Visualization and assessment of saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus
|
|
|
- Dale Barker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 cta Oto-aryngologica, 2011; 131: ORIGIN RTIE Visualization and assessment of saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus HIDEO YMNE 1, MHIRO TKYM 1, KIHIKO UNMI 1, HIRMORI KMOTO 1, THIO IMOTO 1 & MTTI NNIKO 2 1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Osaka ity University Graduate chool of Medicine, Osaka, Japan and 2 Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Head & Neck urgery, Uppsala University Hospital, Uppsala, weden bstract onclusion: The saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus run in the bony groove, before reaching the orifice of the vestibular aqueduct. We first clinically visualized this sulciform groove using three-dimensional (3D) cone beam T images. This strategy can be useful to assess the condition of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus concerning the longitudinal flow system of endolymph. Objective: To assess the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus in the endolymphatic system in order to advance clinical studies on inner ear dysfunction. Methods: The sulciform groove of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus of human subjects was analyzed by cone beam T and compared with that of a cadaver. Results: We could obtain reconstructed 3D T images of the sulciform groove of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus using several T window levels. Keywords:, saccule, bony groove, longitudinal flow, T image, endolymphatic hydrops, endolymphatic duct, rendering Introduction The saccule connects with two ducts, the reuniting and saccular ducts, which are respectively the paths of endolymph. These paths are important in the longitudinal flow theory [1], whereby the endolymph goes directly from the cochlea to the endolymphatic sac. This theory explains the cause of Meniere s disease, which exhibits endolymphatic hydrops [2,3]. From this viewpoint, the vestibular aqueduct that follows the saccular duct was initially clinically visualized and used as a diagnostic tool for Meniere s disease [4,5]. We also clinically analyzed the reuniting duct by visualizing it with three-dimensional computed tomography (3D T) to diagnose Meniere s disease [6 8]. However, the saccular duct has not been clinically visualized. The reason is that the saccular duct is membranous, facing endolymph inside and perilymph outside, and so T and MRI have limitations for visualizing it. The saccular duct becomes endolymphatic sinus running in the bony sulciform groove before ending in the vestibular aqueduct, which may be visualized in 3D T images as a bony substance, like the bony groove of the reuniting duct (YT groove) in a previous study [6,7]. In the present study, we investigated whether the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus could be demonstrated on clinical images using cone beam 3D T. Material and methods We investigated the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus and their sulciform groove in the temporal bones of bilaterally healthy ears of 12 controls (6 males and 6 females; mean age 58.4 years, range years), which had been included in a previous study orrespondence: Hideo Yamane MD, Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Osaka ity University Graduate chool of Medicine, sahimachi, benoku, Osaka , Japan. Tel: Fax: ent-yamane@med.osaka-cu.ac.jp (Received 30 July 2010; accepted 12 October 2010) IN print/in online Ó 2011 Informa Healthcare DOI: /
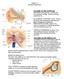
2 470 H. Yamane et al. YT T accular duct & endolymphatic sinus Reuniting duct ED E Utricular valve D Figure 1. Macroscopic findings of the vestibule in the cadaver (left ear). () Membranous composition of the saccule and its intact connecting duct. rrows show the reuniting duct, and arrowheads show the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus. () Membranous compositions of the saccule and reuniting duct were removed. rrows show the YT groove of the reuniting duct. rrowheads, saccular duct. () The sulciform groove of the saccular duct (white dashed arrows) and endolymphatic sinus (white arrows) reach the orifice of the vestibular aqueduct. (D) chematic view of the YT groove (bold arrows) of the reuniting duct and sulciform groove (dashed arrows) of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus., cochlear recess; ED, endolymphatic duct; E, endolymphatic sac;, internal auditory canal;, lateral semicircular canal;, osseous spiral lamina;, posterior semicircular canal;, superior semicircular canal;, saccule;, saccular recess;, utricular recess. [8] employing cone beam T (3D ccuitomo; J. Morita Mfg orp., Kyoto, Japan) and the temporal bone of a cadaver donated to our medical university of anatomy, with the consent of the deceased and our university, to compare the findings in human subjects with those in the cadaver. T images were investigated using cone beam T to obtain images under the following conditions: 80 kv, 6 m, voxel mm, slice thickness 0.5 mm. T images of this region were taken as a column with a diameter and height of 6 cm. Reconstructed 3D images of the inner ear were obtained using rendering software (IVIEW; J. Morita Mfg orp.) using a perspective view with a viewing angle of 15 and a 0.25 mm voxel ( mm). To obtain 3D T images of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus in accordance with cadaver specimens, we adopted the landmarks reported in a previous study to reduce discrepancies due to rendering effect [7]. 3D T images are manipulated so that the saccule, YT groove, and vestibular portion of the posterior semicircular canal and ridge of the cochlea just sloping down to the vestibule in front are all viewed in one frame. With this view, the bony sulciform groove of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus is visible. Then, this image can be manipulated through pitch or yaw to yield a view from directly above the sulciform groove to decrease the artifact by rendering effects. lso, several T window levels were used in one view to visualize the groove from the surrounding
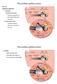
3 Visualization of saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus 471 Figure 2. Direction of T examination and T findings in the cadaver. () This position of the temporal bone is suitable to obtain more accurate T images of the saccule, saccular duct, and endolymphatic sinus. Note that the remnant membranous labyrinth, shown in black, is visible. Insert: Higher magnification of the groove of the saccular duct (white dashed arrows) and endolymphatic sinus (white arrows). () The sulciform groove-like 3D T image of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus of the same specimen as in (), which was examined in the same direction as in () with a bone T window level. () The same specimen as in () with T window levels of bone and soft tissue. The membranous composition of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus in purple (white arrows) are surrounded by the artificial shadow of a rendering effect. The details of the aspects are consistent with macroscopic specimens. urple indicates soft tissue., cochlear recess;, internal auditory canal;, lateral semicircular canal;, osseous spiral lamina;, posterior semicircular canal;, superior semicircular canal;, saccular recess;, utricular recess. architecture. pproval was obtained from the ethics committee of Osaka ity University Graduate chool of Medicine. Results sulciform groove from the saccular fossa to the orifice of the vestibular aqueduct in which the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus run could be localized in the cadaver specimen (Figure 1 D). The sulciform groove of the endolymphatic sinus was distinct but that of the saccular duct was unclear (Figures 1 and 2). Employing a direction in which the saccule and saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus can be seen from directly above, the groove-like 3D T image of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus were consistent with macroscopic findings (Figure 2 ). This groove-like image was made up of two colors when T was imaged with these bone and soft tissue T window levels (Figure 2). Further, this image was consistent with macroscopic cadaveric findings because there was a torn membranous labyrinth around the groove that could be imaged as soft tissue by T. Groove-like 3D T images of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus were obtained in all 12 human subjects. The aspects of the groove were similar among the 12 healthy subjects (Figures 3 and 4). The images of the groove reconstructed using several T window levels such as a high or low density of bone revealed more accurate images (Figure 3 and ), especially the lumen of the
