Mechanisms of presentation of caroticocavernous
|
|
|
- Francine Hampton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brit.. Ophthal. (1970) 54, I86 Mechanisms of presentation of caroticocavernous fistulae EDWIN R. BICKERSTAFF The Midland CentreJor Neurosurgery and Neurology, Smethwick The clinical features of carotico-cavernous fistulae are too well known for detailed description to be necessary. The proptosis, chemosis, venous engorgement in and around the orbit, oculomotor palsy, pulsation of the globe, and the subjective and objective bruit over the orbit and forehead are familiar to all. It is perhaps not always appreciated that the bruit may, on occasions, precede the appearance of the other features by weeks or even months. There are, however, several modes of clinical presentation, and a number of different aetiological processes responsible. The lesion may present as the conventional unilateral carotico-cavernous fistula; the bilateral fistula; the contralateral fistula, in which the pulsating exophthalmos is on the side opposite to the actual fistula; or the alternating fistula. This has been written in these words advisedly, because there is a tendency to accept such expressions too readily and too literally without giving enough thought to their meaning. For instance, does bilateral pulsating exophthalmos mean that the patient has two symmetrical carotico-cavernous fistulae? Or does the alternation of ocular symptoms mean that one fistula has healed but by coincidence the same patient has developed another on the opposite side? It is because this must very rarely be the case that this paper has been written, to consider the mechanismn by which clinical presentations of different types comes about, and also to describe two unfamiliar aetiological processes. Anatomical considerations (Fig. Ia, opposite) The cavernous sinuses lie lateral to the pituitary fossa between two layers of dura. They connect anteriorly with the superior ophthalmic veins, and throtugh these with the supraorbital, angular, and inferior orbital veins. Posteriorly they are connected to the superior petrosal sinuses, and the inferior petrosal sinuses, and through the latter to the jugular veins. They are not isolated structures, however, but are joined together by the intercavernous sinuses, anterior and posterior, before and behind the pituitary fossa, and also through the basal venous plexus lying on the clivus, and other less important communications. The degree of patency and the relative importance of these connections varies. The sinuses themselves are not just flaccid containers of blood, but are named from the fibrous trabeculations which traverse them giving the appearance of cavernous tissue. They are the only places in the body wvhere a major artery lies bathed in venous blood. When considering the mechanism of carotico-cavernous fistulae, the important structures involved are the superior ophthalmic veins and the intercavernous sinuses, particularly the anterior. Their anatomical relationships vary, as does the relationship of the carotid artery to them. Received for publication September 17, 1969 Address for reprints: The Midland Centre for Neurosurgery and(l Neurology, Holly' Lane, Smnethsick, WVarley, Worcs. Based on a paper presented to the ophthalmic section of the Royal Society of Medicine, Londoni, in February, i969.
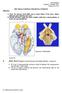
2 Carotico-cavernousfistulae F I G. i Diagrammatic representation of cavernous sinus and connecting veins (a) normal (b) ipsilateral carotico-cavernous fistula (c) arterial blood crossing by the intercavernous sinus gives impression of bilateral fistulm (d) ipsilateral ophthalmic vein thrombosed but intercavernous sinus patent allowing contralateral syndrome to develop. Clinical material The material for this study comes from a series of eleven consecutive cases of caroticocavernous fistulae, ten of which were female, one of which was "bilateral", one contralateral, and three "alternating". All were non-traumatic in origin. Aetiological factors According to Walsh (I957), trauma is responsible for 75 per cent. of all cases and men are most frequently affected. In the present series, however, the chief cause of the condition is the rupture of a hypertensive atherosclerotic internal carotid artery, or of a pre-existing intracavernous aneurysm, or a combination of aneurysm, hypertension, and atheroma. Women predominate, and most of them are elderly (e.g. Case i). Spontaneous I87
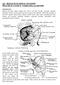
3 IU8 Edwin R. Bickerstaf fistule may on rare occasions occur in younger patients, however, in which neither trauma nor aneurysm play any part, and two of these unusual mechanisms are mentioned later in this paper. Mechanism of production of clinical symptoms Fig. I (b-d) is intended to illustrate in diagrammatic fashion the principal events which occur. When rupture occurs, arterial blood escapes from the carotid artery, enters the sinus, tracks through the trabeculae (which may delay the development of the full clinical picture), and then enters the superior ophthalmic vein (Fig. ib), which becomes engorged, enlarged, and tortuous. These changes are passed forwards to the supraorbital, angular, and inferior ophthalmic veins, and arteriography will, in the lateral view, show the dye escaping into the sinus and along the distended superior ophthalmic veins to the orbit (Fig. 2). This is the mechanism of the conventional unilateral fistula with ipsilateral pulsating exophthalmos. It depends upon the superior ophthalmic vein being patent, and the intercavernous sinus being relatively unimportant. THE "BILATERAL FITULA (Fig. Ic) FIG. 2 Internal carotid arteriogram (subtraction technique) showing dye entering cavernous I 11 I r ssinus and passing along dilated superior ophthalmic vein to the If both superior ophthalmic veins are patent and in the normal position, and if the intercavernous sinus is patenit, or becomes so as a result of the pressure of arterial blood in the cavernous sinus, this blood can not only pass into the superior ophthalmic vein on the side of the fistula, but can also pass across the mid-line and enter the other sinus and the other superior ophthalmic vein, thus causing bilateral pulsating exophthalmos and bruit. There is however still only one fistula, which is a point of great importance, for if this can be demonstrated arteriographically only one carotid artery need be sacrificed for both eyes to be cured. THE CONTRALATERA FISTULA (Fig. Id) If the superior ophthalmic vein on the side of the fistula is an unimportant structure in that particular patient, or has an unusual mode of communication, or becomes thrombosed
