Direct carotid-cavernous fistula and glaucoma: case reports
|
|
|
- Sharyl Foster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 D. Petraru et al Direct carotid-cavernous fistula and glaucoma Direct carotid-cavernous fistula and glaucoma: case reports D. Petraru 1, D. Costin 2, G. Mihalache nd Ophthalmological Clinic, Clinical Emergency Neurosurgical Hospital Iasi 2 University of Medicine and Pharmacy Gr.T. Popa Iasi, 2 nd Ophthalmological Clinic, Clinical Emergency Neurosurgical Hospital 3 University of Medicine and Pharmacy Gr.T. Popa Iasi, Romania Abstract A carotid-cavernous fistula is an abnormal communication between carotid artery system and the cavernous system. The causes that determines the onset of the fistula are trauma or spontaneous. The fistula receives venous blood from the eye and the brain, from the ophthalmic veins and the superficial middle cerebral vein. The abnormal shunt determines raised venous pressure on the cavernous sinus, determining ophthalmic veins stasis. It appear ocular congestion, raised intraocular pressure, exophthalmia, diplopia, decreased visual acuity or cranial nerves paralysis. Glaucoma is a potential complication that appear in carotid-cavernous fistula from increased pressure in the episcleral veins. Carotid-cavernous fistula diagnosis can be determined clinically and imagistically. This pathology is treated successfully in 90% of all cases, the mortality and morbidity rates are very low. This study presents two case reports, diagnosed with direct carotid-cavernous fistula and glaucoma. Keywords: direct carotid-cavernous fistula, glaucoma Direct carotid-cavernous fistula appears in 70-90% of all cases with carotidcavernous fistulae cited by Keltner et al. in 1987, Debrun et al. in (1) Direct fistula can be localized in any intracavernous portion of internal carotid artery. Iatrogenic fistulae are reported in transsphenoidal surgery of the pituitary gland or internal carotid artery lesion in endarterectomy or ethmoidal sinus surgery. Some direct fistulae can be caused by rupture of an intracavernous aneurysm. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, arterial hypertension or artheriosclerosis were associated with carotid-cavernous fistula.(2) Cerebral trauma causes 75% of carotidcavernous fistulae at young patients, with pulsatile exophthalmia. 25% of carotidcavernous fistulae are spontaneous, specially middle aged women with atherosclerosis. (3) Glaucoma is a potential complication of the direct untreated carotid-cavernous fistula, mentioned by Sugar and Meyer in 1940, and by Madsen in 1970, that appears in 30-50% of all cases.(3) Case I A 63 year old female patient, B.I., presented with ocular congestion that appears two weeks ago, retro-orbital mild pain and left eye diplopia. Clinical exam revealed the 6 th left nerve palsy, 3 mm exophthalmia, discreet orbital
2 Romanian Neurosurgery (2011) XIX bruit and dilated conjunctival vessels. On Goldmann tonometry the intraocular pressure was mm Hg. During hospitalization were administered topical ocular hipotensors and the diurnal pressure curve was assessed, the pressure normalized between 16 and 18 mm Hg. The MRIangiography revealed a left carotidcavernous fistula; the patient was transferred in a neurosurgical clinic. All ocular symptoms and signs resolved in four weeks after intravascular closure of the fistula with a detachable balloon ( Figure 1a, 1b). The patient continued the ocular hipotensors treatment during neurosurgical hospitalization. At eight weeks, the patient presents in the ophthalmological clinic for re-assessment, the intraocular pressure was between mm Hg, without antiglaucomatous medication. The ophthalmoscopic exam didn t revealed pathological findings of the cup-disc ratio, that was , the visual field was normal as well, regarding to her age. Case II A 25 year old male pacient, D.M., diagnosed with traumatic carotid-cavernous fistula, presented in the ophthalmological clinic with right eye chronic glaucoma. Clinical exam revealed a discreet right eye exophthalmia, dilated conjunctival vessels and the left anterior pole didn t present any pathological finding. On Goldmann tonometry, the intraocular pressure was between 32 and 38 mm Hg. The ophthalmoscopic exam on the right eye revealed a mild glaucomatous cupping, cup-disc ratio 0.6 and in the left eyes a normal aspect, without pathological cupping. The MRI-angiography revealed the presence of a carotid-cavernous fistula (Figure 2); the patient refused the neurosurgical treatment. Figure 1a Cerebral angiography of the carotidcavernous fistula Figure 1b Intravascular closure of the fistula with a detachable balloon During hospitalization we administered antiglaucomatous topical medication, intraocular pressure was above normal level (32-34 mm Hg); we performed filtering surgery (trabeculectomy) for intraocular pressure decrease; after surgery the intraocular pressure level normalize, between 16 and 18 mm Hg. At six weeks after the surgery, the patient had under antiglaucomatous topical treatment values of intraocular pressure between 14 and 16 mm Hg. The ophthalmoscopic exam revealed on the right eye a glaucomatous cupping, the left eye was normal. We prescribed antiglaucomatous topical therapy to continue on right eye and periodical ophthalmological assessment.