4 472 H. Yamane et al. Figure 3. Findings of a representative 3D T image of a healthy human subject (left ear). () With low-level bone T window (blue color). () With low - and high- level bone T windows (blue and green color). () The image shows a view from directly above the sulciform groove with the same T window level as in (). more accurate image of the sulciform groove of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus can be judged by referring to the T images in (,, and ) The method in () is suitable for assessment of the sulciform groove of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus. With two different bone densities the T view manifests more three-dimensionally. The cochlear lateral wall and basal portion of the osseous spiral lamina in green seem to be denser in bone density than the vestibule and the apex of the cochlea in blue., cochlear recess;, internal auditory canal;, osseous spiral lamina;, posterior semicircular canal;, saccular recess;, utricular recess. lack arrows, YT groove; white arrows, the sulciform groove of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus. groove, which was more manifested three-dimensionally compared with single T window levels (Figure 3 ). Discussion The vestibular aqueduct has been assessed in relation to the etiology of Meniere s disease, where the endolymphatic duct runs and reaches the endolymphatic sac. This clinical strategy is based on the fact that idiopathic endolymphatic hydrops, a pathological entity of Meniere s disease, is caused by the blockage of endolymph in the endolymphatic duct or sac [9,10]. However, there are few reports on the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus despite these sites and the vestibular aqueduct being directly connected. Most saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus studies are limited to animal experiments or specimens of human temporal bone [3,10], because the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus are too small and membranous to assess clinically. The saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus are not a bony groove themselves but run in the bony groove, which could be visualized clinically using 3D T. When the saccular duct or endolymphatic sinus is involved as a lesion in inner ear disease, their bony grooves may reflect the lesional effect. similar strategy was adopted to assess
5 Visualization of saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus 473 duct directly connects with the saccule, we cannot deny the possibility that dislodged otoconia from the saccule may enter the saccular duct or endolymphatic sinus in a similar manner to that in the reuniting duct. Investigating the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus will provide novel information regarding inner ear diseases caused by longitudinal flow disturbances of endolymph, especially Meniere s disease. We will also further investigate the role of these architectures. cknowledgment Figure 4. Findings of other representative 3D T images in a healthy human subject (left ear)., cochlear recess;, internal auditory canal;, osseous spiral lamina;, posterior semicircular canal;, saccular recess;, utricular recess. White arrows, the sulciform groove of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus. the reuniting duct to visualize the YT groove in a previous study [6,7]. The rendering strategy for 3D T analysis sometimes leads to a misunderstanding [7]. The T image of the cadaver with a double T window level such as bone and soft tissue showed the groove and its circumscribing torn membranous labyrinth, in which the image was consistent with the macroscopic cadaverbased findings. Therefore, we judged that our strategy could markedly reduce the negative effect of rendering. s precise differentiation of the saccular duct from the endolymphatic sinus was difficult when employing 3D T images, we assessed both portions as one unit in the present study. In human cases, the T images of the sulciform groove of the saccular duct and endolymphatic sinus from directly above using different bone T window levels on one image were consistent with cadaver specimen findings, and much more informative than the images employing a single bone T level. We previously reported the importance of assessing the reuniting duct, which is frequently involved in Meniere s lesions, and dislodged otoconia from the saccule into the reuniting duct [8]. s the saccular We greatly appreciate the valuable technical assistance of Dr Hiroshi radate of J. Morita Mfg orp. Declaration of interest: The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper. References [1] Guild. The circulation of the endolymph. m J nat 1927;39: [2] Kimura R, chuknecht HF. Membranous hydrops in the inner ear of the guinea pig after obliteration of the endolymphatic sac. ract Otorhinolaryngol 1965;27: [3] Kitamura K, chuknecht H, Kimura R. r hydrops is associated with collapsed saccule and ductus reuniens. nn Otol 1982;91:5 13. [4] tahle J, Wilbrand H. The vestibular aqueduct in patients with Meniere s disease. tomographic and clinical investigation. cta Otolaryngol 1974;78: [5] Yamamoto E, Mizukami, Isono M, Ohmura M, Hirono Y. Observation of the external aperture of the vestibular aqueduct using three-dimensional surface reconstruction imaging. aryngoscope 1991;101: [6] Yamane H, Takayama M, unami K, akamoto H, Mchizuki K, Inoue Y. Three-dimensional images of the reuniting duct using cone beam T. cta Otolaryngol 2009;129: [7] Yamane H, Takayama M, unami K, akamoto H, nniko M. ssessment of the reuniting duct by threedimensional T rendering. cta Otolaryngol 2009;129: [8] Yamane H, Takayama M, unami K, akamoto H, Imoto T, nniko M. lockage of reuniting duct in Meniere s disease. cta Otolaryngol 2010;130: [9] Kimura R, chuknecht HF. Membranous hydrops in the inner ear of the guinea pig after obliteration of the endolymphatic sac. ract Otorhinolaryngol 1965;27: [10] chuknecht HF, Rüther. lockage of longitudinal flow in the endolymphatic hydrops. Eur rch Otorhinolaryngol 1991;248:
Blockage pattern of longitudinal flow in Meniere s disease
 cta Oto-Laryngologica, 2013; 133: 692 698 ORIGINL RTICLE lockage pattern of longitudinal flow in Meniere s disease SKURKO TKNO 1, HIROYOSHI IGUCHI 1, HIRMORI SKMOTO 1, HIDEO YMNE 1 & MTTI NNIKO 2 1 Department
cta Oto-Laryngologica, 2013; 133: 692 698 ORIGINL RTICLE lockage pattern of longitudinal flow in Meniere s disease SKURKO TKNO 1, HIROYOSHI IGUCHI 1, HIRMORI SKMOTO 1, HIDEO YMNE 1 & MTTI NNIKO 2 1 Department
Ear. Utricle & saccule in the vestibule Connected to each other and to the endolymphatic sac by a utriculosaccular duct
 Rahaf Jreisat *You don t have to go back to the slides. Ear Inner Ear Membranous Labyrinth It is a reflection of bony labyrinth but inside. Membranous labyrinth = set of membranous tubes containing sensory
Rahaf Jreisat *You don t have to go back to the slides. Ear Inner Ear Membranous Labyrinth It is a reflection of bony labyrinth but inside. Membranous labyrinth = set of membranous tubes containing sensory
Bony and membranous labyrinth. Vestibular system. János Hanics M.D.
