERIAL AND METHODS Cerebral blood vessels of 30 cats and 11 baboons were filled with latex. After fixation in acid alcohol the arterial circle was morphologically estimated. By means of microscopic operation the cortical and deep branches of the anterior and middle cerebral arteries were dissected. Address for correspondence: Mirosław Topol, ul. Narutowicza 60, Łódź, Poland, tel: , tel./fax:
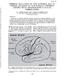
2 Folia Morphol., 2002, Vol. 61, No. 4 RESULTS We discovered that there were differences between these two groups of animals in places where the deep branches arose and in their course. In the cat the deep branches running through this area arose from the beginning part of the middle cerebral artery in numbers 5 10 and entered the brain in the olfactory tubercle (Fig. 1). These branches were from 70 to 140 µm in diameter (Fig. 2). The bigger arteries of this group gave superficially running branches to the cerebral cortex as well. In 6% of specimens of the investigated cat brains the deep branches arising from the middle cerebral artery gave broad but not numerous anastomoses of 70 µm in diameter in their extracerebral segments. In the baboon the deep branches arose from two sources: the middle cerebral artery and the anterior cerebral artery. The deep branches of the middle cerebral artery went through the anterior perforated substance, forming two groups of branches: lateral and medial (Fig. 3). Usually one or two bigger stems arose from the anterior cerebral artery at a distance of mm of its beginning. This stem, of diameter µm, went back and, after about 5.0 mm, it divided into several branches (mostly 6 8). They were running in the direction of the medial part of the anterior perforated substance and olfactory trigone (Fig. 4). A branch of diameter µm arose from the beginning part of the medial cerebral artery usually about 1.0 cm of its length ( cm). This branch typically had a diameter slightly bigger than the branch arising from the anterior cerebral artery ( µm). This ramification of the medial cerebral artery ran medially and after about 5 mm it divided into several branches (8 14), which further penetrated into the Figure 1. The brain of a cat. Topography of the deep branches of the middle cerebral artery in the area of the olfactory tubercle of the right cerebral hemisphere. Arteries filled with latex. Scale bar 1 mm; 1 olfactory tubercle, 2 middle cerebral artery, 3 arteries arising from the middle cerebral artery. Figure 2. The brain of a cat. The left hemisphere. Topography of the deep branches of the middle cerebral artery entering the brain and superficial branches going to the cortex. Arteries filled with latex. Scale bar 1 mm; 1 middle cerebral artery, 2 deep branches of the middle cerebral artery, 3 superficial branches running to the cortex. 266
3 Ewa Nachman et al., Arterial supply of the olfactory trigone and the anterior perforated substance Figure 3. The brain of a baboon. Topography of the deep branches of the middle lobar artery and anterior cerebral artery in the area of the olfactory trigone and the anterior perforated substance of the right cerebral hemisphere. Arteries filled with latex. Scale bar 1 mm; 1 middle cerebral artery, 2 anterior cerebral artery, 3 deep branches forming medial group of arteries, 4 deep branches forming lateral group of arteries, 5 deep branches of the anterior cerebral artery. Figure 4. The brain of a baboon. Topography of the deep branches of the anterior cerebral artery in the area of the anterior perforated substance of the left cerebral hemisphere. Arteries filled with latex. Scale bar 1 mm; 1 anterior cerebral artery, 2 deep branches of the anterior cerebral artery and their ramifications, 3 middle cerebral artery. 267
4 Folia Morphol., 2002, Vol. 61, No. 4 anterior perforated substance (Fig. 4). Two or three of its bigger branches went superficially to a lateral part of the olfactory trigone penetrating into the cerebral cortex. In contrast to the extracerebral segments of the deep branches of the middle cerebral artery in cat brains, we did not find arterial anastomoses in these segments in the baboons. DISCUSSION Chadzypanagiotis [3] noted that in the brain of a cat the anterior cerebral artery gave three groups of branches: arteries supplying the archicortex of the olfactory splenium, the artery of the olfactory bulb and the arteries supplying the neocortex. Another paper of this author [4] distinguished three types of division of the middle cerebral artery. He noticed that numerous branches arose directly from this artery as well, and they penetrated the olfactory lobes, which was in accordance with our research, where we observed 5 10 branches of the middle cerebral artery entering the brain in the olfactory tubercle. Chadzypanagiotis [5] similarly described in the cat brain the distribution of the arteries supplying the archicortex and neocortex, which were branches of the anterior cerebral artery and the posterior cerebral artery. He determined the ranges of supplying these arteries and their individual variability. Our studies revealed that in only 6% of specimens of the investigated cat brains the deep branches arising from the middle cerebral artery gave a few broad anastomoses in their extracerebral segments, whereas, according to Sztamska and Goetzen [14], these arteries in cat and sheep brains formed numerous anastomoses and, thus, they created anatomical connections for collateral circulation. The comparative research on deep branches running to the striatum and internal capsule of the cat and the human were described by Nachman and Nachman [13]. They gave evidence of real differences between branches arising from the