3 D. Petraru et al Direct carotid-cavernous fistula and glaucoma Figure 2 Cerebral angiography of the carotidcavernous fistula in case 2 Discussions Direct carotid-cavernous fistula has a frequency up to 90% of all carotidcavernous fistulae and glaucoma is a potential complication of untreated direct carotid-cavernous fistula. In 1970, Madsen mention untreated carotid-cavernous fistula and glaucoma association. (1) Henderson and Schneider find that glaucoma was diagnosed on 30-50% of all cases with untreated fistula. (1) The most common form is determined by the raise of pressure in episcleral veins. In 1973,Spencer et al. mention cases of patients diagnosed with direct carotidcavernous fistula and neovascular glaucoma, always associated with retinal chronic hypoxia and retinal neovascularization, after central retinal vein occlusion. (1) Ocular findings of the first patient are related with blood redistribution from the orbital veins, determining decreased arterial blood flow at the cranial nerves level, venous stasis in anterior and posterior circulation in the eye and the orbit, raised pressure in episcleral veins. Ocular findings are localized unilateral, same path with the fistula, may be bilateral or in rare cases contralateral. Ocular finding path depends of venous blood drainage thru cavernous sinus, especially the intercavernous system and the basilar system, with thrombosis at the sinus level or the superior ophthalmic vein. Trauma can determine bilateral cavernous sinus fistula. Carotid-cavernous fistulae (direct communications between internal carotid artery and the cavernous sinus) (4), determine a high blood flow, accompanied by unilateral or bilateral pulsatile exophthalmia, orbital bruit, ocular chemosis and diplopia. (5) Fistula associates with moderate or severe eyelid inflammation, cyanoses and palpebral derma thickening appear in chronic disease. (6) Ocular pulsation is caused by a pulsatile wave from the internal carotid artery level or the ophthalmic artery thru dilated ophthalmic veins. Orbital veins become tortuous and secondary congestion of the orbital soft tissue appears, increase of the venous pressure and decrease of the arterial perfusion, local hypoxia, that determines tissue edema and a certain degree of ophthalmoplegia, resulting in anterior segment ischemia. Conjunctival chemosis appears in almost all patients diagnosed with direct carotidcavernous fistula, preceeding the exophthalmia in most cases. (7) Dilation of the conjunctival vessels is the most obvious sign of this disease. Keratopathy is diagnosed frequently, associated with the exophthalmia. (8) Cornea can present an edematous aspect, due to secondary glaucoma or anterior segment ischemia. Diplopia is caused by common oculomotor nerves damage, ocular movement is limited, complete ophthalmoplegia can occur. Ophthalmoplegia cand be caused by the damage of one or multiple oculomotor
4 Romanian Neurosurgery (2011) XIX nerves due to compression or ischemia; the most affected oculomotor nerve is the abducens nerve, but also the trochlear nerve can be affected, which is situated in the profound layer of the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus. The decrease in the visual acuity produces immediately, being caused by optic nerve damage or it can appear late due to vitreous hemorrhage, retinal dysfunction, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy or corneal ulcer. Visual acuity decrease pathology is explained by retinal dysfunction, decreased perfusion pressure in ophthalmic artery and increased venous pressure. The result is chronic hypoxia of the retinal cells. The eye fundus exam reveals dilated veins with spontaneous pulsation, optic disc swelling, retinal hemorrhage, venous stasis retinopathy or venous occlusion. Sever pain and local inflammation can suggest ophthalmic vein thrombosis, which can be diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging or ocular echography. Ocular and orbital pain, facial hyperesthesia can be caused by compression of the maxillary and the ophthalmic trunks of trigeminal nerve at the cavernous sinus level. Glaucoma is a potential complication which can appear in direct carotidcavernous fistula. (1) The most common form of glaucoma is caused by increased pressure in the episcleral veins as we presented in the two cases. (8) Intraocular pressure is moderately raised (24 mm Hg), but cases cited have intraocular pressure up to mm Hg, the normal level being mm Hg, the fistula often associates with central retinal artery occlusion. Orbital congestion is associated with glaucoma, intraocular pressure in these cases being severely raised and the medical treatment is difficult. Neovascular glaucoma can appear in patients with carotid-cavernous fistula, following chronic retinal hypoxia, retinal neovascularization or after central retinal vein occlusion. In rare cases, some patients develop angle closure glaucoma by raised pressure in the orbital veins which determines choroidal and iris congestion with forward pulling of the iridolenticular diaphragm, determining angle closure. The diagnosis is based on the clinical findings: rapidly developed conjunctival chemosis, exophthalmia and ocular congestion. Patient can present a trauma in the past, am intracavernous aneurysm rupture or diplopia. The paraclinical exams used to establish the diagnosis are: tonometry, CT scan, MRI-angiography, ocular echography, cerebral angiography (which helps identifying the presence of the fistula). The optimal treatment of direct fistula is the closure of the abnormal communication with preserving of the internal carotid artery. There are many surgical options for closure: direct surgical closure of the affected intracavernous portion of the internal carotid artery, isobutyl-2- cyanoacrilate embolization, particles of polyvinyl alcohol or a detachable balloon placed in the cavernous sinus, in the arterial or venous path, thru inferior petrous sinus or superior ophthalmic vein, directly in cavernous sinus. (9) Once the balloon has reached the cavernous sinus it is inflated and detached determining fistula closure. The complications of this therapeutically method include transitory or permanent cranial nerve palsies, visual field loss or pseudo-aneurysm development. (10) It was mentioned in the literature spontaneous closure of fistula in 3 days up to 18 months in 10-60% of all patients. (1)
5 D. Petraru et al Direct carotid-cavernous fistula and glaucoma After the successfully closure of the fistula, almost all symptoms and ocular signs disappear or improve. (11) Ocular pulsation, eyelid edema, conjunctival chemosis, conjunctival vessels dilation, stasis retinopathy, optic disc swelling and raised intraocular pressure disappear immediately. Exophthalmia decreases but it may not disappear entirely. Similarly, the patients with ophthalmoplegia can have a normal motility and diplopia can disappear. The only symptom of the direct carotidcavernous fistula that don t improve is the visual acuity loss due to optic neuropathy, that s why the treatment must be commenced as urgent as possible that the irreversible optic nerve lesions don t appear. Glaucoma necessitated rapid treatment; ocular hypotensors were administered in the first case or the surgical treatment (trabeculectomy) in the second case. The therapy target was to normalize the intraocular pressure and to reduce ischemia and ocular necrosis. Beta adrenergic antagonists, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and alpha 2 agonists have reduced the intraocular pressure in the first case. Pilocarpine and prostaglandin analogues are not efficient in this case. Prostaglandin analogues treatment can be associated with episcleral venous dilation. Filtering surgery was efficient in the second case and made a stable, uniform decrease of the intraocular pressure, when the medical treatment cannot be administered, the patient refused it. In the second case, the trabeculectomy was the surgical method we choose: a scleral flap was created, two-thirds thickening, a rectangular shape (six by four mm), 1,5 mm advance in clear cornea, the profound scleral flap was excised, approximately 2 by 2 mm at the limboscleral junction (the gray zone), tissue that contain the trabecular meshwork. (12) When the trabeculectomy doesn t provide an efficiently result, we recommend the artificial drainage systems or the trabeculectomy augmented with antimetabolites (5-fluorouracile or mytomicin C). Conclussions Direct carotid-cavernous fistula doesn t necessitates rapid treatment, it can be delayed; the untreated fistula lead to progressive ocular symptoms. In months or years, this disease evolves to exophthalmia, chemosis and total visual acuity loss due to glaucoma, ischemic optic neuropathy. In the first case, ocular symptoms necessitate paraclinical exams which showed the carotid-cavernous fistula, surgically treated, the ocular symptomatology disappear after the surgical treatment. The other case with carotid-cavernous fistula necessitates filtering surgery for ocular pressure balance and visual parameters normalize because the patient refused the neurosurgical treatment and doesn t accept the anti-glaucomatous therapy. Even if the direct carotid-cavernous fistula doesn t present vital risk, it can produce intracerebral hemorrhage, ischemic optic neuropathy, secondary glaucoma and primary open angle glaucoma, diseases that without treatment determine irreversible visual loss. References 1. Neil R., Miller, M.D. Walsh and Hoyt s, Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology, 4th Edition Volume Four, 1982.