 Bony and membranous labyrinth. Vestibular system. János Hanics M.D. The position of the inner ear The labyrinthes of the inner ear - Continuous cavity system in the petrous part of temporal bone - Cavity
Bony and membranous labyrinth. Vestibular system. János Hanics M.D. The position of the inner ear The labyrinthes of the inner ear - Continuous cavity system in the petrous part of temporal bone - Cavity
Visualization of the membranous structures of the inner ear
 Published April 3, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1036 REVIEW ARTICLE J.I. Lane R.J. Witte B. Bolster M.A. Bernstein K. Johnson J. Morris State of the Art: 3T Imaging of the Membranous Labyrinth SUMMARY: This article
Published April 3, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1036 REVIEW ARTICLE J.I. Lane R.J. Witte B. Bolster M.A. Bernstein K. Johnson J. Morris State of the Art: 3T Imaging of the Membranous Labyrinth SUMMARY: This article
AUDITORY APPARATUS. Mr. P Mazengenya. Tel 72204
 AUDITORY APPARATUS Mr. P Mazengenya Tel 72204 Describe the anatomical features of the external ear Describe the tympanic membrane (ear drum) Describe the walls of the middle ear Outline the structures
AUDITORY APPARATUS Mr. P Mazengenya Tel 72204 Describe the anatomical features of the external ear Describe the tympanic membrane (ear drum) Describe the walls of the middle ear Outline the structures
Anatomy of the Ear Region. External ear Middle ear Internal ear
 Ear Lecture Objectives Make a list of structures making the external, middle, and internal ear. Discuss the features of the external auditory meatus and tympanic membrane. Describe the shape, position,
Ear Lecture Objectives Make a list of structures making the external, middle, and internal ear. Discuss the features of the external auditory meatus and tympanic membrane. Describe the shape, position,
Meniere s disease and Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
 Meniere s disease and Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Tsutomu Nakashima 1,2 1 Ichinomiya Medical Treatment & Habilitation Center, Ichinomiya, Japan 2 Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Nagoya University,
Meniere s disease and Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Tsutomu Nakashima 1,2 1 Ichinomiya Medical Treatment & Habilitation Center, Ichinomiya, Japan 2 Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Nagoya University,
Morphological Aspects of Inner Ear Disease
 Morphological Aspects of Inner Ear Disease Yasuya Nomura Morphological Aspects of Inner Ear Disease Yasuya Nomura President The Society for Promotion of International Oto-Rhino-Laryngology Tokyo, Japan
Morphological Aspects of Inner Ear Disease Yasuya Nomura Morphological Aspects of Inner Ear Disease Yasuya Nomura President The Society for Promotion of International Oto-Rhino-Laryngology Tokyo, Japan
The Temporal Bone Anatomy & Pathology
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego The Temporal Bone Anatomy & Pathology John R. Hesselink, M.D. Temporal Bone Axial View Temporal Bone Coronal View Longitudinal Fracture The Temporal
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego The Temporal Bone Anatomy & Pathology John R. Hesselink, M.D. Temporal Bone Axial View Temporal Bone Coronal View Longitudinal Fracture The Temporal
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium!
 Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! Chapter 17 Part 2 Special Senses! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium!
 Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Taste buds Gustatory cells extend taste hairs through a narrow taste pore
 The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
3D Accuitomo Clinical Case Evidence
 3D Accuitomo Clinical Case Evidence The Advantages of DVT for Ear-, Nose- & Throat-Diagnostic Thinking ahead. Focused on life. Editorial Dear Colleagues, Index of Contents I am very happy to present you
3D Accuitomo Clinical Case Evidence The Advantages of DVT for Ear-, Nose- & Throat-Diagnostic Thinking ahead. Focused on life. Editorial Dear Colleagues, Index of Contents I am very happy to present you
Otoconia: Calcium carbonate crystals Gelatinous mass. Cilia. Hair cells. Vestibular nerve. Vestibular ganglion
 VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Balance/Equilibrium) The vestibular stimulus is provided by Earth s, and. Located in the of the inner ear, in two components: 1. Vestibular sacs - gravity & head direction 2. Semicircular
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Balance/Equilibrium) The vestibular stimulus is provided by Earth s, and. Located in the of the inner ear, in two components: 1. Vestibular sacs - gravity & head direction 2. Semicircular