maternal stems and running to striatum and their course in the subarachnoid cisternes of the cat and of the human, because in cat brains they gave few anastomoses between them, which were absent in human brains. Our studies showed that a smaller number of deep branches of the middle cerebral artery of the cat brains entered the brain in a spot corresponding with the anterior perforated substance in humans. In some other macrosmatic animals, for example in a dog, the branches penetrating the anterior perforated substance came from the branches of the anterior communicating artery, similar to the recurrent artery of Heubner in humans, and from the middle cerebral artery [1]. Although some animals had a single source of the perforating arteries, most had two or more. Occlusion of all microscopically visible perforators to the anterior perforated substance reliably resulted in infarction of the internal capsule (100%), caudate nucleus (91 100%), putamen and globus pallidus (82 91%), and (73%) anterior commissure [1]. Librizzi et al. [11] reported that in the guinea pig, the middle cerebral artery and the rostral and caudal posterior cerebral arteries supplied the limbic cortices and some related subcortical regions with a very broad overlap between the distal territories of these vessels. The demonstration of an extensive superimposition between the arterial supply of the entorhinal and perirhinal regions suggests the presence of anastomotic connections that potentially are protective against ischaemic events. Coyle and Jokelainen [6] showed that distal branches of the anterior cerebral artery were joined by interarterial anastomoses to the rami of the middle cerebral artery in the normal Wistar rat in 36- and 56-day-old animals. There were about 29 junctions per hemisphere. In our research on baboons the middle part of the olfactory trigone and anterior perforated substance was supplied by branches of the anterior cerebral artery and the lateral part of that territory by branches of the middle cerebral artery. This is compatible with the research of Liu et al. [12], where in baboons the boundary region between the territories of the anterior and middle cerebral arteries lay within 10 mm of the midline. In our research we did not find anastomoses between deep branches in the extracerebral segments of baboon brains, similarly to Sztamska and Goetzen [14] in human brains. However, Watanabe et al. [15] claim that in the middle cerebral artery territory in primates the extremely abundant leptomeningeal anastomoses would be among the major factors leading to the variability in the clinicopathological pictures seen in the models of the proximal middle cerebral artery occlusion. According to Lake et al. [10] the blood supply of the primates (including the baboon Papio ursinus) was found to be similar to that of man in each case. Like man they have a complete circulus arteriosus, but they have a single anterior cerebral artery, whereas man has paired anterior cerebral arteries. 268
5 Ewa Nachman et al., Arterial supply of the olfactory trigone and the anterior perforated substance Our studies reveal that there are differences between macrosmatic and microsmatic animals in the arterial supply of the olfactory trigone and the anterior perforated substance. Furthermore, there are differences in the opinions of authors who have studied arterial anastomoses in the limbic territory [1, 6, 11, 14, 15]. REFERENCES 1. Brenowitz G, Yonas H (1990) Selective occlusion of blood supply to the anterior perforated substance of the dog: a highly reproducible stroke model. Surg Neurol, 33 (4): Chadzypanagiotis D, Kubasiak A (1968) Tętnice doprowadzające krew do mózgu kota. Folia Morphol (Warsz), 27(4): Chadzypanagiotis D (1986) Some features of the blood supply of the cerebral cortex in the cat. Folia Morphol (Warsz), 45 (3): Chadzypanagiotis D (1974) Arteries on the surface of the cerebral hemisphere in the cat. I. Branches of the middle cerebral artery. Folia Morphol (Warsz), 33 (4): Chadzypanagiotis D (1975) Arteries on the surface of the cerebral hemisphere in the cat. II. Branches of the anterior and posterior cerebral arteries. Folia Morphol (Warsz), 34 (3): Coyle P, Jokelainen PT (1982) Dorsal cerebral arterial collaterals of the rat. Anat Rec, 203 (3): Goetzen B, Sztamska E (1992) Comparative anatomy of the arterial vascularization of the hippocampus in man and in experimental animals (cat, rabbit and sheep). Neuropatol Pol, 30 (2): Jabłoński R, Wiland C (1973) Variations of the arteries of the base of the brain in sheep. Folia Morphol (Warsz), 32 (3): James IM, Milnar RA, Purves MJ (1969) Observations on the extrinsic neural control of CBF in the baboon. Circ Res, 25 (1): Lake AR, Van Niekerk IJ, Le Roux CG, Trevor-Jones TR, De Wet PD (1990) Angiology of the brain of the baboon Papio ursinus, the vervet monkey Ceropithecus pygerithrus, and the bushbaby Galago senegalensis. Am J Anat, 187 (3): Librizzi L, Biella G, Cimino C, De Curtis M (1999) Arterial supply of limbic structures in the guinea pig. J Comp Neurol, 411 (4): Liu XG, Branston NM, Kawauchi M, Symon L (1992) A model of acute focal ischemia in the territory of the anterior cerebral artery in baboons. Stroke, 23 (1): Nachman E, Nachman M (1983) Unaczynienie jąder prążkowia i torebki wewnętrznej mózgowia kota. Neuropatol Pol, 21 (2): Sztamska E, Goetzen B (1997) Comparative anatomy of arterial vascularization of the rhinencephalon in man, cat and sheep. Folia Neuropathol, 35 (1): Watanabe O, Bremer AM, West CR (1977) Experimental regional cerebral ischemia in the middle cerebral artery territory in primates. Part 1: Angioanatomy and description of an experimental model with selective embolization of the internal carotid artery bifurcation. Stroke, 8 (1): Wiland C (1966) Tętnica podstawna mózgu lisów. Folia Morphol (Warsz); 25 (4), Wiland C (1968) Tętnice podstawy mózgowia królika domowego. Folia Morphol (Warsz), 27 (3): Wiland C (1973) Variation of the basal arteries of the brain in dogs. Folia Morphol (Warsz), 32 (1):