6 Romanian Neurosurgery (2011) XIX 2. Niamtu J 3rd, Campbell RL, Carotid cavernous fistula, Journal of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery 1982 Jan;40(1): Joel S. Glaser Neuro-ophthalmology, Third Edition, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Masaki Komiyama, Hideki Nakajima, Misao Nishikawa, and Masanori Kan, Traumatic Carotid Cavernous Sinus Fistula:Serial Angiographic Studies from the Day of Trauma, AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19: , October American Academy of Ophthalmology Basic and Clinic Science Course, San Francisco, 2004/vol. 6,7,8,9,11, Keltner JL, Satterfield D, Dublin AB, Lee BCP. Dural and carotid cavernous sinus fistulas.ophthalmology 1987; 94 : Anthony E. Harris, MD; Patrick G. McMenamin, Carotid Artery Cavernous Sinus Fistula, Archives of Otolaryngology- Head and Neck Surgery. 1984;110(9): John C.Morrison, Irvin P.Pollack Glaucoma, Science and Practice, Thieme, Yang ZJ, Li HW, Wu LG, Zheng JN, Zhang JD, Shi XW, Chu GR., Prognostic analysis and complications of traumatic carotid cavernous fistulas after treatment with detachable balloon and/or coil embolization ; Chin J.Traumatology 2004 Oct; 7(5): Stanley L Barnwell, Oisin R O Neill, Endovascular Therapy of Carotid Cavernous Fistulas, Endovascular Approach to Central Nervous System Disease, vol.5, nr.3, p.485, July, Philippe Hantsona Benoît Espeela, Jean-Michel Guéritb, Pierre Goffettec, Bilateral carotid-cavernous fistula following head trauma: Possible worsening of brain injury following balloon catheter occlusion? Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery,Volume 108, Issue 6, Pages (September 2006). 12.Kanski J., Jack, Clinical ophthalmology A Systematic Approach, , Elsevier Science Limited, 2003.
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
Carotid Cavernous Fistula
 Chief Complaint: Double vision. Carotid Cavernous Fistula Alex W. Cohen, MD, PhD; Richard Allen, MD, PhD May 14, 2010 History of Present Illness: A 46 year old female patient presented to the Oculoplastics
Chief Complaint: Double vision. Carotid Cavernous Fistula Alex W. Cohen, MD, PhD; Richard Allen, MD, PhD May 14, 2010 History of Present Illness: A 46 year old female patient presented to the Oculoplastics
Ophthalmoplegia in carotid cavernous sinus fistula
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1984, 68, 128-134 Ophthalmoplegia in carotid cavernous sinus fistula T. J. K. LEONARD, I. F. MOSELEY, AND M. D. SANDERS From the Departments ofneuro-ophthalmology and
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1984, 68, 128-134 Ophthalmoplegia in carotid cavernous sinus fistula T. J. K. LEONARD, I. F. MOSELEY, AND M. D. SANDERS From the Departments ofneuro-ophthalmology and
Ocular Manifestations and Prognosis of Secondary Glaucoma in Patients with Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 Ocular Manifestations and Prognosis of Secondary Glaucoma in Patients with Carotid-Cavernous Fistula Kiyotaka Ishijima*, Kenji Kashiwagi*, Kenichi Nakano*, Takashi Shibuya, Toyoaki Tsumura and Shigeo Tsukahara*
Ocular Manifestations and Prognosis of Secondary Glaucoma in Patients with Carotid-Cavernous Fistula Kiyotaka Ishijima*, Kenji Kashiwagi*, Kenichi Nakano*, Takashi Shibuya, Toyoaki Tsumura and Shigeo Tsukahara*
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetazolamide, in idiopathic intracranial hypertension, 49 52, 60 Angiography, computed tomography, in cranial nerve palsy, 103 107 digital
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetazolamide, in idiopathic intracranial hypertension, 49 52, 60 Angiography, computed tomography, in cranial nerve palsy, 103 107 digital
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment
 166 Chiriac et al Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*, St.M. Iencean, I. Poeata
166 Chiriac et al Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*, St.M. Iencean, I. Poeata
A neurysms arising from the cavernous portion of the
 863 PAPER Long term visual and neurological prognosis in patients with treated and untreated cavernous sinus aneurysms N Goldenberg-Cohen, C Curry, N R Miller, R J Tamargo, K P J Murphy... See end of article
863 PAPER Long term visual and neurological prognosis in patients with treated and untreated cavernous sinus aneurysms N Goldenberg-Cohen, C Curry, N R Miller, R J Tamargo, K P J Murphy... See end of article
Neovascular Glaucoma Associated with Cilioretinal Artery Occlusion Combined with Perfused Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
 Neovascular Glaucoma Associated with Cilioretinal Artery Occlusion Combined with Perfused Central Retinal Vein Occlusion Man-Seong Seo,* Jae-Moon Woo* and Jeong-Jin Seo *Department of Ophthalmology, Chonnam
Neovascular Glaucoma Associated with Cilioretinal Artery Occlusion Combined with Perfused Central Retinal Vein Occlusion Man-Seong Seo,* Jae-Moon Woo* and Jeong-Jin Seo *Department of Ophthalmology, Chonnam
Glaucoma Clinical Update. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012
 Glaucoma Clinical Update Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Objectives Understand the different categories of glaucoma Recognize the symptoms and signs of open angle and angle-closure
Glaucoma Clinical Update Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Objectives Understand the different categories of glaucoma Recognize the symptoms and signs of open angle and angle-closure
Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
 Pan et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0121-z CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION COMMENTARY Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
Pan et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0121-z CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION COMMENTARY Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience
 230 Chiriac et al - Superior ophthalmic vein approach The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin 1, Georgiana Ion
230 Chiriac et al - Superior ophthalmic vein approach The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin 1, Georgiana Ion
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA
 OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Departmental guidelines
 Michele Long Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Departmental guidelines Anatomy- cavernous sinus 2cm in
Michele Long Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Departmental guidelines Anatomy- cavernous sinus 2cm in
 measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
measure of your overall performance. An isolated glucose test is helpful to let you know what your sugar level is at one moment, but it doesn t tell you whether or not your diabetes is under adequate control
High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils
 High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils Guido Guglielmi, Fernando Viñuela, Gary Duckwiler, Jacques Dion, and Alfredo Stocker Summary: We present one case of
High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils Guido Guglielmi, Fernando Viñuela, Gary Duckwiler, Jacques Dion, and Alfredo Stocker Summary: We present one case of
Literature Review: Neurosurgery
 NANOS 2018 Kona, Hawaii Literature Review: Neurosurgery Neil R. Miller, MD FACS Frank B. Walsh Professor of Neuro-Ophthalmology Professor of Ophthalmology, Neurology & Neurosurgery Johns Hopkins University
NANOS 2018 Kona, Hawaii Literature Review: Neurosurgery Neil R. Miller, MD FACS Frank B. Walsh Professor of Neuro-Ophthalmology Professor of Ophthalmology, Neurology & Neurosurgery Johns Hopkins University
53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note.