1. Axial view, left temporal bone. Plane through the upper antrum (A), superior semicircular canal (SSC) and IAC.
 PA IAC SSC A 1. Axial view, left temporal bone. Plane through the upper antrum (A), superior semicircular canal (SSC) and IAC. IAC VII M I LSC Plane through the IAC, malleus head and incus and the lateral
PA IAC SSC A 1. Axial view, left temporal bone. Plane through the upper antrum (A), superior semicircular canal (SSC) and IAC. IAC VII M I LSC Plane through the IAC, malleus head and incus and the lateral
Anatomy of the ear: Lymphatics
 Anatomy of the ear: 1. External ear which consist of auricle and external auditory canal. The auricle has a framework of cartilage except the lobule, the skin is closely adherent to perichonderium at the
Anatomy of the ear: 1. External ear which consist of auricle and external auditory canal. The auricle has a framework of cartilage except the lobule, the skin is closely adherent to perichonderium at the
Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Ear Lab
 Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Ear Lab 1. Launch the view! Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Eye and Ear Lab section. Launch Augmented Reality mode and scan the
Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Ear Lab 1. Launch the view! Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Eye and Ear Lab section. Launch Augmented Reality mode and scan the
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR
 Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Pediatric Temporal Bone
 Pediatric Temporal Bone Suresh K. Mukherji, MD, FACR Professor and Chief of Neuroradiology Professor of Radiology, Otolaryngology Head Neck Surgery, Radiation Oncology and Periodontics & Oral Medicine
Pediatric Temporal Bone Suresh K. Mukherji, MD, FACR Professor and Chief of Neuroradiology Professor of Radiology, Otolaryngology Head Neck Surgery, Radiation Oncology and Periodontics & Oral Medicine
15 Marzo 2014 Aspetti radiologici dei disordini vestibolari: approccio multidisciplinare
 15 Marzo 2014 Aspetti radiologici dei disordini vestibolari: approccio multidisciplinare MR Imaging of inner ear endo-perilymphatic spaces at 3T after intratympanic contrast agent administration in Definite
15 Marzo 2014 Aspetti radiologici dei disordini vestibolari: approccio multidisciplinare MR Imaging of inner ear endo-perilymphatic spaces at 3T after intratympanic contrast agent administration in Definite
THE COCHLEA AND AUDITORY PATHWAY
 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD February 23, 2012 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea
Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD February 23, 2012 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea
COCHLEAR IMPLANTS Aetiology of Deafness. Bruce Black MD
 COCHLEAR IMPLANTS Aetiology of Deafness Heterochromia iridis. Cases may be healthy or associated with a variety of conditions, e.g. Waardenburg syndrome. Waardenburg syndrome. Note the snowy lock of hair
COCHLEAR IMPLANTS Aetiology of Deafness Heterochromia iridis. Cases may be healthy or associated with a variety of conditions, e.g. Waardenburg syndrome. Waardenburg syndrome. Note the snowy lock of hair
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR. Assignment: Head to Toe Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
 Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Professor.Dr. M.K.Rajasekar MS., DLO.,
 VESTIBULAR SYSTEM ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Professor.Dr. M.K.Rajasekar MS., DLO., Life is hard for those who don t have a VOR During a walk I found too much motion in my visual picture of the surroundings
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Professor.Dr. M.K.Rajasekar MS., DLO., Life is hard for those who don t have a VOR During a walk I found too much motion in my visual picture of the surroundings
A&P 1. Ear, Hearing & Equilibrium Lab. Basic Concepts. These notes follow Carl s Talk at the beginning of lab
 A&P 1 Ear, Hearing & Equilibrium Lab Basic Concepts These notes follow Carl s Talk at the beginning of lab In this "Lab Exercise Guide", we will be looking at the basics of hearing and equilibrium. NOTE:
A&P 1 Ear, Hearing & Equilibrium Lab Basic Concepts These notes follow Carl s Talk at the beginning of lab In this "Lab Exercise Guide", we will be looking at the basics of hearing and equilibrium. NOTE:
Clinical Characteristics of Labyrinthine Concussion
 online ML Comm ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Audiol 2013;17:13-17 pissn 2092-9862 / eissn 2093-3797 http://dx.doi.org/10.7874/kja.2013.17.1.13 Clinical Characteristics of Labyrinthine Concussion Mi Suk Choi,
online ML Comm ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Audiol 2013;17:13-17 pissn 2092-9862 / eissn 2093-3797 http://dx.doi.org/10.7874/kja.2013.17.1.13 Clinical Characteristics of Labyrinthine Concussion Mi Suk Choi,
Vestibular Function and Anatomy. UTMB Grand Rounds April 14, 2004 Gordon Shields, MD Arun Gadre, MD
 Vestibular Function and Anatomy UTMB Grand Rounds April 14, 2004 Gordon Shields, MD Arun Gadre, MD System of balance Membranous and bony labyrinth embedded in petrous bone 5 distinct end organs 3 semicircular
Vestibular Function and Anatomy UTMB Grand Rounds April 14, 2004 Gordon Shields, MD Arun Gadre, MD System of balance Membranous and bony labyrinth embedded in petrous bone 5 distinct end organs 3 semicircular
A&P 1. Ear, Hearing & Equilibrium Lab. Basic Concepts. Pre-lab Exercises
 A&P 1 Ear, Hearing & Equilibrium Lab Basic Concepts Pre-lab Exercises In this "Lab Exercise Guide", we will be looking at the basics of hearing and equilibrium. NOTE: these notes do not follow the order
A&P 1 Ear, Hearing & Equilibrium Lab Basic Concepts Pre-lab Exercises In this "Lab Exercise Guide", we will be looking at the basics of hearing and equilibrium. NOTE: these notes do not follow the order
THE COCHLEA AND AUDITORY PATHWAY
 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD April 14, 2010 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea HyperBrain
Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD April 14, 2010 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea HyperBrain
High Signal from the Otic Labyrinth on Onenhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 High Signal from the Otic Labyrinth on Onenhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging JaneL. Weissman, 1 Hugh D. Curtin, 1 3 Barry E. Hirsch, 2 and William L. Hirsch, Jr. 1 Summary: High signal from the otic labyrinth
High Signal from the Otic Labyrinth on Onenhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging JaneL. Weissman, 1 Hugh D. Curtin, 1 3 Barry E. Hirsch, 2 and William L. Hirsch, Jr. 1 Summary: High signal from the otic labyrinth
European Radiology Experimental
 Venkatasamy et al. European Radiology Experimental (2017) 1:14 DOI 10.1186/s41747-017-0020-7 European Radiology Experimental ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Imaging of the saccule for the diagnosis of endolymphatic
Venkatasamy et al. European Radiology Experimental (2017) 1:14 DOI 10.1186/s41747-017-0020-7 European Radiology Experimental ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Imaging of the saccule for the diagnosis of endolymphatic
syndrome (LEDS) and its associated anomalies, with clinical features.