4 Carotico-cavernous fistulae by damage to its walls from the rush into it of arterial blood; and if the intercavernous sinus is patent or becomes so, the arterial blood can track across to.the other side, entering the other superior ophthalmic vein, and so cause unilateral pulsating exophthalmos on the side opposite to the fistula. That this is not merely hypothetical was shown by Dandy and Follis (I94I); there have been others in the literature, and the following patient from this series illustrated the point very clearly. Case i A woman aged 58 suddenly developed a sensation of something having snapped inside her head. For 48 hours she had severe headache and developed a pulsating noise inside the head. Over the next 6 months a right-sided unilateral pulsating exophthalmos gradually became apparent with a loudly audible systolic bruit. However, when the right carotid arteriogram was carried out by Dr. Philip Moxon, no abnormality was seen. The procedure was repeated on the left side, and here it was clearly demonstrated that there was a left-sided carotico-cavernous fistula, and the dye could be seen to be tracking through the anterior intercavernous sinus to the right side, and along the right superior ophthalmic vein to the orbit. The ipsilateral ophthalmic vein did not appear to be patent. Immediately after arteriography all the symptoms ceased and all the physical signs subsided. A very careful repetition of the left carotid arteriogram was then carried out and this showed that, whereas the dye still escaped from the artery into the left cavernous sinus, the intercavernous connection had become occluded at its mid-point. This patient has remained perfectly well for over 5 years. THE "ALTERNATING FISTULA If, after a conventional carotico-cavernous fistula syndrome has developed, the superior ophthalmic vein thromboses, the symptoms will settle down. It has been seen, however, in Case I that the fistula may remain open, and this may cause the intercavernous sinus to open up gradually, until finally arterial blood is allowed to enter the contralateral superior ophthalmic vein (Fig. id), so that the pulsating exophthalmos will re-appear, but on the opposite side. It is still only the one fistula which is present and which may require treatment. Much of what has been said may be hypothesis, but it is clearly proven in Case i, and it seems so much more likely that a sequence of events of this type may take place than that identical fistulae should develop coincidentally in the two carotid arteries at the same or different times. Some additional aspects of aetiology The commonest causes of non-traumatic carotico-cavernous fistulae have been mentioned earlier, but in the youinger, non-atheromatous, normotensive patient, there must be some unusual defect in the wall of the carotid artery. The type of intracavernous aneurysm which affects the older patients is uncommon in the young, and haemorrhagic disorders rarely cause such symptoms. There may occasionally, however, exist a hereditary fragility of the vessel wall, or the vessel may come to be eroded from outside. Case 2 A 21-year-old female patient had suffered a thrombosis of the right internal carotid artery after an acute infection of the middle ear and petrous bone, and 2 years later she suddenly developed a leftsided intracranial bruit which after 2 months was followed by pulsating exophthalmos on that side. Arteriography proved the presence of a carotico-cavernous fistula, but there was no aneurysm. She gave a history, however, of having had many spontaneous haemorrhages in previous years in the I89
5 Igo Edwin R. Bickerstqff subcutaneous tissues, the muscles, and around both orbits, and any interference with her arterial walls (such as during carotid arteriography) had produced very troublesome haemorrhage. Her mother had shown exactly the same type of vascular fragility. Their blood coagulation factors were all quite normal, and sections of her arterial wall examined by light and electron microscopy showed no recognizable abnormality. The nature of this fragility was quite obscure but it seemed possible that the excessive demands made upon the one vessel to supply both hemispheres was such that in the presence of this fragility spontaneous rupture occurred. Case 3 A mildly hypertensive male patient aged 50 suddenly developed the typical signs and symptoms of a left-sided carotico-cavernous fistula. On examination, however, he presented in addition the full clinical picture of marked hypopituitarism, which had previously passed unnoticed, and without visual field defect. Plain x rays of the skull showed a ballooned sella turcica, and by contrast radiography the presence both of a pituitary tumour and of a carotico-cavernous fistula was confirmed. The tumour was removed and the fistula occluded (by Mr. Jack Small) at two operations, and it was seen that there had been a lateral projection of the pituitary tumour which had infarcted and presumably eroded the carotid artery wall. Two other cases in which lateral projections of pituitary tumours have almost encircled the