 Case 1 Normal Tension Glaucoma 53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note. Table 1. Right Eye Left Eye Visual acuity 6/6 6/6 Ishihara
Case 1 Normal Tension Glaucoma 53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note. Table 1. Right Eye Left Eye Visual acuity 6/6 6/6 Ishihara
The Ishikawa Classification of Cavernous Sinus Lesions by Clinico-anatomical Findings
 The Ishikawa Classification of Cavernous Sinus Lesions by Clinico-anatomical Findings Mutsumi Yoshihara, Noriko Saito, Yoji Kashima and Hiroshi Ishikawa Department of Ophthalmology, Nihon University School
The Ishikawa Classification of Cavernous Sinus Lesions by Clinico-anatomical Findings Mutsumi Yoshihara, Noriko Saito, Yoji Kashima and Hiroshi Ishikawa Department of Ophthalmology, Nihon University School
Mild NPDR. Moderate NPDR. Severe NPDR
 Diabetic retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of blindness in adults aged 35-65 years-old. Hyperglycaemia is thought to cause increased retinal blood flow and abnormal metabolism in
Diabetic retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of blindness in adults aged 35-65 years-old. Hyperglycaemia is thought to cause increased retinal blood flow and abnormal metabolism in
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME)
 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 1 Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) Sadrina T. Shaw OMT I Student July 26, 2014 Advisor: Dr. Uwaydat Clinically Significant Macular Edema (CSME) 2
Ocular Lecture. Sue Bednar NP Ali Atwater PA-C
 Ocular Lecture Sue Bednar NP Ali Atwater PA-C Triaging Ocular Complaints Painful Eye/Red eye +/-blurry vision +/-visual loss +/-floaters +/-fevers If any of the above findings exist, pt is likely to have
Ocular Lecture Sue Bednar NP Ali Atwater PA-C Triaging Ocular Complaints Painful Eye/Red eye +/-blurry vision +/-visual loss +/-floaters +/-fevers If any of the above findings exist, pt is likely to have
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Mechanisms of presentation of caroticocavernous
 Brit.. Ophthal. (1970) 54, I86 Mechanisms of presentation of caroticocavernous fistulae EDWIN R. BICKERSTAFF The Midland CentreJor Neurosurgery and Neurology, Smethwick The clinical features of carotico-cavernous
Brit.. Ophthal. (1970) 54, I86 Mechanisms of presentation of caroticocavernous fistulae EDWIN R. BICKERSTAFF The Midland CentreJor Neurosurgery and Neurology, Smethwick The clinical features of carotico-cavernous
GNK485 The eye and related structures. Prof MC Bosman 2012
 GNK485 The eye and related structures Prof MC Bosman 2012 Surface anatomy Bony orbit Eyeball and Lacrimal apparatus Extra-ocular muscles Movements of the eye Innervation Arterial supply and venous drainage
GNK485 The eye and related structures Prof MC Bosman 2012 Surface anatomy Bony orbit Eyeball and Lacrimal apparatus Extra-ocular muscles Movements of the eye Innervation Arterial supply and venous drainage
Taiwan Journal of Ophthalmology
 Taiwan Journal of Ophthalmology 3 (2013) 168e172 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Taiwan Journal of Ophthalmology journal homepage: www.e-tjo.com Case report Central retinal vein occlusion
Taiwan Journal of Ophthalmology 3 (2013) 168e172 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Taiwan Journal of Ophthalmology journal homepage: www.e-tjo.com Case report Central retinal vein occlusion
Occipital lobe infarction: a rare presentation of bilateral giant cavernous carotid aneurysms: a case report
 Vanikieti et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:25 DOI 10.1186/s12886-018-0687-4 CASE REPORT Open Access Occipital lobe infarction: a rare presentation of bilateral giant cavernous carotid aneurysms: a case
Vanikieti et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:25 DOI 10.1186/s12886-018-0687-4 CASE REPORT Open Access Occipital lobe infarction: a rare presentation of bilateral giant cavernous carotid aneurysms: a case
Clinical Study Choroidal Thickness in Eyes with Unilateral Ocular Ischemic Syndrome
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 215, Article ID 62372, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/62372 Clinical Study Choroidal Thickness in Eyes with Unilateral Ocular Ischemic
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 215, Article ID 62372, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/62372 Clinical Study Choroidal Thickness in Eyes with Unilateral Ocular Ischemic
OCULAR MANIFESTATIONS OF SYSTEMIC DISEASES THUCANH MULTERER, MD
 OCULAR MANIFESTATIONS OF SYSTEMIC DISEASES THUCANH MULTERER, MD UNDERGRADUATE: Philadelphia College of Pharmacy and Science 1996 MEDICAL SCHOOL: MCP Hahnemann School of Medicine, Philadelphia PA 2000 RESIDENCY:
OCULAR MANIFESTATIONS OF SYSTEMIC DISEASES THUCANH MULTERER, MD UNDERGRADUATE: Philadelphia College of Pharmacy and Science 1996 MEDICAL SCHOOL: MCP Hahnemann School of Medicine, Philadelphia PA 2000 RESIDENCY:
LECTURE # 7 EYECARE REVIEW: PART III
 LECTURE # 7 EYECARE REVIEW: PART III HOW TO TRIAGE EYE EMERGENCIES STEVE BUTZON, O.D. EYECARE REVIEW: HOW TO TRIAGE EYE EMERGENCIES FOR PRIMARY CARE PHYSICIANS Steve Butzon, O.D. Member Director IDOC President
LECTURE # 7 EYECARE REVIEW: PART III HOW TO TRIAGE EYE EMERGENCIES STEVE BUTZON, O.D. EYECARE REVIEW: HOW TO TRIAGE EYE EMERGENCIES FOR PRIMARY CARE PHYSICIANS Steve Butzon, O.D. Member Director IDOC President
Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid Cavernous Fistula after Surgery for Maxillary Cancer
 Case Report J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (1) : 89-93, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.1206.001 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid Cavernous Fistula after
Case Report J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (1) : 89-93, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.1206.001 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid Cavernous Fistula after
Neuro-Ocular Grand Rounds
 Neuro-Ocular Grand Rounds Anthony B. Litwak,OD, FAAO VA Medical Center Baltimore, Maryland Dr. Litwak is on the speaker and advisory boards for Alcon and Zeiss Meditek COMMON OPTIC NEUROPATHIES THAT CAN
Neuro-Ocular Grand Rounds Anthony B. Litwak,OD, FAAO VA Medical Center Baltimore, Maryland Dr. Litwak is on the speaker and advisory boards for Alcon and Zeiss Meditek COMMON OPTIC NEUROPATHIES THAT CAN
Speaker Disclosure Statement. " Dr. Tim Maillet and Dr. Vladimir Kozousek have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
 Speaker Disclosure Statement Dr. Tim Maillet and Dr. Vladimir Kozousek have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Diabetes Morbidity Diabetes doubles the risk of stroke. Diabetes quadruples the risk of
Speaker Disclosure Statement Dr. Tim Maillet and Dr. Vladimir Kozousek have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Diabetes Morbidity Diabetes doubles the risk of stroke. Diabetes quadruples the risk of
Papilledema. Golnaz Javey, M.D. and Jeffrey J. Zuravleff, M.D.