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 4, pp. 287 291 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The topography of the superficial veins of the hind leg in the baboon
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 4, pp. 287 291 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The topography of the superficial veins of the hind leg in the baboon
The femoral artery and its branches in the baboon Papio anubis
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 66, No. 4, pp. 291 295 Copyright 2007 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The femoral artery and its branches in the baboon Papio anubis Dyl
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 66, No. 4, pp. 291 295 Copyright 2007 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The femoral artery and its branches in the baboon Papio anubis Dyl
I T IS well known that aneurysms occur at
 The Lateral Perforating Branches of the Anterior and Middle Cerebral Arteries* HARRY A. KAPLAN, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Seton Hall College of Medicine, and Jersey City Medical Center, Jersey City,
The Lateral Perforating Branches of the Anterior and Middle Cerebral Arteries* HARRY A. KAPLAN, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Seton Hall College of Medicine, and Jersey City Medical Center, Jersey City,
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
Blood Supply. Allen Chung, class of 2013
 Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
OBJECTIVES. At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries.
 DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
Acute stroke. Ischaemic stroke. Characteristics. Temporal classification. Clinical features. Interpretation of Emergency Head CT
 Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
THE ORGANIZATION OF AMYGDALOPETAL PROJECTIONS FROM THE LATERAL HYPOTHALAMUS AND PREOPTIC AREA IN THE RAT
 ACTA NEUROBIOL. EXP. 1977, 37: 247-252 THE ORGANIZATION OF AMYGDALOPETAL PROJECTIONS FROM THE LATERAL HYPOTHALAMUS AND PREOPTIC AREA IN THE RAT Liliana NITECKA, Olgierd NARKIEWICZ and Czeslaw JAKIEL Department
ACTA NEUROBIOL. EXP. 1977, 37: 247-252 THE ORGANIZATION OF AMYGDALOPETAL PROJECTIONS FROM THE LATERAL HYPOTHALAMUS AND PREOPTIC AREA IN THE RAT Liliana NITECKA, Olgierd NARKIEWICZ and Czeslaw JAKIEL Department
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP:
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
WACH J Arteries of the brain in wild European rabbit Oryctolagus cuniculus. (Linnaeus, 1758)
 PL-ISSN 0015-5497 (print), ISSN 1734-9168 (online) Folia Biologica (Kraków), vol. 60 (2012), No 3-4 Ó Institute of Systematics and Evolution of Animals, PAS, Kraków, 2012 doi:10.3409/fb60_3-4.189-194 Arteries
PL-ISSN 0015-5497 (print), ISSN 1734-9168 (online) Folia Biologica (Kraków), vol. 60 (2012), No 3-4 Ó Institute of Systematics and Evolution of Animals, PAS, Kraków, 2012 doi:10.3409/fb60_3-4.189-194 Arteries
Cerebrovascular diseases-2
 Cerebrovascular diseases-2 Primary angiitis of CNS - Other causes of infarction i. Hypercoagulable states ii. Drug-abuse such as amphetamine, heroin and cocain Note - The venous side of the circulation
Cerebrovascular diseases-2 Primary angiitis of CNS - Other causes of infarction i. Hypercoagulable states ii. Drug-abuse such as amphetamine, heroin and cocain Note - The venous side of the circulation
Outline of the next three lectures
 Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Blood Supply of the CNS
 Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Intrahepatic ramifications of the portal vein in the horse
 Intrahepatic ramifications of the portal vein in the horse Tadjalli, M. 1* and Moslemy, H. R. 2 1 Department of Anatomical Sciences, School of Veterinary Medicine, University of Shiraz, Shiraz, Iran; 2
Intrahepatic ramifications of the portal vein in the horse Tadjalli, M. 1* and Moslemy, H. R. 2 1 Department of Anatomical Sciences, School of Veterinary Medicine, University of Shiraz, Shiraz, Iran; 2
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Dorsal Cerebral Arterial Collaterals of the Rat
 THE ANATOMICAL RECORD 203:397-404 (1982) Dorsal Cerebral Arterial Collaterals of the Rat PK'I'EK COYLE ANI) PEN'WI 'I'. JOKELAINEN lhpurtment of Anatomy and (bll Biology, The Unirwsity of Michigan Medical
THE ANATOMICAL RECORD 203:397-404 (1982) Dorsal Cerebral Arterial Collaterals of the Rat PK'I'EK COYLE ANI) PEN'WI 'I'. JOKELAINEN lhpurtment of Anatomy and (bll Biology, The Unirwsity of Michigan Medical
The occipital lobe is involved in many aspects of
 728 Distribution of the Occipital Branches of the Posterior Cerebral Artery Correlation With Occipital Lobe Infarcts Slobodan V. Marinkovic", MD, Milan M. Milisavljevic", MD, Vera Lolid-Draganid, MD, and
728 Distribution of the Occipital Branches of the Posterior Cerebral Artery Correlation With Occipital Lobe Infarcts Slobodan V. Marinkovic", MD, Milan M. Milisavljevic", MD, Vera Lolid-Draganid, MD, and
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Early Angiographic and CT Findings in Patients with Hemorrhagic Infarction in the Distribution of the Middle Cerebral Artery
 1115 Early Angiographic and CT Findings in Patients with Hemorrhagic Infarction in the Distribution of the Middle Cerebral Artery L. Bozzao 1 U. Angeloni S. Bastianello L. M. Fantozzi A. Pierallini C.