carotid artery have recently been seen and which, if a more advanced stage had been reached, might have been expected to erode the artery wall and result in a fistula. Conclusion It has been the aim of this paper to stress the need for viewing the cavernous sinus and its communicating veins not as rigid structures, but as part of the dynamics of the cerebral circulation. When a fistula occurs, some vessels open up, others close down, and new channels may appear, but throughout all this the patients themselves can respond by showing only a limited clinical picture. It is therefore most important in such cases, if their age and physical condition justifies it, that the most meticulous arteriographic studies should be carried out bilaterally, in order that the precise potential for surgical correction of the lesion may be assessed. Another interesting aspect shown in this series, which is well-known, and is illustrated clearly in Case i, but for which no very adequate explanation has been arrived at, is that either the process of arteriography, or in other cases the trial period of carotid compression usually required before the carotid is interrupted surgically, may result in closure of either the fistula or its associated channels, so that the symptoms settle down without further interference being required. Summary Mechanisms are described by which the so-called bilateral, contralateral, and alternating carotico-cavernous fistulae may be produced by a single arteriovenous communication. Attention is also drawn to two unusual pathological processes which may be the cause of such fistulae. I am most grateful to Dr. Philip Moxon for carrying out the arteriograms on these patients; to Mr. I. S. Chatha for drawing my attention to the contralateral fistulm; and to Mr. E. Lowe for the diagrams. References DANDY, W. E., and FOLLIS, R. H. (1941) Amer. J. Ophthal., 24, 365 WALSH, F. B. (1957) "Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology", 2nd ed. Williams and Wilkins, Baltinmore
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
Ophthalmoplegia in carotid cavernous sinus fistula
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1984, 68, 128-134 Ophthalmoplegia in carotid cavernous sinus fistula T. J. K. LEONARD, I. F. MOSELEY, AND M. D. SANDERS From the Departments ofneuro-ophthalmology and
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1984, 68, 128-134 Ophthalmoplegia in carotid cavernous sinus fistula T. J. K. LEONARD, I. F. MOSELEY, AND M. D. SANDERS From the Departments ofneuro-ophthalmology and
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE NORMAL OPHTHALMIC
 Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 473. ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE NORMAL OPHTHALMIC ARTERY AND CHOROIDAL PLEXUS OF THE EYE* BY P. H. SCHURR From the Department of Neurosurgery, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford THE ophthalmic
Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 473. ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE NORMAL OPHTHALMIC ARTERY AND CHOROIDAL PLEXUS OF THE EYE* BY P. H. SCHURR From the Department of Neurosurgery, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford THE ophthalmic
Carotid Cavernous Fistula
 Chief Complaint: Double vision. Carotid Cavernous Fistula Alex W. Cohen, MD, PhD; Richard Allen, MD, PhD May 14, 2010 History of Present Illness: A 46 year old female patient presented to the Oculoplastics
Chief Complaint: Double vision. Carotid Cavernous Fistula Alex W. Cohen, MD, PhD; Richard Allen, MD, PhD May 14, 2010 History of Present Illness: A 46 year old female patient presented to the Oculoplastics
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Treatment of carotid-cavernous fistula using a balloon-tipped intra-arterial catheter
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 996-1000 Treatment of carotid-cavernous fistula using a balloon-tipped intra-arterial catheter U. M. CHOWDHARY From the Department of Neurology,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 996-1000 Treatment of carotid-cavernous fistula using a balloon-tipped intra-arterial catheter U. M. CHOWDHARY From the Department of Neurology,
Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
 Pan et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0121-z CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION COMMENTARY Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
Pan et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0121-z CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION COMMENTARY Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
The orbit-1. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE
 Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Departmental guidelines
 Michele Long Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Departmental guidelines Anatomy- cavernous sinus 2cm in
Michele Long Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Departmental guidelines Anatomy- cavernous sinus 2cm in
Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:2016 2020, November/December 1999 Case Report Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal Robert Ernst, Robert Bulas,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:2016 2020, November/December 1999 Case Report Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal Robert Ernst, Robert Bulas,
B OTH the rare persistent trigeminal. Persistent trigeminal artery" its relationship to the normal branches of the cavernous carotid
 Persistent trigeminal artery" its relationship to the normal branches of the cavernous carotid DWIGHT PARKINSON, M.D., AND CHRISTOPHER B. SHIELDS, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine,
Persistent trigeminal artery" its relationship to the normal branches of the cavernous carotid DWIGHT PARKINSON, M.D., AND CHRISTOPHER B. SHIELDS, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine,