 Papilledema Golnaz Javey, M.D. and Jeffrey J. Zuravleff, M.D. Papilledema specifically refers to optic nerve head swelling secondary to increased intracranial pressure (IICP). Optic nerve swelling from
Papilledema Golnaz Javey, M.D. and Jeffrey J. Zuravleff, M.D. Papilledema specifically refers to optic nerve head swelling secondary to increased intracranial pressure (IICP). Optic nerve swelling from
Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
Professor Helen Danesh-Meyer. Eye Institute Auckland
 Professor Helen Danesh-Meyer Eye Institute Auckland Bitten by Ophthalmology Emergencies Helen Danesh-Meyer, MBChB, MD, FRANZCO Sir William and Lady Stevenson Professor of Ophthalmology Head of Glaucoma
Professor Helen Danesh-Meyer Eye Institute Auckland Bitten by Ophthalmology Emergencies Helen Danesh-Meyer, MBChB, MD, FRANZCO Sir William and Lady Stevenson Professor of Ophthalmology Head of Glaucoma
VI.2.2 Summary of treatment benefits
 EU-Risk Management Plan for Bimatoprost V01 aetiology), both OAG and ACG can be secondary conditions. Secondary glaucoma refers to any case in which another disorder (e.g. injury, inflammation, vascular
EU-Risk Management Plan for Bimatoprost V01 aetiology), both OAG and ACG can be secondary conditions. Secondary glaucoma refers to any case in which another disorder (e.g. injury, inflammation, vascular
The Orbit. The Orbit OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION 9/25/2014. The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? Openings in the orbit
 The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION JEFFREY M. GAMBLE, OD COLUMBIA EYE CONSULTANTS OPTOMETRY & UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY CLINICAL
The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION JEFFREY M. GAMBLE, OD COLUMBIA EYE CONSULTANTS OPTOMETRY & UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY CLINICAL
Dr/ Marwa Abdellah EOS /16/2018. Dr/ Marwa Abdellah EOS When do you ask Fluorescein angiography for optic disc diseases???
 When do you ask Fluorescein angiography for optic disc diseases??? 1 NORMAL OPTIC DISC The normal optic disc on fluorescein angiography is fluorescent due to filling of vessels arising from the posterior
When do you ask Fluorescein angiography for optic disc diseases??? 1 NORMAL OPTIC DISC The normal optic disc on fluorescein angiography is fluorescent due to filling of vessels arising from the posterior
MRI masterfile Part 5 WM Heme Strokes.ppt 1
 Ocular and Orbital Trauma Eye Trauma: Incidence 1.3 million eye injuries in the US per year. 40,000 of these injuries lead to blindness in the US. Patrick Sibony, MD March 23, 2013 Ophthalmic Emergencies
Ocular and Orbital Trauma Eye Trauma: Incidence 1.3 million eye injuries in the US per year. 40,000 of these injuries lead to blindness in the US. Patrick Sibony, MD March 23, 2013 Ophthalmic Emergencies
Neuro-Ocular Grand Rounds Anthony B. Litwak,OD, FAAO VA Medical Center Baltimore, Maryland
 Neuro-Ocular Grand Rounds Anthony B. Litwak,OD, FAAO VA Medical Center Baltimore, Maryland Dr. Litwak is on the speaker and advisory boards for Alcon and Zeiss Meditek COMMON OPTIC NEUROPATHIES THAT CAN
Neuro-Ocular Grand Rounds Anthony B. Litwak,OD, FAAO VA Medical Center Baltimore, Maryland Dr. Litwak is on the speaker and advisory boards for Alcon and Zeiss Meditek COMMON OPTIC NEUROPATHIES THAT CAN
THE SWOLLEN DISC. Valerie Biousse, MD Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, GA
 THE SWOLLEN DISC Valerie Biousse, MD Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, GA Updated from: Neuro-Ophthalmology Illustrated. Biousse V, Newman NJ. Thieme, New-York,NY. 2 nd Ed, 2016. Edema of the
THE SWOLLEN DISC Valerie Biousse, MD Emory University School of Medicine Atlanta, GA Updated from: Neuro-Ophthalmology Illustrated. Biousse V, Newman NJ. Thieme, New-York,NY. 2 nd Ed, 2016. Edema of the
No Financial Interest
 Pituitary Apoplexy Michael Vaphiades, D.O. Professor Department of Ophthalmology, Neurology, Neurosurgery University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL No Financial Interest N E U R O L O G I C
Pituitary Apoplexy Michael Vaphiades, D.O. Professor Department of Ophthalmology, Neurology, Neurosurgery University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL No Financial Interest N E U R O L O G I C
Collaboration in the care of glaucoma patients and glaucoma suspects. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Nico Ristorante November 29, 2012
 Collaboration in the care of glaucoma patients and glaucoma suspects Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Nico Ristorante November 29, 2012 Goals of Collaboration Patient-centred and evidence based approach Timely access
Collaboration in the care of glaucoma patients and glaucoma suspects Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Nico Ristorante November 29, 2012 Goals of Collaboration Patient-centred and evidence based approach Timely access
Neuro-ophthalmologyophthalmology. Marek Michalec, MD.
 Neuro-ophthalmologyophthalmology Marek Michalec, MD. Neuro-ophthalmology Study integrating ophthalmology and neurology Disorders affecting parts of CNS devoted to vision or eye: Afferent system (visual
Neuro-ophthalmologyophthalmology Marek Michalec, MD. Neuro-ophthalmology Study integrating ophthalmology and neurology Disorders affecting parts of CNS devoted to vision or eye: Afferent system (visual
8/30/2018. Eye Disorders. Patrick Sarte. Anatomy of the Eye Uveitis Scleritis vs. Episcleritis Glaucoma Retinal Findings Eyelids
 Eye Disorders Patrick Sarte Anatomy of the Eye Uveitis Scleritis vs. Episcleritis Glaucoma Retinal Findings Eyelids 1 Anatomy of the Eye Anatomy of the Eye 2 Anatomy of the Eye 3 4 A 26 year old woman
Eye Disorders Patrick Sarte Anatomy of the Eye Uveitis Scleritis vs. Episcleritis Glaucoma Retinal Findings Eyelids 1 Anatomy of the Eye Anatomy of the Eye 2 Anatomy of the Eye 3 4 A 26 year old woman
Diabetic Retinopathy. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012
 Diabetic Retinopathy Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Outline Statistics Anatomy Categories Assessment Management Risk factors What do you need to do? Objectives Summarize the
Diabetic Retinopathy Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Outline Statistics Anatomy Categories Assessment Management Risk factors What do you need to do? Objectives Summarize the
Glaucoma. Glaucoma. Optic Disc Cupping
 Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Bruce James A group of diseases in which damage to the optic nerve occurs as a result of intraocualar pressure being above the physiological norm for that eye Stoke Mandeville
Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Bruce James A group of diseases in which damage to the optic nerve occurs as a result of intraocualar pressure being above the physiological norm for that eye Stoke Mandeville
PRECISION PROGRAM. Injection Technique Quick-Reference Guide. Companion booklet for the Video Guide to Injection Technique
 Injection Technique Quick-Reference Guide PRECISION PROGRAM Companion booklet for the Video Guide to Injection Technique Available at www.ozurdexprecisionprogram.com Provides step-by-step directions with
Injection Technique Quick-Reference Guide PRECISION PROGRAM Companion booklet for the Video Guide to Injection Technique Available at www.ozurdexprecisionprogram.com Provides step-by-step directions with
Recurrent intraocular hemorrhage secondary to cataract wound neovascularization (Swan Syndrome)
 Recurrent intraocular hemorrhage secondary to cataract wound neovascularization (Swan Syndrome) John J. Chen MD, PhD; Young H. Kwon MD, PhD August 6, 2012 Chief complaint: Recurrent vitreous hemorrhage,
Recurrent intraocular hemorrhage secondary to cataract wound neovascularization (Swan Syndrome) John J. Chen MD, PhD; Young H. Kwon MD, PhD August 6, 2012 Chief complaint: Recurrent vitreous hemorrhage,
Goals. Glaucoma PARA PEARL TO DO. Vision Loss with Glaucoma
 Glaucoma Janet R. Fett, OD Drs. Kincaid, Fett and Tharp So Sioux City, NE eyewear21@hotmail.com Goals Understand Glaucoma Disease process Understand how your data (objective and subjective) assists in
Glaucoma Janet R. Fett, OD Drs. Kincaid, Fett and Tharp So Sioux City, NE eyewear21@hotmail.com Goals Understand Glaucoma Disease process Understand how your data (objective and subjective) assists in
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit
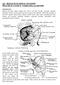 213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit OSTEOLOGY Identify the bones which comprise the walls of the orbit: maxilla, zygomatic, ethmoid, lachrymal, frontal, and
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit OSTEOLOGY Identify the bones which comprise the walls of the orbit: maxilla, zygomatic, ethmoid, lachrymal, frontal, and
CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with all of the latest changes.
CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with all of the latest changes.
Diabetic Retinopathy
 Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes can be classified into type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus, formerly known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and non-insulin diabetes mellitus, respectively.
Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes can be classified into type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus, formerly known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and non-insulin diabetes mellitus, respectively.
Treatment of carotid-cavernous fistula using a balloon-tipped intra-arterial catheter
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 996-1000 Treatment of carotid-cavernous fistula using a balloon-tipped intra-arterial catheter U. M. CHOWDHARY From the Department of Neurology,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 996-1000 Treatment of carotid-cavernous fistula using a balloon-tipped intra-arterial catheter U. M. CHOWDHARY From the Department of Neurology,
OPHTHALMOLOGY REFERRAL GUIDE FOR GPS
 OPHTHALMOLOGY REFERRAL GUIDE FOR GPS A guidebook to support general practitioners in the management and referral of a range of common eye problems. Contents 3 Introduction 4 Ophthalmic Workup 6 Acute Visual
OPHTHALMOLOGY REFERRAL GUIDE FOR GPS A guidebook to support general practitioners in the management and referral of a range of common eye problems. Contents 3 Introduction 4 Ophthalmic Workup 6 Acute Visual
Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Orbital facia. Periororbital facia Orbital septum Bulbar facia Muscular facia
 Anatomy Orbital facia Periororbital facia Orbital septum Bulbar facia Muscular facia Physiology of symptoms 1) Proptosis ( exophthalmos) Pseudoproptosis Axial Non axial Pulsating Positional Intermittent
Anatomy Orbital facia Periororbital facia Orbital septum Bulbar facia Muscular facia Physiology of symptoms 1) Proptosis ( exophthalmos) Pseudoproptosis Axial Non axial Pulsating Positional Intermittent
A Curious Case of Bilateral Optic Disc Edema Brittney Dautremont, DO, MPH
 A Curious Case of Bilateral Optic Disc Edema Brittney Dautremont, DO, MPH PGY2 Ophthalmology Resident Grandview Medical Center Dayton, OH CASE PRESENTATION 51 year old white female presenting with blurred
A Curious Case of Bilateral Optic Disc Edema Brittney Dautremont, DO, MPH PGY2 Ophthalmology Resident Grandview Medical Center Dayton, OH CASE PRESENTATION 51 year old white female presenting with blurred
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation
 206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
NEPTUNE RED BANK BRICK
 NEPTUNE RED BANK BRICK Diabetes & The Eye Diabetics are more likely to develop Cataracts at a younger age. Diabetics are twice as likely to develop Glaucoma when compared to non-diabetics. The primary
NEPTUNE RED BANK BRICK Diabetes & The Eye Diabetics are more likely to develop Cataracts at a younger age. Diabetics are twice as likely to develop Glaucoma when compared to non-diabetics. The primary
Unruptured Aneurysms with Cranial Nerve Symptoms: Efficacy of Endosaccular Guglielmi Detachable Coil Treatment
 nruptured Aneurysms with Cranial Nerve Symptoms: Efficacy of Endosaccular Guglielmi Detachable Coil Treatment Dong Joon Kim, MD Dong Ik Kim, MD Seung-Koo Lee, MD Si Yeon Kim, MD Objective: To evaluate
nruptured Aneurysms with Cranial Nerve Symptoms: Efficacy of Endosaccular Guglielmi Detachable Coil Treatment Dong Joon Kim, MD Dong Ik Kim, MD Seung-Koo Lee, MD Si Yeon Kim, MD Objective: To evaluate
Secondary Glaucomas. Mr Nick Strouthidis MBBS MD PhD FRCS FRCOphth FRANZCO Consultant Ophthalmologist, Glaucoma Service, Moorfields Eye Hospital
 Secondary Glaucomas Mr Nick Strouthidis MBBS MD PhD FRCS FRCOphth FRANZCO Consultant Ophthalmologist, Glaucoma Service, Moorfields Eye Hospital Introduction: What is glaucoma? Glaucoma is the name given
Secondary Glaucomas Mr Nick Strouthidis MBBS MD PhD FRCS FRCOphth FRANZCO Consultant Ophthalmologist, Glaucoma Service, Moorfields Eye Hospital Introduction: What is glaucoma? Glaucoma is the name given
A Patient Presenting with Ptosis, Ophthalmoplegia, and Decreased Periorbital Sensations and Facial Droop in Tolosa-Hunt Syndrome
 A Patient Presenting with Ptosis, Ophthalmoplegia, and Decreased Periorbital Sensations and Facial Droop in Tolosa-Hunt Syndrome medicine2.missouri.edu/jahm/patient-presenting-ptosis-ophthalmoplegia-decreased-periorbital-sensations-facial-drooptolosa-hunt-syndrome/
A Patient Presenting with Ptosis, Ophthalmoplegia, and Decreased Periorbital Sensations and Facial Droop in Tolosa-Hunt Syndrome medicine2.missouri.edu/jahm/patient-presenting-ptosis-ophthalmoplegia-decreased-periorbital-sensations-facial-drooptolosa-hunt-syndrome/
NEW YORK UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES AND GOALS
 NEW YORK UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES AND GOALS Revision Date: 6/30/06 Distribution Date: 7/6/06 The Department of Ophthalmology at the NYU Medical Center
NEW YORK UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES AND GOALS Revision Date: 6/30/06 Distribution Date: 7/6/06 The Department of Ophthalmology at the NYU Medical Center
GLAUCOMA SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES
 SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES Introduction These are summary benchmarks for the Academy s Preferred Practice Pattern (PPP) guidelines. The Preferred Practice Pattern series
SUMMARY BENCHMARKS FOR PREFERRED PRACTICE PATTERN GUIDELINES Introduction These are summary benchmarks for the Academy s Preferred Practice Pattern (PPP) guidelines. The Preferred Practice Pattern series
Post-traumatic persistent trigeminal artery-cavernous fistula: a case report and review of literature
 . 252. Post-traumatic persistent trigeminal artery-cavernous fistula: a case report and review of literature HU Wei-peng 胡伟鹏 *, HUANG Tian-zao 黄天造, GAO Hong-zhi 高宏志, YU Mao-qing 余茂清 and XU Chao-yang 徐朝阳
. 252. Post-traumatic persistent trigeminal artery-cavernous fistula: a case report and review of literature HU Wei-peng 胡伟鹏 *, HUANG Tian-zao 黄天造, GAO Hong-zhi 高宏志, YU Mao-qing 余茂清 and XU Chao-yang 徐朝阳
OPHTHALMOLOGIC PEARLS FOR THE NON- OPHTHALMOLOGIST. David G. Gross D.O. Deen-Gross Eye Centers Merrillville-Hobart Deengrosseye.