1115 Early Angiographic and CT Findings in Patients with Hemorrhagic Infarction in the Distribution of the Middle Cerebral Artery L. Bozzao 1 U. Angeloni S. Bastianello L. M. Fantozzi A. Pierallini C.
Anatomy of the basal ganglia. Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410
 Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
The choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle and its arteries
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 3, pp. 194 198 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle and its arteries Mansoor
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 3, pp. 194 198 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle and its arteries Mansoor
LIMBIC SYSTEM. Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
 LIMBIC SYSTEM Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy Learning Objectives Define the limbic system Identify the parts of the limbic system Describe the circulation of the limbic system
LIMBIC SYSTEM Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy Learning Objectives Define the limbic system Identify the parts of the limbic system Describe the circulation of the limbic system
Neuro Vascular Relationship between Superior Cerebellar Artery and Trigeminal Nerve
 Neuro Vascular Relationship between Superior Cerebellar Artery and Trigeminal Nerve Pages with reference to book, From 140 To 143 Nawab Mohammad Khan, Mohammad Afzal Khan, Fazal Karim Aasi ( Department
Neuro Vascular Relationship between Superior Cerebellar Artery and Trigeminal Nerve Pages with reference to book, From 140 To 143 Nawab Mohammad Khan, Mohammad Afzal Khan, Fazal Karim Aasi ( Department
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas. Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template
 Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES. nuclei. The lateral ventricles. White substance of cerebral hemispheres. course 1
 Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline Human Anatomy Module 2 Content module 11 Study subject The olfactory brain. Basal nuclei. The lateral ventricles. White substance of cerebral
Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline Human Anatomy Module 2 Content module 11 Study subject The olfactory brain. Basal nuclei. The lateral ventricles. White substance of cerebral
The study of arterial anastomoses in the region of the alveolar process and the anterior maxilla wall in foetuses
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 2, pp. 65 69 Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The study of arterial anastomoses in the region of the alveolar process
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 68, No. 2, pp. 65 69 Copyright 2009 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The study of arterial anastomoses in the region of the alveolar process
Module 3. The Blood Supply of the Brain
 Module 3. The Blood Supply of the Brain Relating Vascular and Functional Anatomy Objectives for Module 3 Knowledge! Describe or sketch the course of the major arteries and their branches that comprise
Module 3. The Blood Supply of the Brain Relating Vascular and Functional Anatomy Objectives for Module 3 Knowledge! Describe or sketch the course of the major arteries and their branches that comprise
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
 IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Perforating Branches of the Middle Cerebral Artery
 1022 Perforating Branches of the Middle Cerebral Artery Microanatomy and Clinical Significance of Their Intracerebral Segments SLOBODAN V. MARINKOVIC, M.D.* MILAN M. MILISAVLJEVIC, M.D.,* MIROSLAV S. KOVACEVIC,
1022 Perforating Branches of the Middle Cerebral Artery Microanatomy and Clinical Significance of Their Intracerebral Segments SLOBODAN V. MARINKOVIC, M.D.* MILAN M. MILISAVLJEVIC, M.D.,* MIROSLAV S. KOVACEVIC,
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
 IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
The subarachnoid space develops early in the human embryonic period
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 3, pp. 212 216 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The subarachnoid space develops early in the human embryonic period
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 3, pp. 212 216 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The subarachnoid space develops early in the human embryonic period
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta.
 Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
A bilateral cortico-striate projection
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1965, 28, 71 J. B. CARMAN, W. M. COWAN, T. P. S. POWELL, AND K. E. WEBSTER From the Departments of Anatomy, University of Oxford, and University College, London During
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1965, 28, 71 J. B. CARMAN, W. M. COWAN, T. P. S. POWELL, AND K. E. WEBSTER From the Departments of Anatomy, University of Oxford, and University College, London During
THE VARIATIONS AND PATTERNS OF RENAL ARTERIES IN DOGS
 Sajjarengpong K. & Adirektaworn A./TJVM 36(1): 39-46. 39 Original Article THE VARIATIONS AND PATTERNS OF RENAL ARTERIES IN DOGS Kriengyot Sajjarengpong * Adisorn Adirektaworn Abstract Kriengyot Sajjarengpong
Sajjarengpong K. & Adirektaworn A./TJVM 36(1): 39-46. 39 Original Article THE VARIATIONS AND PATTERNS OF RENAL ARTERIES IN DOGS Kriengyot Sajjarengpong * Adisorn Adirektaworn Abstract Kriengyot Sajjarengpong
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
EMBOLIC OCCLUSION OF THE SUPERIOR AND IN- FERIOR DIVISIONS OF THE MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY WITH ANGIOGRAPHIC-CLINICAL CORRELATION*
 MARCH, 1976 Pre EMBOLIC OCCLUSION OF THE SUPERIOR AND IN- FERIOR DIVISIONS OF THE MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY WITH ANGIOGRAPHIC-CLINICAL CORRELATION* ABSTRACT: Superior Rolandlc rolandic By L. REED ALTEMUS,
MARCH, 1976 Pre EMBOLIC OCCLUSION OF THE SUPERIOR AND IN- FERIOR DIVISIONS OF THE MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY WITH ANGIOGRAPHIC-CLINICAL CORRELATION* ABSTRACT: Superior Rolandlc rolandic By L. REED ALTEMUS,
PHY3111 Mid-Semester Test Study. Lecture 2: The hierarchical organisation of vision
 PHY3111 Mid-Semester Test Study Lecture 2: The hierarchical organisation of vision 1. Explain what a hierarchically organised neural system is, in terms of physiological response properties of its neurones.
PHY3111 Mid-Semester Test Study Lecture 2: The hierarchical organisation of vision 1. Explain what a hierarchically organised neural system is, in terms of physiological response properties of its neurones.
CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES By: Shifaa AlQa qa Cerebrovascular diseases Brain disorders caused by pathologic processes involving blood vessels 3 pathogenic mechanisms (1) thrombotic occlusion, (2) embolic
CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASES By: Shifaa AlQa qa Cerebrovascular diseases Brain disorders caused by pathologic processes involving blood vessels 3 pathogenic mechanisms (1) thrombotic occlusion, (2) embolic
Arterial vascularisation of the anterior
 Original Article Singapore Med J 2011; 52(6) 410 Arterial vascularisation of the anterior perforated substance Sen T, Esmer A F, Acar H I, Karahan S T, Tuccar E ABSTRACT Introduction: The arteries of the
Original Article Singapore Med J 2011; 52(6) 410 Arterial vascularisation of the anterior perforated substance Sen T, Esmer A F, Acar H I, Karahan S T, Tuccar E ABSTRACT Introduction: The arteries of the
DSTAL branches of the 3 major cerebral arteries
 407 Blood Flow Through Cerebral Collateral Vessels One Month After Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Peter Coyle and Donald D. Heistad Acute occlusion of a middle cerebral artery (MCA) reduces cerebral
407 Blood Flow Through Cerebral Collateral Vessels One Month After Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Peter Coyle and Donald D. Heistad Acute occlusion of a middle cerebral artery (MCA) reduces cerebral
DIAMETER OF ANTERIOR CEREBRAL ARTERY ON MRI ANGIOGRAMS
 Original Research Article DIAMETER OF ANTERIOR CEREBRAL ARTERY ON MRI ANGIOGRAMS Navita Aggarwal *, Molly M. Paul, Madhumita Mukherjee. ABSTRACT Background: Magnetic Resonance Imaging, by far, has been
Original Research Article DIAMETER OF ANTERIOR CEREBRAL ARTERY ON MRI ANGIOGRAMS Navita Aggarwal *, Molly M. Paul, Madhumita Mukherjee. ABSTRACT Background: Magnetic Resonance Imaging, by far, has been
Cerebral Cortex 1. Sarah Heilbronner
 Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
THE DOG is used a great deal in physiological
 Anatomy of the Ventricular Coronary Arteries in the Dog THE DOG is used a great deal in physiological and surgical research on the heart. In view of this, it is surprising that information with regard
Anatomy of the Ventricular Coronary Arteries in the Dog THE DOG is used a great deal in physiological and surgical research on the heart. In view of this, it is surprising that information with regard
Fig.1: A, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a
 Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]
![[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD] [(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]](/thumbs/89/98619893.jpg) 2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
Cortical Control of Movement
 Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
CT INTERPRETATION COURSE
 CT INTERPRETATION COURSE Refresher Course ASTRACAT October 2012 Stroke is a Clinical Diagnosis A clinical syndrome characterised by rapidly developing clinical symptoms and/or signs of focal loss of cerebral
CT INTERPRETATION COURSE Refresher Course ASTRACAT October 2012 Stroke is a Clinical Diagnosis A clinical syndrome characterised by rapidly developing clinical symptoms and/or signs of focal loss of cerebral
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
11.1 The Aortic Arch General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta
 456 11 Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta 11.1 The Aortic Arch 11.1.1 General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgery of the is one of the most challenging areas of cardiac and vascular surgery,
456 11 Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta 11.1 The Aortic Arch 11.1.1 General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgery of the is one of the most challenging areas of cardiac and vascular surgery,