CAROTID-OPHTHALMIC ANASTOMOSES*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1956) 40, 497. CAROTID-OPHTHALMIC ANASTOMOSES* FREQUENCY OF EXTERNAL CAROTID AND OPHTHALMIC ARTERY ANASTOMOSES BY MICHAEL SHEAt Toronto, Canada ANATOMICAL studies in man on the degree
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1956) 40, 497. CAROTID-OPHTHALMIC ANASTOMOSES* FREQUENCY OF EXTERNAL CAROTID AND OPHTHALMIC ARTERY ANASTOMOSES BY MICHAEL SHEAt Toronto, Canada ANATOMICAL studies in man on the degree
CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS PRESENTING WITH VISUAL FIELD DEFECTS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 251 CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS PRESENTING WITH VISUAL FIELD DEFECTS* BY University Department of Ophthalmology and Royal Infirmary, Edinburgh ANEURYSMS occur more frequently within
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 251 CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS PRESENTING WITH VISUAL FIELD DEFECTS* BY University Department of Ophthalmology and Royal Infirmary, Edinburgh ANEURYSMS occur more frequently within
Artificial embolization of carotid-cavernous fistula with post-operative patency of internal carotid
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1970, 33, 674-678 Artificial embolization of carotid-cavernous fistula with post-operative patency of internal carotid artery FABIAN ISAMAT, V. SALLERAS, AND A. M. MIRANDA
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1970, 33, 674-678 Artificial embolization of carotid-cavernous fistula with post-operative patency of internal carotid artery FABIAN ISAMAT, V. SALLERAS, AND A. M. MIRANDA
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
Passive ocular proptosis
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1977, 40, 1198-1202 Passive ocular proptosis BRIAN P. O'NEILL From the Department of Neurology, University of Michigan Medical Center, and the Neurology
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1977, 40, 1198-1202 Passive ocular proptosis BRIAN P. O'NEILL From the Department of Neurology, University of Michigan Medical Center, and the Neurology
Transient third nerve palsy after electrometallicthrombosis of carotid cavernous fistulae
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 854-860 Transient third nerve palsy after electrometallicthrombosis of carotid cavernous fistulae W. BRUCE WILSON,1 P. R. BRINGEWALD, Y. HOSOBUCHI,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 854-860 Transient third nerve palsy after electrometallicthrombosis of carotid cavernous fistulae W. BRUCE WILSON,1 P. R. BRINGEWALD, Y. HOSOBUCHI,
High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils
 High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils Guido Guglielmi, Fernando Viñuela, Gary Duckwiler, Jacques Dion, and Alfredo Stocker Summary: We present one case of
High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils Guido Guglielmi, Fernando Viñuela, Gary Duckwiler, Jacques Dion, and Alfredo Stocker Summary: We present one case of
The Ishikawa Classification of Cavernous Sinus Lesions by Clinico-anatomical Findings
 The Ishikawa Classification of Cavernous Sinus Lesions by Clinico-anatomical Findings Mutsumi Yoshihara, Noriko Saito, Yoji Kashima and Hiroshi Ishikawa Department of Ophthalmology, Nihon University School
The Ishikawa Classification of Cavernous Sinus Lesions by Clinico-anatomical Findings Mutsumi Yoshihara, Noriko Saito, Yoji Kashima and Hiroshi Ishikawa Department of Ophthalmology, Nihon University School
Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report
 Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report BY JIRI J. VITEK, M.D., JAMES H. HALSEY, JR., M.D., AND HOLT A. McDOWELL, M.D. Abstract: Occlusion of All Four
Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report BY JIRI J. VITEK, M.D., JAMES H. HALSEY, JR., M.D., AND HOLT A. McDOWELL, M.D. Abstract: Occlusion of All Four
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents
 Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Coincidental aneurysms with tumours of pituitary origin
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 972-979 Coincidental aneurysms with tumours of pituitary origin JAN JAKUBOWSKI AND BRIAN KENDALL From the Gough Cooper Department of Neurological
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 972-979 Coincidental aneurysms with tumours of pituitary origin JAN JAKUBOWSKI AND BRIAN KENDALL From the Gough Cooper Department of Neurological
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Omran Saeed. Luma Taweel. Mohammad Almohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
HEAD/NECK VESSELS. Objectives
 Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment
 166 Chiriac et al Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*, St.M. Iencean, I. Poeata
166 Chiriac et al Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*, St.M. Iencean, I. Poeata
Investigations. The blood count was normal with an erythrocyte. sedimentation rate of 5 mm. ist hr, and negative Waaler-
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I975) 59, 149 Tolosa-Hunt syndrome The dangers of an eponym T. J. FOWLER, C. J. EARL, V. L. McALLISTER, AND W. I. McDONALD From the Institute of Neurology, National Hospitalfor Nervous
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I975) 59, 149 Tolosa-Hunt syndrome The dangers of an eponym T. J. FOWLER, C. J. EARL, V. L. McALLISTER, AND W. I. McDONALD From the Institute of Neurology, National Hospitalfor Nervous
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Cranial cavity. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-DURA MATER 2-ARACHNOID MATER 3-PIA MATER
Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-DURA MATER 2-ARACHNOID MATER 3-PIA MATER
Anatomy of the cavernous. FRANK S. HARRIS, M.D., AND ALnERT L. RHOTON, JR., M.D.