 OPHTHALMOLOGIC PEARLS FOR THE NON- OPHTHALMOLOGIST David G. Gross D.O. Deen-Gross Eye Centers Merrillville-Hobart Deengrosseye.com A FEW OF THE AREAS WE WILL DISCUSS Red Eye Glaucoma Neuro ophthalmic tid
OPHTHALMOLOGIC PEARLS FOR THE NON- OPHTHALMOLOGIST David G. Gross D.O. Deen-Gross Eye Centers Merrillville-Hobart Deengrosseye.com A FEW OF THE AREAS WE WILL DISCUSS Red Eye Glaucoma Neuro ophthalmic tid
The Prevalence of diabetic optic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus
 The Prevalence of diabetic optic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus Received: 25/4/2016 Accepted: 8/12/2016 Introduction Diabetic papillopathy is an atypical form of non-arteritic anterior ischemic
The Prevalence of diabetic optic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus Received: 25/4/2016 Accepted: 8/12/2016 Introduction Diabetic papillopathy is an atypical form of non-arteritic anterior ischemic
Jacqueline Theis, O.D., F.A.A.O.
 Neuro-Ophthalmological Emergencies Presenting in Primary Care Optometry Describes the symptoms, signs, and management of neuro-ophthalmological emergencies. Signs/Symptoms to be Concerned about (especially
Neuro-Ophthalmological Emergencies Presenting in Primary Care Optometry Describes the symptoms, signs, and management of neuro-ophthalmological emergencies. Signs/Symptoms to be Concerned about (especially
Rare Presentation of Ocular Toxoplasmosis
 Case Report Rare Presentation of Ocular Toxoplasmosis Rakhshandeh Alipanahi MD From Department of Ophthalmology, Nikookari Eye Hospital, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran. Correspondence:
Case Report Rare Presentation of Ocular Toxoplasmosis Rakhshandeh Alipanahi MD From Department of Ophthalmology, Nikookari Eye Hospital, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran. Correspondence:
Delayed Correction of Hypotony Maculopathy in a Patient with Glaucoma and Thyroid-Related Orbitopathy
 Published online: October 14, 2015 2015 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 1663 2699/15/0063 0356$39.50/0 This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International
Published online: October 14, 2015 2015 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 1663 2699/15/0063 0356$39.50/0 This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International
3/16/2018. Ultrasound Biomicroscopy in Glaucoma By Ahmed Salah Abdel Rehim. Prof. of Ophthalmology Al-Azhar University
 Ultrasound Biomicroscopy in Glaucoma By Ahmed Salah Abdel Rehim Prof. of Ophthalmology Al-Azhar University 1 Ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) is a recent technique to visualize anterior segment with the
Ultrasound Biomicroscopy in Glaucoma By Ahmed Salah Abdel Rehim Prof. of Ophthalmology Al-Azhar University 1 Ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) is a recent technique to visualize anterior segment with the
Dr. Esam Ahmad Z. Omar BDS, MSc-OMFS, FFDRCSI. Monitor the vital signs. Monitor the vital signs. Complications of Facial Traumas.
 Complications of Facial Traumas 1) Immediate Complications 2) Late Complications Dr. Esam Ahmad Z. Omar BDS, MSc-OMFS, FFDRCSI Assistant Professor Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Taibah University Monitor
Complications of Facial Traumas 1) Immediate Complications 2) Late Complications Dr. Esam Ahmad Z. Omar BDS, MSc-OMFS, FFDRCSI Assistant Professor Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Taibah University Monitor
11/30/2009. Glaukosis: ancient greek term meaning sparkling or shining appearance of pupil
 Normal Ocular Anatomy Glaucoma Dr Sunil Deokule, MD Asst. Prof and Glaucoma Specialist University of Kentucky Definition Glaukosis: ancient greek term meaning sparkling or shining appearance of pupil Optic
Normal Ocular Anatomy Glaucoma Dr Sunil Deokule, MD Asst. Prof and Glaucoma Specialist University of Kentucky Definition Glaukosis: ancient greek term meaning sparkling or shining appearance of pupil Optic
Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball
 Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball - The bony orbit: it is protecting our eyeball and resembling a pyramid: With a base directed: anterolaterally. And an apex directed: posteromedially. Notes:
Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball - The bony orbit: it is protecting our eyeball and resembling a pyramid: With a base directed: anterolaterally. And an apex directed: posteromedially. Notes:
The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3%
 The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3% of our population age > 40 have glaucoma In the past:
The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3% of our population age > 40 have glaucoma In the past:
Palliative Treatment of Chronic Carotid-cavernous Fistula: A Case Report
 149 Palliative Treatment of Chronic Carotid-cavernous Fistula: A Case Report Kao-Chang Lin 1, Chow-Hong Yeh 2, and Tsung-Chia Tsai 3 Abstract- We presented a case of direct type carotid-cavernous fistula
149 Palliative Treatment of Chronic Carotid-cavernous Fistula: A Case Report Kao-Chang Lin 1, Chow-Hong Yeh 2, and Tsung-Chia Tsai 3 Abstract- We presented a case of direct type carotid-cavernous fistula
Pearls, Pitfalls and Advances in Neuro-Ophthalmology
 Pearls, Pitfalls and Advances in Neuro-Ophthalmology Nancy J. Newman, MD Emory University Atlanta, GA Consultant for Gensight Biologics, Santhera Data Safety Monitoring Board for Quark AION Study Medical-legal
Pearls, Pitfalls and Advances in Neuro-Ophthalmology Nancy J. Newman, MD Emory University Atlanta, GA Consultant for Gensight Biologics, Santhera Data Safety Monitoring Board for Quark AION Study Medical-legal
Ischaemic ocular necrosis from carotid-cavernous fistula
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, I45 Communications Ischaemic ocular necrosis from carotid-cavernous fistula Pathology of stagnant anoxic "inflammation" in orbital and ocular tissues W. H. SPENCER, H. S. THOMPSON,*
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, I45 Communications Ischaemic ocular necrosis from carotid-cavernous fistula Pathology of stagnant anoxic "inflammation" in orbital and ocular tissues W. H. SPENCER, H. S. THOMPSON,*
Work Sheet And Course Hand Out
 Work Sheet And Course Hand Out This course provides the primary care health professional with a basic understanding of the eye, its function and the assessment of common sight- and non-sight threatening
Work Sheet And Course Hand Out This course provides the primary care health professional with a basic understanding of the eye, its function and the assessment of common sight- and non-sight threatening
Embryology of the Ophthalmic Artery: a Revived Concept
 www.centauro.it Interventional Neuroradiology 15: 363-368, 2009 Letter to the Editor Embryology of the Ophthalmic Artery: a Revived Concept M. KOMIYAMA Department of Neurosurgery, Osaka City General Hospital;
www.centauro.it Interventional Neuroradiology 15: 363-368, 2009 Letter to the Editor Embryology of the Ophthalmic Artery: a Revived Concept M. KOMIYAMA Department of Neurosurgery, Osaka City General Hospital;