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere)
 Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
THE SURGEON S LIBRARY
 THE SURGEON S LIBRARY THE HISTORY AND SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE VAGUS NERVE Lee J. Skandalakis, M.D., Chicago, Illinois, Stephen W. Gray, PH.D., and John E. Skandalakis, M.D., PH.D., F.A.C.S., Atlanta, Georgia
THE SURGEON S LIBRARY THE HISTORY AND SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE VAGUS NERVE Lee J. Skandalakis, M.D., Chicago, Illinois, Stephen W. Gray, PH.D., and John E. Skandalakis, M.D., PH.D., F.A.C.S., Atlanta, Georgia
Experimental Regional Cerebral Ischemia in the Middle Cerebral Artery Territory in Primates
 Experimental Regional Cerebral Ischemia in the Middle Cerebral Artery Territory in Primates 6 Part : Angio-Anatomy and Description of an Experimental Model With Selective Embolization of the Internal Carotid
Experimental Regional Cerebral Ischemia in the Middle Cerebral Artery Territory in Primates 6 Part : Angio-Anatomy and Description of an Experimental Model With Selective Embolization of the Internal Carotid
to Regulation of the Brain Vessels
 Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 34,193-197,1984 The Relevance of Cardio-pulmonary-vascular Reflex to Regulation of the Brain Vessels Masatsugu NAKAI and Koichi OGINO Department of Cardiovascular
Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 34,193-197,1984 The Relevance of Cardio-pulmonary-vascular Reflex to Regulation of the Brain Vessels Masatsugu NAKAI and Koichi OGINO Department of Cardiovascular
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
BASAL GANGLIA. Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY
 BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
-Zeina Assaf. -Omar Odeh. - Maha Beltagy
 -3 -Zeina Assaf -Omar Odeh - Maha Beltagy 1 P a g e The Inferior Surface Of The Brain The inferior surface of the brain is divide by the stem of the lateral fissure into 2 parts : The orbital surface and
-3 -Zeina Assaf -Omar Odeh - Maha Beltagy 1 P a g e The Inferior Surface Of The Brain The inferior surface of the brain is divide by the stem of the lateral fissure into 2 parts : The orbital surface and
10/3/2016. T1 Anatomical structures are clearly identified, white matter (which has a high fat content) appears bright.
 H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
The arteries of the human kidney
 J. Anat. (1966), 100, 4, pp. 881-894 881 With 8 figures Printed in Great Britain The arteries of the human kidney BY H. FINE AND E. N. KEEN Department of Anatomy, University of Natal INTRODUCTION A study
J. Anat. (1966), 100, 4, pp. 881-894 881 With 8 figures Printed in Great Britain The arteries of the human kidney BY H. FINE AND E. N. KEEN Department of Anatomy, University of Natal INTRODUCTION A study
Gross Anatomy: Upper Extremity Arteries
 Gross Anatomy: Upper Extremity Arteries By: Trevor Lohman DPT Illustrated by: Dennis Breese 1 Subclavian and Axillary arteries Hardening of the heart ages people more quickly than hardening of the arteries
Gross Anatomy: Upper Extremity Arteries By: Trevor Lohman DPT Illustrated by: Dennis Breese 1 Subclavian and Axillary arteries Hardening of the heart ages people more quickly than hardening of the arteries
Anatomical variations of the median nerve distribution and communication in the arm
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 63, No. 3, pp. 313 318 Copyright 2004 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Anatomical variations of the median nerve distribution and communication
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 63, No. 3, pp. 313 318 Copyright 2004 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Anatomical variations of the median nerve distribution and communication
Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report
 Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
: ~-~ '. '.- :'.~:;;,' _ ~-- '. '. _ --:... ~... ~ ~:~:;::~~~~
 56 Accessory Middle Cerebral Artery: Is It a Variant Form of the Recurrent Artery of Heubner?.......-... -.... ;. ".P,n~}~ : ~-~ '. '.- :'.~:;;,' _ ~-- '. '. _ --:... ~... ~ ~:~:;::~~~~ Shoki Takahashi
56 Accessory Middle Cerebral Artery: Is It a Variant Form of the Recurrent Artery of Heubner?.......-... -.... ;. ".P,n~}~ : ~-~ '. '.- :'.~:;;,' _ ~-- '. '. _ --:... ~... ~ ~:~:;::~~~~ Shoki Takahashi
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
Surgical anatomy of the biliary tract
 HPB, 2008; 10: 7276 REVIEW ARTICLE Surgical anatomy of the biliary tract DENIS CASTAING Centre hépato-biliaire, Hôpital Paul Brousse, Assistance Publique- Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Paris XI, Paris,
HPB, 2008; 10: 7276 REVIEW ARTICLE Surgical anatomy of the biliary tract DENIS CASTAING Centre hépato-biliaire, Hôpital Paul Brousse, Assistance Publique- Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Paris XI, Paris,
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE Scalp 2. Cranium. 13. Superior sagittal sinus
 TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
 This article was originally published in a journal published by Elsevier, and the attached copy is provided by Elsevier for the author s benefit and for the benefit of the author s institution, for non-commercial
This article was originally published in a journal published by Elsevier, and the attached copy is provided by Elsevier for the author s benefit and for the benefit of the author s institution, for non-commercial
Leah Militello, class of 2018
 Leah Militello, class of 2018 Objectives 1. Describe the general organization of cerebral hemispheres. 2. Describe the locations and features of the different functional areas of cortex. 3. Understand
Leah Militello, class of 2018 Objectives 1. Describe the general organization of cerebral hemispheres. 2. Describe the locations and features of the different functional areas of cortex. 3. Understand
The human brain. of cognition need to make sense gives the structure of the brain (duh). ! What is the basic physiology of this organ?