 Anatomy of the cavernous sinus A microsurgical study FRANK S. HARRIS, M.D., AND ALnERT L. RHOTON, JR., M.D. Department of Neurological Surgery, University of Florida Health Center, Gainesville, Florida
Anatomy of the cavernous sinus A microsurgical study FRANK S. HARRIS, M.D., AND ALnERT L. RHOTON, JR., M.D. Department of Neurological Surgery, University of Florida Health Center, Gainesville, Florida
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetazolamide, in idiopathic intracranial hypertension, 49 52, 60 Angiography, computed tomography, in cranial nerve palsy, 103 107 digital
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetazolamide, in idiopathic intracranial hypertension, 49 52, 60 Angiography, computed tomography, in cranial nerve palsy, 103 107 digital
Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma
 ISSN 1507-6164 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.889610 Received: 2013.07.25 Accepted: 2013.08.08 Published: 2013.10.28 Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma Authors Contribution:
ISSN 1507-6164 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.889610 Received: 2013.07.25 Accepted: 2013.08.08 Published: 2013.10.28 Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma Authors Contribution:
FRONTO-ETHMOIDAL MUCOCOELE AS A CAUSE OF UNILATERAL PROPTOSIS*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 833 FRONTO-ETHMOIDAL MUCOCOELE AS A CAUSE OF UNILATERAL PROPTOSIS*t BY P. W. R. M. ALBERTI, H. F. MARSHALL, AND J. I. MUNRO BLACK Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 833 FRONTO-ETHMOIDAL MUCOCOELE AS A CAUSE OF UNILATERAL PROPTOSIS*t BY P. W. R. M. ALBERTI, H. F. MARSHALL, AND J. I. MUNRO BLACK Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne
Palliative Treatment of Chronic Carotid-cavernous Fistula: A Case Report
 149 Palliative Treatment of Chronic Carotid-cavernous Fistula: A Case Report Kao-Chang Lin 1, Chow-Hong Yeh 2, and Tsung-Chia Tsai 3 Abstract- We presented a case of direct type carotid-cavernous fistula
149 Palliative Treatment of Chronic Carotid-cavernous Fistula: A Case Report Kao-Chang Lin 1, Chow-Hong Yeh 2, and Tsung-Chia Tsai 3 Abstract- We presented a case of direct type carotid-cavernous fistula
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
Dilated Intercavernous Sinuses: An MR Sign of Carotid-Cavernous and Carotid Dural Fistulas
 641 ilated Intercavernous Sinuses: An MR Sign of Carotid-Cavernous and Carotid ural Fistulas Allen. Elster 1 Michael Y. M. Chen 1 an N. Richardson 1 Patrick R. Yeatts 2 ilated venous channels traversing
641 ilated Intercavernous Sinuses: An MR Sign of Carotid-Cavernous and Carotid ural Fistulas Allen. Elster 1 Michael Y. M. Chen 1 an N. Richardson 1 Patrick R. Yeatts 2 ilated venous channels traversing
The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience
 230 Chiriac et al - Superior ophthalmic vein approach The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin 1, Georgiana Ion
230 Chiriac et al - Superior ophthalmic vein approach The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin 1, Georgiana Ion
Anatomy of Pituitary Gland
 Anatomy of Pituitary Gland Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Anatomy of Pituitary Gland Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
The sebaceous glands (glands of Zeis) open directly into the eyelash follicles, ciliary glands (glands of Moll) are modified sweat glands that open
 The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
OBJECTIVES. At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries.
 DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
Tikrit University College of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y.
 Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
*in general the blood supply of the nose comes from branches of the internal and external carotid arteries.