 Relationship of the rea Measurement of the Large Endolymphatic Duct and Sac Syndrome as well as the Clinical Symptoms with CT and MR Imaging Results 1 Ji-Sang Park, M.D., Hyun Sook Hong, M.D., Jong-Sea
Relationship of the rea Measurement of the Large Endolymphatic Duct and Sac Syndrome as well as the Clinical Symptoms with CT and MR Imaging Results 1 Ji-Sang Park, M.D., Hyun Sook Hong, M.D., Jong-Sea
THE EAR AND HEARING Be sure you have read and understand Chapter 16 before beginning this lab. INTRODUCTION: hair cells outer ear tympanic membrane
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
Decompression of the Endolymphatic Sac: Vertigo and Hearing Analysis
 Original Article Decompression of the Endolymphatic Sac: Vertigo and Hearing Analysis Nelson Álvares Cruz Filho*, José Evandro P. de Aquino**, Tobias Garcia Torres***. * Doctoral Degree in Otorhinolaryngology
Original Article Decompression of the Endolymphatic Sac: Vertigo and Hearing Analysis Nelson Álvares Cruz Filho*, José Evandro P. de Aquino**, Tobias Garcia Torres***. * Doctoral Degree in Otorhinolaryngology
Case Report An Unusual Case of Bilateral Agenesis of the Cochlear Nerves
 Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2012, rticle D 581920, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/581920 Case Report n Unusual Case of Bilateral genesis of the Cochlear Nerves Vítor Yamashiro Rocha oares, 1
Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2012, rticle D 581920, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/581920 Case Report n Unusual Case of Bilateral genesis of the Cochlear Nerves Vítor Yamashiro Rocha oares, 1
J.P.S. Bakshi Manual of Ear, Nose and Throat
 J.P.S. Bakshi Manual of Ear, Nose and Throat Reading excerpt Manual of Ear, Nose and Throat of J.P.S. Bakshi Publisher: B. Jain http://www.narayana-publishers.com/b5603 Copying excerpts is not permitted.
J.P.S. Bakshi Manual of Ear, Nose and Throat Reading excerpt Manual of Ear, Nose and Throat of J.P.S. Bakshi Publisher: B. Jain http://www.narayana-publishers.com/b5603 Copying excerpts is not permitted.
Quantitative evaluation of endolymphatic hydrops and acceptance testing in patients with Menière's disease
 Quantitative evaluation of endolymphatic hydrops and acceptance testing in patients with Menière's disease Award: Certificate of Merit Poster No.: C-0185 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Quantitative evaluation of endolymphatic hydrops and acceptance testing in patients with Menière's disease Award: Certificate of Merit Poster No.: C-0185 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
The Ear. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The Ear Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Ear The ear consists of the external ear; the middle ear (tympanic cavity); and the internal ear (labyrinth), which contains
The Ear Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Ear The ear consists of the external ear; the middle ear (tympanic cavity); and the internal ear (labyrinth), which contains
Segmentation and reconstruction of the 3D geometry of the middle and inner ear
 Segmentation and reconstruction of the 3D geometry of the middle and inner ear Yanfei Lu 1,* 1 Warsaw University of Technology, Faculty of Production Engineering, Institute of Mechanics and Printing, Department
Segmentation and reconstruction of the 3D geometry of the middle and inner ear Yanfei Lu 1,* 1 Warsaw University of Technology, Faculty of Production Engineering, Institute of Mechanics and Printing, Department
Visualisation of the Cochlea Implant/Tissue Interface
 Visualisation of the Cochlea Implant/Tissue Interface Christopher Wong 1, 4, Ian S. Curthoys 2, Stephen O Leary 3,4, Allan S. Jones 1 1 Australian Centre for Microscopy and Microanalysis, University of
Visualisation of the Cochlea Implant/Tissue Interface Christopher Wong 1, 4, Ian S. Curthoys 2, Stephen O Leary 3,4, Allan S. Jones 1 1 Australian Centre for Microscopy and Microanalysis, University of
Chapter 15 Hearing & Equilibrium
 Chapter 15 Hearing & Equilibrium ANATOMY OF THE OUTER EAR EAR PINNA is the outer ear it is thin skin covering elastic cartilage. It directs incoming sound waves to the EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL, which is
Chapter 15 Hearing & Equilibrium ANATOMY OF THE OUTER EAR EAR PINNA is the outer ear it is thin skin covering elastic cartilage. It directs incoming sound waves to the EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL, which is
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing
 Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
The Relationship Between Endolymphatic Hydrops in the Vestibule and Low-Frequency Air-Bone Gaps
 The Laryngoscope VC 2017 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Relationship Between Endolymphatic Hydrops in the Vestibule and Low-Frequency Air-Bone Gaps Satofumi
The Laryngoscope VC 2017 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Relationship Between Endolymphatic Hydrops in the Vestibule and Low-Frequency Air-Bone Gaps Satofumi
Radiologic Evaluation of Petrous Apex Masses. Pavan Kavali, MS-IV Morehouse School of Medicine November 16, 2009
 Radiologic Evaluation of Petrous Apex Masses Pavan Kavali, MS-IV Morehouse School of Medicine November 16, 2009 Roadmap Petrous Apex Anatomy Patient D.S.: Clinical Presentation Differential diagnosis of
Radiologic Evaluation of Petrous Apex Masses Pavan Kavali, MS-IV Morehouse School of Medicine November 16, 2009 Roadmap Petrous Apex Anatomy Patient D.S.: Clinical Presentation Differential diagnosis of
to vibrate the fluid. The ossicles amplify the pressure. The surface area of the oval window is
 Page 1 of 6 Question 1: How is the conduction of sound to the cochlea facilitated by the ossicles of the middle ear? Answer: Sound waves traveling through air move the tympanic membrane, which, in turn,
Page 1 of 6 Question 1: How is the conduction of sound to the cochlea facilitated by the ossicles of the middle ear? Answer: Sound waves traveling through air move the tympanic membrane, which, in turn,
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr.