 The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Proc SPIE. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 February 07.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc SPIE. 2007 March 5; 6512: 651236. doi:10.1117/12.708950. Semi-Automatic Parcellation of the Corpus Striatum Ramsey Al-Hakim a,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Proc SPIE. 2007 March 5; 6512: 651236. doi:10.1117/12.708950. Semi-Automatic Parcellation of the Corpus Striatum Ramsey Al-Hakim a,
Anatomy of the Middle Cerebral Artery: The Temporal Branches
 Anatomy of the Middle Cerebral Artery: The Temporal Branches BY W. BRADFORD DeLONG, M.D., F.A.C.S. Abstract: Anatomy of the Middle Cerebral Artery: The Temporal Branches Nineteen out of 23 middle cerebral
Anatomy of the Middle Cerebral Artery: The Temporal Branches BY W. BRADFORD DeLONG, M.D., F.A.C.S. Abstract: Anatomy of the Middle Cerebral Artery: The Temporal Branches Nineteen out of 23 middle cerebral
Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 3 TA: Jürgen Germann
 Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 3 TA: Jürgen Germann e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. Meninges 2. Cerebral cortex-cytoarchitecture 3. Diencephalon (thalamus/hypothalamus) (this replaces
Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 3 TA: Jürgen Germann e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. Meninges 2. Cerebral cortex-cytoarchitecture 3. Diencephalon (thalamus/hypothalamus) (this replaces
An x-ray microscopic study of the vasa vasorum
 Thorax (1964), 19, 561. An x-ray microscopic study of the vasa vasorum of normal human pulmonary arteries JOHN A. CLARKE From the Department of Anatomy, University of Glasgow The first description of the
Thorax (1964), 19, 561. An x-ray microscopic study of the vasa vasorum of normal human pulmonary arteries JOHN A. CLARKE From the Department of Anatomy, University of Glasgow The first description of the
P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center. Wednesday, 16 March 2009, 1:00p.m. 2:00p.m.
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX
 CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
Gross Anatomy Coloring Book Series. Lower Extremity Arteries
 Gross Anatomy Coloring Book Series Lower Extremity Arteries 1 Femoral Artery and Associated Branches For the life of the flesh is in the blood. Leviticus 17:11 Femoral Artery and Associated Branches After
Gross Anatomy Coloring Book Series Lower Extremity Arteries 1 Femoral Artery and Associated Branches For the life of the flesh is in the blood. Leviticus 17:11 Femoral Artery and Associated Branches After
A STUDY OF TEMPORAL BRANCHES OF MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY
 J. Anat. Sciences, 23(2) : Dec. 2015, 15-21 Original Article A STUDY OF TEMPORAL BRANCHES OF MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY Medha Das*, Shirin Jahan*, Pranjal Pankaj** * Department of Anatomy, Rama Medical College,
J. Anat. Sciences, 23(2) : Dec. 2015, 15-21 Original Article A STUDY OF TEMPORAL BRANCHES OF MIDDLE CEREBRAL ARTERY Medha Das*, Shirin Jahan*, Pranjal Pankaj** * Department of Anatomy, Rama Medical College,
Sensory systems. Taste/gustatory
 Sensory systems Taste/gustatory Sensory systems basic concepts Modality of Sensation Receptor Sensory Tract primary neuron secondary neuron tertiary neuron termination Receptors of sensory systems - primary
Sensory systems Taste/gustatory Sensory systems basic concepts Modality of Sensation Receptor Sensory Tract primary neuron secondary neuron tertiary neuron termination Receptors of sensory systems - primary
57. Trajectory o f Primary Vestibular Fibers Originating f rom the Lateral, Anterior, and Posterior Semicircular Canals in the Cat
 No. 7] Proc. Japan Acad., 58, Ser. B (1982) 237 57. Trajectory o f Primary Vestibular Fibers Originating f rom the Lateral, Anterior, and Posterior Semicircular Canals in the Cat By Haj ime MANNEN, Sei-ichi
No. 7] Proc. Japan Acad., 58, Ser. B (1982) 237 57. Trajectory o f Primary Vestibular Fibers Originating f rom the Lateral, Anterior, and Posterior Semicircular Canals in the Cat By Haj ime MANNEN, Sei-ichi
nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
 Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
CADAVERIC STUDY: MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF BRANCHES OF FEMORAL ARTERY IN FRONT OF THIGH
 CADAVERIC STUDY: MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF BRANCHES OF FEMORAL ARTERY IN FRONT OF THIGH *Suthar K. 1, Patil D. 1, Mehta C. 1, Patel V. 2, Prajapati B. 1 and Bhatt C. 1 1 Department of Anatomy, Government
CADAVERIC STUDY: MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF BRANCHES OF FEMORAL ARTERY IN FRONT OF THIGH *Suthar K. 1, Patil D. 1, Mehta C. 1, Patel V. 2, Prajapati B. 1 and Bhatt C. 1 1 Department of Anatomy, Government