 In the previous lecture we talked about the anatomy of the nasal cavity, today we will talk about its blood supply, venous drainage, innervations, and finally about the paranasal sinuses. When we describe
In the previous lecture we talked about the anatomy of the nasal cavity, today we will talk about its blood supply, venous drainage, innervations, and finally about the paranasal sinuses. When we describe
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
Bilateral superior ophthalmic vein enlargement associated with diffuse cerebral swelling
 J Neurosurg 86:893 897, 1997 Bilateral superior ophthalmic vein enlargement associated with diffuse cerebral swelling Report of 11 cases ROHIT K. KHANNA, M.D., CHRISTOPHER J. PHAM, D.O., GHAUS M. MALIK,
J Neurosurg 86:893 897, 1997 Bilateral superior ophthalmic vein enlargement associated with diffuse cerebral swelling Report of 11 cases ROHIT K. KHANNA, M.D., CHRISTOPHER J. PHAM, D.O., GHAUS M. MALIK,
THE VISUAL PATHWAY FOR DENTAL STUDENTS
 Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. February 16, 2012 Objectives: THE VISUAL PATHWAY FOR DENTAL STUDENTS A. Draw the expected visual fields seen in classic lesions of the nerve, chiasm, thalamus, optic
Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. February 16, 2012 Objectives: THE VISUAL PATHWAY FOR DENTAL STUDENTS A. Draw the expected visual fields seen in classic lesions of the nerve, chiasm, thalamus, optic
Occipital lobe infarction: a rare presentation of bilateral giant cavernous carotid aneurysms: a case report
 Vanikieti et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:25 DOI 10.1186/s12886-018-0687-4 CASE REPORT Open Access Occipital lobe infarction: a rare presentation of bilateral giant cavernous carotid aneurysms: a case
Vanikieti et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:25 DOI 10.1186/s12886-018-0687-4 CASE REPORT Open Access Occipital lobe infarction: a rare presentation of bilateral giant cavernous carotid aneurysms: a case
A.J. Hauer Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae
 A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations and Fistulae (DAVM S DAVF S)
 Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Cranial cavity. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Cerebrum Cerebral hemispheres The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-THE DURA
Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Cerebrum Cerebral hemispheres The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-THE DURA
The SCALP. Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 The SCALP By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The SCALP includes FIVE layers external to the Calvaria. These are: S: Skin & Superficial Fascia C: Connective Tissue A: Aponeurosis (Epicranial) L: Loose
The SCALP By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The SCALP includes FIVE layers external to the Calvaria. These are: S: Skin & Superficial Fascia C: Connective Tissue A: Aponeurosis (Epicranial) L: Loose
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas
 External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Giant aneurysms of the carotid system presenting as visual field defect
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1980, 43, 1053-1064 Giant aneurysms of the carotid system presenting as visual field defect J B PEIRIS AND R W ROSS RUSSELL From the Institute of Neurology,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1980, 43, 1053-1064 Giant aneurysms of the carotid system presenting as visual field defect J B PEIRIS AND R W ROSS RUSSELL From the Institute of Neurology,
Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving the Laterocavernous Sinus
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 1 7 Online November 9, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0062 Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 1 7 Online November 9, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0062 Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving
BERNARD J. AI/PEKS * REPORT OF CASES
 C A R O T I D - C A V E R N 0 US FISTULA BERNARD J. AI/PEKS * The clinical features of cerebral aneurysm have become more clearly defined in recent years, due largely to advances made possible by arteriography
C A R O T I D - C A V E R N 0 US FISTULA BERNARD J. AI/PEKS * The clinical features of cerebral aneurysm have become more clearly defined in recent years, due largely to advances made possible by arteriography
Endovascular Embolization of Taumatic Intracavernous Pseudoaneurysm of Internal Carotid Artery
 Endovascular Embolization of Taumatic Intracavernous Pseudoaneurysm of Internal Carotid Artery Tanveer Ul Haq,Shahzad Ahmad Khan,Imtiaz Hussain Rizvi ( Department of Radiology, The Aga Khan University
Endovascular Embolization of Taumatic Intracavernous Pseudoaneurysm of Internal Carotid Artery Tanveer Ul Haq,Shahzad Ahmad Khan,Imtiaz Hussain Rizvi ( Department of Radiology, The Aga Khan University
Carotid Artery Dissection Causing an Isolated Hypoglossal. Nerve Palsy
 Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550035 Volume 2, Issue 5 Case Report Carotid Artery Dissection Causing an Isolated Hypoglossal Muzzammil Ali*, Yatin Sardana Nerve Palsy
Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550035 Volume 2, Issue 5 Case Report Carotid Artery Dissection Causing an Isolated Hypoglossal Muzzammil Ali*, Yatin Sardana Nerve Palsy
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Percutaneous Embolization of Arteriovenous Fistulas of the External Carotid Artery
 937 Percutaneous Embolization of rteriovenous Fistulas of the External Carotid rtery lex erenstein 1 John Scote In Sup Choi 1 Mark Persky3 Nineteen arteriovenous fistulas of the external carotid branches
937 Percutaneous Embolization of rteriovenous Fistulas of the External Carotid rtery lex erenstein 1 John Scote In Sup Choi 1 Mark Persky3 Nineteen arteriovenous fistulas of the external carotid branches
Posterior fossa veins: Embryology, anatomy, variations and pathology
 Posterior fossa veins: Embryology, anatomy, variations and pathology Poster No.: C-2668 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: S. Nair, D. B. Sarkar, J. J. Bhattacharya, M.
Posterior fossa veins: Embryology, anatomy, variations and pathology Poster No.: C-2668 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: S. Nair, D. B. Sarkar, J. J. Bhattacharya, M.
NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES
 NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES Leslie M. Scoutt, MD, FACR Professor of Diagnostic Radiology & Surgery Vice Chair, Dept of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging Chief, Ultrasound Section
NON-ATHEROSCLEROTIC PATHOLOGY OF THE CAROTID ARTERIES Leslie M. Scoutt, MD, FACR Professor of Diagnostic Radiology & Surgery Vice Chair, Dept of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging Chief, Ultrasound Section
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
ANTERIOR MENINGEAL BRANCH OF THE VERTEBRAL ARTERY IN EXTRA-AXIAL POSTERIOR FOSSA LESIONS*
 VOL. 122, No. 3 ANTERIOR MENINGEAL BRANCH OF THE VERTEBRAL ARTERY IN EXTRA-AXIAL POSTERIOR FOSSA LESIONS* By HAROLD PACHTMAN, M.D.,f and ROBERT WALDRON, II, M.D4 T HE anterior meningeal branch of the vertebral
VOL. 122, No. 3 ANTERIOR MENINGEAL BRANCH OF THE VERTEBRAL ARTERY IN EXTRA-AXIAL POSTERIOR FOSSA LESIONS* By HAROLD PACHTMAN, M.D.,f and ROBERT WALDRON, II, M.D4 T HE anterior meningeal branch of the vertebral
Vascular and Parameningeal Infections of the Head and Neck
 Vascular and Parameningeal Infections of the Head and Neck Kevin B. Laupland, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor Departments of Medicine, Critical Care Medicine, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and
Vascular and Parameningeal Infections of the Head and Neck Kevin B. Laupland, MD, MSc, FRCPC Associate Professor Departments of Medicine, Critical Care Medicine, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit
 213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit OSTEOLOGY Identify the bones which comprise the walls of the orbit: maxilla, zygomatic, ethmoid, lachrymal, frontal, and
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit OSTEOLOGY Identify the bones which comprise the walls of the orbit: maxilla, zygomatic, ethmoid, lachrymal, frontal, and
Unilateral glaucoma. (Itienne, i969a). The earlier publications are unhelpful because of the lack of differentiation
 254 Unilateral glaucoma R. 1:TIENNE Lyon, France Unilateral glaucoma is usually secondary, and a careful systematic ocular examination may help to detect the reason for the hypertension. Much more interesting
254 Unilateral glaucoma R. 1:TIENNE Lyon, France Unilateral glaucoma is usually secondary, and a careful systematic ocular examination may help to detect the reason for the hypertension. Much more interesting
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull
Direct carotid-cavernous fistula and glaucoma: case reports
 D. Petraru et al Direct carotid-cavernous fistula and glaucoma Direct carotid-cavernous fistula and glaucoma: case reports D. Petraru 1, D. Costin 2, G. Mihalache 3 1 2 nd Ophthalmological Clinic, Clinical
D. Petraru et al Direct carotid-cavernous fistula and glaucoma Direct carotid-cavernous fistula and glaucoma: case reports D. Petraru 1, D. Costin 2, G. Mihalache 3 1 2 nd Ophthalmological Clinic, Clinical
Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein
 J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 129-134 Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein Shih-Wei Hsu 1 Yeh-Lin Kuo 1 Min-Hsiung Cheng 2 Department of Diagnostic
J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 129-134 Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein Shih-Wei Hsu 1 Yeh-Lin Kuo 1 Min-Hsiung Cheng 2 Department of Diagnostic
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: OBJECTIVES OSTEOLOGY. Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD
 Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations is often extensive
 NOVEMBER, 1974 ROENTGENOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS OF THE OCCIPITAL LOBE* By B. TODD TROOST, M.D.,t and THOMAS H. NEWTON, M.D4 T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations
NOVEMBER, 1974 ROENTGENOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS OF THE OCCIPITAL LOBE* By B. TODD TROOST, M.D.,t and THOMAS H. NEWTON, M.D4 T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations
COMMUNICATIONS OCULAR MANIFESTATIONS OF INTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY OCCLUSION*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 257. COMMUNICATIONS OCULAR MANIFESTATIONS OF INTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY OCCLUSION* BY NEIL GORDONt St. Mary's Hospital, London THE syndrome of "carotid hemiplegia" referred to
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 257. COMMUNICATIONS OCULAR MANIFESTATIONS OF INTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY OCCLUSION* BY NEIL GORDONt St. Mary's Hospital, London THE syndrome of "carotid hemiplegia" referred to
MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION!