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
Structure, Energy Transmission and Function. Gross Anatomy. Structure, Function & Process. External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer Ear
 Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
HISAKUNI FUKUOKA 1, YUTAKA TAKUMI 1, KEITA TSUKADA 1, MAIKO MIYAGAWA 1, TOMOHIRO OGUCHI 1, HITOSHI UEDA 2, MASUMI KADOYA 2 & SHIN-ICHI USAMI 1
 Acta Oto-Laryngologica, 2012; 132: 141 145 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the diagnostic value of 3 T MRI after intratympanic injection of GBCA, electrocochleography, and the glycerol test in patients
Acta Oto-Laryngologica, 2012; 132: 141 145 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the diagnostic value of 3 T MRI after intratympanic injection of GBCA, electrocochleography, and the glycerol test in patients
NIDCD NATIONAL TEMPORAL BONE, HEARING AND BALANCE PATHOLOGY RESOURCE REGISTRY
 NIDCD NATIONAL TEMPORAL BONE, HEARING AND BALANCE PATHOLOGY RESOURCE REGISTRY Guidelines for Removal of Temporal Bones for Pathological Study The temporal bones should be removed as soon as possible. If
NIDCD NATIONAL TEMPORAL BONE, HEARING AND BALANCE PATHOLOGY RESOURCE REGISTRY Guidelines for Removal of Temporal Bones for Pathological Study The temporal bones should be removed as soon as possible. If
MR Evaluation of Vestibulocochlear Anomalies Associated with Large Endolymphatic Duct and Sac
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1435 1441, September 1999 MR Evaluation of Vestibulocochlear Anomalies Associated with Large Endolymphatic Duct and Sac H. Christian Davidson, H. Ric Harnsberger, Marc M. Lemmerling,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1435 1441, September 1999 MR Evaluation of Vestibulocochlear Anomalies Associated with Large Endolymphatic Duct and Sac H. Christian Davidson, H. Ric Harnsberger, Marc M. Lemmerling,
Flow behaviour in normal and Meniere s disease of endolymphatic fluid inside the inner ear
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Flow behaviour in normal and Meniere s disease of endolymphatic fluid inside the inner ear To cite this article: Muhammad Sufyan
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Flow behaviour in normal and Meniere s disease of endolymphatic fluid inside the inner ear To cite this article: Muhammad Sufyan
Presentation On SENSATION. Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur
 Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
The Senses. Chapter 10 7/8/11. Introduction
 Chapter 10 The Senses Introduction A. Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment and stimulate neurons to send nerve impulses to the brain. B. A sensation is formed based on the sensory input.
Chapter 10 The Senses Introduction A. Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment and stimulate neurons to send nerve impulses to the brain. B. A sensation is formed based on the sensory input.
Visualization of Endolymphatic Hydrops after Intratympanic Injection of Gd-DTPA: Comparison of 2D and 3D Real Inversion Recovery Imaging
 Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 101 106, 2011 MAJOR PAPER Visualization of Endolymphatic Hydrops after Intratympanic Injection of Gd-DTPA: Comparison of 2D and 3D Real Inversion Recovery Imaging
Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 101 106, 2011 MAJOR PAPER Visualization of Endolymphatic Hydrops after Intratympanic Injection of Gd-DTPA: Comparison of 2D and 3D Real Inversion Recovery Imaging
What is the effect on the hair cell if the stereocilia are bent away from the kinocilium?
 CASE 44 A 53-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of feeling like the room is spinning, dizziness, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, and fullness in both ears. He states
CASE 44 A 53-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of feeling like the room is spinning, dizziness, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, and fullness in both ears. He states
Effects of Hyperbaric Therapy on Function and Morphology of Guinea Pig Cochlea with Endolymphatic Hydrops
 Otology & Neurotology 25:553 558 2004, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Effects of Hyperbaric Therapy on Function and Morphology of Guinea Pig Cochlea with Endolymphatic Hydrops Fang-Lu Chi, Qin Liang, and
Otology & Neurotology 25:553 558 2004, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Effects of Hyperbaric Therapy on Function and Morphology of Guinea Pig Cochlea with Endolymphatic Hydrops Fang-Lu Chi, Qin Liang, and
Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism
 Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism Objectives (1) Anatomy of the inner ear Functions of the cochlear and vestibular systems Three compartments within the cochlea and membranes
Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism Objectives (1) Anatomy of the inner ear Functions of the cochlear and vestibular systems Three compartments within the cochlea and membranes
Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear
 Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear - The ear is an organ with 2 functions: Hearing. Maintenance of equilibrium/balance. - The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear. Middle ear (which is also known
Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear - The ear is an organ with 2 functions: Hearing. Maintenance of equilibrium/balance. - The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear. Middle ear (which is also known
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology I. Professor Dave Furness Keele University
 Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology I Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of these lectures Introduction to gross anatomy of the cochlea Focus (1) on
Cochlear anatomy, function and pathology I Professor Dave Furness Keele University d.n.furness@keele.ac.uk Aims and objectives of these lectures Introduction to gross anatomy of the cochlea Focus (1) on
What is Meniere's disease? What causes Meniere's disease?
 NIH Publication No 95-3403 November 1994 What is Meniere's disease? Meniere's disease is an abnormality of the inner ear causing a host of symptoms, including vertigo or severe dizziness, tinnitus or a
NIH Publication No 95-3403 November 1994 What is Meniere's disease? Meniere's disease is an abnormality of the inner ear causing a host of symptoms, including vertigo or severe dizziness, tinnitus or a
Section 1 EAR. Section Outlines
 Section 1 EAR Section Outlines Development of the Ear Anatomy of the Ear Physiology of the Ear History Taking with Symptomatology of Ear Diseases Examination of the Ear Congenital Diseases of the External
Section 1 EAR Section Outlines Development of the Ear Anatomy of the Ear Physiology of the Ear History Taking with Symptomatology of Ear Diseases Examination of the Ear Congenital Diseases of the External
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear
 ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
Cochlear Implant Failure: Imaging Evaluation of the Electrode Course
 Clinical Radiology (2003) 58: 288 293 doi:10.1016/s0009-9260(02)00523-8, available online at www.sciencedirect.com Pictorial Review Cochlear Implant Failure: Imaging Evaluation of the Electrode Course
Clinical Radiology (2003) 58: 288 293 doi:10.1016/s0009-9260(02)00523-8, available online at www.sciencedirect.com Pictorial Review Cochlear Implant Failure: Imaging Evaluation of the Electrode Course
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
7. Sharp perception or vision 8. The process of transferring genetic material from one cell to another by a plasmid or bacteriophage
 1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1
 SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
For this lab you will use parts of Exercise #18 in your Wise lab manual. Please be sure to read those sections before coming to lab
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise The Eye and Ear Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 17 For this lab you will use parts
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise The Eye and Ear Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 17 For this lab you will use parts
Histology of Ear. Histology Department Medical Faculty University of Sumatera Utara 2008
 Histology of Ear Histology Department Medical Faculty University of Sumatera Utara 2008 References: Gartner LP, Hiatt JL. Color textbook of histology. 2 nd ed. Philadelphia. WB Saunders company. 2001 Kierszenbaum
Histology of Ear Histology Department Medical Faculty University of Sumatera Utara 2008 References: Gartner LP, Hiatt JL. Color textbook of histology. 2 nd ed. Philadelphia. WB Saunders company. 2001 Kierszenbaum
The cochlea: auditory sense. The cochlea: auditory sense
 Inner ear apparatus 1- Vestibule macula and sacculus sensing acceleration of the head and direction of gravity 2- Semicircular canals mainly for sensing direction of rotation of the head 1 3- cochlea in
Inner ear apparatus 1- Vestibule macula and sacculus sensing acceleration of the head and direction of gravity 2- Semicircular canals mainly for sensing direction of rotation of the head 1 3- cochlea in
Hearing Function After Intratympanic Application of Gadolinium- Based Contrast Agent: A Long-term Evaluation
 The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Hearing Function After Intratympanic Application of Gadolinium- Based Contrast Agent: A Long-term Evaluation
The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Hearing Function After Intratympanic Application of Gadolinium- Based Contrast Agent: A Long-term Evaluation
Delayed Endolymphatic Hydrops: Episodic Vertigo of Delayed Onset after Profound Inner Ear Hearing Loss
 Delayed Endolymphatic Hydrops: Episodic Vertigo of Delayed Onset after Profound Inner Ear Hearing Loss Tamio Kamei 1, MD, PhD and Kenji Watanabe 2, MD 1 Professor emeritus at Gunma University, Japan 2
Delayed Endolymphatic Hydrops: Episodic Vertigo of Delayed Onset after Profound Inner Ear Hearing Loss Tamio Kamei 1, MD, PhD and Kenji Watanabe 2, MD 1 Professor emeritus at Gunma University, Japan 2
87th TEMPORAL BONE DISSECTION COURSE
 87th TEMPORAL BONE DISSECTION COURSE Endorsed by the European Academy of Otology and Neuro-Otology, Royal European Academy of Doctors and with the support of Clarós Foundation BARCELONA, SPAIN November
87th TEMPORAL BONE DISSECTION COURSE Endorsed by the European Academy of Otology and Neuro-Otology, Royal European Academy of Doctors and with the support of Clarós Foundation BARCELONA, SPAIN November
The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect. absolute threshold. Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information.
 absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
Progression of Endolymphatic Hydrops in Ménière s Disease as Evaluated by Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Otology & Neurotology 32:1152Y1157 Ó 2011, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Progression of Endolymphatic Hydrops in Ménière s Disease as Evaluated by Magnetic Resonance Imaging *Francesco Fiorino, Francesca
Otology & Neurotology 32:1152Y1157 Ó 2011, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Progression of Endolymphatic Hydrops in Ménière s Disease as Evaluated by Magnetic Resonance Imaging *Francesco Fiorino, Francesca
The Sense Organs 10/13/2016. The Human Eye. 1. Sclera 2. Choroid 3. Retina. The eye is made up of three layers:
 The human body gathers information from the outside world by using the five senses of: The Sense Organs 12.3 Sight Hearing Taste Smell Touch This information is essential in helping the body maintain homeostasis.
The human body gathers information from the outside world by using the five senses of: The Sense Organs 12.3 Sight Hearing Taste Smell Touch This information is essential in helping the body maintain homeostasis.
Morphologic examination of the temporal bone by cone beam computed tomography: Comparison with multislice helical computed tomography
 European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2011) 128, 230 235 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Morphologic examination of the temporal bone by cone beam computed tomography: Comparison with multislice
European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2011) 128, 230 235 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Morphologic examination of the temporal bone by cone beam computed tomography: Comparison with multislice
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
 COCHLEAR IMPLANTATION: A SURGEON S PERSPECTIVE Ravi N. Samy, M.D., F.A.C.S. Ravi.Samy@UC.edu Director, Adult Cochlear Implant Program Program Director, Neurotology Fellowship CONFLICTS OF INTEREST RESEARCH
COCHLEAR IMPLANTATION: A SURGEON S PERSPECTIVE Ravi N. Samy, M.D., F.A.C.S. Ravi.Samy@UC.edu Director, Adult Cochlear Implant Program Program Director, Neurotology Fellowship CONFLICTS OF INTEREST RESEARCH
The Visible Ear Simulator Dissection Manual.
 The Visible Ear Simulator Dissection Manual. Stereoscopic Tutorialized Version 3.1, August 2017 Peter Trier Mikkelsen, the Alexandra Institute A/S, Aarhus, Denmark Mads Sølvsten Sørensen & Steven Andersen,
The Visible Ear Simulator Dissection Manual. Stereoscopic Tutorialized Version 3.1, August 2017 Peter Trier Mikkelsen, the Alexandra Institute A/S, Aarhus, Denmark Mads Sølvsten Sørensen & Steven Andersen,
84th TEMPORAL BONE DISSECTION COURSE
 84th TEMPORAL BONE DISSECTION COURSE Endorsed by the European Academy of Otology and Neuro-Otology, Royal European Academy of Doctors and with the support of Clarós Foundation BARCELONA, SPAIN March 5-6,
84th TEMPORAL BONE DISSECTION COURSE Endorsed by the European Academy of Otology and Neuro-Otology, Royal European Academy of Doctors and with the support of Clarós Foundation BARCELONA, SPAIN March 5-6,
Anomalous Facial Nerve Canal with Cochlear Malformations
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:838 844, May 2001 Anomalous Facial Nerve Canal with Cochlear Malformations Laura Vitale Romo and Hugh D. Curtin BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Anteromedial migration of the first segment
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:838 844, May 2001 Anomalous Facial Nerve Canal with Cochlear Malformations Laura Vitale Romo and Hugh D. Curtin BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Anteromedial migration of the first segment
Comparison of visualization of the middle ear by microscope and endoscopes of 30 and 45 through posterior tympanotomy
 Case report Videosurgery Comparison of visualization of the middle ear by microscope and endoscopes of 30 and 45 through posterior tympanotomy Emilia B. Karchier, Kazimierz Niemczyk, Adam Orłowski Department
Case report Videosurgery Comparison of visualization of the middle ear by microscope and endoscopes of 30 and 45 through posterior tympanotomy Emilia B. Karchier, Kazimierz Niemczyk, Adam Orłowski Department
Added Value of MDCT in Cochlear Parameters Assessment in Patients with Sensory Neural Hearing Loss Candidates for Cochlear Implantation
 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2018; 6(4): 33-39 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20180604.11 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN: 2330-832X (Online) Added Value of
International Journal of Medical Imaging 2018; 6(4): 33-39 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20180604.11 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN: 2330-832X (Online) Added Value of
Vestibular Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Vestibular Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the structure and function of the vestibular organs.
Vestibular Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the structure and function of the vestibular organs.