Carotid Arterial Supply of the Feline Brain
 Carotid Arterial Supply of the Feline Brain APPLICATIONS TO THE STUDY OF REGIONAL CEREBRAL ISCHEMIA BY YOSHINARI KAMIJYO, M.D., AND JULIO H. GARCIA, M.D. Abstract: Carotid Arterial Supply of the Feline
Carotid Arterial Supply of the Feline Brain APPLICATIONS TO THE STUDY OF REGIONAL CEREBRAL ISCHEMIA BY YOSHINARI KAMIJYO, M.D., AND JULIO H. GARCIA, M.D. Abstract: Carotid Arterial Supply of the Feline
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Blood Supply of Brain and Spinal Cord Arterial Supply of Brain The brain receives blood
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Blood Supply of Brain and Spinal Cord Arterial Supply of Brain The brain receives blood
Case Report 1. CTA head. (c) Tele3D Advantage, LLC
 Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
of the Axillary Artery
 Variation in the Origins of the Branches of the Axillary Artery DONALD F. HUELKE Department of Anatomy, The University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan Variability in the origin of certain
Variation in the Origins of the Branches of the Axillary Artery DONALD F. HUELKE Department of Anatomy, The University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan Variability in the origin of certain
History of revascularization
 History of revascularization Author (year) Kredel, 1942 Woringer& Kunlin, 1963 Donaghy& Yasargil, 1968 Loughheed 1971 Kikuchini & Karasawa1973 Karasawa, 1977 Story, 1978 Sundt, 1982 EC/IC bypass study
History of revascularization Author (year) Kredel, 1942 Woringer& Kunlin, 1963 Donaghy& Yasargil, 1968 Loughheed 1971 Kikuchini & Karasawa1973 Karasawa, 1977 Story, 1978 Sundt, 1982 EC/IC bypass study
Proximal Humerus Fractures
 Proximal Humerus Fractures Trafford General Hospital, June 2010 Nehmat Singh, Jawad Sultan Anatomy of the Proximal Humerus Consists of four parts: humeral head, surgical neck and greater and lesser tubercles
Proximal Humerus Fractures Trafford General Hospital, June 2010 Nehmat Singh, Jawad Sultan Anatomy of the Proximal Humerus Consists of four parts: humeral head, surgical neck and greater and lesser tubercles
How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR
 How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR Jürg Schmidli Chief of Vascular Surgery Inselspital Hamburg 2017 Dept Cardiovascular Surgery, Bern, Switzerland Disclosure No Disclosures
How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR Jürg Schmidli Chief of Vascular Surgery Inselspital Hamburg 2017 Dept Cardiovascular Surgery, Bern, Switzerland Disclosure No Disclosures
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa3.0/
BIODIVERSITY OF THE CORONARY ARTERIES IN CATTLE - MACROSCOPIC STUDY
 Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LXII (2) ISSN 2065-1295; ISSN 2343-9394 (CD-ROM); ISSN 2067-3663 (Online); ISSN-L 2065-1295 BIODIVERSITY OF THE CORONARY ARTERIES IN CATTLE - MACROSCOPIC
Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LXII (2) ISSN 2065-1295; ISSN 2343-9394 (CD-ROM); ISSN 2067-3663 (Online); ISSN-L 2065-1295 BIODIVERSITY OF THE CORONARY ARTERIES IN CATTLE - MACROSCOPIC
The morphology of circulus arteriosus cerebri in the porcupine (Hystrix cristata)
 The morphology of circulus arteriosus cerebri in the porcupine (Hystrix cristata) A. AYDIN 1, S. YILMAZ 1, G. DINC 1, D. OZDEMIR 2, M. KARAN 1 1 Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Firat
The morphology of circulus arteriosus cerebri in the porcupine (Hystrix cristata) A. AYDIN 1, S. YILMAZ 1, G. DINC 1, D. OZDEMIR 2, M. KARAN 1 1 Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Firat
Primary pouches: prosencephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon Secondary pouches: telencephalon diencephalon
 Telencephalon Ontogenic development of CNS Primary pouches: prosencephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon Secondary pouches: telencephalon diencephalon mesencephalon metencephalon ---- pons (pons Varoli),
Telencephalon Ontogenic development of CNS Primary pouches: prosencephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon Secondary pouches: telencephalon diencephalon mesencephalon metencephalon ---- pons (pons Varoli),
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans
 PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
Regional cerebral blood flow, sensory evoked potentials, and intracranial pressure in dogs with MCA occlusion by embolization or trapping
 J Neurosurg 58:500-507, 1983 Regional cerebral blood flow, sensory evoked potentials, and intracranial pressure in dogs with MCA occlusion by embolization or trapping YOSHIKAZU OKADA, M.D., TAKESHI SHIMA,
J Neurosurg 58:500-507, 1983 Regional cerebral blood flow, sensory evoked potentials, and intracranial pressure in dogs with MCA occlusion by embolization or trapping YOSHIKAZU OKADA, M.D., TAKESHI SHIMA,