 CASE REPORT MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION! Shagufta Wahab 1, Rizwan Ahmad Khan 2, Manjari Thapa Manger 3 1. Radiodiagnosis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh,
CASE REPORT MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION! Shagufta Wahab 1, Rizwan Ahmad Khan 2, Manjari Thapa Manger 3 1. Radiodiagnosis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh,
GNK485 The eye and related structures. Prof MC Bosman 2012
 GNK485 The eye and related structures Prof MC Bosman 2012 Surface anatomy Bony orbit Eyeball and Lacrimal apparatus Extra-ocular muscles Movements of the eye Innervation Arterial supply and venous drainage
GNK485 The eye and related structures Prof MC Bosman 2012 Surface anatomy Bony orbit Eyeball and Lacrimal apparatus Extra-ocular muscles Movements of the eye Innervation Arterial supply and venous drainage
A PLEA FOR LATERAL ORBITOTOMY WITH CERTAIN MODIFICATIONS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 718. A PLEA FOR LATERAL ORBITOTOMY WITH CERTAIN MODIFICATIONS* BY H. B. STALLARD London THE frontiers of human interest and work are often disputed and, there is no exception
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 718. A PLEA FOR LATERAL ORBITOTOMY WITH CERTAIN MODIFICATIONS* BY H. B. STALLARD London THE frontiers of human interest and work are often disputed and, there is no exception
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS
 HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Literature Review: Neurosurgery
 NANOS 2018 Kona, Hawaii Literature Review: Neurosurgery Neil R. Miller, MD FACS Frank B. Walsh Professor of Neuro-Ophthalmology Professor of Ophthalmology, Neurology & Neurosurgery Johns Hopkins University
NANOS 2018 Kona, Hawaii Literature Review: Neurosurgery Neil R. Miller, MD FACS Frank B. Walsh Professor of Neuro-Ophthalmology Professor of Ophthalmology, Neurology & Neurosurgery Johns Hopkins University
Visual pathways in the chiasm
 Visual pathways in the chiasm Intracranial relationships of the optic nerve Fixation of the chiasm Chiasmatic pathologies The function of the optic chiasm may be altered by the presence of : 4) Artero
Visual pathways in the chiasm Intracranial relationships of the optic nerve Fixation of the chiasm Chiasmatic pathologies The function of the optic chiasm may be altered by the presence of : 4) Artero
SSRG International Journal of Medical Science ( SSRG IJMS ) Volume 4 Issue 10 October 2017
 Cerebral Infarction Following Traumatic Carotid Cavernous Fistula in Adolescent Male; a Case Report Ali Alaseeri, MD 1 1 Internal Medicine department, College of Medicine, Prince Sattam University, Al
Cerebral Infarction Following Traumatic Carotid Cavernous Fistula in Adolescent Male; a Case Report Ali Alaseeri, MD 1 1 Internal Medicine department, College of Medicine, Prince Sattam University, Al
Thermography in the management of carotid-cavernous fistulas RAFAEL GALERA G., M.D., AND ALBERTO MARTINEZ C., M,D.
 Thermography in the management of carotid-cavernous fistulas RAFAEL GALERA G., M.D., AND ALBERTO MARTINEZ C., M,D. Department of Neurosurgery, Vargas Medical School, Central University of Venezuela, Caracas
Thermography in the management of carotid-cavernous fistulas RAFAEL GALERA G., M.D., AND ALBERTO MARTINEZ C., M,D. Department of Neurosurgery, Vargas Medical School, Central University of Venezuela, Caracas
A Rare Complication of Rhinoplasty: A Case Report. Alarfaj, Ahmed M.D, Abdulaziz University Hospital, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
 A Rare Complication of Rhinoplasty: A Case Report Alarfaj, Ahmed M.D, Ahmed Mohammed Al Arfaj, M.D: Associate Professor, Division of Facial Plastic Surgery, Dept. of ENT & HNS, King Abdulaziz University
A Rare Complication of Rhinoplasty: A Case Report Alarfaj, Ahmed M.D, Ahmed Mohammed Al Arfaj, M.D: Associate Professor, Division of Facial Plastic Surgery, Dept. of ENT & HNS, King Abdulaziz University
Post-traumatic right carotid-cavernous fistula resulting in symptoms in the contralateral eye: a case report and literature review
 Zhu et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:183 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-018-0863-6 CASE REPORT Open Access Post-traumatic right carotid-cavernous fistula resulting in symptoms in the contralateral eye:
Zhu et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:183 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-018-0863-6 CASE REPORT Open Access Post-traumatic right carotid-cavernous fistula resulting in symptoms in the contralateral eye:
Vascular Malformations of the Brain. William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist. September 8, 2014
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
Baseline peripheral prolactin levels were normal in all occult and EAS patients. Four
 1 Supplemental Data 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Prolactin levels at baseline and post-crh stimulation peripheral prolactin levels were normal in all occult and EAS patients.
1 Supplemental Data 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 Prolactin levels at baseline and post-crh stimulation peripheral prolactin levels were normal in all occult and EAS patients.
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Intro: Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Basic understanding of interventional radiology. Gain knowledge of key terms and phrases
 Slide 1 Intro: PRESENTED BY: Selena M. Moore, AAS, CCS, CPC HIMS Physician Liaison Coder This is a modified/updated presentation that was originally written by: Rosemary Waligorski, RHIT, CCS, RCC and
Slide 1 Intro: PRESENTED BY: Selena M. Moore, AAS, CCS, CPC HIMS Physician Liaison Coder This is a modified/updated presentation that was originally written by: Rosemary Waligorski, RHIT, CCS, RCC and