1 Eyelids. Lacrimal Apparatus. Orbital Region. 3 The Orbit. The Eye
 1 1 Eyelids Orbital Region 2 Lacrimal Apparatus 3 The Orbit 4 The Eye 2 Eyelids The eyelids protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure. The upper eyelid is larger and more mobile
1 1 Eyelids Orbital Region 2 Lacrimal Apparatus 3 The Orbit 4 The Eye 2 Eyelids The eyelids protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure. The upper eyelid is larger and more mobile
Ocular Urgencies and Emergencies
 Ocular Urgencies and Emergencies Pam Boyce, O.D., F.A.A.O. Boyce Family Eye Care, Ltd. 528 Devon Ave. Park Ridge, IL 60068 847-518-0303 Somebody s going to lose an eye Epidemiology 2.4 million ocular and
Ocular Urgencies and Emergencies Pam Boyce, O.D., F.A.A.O. Boyce Family Eye Care, Ltd. 528 Devon Ave. Park Ridge, IL 60068 847-518-0303 Somebody s going to lose an eye Epidemiology 2.4 million ocular and
Optical Coherence Tomograpic Features in Idiopathic Retinitis, Vasculitis, Aneurysms and Neuroretinitis (IRVAN)
 Columbia International Publishing Journal of Ophthalmic Research (2014) Research Article Optical Coherence Tomograpic Features in Idiopathic Retinitis, Vasculitis, Aneurysms and Neuroretinitis (IRVAN)
Columbia International Publishing Journal of Ophthalmic Research (2014) Research Article Optical Coherence Tomograpic Features in Idiopathic Retinitis, Vasculitis, Aneurysms and Neuroretinitis (IRVAN)
A. Incorrect! Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor given orally or by intravenous injection.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 20: Drugs that Treat Glaucoma Question No. 1 of 10 1. is a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Question #01 (A) Acetazolamide (B) Clonidine (C) Dorzolamide (D) Apraclonidine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 20: Drugs that Treat Glaucoma Question No. 1 of 10 1. is a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Question #01 (A) Acetazolamide (B) Clonidine (C) Dorzolamide (D) Apraclonidine
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Artificial embolization of carotid-cavernous fistula with post-operative patency of internal carotid
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1970, 33, 674-678 Artificial embolization of carotid-cavernous fistula with post-operative patency of internal carotid artery FABIAN ISAMAT, V. SALLERAS, AND A. M. MIRANDA
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1970, 33, 674-678 Artificial embolization of carotid-cavernous fistula with post-operative patency of internal carotid artery FABIAN ISAMAT, V. SALLERAS, AND A. M. MIRANDA
EYE TRAUMA: INCIDENCE
 Introduction EYE TRAUMA: INCIDENCE 2.5 million eye injuries per year in U.S. 40,000 60,000 of eye injuries lead to visual loss Introduction Final visual outcome of many ocular emergencies depends on prompt,
Introduction EYE TRAUMA: INCIDENCE 2.5 million eye injuries per year in U.S. 40,000 60,000 of eye injuries lead to visual loss Introduction Final visual outcome of many ocular emergencies depends on prompt,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Park KH, Kim YK, Woo SJ, et al. Iatrogenic occlusion of the ophthalmic artery after cosmetic facial filler injections: a national survey by the Korean Retina Society. JAMA
Supplementary Online Content Park KH, Kim YK, Woo SJ, et al. Iatrogenic occlusion of the ophthalmic artery after cosmetic facial filler injections: a national survey by the Korean Retina Society. JAMA
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Saharsh Patel, 1 Kyle M Fargen, 2 Keith Peters, 3 Peter Krall, 1 Hazem Samy, 1 Brian L Hoh 2 CASE REPORT. Hemorrhagic stroke
 1 Department of Ophthalmology, 2 Department of Neurosurgery, 3 Department of Radiology, Correspondence to Dr Kyle Michael Fargen, Department of Neurosurgery, Box 100265, Gainesville, Florida 32610, USA;
1 Department of Ophthalmology, 2 Department of Neurosurgery, 3 Department of Radiology, Correspondence to Dr Kyle Michael Fargen, Department of Neurosurgery, Box 100265, Gainesville, Florida 32610, USA;
Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Scanning Computerized Ophthalmic Diagnostic Imaging (SCODI) (L34431)
 Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Scanning Computerized Ophthalmic Diagnostic Imaging (SCODI) (L34431) Links in PDF documents are not guaranteed to work. To follow a web link, please use the MCD Website.
Local Coverage Determination (LCD): Scanning Computerized Ophthalmic Diagnostic Imaging (SCODI) (L34431) Links in PDF documents are not guaranteed to work. To follow a web link, please use the MCD Website.
Orbital cellulitis. Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9,
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 143-148 Orbital cellulitis D. P. MARTIN-HIRSCH, S. HABASHI, A. H. HINTON & B. KOTECHA University Department of ENT Surgery, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Manchester
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 143-148 Orbital cellulitis D. P. MARTIN-HIRSCH, S. HABASHI, A. H. HINTON & B. KOTECHA University Department of ENT Surgery, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Manchester
Traumatic A-V A V Fistula
 Traumatic A-V A V Fistula PRESENT HISTORY PAST HISTORY 30 year-old, male ( XX); Denied other systemic disease before. PRESENT HISTORY A deep stabbing wound (3*1 cm) noted on 07/01/2002 over Right anterior
Traumatic A-V A V Fistula PRESENT HISTORY PAST HISTORY 30 year-old, male ( XX); Denied other systemic disease before. PRESENT HISTORY A deep stabbing wound (3*1 cm) noted on 07/01/2002 over Right anterior
NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES
 NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES Leslie M. Scoutt, MD, FACR Professor of Diagnostic Radiology & Surgery Vice Chair, Dept of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging Chief, Ultrasound Section
NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES Leslie M. Scoutt, MD, FACR Professor of Diagnostic Radiology & Surgery Vice Chair, Dept of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging Chief, Ultrasound Section
The Case: A 64 yo man with chronic back pain has elective multilevel lumbar spinal surgery
 The Case: A 64 yo man with chronic back pain has elective multilevel lumbar spinal surgery The Case: Upon awakening from anesthesia, he is blind in both eyes After Non-Ocular Surgeries Nancy J. Newman,
The Case: A 64 yo man with chronic back pain has elective multilevel lumbar spinal surgery The Case: Upon awakening from anesthesia, he is blind in both eyes After Non-Ocular Surgeries Nancy J. Newman,
Ophthalmology Unit Referral Guidelines
 Ophthalmology Unit Referral Guidelines Austin Health Ophthalmology Unit holds sub-specialty sessions to discuss and plan the treatment of patients with specific ocular conditions. General including cataract
Ophthalmology Unit Referral Guidelines Austin Health Ophthalmology Unit holds sub-specialty sessions to discuss and plan the treatment of patients with specific ocular conditions. General including cataract