A surgical approach for a cochlear implant: An anatomical study
 A surgical approach for a cochlear implant: An anatomical study By GRAEME M. CLARK (Melbourne) Introduction THERE is now increased interest in the possibility of restoring brain and nerve function by applying
A surgical approach for a cochlear implant: An anatomical study By GRAEME M. CLARK (Melbourne) Introduction THERE is now increased interest in the possibility of restoring brain and nerve function by applying
The close anatomic relationship between the cochlea and
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.J. Young D.R. Shatzkes J.S. Babb A.K. Lalwani The Cochlear-Carotid Interval: Anatomic Variation and Potential Clinical Implications BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: A temporal bone CT study
ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.J. Young D.R. Shatzkes J.S. Babb A.K. Lalwani The Cochlear-Carotid Interval: Anatomic Variation and Potential Clinical Implications BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: A temporal bone CT study
Comparison of Image quality in temporal bone MRI at 3T using 2D selective RF excitation versus a routine SPACE sequence
 Comparison of Image quality in temporal bone MRI at 3T using 2D selective RF excitation versus a routine SPACE sequence Poster No.: C-1065 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit
Comparison of Image quality in temporal bone MRI at 3T using 2D selective RF excitation versus a routine SPACE sequence Poster No.: C-1065 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit
Abnormal direction of internal auditory canal and vestibulocochlear nerve
 Medicine Otorhinolaryngology fields Okayama University Year 2004 Abnormal direction of internal auditory canal and vestibulocochlear nerve Shin Kariya kazunori Nishizaki Hirofumi Akagi Michael M. Paparella
Medicine Otorhinolaryngology fields Okayama University Year 2004 Abnormal direction of internal auditory canal and vestibulocochlear nerve Shin Kariya kazunori Nishizaki Hirofumi Akagi Michael M. Paparella
Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Digge, R. K. N. Solanki, S. M. Paruthikunnan, D. S. Shah ; 1
 High-field MRI versus high-resolution CT of temporal bone in inner ear pathologies of children with bilateral profound sensorineural hearing loss: A pictorial essay. Poster No.: C-0867 Congress: ECR 2015
High-field MRI versus high-resolution CT of temporal bone in inner ear pathologies of children with bilateral profound sensorineural hearing loss: A pictorial essay. Poster No.: C-0867 Congress: ECR 2015
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences
 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Morphometric Analysis of Internal Acoustic Meatus and Its Surgically Relevant Relations in Human Temporal Bones. Rajanigandha Vadagaonkar
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Morphometric Analysis of Internal Acoustic Meatus and Its Surgically Relevant Relations in Human Temporal Bones. Rajanigandha Vadagaonkar
Review of Nervous System Anatomy
 For the real amazement, if you wish to be amazed, is this process. You start out as a single cell derived from the coupling of a sperm and an egg; this divides in two, then four, then eight, and so on,
For the real amazement, if you wish to be amazed, is this process. You start out as a single cell derived from the coupling of a sperm and an egg; this divides in two, then four, then eight, and so on,
Cochlear Implant Impedance Fluctuation in Ménière s Disease: A Case Study
 Otology & Neurotology xx:xx xx ß 2016, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Cochlear Implant Impedance Fluctuation in Ménière s Disease: A Case Study Celene McNeill and Kate Eykamp Healthy Hearing and Balance Care,
Otology & Neurotology xx:xx xx ß 2016, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Cochlear Implant Impedance Fluctuation in Ménière s Disease: A Case Study Celene McNeill and Kate Eykamp Healthy Hearing and Balance Care,
Title. Author(s) Takahashi, Haruo. Issue Date Right.
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation A case with posterior fossa epiderm symptoms caused by insufficiency of usefulness of free DICOM image view Takasaki, Kenji; Kumagami, Hidetaka
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation A case with posterior fossa epiderm symptoms caused by insufficiency of usefulness of free DICOM image view Takasaki, Kenji; Kumagami, Hidetaka
3D Cone beam CT & Digital Radiography Dedicated to Otorhinolaryngology
 3D Cone beam CT & Digital Radiography Dedicated to Otorhinolaryngology Multi-functional imaging solution3 RAYSCAN m is an unique 2-in-1 imaging solution, combining Cone Beam CT and Digital Radiography,
3D Cone beam CT & Digital Radiography Dedicated to Otorhinolaryngology Multi-functional imaging solution3 RAYSCAN m is an unique 2-in-1 imaging solution, combining Cone Beam CT and Digital Radiography,
Auditory System. Barb Rohrer (SEI )
 Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Lamb Temporal Bone as a Surgical Training Model of Round Window Cochlear Implant Electrode Insertion
 Otology & Neurotology 37:52 56 ß 2015, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Lamb Temporal Bone as a Surgical Training Model of Round Window Cochlear Implant Electrode Insertion Georgios Mantokoudis, Markus E. Huth,
Otology & Neurotology 37:52 56 ß 2015, Otology & Neurotology, Inc. Lamb Temporal Bone as a Surgical Training Model of Round Window Cochlear Implant Electrode Insertion Georgios Mantokoudis, Markus E. Huth,
An optical coherence tomography study for imaging the round window niche and the promontorium tympani
 An optical coherence tomography study for imaging the round window niche and the promontorium tympani T. Just *a, E. Lankenau b, G. Hüttmann b, H.W. Pau a a Department of Otorhinolaryngology, University
An optical coherence tomography study for imaging the round window niche and the promontorium tympani T. Just *a, E. Lankenau b, G. Hüttmann b, H.W. Pau a a Department of Otorhinolaryngology, University
Tumors of the Endolymphatic Sac in von Hippel Lindau Disease
 The new england journal of medicine brief report Tumors of the Endolymphatic Sac in von Hippel Lindau Disease Russell R. Lonser, M.D., H. Jeffrey Kim, M.D., John A. Butman, M.D., Ph.D., Alexander O. Vortmeyer,
The new england journal of medicine brief report Tumors of the Endolymphatic Sac in von Hippel Lindau Disease Russell R. Lonser, M.D., H. Jeffrey Kim, M.D., John A. Butman, M.D., Ph.D., Alexander O. Vortmeyer,
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
Sasan Dabiri, MD, Assistant Professor
 Sasan Dabiri, MD, Assistant Professor Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences October 2015 Outlines Anatomy of Vestibular System
Sasan Dabiri, MD, Assistant Professor Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences October 2015 Outlines Anatomy of Vestibular System
